A Novel framework for Strategic Alliance of Knowledge Management Systems
Автор: Suzan Bandar Al-mutairi, M. Rizwan Jameel Qureshi
Журнал: International Journal of Modern Education and Computer Science (IJMECS) @ijmecs
Статья в выпуске: 4 vol.6, 2014 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Knowledge is the primary strategic resource of many organizations. Knowledge management system (KMS) is a process of knowledge extraction, storage, transformation, analysis, distribution and deployment. Strategic alliance plays an increasing role to a global scale in technology business competition. Organizations are able to use alliances to respond to new technology and deliver new products more efficiently. The relationship between knowledge management and strategic alliance is identified. Knowledge transfer and selecting suitable partner are critical factors in the success of strategic alliance of an organization. In this paper, a novel framework is proposed for KMS strategic alliance. By applying this framework, strategic alliance will be highly achievable in corporate companies.
Knowledge management system, Strategic alliance, Knowledge transfer, knowledge extraction, framework
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/15014646
IDR: 15014646
Текст научной статьи A Novel framework for Strategic Alliance of Knowledge Management Systems
Published Online April 2014 in MECS DOI: 10.5815/ijmecs.2014.04.06
Knowledge is the primary strategic resource of many organizations. Every organization should use knowledge management system (KMS) to facilities extraction, storage, integration, retrieve, transformation, visualization, analysis, distribution, deployment of knowledge. KMS also provides knowledge discovery from database or data warehouse to develop a mechanism of knowledge distribution in the information network [1].
Strategic alliance plays an important role to globally uplift to a company in a technology business competition. Companies of corporate sector are working hard than ever to develop new products and new markets due to rapid and changing requirements of customers. Therefore, organizations are using strategic alliances for achieving their business goals in an environment of strong competition and technological change. Organizations are able to use alliances to respond to new technology and deliver new products more efficiently.
Alliance mangers must decide when and how to select a partner. Top managers can control knowledge at each stage of the alliance process. Knowledge management principles and techniques have critical impact on the success of the alliance. There are several truths about knowledge management in alliance [2]:
-
• alliance can extensively increase organization financial returns if top management is able to manage knowledge correctly;
-
• alliance provides an opportunity to observe, learn and internalize the know-how of their partners.
This article is written to establish a relation between knowledge management and the knowledge management strategic alliance (KMSSA). A framework is proposed for KMS strategic alliance. Strategic alliance will be achievable by applying the proposed framework.
The reminder of this paper is organized as follow: the related work is described in section (II), the problem statement and the proposed solution are described in section (III), and Validation of the Proposed Solution is described in section (IV).
-
II. Related work
Decision supports system for strategic situation has limitation at the intelligence phase like consuming more time due to irrelevant knowledge [3]. The solution of this problem is to filter knowledge and optimize relevant data. Strategic alliance for e-business enterprise is presented [4]. It can be achieved by considering four key issues: persistent customer-oriented viewpoints, choosing the suitable cooperators, keep an enterprise independent and strengthen learning abilities of teams [4].
Studies are illustrated in [5] [6] to address the business strategy requirements of organizations by involving top management. The existing enterprise information resource management model is inefficient [7]. It is important to follow the integrity, history, security and sharing principles to build a model to achieve comprehensive information technology and knowledge innovation [7]. Another business model is presented for new technology-based firms for the main areas of strategic decision-making (locus, modus, focus) [8].
Integration measures are defined for supply chain management in retail business such as optimizing from the supply chain design aspects, use of information technology, use modern logistics thinking and establish strategic alliance [9]. Strategic plan management depends on knowledge and financing [10]. The objective is to show the effect of information system on strategic planning in higher education. There is a close relationship between knowledge management and knowledge management system [11]. A framework is proposed that has 5 phases: strategic awareness, situational analysis, strategy conception, strategy formulation, and strategy implementation planning.
One of the organizational resources that guarantee the sustainability of competitiveness is knowledge [12]. Organization managers must have the ability to manage knowledge process. There are four popular processes of knowledge management that are creation, storage, transfer and application. A case study is presented for a global energy company using knowledge management system. The case study shows an approach to share and control knowledge within the company to achieve success [13].
Strategic alliance is a joint between different business organizations for a set of a period of time. The strategic alliance shares resources, capabilities and core competences. Knowledge management creates and transfers knowledge through alliance enterprises. Interfirm knowledge transfer has two processes that are communication and cognitive processes [14]. Successful technological innovation alliance depends on knowledge sharing and new knowledge creation [15].
-
III. Problem satatement and the proposed solution
Following is the research question derived based on the literature review [7] [8] [9].
“ What is role of knowledge management (KM) in strategic alliance ?”
Three sub questions are raised by dividing the research question.
-
• What is the relation between knowledge management and strategic alliance?
-
• What is the main factor for successful strategic alliance?
-
• What are knowledge management system strategic alliance (KMSSA) phases?
We propose a new phase ‘strategy implementation planning’ into the existing knowledge management framework as shown in fig. 3. The main purpose of this phase is to implement KMS project. The main activities of this phase are defining operations, evaluating budget need and identifying timing and alliance enterprise restrictions.
-
IV. Validation of the Proposed Solution
Validation of the proposed solution is conducted using an electronic survey. An electronic survey is conducted using Twitter, Facebook and email. Questions are divided into four goals. These goals are identifying knowledge management and identifying alliance, determining alliance success factors and importance of knowledge management system in business planning. Identifying of knowledge management system strategic planning (KMSSA) framework and it is phases.
Q1: what is the effect of the knowledge on the business success?
Table 1 shows that 82.5% (where 40% very high and 42.5% high) of respondents are supportive to question 1. 5% of the respondents are disagreed. 12.5% of the respondents are neutral. The results show that this question has a high effect on the business success. Fig. 1 shows the results of Table 1 graphically.
Table 1. Result for Question 1
|
Likert Scale |
Frequency |
Percent |
|
1 |
0 |
0 % |
|
2 |
2 |
5 % |
|
3 |
5 |
12.5 % |
|
4 |
17 |
42.5 % |
|
5 |
16 |
40 % |
|
Total Respondent |
40 |
100% |
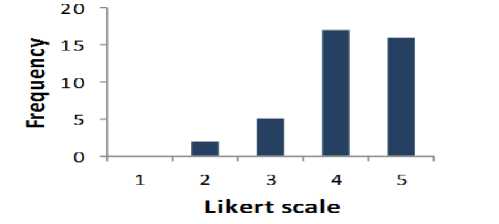
Fig. 1. Graphical Representation of Question 1
Q2: Are you aware of the strategic alliance?
Table 2 shows that 72.5% of the respondents were supportive to question 2. 25% of the people are agreed to very low and low and 35% of the respondents are neutral. Fig. 2 displays the results of Table 2 graphically.
Table 2. Result for Question 2
|
Likert Scale |
Frequency |
Percent |
|
1 |
5 |
12.5 % |
|
2 |
5 |
12.5 % |
|
3 |
14 |
35 % |
|
4 |
13 |
32.5 % |
|
5 |
3 |
7.5 % |
|
Total Respondent |
40 |
100% |
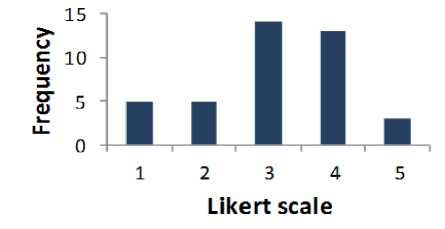
Fig. 2. Graphical Representation of Question 2
Q3: What is the effect of the knowledge on the alliance success?
Table 3 shows that 80 % of respondents are in favour of question 3. The percentage of the people who have a neutral opinion neither agree nor disagree is 20%. Fig. 4 displays the results of Table 3 graphically.
Q4: Does alliance provide an improvement in corporation between business enterprises?
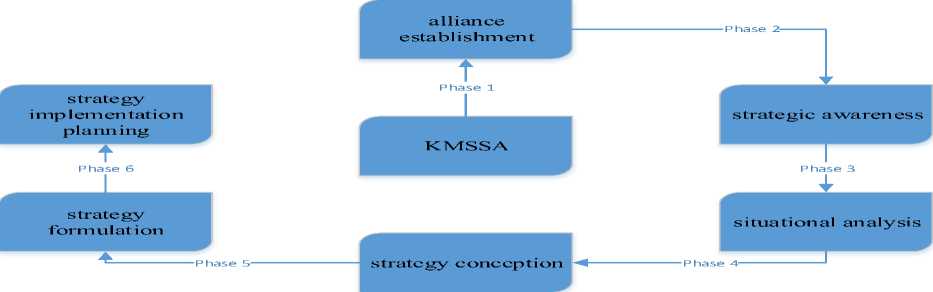
Fig. 3. KMSSA framework phases
Table 3. Result for Question 3
|
Likert Scale |
Frequency |
Percent |
|
1 |
0 |
0 % |
|
2 |
0 |
0 % |
|
3 |
8 |
20 % |
|
4 |
25 |
62.5 % |
|
5 |
7 |
17.5 % |
|
Total Respondent |
40 |
100% |
Table 4. Result for Question 4
|
Likert Scale |
Frequency |
Percent |
|
1 |
1 |
2.5 % |
|
2 |
0 |
0 % |
|
3 |
8 |
20 % |
|
4 |
24 |
60 % |
|
5 |
7 |
17.5 % |
|
Total Respondent |
40 |
100% |
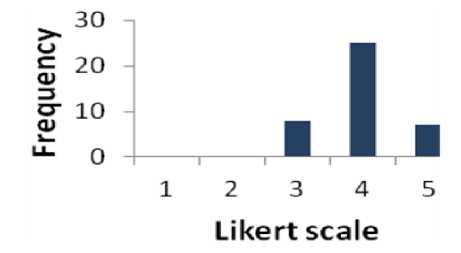
Fig. 4. Graphical Representation of Question 3
Table 4 shows that 77.5% of respondents are supportive to question 4 whereas 2.5% of respondents are disagreed. The percentage of the people who have a neutral opinion neither agree nor disagree is 20%. Fig. 5 shows the results of Table 4 graphically.
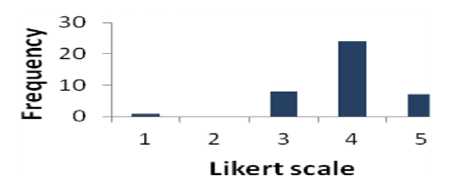
Fig. 5. Graphical Representation of Question 4
Q5: Does knowledge management have important effect on strategic alliance?
Table 5 shows that 77.5% of respondents are supportive to question 5 whereas 2.5% of the people are disagreed. The percentage of the people who have a neutral opinion neither agree nor disagree is 20%. Fig. 6 presents the results of Table 5 graphically.
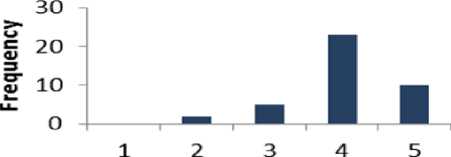
neither agree nor disagree is 20 %. Fig. 8 displays the results of Table 7 graphically.
Table 5. Result for Question 5
|
Likert Scale |
Frequency |
Percent |
|
1 |
0 |
0 % |
|
2 |
1 |
2.5 % |
|
3 |
8 |
20 % |
|
4 |
20 |
50 % |
|
5 |
11 |
27.5 % |
|
Total Respondent |
40 |
100% |
Table 7. Result for Question 7
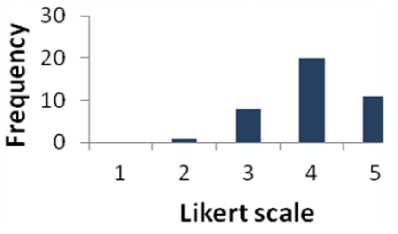
Fig. 6. Graphical Representation of Question 5
|
Likert Scale |
Frequency |
Percent |
|
1 |
0 |
0 % |
|
2 |
2 |
5 % |
|
3 |
8 |
20 % |
|
4 |
24 |
60 % |
|
5 |
6 |
15 % |
|
Total Respondent |
40 |
100% |
CD
ст 10 cu S о
Likert scale
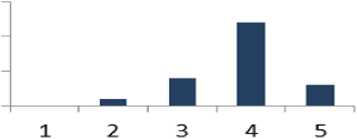
Fig. 8. Graphical Representation of Question 7
Q6: Do you think that the alliance has improved?
Table 6 shows that 55% of respondents are supportive to question 6 whereas 40% of the people are disagreed. The percentage of the people who have a neutral opinion neither agree nor disagree is 5%. Fig. 7 shows the results of Table 6 graphically.
Table 6. Result for Question 6
Q8: What is the effect of "knowledge transfer" in improving the strategic alliance?
Table 8 shows that 72.5% of respondents are supportive to question 8 whereas 5% of the people are disagreed. The percentage of the people who have a neutral opinion neither agree nor disagree is 22.5 %. Fig. 9 presents the results of Table 8 graphically.
|
Likert Scale |
Frequency |
Percent |
|
1 |
0 |
0 % |
|
2 |
2 |
5 % |
|
3 |
16 |
40 % |
|
4 |
12 |
30 % |
|
5 |
10 |
25 % |
|
Total Respondent |
40 |
100% |
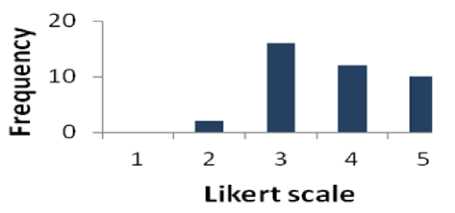
Fig. 7. Graphical Representation of Question 6
Table 8. Result for Question 8
|
Likert Scale |
Frequency |
Percent |
|
1 |
1 |
2.5 % |
|
2 |
1 |
2.5 % |
|
3 |
9 |
22.5 % |
|
4 |
20 |
50 % |
|
5 |
9 |
22.5% |
|
Total Respondent |
40 |
100% |
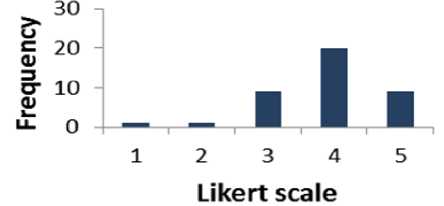
Fig. 9. Graphical Representation of Question 8
Q7: what is the effect of "knowledge transfer" between alliance partners?
Table 7 shows that 75% of respondents are supportive to question 7 whereas 5 % of the people are disagreed. The percentage of the people who have a neutral opinion
Q9: what is the effect of selection of the good partner in improving strategic alliance?
Table 9 shows that 67.5% of respondents were supportive to question 9 whereas 2.5% of the people are disagreed. The percentage of the people who have a neutral opinion neither agree nor disagree is 30 %. Fig. 10 presents the results of Table 9 graphically.
Q10: what is the effect of alliance in business performance of the facilities?
Table 10 shows that 75% of respondents are supportive to question 10 whereas 5% of the people are disagreed. The percentage of the people who have a neutral opinion neither agree nor disagree is 20 %. Fig. 11 shows the results of Table 10 graphically.
Table 9. Result for Question 9
|
Likert Scale |
Frequency |
Percent |
|
1 |
0 |
0 % |
|
2 |
1 |
2.5 % |
|
3 |
12 |
30 % |
|
4 |
15 |
37.5 % |
|
5 |
12 |
30 % |
|
Total Respondent |
40 |
100% |
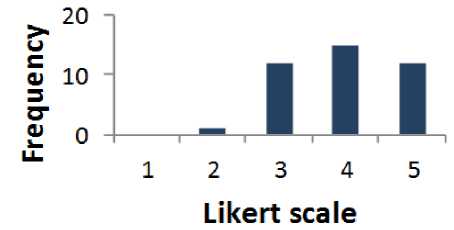
Fig. 10. Graphical Representation of Question 9
Table 11 shows that 80% of respondents are supportive to question 11 whereas 2.5% of the people are disagreed. The percentage of the people who have a neutral opinion neither agree nor disagree is 17.5 %. Fig. 12 presents the results of Table 11 graphically.
Q12: Do you prefer a system to assist you planning the business strategy?
Table 12 shows that 82.5% of respondents are supportive to question 12 whereas 5% of the people are disagreed. The percentage of the people who have a neutral opinion neither agree nor disagree is 12.5%. Fig. 13 displays the results of Table 12 graphically.
Table 11. Result for Question 11
|
Likert Scale |
Frequency |
Percent |
|
1 |
1 |
2.5 % |
|
2 |
0 |
0 % |
|
3 |
7 |
17.5 % |
|
4 |
22 |
55 % |
|
5 |
10 |
25 % |
|
Total Respondent |
40 |
100% |
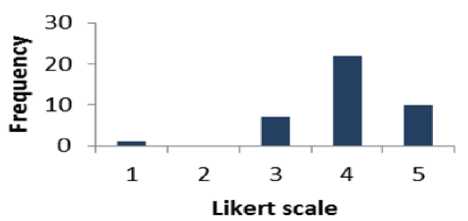
Fig. 12. Graphical Representation of Question 11
Table 10. Result for Question 10
|
Likert Scale |
Frequency |
Percent |
|
1 |
0 |
0 % |
|
2 |
2 |
5 % |
|
3 |
8 |
20 % |
|
4 |
21 |
52.5 % |
|
5 |
9 |
22.5 % |
|
Total Respondent |
40 |
100% |
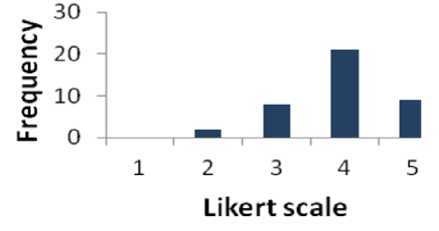
Fig. 11. Graphical Representation of Question 10
Table 12. Result for Question 12
|
Likert Scale |
Frequency |
Percent |
|
1 |
0 |
0 % |
|
2 |
2 |
5 % |
|
3 |
5 |
12.5 % |
|
4 |
23 |
57.5 % |
|
5 |
10 |
25 % |
|
Total Respondent |
40 |
100% |
Likert scale
Fig. 13. Graphical Representation of Question 12
Q11: What is the effect Knowledge management system in business quality improvement?
Q13: What is the effect of enterprise resources in knowledge management?
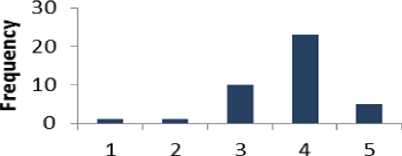
Table 13 shows that 70% of respondents are supportive to question 13 whereas 5% of the people are disagreed. The percentage of the people who have a neutral opinion neither agree nor disagree is 25 %. Fig. 14 shows the results of Table 13 graphically.
Table 13. Result for Question 13
|
Likert Scale |
Frequency |
Percent |
|
1 |
1 |
2.5 % |
|
2 |
1 |
2.5 % |
|
3 |
10 |
25 % |
|
4 |
23 |
57.5 % |
|
5 |
5 |
12.5 % |
|
Total Respondent |
40 |
100% |
Likert scale
Fig. 14. Graphical Representation of Question 13
Q14: Have you use knowledge management system strategic planning in your business?
Table 14 shows that 42.5 % of respondents are in favour of question 14 whereas 22.5% of the people are disagreed. The percentage of the people who have a neutral opinion neither agree nor disagree is 35 %. Fig. 15 presents the results of Table 14 graphically.
Table 14. Result for Question 14
|
Likert Scale |
Frequency |
Percent |
|
1 |
4 |
10 % |
|
2 |
5 |
12.5 % |
|
3 |
14 |
35 % |
|
4 |
8 |
20 % |
|
5 |
9 |
22.5 % |
|
Total Respondent |
40 |
100% |
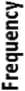

Likert scale
Fig. 15. Graphical Representation of Question 14
Q15: What is the effect of ‘alliance establishment 'phase in improving the efficiency of knowledge management system strategic alliance framework?
Table 15 shows that 67.5% of the respondents are supportive to question 15 whereas 2.5% of the people are disagreed. The percentage of the people who have a neutral opinion neither agree nor disagree is 30%. Fig. 16 displays the results of Table 15 graphically.
Table 15. Result for Question 15
|
Likert Scale |
Frequency |
Percent |
|
1 |
1 |
2.5 % |
|
2 |
0 |
0 % |
|
3 |
12 |
30 % |
|
4 |
18 |
45 % |
|
5 |
9 |
22.5 % |
|
Total Respondent |
40 |
100% |
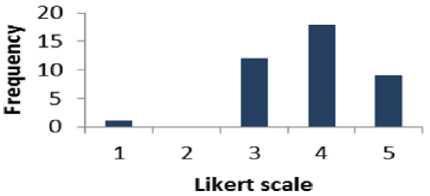
Fig. 16. Graphical Representation of Question 15
Q16: Does the ‘strategic awareness’ makes it clear for the top management to understand the objects and aligning knowledge management system?
Table 16 shows that 70% of the respondents are supportive to question 16 whereas 7.5% of the people are disagree. The percentage of the people who have a neutral opinion neither agree nor disagree is 22.5%. Fig. 17 displays the results of Table 16 graphically.
Table 16. Result for Question 16
|
Likert Scale |
Frequency |
Percent |
|
1 |
1 |
2.5 % |
|
2 |
2 |
5 % |
|
3 |
9 |
22.5 % |
|
4 |
22 |
55 % |
|
5 |
6 |
15 % |
|
Total Respondent |
40 |
100% |
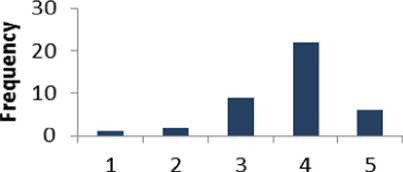
Likert scale
Fig. 17. Graphical Representation of Question 16
Q17: Has the ‘situational analyses’ succeeded to address the fail and success points of the KMS situation?
Table 17 shows that 65% of the respondents are supportive to question 17 whereas 2.5% of the people are disagreed. The percentage of the people who have a neutral opinion neither agree nor disagree is 32.5 %. Fig. 18 presents the results of Table 17 graphically.
Table 17. Result for Question 17
|
Likert Scale |
Frequency |
Percent |
|
1 |
0 |
0 % |
|
2 |
1 |
2.5 % |
|
3 |
13 |
32.5 % |
|
4 |
21 |
52.5 % |
|
5 |
5 |
12.5 % |
|
Total Respondent |
40 |
100% |
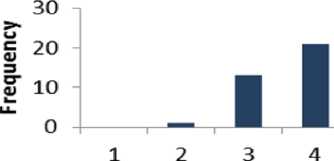

Likert scale
Fig. 18. Graphical Representation of Question 17
Q18: Does strategy formulation succeed to determine the KMS operations, responsibilities and technical architecture?
Table 18 shows that 75% of the respondents are supportive to question 17 whereas 2.5% of the people are disagreed. The percentage of the people who have a neutral opinion neither agree nor disagree is 22.5 %. Fig. 19 displays the results of Table 18 graphically.
Table 18. Result for Question 18
|
Likert Scale |
Frequency |
Percent |
|
1 |
0 |
0 % |
|
2 |
1 |
2.5 % |
|
3 |
9 |
22.5 % |
|
4 |
19 |
47.5 % |
|
5 |
11 |
27.5 % |
|
Total Respondent |
40 |
100% |
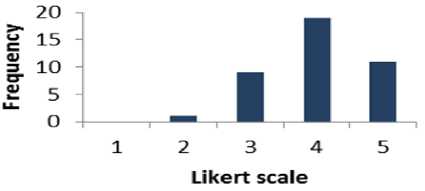
Fig. 19. Graphical Representation of Question 18
-
V. CONCLUSION AND FUTURE WORK
There are several features of this research. First, it demonstrates the close relationship between knowledge management and strategic alliance. According to our study, knowledge transfer and selection partner are critical factors in the success of strategic alliance. The proposed KMSSA includes six phases namely alliance establishment, strategic awareness, situational analysis, strategy conception, strategy formulation and strategy implementation planning. An effective implementation of the proposed framework will increase the chances of alliance success. The result of successful alliance will lead to better corporate performance, reduce cost of solving recurring problems, enhance product quality and increase maturity level. Future research aims to clarify the role of alliance knowledge mangers in implementing KMSSA.
Список литературы A Novel framework for Strategic Alliance of Knowledge Management Systems
- J. Mulyono, H. Harisno and C. Kristianto, “The Development of Knowledge Management System Model in XYZ Corporation,” IEEE, 2013.pp.188-191.
- S. Parise and L. Sasson, “Leveraging knowledge management across strategic alliances”, IBM Institute for Knowledge-Based Organizations, 2002, pp. 1-11.
- S. Zahaf and F. Gargouri, “Towards a strategic decision making aid for the management of business processes,” IEEE, 2010, pp. 330 - 333.
- Z. Zhongke and H. Yujie, “The Strategic Alliance Study of the E-Business Enterprise,” International Conference on E-Business and E-Government, 2010, pp. 413-416.
- A. Babar and B. Wong, “Capturing Strategic Business Requirements: An Exploratory Study,” 19th Asia-Pacific Software Engineering Conference, 2012, pp. 446-451.
- N. Somsuk, T. Laosirihongthong, and M. W. McLean, “Strategic management of university business incubators (UBIs): Resource–based view (RBV) theory,” IEEE ICMIT, 2012, pp. 611-618.
- W. Tao, “Research on management pattern of enterprise based on E-Commerce,” Symposium on Electrical & Electronics Engineering (EEESYM), 2012, pp. 607-610.
- Z. Peng, “New Strategic Management Business Models for New Technology-Based Firms,” Fourth International Conference on Multimedia Information Networking and Security, 2012, pp. 828-831.
- H. Hong, “Study on the integration of supply chain management in retail business,” IEEE, 2010, pp. 1-4.
- L. Luic and D. Boras, “Strategic Planning of the Integrated Business and Information System – A Precondition for Successful Higher Education Management,” 32nd International Conference on Information Technology Interfaces, 2010, pp. 489-494.
- H. S. Beiryaei and M. Jamporazmay, “Propose a Framework for Knowledge Management Strategic Planning (KMSSP),” International Conference on Electronics and Information Engineering, 2010, pp. V2-469-V2-473.
- I. Oyefolahan and P. Dominic, “The Use of KMS in Organizations: A Conceptual Framework and Preliminary Tests of Instruments,” IEEE, 2011.
- A. Murtadho, “Knowledge Management Application System Implementation in Global Energy Company: Opentext 9.7.1 Livelink Global Exploitation,” International Conference on Advanced Computer Science and Information Systems (ICACSIS), 2012, pp. 125-130.
- L. Yunhe, “Empirical Research on the Relationship between Interfirm Knowledge Transfer and Alliance Performance,” IEEE, 2011, pp. 312-316.
- L. Xiang-yi, Z. Qing-pu and L. Hong-yun, “Partners Selection for Strategic Technological Innovation Alliance from the Knowledge Perspective,” IEEE, 2008, pp. 1416-1421.


