Alterations in the phosphorus metabolism during seed germination of Simarouba glauca
Автор: Desai Nivas, Patil Manasi, Narayankar Chirag, Gaikwad D.K.
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 2 т.19, 2023 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Phosphorus (P) is the second most important macronutrient for plant growth and is responsible for plant metabolism. Phosphorus is an important component of nucleic acid and also a component of phospholipids as a basic requirement for cellular organization and function as a membrane building block. Plants respond to Plant Growth Regulators (PGRs) in phosphorus content in a variety of ways. A study was conducted to assess the activities of acid and alkaline phosphatases on seed germination and seedling growth in response to various PGRs of S. glauca at different time intervals. Seeds were subjected to 100 ppm solutions of various PGRs, which include GA, 6-BA, CCC, SA, Cysteine, and Methionine. The activity of the enzymes ATPase, acid phosphatase, and alkaline phosphatase increases in response to the most of PGRs.
Phosphorus metaboliosm, atpase enzyme, alkaline phosphatase, simarouba glauca
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/143180105
IDR: 143180105
Текст научной статьи Alterations in the phosphorus metabolism during seed germination of Simarouba glauca
Phosphorus metabolism is significant in plant growth and development across the plant's life cycle. Phosphorus uptake and distribution are completely reliant on a class of enzymes known as phosphatases, Phosphatases or phosphomonoesterases are the hydrolytic enzymes that cleave the ester bond between the phosphate group and the organic residue of the organic phosphates (Dotaniya et al. , 2019). ATP is almost exclusively found in the plasma membrane, cytoplasm, as well as cell wall. It has also been identified in vacuolar and other endomembranes such as chloroplast thylakoid membranes and inner mitochondrial membranes, including in the plasma membranes of bacteria and blue green algae (Logan, 2006). The energy stored in ATP’s phosphoanhydride bond is used to power a wide range of processes including muscle contraction, cell motility, nerve impulse propagation, and DNA synthesis, among many others (Nirody, 2020). Based on the optimum pH for the activity, phosphatases are of two kinds: acid and alkaline. Acid phosphatases show maximum activity at acidic pH around 6 whereas alkaline phosphatases show maximum activity at alkaline pH around 11 (Dotaniya et al. , 2019). Acid phosphatases catalyze the hydrolysis of Pi from a broad range of phosphomonoesters with an acidic pH optimum (Tran et al. , 2010). Alkaline phosphatase (ALP; E.C.3.I.3.1.) is a ubiquitous membrane-bound glycoprotein that catalyzes the hydrolysis of phosphate monoesters at basic pH values (Sharma et al. , 2013).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Freshly harvested seeds of S. glauca were purchased from Sri Sri Institute of Agriculture, Bangalore. Surface disinfection with 0.1 percent mercuric chloride has been performed. Six treatments with four replicates have been used. The seeds were soaked in 100 ppm solutions of 6BA, GA, CCC, cysteine, SA and Methionone for 48 hours at room temperature. The twenty five seeds were sown in plastic trays that have been densely filled by FYM and soil (1:3).The germinated seeds and seedlings were analyzed to find out the activity of enzymes. The activity of the enzyme ATPase, Acid phosphatase and alkaline phosphatase were determined using the standard published methods.
RESULTS
It is evident from fig 1 -2 In 48 h mechanically broken soaking seeds, the activity of enzyme ATPase increases in regard to 6-BA, GA, CCC, cysteine, and methionine treatments, but decreases in response to SA treatment. After 15 days, the activity of the enzyme ATPase in germinating seedlings declines in reaction to all PGRs, whereas after 30 days and 60 days, the activity of the enzyme ATPase decreases in response to all PGRs. In response to presowing socking treatments, the overall activity of the enzyme ATPase is enhanced in seedlings, cotyledons, and shoots tissue.
From fig 3 and 4 it is observed that After 48 hour of soaking mechanically cracked seeds in PGRs, the enzyme acid phosphatase is activated. It raises in 15-day germination seedlings and then increases again in one-month-old seedlings. After 60 days, the activity of the enzyme acid phosphatase shows a diminishing tendency in cotyledons and an increasing trend in shoot tissues. It's also worth noting that acid phosphatase activity is higher in 15-day-old developing seedlings.
Fig no.5 and 6 indicates that after 48 hours of soaking mechanically split seeds, the enzyme alkaline phosphatase is reduced considerably to GA, CCC, SA, cysteine, and methionine, and induced in response to 6-BA. It is also clear that the activity of alkaline phosphatase is boosted in 15-day-old seedlings in response to all treatments, while the enzyme activity diminishes in 30-day-old seedlings. In 60-day-old seedlings, enzyme activity is decreasing in the cotyledons and increasing in the shoot tissues. It's also worth noting that the overall enzyme activity in 30 day old germinating seedlings is higher.
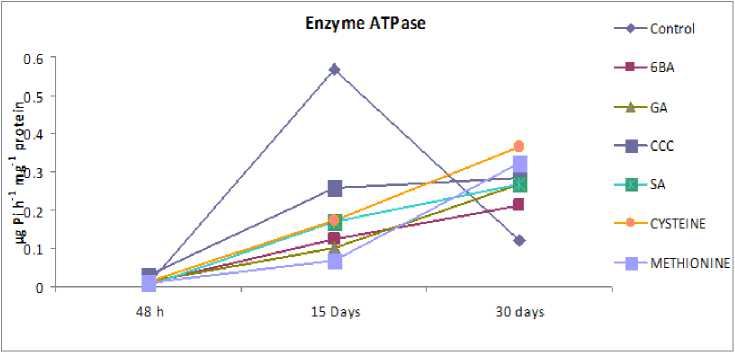
Figure 1 Effect of presowing soaking treatments of PGRs on the activity of enzyme ATPase in seedlings of S. glauca
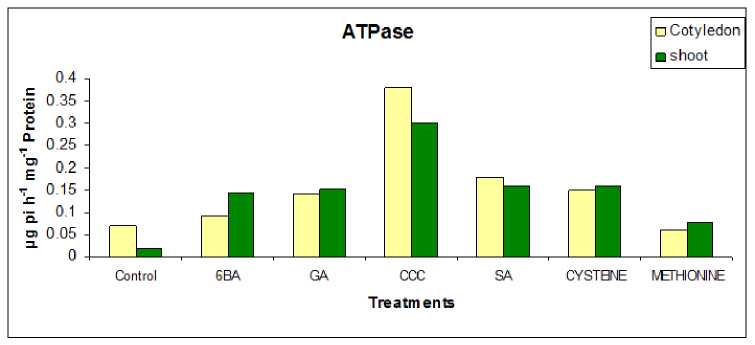
Figure 2 Effect of presowing soaking treatments of PGRs on the activity of enzyme ATPase in 60 days old seedlings of
S. glauca
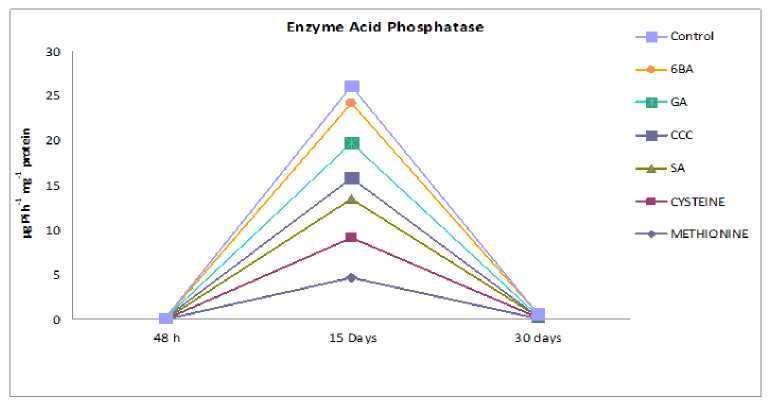
Figure 3 Effect of presowing soaking treatments of PGRs on the activity of enzyme acid phosphatase in seedlings of S.
glauca
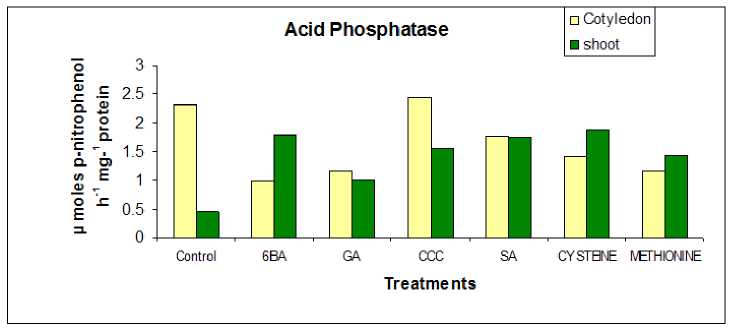
Figure 4 Effect of presowing soaking treatments of PGRs on the activity of enzyme acid phosphatase in 60 days old seedlings of S. glauca
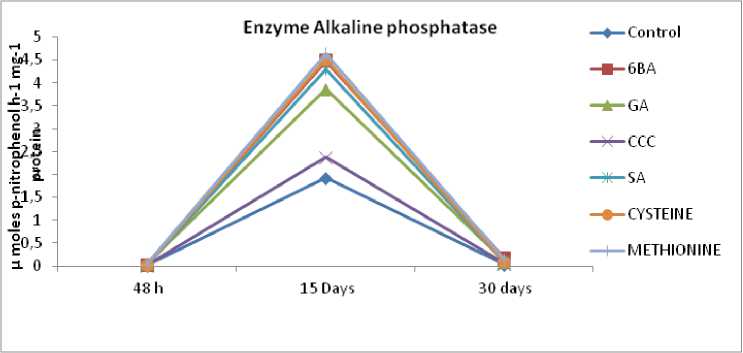
Figure 5 Effect of presowing soaking treatments of PGRs on the activity of enzyme alkaline phophatase in seedlings of S. glauca
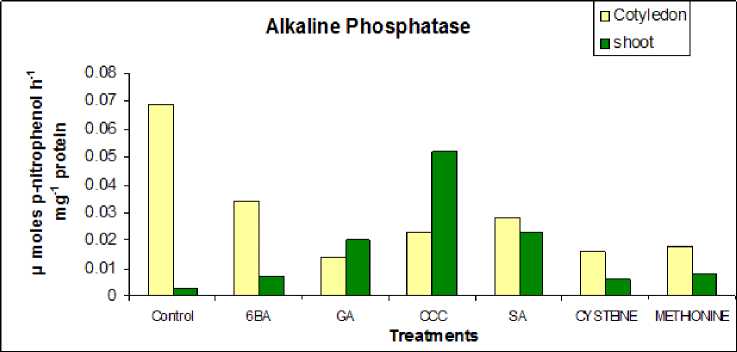
Figure 6 Effect of presowing soaking treatments of PGRs on the activity of enzyme alkaline phophatase in 60 days old seedlings of S. glauca
DISCUSSION
Sen and Mukharji (2004) investigated ATPase and ATP content in Okra at two developmental stages (28 and 58 days after planting). To deal with the low phosphorus level, the activities of both acid and alkaline phosphatases raised dramatically in the winter. The effect of hormones on sucrose absorption and ATPase activity in Citrus sinensis L. Osbeck leaves was examined by Martinez-cortina and Sanz (1994). They discovered that IAA suppressed ATPase activity in isolated plasma membrane vesicles, but GA and ABA had no effect. SA had no influence on the level of ATPase in sugar beet, according to Bourbouloux et al. (1998). Salicylic acid, rather than transcription, may have an impact on plasma membrane H+ ATPase activity. Salicylic acid concentration of 100M had no effect on the plasma membrane's cation permeability. SA treated Vitis vinifera L. cv. Jingxiu plants have stronger plasmalemma H+ and Ca2+-ATPase activity than control plants (Liu et al., 2008). When sucrose, indole butyric acid, or 6-BA were applied exogenously to the seeds of Acacia mangium following 3 days of colchicine treatment, the activities of H+ -PPase, H+ -ATPase, PPi, and ATP-dependent H+ transport were stimulated in 6 day old seedlings, as per Wang et al. (2001). They furthermore concluded that IAA, 6-BA, and sucrose could overcome colchicine's inhibitory effect. Jain et al. (2004) noticed an increase in acid phosphatase activity in pearl millet seeds treated with GA, ABA, and NaCl. In embryos of Sorghum bicolor (L) Moench seeds pretreated with GA and NaCl, acid phosphatase activity increased (Sharma et al., 2004). EI-Shora and Metwally (2009) investigated the effect of phytohormones and group selective reagents on Cladosporium cladosporioides acid phosphatase. According to the researchers, adding GA to the growth medium stimulated acid phosphatase activity. In addition, they discovered that cysteine, L-ascorbic acid, DTT, and GSH act as reducing agents, stimulating enzyme activity in Cladosporium cladosporioides. It has also been reported that alkaline phosphatase is involved in the breakdown and mobilisation of starch and sucrose for the biosynthesis of essential oil in lemongrass (Cymbopogon flexuosus Steud) Wats (Ganjewala et al., 2010). Jain et al. (2004) explored the role of plant growth hormones and salt stress on acid and alkaline phosphatase activities in pearl millet seeds. They realized an increase in alkaline phosphatase activity in the endosperm after treatments with ABA, GA, and NaCl.
CONCLUSION
The higher amount of ATPase activity during germination indicates that ATP is available to carry out metabolic operations during seed germination, this increased activity of ATPase might play a contribution in plant nutrition and growth by sustaining the trans membrane, electrochemical gradient for nutrient absorption and mobilization. The stimulation of acid phosphatase activity during all stages of seed germination of S. glauca might be playing some role in breaking dormancy as indicated. While an increase in activity of acid phosphatase during early stages of germination may act on phytate in cotyledons which will helps to mobilize in the form of organic phosphate during the growth of embryonic axis. The low levels of acid phosphatase activity in germinated seeds also indicated that the activity of acid phosphatase is good indicator of germination. It is noticed that the alkaline phosphatases are found to occur in lower levels during initial period of germination and during shoot formation, while, during vigorous seed germination stage the activity of alkaline phosphatase is elevated. As the alkaline phosphatase play a role in formation of inorganic phosphate for metabolic hydrolysis of metaphosphate to orthophosphate. An increased level of alkaline phosphatase might be beneficial in breakdown of these phosphates or carbohydrate compounds essentially required during germination.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest.
Список литературы Alterations in the phosphorus metabolism during seed germination of Simarouba glauca
- Bourbouloux, A., Raymond, P. and Delrot, S. (1998). Effects of salicylic acid on sugar and amino acid uptake. J. Exp. Bot., 49(319): 239-247.
- Dotaniya, M.L., Aparna, K., Dotaniya, C.K., Mahendra Singh, Regar, K.L. (2019). Role of Soil Enzymes in Sustainable Crop Production, in Enzymes in Food Biotechnology, Edt by : Mohammed Kuddus, Academic Press, Pages 569-589.
- EI-Shora, H. M. and Metwally M. (2009). Effect of phytohormones and group selective reagents on acid phosphatase from Cladosporium cladosporioides. Asian J. Biotech .1(1):1-11.
- Ganjewala, D., Nagaraja, C., Nayak, M. R. and Devi, S.A. (2010). Effects of sodium nitroprusside on activity of acid and alkaline invertases and alkaline phosphatase in lemongrass (Cymbopogon flexuosus Steud) Wats. International Journal of Plant Biology. 1:9 - 12.
- Jain, A.; Sharma, A.D. and Singh, K. (2004). Plant growth hormones and salt stress-mediated changes in acid and alkaline phosphatase activities in the pearl millet seeds. Int. J. Agri Biol., 6(6):960-963.
- Liu, Jian-li. (2008). Effects of 6-BA and GA_3 on Seed Germination of Medicago truncatula Gaertn. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 17.
- Logan, D. C. (2006). The mitochondrial compartment. J Expt Bot., 57(6): 1225-1243.
- Martinez-Cortina, C. and Sanz, A. (1994). Effect of hormones on sucrose uptake and on ATPase activity of Citrus sinensis L. osbeck leaves. Ann Bot, 73(3): 331-335.
- Nirody, J.A., Budin, I., Rangamani, P. (2020). ATP synthase: Evolution, energetics, and membrane interactions. J Gen Physiol. 152(11):e201912475. doi: 10.1085/jgp.201912475. PMID: 32966553; PMCID: PMC7594442.
- Sen, S., Mukherji, S. (2004). Alterations in activities of acid phosphatase, alkaline phosphatase, ATPase and ATP content in response to seasonally varying Pi status in okra (Abelmoschus esculentus). J Environ Biol. 2004 Apr;25(2):181-5. PMID: 15529876.
- Sharma U, Pal D, Prasad R.(2013). Alkaline phosphatase: an overview. Indian J Clin Biochem. Jul;29(3):269-78. doi: 10.1007/s12291-013-0408-y. Epub 2013 Nov 26. PMID: 24966474; PMCID: PMC4062654.
- Sharma, A. D., Thakur, M., Rana, M. and Singh, K. (2004). Effect of plant growth hormones an abiotic stresses on germination, growth and phosphatase activities in Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench seeds. African J. Biotech., 3(6): 308-312.
- Tran, H.T., Hurley, B.A., Plaxton, W.C. (2010). Feeding hungry plants: The role of purple acid phosphatases in phosphate nutrition. Plant Sci. 2010;179:14-27. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2010.04.005.
- Wang, Z. N.; You, R. L. and Chen-Zhu, X. Z. (2001). Effects of colchicine on the accumulation of vacuolar H+-pyrophosphatase and H+-ATPase in germinating Acacia mangium seeds and the recovery effects by sucrose, indole butyric acid and 6-benzyladenine. Plant Growth Regulation, 34: 293-303.


