AI in wealth management and wealthtech
Автор: Ivana Tomic, Bojana Jokanovic, Slavko Ivkovic
Журнал: Social Informatics Journal @socialinformaticsjournal
Статья в выпуске: 2 vol.3, 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The main idea of the paper is researching AI and other technologies for Wealth Management. Implementation of the AI in WealtTech helps in giving the best investment advises. Wealth Management includes retirement planning, inheritance tax, estate planning, and other activities according to investment preferences. WealthTech aims to manage investment funds and assets more efficiently, accessible, and personalized through data-driven insights and smart automation. Besides improving their efficiency, WealthTech aims to automate investment and wealth management services. WealthTech utilizes innovations like blockchain, artificial intelligence, and machine learning to improve investment decisions combining technologies for fund transformation and asset handling. These technologies include a wide range of solutions and include robo-advisors, social trading, robot-retirement, quant advisors, and micro-investing. This approach use the best technology solutions more advanced than typical analysis used in financial institutions. WealthTech AI applications are developed to create wealth data dashboards tailored to the clients needs. The applications enable clients to see full and transparent picture of their entire wealth and visualise wealth maps and data-driven analytics to uncover valuable investment insights. The aim of the applications is to convert diversified investment portfolio in clear reports and graphs. Because of the advancements in AI, the programs provide personalized advice concerning wealth management and business strategies. The Manuscript will present WealthTech solutions on the practical example and recommend the most attractive investment opportunities on the global market.
Blockchain Technology, Healthcare Ethics, Patient Privacy, Data Ownership, Decentralized Governance
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/170207374
IDR: 170207374 | УДК: 330.322:004 | DOI: 10.58898/sij.v3i2.30-36
Текст научной статьи AI in wealth management and wealthtech
d
Wealthtech refers to providing digital solutions that facilitate the wealth management process and automate wealth management services using AI and other technologies for improving their efficiency.
The wide range of solutions under this umbrella term includes robo-advisors, social trading, robo retirement, quant advisors, and micro investing. A key difference between this concept and fintech is that the latter involves catering to a diverse client base.
Theoretical Background
Information-based investments are rapidly growing, especially in the financial and banking sectors [1] For high-tech companies, competitiveness among firms may lead to diversified innovation for a single product, which in turn, may make patent portfolios more complex and difficult to understand by investors [2]
With the deepening integration of internet technology and the financial industry, FinTech has offered the public innovative financial services [3] such as online payment, peer-to-peer lending, budgeting and financial planning, crowdfunding, and savings and investments. [4]
Financial inclusion encompasses various efforts aimed at guaranteeing that individuals and businesses can obtain cost-effective and appropriate financial products and services. This encompasses the provision of savings accounts, credit facilities, insurance coverage, and payment services, along with other financial instruments that facilitate individuals in effectively managing their finances and enhancing their economic welfare. FinTech can positively impact overall traditional financial inclusion because it enables banks to easily reach populations with limited access to banking services or without bank accounts through the use of digital platforms [5]. The rapid growth in cryptocurrencies has led them to garner investors’ interest as a popular diversification choice [6,7,8, 9].
WealthTech is recognized as a specialized subset of FinTech. It focuses on utilizing digital technologies to enhance investment and client portfolio management, providing customized products and services tailored to individual needs [10, 11].
FinTech is being used to attract traditional banking clients, optimize commercial transactions, improve credit granting, and simplify banking operations. Financial services are thus being automated, resulting in a correspondingly necessary and accelerated process of transformation. Among the technologies used in this process are big data, blockchain, artificial intelligence, machine learning and cryptocurrencies [12].
The issue of financial exclusion continues to be an important barrier to equitable development in the global financial landscape, even with all the economic progress we are seeing around the world. [13]
Individuals can now do their financial transactions anytime, anywhere, thanks to FinTech platforms [14]. FinTech relates to the usage of technology to deliver better financial services [15, 16, 17] .
FinTech studies mainly concentrate on the implication of FinTech for bank performance [18, 19] or risktaking [20]. FinTech is a term that has arisen in recent years; it refers to innovative technologies designed to enhance and automate the provision and utilization of financial services [21].
The term FinTech refers to the convergence of finance and technology, with an emphasis on the development of new and improved financial solutions [22,23]. FinTech tools provides consumers with easy access to financial services, fast and easy confirmation of financial transactions, and reduced operational costs [24].
The rapid growth of FinTech adoption and usage has introduced innovative solutions that offer convenience, efficiency, and accessibility [25, 26]. FinTech refers to innovative financial services that use technology to create disruptive new trends in services or rewrite financial services to make them more valuable, reasonable, and secure [27,28, 29].
WealthTech is recognized as a specialized subset of FinTech. It focuses on utilizing digital technologies to enhance investment and client portfolio management, providing customized products and services tailored to individual needs [10, 11].
Artificial intelligence is a pivotal technological advancement that seeks to replicate human cognitive functions through machines and data analysis [30]. Using artificial intelligence in finance means that it can identify, analyze and adjust changes in data patterns on its own.
AI-driven platforms facilitate trade finance access by analyzing non-traditional data points, supply chain data, and payment histories. These platforms provide more inclusive and accurate credit assessments, benefiting underrepresented businesses such as SMEs and closing the financing gap [31].
WealthTech
WealthTech combines wealth management and technology to transform how funds and assets are handled. It utilizes innovations like artificial intelligence, machine learning, and blockchain to improve personal finance and investing. WealthTech developers build applications that automate manual wealth management processes and provide customized financial recommendations powered by AI.
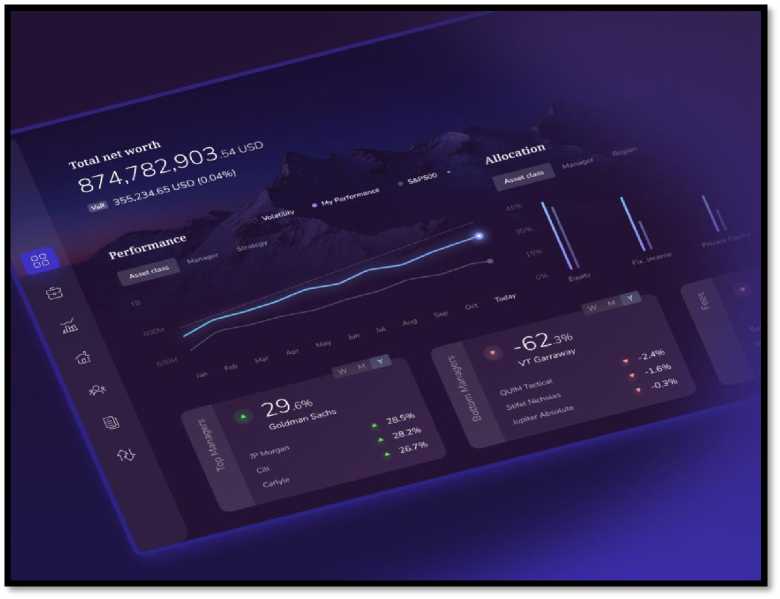
Wealthtech refers to the delivery of an extensive range of financial services for wealth management via digital means. This technology improves investors’ decision-making and enables people to manage their finances efficiently in a manner that is different from how conventional financial institutions work. Because of the advancements in software as a service (SaaS), big data, AI, machine learning, etc., software programs can now provide personalized advice concerning wealth management. Image 1 shows example of Wealth Management application.
Some noteworthy wealthtech solutions and services are as follows:
Robo-Advisors: These are digital tools often utilizing machine-learning-based techniques to carry out operations for the client or the user. Such software can automatically allocate funds to different financial instruments based on how a user configures it.
Quant Advisors: These are extensions of robo-advisors. Such systems actively utilize AI for managing investment strategies.
Robo Retirement: These are a version of robo-advisors and are quite popular. Robo retirement services involve creating retirement portfolios, managing assets, recommending computer system-generated plans, and providing strategies.
Micro Investing: These solutions enable investing via small credits or microcredits. They provide a more interactive experience compared to robo-advisors.
Social Trading: It allows investors to share their own trading experience. It combines the concept of social media with that of trading platforms. In this case, traders are able to mimic the investment models of traders who share their opinions. Hence, novice traders can learn from traders who have more experience.
This subcategory of fintech covers more solutions and services, such as the following: Digital brokers, Algorithmic trading, B2B software services, Online marketplaces, Portfolio management tools and Risks.
WealthTech AI
A recent Gartner report projects the global AI in wealth management market to grow at a CAGR of 23.8% from 2022 to 2027, highlighting the significant rise of these technologies. Image 2 presents US WealthTech Market with prediction until 2030.
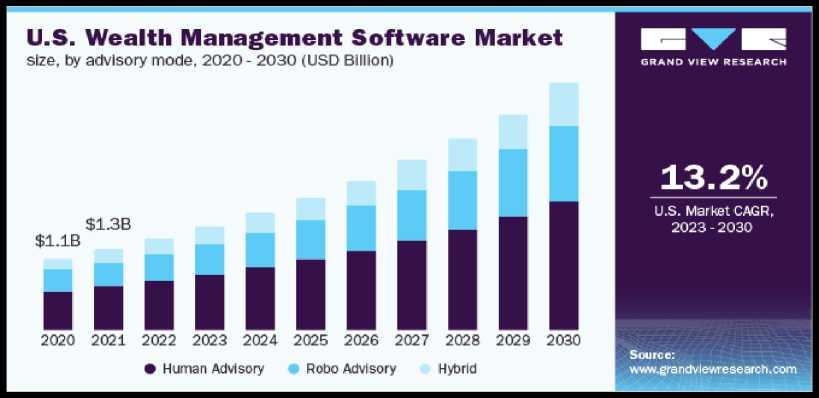
Image 2: US WealthTech Market (Source:
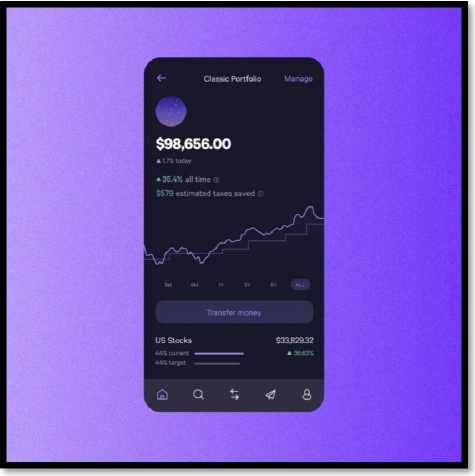
WealthTech AI solutions are tailored for businesses, specializing in translating technological trends into practical and commercially viable applications. Our expertise spans large language models, intelligent automation, time-series forecasting, predictive analytics, search technology, and sophisticated data strategy, architecture, and management. WealthTech mobile application is presented on Image 3.
The future AI-powered landscape for wealth management companies could shape up as follows:
-
1. Personalized Financial Planning: By analyzing a client’s financial history, spending habits, and investment preferences, genAI can help advisors create highly personalized financial plans that evolve as the AI continues to learn from the client’s financial behavior and changing market conditions.
-
2. Risk Assessment and Management: Financial advisors can recommend tailored strategies for risk management based on the client’s specific situation, helping to safeguard their investments and financial health.
-
3. Real-time Market Insights: GenAI can process market data in real-time, providing financial advisors with up-to-the-minute insights to advise clients on immediate actions, such as buying, selling, or holding assets based on current market conditions.
-
4. Predictive Analytics for Financial Products: GenAI can predict which financial products or services a client might need in the future, based on a comprehensive understanding of the client’s financial journey and goals, as well as their past interactions with financial products.
-
5. Automated Portfolio Management: Machine learning models can build and manage investment portfolios using predefined rules and objectives, automatically rebalancing portfolios to optimize performance and manage risk based on real-time market conditions.
-
6. AI-powered Customer Interactions: AI-powered chatbots can handle routine customer inquiries and assist with account management, allowing financial advisors to focus on more complex or strategic tasks and improving overall customer experience.
-
7. Regulatory Compliance: AI systems can monitor real-time data and communications, flagging potential compliance issues and alerting financial advisors to investigate or take action, helping to mitigate risks and ensure regulatory compliance.
-
8. Reducing Back-Office Tasks: AI can significantly reduce the workload of back-office tasks such as data processing, document management, and administrative support, thereby increasing operational efficiencies and allowing staff to focus on higher-value activities.
Share and Maintain Corporate Knowledge: Corporate knowledge agents use AI to manage and optimize the flow of information within the company, ensuring that decision-makers have quick and easy access to accurate and relevant data. This enables more informed decision-making and improves overall corporate governance. (Source: . Image 4 presents AI Driven WealthTech Solutions.
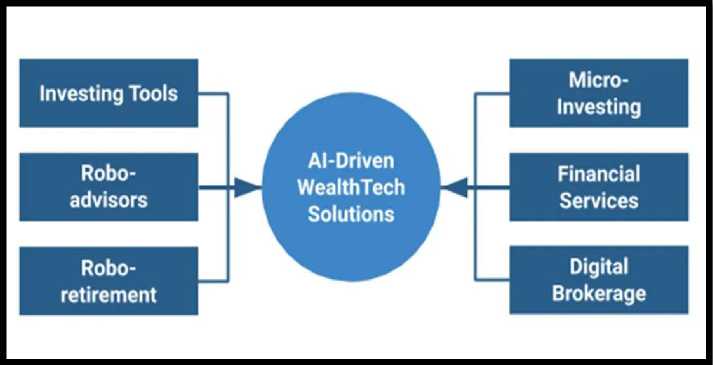
Conclusions
By adopting these technologies, both managers and clients benefit from enhanced services and better outcomes. WealthTech marks an exciting shift towards more user-friendly, effective wealth management software development.
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Список литературы AI in wealth management and wealthtech
- Yi, T.Z.; Rom, N.A.M.; Hassan, N.M.; Samsurijan, M.S.; Ebekozien, (2023) A. The Adoption of Robo-Advisory among Millennials in the 21st Century: Trust, Usability and Knowledge Perception. Sustainability, 15, 6016. https://doi.org/ 10.3390/su15076016
- An, Le Thuy Ngoc, Yoshiyuki Matsuura, Mohammad Ali Tareq, Nurhayati Md Issa, and Norliza Che-Yahya (2023). Impact of Patent Signal on Firm’s Performance at IPO: An Empirical Analysis of Japanese Firms. Economies 11: 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/economies11040101
- Jiang, Y.; Ho, Y.-C.; Yan, X.; Tan, Y. (2018).Investor platform choice: Herding, platform attributes, and regulations. J. Manag. Inf. Syst, 35, 86–116.
- Xie, J.; Ye, L.; Huang, W.; Ye, M. (2021). Understanding FinTech Platform Adoption: Impacts of Perceived Value and Perceived Risk. J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2021, 16, 1893–1911. https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer16050106
- Kamara, Abdul Karim, and Baorong Yu. (2024). The Impact of FinTech Adoption on Traditional Financial Inclusion in Sub-Saharan Africa. Risks 12: 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/risks12070115
- Mansour Nomran, Naji, Abdelkader Laallam, Razali Haron, Aghilasse Kashi, Zakir Hossen Shaikh, and Joji Abey (2024). The Impact of the Cryptocurrency Market on Islamic vs. Conventional Stock Returns: Evidence from Gulf Cooperation Council Countries. Journal of Risk and Financial Management 17: 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm17070305
- Ali, Shoaib, Muhammad Naveed, Hasan Hanif, and Mariya Gubareva (2024). The resilience of Shariah compliant investments: Probing the static and dynamic connectedness between gold backed cryptocurrencies and GCC equity markets. International Review of Financial Analysis 91: 103045.
- Khalil-Oliwa, Oliwia, and Izabela Jonek-Kowalska (2024), Determinants of the Effectiveness of Risk Management in the Project Portfolio in the FinTech Industry. Risks 12: 111. https://doi.org/ 10.3390/risks12070111
- Yang, J.; Jung, S.-U. (2024), Harnessing FinTech for Sustainable Finance in Developing Countries: An Integrated SWOT–Multi-Level Perspective Analysis of Mongolia. Sustainability, 16, 4102. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16104102
- Chishti, S.; Puschmann, T. (2018). The Wealthtech Book: The FinTech Handbook for Investors, Entrepreneurs and Finance Visionaries; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA.
- Dziawgo, T. (2021), Wealth Tech impact on wealth management sector. Eur. Res. Stud. J, XXIV, 141-151.
- Duan, C. (2024), Analyses of Scientific Collaboration Networks among Authors, Institutions, and Countries in FinTech Studies: A Bibliometric Review. FinTech 3, 249–273. https://doi.org/
- Amnas, Muhammed Basid, Murugesan Selvam, and Satyanarayana Parayitam.(2024), FinTech and Financial Inclusion: Exploring the Mediating Role of Digital Financial Literacy and the Moderating Influence of Perceived Regulatory Support. Journal of Risk and Financial Management 17: 108.https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm17030108
- Yang, Tong, and Xun Zhang. (2022). FinTech adoption and financial inclusion: Evidence from household consumption in China. Journal of Banking & Finance 145: 106668.
- Almubarak, Ayth I., and Abdullah A. Aljughaiman. (2024). Corporate Governance and FinTech Innovation: Evidence from Saudi Banks. Journal of Risk and Financial Management 17: 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm17020048
- Thakor, Anjan V. (2020). FinTech and banking: What do we know? Journal of Financial Intermediation 41: 100833.
- Goldstein, Italy,Wei Jiang, and G. Andrew Karolyi (2019),To FinTech and beyond. The Review of Financial Studies 32: 1647–61.
- Al-Matari, Ebrahim Mohammed, Mahfoudh Hussein Mgammal, Mushari Hamdan Alosaimi, Talal Fawzi Alruwaili, and Sultan Al-Bogami (2022). Fintech, Board of Directors and Corporate Performance in Saudi Arabia Financial Sector: Empirical Study. Sustainability 14: 10750.
- Arena, Claudia, Simona Catuogno, and Valeria Naciti. (2023). Governing FinTech for performance: The monitoring role of female independent directors. European Journal of Innovation Management 26: 591–610.
- Deng, Liurui, Yongbin Lv, Ye Liu, and Yiwen Zhao. (2021). Impact of Fintech on Bank Risk-Taking: Evidence from China. Risks 9: 99.
- Balaskas, S.; Koutroumani, M.; Komis, K.; Rigou, M. (2024), FinTech Services Adoption in Greece: The Roles of Trust, Government Support, and Technology Acceptance Factors. FinTech 2024, 3, 83–101. https://doi.org/10.3390/fintech3010006
- Li, B.; Xu, Z. (2021) Insights into financial technology (FinTech): A bibliometric and visual study. Financ. Innov, 7, 69.
- Thakor, A.V. (2020) Fintech and banking: What do we know? J. Financ. Intermediation, 41, 100833.
- Girma, Abebe Gule, and Fariz Huseynov. (2024). The Causal Relationship between FinTech, Financial Inclusion, and Income Inequality in African Economies. Journal of Risk and Financial Management 17: 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm17010002
- Amnas, Muhammed Basid, Murugesan Selvam, Mariappan Raja, Sakthivel Santhoshkumar, and Satyanarayana Parayitam. (2023), Understanding the Determinants of FinTech Adoption: Integrating UTAUT2 with Trust Theoretic Model. Journal of Risk and Financial Management 16: 505. https:// doi.org/10.3390/jrfm16120505
- Chawla, Udit, Rajesh Mohnot, Harsh Vikram Singh, and Arindam Banerjee. (2023), The Mediating Effect of Perceived Trust in the Adoption of Cutting-Edge Financial Technology among Digital Natives in the Post COVID-19 Era. Economies 11: 286. https://doi.
- Chen, F.; Du, X.;Wang,W. (2023). Can FinTech Applied to Payments Improve Consumer Financial Satisfaction? Evidence from the USA. Mathematics, 11, 363. https:// doi.org/10.3390/math11020363
- Alkhowaiter, W.A. (2022),Use and behavioural intention of m-payment in GCC countries: Extending meta-UTAUT with trust and Islamic religiosity. J. Innov. Knowl, 7, 100240.
- Jangir, Kshitiz, Vikas Sharma, Sanjay Taneja, and Ramona Rupeika-Apoga. (2023). The Moderating Effect of Perceived Risk on Users’ Continuance Intention for FinTech Services. Journal of Risk and Financial Management 16: 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/ jrfm16010021
- Ozturk, Ozcan. 2024. The Impact of AI on International Trade: Opportunities and Challenges. Economies 12: 298.
- Rajagopal, Manikandan, Keyurkumar M. Nayak, K. Balasubramanian, Irfan A. Shaikh, Sunil Adhav, and Monika Gupta. 2023. Application of Artificial Intelligence in the Supply Chain Finance. Paper presented at 2023 Eighth International Conference on Science Technology Engineering and Mathematics (ICONSTEM), Chennai, India, April 6–7.


