An Efficient Approach of Power Consumption in Cloud using Scheduling of Resources
Автор: Tanvi Tripathi, Sunita Gond
Журнал: International Journal of Modern Education and Computer Science (IJMECS) @ijmecs
Статья в выпуске: 7 vol.7, 2015 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Cloud computing is the stage for a choice of services like software, infrastructure as a cloud service and each person wants to have the benefit of that cloud services using the cloud computing concept, which ultimately increases the data size and loaded records on cloud servers. Due to increased number of files on the cloud database the retrieval of files becomes much more time consuming and complex. Also this file retrieval doesn't ensure the exact retrieval of files from the storage. Besides, the privacy apprehensions affect to the appropriate documents regained by the cloud user in the afterward phase in view of the fact that they may also enclose sensitive data and make known information about sensitive exploration words or phrase. Here in this paper an efficient approach of power consumption using scheduling of resources is implemented.
Cloud Security, Multi-Keyword, Cloud Computing, SAAS, PAAS, Resource Scheduling
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/15014778
IDR: 15014778
Текст научной статьи An Efficient Approach of Power Consumption in Cloud using Scheduling of Resources
Cloud Computing means a remote server that access through the internet which helps in business applications and functionality along with the convention of system software for respective web application. Cloud computing concept saves capital that cloud users pay out on annual or monthly payment. Due to advantage of cloud services, more and more sensitive information are being centralized into the cloud servers, such as confidential videos and photos, various emails, personal health records information, corporation business data, government documents, etc. So as to privacy problem, data privacy [1] and data loss will be increase in certain circumstances. When users outsource their private onto cloud, the cloud service provider able to monitor the communication between the users and cloud at will trust or untrusted. As cloud computing is promising development in computing concept the confidence increase becomes very important aspect. There are mainly two parameters which can help to get better the confidence on the cloud services. One is to improve efficiency and another for improving security. To improve the efficiency the keyword search method is enhanced as it makes available two way communications between cloud server and the cloud customer. But while deploying security the burden on cloud server gets increased unexpectedly. Consequently it is extremely significant to maintain these two factors so that to improve overall efficiency of the cloud services [2]. Also the world is of mobile devices, so everyone wants to use cloud services on their mobile devices and if the computational cost goes to elevated then it effects into important resource utilization, which is not appropriate for mobile devices. So current scenario is having need of a proficient method is cloud services in the expectations.
Cloud is a service which can be accessed from everywhere if arranged in that way at any path. It causes lots of parties or persons using it for their purpose. In such case the data Various parties may contribute to within them on the cloud server can be secret. In addition every cloud user who uses cloud services doesn’t like to get followed. In such cases it is very important to maintain their privacy [3]. Thus to maintain their privacy the files and even the search requests are encrypted as soon as the request is sent to the server. This encryption may also affect the efficiency of searching techniques as the search should go on in encrypted manner.
Besides, in cloud computing data owners may allocate their outsourced data with a number of cloud users, who strength want to only get back the data files they are paying attention in cloud server. One of the most fashionable ways to do so is throughout keyword-based retrieval. It is like better to get the retrieval outcome with the most significant files that match users’ interest instead of all the files, which indicates that the files should be ranked in the order of relevance by users’ interest and only the files with the highest relevance’s are sent back to cloud users. To develop security exclusive of give up effectiveness, methods here in [4], [5], give you an idea about that they sustain top-k single keyword retrieval under different circumstances. To protect data privacy, confidential data has to be encrypted before outsourcing, so as to provide end-to-end data confidentiality assurance in the cloud. Clouds enable customers to remotely store and access their data by lowering the cost of hardware ownership while providing robust and fast services [6].
The importance and necessity of privacy preserving search techniques are even more pronounced in the cloud applications. Due to the fact that large companies that operate the public clouds like Google or Amazon may access the sensitive data and search patterns, hiding the query and the retrieved data has great importance in ensuring the privacy and security of those using cloud services. We aim to achieve an efficient system where any authorized user can perform a search on a remote database with multiple keywords, not including exposing neither the keywords he/she searches for, nor the pleased of the documents he/she get backs. The main confront of cloud storage is guaranteeing have power over, and the essential integrity and confidentiality of all stored cloud data.
-
II. Literature Survey
2014- A. Q. Lawey et. al. they introduced energy efficient cloud computing services design framework over IP/WDM core networks. They analyzed distribution of clouds, impact of demand, cloud capability, access frequency content popularity along with no. of switches, routers, servers, storage required in cloud [7]. They examined cloud content delivery, virtual machines and storage as a service (StaaS). They developed mixed integer linear programming (MILP) to enhance services of cloud content delivery by replicating content into multiple clouds on which they developed energy efficient cloud content delivery heuristic DEER-CD. They increased power savings by migrating content according to access frequency and by optimizing placement of virtual machines by breaking them into smaller virtual machines and placing them in proximity. They termed replicating content into multiple clouds based on content popularity as OPR scheme. With the help of these schemes they were able to save 92% and 43% network and total power savings respectively. They obtained power savings are by placing Virtual machines using a heuristic (DEER-VM) developed to copy the model behavior in real time [7].
2014 – V. Mathew et. al. identified the operational costs of Internet scale distributes systems(IDS).They proposed a demand response technique in which pricing signals from smart grid makes the system to reduce energy usage [8]. The load is deferred from elastic requests to later time periods reducing server demand and energy usage. They proposed optimal offline algorithm and showed that cost savings can be achieved without increasing in bandwidth cost of IDS .The approach used by them for elastic requests like background downloads, software updates etc. does not require continuous services. The algorithm proposed by them achieved 12% of savings on time of use electricity pricing. They presented a future plan to move load to near data centers for energy saving [8].
2013- S. Zaman et. al. analyzed that the cloud computing resources were provisioned to different virtual machine instances allocated to users for specific period of time which is not efficient allocation economically due to fixed price allocation [9]. They proposed combinatorial auction based allocation which described that user’s demand is taken into account while making provisioning decisions and VM allocation because the existing mechanism do not consider user’s demand. They evaluated the mechanism through simulation experiments which improved utilization of resources of clouds and increased the revenue of cloud provider. They designed mechanism CA-PROVISION which effectively captured market demand, provisioned the computing resources and generated higher revenue as compared to CA-GREEDY [9].
2013- K. Qazi et. al. observed that virtual machines(VM) rent computational resources like memory, network bandwidth etc. to data center owners [10]. They stated that the physical machine that make up cloud termed as machine farms should optimally use these resources without being overload at a point and also minimum machine should continue running. They observed the pattern to help arrange the VM on physical machines. They proposed a framework PoWER that predicts the behavior of cluster and distributes VM in cluster turning off unused physical machines to save energy. They tested PoWER on tested cluster and analyzed its performance resulting in better results compared to FFT based time series method [10].
2013- G. Lahoti et. al. stated that fine grained energy usage data can leak customer information and due to use of this data by online service providers for effectiveness of smart grid technologies, the sharing of data is increasing [11]. They proposed privacy enhanced framework to store, manage and share such data. The mechanism used by them stated that the customer can control the usage information showing to service providers which will be convinced by its authenticity. They implemented a prototype using Green Button data model. Their prototype worked allowing redaction of Green Button data model while sharing data with third party service provider. The presented data can be used for billing and accounting purpose as it can be authenticated and verified by third party using Green Button data model. They planned to work on the working prototype of the model of demand response aggregation service [11].
2013- A. Atrey et. al. remarked that cloud computing as a service across the globe provides high performance at cheaper cost. They also stated that this requires huge data centers using high amount of energy and thereby increasing carbon emission. They focus on green cloud computing to reduce carbon emission and energy consumption by green matrices for cloud computing and green algorithms. Using the existing architecture they adopted and analyzed a search service on private cloud and public cloud and to obtain the results and the advantages and disadvantages which are then stated for future work [12].
2013- T.H. Szymanski explored the technology to achieve efficient energy communications in cloud computing systems. The cloud computing system is global scale as stated which can link 100 data centers and can interconnect 5M servers larger than HPC machines
-
[13] . They explored the use to future internet work using QoS aware router scheduling algorithm with IETF resource reservation technology. They stated that large queuing delays of traditional internet links can be eliminated reducing the latency to minimum value (fiber latency). They used maximum flow and minimum energy routing algorithm to route trunks of high capacity between data centers. They used inter-processor communications onto trunks for improved and efficient latencies, bandwidth and energy. They proposed that cloud computing system can be more efficient in energy and resource utilization by low latency connections and multithreading [13].
2013- F Chen et. al. they stated the large amount of energy consumed by large cloud data centers producing carbon footprints. They gave the idea to minimize energy consumption guaranteeing service level agreements (SLA)
-
[14] .They developed an energy consumption model to profile consumption based on tasks: computation intensive, data intensive and communication intensive. The results given by them consisted of system configuration, work load, system performance etc. be used for designing energy consumption monitors. For generating the results they performed various
experiments and profiled energy consumption with runtime tasks on a cloud system by treating a single task as unit and measured the energy consumed by the task on which the energy consumption and system throughput were analyzed. They analyzed the functional shape of energy consumption model and ran experiments on larger cloud platform [14].
2013- H. Chihiet. al. they remarked that cloud computing can be used for distributed utility computing and can save energy through central management of computational resources like power down servers when not in use. They proposed an approach on unsupervised predictor model in form of unsupervised [15]. They proposed resource administration strategy for energy saving in cloud computational systems. They focused their research on self -adapting computing systems. They proposed an autonomic unsupervised neural predictor and policies for dynamic provisioning for servers in cloud. They stated cloud computing with auto scaling and autonomic provisioning for increment of utilization of server and decrement of its idle time. They proposed future research to self-administration of cloud infrastructure [15].
2012- Y. Tang et. al. provided value added security to cloud storage services. They stated that the need to do so raised due to outsourcing of data backups to third party cloud storage service which reduces cost of data management [16]. They designed FADE to secure this data backup through policy based access control and file assured deletion. FADE is capable of associating backup files with access policies and deletes them on policies revocations. They designed FADE to work atop cloud storage services which is set upon cryptographic key operations providing security. FADE delete files on revocation of file access policies and are non-recoverable by anyone. They described operations on cryptographic keys to obtain access control and deletion [16].
2012- J. Wang et. al. remarked that computational jobs from various resources generated the concern to consumption of energy and computational reliability. This energy consumption can be reduced by cloud computing. They stated that the jobs request can be scheduled and partitioned between computational servers [17]. They proposed a strategy to reduce energy consumption in cloud computing servers by dynamically monitoring the requests at finite time period and then switching servers according to requests. They maintained QoS levels, backlogging and unit penalty cost to monitor computational performance. They developed stochastic integer programs to reduce energy consumptions through scheduling uncertain requests. They addressed job request uncertainty through chance constrained programming and solve them by programming with binary variables examining the effects of backlogging and penalty of unfinished requests. With the help of backlogging the energy consumption was reduced through consolidating requests to later period by servers. The results generated in their research showed little effect on consumption of energy by varying the no. of time intervals/periods whereas increasing time period increased CPU time. The results were given on an assumption of homogenous job requests and server efficiencies were treated as parameters. They presented a future model to examine heterogeneous job requests and other computer resources like disk storage virtual memory etc. In relation with the future work they planned to monitor other server modes to obtain decision variables. They planned to analyze large scale data uncertainty and dynamic decisions using stochastic-tic processes techniques and queuing theories [17].
2011- D. G. doLago et. al. they proposed a virtual machine scheduling algorithm based on concepts green computing. The proposed algorithm by them minimizes the energy consumption in task executions in cloud environment by shutting down underutilized hosts, migrating hosts that are operating below threshold and DVFS [18]. The methodology the proposed comprised of receiving the load by host which is energy efficient given by MIPS ratio as energy consumed by host. The algorithm proposed by them is capable of improving power consumption in clouds containing heterogeneous datacenters. The algorithm presented by them is capable of task scheduling in non -federated datacenters, homogeneous and heterogeneous, with different workload size. The algorithm results showed that its performance was better for heterogeneous and large datacenters. They proposed future work strategy to improve algorithm’s efficiency by measuring size of virtual loads to be processed, modeled as studies in binpacking problem by applying heuristics [18].
2011-Q. Huang et.al.gave the idea to power consumption evaluation. They analyzed that virtualization technology or virtual machine migration apart from bringing resources distribution benefits also increased the power consumption [19]. They stated that employing the consolidation strategy, power overhead is less as compared to regular deployment. Their paper presented cost of live migration for physical layers at source and destination in accordance to CPU utilization. Their results generated the facts that the power impact of live migration falls on increase of CPU utilization whereas the destination server is not influenced by CPU usage of virtual server transferred. Their result showed that time cost for source and destination is not effected by CPU usage of virtual server. They gave their future methodology over power consumption in live migration and determining migration cost [19].
2010-A. Beloglazov et. al. remarked that computational power demand by various applications has created large scale data centers consuming power rapidly [20]. They proposed energy efficient resource management system by continuous consolidation of VM’s. The consolidation in accordance with virtual network topologies, resource utilization, computing nodes thermal condition. They proposed simulation driven evaluation of heuristics. They gave the methodology of live migration of VM’s reallocation according to CPU performance. They presented the de –centralized architecture of energy efficient and aware resource management system. They evaluated the heuristics by simulation using cloudsim toolkit. They set utilization thresholds for flexible adjustment of SLA by MM policy. The policy suggested by them supported heterogeneity of hardware and VM and is independent of type of workload. The results they obtained showed the energy savings by dynamic consolidation of VM [20].
2010- J. Baliga et. al. proposed that network based cloud computing is continously increasing with increase in power consumption.They focussed on energy consuption due to transmission ,switching networks, data processing and data storage because energy used in these processes is significant percentage of whole energy used by cloud.They remarked that cloud computing save energy when tasks are infrequent and also in some situations cloud computing can use more power than conentional computing.They evaluated the energy consumption on storage , software and processing and stated that due to increase in energy consumption in transport public cloud storage uses more energy than private cloud storage still when files are in continous access cloud storage service is efficient compared to hard disks .however they analzed increase in energy consumption when file download frequency increases in cloud storage [21].
2009- R. Bolla et. al. proposed the need of energy efficient network technologies .They proposed feasible power management policies suited to heterogeneous set of modular architectures used for developing network equipment’s. The proposed policies aimed at optimizing the power consumption of each device with respect to its network performance. They applied these policies to SW router platform for evaluating the results. The proposed approach suited with different equipment architectures. The results obtained with COTS SW router provided power saving of 30% in idle states only [22].
-
III. Proposed Methodology
-
1. Create homogenous and heterogeneous cloud environment for public and private and hybrid clouds.
-
2. Establish and initialize datacenters and V.M’s and cloudlets and brokers to access the data to the data centers from users.
-
3. Send all requests 1st time.
-
4. If ‘Pkt’ be the packets to be send from sender to broker for the access of ‘N’ resources R1,R2,R3…..Rn
-
5. The transport power to access the resource Ri is given by
-
6. Find the dirty requests to be sent in next iteration using 2 phase algo.
-
7. Find the zero pages in requests
-
8. If request is zero page, Send 1 byte only “no data”
-
9. Apply the hash similarity function to identify the similar and identical requests
-
10. And more than one identical request are there then send only one.
Where, H is the number of users to send the request for the resource Ri and P tr1 , P IP represents power of consumption for the resource Ri and processing cost.
-
1. If ‘N’ of request are send from User ‘Ui’ to DataCenter ‘Di’
-
2. If ‘Ri’ is the resources to be involved in the communication.
-
3. For each of ‘Ri’ ^ ‘Di’
-
4. Compute power for each of the resource
-
5. If check ‘Rold’==Rnew’ request for new resource and new resource is same or not.
-
6. Send only ‘Rold’
-
7. Else
-
8. Send Rnew
-
9. End
Resource Scheduling Technique While (true){
Tcurrent = get Raccess from VM;
for each Resource{
//resource is unallocated
If (!Tcurrent[Resource]) For each Useri ^ Resource Allot Useri ^ Tcurrent
Else
Wait'l l till Resource(Alloted)
End
End
-
IV. Result Analysis
The figure shown below is the comparative analysis of power consumption on various simulators such as Green cloud and Cloud simulator. The comparison is done for various devices such as resources used by the data centers including old and mid-range computers and laptops, terminals and HDD. The analysis is done on the basis of simulations provided to consume power during the access of these devices on cloud environment. The proposed technique implemented here for the resource utilization or access on the data centers using cloud simulator is more efficient and easy to use as well consumes less power as compared to the existing consumption on Green Cloud.
Compariosn of Power Consumtion in Watts
|
CL 112050550000 E D C О О Ф о а. |
||||||
|
M od er n Mi d… |
Ol d Mi dra n… |
M od er n hig h… |
Lo wen d lap t… |
Te rm ina l |
2.5 " HD D |
|
|
—•— Existing work on Green Cloud |
110 |
210 |
175 |
18 |
8 |
2.5 |
|
- ■ - Proposed Work on CloudSim |
78 |
162 |
92 |
10 |
4 |
1.645 |
Fig.1. Comparison of power consumption on various simulators
The table shown below is the analysis of the existing and proposed work when applied on varios power cnsuming devices such as server, LAN and routers these devices are used in the cloud environemnt during the access of datacenters by users, hence the devices takes power which is analysed in existing and proposed mwork.
Table 1. Analysis on devices used for the communication
|
Existing work |
Equipment |
Capacity |
Power Consumption |
|
Storage |
HP 8100 EVA |
604.8 Tb |
4.9 kw |
|
Content Server |
HP DL380 G5 |
800 Mb/s |
225 kw |
|
Computation Server |
HP DL380 G5 |
355 kw |
|
|
LAN |
Cisco 6509 |
320 Gb/s |
3.8 kw |
|
Gateway Router |
Jupiter MX-960 |
660 Gb/s |
5.1 kw |
|
Proposed Work |
Equipment |
Capacity |
Power Consumption |
|
Storage |
HP 8100 EVA |
604.8 Tb |
2.74 kw |
|
Content Server |
HP DL380 G5 |
800 Mb/s |
186 kw |
|
Computation Server |
HP DL380 G5 |
291 kw |
|
|
LAN |
Cisco 6509 |
320 Gb/s |
2.56 kw |
|
Gateway Router |
Jupiter MX-960 |
660 Gb/s |
3.61 kw |
The table shown below is the result analysis of the existing work in respect to storage, transport and processing of the simulator. Here the analysis is done on the basis of public and private cloud for software as a service and storage as a service.
Table 2. Existing work analysis on various parameters
|
Energy Component |
Service Type |
Storage as a service |
Software as a service |
|
Transport |
public |
High frame rates |
always |
|
private |
never |
high download rates |
|
|
Storage |
public |
never |
low download rates |
|
private |
never |
low download rates |
|
|
Processing |
public |
few users per server |
never |
|
private |
few users per server |
high download rates |
The figure shown below is the result analysis of the proposed work in respect to storage, transport and processing of the simulator. Here the analysis is done on the basis of public and private cloud for software as a service and storage as a service.
Table 3. Existing work analysis on various parameters
|
Energy Component |
Service Type |
Storage as a service |
Software as a service |
|
Transport |
public |
medium frame rates |
always and unlimited |
|
private |
never |
high download rates |
|
|
Storage |
public |
never |
efficient and dynamic |
|
private |
never |
efficient and dynamic |
|
|
Processing |
public |
depends on the users request |
depends on the users request |
|
private |
depends on the users request |
high download rates |
The table shown below is the analysis of the existing and proposed methodology for various user when access datacenters. Here for the analysis of the total power consumption during the accessibility of users on datacenters is computed.
Table 4. Result Analysis of total power consumption
|
Power Consumption |
||
|
No. of users |
Existing Work |
Proposed Work |
|
100 |
67.43 |
34.76 |
|
200 |
84.27 |
56.36 |
|
300 |
104.33 |
86.24 |
|
400 |
126.47 |
103.85 |
|
500 |
142.65 |
128.34 |
|
600 |
162.47 |
137.42 |
|
700 |
182.22 |
148.65 |
|
800 |
193.87 |
169.18 |
|
900 |
210.32 |
184.63 |
|
1000 |
223.43 |
201.75 |
The figure shown below is the analysis of the existing and proposed methodology for various user when access datacenters. Here for the analysis of the total power consumption during the accessibility of users on datacenters is computed.
Comparison of Power Consumption
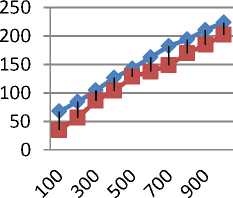
—ф— Existing Work
- ■ - Proposed Work
No. of User Requests
Fig.2. Result Analysis of total power consumption
The proposed technique implemented here for the power consumption in cloud environment is efficient as compared to the existing technique. The comparison is done on the basis of certain parameters such as Storage, Capacity on the basis of equipments used as cloud resources. The total percentage of power consumption of the proposed work is more than the existing technique used for power consumption.
Although the technique is efficient and provides less power consumption but further enhancements can be done for the scheduling of resources using some scheduling technique and also dynamic virtual data centers are created for the minimization of power.
Список литературы An Efficient Approach of Power Consumption in Cloud using Scheduling of Resources
- Cloud Security Alliance, "Top Threats to Cloud Computing," http://www.cloudsecurityalliance.org, 2010.
- Kui Ren, Cong Wang and Qian Wang, "Toward Secure and Effective Data Utilization in Public Cloud", IEEE Network, November/December, 2012.
- Cong Wang, Sherman S.M. Chow, Qian Wang, Kui Ren, and Wenjing Lou, "Privacy-Preserving Public Auditing for Secure Cloud Storage", IEEE Transactions on Computers, Vol. 62, No. 2, February 2013.
- N. Cao, C. Wang, M. Li, K. Ren, and W. Lou, "Privacy-Preserving Multikeyword Ranked Search over Encrypted Cloud Data," Proc. IEEE INFOCOM, 2011.
- H. Hu, J. Xu, C. Ren, and B. Choi, "Processing Private Queries over Untrusted Data Cloud through Privacy Homomorphism," Proc. IEEE 27th Int'l Conf. Data Eng. (ICDE), 2011.
- L. M. Vaquero, L. Rodero-Merino, J. Caceres, and M. Lindner, "A break in the clouds: towards a cloud definition", SIGCOMM Comput. Commun. Rev., 39:50{55, December 2008.
- Ahmed Q. Lawey, Taisir E. H. El-Gorashi, and Jaafar M. H. Elmirghani, "Distributed Energy Efficient Clouds Over Core Networks", Journal of Lightwave Technology, VOL. 32, NO. 7, APRIL 1, 2014.
- Virnal Mathewt, Rarnesh K. Sitararnan t and Prashant Shenoy, "Reducing Energy Costs In Internet-Scale Distributed Systems Using Load Shifting", 978-1-4799-3635-9/14, 2014.
- Sharrukh Zaman, "A Combinatorial Auction-Based Mechanism for Dynamic VM Provisioning and Allocation in Clouds", IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CLOUD COMPUTING, 2013.
- Kashifuddin Qazi, Yang Li, and Andrew Sohn, "Power Prediction of Workload for Energy Efficient Relocation of Virtual Machines", ACM 978-1-4503-2428, 2010.
- Gaurav Lahoti, "Customer-centric Energy Usage Data. Management and Sharing in Smart Grid Systems", ACM 978-1-4503-2492, 2013.
- T.H. Szymanski, "Low Latency Energy Efficient Communications in Global Scale Cloud Computing Systems", EEHPDC'13, June 17, 2013, New York, NY, USA, 2013.
- Feifei Chen, John Grundy, Yun Yang, Jean-Guy Schneider and Qiang He, "Experimental Analysis of Task-based Energy Consumption in Cloud Computing Systems", ICPE'13, April 21–24, 2013, Prague, Czech Republic, 2013.
- Hanen Chihi, Walid Chainbi, "An Energy-Efficient Self-Provisioning Approach for Cloud Resources Management", IEEE 2013.
- Yang Tang, Patrick P.C. Lee, "Secure Overlay Cloud Storage with Access Control and Assured Deletion", Ieee Transactions On Dependable And Secure Computing, Vol. 9, No. 6, November/December 2012".
- Jue Wang, "Risk and Energy Consumption Tradeoffs in Cloud Computing Service via Stochastic Optimization Models", IEEE/ACM Fifth International Conference on Utility and Cloud Computing, 2012.
- Daniel Guimaraes do Lago1, "Power-Aware Virtual Machine Scheduling on Clouds Using Active Cooling Control and DVFS", ACM 978-1-4503-1068, 2011.
- Qiang Huang, Fengqian Gao, Rui Wang, Zhengwei Qi, "Power Consumption of Virtual Machine Live Migration in Clouds", Third International Conference on Communications and Mobile Computing, 2011.
- Anton Beloglazov, "Energy efficient resource management in virtualized data centers", IEEE/ACM International conference on cluster, cloud and grid computing, 2010.
- Jayant Baliga, Robert W. A. Ayre, Kerry Hinton, "Green Cloud Computing: Balancing Energy in Processing, Storage, and Transport", IEEE 2010.
- Raffaele Bolla, Roberto Bruschi, Franco Davoli, Andrea Ranieri, "Energy-Aware Performance Optimization for Next-Generation Green Network Equipment", ACM 978-1-60558-446-1/09/08, 2009.


