Activation of cell death in the sugar cane suspension culture by the exposure to high temperature
Автор: Lyubushkina I.V., Fedyaeva A.V., Pobezhimova T.P., Stepanov A.V., Rikhvanov E.G.
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 4 т.10, 2014 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The process of cell death in a sugar cane suspension culture after exposure to high temperature (45, 50, 55 and 60 °C) during 10 min has been studied. It has been revealed that treatment of cell culture at 50 °C did not cause an immediate cell death, but 50% of the cells were dying for the next 48 h. Exposure of cell culture to more high temperature (55 - 60 °C) caused a massive cell death occurred instantly after treatment. The development of cell death after the treatment at 50 °C was accompanied by the protoplast condensation, increased generation of reactive oxygen species and hyperpolarization of the mitochondrial inner membrane. Obtained results indicate on the active character of the cell death process, induced by the moderate heat shock in sugar cane suspension culture.
Saccharum officinarum l, suspension culture, high temperatures, programmed cell death, reactive oxygen species, electrochemical transmembrane potential
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14323904
IDR: 14323904
Текст научной статьи Activation of cell death in the sugar cane suspension culture by the exposure to high temperature
Программируемая клеточная гибель (ПКГ) у реализации программы развития, начиная от растений является ключевым процессом для эмбриогенеза, дифференцировки клеток и тканей и заканчивая старением организма (Jones, 2001). Кроме того, этот процесс также вовлечен в ответные реакции растения на абиотические и биотические стрессовые воздействия, такие как засоление, окислительный стресс, температурные воздействия и многие другие (Jones, 2001). Известно, что ПКГ у растений может сопровождаться рядом специфических структурно-морфологических и биохимических изменений: конденсацией хроматина с последующим распадом ядра и межнуклеосомной фрагментацией ядерной ДНК, уплотнением и вакуолизацией цитоплазмы, уменьшением клетки в объеме и отставанием протопласта от клеточной стенки, выходом цитохрома с из митохондрий в цитоплазму, активацией эндонуклеаз и каспазоподобных белков, образованием активных форм кислорода (АФК), кратковременной гиперполяризацией внутренней митохондриальной мембраны (Bras et al., 2005; Reape et al., 2008). Однако в зависимости от условий активации процесса гибели и участия в его реализации таких органелл, как хлоропласты, митохондрии и вакуоли, структурно-морфологические и биохимические параметры ПКГ у растений могут значительно варьировать (Krishnamurthy et al., 2000).
Температура является одним из важнейших абиотических факторов, определяющих рост и развитие растений. Значительное отклонение температуры окружающей среды от оптимальной может вызывать необратимые нарушения клеточного гомеостаза, и в итоге привести к гибели отдельных клеток, тканей и целого растительного организма (Hasanuzzaman et al., 2013). У многих растений температура выше 40 °С вызывает клеточные повреждения, ограничивающие эффективность фотосинтеза и влияющие на белковый метаболизм (Xu et al., 2008). Известно, что одной из причин повреждений в условиях теплового стресса является чрезмерная продукция АФК. Накопление АФК в клетке приводит к развитию окислительного стресса и, как следствие, вызывает перекисное окисление липидов мембран, денатурацию белков, повреждение нуклеиновых кислот (Akladious, 2014). При значительном уровне внутриклеточных повреждений, когда клетка становится не способна к их репарации, реализуется один из возможных сценариев ее гибели. Если накопление повреждений происходит в течение достаточно продолжительного периода времени (от нескольких часов до нескольких дней), то в клетке активируется управляемый, генетически запрограммированный процесс ее деструкции - ПКГ (Bras, 2005).
Изучение реализации процесса ПКГ у растений в условиях теплового стресса активно ведется в последние годы (Vacca et al ., 2006; Li et al ., 2012). Показано, что активный тип клеточной гибели у растений, индуцированный действием повышенных температур, сопровождается морфологическими и биохимическими изменениями, сходными с теми, что наблюдаются при действии иных факторов внешней среды - конденсацией протопласта, увеличением содержания АФК, фрагментацией ядерной ДНК и рядом других (Zuppini et al. , 2007).
И хотя в настоящее время достигнут значительный прогресс в данной области исследований, до сих пор остается не известным, какие из биохимических и физиологических изменений, происходящих в растительной клетке на ранних этапах активации ПКГ, являются ключевыми для реализации именно этого типа гибели. В связи с этим, в данной работе были изучены структурноморфологические и биохимические параметры процесса гибели клеток суспензионной культуры сахарного тростника при действии ряда повышенных температур. Особый интерес представляло сравнение данных изменений, характерных для процесса гибели, развивающегося во времени, с соответствующими изменениями, происходящими при мгновенной массовой гибели, вызываемыми действием повышенных температур.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
В работе использовали суспензионную культуру клеток сахарного тростника Saccharum officinarum (L.), сорт POJ2878, линия, устойчивая к аноксии, полученной в ИФР РАН и любезно предоставленной к.б.н., с.н.с. лаборатории генетической инженерии СИФИБР СО РАН В.Н. Шмаковым. Культура выращивалась при 26 °С на МС-среде (Murashige and Scoog, 1962), содержащей сахарозу (3%), тиамин (1,0 мг/л), пиридоксин (0,5 мг/л), никотиновую кислоту (0,5 мг/л), 2,4-Д (2,5 мг/л), инозитол (0,01 %) и дитиокарбамат натрия (0,0005 %). Культуру пересевали каждые 14 дней с разведением свежей средой в 10 раз. Культуру подвергали кратковременному воздействию повышенной температуры: 45, 50, 55 или 60 °С в течение 10 мин, затем переносили в контрольные условия (26 °С) на 48 ч.
Микроскопический анализ клеток проводили с помощью инвертированного флюоресцентного микроскопа AxioObserver Z1 («Carl Zeiss», Германия) с цифровой монохромной камерой AxioCam MRm3 и пакетом программного обеспечения для захвата и анализа изображений «AxioVision Rel.4.6». В работе были использованы следующие фильтры: Filter set 15 (EX BP 546/12, BS FT 580, EM LP 590) и Filter set 10 (EX BP 450490, BS FT 510, EM BP 565).
Выживаемость клеток определяли с помощью двойного окрашивания флюоресцентными красителями: витальным красителем FDA (флюоресцеин диацетат, конечная концентрация 50 мкМ) и летальным красителем PI (пропидий йодид, конечная концентрация 7 мкМ). По 100 мкл культуры помещали в микроцентрифужные пробирки объёмом 2 мл, инкубировали в течение 2 мин при 26 °С на минитермошейкере TS-100 («BioSan», Латвия) и использовали для микроскопического анализа.
Для изучения образования АФК в клетках суспензионной культуры сахарного тростника использовали H2DCF-DA (2,7- дихлородигидрофлюоресцеин диацетат, 1 мкМ), который добавляли в культуральную среду, после чего инкубировали при 26 °С (контрольный образец) или при соответствующей повышенной температуре (опытные образцы) в течение 10 мин и анализировали свечение образованного флуоресцеина. H2DCF-DA является прижизненным красителем, легко проникающим в клетки. Он подвергается модификации эстеразами, после чего, реагируя с АФК (перекись водорода, супероксид анион, гидроксил анион) и оксидом азота, начинает флюоресцировать зеленым (Polesskaia, 2007). Длины волн возбуждения и эмиссии: 488 и 520 нм, соответственно (Maxwell et al., 1999). В качестве положительного контроля использовали культуру клеток, инкубировавшуюся с H2DCF-DA при 26 °С в течение 10 мин в присутствии 5 мМ H2O2. Отрицательным контролем служила культура клеток, обработанная 100 мМ аскорбиновой кислотой при 26 °С в течение 10 мин. Увеличение (в случае H2O2) или снижение (в случае аскорбиновой кислоты) интенсивности флюоресценции в присутствии данных веществ свидетельствовали о специфичности окрашивания H2DCF-DA в зависимости от уровня АФК в клетках. Определение электрохимического потенциала на внутренней митохондриальной мембране
Для качественной визуализации величины потенциала на внутренней митохондриальной мембране (∆Ψm) использовали потенциалзависимый катионный краситель JC-1 (5,5',6,6'-тетрахлор-1,1',2,2'-тетраэтилбензимидазоло-карбоцианин, 20 мкМ). Клетки культуры сахарного тростника переносили по 100 мкл в микроцентрифужные пробирки объёмом 2 мл, добавляли 100 мкл буфера для окрашивания (25 мМ MES, 2% глицерин, рН 5,5) и инкубировали в течение 10 мин при 26 °С (контрольный образец) или при соответствующей повышенной температуре (опытные образцы) с добавлением красителя. Положительным контролем служила культура клеток, обработанная 20 мкМ олигомицином в течение 10 мин при 26 °С с добавлением красителя JC-1, а отрицательным - культура, обработанная 4 мкМ карбонилцианид m-хлорфенилгидразоном (СССР) также в течение 10 мин при 26 °С с JC-1. Увеличение (в случае олигомицина) или снижение (в случае СССР) интенсивности красной флюоресценции при добавлении данных веществ свидетельствовали о специфичности окрашивания JC-1 в зависимости от величины ∆Ψm на внутренней митохондриальной мембране.
JC-1 является липофильным соединением, легко проникающим через мембраны. Он формирует J-агрегаты при определенной концентрации красителя, рН и ионной силе. Липофильные флюорохромные молекулы накапливаются в матриксе энергизированных митохондрий, что впоследствии приводит к формированию J-агрегатов в зависимости от значения ∆Ψ m . В живых клетках JC-1 существует в виде мономеров при деполяризованном потенциале (от положительных значений до -100 мВ). Данные мономеры флюоресцируют зеленым после освещения светом с длиной волны 490 нм.
При гиперполяризованном потенциале (значения ниже -140 мВ) происходит формирование J-агрегатов, флюоресцирующих красным. Таким образом, краситель JC-1 позволяет визуализировать митохондрии с низким и высоким значениями ∆Ψ m (Simeonova et al. , 2004).
Данные обработаны статистически. Приведены средние арифметические и стандартные отклонения (Glantz, 1998).
RESULTS
Влияние повышенных температур на жизнеспособность и конденсацию протопласта в клетках суспензионной культуры сахарного тростника
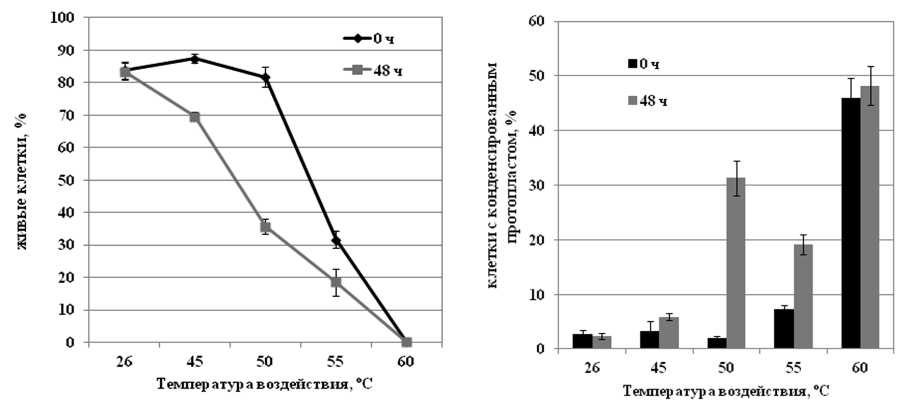
На первом этапе работы необходимо было выявить повышенную температуру, вызывающую постепенную гибель клеток в культуре сахарного тростника и сравнить особенности реализации данного процесса с мгновенной гибелью клеток. Обработка при температуре 45 °С (10 мин) не вызывала значительной гибели клеток сахарного тростника как сразу же после обработки, так и через 48 часов инкубации при обычной температуре. Конденсации протопласта - одного из морфологических маркеров программируемой клеточной гибели - также не наблюдалось (Рис. 1 а, б). Воздействие при температуре 60 °С (10 мин) приводило к мгновенной, массовой гибели клеток. Обработка при температуре 55 °С (10 мин) вызывала мгновенную гибель почти 50% клеток сразу же после обработки, и около 10% клеток погибало в последующие 48 ч инкубации (Рис. 1 а, б). Следует отметить, что доля клеток с конденсированным протопластом в культуре возрастала в соответствии с процессом отсроченной гибели клеток - на 10% через 48 ч после воздействия (Рис. 1 б). Действие температуры 60 °С на культуру сахарного тростника вызывало мгновенную гибель всех клеток в культуре сразу же после обработки, то есть отсроченного процесса гибели не наблюдалось. Тем не менее, доля клеток с конденсированным протопластом в культуре возрастала почти на 50% (Рис. 1 б).
Среди изученных температурных обработок процесс гибели, имеющий признаки ПКГ, вызывало тепловое воздействие 50 °С, которое не приводило к мгновенной гибели клеток сразу же после обработки. Однако данное тепловое воздействие вызывало постепенную гибель клеток в культуре в течение последующих 48 ч инкубации. За данный период доля живых клеток в культуре снижалась с 80 до 35% , (Рис. 1 а ). В то же время почти на 30% возрастала доля клеток с конденсированным протопластом, т.е. конденсация протопласта в клетках происходила по мере развития процесса гибели уже после окончания действия температуры (Рис. 1 б ).
Изменение содержания активных форм кислорода в клетках культуры сахарного тростника под действием повышенных температур
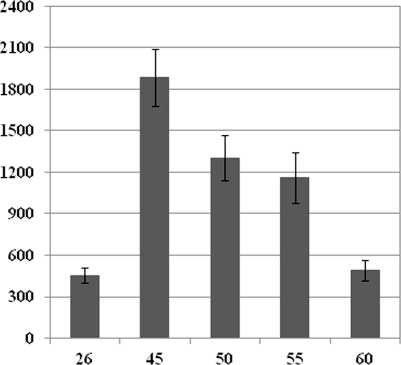
Вызываемое действием стрессора повышение уровня АФК в клетках очень часто является главной причиной их гибели. В связи с этим, необходимо было изучить изменение содержания АФК в клетках сахарного тростника при действии повышенных температур. Было показано, что действие температур 45 и 50 °С (10 мин) приводило к значительному увеличению содержания АФК в клетках (Рис. 2 а, б). Выраженное повышение уровня АФК наблюдалось и после действия температуры 55 °С, хотя данная обработка приводила к массовой гибели клеток в культуре уже во время экспонирования (Рис. 1 а, 2 а, б). Через 48 ч после действия температуры 55 °С доля живых клеток в культуре сахарного тростника уменьшалась, и можно с уверенностью предположить, что увеличенный уровень АФК явился одной из основных причин гибели клеток. В то же время, после обработки культуры температурой 60 °С, вызывавшей гибель 100% клеток, увеличения уровня АФК не наблюдалось (Рис. 1 а, 2 а, б), что свидетельствует об адекватности применяемого метода.
Изменение электрохимического потенциала на внутренней митохондриальной мембране в клетках суспензионной культуры сахарного тростника под действием повышенных температур
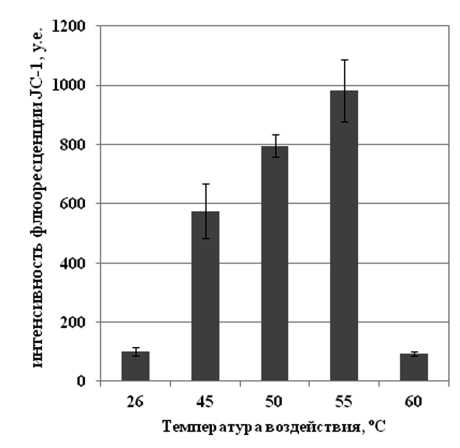
Изучение ∆Ψm представляется весьма важным, поскольку позволяет соотнести изменения данного параметра с меняющимся в результате высокотемпературного воздействия уровнем АФК в клетках и выявить возможную взаимосвязь между этими двумя показателями. Гиперполяризация внутренней митохондриальной мембраны на ранних этапах процесса активной гибели клеток может также свидетельствовать об участии митохондрий в регуляции и реализации данного процесса. В данной работе было показано, что действие всех повышенных температур, за исключением температуры 60 °С, обработка которой приводила к гибели всех клеток в культуре (Рис. 1 а), вызывало гиперполяризацию внутренней митохондриальной мембраны в клетках культуры сахарного тростника (Рис. 3 а, б). Интересным оказался результат сравнения изменений ∆Ψm с изменениями уровня АФК, вызываемых исследуемыми воздействиями. Так, в случае действия температуры 45 °С, когда гибели клеток не происходило, наиболее выраженное увеличение содержания АФК сочеталось с наименее интенсивным увеличением ∆Ψm (Рис. 2 а, 3 а), что свидетельствует о незначительном вкладе митохондрий в процесс генерации АФК в клетках сахарного тростника. Действие температуры 55 °С на клетки культуры вызывало, напротив, наиболее значимое повышение ∆Ψm из наблюдавшихся и наименее выраженное увеличение АФК (Рис. 2 а, 3 а). Эффект от действия температуры 50 °С занимал промежуточное положение: повышение ∆Ψm, также как и увеличение содержания АФК в клетках, наблюдалось, но в обоих случаях увеличение интенсивности флюоресценции соответствующих красителей было не самым значимым (Рис. 2 а, 3 а).
А Б
Figure 1 . Влияние повышенных температур на жизнеспособность клеток (а) и конденсацию протопласта (б) в суспензионной культуре сахарного тростника.
Обозначения : 26 °С - контрольная культура клеток, выращенная при температуре 26 °С; 45, 50, 55, 60 °С - культуры клеток, подвергнутые 10-минутной обработке соответствующими повышенными температурами; 0 ч и 48 ч - время после воздействия. M±S.D. n=3-5.
интенсивность флюоресценции DCF, у.е.
Т емпер атур а в оздейс твия, °C
А
Б
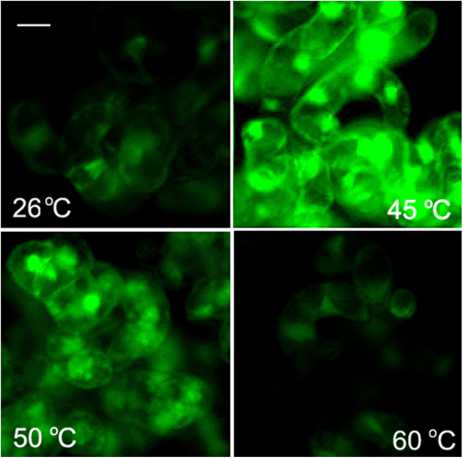
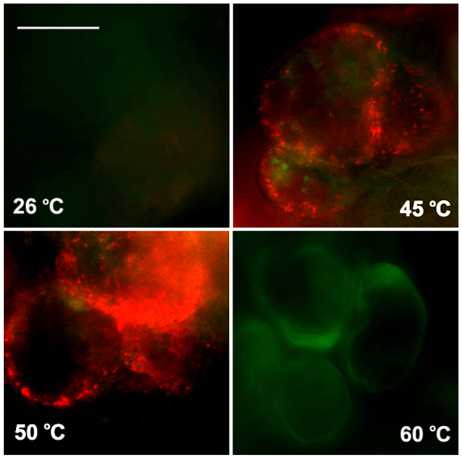
Figure 2 . Изменение содержания активных форм кислорода в клетках суспензионной культуры сахарного тростника под действием повышенных температур. Количественный обсчет данных флюоресцентной микроскопии (а) и микрофотография клеток сахарного тростника (б). Для определения АФК использовался флюоресцентный краситель H2DCF-DA (1 мкМ, 10 мин при 26 °С).
Обозначения : 26 °С - контрольная культура клеток, выращенная при температуре 26 °С; 45, 50, 55, 60 °С - культуры клеток, подвергнутые 10-минутной обработке соответствующими повышенными температурами. Бар равен 20 мкм. M±S.D. n=3-5.
А
Б
Figure 3 . Изменение электрохимического потенциала на внутренней митохондриальной мембране в клетках суспензионной культуры сахарного тростника под действием повышенных температур. Количественный обсчет данных флюоресцентной микроскопии (а) и микрофотография клеток сахарного тростника (б). Использовали потенциал-зависимый катионный краситель JC-1 (10 мкМ, 10 мин при 26 °С).
Обозначения : 26 °С - контрольная культура клеток, выращенная при температуре 26 °С; 45, 50, 55, 60 °С - культуры клеток, подвергнутые 10-минутной обработке соответствующими повышенными температурами. Бар равен 20 мкм. M±S.D. n=3-5.
DISCUSSION
Изучение процесса ПКГ у растений сопряжено с рядом трудностей. Так, наличие хлоропластов и вакуолей, наряду с митохондриями, их участие в реакции клетки на действие внешних факторов, приводит к тому, что активный тип гибели может иметь различные морфологические и биохимические проявления, в зависимости от вклада данных органелл в реализацию процесса гибели (Krishnamurthy et al., 2000). В связи с этим, в ряде случаев идентификация наблюдаемого типа гибели бывает затруднена. Тем не менее, имеется ряд параметров, наличие которых является убедительным свидетельством в пользу отнесения процесса гибели к ПКГ. Одним из таких параметров, наблюдаемых в нашей работе при изучении различных типов гибели клеток, вызываемых действием повышенных температур в суспензионной культуре сахарного тростника, явилась конденсация протопласта в клетках. Некоторые авторы, изучающие ПКГ у растений, представляют данный параметр как один из важнейших морфологических маркеров ПКГ и при характеристике процесса клеточной гибели ориентируются, главным образом, именно на него (Diamond et al., 2013). В данной работе мы наблюдали увеличение доли клеток с конденсированным протопластом при действии температур 50, 55 и 60 °С, но если действие температур 55 и 60 °С приводило к массовой единомоментной гибели клеток уже во время обработки, то температура 50 °С активировала процесс длительной гибели, развитие которого происходило на протяжении последующих 48 ч. Именно данное сочетание параметров – длительность процесса гибели клеток, происходящего после снятия действия стрессового фактора, и конденсация протопласта в клетках – характерно для ПКГ (Reape et al., 2008). Следует отметить, однако, что и при обработке культуры клеток сахарного тростника температурой 50 °С доля клеток с конденсированным протопластом в ходе экспериментов была меньше доли погибших клеток. Возможно, это связано с тем, что у растительных клеток реализация ПКГ может осуществляться различными путями с проявлением разных морфологических признаков (Krishnamurthy et al., 2000).
В связи с тем, что активный тип гибели у растений может осуществляться разными путями и его морфологические проявления также могут быть весьма разнообразны (Rogers, 2005; Reape et al., 2008), об идентификации гибели клеток как ПКГ в определенных условиях следует судить по общей цитологической и биохимической картине гибели (Vaniushin, 2001). Так, увеличение содержания АФК в клетке считается одним из первых сигналов при активации ПКГ (Tiwari et al., 2002; Gao et al., 2008; Wu et al., 2011). В данной работе происходило повышение уровня АФК в клетках сахарного тростника после действия температуры 50 °С, хотя температуры 45 и 55 °С также вызывали его увеличение. Вероятно, важным фактором, играющим ключевую роль в активации ПКГ у растений, является не только изменение уровня АФК, но и сочетание данного параметра с другими физиологическими изменениями в клетках, например, с показателями активности митохондрий.
В ряде работ показано, что на ранних стадиях активации ПКГ у растений наряду с увеличением содержания АФК в клетках происходят изменения электрохимического потенциала на внутренней митохондриальной мембране, ΔΨ m (Petit et al. , 1996; Reape and McCabe, 2010). Действительно, исследования изменений ΔΨ m в нашей работе показало, что действие повышенных температур (45, 50 и 55 °С) приводило к гиперполяризации внутренней митохондриальной мембраны. Интересно отметить, что, как и в случае с увеличением содержания АФК, повышение ΔΨ m после обработки температурой 50 °С было не самым выраженным. Можно предположить, что для культуры сахарного тростника в условиях повышенных температур на ранних этапах активации гибели, важным фактором для определения пути гибели клетки, является функциональная активность митохондрий. Действие стрессового фактора должно быть достаточным, чтобы повысить уровень АФК выше критического, но не настолько интенсивным, чтобы привести к немедленному и необратимому повреждению митохондрий.
Таким образом, в результате проведенных исследований можно заключить, что повышенные температуры, а именно температура 50 °С, вызывают активацию отсроченной гибели клеток в культуре клеток сахарного тростника, развитие которой происходит на протяжении 48 ч после обработки, и сопровождается структурноморфологическими и биохимическими изменениями, характерными для ПКГ.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
Работа выполнена при поддержке гранта РФФИ №14-04-32126.
Список литературы Activation of cell death in the sugar cane suspension culture by the exposure to high temperature
- Akladious, S.A. (2014) Influence of thiourea application on some physiological and molecular criteria of sunflower (Heliantus annuus L.) plants under conditions of heat stress. Protoplasma, 251, 625-638
- Bras, M. (2005) Programmed cell death via mitochondria: different modes of dying. Biochem., 70, 231-239
- Diamond, M., Reape, T.J., Rocha, O., Doyle, S.M., Kacprzyk, J., Doohan, F.M., McCabe, P.F. (2013) The Fusarium mycotoxin deoxynivalenol can inhibit plant apoptosis-like programmed cell death. PLOS ONE, 8, 1-8
- Gao, C. Zhang, L., Wen, F., Xing D. (2008) Sorting out the role of reactive oxygen species during plant programmed cell death induced by ultraviolet C overexposure. Plant Signaling & Behavior, 3, 197-198
- Glantz, S.A. (1998) Primer of biostatistics. McGraw-Hill, New-York. 473 p
- Hasanuzzaman, M., Nahar, K., Alam, Md.M, Roychowdhury, R., Fujita, M. (2013) Physiological, biochemical, and molecular mechanisms of heat stress tolerance in plants. Int.J.Mol.Sci., 14, 9643-9684
- Jones, A.M. (2001) Programmed cell death in development and defense. Plant Physiol., 125, 94-97
- Krishnamurthy, K.V., Krishnaraj, R., Chozhavendan, R., Christopher, F.S. (2000) The programme of cell death in plants and animals -a comparison. Curr. Sci., 79, 1169-1181
- Li, Z., Yue, H., Xing, D. (2012) MAP Kinase-6-mediated activation of vacuolar processing enzyme modulates heat shock induced programmed cell death in Arabidopsis. New Phytol., 195, 85-96
- Maxwell, D.P., Wang, Y., McIntosh, L. (1999) The alternative oxidase lowers mitochondrial reactive oxygen production in plant cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 96, 8271-8276
- Murashige, T., Scoog, F. (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant., 15, 473-497
- Petit, P.X., Susin, S.-A., Zamzami, N., Mignotte, B., Kroemer, G. (1996) Mitochondria and programmed cell death: back to the future. FEBS Lett, 396, 7-13
- Polesskaia, O.G. (2007) Rastitel’naia kletka I aktivnyie formy kisloroda: ucheb. posobie. M.: KDU, 140 p
- Reape, T.J., Molony, E.M., McCabe, P.F. (2008) Programmed cell death in plants: distinguishing between different modes. J. Exp. Bot., 59, 435-444
- Reape, T.J., McCabe, P.F. (2010) Apoptotic-like regulation of programmed cell death in plants. Apoptosis, 15, 249-256
- Rogers, H.J. (2005) Cell death and organ development in plants. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol., 71, 225-261
- Simeonova, E. Garstka, M., Kozioł-Lipińska, J., Mostowska, A. (2004) Monitoring the mitochondrial transmembrane potential with the JC-1 fluorochrome in programmed cell death during mesophyll leaf senescence. Protoplasma, 223, 143-153
- Tiwari, B.S. Belenghi, B., Levine, A. (2002) Oxidative stress increased respiration and generation of reactive oxygen species, resulting in ATP depletion, opening of mitochondrial permeability transition, and programmed cell death. Plant Physiol, 128, 1271-1281
- Vacca, R.A., Valenti, D., Bobba, A., Merafina, R.S., Passarella, S., Marra, E. (2006) Cytochrome c is released in a reactive oxygen species-dependent manner and is degraded via caspase-like proteases in tobacco Bright-Yellow 2 cells en route to heat shock-induced cell death. Plant Physiol., 141, 208-219
- Vaniushin, B.F. (2001) Apoptoz u rasteniy. Uspehi biol. himii, 41, 3-38
- Wu, M., Huang, J., Xu, S., Ling, T., Xie, Y., Shen, W. (2011) Haem oxygenase delays programmed cell death in wheat aleurone layers by modulation of hydrogen peroxide metabolism. J. Exp. Bot., 62, 235-248
- Xu, J., Belanger, F., Huang, B. (2008) Differential gene expression in shoots and roots under heat stress for a geothermal and non-thermal Agrostis grass species contrasting in heat tolerance. Environ. Exp. Bot., 63, 240-247
- Zuppini, A., Andreoli, C., Baldan, B. (2007) Heat stress: an inducer of programmed cell death in Chlorella saccharophila. Plant Cell Physiol., 48, 1000-1009


