A comparison of innovation strategies of regional development agencies in Turkey
Автор: Ozen Berna Sezen, Baycan Tzin
Журнал: Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast @volnc-esc-en
Рубрика: Global experience
Статья в выпуске: 3 т.15, 2022 года.
Бесплатный доступ
This paper aims to assess the regional innovation system of Turkey by comparing regional innovation strategies developed by regional development agencies. Focusing on the specific regional innovation strategy documents and addressing first, reports, researches and publications on the official websites of the agencies, and next, the in-depth interviews conducted with the representatives of regional development agencies by phone and/or e-mail, the paper examines and comparatively evaluates the efforts of the regional development agencies contributing to the regional innovation system. Comparative evaluation reveals that some regional development agencies have created a specific regional innovation strategy whereas the others have not yet developed such strategies, but conduct various studies on different innovation dimensions, although these studies are exclusive and far from a holistic approach. The comparative evaluation also reveals that regional innovation strategies differ in terms of regional priorities. Nevertheless, similar strategies developed by regional development agencies address the following issues: developing the research and innovation culture; research and innovation infrastructure; institutional structure; human resources; financial resources; effective communication, cooperation and coordination; entrepreneurship and innovation ecosystem; awareness of innovation activities; clusters; priority sectors; social innovation; intellectual property rights and commercialization. Although there are some efforts to improve the regional innovation systems by regional development agencies, the comparative evaluation demonstrates that they have not yet reached the desired level of producing a holistic regional innovation strategy and they should be more effective as a key actor in the regional innovation systems.
Regional innovation system, regional development agencies, regional innovation strategies, turkey
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147238051
IDR: 147238051 | УДК: 338(560) | DOI: 10.15838/esc.2022.3.81.13
Текст научной статьи A comparison of innovation strategies of regional development agencies in Turkey
Innovation is increasingly regarded as one of the key engines for economic growth and prosperity. In a knowledge-based economy, economic performance depends on competition as a driver of improved productivity, and innovation as new technologies, techniques and ways of working that drive improved productivity. Innovation is increasingly acknowledged as an important driver of value creation, economic growth and social welfare, while innovation performance is an important criterion for improving international competitive power (Ozen, Baycan, 2014).
The production of goods and services is becoming more and more knowledge/science/ technology and skills-intensive1. As a reflection of this knowledge/science/technology/skills-intensive global competitive structure, challenges on innovation make the innovation systems, policies and strategies diversified both in national and regional levels. In this context, there are different responses and reactions of different countries and regions to this competitive environment.
Every structure from micro to macro scale (firm, region, nation etc.) strives in this competitive environment in such a way that some try to create changes by pioneering, while others try to recognize, follow and adapt these changes. Globalization increases the need for innovation policy, and also affects the design and implementation of innovation policies (Edquist, 2008); every society strives for innovation that corresponds to its needs and capabilities2.
Due to the production, development, diffusion, application and use of technology and knowledge, innovation systems have become the focus of interest not only for academics but also for decision makers at the national and regional level in terms of economic development and social welfare.
Improving the coordination mechanisms (Pellegrin et al., 2010, p. 16) and the flows of knowledge3, technology and information4 among these various actors strengthen innovation processes by promoting systematic and qualified interactions (Pellegrin et al., 2010, p. 16) and dynamic networks (Feinson, 2003, p. 19) between them.
Regional innovation systems are complex and interactive networks not only in national but also in global ties and connections via international agencies and innovation systems. Within these systems, regions not only have innovation performances at different levels, but also make progress in different ways depending on factors like their positions in the system and changes in national policies.
Despite the free movement of capital and labor as a result of globalization, the importance of regions is increasing as a process of knowledge production, use and “accumulation of knowledge remains locally embedded and spatially concentrated”5. The regional innovation system approach helps to explain the regional dimension of production and the regional disparities of innovation capacity and economic power (Schrempf et al., 2013), and highlights the diversity of regions in the countries, the differing dynamics of innovation and the interactions between organizations in a particular system6. The analysis of a regional innovation system allows creating and disseminating economically relevant information in a certain region, and also identifying key actors and resources (such as existing infrastructures, sources of information and resources of expertise, financing, etc.). A system concept helps to clarify what kind of support is established and what inter-regional cooperation opportunities are at which policy level (local, regional, national, transnational)7. The regional innovation systems concept is composed of different types of actors (big or small, local or multinational firms, universities, public research facilities, technology centers and cluster associations etc.) and the linkages and relationships between these actors8 (Edquist, 2005; Asheim et al., 2013; zen et al, 2018). Regional innovation systems have recently been of great importance. The OECD9 explains why regions occupy an increasing role in regional innovation policies and why they are key actors in forming and shaping virtuous innovation trajectories, and mobilising untapped potential for national growth. Especially when they have set up the necessary administrative mechanisms to support clusters and innovative enterprises, regions represent economically more meaningful communities, and can easily define the flow of real economic activities and make use of the synergy and connections between economic actors (Cooke et al., 2000; Cook, Memedovic, 2003). The emergence of clusters as a local innovation system and the emphasis on competition superiority are related to the presence of regional and local innovation systems. Hence, it shows that regional innovation systems form the basis for national competitive advantage (McCall, 2010).
With having local dynamics and knowledge, regional level is important for economic development and for the design and implementation of innovation policies and strategies. Therefore institutional structure at regional level gains importance. Thanks to regional dynamics, interactions, networks, flows and linkages, regional development agencies (RDAs) are effective regional actors in regional planning and regional innovation systems.
Since regional innovation strategy projects were launched by the European Union (EU) in 1994, the strategies on innovation systems are recognized as a key issue in capacity and performances of regional innovation systems. In order to implement and manage an effective innovation system, the regional innovation strategy is an important tool for regional stakeholders within a framework of a common platform to define the strategic objectives and the sequence of activities of the R&D and innovation of the region to reach the goals over the long term (Zabala-Iturriagagoitia et al, 2008; Lewandowska, 2012).
Aim and structure of the research
This paper aims to assess the regional innovation system of Turkey by making a comparison of regional innovation strategies developed by RDAs. For this assessment, in-depth interviews with the representatives (heads of departments and specialists) from the RDAs were carried out by phone and/or e-mail to determine how RDAs approach innovation. In these in-depth interviews, the representatives were asked whether they have regional innovation strategies, financial support programs or any other initiatives in this regard. Therefore the data and information were collected from in-depth interviews with the representatives in addition to the official websites of the RDAs including regional plans, work programs, action plans, support programs, reports, publications of strategies and researches as thematic and sector analyses. On the basis of collected data and information, regional innovation strategies or the inititatives of the RDAs were compared and assessed.
The importance of regional innovation systems, regional innovation policies and the RDAs are described briefly in the introduction. In this section, the research aim and structure of the study are explained. The third section focuses on the historical development process of regional innovation systems and RDAs in Turkey, presents the structure of the regions at NUTS-2 level and makes an assessment on evolution of RDAs and policies over time. In order to assess Turkey’s regional innovation system, final section focuses on the examination, interpretation and a comparison of regional innovation strategies of the RDAs and the challenges they have faced.
Regional innovation systems in Turkey
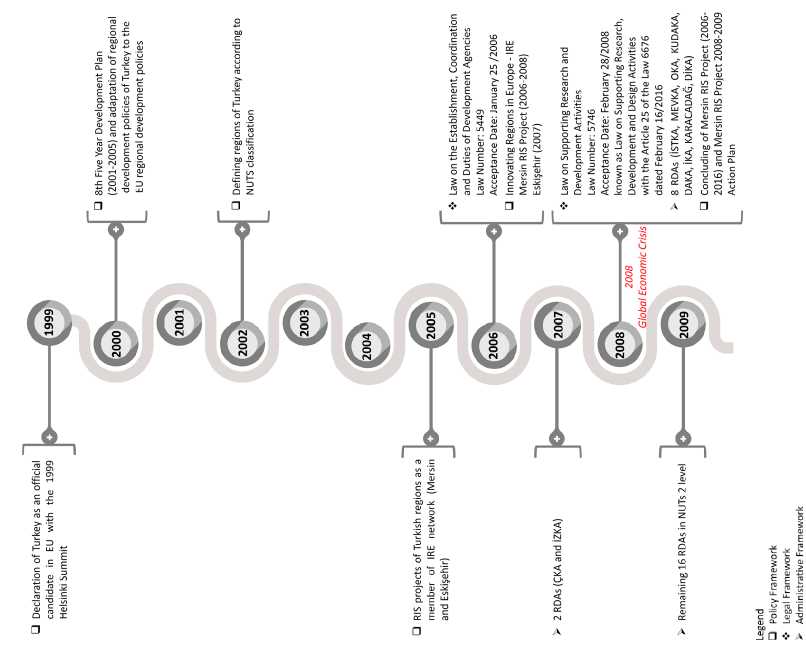
Regional development policies in Turkey have been restructured and transformed with the declaration of Turkey as an official candidate in the EU at the 1999 Helsinki Summit, and have become a hot topic with a totally new perspective to provide a cohesion to the EU policies. In line with this cohesion process, as a beginning step, Turkey accepted the Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics (NUTS) classification and defined its new regions as compatible to NUTS in 200210 and decided to establish development agencies (DAs)11. As a result, today Turkey has 26 RDAs, respectively 2 RDAs (Izmir and Qukurova) in 2007 12 ,
8 RDAs (Istanbul, Konya, Samsun, Erzurum, Van, Gaziantep, Diyarbakir and Mardin) in 2008 13 and finally 16 remaining RDAs in 200914. Therefore, the development of RDAs15 can be mentioned as one of the milestones in the historical background of the regional structure of Turkey.
Besides having a regional structure at NUTS-2 level, within the scope of the Innovating Regions of Europe (IRE) Network, in 2005, just like Bulgaria, Czech Republic, Estonia, Hungary, Israel, Lithuania, Malta, Norway, Poland, Romania, Slovakia, Switzerland, Turkey has also been involved 33 New-RIS projects in certain regions such as Mersin and Eskisehir (Metin, 2010).
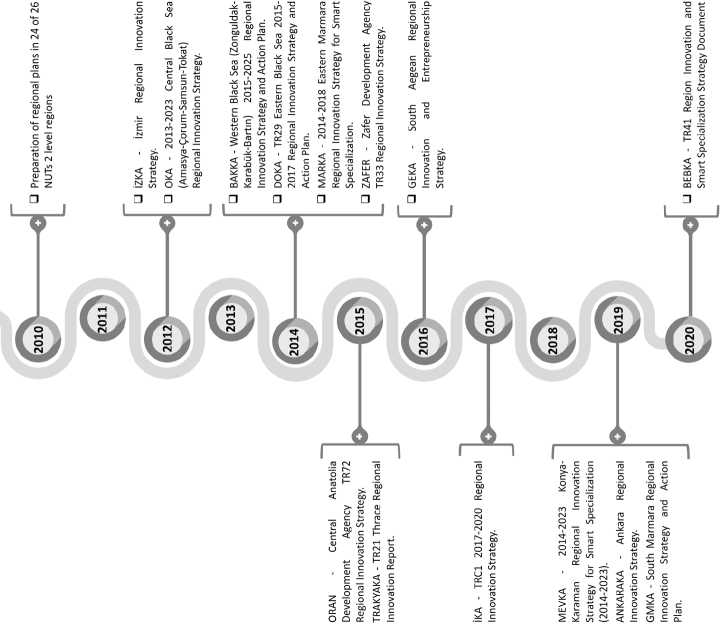
Also, in the 2011 Progress Report16, the preparation of regional plans in 24 of the 26 NUTS-2 regions under the coordination of DAs is shown as a progress within the institutional framework. Regional plans determine the relationships among plans, policies and strategies produced at the national level and the activities to be carried out at the local level. Besides producing the regional plans, with the production of regional innovation strategy documents in two RDAs (Izmir Development Agency and Middle Black Sea Development Agency denoted as iZKA and OKA, respectively) in 2012, the agencies have shown that they are playing a concrete role in innovation with their effective work. In addition to these two agencies, some other RDAs have also created regional innovation strategy documents in the following years. Therefore, the pioneering of these regional innovation strategy documents in 2012 is a milestone in regional innovation systems.
Regional innovation strategies of regional development agencies in Turkey
The RIS-Mersin project, started in 2005 as a region in IRE Network within the 6th Framework Programme of the EU, has an importance according to the reason of being the first regional innovation systems project of Turkey covering only Mersin province independently from the development agency.
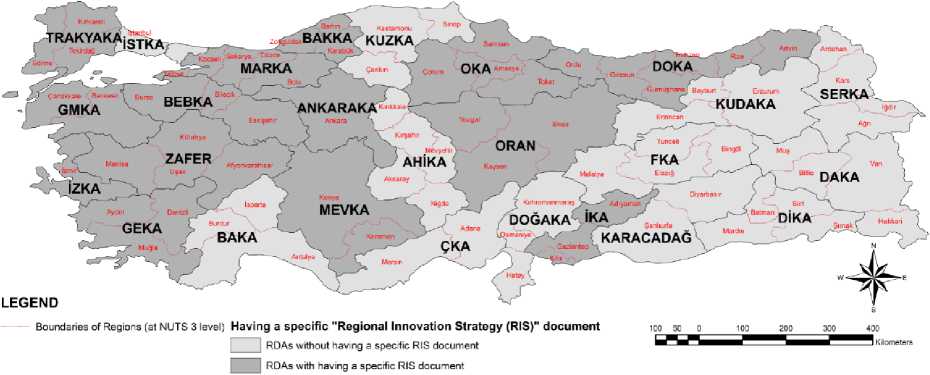
Examination of the regional innovation strategies of the RDAs shows that some have already started to create regional innovation strategies since 2012 (Fig. 1 and 2) . A comparison of the regional innovation strategies is evaluated in terms of the visions in the regional plans and regional innovation strategies (Tab. 1) , main provisions of innovation strategies (Tab. 2) and studies of the RDAs after regional innovation strategy17 as implementation, evaluation and monitoring mechanisms (Fig. 3) .
Figure 1. RDAs having a specific “Regional Innovation Strategies” document
|
Regional Development Agencies in Turkey (NUTS-2 Level) |
||||
|
NUTS 2 |
RDA |
PROVINCES IN Till REGION |
ESTA BUSH MENГ YEAR |
|
|
1 |
IK 62 \ |
Cakumva 1) -V ((. K A i |
Adana. Mcfvn |
ZOi :7 |
|
TR31 ; |
i/trr Ь. Л. (i/к A) |
Izmir |
2007 |
|
|
3 |
TRIO 1 |
Kiarbnl D A. (ISTKA) |
Istanbul |
2008 |
|
4 |
TR 52 \ |
Mevlana D. A. (MEVKAi |
Karainan, Kuma |
2003 |
|
s |
TR83 1 |
Micdlc Black Sen D. A (UKA) |
Amasva. Voram. Samsun, lokat |
2008 |
|
6 |
TRAl 1 |
N nj-.CJM Anatolia 1). A (KI IDAKA) |
Baybur. Erzincan. Erzurum |
2008 |
|
7 |
ГК В 2 : |
Eastern Anatolia 1). A. (DAK Al |
Hillis. Hakkari, Мщ, Van |
2008 |
|
8 |
IK Cl 1 |
Siliuoad 1). A. (IKA) |
Ac: iva irian. Gazianlep, KilK |
2008 |
|
9 |
TRC2 i |
К a racada и 1). Л. (К A R A (’ A D A GI |
Divarbakir. San nirla |
2008 |
|
10 |
TRC3 1 |
Tigris D. A. iDTK A) |
Batman, Mardin, Snrak, Siirt |
2008 |
|
11 |
TR21 ; |
Trakva D. A. t TRAKYAKA, |
Ecirce, KirklarelL Tekirdag |
2009 |
|
12 |
TR22 \ |
South Marmara Г). A. (GMKA) |
Bahkcsir. Ganakxalc |
2009 |
|
В |
1 R 32 | |
Southern Aegean 1). A. (GhKA) |
Aydin. Dcnizli. Mu cl a |
'2009 |
|
14 |
1 R 33 i |
Zafer 1). A. (ZAU R) |
Afyonkarahbar. Kiitahva. Матчи I ^aX |
2009 |
|
15 |
TR41 | |
Bursa. Eski^chii. BiLcik D A. (BEBKA) |
Bilucik. Bursa. Eskisehir |
2009 |
|
16 |
IK 42 ' |
1 ;:si Marmara 1) A. (MARKA) |
Buhl, Dii/.;:c. Kmaeli. Saka va. Yalova |
2009 |
|
17 |
TR 51 |
Ankara 1). Л. (ANKARAKA) |
Ankara |
2009 |
|
18 |
TR61 ' |
We-u Mediterranean D Л (ВАКА) |
Antalya, Burdur, Isparta |
2009 |
|
19 |
TR63 \ |
Eastern Medi.cnancan D. A. (DOGAKA) |
Hatav, Kalnamanmara^ Osmaniye |
2009 |
|
20 |
TR 71 | |
Ahiler 1). A. (AHikA) |
Aksarav. Kirikkale, Kirsehir. Nigdc. Nev^ehir |
2009 |
|
21 |
TR 72 | |
Central Anatolia 1). A. (ORAN) |
Kavscri, Nivas. Yo/^at |
2009 |
|
TR 81 |
Western В1асл Sea D. A. (ВАККА) |
Ballin, Karabiik. Zonguldak |
2009 |
|
|
TR82 ' |
North Anatolian 1). A. (KI l/KA) |
Gankin. Kaslamonu. Sinop |
2009 |
|
|
24 |
TR90 i |
1 еыст Black Sea 1). A. (DOKA) |
Arlvin, ( iirc^un. (iiimiishanc, Urdu. Rr/c. 'I rabznn |
2009 |
|
25 |
TRA2 1 |
Serial D. A. (SFRKA) |
Agn. Ardahan. Tgdir, Kars |
2009 |
|
26 |
TRBl 1 |
Firat D. A. (FKA) 1 |
Bingol, Elazig, Malatya, Tunceli |
2009 |
|
(*): Central provinces of the RD As are given in bold in the text |
||||
□ □ □ □
□ □ □ □
□ □ □ □
□ □
: 1ZKA - Izmir Regional Innovation Strategy.
: OKA - Middle Black Sea ( Amasya-^orum-Samsun-Tokat) Regional Innovation Strategy (2013-2023).
: ВЛККЛ - Western Black Sea (Zonguldak-Karabiik-Bartm) 2015-2025 Regional Innovation Strategy and Action Plan.
-
: DOKA - TR90 Eastern Black Sea Regional Innovation Strategy and Action Plan 2015-2017.
-
: MARKA - East Marmara Regional Innovation Strategy for Smart Specialization 2014-2018.
-
: ZAFER - Zafer Development Agency TR33 Regional Innovation Strategy.
-
: ORAN - Central Anatolia Development Agency TR72 Regional Innovation Strategy
-
: TRAKYAKA - TR21 Thrace Regional Innovation Report.
-
: GEKA - South Aegean Regional Innovation and Entrepreneurship Strategy.
-
: IKA - TRC1 2017-2020 Regional Innovation Strategy.
-
: MEVKA - Konya-Karaman Regional Innovation Strategy for Smart Specialization (2014-2023).
-
: ANKARAKA - Ankara Regional Innovation Strategy
-
: GMKA - South Marmara Regional Innovation Strategy and Action Plan.
-
; ВЕВКЛ - TR41 Region Innovation and Smart Specialization Strategy Document
Source: own elaboration.
Figure 2. Milestones of historical development process of regional innovation systems in Turkey
□ □ □ ООО
Source: own elaboration.
with a participation of representatives of relevant public and private sector actors, non-governmental organisations, universities and representatives from national institutions, SWOT and/or PEST analyses, stakeholder analysis, examination of different parameters, defining regional innovation ecosystem, measurement of innovation potential, supply, demand and capacity, determination of vision, priorities, innovation strategies, targets and actions.
When the visions in the regional plans of these 14 RDAs are examined; it is seen that most of the RDAs (iZKA, DOKA, MARKA, TRAKYAKA,
GEKA, IKA, ANKARAKA and BEBKA) put emphasize on innovation in their visions of the regional plans. Although remaining RDAs are not directly focused on innovation in the regional vision, they have included innovation-related concepts such as learning region, competitiveness, knowledge, human and social capital. If the visions in the regional plans and the regional innovation strategies are compared, it has been determined that some agencies have defined innovation visions to create regional innovation strategies, and some have produced strategies in line with their regional plans without creating an innovation vision (see Tab. 1).
Table 1. Comparison of the visions
|
RDA |
Vision in the regional plan |
Innovation vision in the regional innovation strategies |
|
iZKA |
“izmir as the centre of attraction of the Mediterranean, producing information, design and innovation” (izmir Development Agency, 2014-2023 izmir Regional Plan). |
The regional innovation vision was not defined (izmir Regional Innovation Strategy). |
|
OKA |
An environmentally sensitive, competitive, rapidly developing region, which has become Turkey’s gateway to the Black Sea and which has raised its quality of life (Ye?ilirmak Basin Development Project (Amasya, Qorum, Samsun, Tokat) Regional Development Master Plan, 2006). |
“Thanks to innovative and entrepreneur society together with its competitive sectors, Middle Black Sea Region will be a pioneer region for development at national and international level in 2023 (Middle Black Sea (Amasya-Qorum-Samsun-Tokat) Regional Innovation Strategy (2013-2023))”. |
|
BAKKA |
Becoming a region which has broken its dependent economic condition and raised its life quality (20142023 Western Black Sea Regional Plan). |
Becoming a region with a high level of prosperity and quality of life which have succeeded the sustainable development with innovative and powerful sectors and competitive brandmarks in both national and international area in 2025 (Western Black Sea (Zonguldak-Karabuk-Bartin) 2015-2025 Regional Innovation Strategy and Action Plan). |
|
DOKA |
The Eastern Black Sea with innovative and competitive economy, improved social welfare and quality of life by ensuring rural-urban integration, livable spaces, a sustainable environment and high human quality (TR90 Eastern Black Sea Regional Plan 2014-2023). |
Eastern Black Sea Region converting its original values and unique resources into competitive and dynamic products and services. Competitive and dynamic Eastern Black Sea (TR90 Eastern Black Sea Regional Innovation Strategy and Action Plan 20152017). |
|
MARKA |
To be a human and knowledge-oriented and open to innovations trademark region in global competition and sustainable development, powered by its strategic location and collaboration networks, producing value with its versatile economic structure, steering the future with its rich human potential, making a difference with its quality of life (East Marmara 2014-2023 Regional Plan). |
“Becoming a national technology commercialization center that can produce information and develop technology, follow global innovations and shapes itself, has specialized in automotive, machinery and electrical machines, and develops key enabling technologies (East Marmara Regional Innovation Strategy for Smart Specialization 2014-2018).” |
|
ZAFER |
A learning region that pursues ecological balance, creates added value with its knowledge-based economy, increases competitiveness and quality of life, develops in a balanced way (TR33 Regional Plan 2014-2023). |
The starting point of this project is to increase the competitiveness, which is in the vision and one of the development axes determined in the 2010-2013 Regional Plan (TR33 Regional Innovation Strategy). |
End of Table 1
|
RDA |
Vision in the regional plan |
Innovation vision in the regional innovation strategies |
|
ORAN |
“Competitive in national and international level, accessible to humanity and social capital, improved potentials, improved quality of life by improving urban and social infrastructures, accessible Central Anatolia (TR72 Region 2014-2023 Regional Plan)”. |
It has been defined that a «Regional innovation strategy» will be developed under the priority of Competitiveness Axis «Development of R&D and Innovation» in the TR72 Region 2014-2023 Regional Plan. Innovation committees were formed from the relevant institutions and individuals in the provinces and their opinions were taken and the innovation vision and innovation strategies were determined (Central Anatolia Development Agency TR72 Regional Innovation Strategy). |
|
TRAKYAKA |
“Thrace developing with its high added value production whilst preserving its natural and cultural values, where collaboration and innovation prevails, and where the standard of life and wellbeing is at its highest (TR21 Thrace Region 2014-2023 Regional Plan Summary)”. |
The regional innovation vision was not defined, and it was stated that the study was carried out to increase the innovation capacity of the region based on the regional vision in the Regional Plan (TR21 Thrace Regional Innovation Report). |
|
GEKA |
South Aegean as a global tourism focus with a high quality of life, producing based on innovation, protecting its nature (TR32 Level 2 Region 20142023 Region Plan). |
The regional innovation vision was not defined (South Aegean Regional Innovation and Entrepreneurship Strategy). |
|
iKA |
Silkroad as the center of attraction of the Middle East, with high quality of life, strong human capital, competitive and innovative capacity (TRC1 Gaziantep-Adiyaman-Kilis Regional Plan 2014-2023). |
Center of Innovation from Tradition to Future: Silk Road (TRC1 Regional Innovation Strategy 2017-2020). |
|
MEVKA |
Becoming a region with high and balanced prosperity level, integrated with international economies, preferred by people to work, produce and live in under the principle of compassion and tolerance (Konya-Karaman 2014-2023 Region Plan). |
The regional innovation vision was not defined, and it was stated that the study was carried out based on the regional vision in the Regional Plan because this document is a substrategy document of the 2014-2023 Regional Plan (Konya-Karaman Regional Innovation Strategy for Smart Specialization (2014-2023)). |
|
ANKARAKA |
“Presenting a High Quality of Life and Competing With the World, the Capital of Knowledge and Innovation Ankara (Ankara Regional Plan 2014-2023)”. |
Visions in the health, informatics and agriculture-food sectors, which are the 3 pilot sectors selected within the scope of creating a future vision within the scope of the Regional Innovation Strategy, adhering to the regional vision in the Ankara Regional Plan (Ankara Regional Innovation Strategy). |
|
GMKA |
“A South Marmara with more qualified labor, competitiveness and viability (TR22 South Marmara Regional Plan 2014-2023)”. |
The South Marmara Region will be a region that has achieved its development goal in 2023 with its trained human resources, educational institutions, innovation and entrepreneurship culture and competitive sectors. (South Marmara Regional Innovation Strategy and Action Plan) |
|
BEBKA |
Internationally competitive, sustainable production, innovation and life center carrying the heritage of the past from establishment to salvation into the future by adding value (Bursa, Eskisehir, Bilecik Regional Plan 2014-2023). |
The regional innovation vision was not defined, and it was stated that the study was carried out based on the regional vision in the Regional Plan. The innovation and smart specialization strategy prepared for the TR41 Region has also been considered within the framework of the vision defined in the regional plan, and it adopts a more competitive, more innovative and more sustainable approach taking regional characteristics into account (TR41 Region Innovation and Smart Specialization Strategy Document). |
|
Source: own elaboration based on the regional plans and the regional innovation strategies documents of RDAs. |
||
Table 2. Comparison of main strategies in the regional innovation strategy documents
|
RDA |
Innovation strategies |
|
iZKA |
Strategic Priorities:
|
|
OKA |
Strategic Goals:
|
Continuation of Table 2
|
RDA |
Innovation strategies |
|
BAKKA |
Strategic Goals:
Strategic Breakthroughs:
|
|
DOKA |
Development Axes:
|
|
MARKA |
Strategic Priorities:
|
|
ZAFER |
Strategic Priorities:
|
|
ORAN |
Strategic Priorities:
|
|
TRAKYAKA |
Strategic Goals:
|
|
GEKA |
1. Problems and recommendations regarding competitive sectors in Aydin |
|
|
|
|
|
End of Table 2
|
RDA |
Innovation strategies |
|
iKA |
Priority Axes:
|
|
MEVKA |
Strategic Goals:
|
|
ANKARAKA |
Priority strategies for five prominent sectors: IT Sector
Medicine and Medical Devices Sector
Construction Machinery Sector
Defence and Aviation Sector
Agriculture and Food Sector
|
|
GMKA |
Strategic Priorities:
|
|
BEBKA |
Eight intervention areas forming the TR41 Region Smart Specialization Strategy Action Plan:
|
|
Source: own elaboration based on the regional plans and the regional innovation strategies documents of RDAs. |
|
According to the regional innovation strategies of the RDAs, only 14 of the RDAs currently have a specific regional innovation strategy including iZKA and OKA as the leading agencies to produce regional innovation strategies. Although some RDAs do not have specific regional innovation strategies, they have various studies on different innovation dimensions, but these studies are exclusive and far from a holistic approach. Unfortunately, some agencies are currently unable to prioritize innovation.
While 12 (iZKA, OKA, BAKKA, DOKA, MARKA, ZAFER, ORAN, TRAKYAKA, iKA, MEVKA, GMKA and BEBKA) of these 14 agencies produced strategies on innovation dimensions, only two (GEKA and ANKARAKA) created sectoral strategies. GEKA defined problems and recommendations regarding competitive sectors in each province, and ANKARAKA developed priority strategies, targets and action plans for five prominent sectors (Tab. 2) .
If the regional innovation strategies of these 14 agencies are evaluated, they are similarly focusing on the following:
– creating and developing the research and innovation culture,
– strengthening the research and innovation infrastructure,
– developing the institutional structure,
– developing human resources,
– increasing the accessibility to various financial resources (funding, support programmes etc.),
– improving effective communication, cooperation and coordination,
– developing the entrepreneurship and innovation ecosystem,
– organizing and increasing the awareness activities,
– establishing and developing clusters,
– focusing on specialized/priority/prominent/ strategic sectors,
– encouraging social innovation,
– increasing IPR and commercialization.
When the agency studies conducted after the regional innovation strategies are examined, it is seen that the agencies that produced the strategies in the past years have made substantial headway.
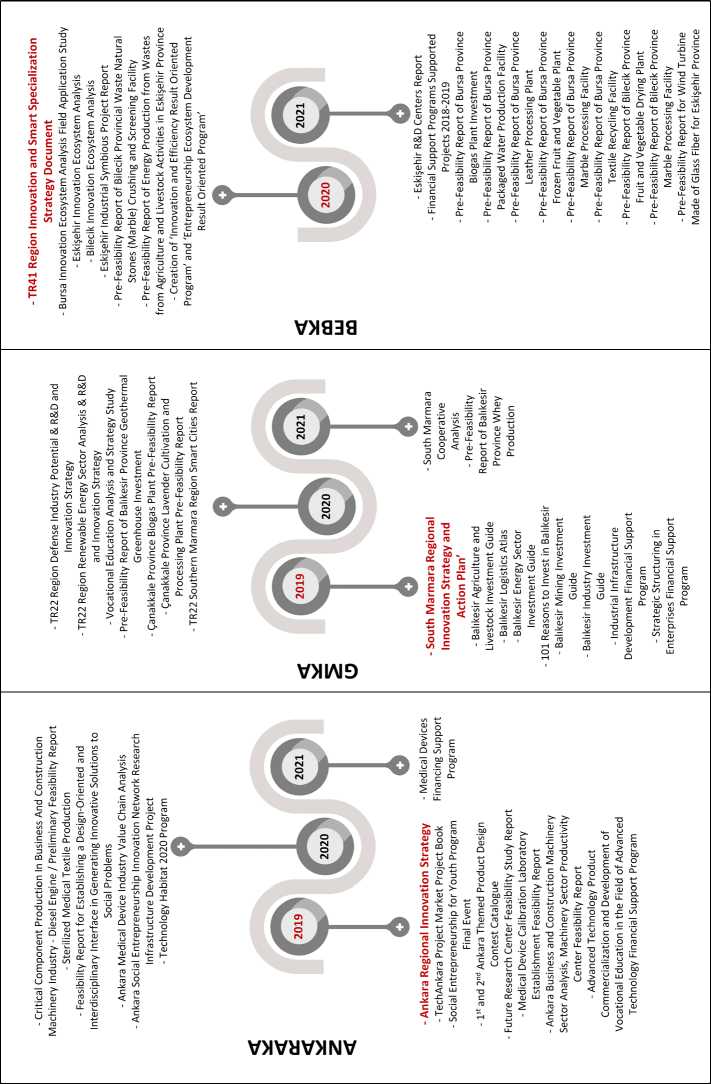
As the next step, the support programs, reports, publications, strategies and researches as thematic and sector analyses produced by the RDAs were examined in detail in order to understand whether the implementation of the regional innovation strategies could be realized or not. Although producing and implementing dates of the regional innovation strategies of the RDAs differ from one another, RDAs have studies focusing on the local production and prominent sectors of the regions. The main reasons why regions vary in success of the regional innovation strategies are related to the diversities in the dynamics/features, local production, sectoral specialization and the R&D, knowledge and innovation potentials of the regions (Fig. 3) .
After the regional innovation strategy, it has been determined that iZKA’s works and financial support programs are focused mainly on knowledge, entrepreneurship, information communication technologies, renewable energy, small and mediumsized enterprises (SMEs), small scale industrial zones, clusters and prominent sectors especially environmental technologies. The innovation success stories, the measurement of innovation indicators, the production of innovation ecosystem analysis and monitoring reports, and the creation of evaluation reports of financial support programs after the regional innovation strategies make ZKA successful at the achiving the goals.
DOKA’s works and financial support programs are related mainly on clusters, SMEs, alternative financing sources, local products, women and youth entrepreneurship, geographical indications, foreign trade and target market. As previous RDAs, DOKA has many pre-feasibility reports in various sectors based on agro-industries. There are evaluation and impact analysis reports after the financial support programs.
ZAFER works on exports, branding and marketing, industrial inventory, SMEs, clusters, professional competencies, entrepreneurship, vocational education, competitiveness, product diversity, local products, logistic centers, patent and trademark capacities, OIZs, and various prominent sectors mainly on traditional arts, gastronomy, machinery, mining, agriculture, environment and energy.
Figure 3. Studies of the RDAs after regional innovation strategy
- Izmir Regional Innovation Strategy - Izmir Knowledge SocietyBased Development Strategy - Izmir Entrepreneurship Ecosystem Strategy - Renewable Energy and Environment Financial
-
- Izmir Current Situation Analysis 2013
-
- Peninsula Sustainable Development Strategy - Small Scale Infrastructure Financial Support Program for the Development of Industrial Zones -Transformation to Information Society and Information Communication Technologies Financial Support Program
Support Pro
-
- Izmir Entrepreneurship Ecosystem Development Strategy - Izmir Clustering Strategy -Izmir Fisheries Sector Strategy - Post Implementation Evaluation Studies of 2008 SME Financial Support Program and Social Development Financial Support Program
-
- Izmir 2012 Cultural Economy and Cultural Infrastructure Inventory and Izmir Cultural Economy Development Strategy - Determination of Functional Regions and Sub-Regions and Interregional Relations for the Preparation of Izmir Province Regional Plan
-
- Renewable Energy and Environmental Technologies Financial Support Program - Financial Support Program for the Development of Small Scale Industrial
-
- Izmir Innovation Success Stories
-
- Izmir Health Biotechnology Sector Report - Izmir Solar Energy Industry
-
- Investment in Wind Energy Industry in
-
- Izmir Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) Sector - Evaluation Report After Implementation 2009 Tourism and Environmental Financial Support Program
-
- Renewable Energy and Environmental Technologies Financial Support Program - Small Scale Industrial Zones Development Financial Support Program
-
- Evaluation Report After Implementation of Competitiveness and Innovation in Tourism Financial Support Program for 2010
-
-
- Izmir Innovation Indicators and Analysis of the Innovation Ecosystem for 2016 - Izmir Innovation Ecosystem Monitoring Report (2018) - Initiation of Innovation, Entrepreneurship and Technology Production Result Oriented
-
- Izmir with the SocioEconomic Indicators (2004-2019) - Izmir Innovation Ecosystem 2020 Monitoring Report - Analysis of Prominent Sectors in Resource Use and Waste Production in
-
- Biogasand Organic Fertilizer Production Potential Report in Izmir
-
- Evaluation of TCDD Izmir Alsancak Port in terms of Regional Economy from Past to Present - Financial Support Program for Strengthening the Institutional Capacity and Competitiveness of the Private Sector
-
- Izmir Innovation Ecosystem 2019 Monitoring Report - Wind Energy Sector in
-
- Analysis of the Creative Industries in Turkey at Nuts-2 Regions Level: Focus on Izmir - Sustainability and Green Building Practices in the Construction Sector
-
- Izmir Regional Input-Output Analysis
-
- Wind Energy Sector and Izmir Offshore Wind Energy Roadmap - Izmir Industrial Heritage Inventory
-
- 2013-2023 Middle Black Sea (Amasya-^orum-Samsun-Tokat) Regional Innovation Strategy
-
- 'Middle Black Sea Development Agency Entrepreneurship Concept and Entrepreneurship in Turkey' - Corum Defense Industry Sectoral Research Report
-
- Regional Innovation Competition and Project Market
-
- TR83 Region Foreign Trade Analysis Report
-Textile and Ready-to-WearSector Report
-
- R&D and Innovation and Renewable Energy Survey Results in TR83 Region - OKA Manufacturing Sector Export Survey
-
- Middle Black Sea Region Crossborder Cooperation Business Forum
-
- 2009 SME Financial Support Program Audit and Evaluation Report
-
- TR83 Region Districts Socio-Economic Development Index
-
- Middle Black Sea Regional Innovation Strategy (20132023) Mid-Term Evaluation Report
-
- 'Report of TR83 Region Current Situation and Policy Recommendations In Terms of Competition, Industry and Employment' within the scope of the project 'Increasing Youth Employment in the Field of Industrial Design' with the financial contribution of the European Union and the Republic of Turkey.
-Aquaculture and Fisheries Sector Report - Wood Products and Furniture Sector Report -Samsun Export Strategy and Action Plan
-
- Regional Business Incubation Centers Network Project (2013-2015)
- Regional Innovation Strategy Activities - Report on Added Value Approach In Export and Import Facilities of TR83 Region -2010 Infrastructure Financial Support Program Audit and Evaluation
Report
-
- Increasing Competitiveness of Middle Black Sea Region (TR83)' Report of'Increasing Competitiveness of Middle Black Sea Region (TR83)' Project applied by the Middle Black Sea Development Agency in 20162017 under the Competitive Sectors Program, of which the Ministry of Science, Industry and Technology is the program authority, and funded by the European Union and the Republic of Turkey.
-
- Organized Industrial Zones Needs Analysis Report - Impact Analysis of 2011 and 2014 Financial Support Programs for SMEs
- Public-University-Industry Collaboration Analysis and Action Plan
-
-
- A workshop called 'Social Innovation Search Workshop in Middle Black Sea Region' - Social Innovation Summer School
-
- Evaluation of (ar§amba District in terms of Agricultural Product Potential - R&D Centers Fact Sheets - Domestic and National Automobile Production in
-
- TR83 Region Resource Efficiency Needs Analysis Report
-
- Corum Manufacturing Industry Research and Sector Report
-
-
- Report on Added Value Approach In Export and Import Facilities of TR83 Region -TR83 Regional Workforce and Vocational Education Sector Analysis Within The Scope of Future Professions -TR83 Region Vocational and Technical Education Summary Current Situation - Middle Black Sea Region Geographically Indicated Products
- Many Pre-Feasibility Reports in Various Sectors (as Laurel Drying, Packaging and Laurel Oil Production, Chestnut Tree Blossom Tea Production, Greenhouse Tomato Production, Turkish Salmon Processing Facility in Samsun Province; Block and Processed Marble Production, Production of Frozen Bakery Products, Dried Tomato Production, Marble Mosaic Production, Whey Powder Production, Ceramic Home and Ornamental Goods Production, Brick Production, Essential Oil Production Plant from Medicinal and Aromatic Plants, Sunflower Oil Production Facility in Tokat Province; Hot Dip Galvanized Plant Installation in Corum Province;
Poultry Slaughterhouse, Cooking Products Manufacturing, Onion Processing and Packaging Facility, Cable Car Line Installation in Amasya Province; Portable Ultrasound Device Manufacturing in Samsun Province)
Continuation of Figure 3
-
- Western Black Sea (Zonguldak-Karabiik-Bartin) 2015-2025 Regional Innovation Strategy and Action Plan
-
- Analysis of the Sectoral Structure and Competitiveness of TR81 Level 2 Region With InputOutput Model
-
- Socio-Economic Reasons of Migration in Zonguldak Province and Measures That Can Be Taken
-
- Devrek Walking Stick Current Situation Analysis and Inventory Study
-
- Safranbolu Chamber of Craftsmen and Artisans Women Workforce Problems and Solutions Research Project Report
- Branding Studies Project for Zonguldak Chestnut and
Walnut
-
- Eregli OIZ Export Attack
-
- SMEs Financial Support Program - Export Summit Final Report
-
- Bartin Province R&D and Innovation Potential Report for 2017
-
- Cut Flower and Outdoor Ornamental Plants Cultivation Pre-Feasibility Report
-Zonguldak Derekoy Goat Valley Project Preliminary Feasibility Report
-
- Integrated Broiler Slaughterhouse Pre-Feasibility Report - Buffalo Specialized OIZ Pre-Feasibility Report - Laurel Processing and Packaging Plant Pre-Feasibility - 2014 Social Development Financial Support Program Successful Projects Booklet
-
- 2014 SME Financial Support Program Successful Projects Booklet
-Zonguldak Furniture Specialized OIZ Feasibility Report - Cultivated Mushroom Cultivation Pre-Feasibility Report - Small Scale Infrastructure Financial Support Program
-2010-2011 SME Impact Assessment Report - Western Black Sea Region Geographical Indications
-
- Gok^ebey OIZ Establishment Research and Pre-Feasibility Report
-
- Research Study on the Evaluation of NonWood Forest Products in Bartin
-
- Zonguldak Province Licensed Warehousing Pre-Feasibility Report -Zonguldak Province Integrated Broiler Slaughterhouse Pre-Feasibility Report
-
- Zonguldak Province Sea Snail Pre-Feasibility Report
-
- Zonguldak Province Laurel Processing and Packaging Facility Pre-Feasibility Report
-
- Zonguldak Province Cultivated Mushroom Cultivation Pre-Feasibility Report - Zonguldak Province Goat Valley PreFeasibility Report
-
- Bartin Province Sea Snail Processing and Seafood Cold Storage Facility Pre-Feasibility Report
-
- Bartin Province Biogas and Biomass Potential Pre-Feasibility Report
CO
Products
^C^O^O^G
- Bartin Provint
Province R&D
-
- Karabiik Eskipazar Metal and Metal Products Specialized OIZ Preliminary Research & Information Report - Eregli OIZ Test And Technology Center Project Feasibility Study - Clustering and Rail Systems Analysis Study in Karabiik
-
- Black Sea and Balkan Economic and Political Studies Symposium - Zonguldak Province Investment Environment Assessment - SMEs Financial Support Program - Local Values Financial Support Program
- KarabQk Labor Market Research Report - TR81 Region Licensed Warehousing Investment PreFeasibility Report - Social Impact Assessment Report for the years 2011,2013 and 2014 - Greenhouse Specialized OIZ Functional Design and Pre-Feasibility Report
-
- 2015 SME Financial Support Program Successful Projects Booklet
-
- Cluster Analysis of Western Black Sea Steel
-
- Bartin Province Agricultural Greenhouse Specialized OIZ Pre-Feasibility Report - Pre-Feasibility Report for Calculation of Biogas and Biomass Potential of Bartin Province - Pre-Feasibility Report on Quality and Standardization of Honey Produced In Bartin Province
-
- Sea Snail Processing Facility and Cold Storage Pre-Feasibility Report for Alternative Seafood - Evaluation Report After 2013-2014 SME Program
Innovation and
Entrepreneurship Ecosystem Analysis - Mining Machinery Market Research Report - Zonguldak Province Sea Bass, Rainbow Trout and Sea Trout Pre-Feasibility Report
-
- TR90 Eastern Black Sea 2015-2017 Regional Innovation Strategy and Action Plan
-
- TR90 Region Clustering Strategy and Action Plan - Effects of SMEs on Regional Development - TR90 Region Alternative Financing Sources Report
- Pre-Feasibility Reports for Trabzon Province (as (i): Pasta Production, (ii): Elevator Cabin and Door Manufacturing, (iii): Biscuit Production, (iv): Hazelnut Cracking Plant, (v): Goat Farm, (vi): Dairy Installation, (vii): Greenhouse Cultivation, (viii): Cold Storage) - Fish Feed Production Facility Feasibility Report
-
- TR90 Eastern Black Sea Region Local Products Strategy and Action Plan 2015-2017 -Agro-Industrial Financial Support Program Evaluation and Impact Analysis Report
-
- TR90 Eastern Black Sea Region Berries Report
- Strategy Document on the Status of Women and their Integration into the Development Process - TR90 Region Women Entrepreneurship Support Strategy - TR90 Region Youth Entrepreneurship Support Strategy
о
- TR90 Eastern Black Sea Region District Based Socio-Economic Development Index and Classification
Entrepreneurship Report in Ordu and Giresun Provinces funded by the European Union and The Republic of Turkey
-
- Eastern Black Sea Geographical Indication Strategy Research Report and 2020-2022 Action Plan
-
- Evaluation Report after 2013-2014 Manufacturing Industry Financial Support Programs
-
- East Marmara Regional Innovation Strategy for Smart Specialization 2014-2018
-
- East Marmara Automotive and Automotive SubIndustry Sector Report
-
- East Marmara Ornamental Plants Sector Report
-
- East Marmara Plastic and Rubber Sector Report
-
- East Marmara Automotive Sector Report
-
- Diizce Province Livestock Specialization OIZ Feasibility Report
-
- Soil Fertility Inventory for Conscious Use of Fertilizer Project
-
- Foreign Trade and Target Market Analysis seperately for Rize and Giresun provinces. - Many pre-feasibility reports for Gumu$hane with Gumii§hane Chamber of Commerce and Industry Within The Scope of The Project of Preparing Feasibility Reports For Suitable Investments In Gumu§hane (as Tempered Glass and Thermal Glass Manufacturing, Ornamental Plants Culture, Vinegar Production Facility, Greenhouse Construction, PVC/Aluminum Glass Balcony Manufacturing, Polypropylene Bag Production Facility, Plastic Building Materials Production, Plastic Recycling Materials Production, PlasticBased Packaging Production Facility, Fruit Vegetable Drying and Packaging Facility, Fruit Vegetable Processing Facility, Fruit Vegetable Processing Production Facility, Metal Door, Window and Wrought-Iron Manufacturing, Metal Kitchen Apparels Manufacturing, Metal Appliance Manufacturing, Marble Processing Facility, Mushroom Production and Packaging Facility, Carton Box Production Facility, Ready Kitchen Products Manufacturing, Roof Type Solar Power Plant Installation In Gumu$hane OIZ, Frozen Fruit and Vegetable Manufacturing, Exterior Insulation EPS Production, Pulses Processing Packaging Facility, Acrylic Bathroom Products Manufacturing) and Medical and Aromatic Plants Processing and Packaging Facility Feasibility Report.
Continuation of Figure 3
-
-
- (i): Corum Assessment Research Report (ii): Agriculture Sector and Samsun Assessment Research Report in terms of Free Trade Agreement between the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland and the Republic of Turkey
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- Logistics Center Kocaeli Report
-
- Izmit Bay Fishing Project Feasibility Report
-
- Integration of Immigration in Kocaeli
-
- Mentoring Financial Support Program for Enterprises - Capacity Building Financial Support Program in the Information Sector
-
- Financial Support Program Based on Commercialization of Technology Transfer - Cleaner Production Financial Support Program - Machine Manufacturing Sector Development Financial Support Program
- Vocational Education and Training Mobility Accreditation Cooperation & Good Practice Sharing Workshop Final Report - Development Indicators of East Marmara Region - East Marmara - Paper Sector Report
-
- TR42 Region Social Analysis Report
-
- Technology Transfer Situation Analysis and Mapping Study in Gebze Region
-
- East Marmara Shipbuilding Sector Report
-
- IT Valley Investment Guide
-
- Diizce Logistics Market Strategy and Potential Identification Report - Qualified Vocational Employment and Sustainable Strategies Development Project - Cleaner Production Financial Support Program
-
- Machine Manufacturing Sector Development Financial Support Program
-
- Investment Support and Promotion Strategy and 2018 Action Plans" for each province - Provincial Meetings for the Future of Industry on the Way of National Technology and a Strong Industry Movement
-
- Entrepreneurial Child Workshop Activity Report
-
- East Marmara Project Database (2009-2017) - Financial Support Program for Strengthening the Value Chains of Transportation Vehicles and Systems
-
- Financial Support Program for the Development of Vocational Education for the Manufacturing Industry -Small-Scale Infrastructure Financial Support Program for Development of Production Infrastructures
-
Within the scope of Innoteam2017, innovation mentorship was provided to 10 SMEs.
- Private Sector R&D Centers Report - Entrepreneurial Child Workshop - Machine Manufacturing Sector Development Financial Support Program - Small-Scale Infrastructure Financial Support Program for Development of Production Infrastructures
-
-
-
- East Marmara Informatics Sector Report
-
- East Marmara Informatics Sector and Informatics Valley Strategy Development Workshop Final Report - East Marmara Chemical Sector Report - Financial Support Program for the Development of Vocational Education for the Manufacturing Industry - Small-Scale Infrastructure Financial Support Program for Development of Production Infrastructures
MARKA Project Database 21 Version
-
- Zafer Development Agency TR33 Regional Innovation Strategy - Increasing Added Value and Exports In The Marble Industry
-
- Feasibility Study of Branding and Marketing of Kutahya Tile
-
- Determination and Analysis of the Production Structure and Level of the TR33 Region
-
- Feasibility Study for Establishing the Industrial Inventory of Kutahya Province - Basic Branding Guide for SMEs
-
- Investigation of Professional Competencies of Employed and Future Employees in Manisa Province - Gastronomic Determination of U$ak Local Foods, Branding, Entrepreneurship and Investigation of Their Contribution to Employment
-
- Research for Capacity Building of Vocational High Schools in Afyonkarahisar
-
- Competitive-SME Financial Support Program
-
- Determining the Strategic Roadmap for U$ak Business World to Provide Added Value and Product Diversity - Manisa Province Organic Agriculture and Organic Livestock Strategy and Action Plan - Innovative-SME Financial Support Program
-
- Establishment of a Soma-based Logistics Center and Investigation of the Effects of Qandarh Port and Istanbul Highway on the Provincial Economy
- TR33 Region Domestic Automobile Factory Feasibility Study -2nd Local Economic Development Program (Disaster Management, Urban Services, People and Society) for each province
-
- Model Proposal for Manisa for Increasing the Patent and Trademark Capacities of Enterprises within the Scope of Protection of Innovation - Site Selection and Feasibility Study for the Establishment of Banaz OIZ
-
- Strategic Communication and Promotion Plan Booklet of Karahalh and Karahalh OIZ
-
- Kutahya - Alayunt Logistic-Specialized OIZ Project Feasibility Report
-
- Determining the Strategic Roadmap for U§ak Business World to Provide Added Value and Product Diversity
-
- Research Report on Understanding the Economic Value of Local Products
-
- U§ak Regenerated Textile Industry Value Chain Analysis
-
- Akhisar Carpenters and Furniture Industry Analysis - Developing-SME Financial Support Program
Ш
N
- Afyonkarahisar Conference and Congress Center Feasibility Study - Financial Support Program for the Development of Vocational Education
-
-
- Manisa Machinery-Molding and Equipment Sector Clustering Roadmap - Ujak Gastronomic Values Investment Feasibility - 1th Local Economic Development Program (Tourism, Industry, Transportation) for each province.
-
- Financial Support Program for Improving Competitiveness in the Industry
-
- Pre-Feasibility Study for the Establishment of Kutahya Mining Specialized OIZ - Kiitahya Traditional Arts History and Culture Tourism Natural Resources and Beauties
-
- 3rd Local Economic Development Program (Agriculture, Mining, Environment, Energy) for each province
-
- U§ak Province Textile Recycling Sector Report - Ala§ehir Agriculture-Based Specialized Greenhouse OIZ Feasibility Report - New Generation Education Financial Support Program (Within the scope of the program, robotic coding and data generation are carried out in order to improve the design, innovation and productivity capacities of school-age children.)

TR33 Region Technical Textile Production Roadmap
Continuation of Figure 3
-
- TR72 Region Furniture Industry Report
-
- Importance of Uranium Mine for the Region and Roadmap
-
- Suitable Model Agricultural Applications Feasibility for Regional Agriculture - Emerging Industry Financial Support Program - Financial Support Program for the Improvement of Urban and Social Infrastructure - Micro Enterprises Financial Support Program
- Kayseri Electrical Appliances Sector Value Chain Analysis, Sector Strategy and Upgrade Plan Report - Medical Sage
-
- A special research report titled 'Angel Investment From Past To Present'
-
- Pre-Feasibility Report of Kayseri Province Beydegirmeni Biogas
-
- Bayindirhiiyiik Integrated Agriculture and Fruit Growing Feasibility Report
- Feasibility Report of Evaluating Sheep Wool and Bringing it to the
- 2019 Year Vocational Education Financial Support Program
- Central Anatolia Development Agency TR72 Regional Innovation Strategy - Prominent Sectors In The TR72 Region - Sivas Railway Machinery and
-TR72 Entrepreneurship Profile Analysis
-
- Development of A Clustering Model forTR72 Region Agricultural Products
-
- Final Report of the Project Titled 'Developing Lavender Growing in Cayiralan District of Yozgat Province'
-
- Kayseri OIZ Industrial Symbious Research Project Report
Equipment Industry Clustering - Kayseri Furniture Industry Strategic Action Plan (2017-2023)
Strategy and Action Plan Report - Medical and Aromatic Plants
Sector Report
-
- Kayseri Competition Index 2013-2014
-
- Renewable Energy And Sustainable Competition Financial Support Program - Sivas Vocational Education, Innovation and
-
- Industrial Development and Efficiency Financial Support Program
-
- Financial Support Program for Improvement of Urban and Social Infrastructure
-
- Financial Support Program for New and Renewable Agricultural Practices
- Many Investment Feasibility Reports in Various Sectors (as Giirun Energy Specialized Industrial Zone, Agricultural Equipment Manufacturing Facility, Plastic Recycling Products Plant, Organic Chicken Farming, Timber Processing Plant,
Entrepreneurship Development Pasta Production Plant, Cardboard Box Production Facility,
-
- Prominent Sectors Report in TR72 Region - Kayseri Provincial Digital Marketing Center Preliminary Research Report - Value Chain Analysis of Kayseri Furniture
-
- Pre-Feasibility Reports (as Yozgat Province Timber Processing Facility, Yozgat Province Hemp Fiber Production Facility, Yozgat Province CLT Production Facility, Sivas Province Activated Carbon Production, Kayseri Province Egg Powder Production, Gelatin Production from Bovine Bone in Kayseri Province, Dry Cargo Container Production in Kayseri Province, Kayseri Province Natural Vinegar Production, Kayseri Province Trout Feed Production)
се
Center Feasibility - Pre-Feasibility Report Of Kayseri Logistics Center
Mixed Feed Production Facility, Integrated Meat Plant, EPS Production Facility)
- Korkudere Valley Quince and Grape Feasibility Project
-
- Edirne Development and Competitiveness Project - TR21 Thrace Region Industrial Symbiosis Potential Research
-
- Vineyard and Vineyard Products Sector Report
-
- Economic Development Financial Support Program - Socio-Economic Development Financial Support Program
-
- Small Scale Infrastructure Financial Support Program
-
- 2016 Entrepreneurship Financial Support Program - Career Planning Guide
- Needs Analysis for Career Services - Regional Job Market Assessment
-
- TR21 Thrace Region Competition Analysis - Incentives for the Defense and Aerospace Industry - Vocational Training Workshop - Dairy Cattle Farm Feasibility Report
-
- 2018 Economic Development Financial Support Program - 2018 Small Scale Infrastructure Financial Support Program
'Lean Manufacturing Application Report'
-
- TR21 Thrace Regional Innovation Report
-
- Milk and Dairy Products Sector Report of Thrace Region
-
- Medicinal-aromatic plants and ornamental plants that can be included in the agricultural production of TR21 Thrace Region
-
- Floristry Feasibility in Suleymanpa§a Greenhouse - Economic Development Financial Support Program - Socio-Economic Development Financial Support Program
-
- Small Scale Infrastructure Financial Support Program - "My New Business Entrepreneurship" Program has been carried out since 2015 to support and popularize Innovation Oriented Entrepreneurship.
-
- 'Regional Development Dynamics: Exit Strategies From The Unplanned Industrialization Trap And 2023 Scenarios' for each province.
-
- Kirklareli Province Food and Beverage Industry Sector Analysis and Action Plan
-
- Feasibility Study for Biogas Electricity Production Facility
- TR21 Thrace Region Agricultural Machines Sector Report - Tekirdag Province Agricultural Waste Potential Determination and Disposal Methods Project - Since 2017, maker training has been provided in the region, especially in secondary and high schools, and more than 1000 students have been reached. Within the scope of the two-day training; 3D modeling, 3D printer and arduino kit programming are taught.
- Geographical Indications in the Thrace Region - 2019 Financial Support Program For The Development Of Vocational Education In The Manufacturing Industry
Continuation of Figure 3
-
-
-
- South Aegean Regional Innovation and Entrepreneurship Strategy
-
- Current Situation Analysis and Development Strategies of Production Focused
Cooperatives in the South Aegean Region
-
- Mugla Province Manufacturing Industry Inventory
-
- Bringing ^ameli-Specific Walnut Types and Bean Varieties to the National Economy Project Final Report
-
- "Determining and developing the level of financial literacy in the TR32 Region" Project
-
- Rural Development Potential of Mugla Province Determination Project
- Pre-Feasibility of Fruit and Vegetable Drying Plant
-
- Aydin 2023 Employment Strategy (2017-2020 Action Plan) - Fethiye and Seydikemer Organized Industrial Zone Feasibility Study - New and Strategic Sector Analysis for Denizli - Aydin Province Livestock Report - Denizli Qardak Ozdemir Sabanci Organized Industrial Zone Growth and Promotion Strategy Report
-
- iztuzu Beach Solar Power Plant and Biological Treatment Plant Establishment Feasibility Project - Mugla Organic Agriculture Investment Report
-
- South Aegean Region Machinery Industry Sector Analysis - Beekeeping Products Sector Analysis - South Aegean Region (Aydin, Denizli, Mugla) Olive Oil Sector Report - Denizli's Agriculture, AgroBased Industry and Investment Potential - Mugla Agriculture and Livestock Sector Investment Report
-
- Financial support program on Strong Industry and Cleaner Production, R&D and Innovation

-
- Pre-Feasibility Report of Karaman Province Vinegar Production Facility (Apple-Grape) - Pre-Feasibility Report of Konya Province Licensed Warehousing Investment - Pre-Feasibility Report of Konya Province Cold Forged Barrel Production
-
- Pre-Feasibility Report of Konya Province Gelatin Production
-
- Pre-Feasibility Report of Konya Province Wheat Bran and Gluten Production
-
- Impact Assessment Report of the 'Improving Competitiveness in Economic Enterprises Program (2011)'


- Konya-Karaman Regional Innovation Strategy for Smart Specialization (2014-2023) - Impact Assessment Report of 2010 Economic Development Financial Support Program - Within the scope of TR52 Region Entrepreneurship Ecosystem Development Program, 'Modul 1: Mentor Training Program', 'Module 2: Maker Hackaton', 'Modul 3: Maker Workshop' and 'Module 4: Demo Day Crowdfunding and Maker Faire'
modules are available.

- Pre-Feasibility Report of Pectin Production Facility from Fruit Pulp in Karaman Province - Pre-Feasibility of Karaman Marble Processing Plant
End of Figure 3
-
-
ORAN deals with entrepreneurship, logistic centers, competitiveness, industrial symbiosis, renewable energy, vocational education, clusters, digital marketing, and sectors mainly as furniture industry, medical services, energy and agriculture. There are many pre-feasibility reports based on production and investment related to the prominent sectors. There is also a special research report on angel investments.
TRAKYAKA’s works focus on issues such as competitiveness, industrial symbiosis, entrepreneurship, career services, job market, vocational education, maker training, geographical indications, and the RDA has sectoral reports mainly based on agriculture and livestock. In order to support and popularize innovation oriented entrepreneurship, a program also has been carried out since 2015 by TRAKYAKA.
IKA focuses on entrepreneurship, agricultural competitiveness, target market, migration policies, empowerment and cooperatives of women, and various sectors especially agriculture.
MEVKA has entrepreneurship ecosystem development program. The RDA has some prefeasibility reports related to various sectors. MEVKA also produced impact assessment reports of previous programs.
ANKARAKA focuses on market, social entrepreneurship for youth program, “product commercialization and development of vocational education in the field of advanced technology”, social entrepreneurship, and sectors such as the IT sector, medicine and medical devices sector, construction machinery sector, defence and aviation sector and agriculture and food sector.
Comparative evaluation and concluding remarks
This paper evaluates the regional innovation system of Turkey by comparing the regional innovation strategies of RDAs. It was seen that only 14 RDAs have regional innovation strategies. When the visions in the regional plans of these are examined, it is observed that most of these 14 RDAs focused on innovation in their visions of the regional plans, however some RDAs did not put emphasize directly on innovation in the regional vision but included some innovation-related concepts. In order to produce regional innovation strategies, some of the RDAs have created innovation visions, while the others made progresses in innovation strategies in line with their regional plans without creating an innovation vision. The paper states that the visions defined in the regional plans and regional innovation strategies of the RDAs differ in terms of regional dynamics.
Comparative evaluation reveals that some agencies have created a specific regional innovation strategy whereas the others have not yet developed specific regional innovation strategies and have various studies on different innovation dimensions, but these studies are exclusive and far from a holistic approach. The comparative evaluation also reveals that regional innovation strategies of the RDAs differ in terms of regional priorities. Nevertheless, similar strategies created by the RDAs address developing the research and innovation culture; research and innovation infrastructure; institutional structure; human resources; financial resources; effective communication, cooperation and coordination; entrepreneurship and innovation ecosystem; awareness of innovation activities clusters, specialized/priority/prominent/strategic sectors; social innovation, IPR and commercialization, etc.
Although there are some efforts to improve the regional innovation systems by the RDAs, the comparative evaluation demonstrates that RDAs have not yet reached the desired level of producing a holistic regional innovation strategy and they should be more effective as a key actor in the regional innovation systems.
Most of the agencies create studies, publications, action plans, work plans and support programs to realize their innovation strategies and generally give priorities to innovation in the financial support programs. In addition, iZKA and OKA, as the leading agencies, create innovation ecosystem analysis, evaluation and monitoring reports in certain years to reveal how much they have achieved their innovation strategies.
On the one hand, the success of produced innovation strategies depends on the future work of these RDAs. On the other hand, in order to be successful, it is essential to determine how the strategies will be reflected and integrated with the spatial patterns.
Regional innovation system of Turkey will be successful if these efforts can be evaluated and implemented with a broad participation of actors including the representatives of relevant public and private sector, NGOs, universities and national institutions that are effective in regional innovation system and an integrated interactive innovation process including a defined realistic regional vision, strategic goals, strategic breakthroughs and action plans. If the determination of how these strategies will be reflected and integrated into spatial patterns is not considered as an important issue, the strategies will remain only in theory.
Designing and developing regional innovation strategies is not enough to establish and manage an effective regional innovation system. It is important that these strategies should be carried out with the responsible stakeholders within the specified time periods. Potential factors that would limit the implementation of the strategies should be determined in advance and minimized. Furthermore, the implementation of the strategies, monitoring, evaluation and performance measurement gain importance in innovation processes.
Список литературы A comparison of innovation strategies of regional development agencies in Turkey
- Asheim B., Bugge M., Coenen L., Herstad S. (2013). What does evolutionary economic geography bring to the table? Reconceptualising regional innovation systems. CIRCLE Papers, 5.
- Cook P., Memedovic O. (2003). Strategies for Regional Innovation Systems: Learning Transfer and Applications. Vienna: UNIDO.
- Cooke P., Boekholt P., Tödtling F. (2000). The Governance of Innovation in Europe. London: Pinter.
- Edquist C. (2005). Systems of innovation – perspectives and challenges. In: Fagerberg J., Mowery D.C., Nelson, R.R. (Eds.). The Oxford Handbook of Innovation. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Edquist C. (2008). Identification of policy problems in systems of innovation through diagnostic analysis. In: The 6th Globelics International Conference. Mexico, Mexico City, dated September 24–26, 2008. Available at: https://smartech.gatech.edu/bitstream/handle/1853/36896/Charles_%20Edquist_Identification%20_of_%20Policy_Problems.pdf?sequence=1
- Edquist C., Johnson B. J. (2000). Institutions and organisations in systems of innovation. Chapter 8. In: Edquist C., McKelvey M. (Eds.). Systems of Innovation: Growth, Competitiveness and Employment. UK: Edward Elgar Publishing. ISBN: 1858985730
- Feinson S. (2003). National innovation systems overview and country cases. In: Knowledge Flows and Knowledge Collectives: Understanding the Role of Science and Technology Policies in Development. Volume 1: Knowledge Flows, Innovation, and Learning in Developing Countries. Center for Science, Policy and Outcomes, Columbia University. Pp. 13–38.
- Lewandowska A. (2012). Regional innovation strategy as a management instrument of innovation policy in the region. Poland. Regional management. Theory, Practice and Development, Scientific Papers, 129–133. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/273949395_Regional_Innovation_Strategy_as_a_management_instrument_of_innovation_policy_in_the_region_Poland
- McCall T. (2010). Regional Innovation Systems. Institute for Regional Development, University of Tasmania. Available at: http://www.utas.edu.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0007/61936/McCall.-T.-2010,-Regional-Innovationsystems.pdf
- Metin H. (2010). Social and Institutional Impacts of Mersin Regional Innovation Strategy: Stakeholders’ Perspective. A Thesis Submitted to the Graduate School of Natural and Applied Sciences of Middle East Technical University, in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Master of Science in City and Regional Planning, April 2010. Available at: https://etd.lib.metu.edu.tr/upload/12611821/index.pdf
- Özen, B.S., Baycan T. (2014). Turkey’s national innovation system performance: Recent progress and ongoing challenges. In: 54th Congress of European Regional Science Association (ERSA) Regional Development & Globalization: Best Practices, August 26–29, 2014. Russia: Saint Petersburg.
- Özen B.S,. ve Baycan T. (2015). An Assessment of Turkish regional innovation system over regional innovation strategies developed by regional development agencies. In: 55th Congress of European Regional Science Association (ERSA) World Renaissance: Changing Roles for People and Places, August 25–29, 2015. Portugal: Lisbon.
- Özen B.S., Baycan T., Filiztekin A. (2018). Türkiye’de Bölgesel İnovasyon Performanslarının 2000 Yılından Günümüze Değişimi. In: M. Karagül, L.G. Kaya, O. Sungur (Eds.). Bölgesel Kalkınma ve Bölge Bilimi Üzerine Yazılar. Nobel Akademik Yayıncılık (in Turkish).
- Pellegrin I., Balestro M.V., Valle J.A. et al. (2010). Dynamizing innovation systems through induced innovation networks: A conceptual framework and the case of the oil industry in Brazil. Journal of Technology Management and Innovation, 5(3), 15–35. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.4067/s0718- 27242010000300002
- Schrempf B., Kaplan D., Schroeder D. (2013). National, regional, and sectoral systems of innovation — an overview. Report for FP7 Project “Progress”. Available at: progressproject.eu
- Zabala-Iturriagagoitia J.M., Jiménez-Sáez F., Castro-Martínez E. (2008). Evaluating European Regional Innovation Strategies. European Planning Studies, 16(8), 1145–1160. DOI: 10.1080/09654310802315849


