Анализ социальных сетей и статистическая обработка твитов о COVID-19
Автор: Золотарев Олег Васильевич, Хакимова Аида Хатифовна
Рубрика: Управление сложными системами
Статья в выпуске: 2, 2022 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Анализируются сообщения в «Твиттере» для выделения наиболее актуальных тем, связанных с распространением коронавируса в мире на примере русскоязычного сегмента «Твиттера». Для анализа близости слов в тексте и формирования терминологических цепочек слов использовался метод машинного обучения word2vec. Были выделены наиболее распространенные n-граммы, связанные с COVID-19. Авторы предлагают оригинальную методику выявления тематических групп твитов и оценки их значимости, которую можно использовать не только для коротких сообщений в «Твиттере», но и для анализа текстовых документов. В результате исследования выделяются n-граммы различной длины, проводится их статистический анализ, формируются тематические группы, включающие наиболее релевантные n-граммы, и определяются их веса. Для оценки популярности тем предлагается численный показатель. Учитывается актуальная популярность тем и их динамика. Отмечается, что происходит эволюция тем обсуждений и образование новых терминов, связанных с пандемией.
Анализ социальных сетей, covid-19, n-грамм, твиты, тематическая группа
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/148324976
IDR: 148324976 | УДК: 004.9 | DOI: 10.18137/RNU.V9187.22.02.P.084
Текст научной статьи Анализ социальных сетей и статистическая обработка твитов о COVID-19
Коронавирусная болезнь 2019 г. (COVID-19) – это новое заболевание, впервые зарегистрированное в Ухане (Китай) в декабре 2019 г. В марте 2020 г. Всемирная организация здравоохранения (ВОЗ) объявила COVID-19 пандемией, поскольку вирус распространился по всему миру [26]. По последним статистическим данным (на 3 июня 2022 г.),
Анализ социальных сетей и статистическая обработка твитов о COVID-19
Золотарев Олег Васильевич кандидат технических наук, доцент, заведующий кафедрой информационных систем в экономике и управлении. Российский новый университет, Москва. Сфера научных интересов: компьютерная лингвистика. Автор 80 опубликованных научных работ.
во всем мире коронавирусом заболели 534 301 348 человек, а за время пандемии умерло 6 317 894 человек [27].
Распространение COVID-19 сопровождается инфодемией, то есть избытком информации о вспышке вируса [25]. При этом наблюдаются как всплеск научных публикаций [13], так и растущий объем дискуссий в социальных сетях, которые доступных практически в режиме реального времени и несут реальное представление о реакции общественности на пандемию.
Люди высказывают мнения и идеи, делятся ими на социальных платформах. Анализ настроений позволяет наблюдать за крупными сообществами при низких затратах [5]. Таким образом, анализ настроений является мощным инструментом для понимания наиболее важных событий и тенденций. Набор данных в «Твиттере» предоставляет широкий спектр актуальной информации, связанной с поведением пользователей, эмоциями и мнениями о событиях в мире [16]. С начала пандемии коронавируса многие исследователи изучали и анализировали данные «Твиттера», применяя методы анализа настроений для разных целей. Samuel и др. [20] провели текстовый анализ твитов в США во время пика заболеваемости COVID-19, чтобы проследить эволюцию настроения триады страх – паника – отчаяние, связанной с COVID-19. Bhat и др. [3] проанализировали настроение более 80 000 твитов о распространении COVID-19. Выяснилось, что 51,97, 34,05 и 13,96 % твитов выражали положительные, нейтральные и отрицательные настроения соответственно. Влияние социальных сетей во время пандемии изучали Shietal [21]. Они продемонстрировали роль социальных ботов в манипулировании общественным мнением в социальных сетях в пиковые периоды пандемии. Было проведено сравнение мнений и выражений, генерируемых социальными ботами и пользователями. Выяснилось, что социальные боты чаще использовались для негативных высказываний о ситуации.
Изучение эмоций человека по поводу пандемии COVID-19 в социальных сетях обсуждалось в работах [7, 11]. Испанские исследователи использовали социальные сети в качестве источника данных для анализа гнева, страха и общественных настроений во время пандемии. Анализ настроения включал классификацию различных эмоций, таких как печаль, тревога, счастье и др. Анализ настроения на арабском языке был проведен Aljameeletal [1] для оценки осведомленности населения о мерах предосторожности в период карантина в нескольких регионах Королевства Саудовской Аравии.
В большинстве исследований подчеркивается важность использования инструментов больших данных, таких как анализ настроений из социальных сетей, для борьбы с возникающими эпидемиями. Исследователи также указывают на важность анализа мнений из неструктурированных источников данных, таких как социальные сети, при формулировании государственных национальных рекомендаций по вопросам здоровья и эпидемий в настоящее время [22]. Анализ тональности – одна из самых популярных задач обработки естественного языка; проведено множество исследований, и достигнут прогресс в решении этой задачи. Глубокие нейронные сети широко используются для классификации полярности настроения; однако для этого часто требуется огромное количество обучающих данных.
Для текстовой аналитики используется широкий спектр методов и инструментов в зависимости от характера текстовых данных, целей исследования и размера набора данных. Данные «Твиттера» широко используются для текстового и эмоционального анализа. Одним из ключевых выводов текстовой аналитики является определение тональности, связанной с анализируемым текстом. Анализ настроений в широком смысле описывается как присвоение оценок и категорий настроений на основе ключевых слов и фразового соответствия тональным словарям. Оценки настроения варьируются от отрицательных (около минус 1) до положительных (около плюс 1) [19].
N -граммы широко используются для анализа твитов. N -грамма слова – это последовательность из n слов, взятых из любого текстового документа. Например, словарные n -граммы для предложения «коронавирус заразен» представляется следующим образом: n = 1, униграммы: coronavirus, is, contagious; n = 2, биграммы: coronavirus is, iscontagious; n = 3, триграммы: coronavirus iscontagious [17]. Словарные N -граммы эффективны для анализа настроений. Например, «COVID positive» – это биграмма, которая может идентифицировать человека как COVID-положительного.
Nieuwenhuis и Wilkens [18] представили гендерную классификацию текстов и изображений с использованием модели N -грамм. Они использовали N -граммы слов и символов в качестве текстовых характеристик в дополнение к некоторым основным характеристикам изображения, чтобы предсказать пол пользователя «Твиттера». Наилучшие результаты были достигнуты при использовании только текстовых функций. Кроме того, нет зависимости от предварительно обученных вложений слов или больших обучающих корпусов.
Hassan и др. [9] применили анализ N -грамм на основе слов для разделения твитов на заслуживающие доверия и не заслуживающие доверия. В работе Kimetal [14] при исследовании использования n -грамм в качестве признаков для классификации коротких текстов были представлены десять наиболее важных признаков униграмм, биграмм и триграмм [4].
Задачи исследования преследовали двоякую цель: извлечь потенциально тональные слова социально-психологической тематики из русскоязычных твитов, связанных с хештегом #коронавирус, и выделить наиболее значимые тематические группы твитов. В тематические группы входят близкие по смыслу термины из множества S . Подобные подходы использовались ранее в предыдущих работах авторов [12].
В настоящей работе изучены некоторые аспекты, которые еще не были рассмотрены другими авторами. Основные вклады:
-
1. Анализ русскоязычных твитов, связанных с коронавирусом.
-
2. Использование словесных n -грамм для выбора темы обсуждения в «Твиттере».
-
3. Изучение эволюции основных тем обсуждения коронавируса в «Твиттере».
-
4. Разработка программы извлечения n -грамм с измененным набором стоп-слов.
Анализ социальных сетей и статистическая обработка твитов о COVID-19
Материалы и методы
Данные для исследования были загружены из «Твиттера» в апреле 2021 г. (с 03.04.2021 по 16.04.2021) и в июле (с 03.07.2021 по 16.07.2021). Выгрузка осуществлялась с использованием аналитических механизмов «Твиттера» (Vicinitas) [24], позволяющих выгружать хэштеги, учетные записи пользователей и ключевые слова. В соответствии с ранее опубликованной методикой ретвиты исключались [23].
Это исследование содержит русскоязычные твиты. При этом пользователи не привязаны к конкретному месту жительства. За период исследования были проанализированы: а) 24386 твитов (апрель) от 10496 пользователей; б) 16320 твитов (июль) от 8024 пользователей.
В качестве начального подхода использовался метод визуализации данных твитов по запросу коронавируса в виде облака слов [15]. Например, облако слов было построено для твитов за период с 03.04.2021 по 10.04.2021. Тексты твитов были переведены на английский язык с целью сокращения лексического разнообразия. Затем стоп-слова были удалены.
Для анализа корпуса текстов разработана программа генерации n- грамм. Это позволило выявить наиболее значимые n -граммы из корпуса текстов длиной от 1 до 3 ( n -граммы длиннее 3 слов составляют незначительную долю от общего числа n -грамм). Работа проводилась в несколько этапов. Сначала были загружены тексты сообщений из «Твиттера», затем проведен анализ близости слов с помощью метода машинного обучения word2vec. В то же время была переработана структура стандартного списка стоп-слов Python, а также значительно увеличен список стоп-слов (обсуждается ниже). Это позволило изначально отсечь термины, не являющиеся существенными для выбранной области исследования.
Использовалась комбинация машинного и экспертного подходов. Эксперты сформулировали предварительные темы, связанные с различными аспектами пандемии коронавируса. Для предварительных тем автоматически отбирались наиболее релевантные слова и словосочетания на основе метода word2vec, который мы использовали ранее [28]. Эксперты оценивали отношение слов и словосочетаний к заявленной теме.
Для извлечения n -грамм из полнотекстовых сообщений использовалась специальная программа, анализирующая синтаксическое окружение термина. Поиск терминов осуществлялся в несколько этапов с использованием расширенного набора стоп-слов. В результате был получен набор терминов и словосочетаний, как широко употребляемых, так и вошедших в обиход во время пандемии в результате словообразования, основанного на распространении процессов во время пандемии (вакцинация, тестирование, заражение и др.). Таким образом, разработанная программа может идентифицировать новые термины по мере их появления в лексиконе пользователей социальных сетей.
Оригинальная программа извлечения n -грамм была разработана с усовершенствованием классического подхода для автоматического извлечения n -грамм из полнотекстовых сообщений. Улучшение заключалось в следующем. Для определения n -грамм в тексте как устойчивое словосочетание извлекалось главное существительное с определителями (см. Рисунок 1).
Разработан расширенный набор стоп-слов, позволяющий гибко управлять процессом определения значимых n-грамм, как широко используемых, так и новых, возникающих в ответ на те или иные события. При извлечении терминов из твитов с использованием стандартного набора стоп-слов Python (в стандартный набор входили только со- юзы, междометия, которые исключались из рассмотрения) основной проблемной был «шум» – большое количество слов, не относящихся к исследуемой теме.
def isThisATerm(WordStr):
import nltk tokens = nltk.word_tokenize(WordStr)
tagged = nltk.pos_tag(tokens)
Lent = len(tagged) ind = 0
while ind < Lent:
if (('NN* in tagged(indj) or ('FW in tagged[ind]) or
('VBG' in tagged[ind]) and |(WordStr not in stopwords)): return(l)
ind = ind * 1 return(0)
Рисунок 1. Формирование n -грамм
Значительно расширен набор стоп-слов для обработки твитов. По результатам экспертного анализа добавлены категории стоп-слов (географические названия, даты, дни недели, названия месяцев, собственные имена, названия учреждений, должностей и др.). Набор стоп-слов регулярно пополняется новыми элементами, что помогает значительно снизить количество «шума» при извлечении терминов из твитов посредством автоматической обработки. Программа генерирует n -граммы по тематике, заданной поисковым запросом при формировании корпуса текстов.
Для текстовой аналитики на раннем этапе использовалось Wordcloud – визуализация данных, состоящая из размера и визуального акцента слов, взвешенных по частоте их появления в текстовом корпусе, которая используется для графического изображения значимых слов в текстовом корпусе [6]. В этом исследовании использовался графический пакет Wordcloud [10].
На основе анализа корпуса текстов построена визуализация значимых терминов (облака слов) с помощью инструмента Wordcloud по частоте употребления термина в корпусе твитов. Термины могут быть представлены n -граммами разного размера.
В работе рассчитывается частота встречаемости терминов в твитах по n -граммам. N -граммы длиннее 4 слов не учитываются из-за низкой частоты появления в твитах:
S =
где S – набор значащих n -грамм, извлеченных из корпуса текстов; N – набор с общим количеством n -граммов; F – частота n -грамм в текстовом корпусе; W – вес n -граммы в определенном наборе n -грамм (обсуждается ниже).
В ходе анализа было выявлено 3 набора значимых n -грамм по разным темам: S 1 (униграммы), S 2 (биграммы), S 3 (триграммы). В каждом наборе n -граммы (термы) сортируются по убыванию частоты, n -грамма с наибольшим количеством встречаемости в текстовом корпусе получает максимальный вес 10, поскольку каждый набор n -грамм содержит 10 наиболее часто встречающихся терминов, отсортированных по частоте в порядке убывания.
Для каждой тематической группы рассчитывается общий вес для определения ее значимости. В тематическую группу могут входить любые n -граммы из множества S . Формирование тематических групп осуществлялось группой экспертов. Одни и те же термины могут быть отнесены к разным тематическим группам в зависимости от контекста. По-
Анализ социальных сетей и статистическая обработка твитов о COVID-19 этому термины (словосочетания) в зависимости от контекста могут быть отнесены к разным тематическим группам. Многозначность разрешается путем оценки семантического сходства контекстов с использованием метода Word2vec. В ходе анализа выявлены наиболее значимые тематические группы терминов (как наиболее популярные).
Введем понятие веса ( W x , здесь x изменяется от 1 до 3 в зависимости от числа подмножеств n -грамм) внутри одного из подмножеств множества S ( S 1, S 2, S 3), в данном случае n -грамма с максимальной частотой в каждом подмножестве получает максимальный вес, равный 10. Остальные n -граммы подмножества получают веса Wk x по убыванию ( k варьируется от 1 до 10). После объединения в тематические группы можно рассчитать вес каждой тематической группы W x :
W = 2 n == 0 W (2)
Мы не можем судить о важности тематических групп только по весам. Для более точного подсчета необходимо использовать величину приведенной частотности ( F redx ) для каждой тематической группы:
F redx = Q X (3)
Q cor где Qx – количество использований n-грамм; Qcor – частота употребления термина «коронавирус».
В русскоязычных твитах термин «коронавирус» встречается гораздо чаще, чем «COVID-19». Так, в корпусе твитов в апреле доля последних составила 9,4 %, а в июле – 9,8 %. Поэтому для анализа был выбран термин «коронавирус».
Введем новый показатель L x – показатель употребимости для оценки распространенности данного термина в обсуждаемых темах, рассчитываемый по следующей формуле:
L x 2 "k = 1 F^ . W kx , (4)
здесь n – общее количество n -грамм выбранной тематической группы (в нашем случае n = 10). Эта характеристика была введена для того, чтобы иметь возможность сравнивать важность тематических групп.
Результаты
На Рисунке 2 видно, что использованные твиты в основном посвящены новостям о том, что у президента Аргентины, привитого вакциной Sputnik V в январе, обнаружен коронавирус [2].
Идентификация n -грамм позволяет более тонко выделить наиболее значимые n -граммы в корпусе текстов и интерпретировать их значение. В таблицах 1–4 представлены результаты обработки корпусов текстов для каждой из трех n -грамм с 10 наиболее распространенными n -граммами, отобранными с помощью специально разработанной программы. С одной стороны, униграммы действительно являются самым большим набором извлекаемых слов, с другой – они менее информативны по сравнению с другими типами n -грамм (см. Таблицу 1).

Рисунок 2. Пример облака слов по данным «Твиттера» (русскоязычные твиты переведены на английский язык)
Таблица 1
Распространенные униграммы
|
Апрель |
Июль |
||
|
Униграммы |
F redx |
Униграммы |
F redx |
|
Тест (на коронавирус) |
8,76 |
Победить |
9,15 |
|
Вакцинация |
6,92 |
Тест (на коронавирус) |
8,10 |
|
Вакцина |
5,27 |
Заразить(ся) |
5,54 |
|
Волна |
4,18 |
Вакцинация |
5,17 |
|
Инфекция |
2,39 |
Вакцина |
3,83 |
|
Штамм |
2,15 |
Рост |
3,63 |
|
Туберкулез |
2,12 |
Карантин |
3,24 |
|
Прививка |
1,55 |
Вакцинировать |
3,08 |
|
Смерть |
1,22 |
Восстановиться |
3,01 |
|
Умереть |
1,16 |
Пациент |
2,83 |
Таблица 1 показывает, что термины «тест» (на коронавирус), «вакцинация», «вакцина» устойчиво лидируют. Если в апреле в топ вошли термины, связанные с трагическим исходом болезни («смерть», «умереть»), то в июле их сменили более позитивные слова («победить», «восстановиться»).
Для биграмм была проведена лемматизация (см. Таблицу 2). С апреля по июль сохранили актуальность биграммы «обнаружить коронавирус», «победить коронавирус», «тест (на) коронавирус».
Анализ социальных сетей и статистическая обработка твитов о COVID-19
Таблица 2
Распространенные биграммы
|
Апрель |
Июль |
||
|
Биграммы |
F d |
Биграммы |
F d |
|
Скандал вакцина |
2,56 |
Тест коронавирус |
3,44 |
|
Тест коронавирус |
2,13 |
Заболеть коронавирус |
3,28 |
|
Новый штамм |
2,00 |
Интенсивный уход |
3,08 |
|
Заразиться коронавирус |
1,91 |
Повреждение легких |
3,01 |
|
Доступность вакцинации |
0,67 |
Снижение коронавируса |
2,58 |
|
Найти коронавирус |
0,66 |
Коронавирус катастрофа |
2,58 |
|
Положительный результат |
0,66 |
Победить коронавирус |
2,42 |
|
Обнаружить коронавирус |
0,65 |
Остановить коронавирус |
1,17 |
|
Победить коронавирус |
0,59 |
Обнаружить коронавирус |
1,15 |
|
Туберкулез коронавирус |
0,54 |
Определить коронавирус |
1,13 |
Таблица 3
Распространенные триграммы
|
Апрель |
Июль |
||
|
Триграммы |
F redx |
Триграммы |
F redx |
|
Положительный тест коронавирус |
2,18 |
Соблюдать меры безопасности |
3,22 |
|
Прививка коронавирус Спутник (V) |
0,88 |
Победить коронавирус давно |
3,22 |
|
Коронавирус туберкулез обнаружить |
0,73 |
Быстрое полное выздоровление |
3,01 |
|
Прививка вакцина Спутник |
0,71 |
Пожелать Covid победить |
3,01 |
|
Коронавирус Талибан Эбола |
0,61 |
Отменить карантин ограничения |
2,58 |
|
Вакцинация необходимо ускорить |
0,60 |
Коронавирус Коммунарка реанимация |
1,87 |
|
Повторный тест коронавирус |
0,54 |
Отрицательный тест коронавирус |
0,92 |
|
Подтвердить туберкулез коронавирус |
0,52 |
Пациент соблюдать изоляция |
0,92 |
|
Институт разработал Спутник |
0,51 |
Тест результат Covid |
0,92 |
|
Сдать тест коронавирус |
0,40 |
Поддельный сертификат прививка |
0,76 |
Триграммы более конкретны по содержанию и часто отражают конкретные события, например, триграмма «Коронавирус Коммунарка реанимация» относится к госпитализации известного музыканта П. Мамонова в тяжелом состоянии (Коммунарка – больница для лечения ковидных больных в Москве). Топ-10 триграмм относятся к следующим основным темам: 1) «Тестирование» (в апреле – «положительный тест на коронавирус», «повторный тест на коронавирус», «сдать тест на коронавирус»; в июле – «отрицательный тест на коронавирус», «результат теста на ковид»; 2) «Вакцинация» (в апреле – «прививка коронавирус Спутник V», «прививка вакцина Спутник V», «вакцинация необходимо ускорить»; в июле – «поддельный сертификат прививка».
Так как в n -граммах четко прослеживается тематика, нами были выделены тематические группы терминов: 1) «вакцинация»; 2) «тестирование»; 3) «распространение болезни»; 4) «борьба с коронавирусом»; 5) «выявление коронавируса», «прогрессирование заболевания».
Всем топовым граммам присваивались веса по убыванию от 10 до 1 в соответствии с местом в топе (1-е место – 10, 2-е место – 9 и т.д.). Далее вычислялась сумма весов по каждой тематической группе, включая униграммы, биграммы, триграммы. Далее по каждой из пяти тематических групп выделялись n -граммы, и рассчитывался вес каждой тематической группы в соответствии с формулой (3).
Вес тематической группы «Вакцинация» за апрель составил 76, за июль – 26; группы «Тестирование» за апрель – 40, за июль – 31; группы «Распространение болезни» за апрель – 50, за июль – 42; тематической группы «Борьба с коронавирусом» за апрель – 2, за июль – 78; тематической группы «Выявление коронавируса, прогрессирование заболевания» за апрель – 27, за июль – 29.
Следовательно, с апреля по июль значительно снизилось обсуждение вакцинации (как видно из Рисунка 3, значение L x уменьшилось в 2,56 раза) и значительно возросло обсуждение борьбы с коронавирусом с целью победить заболевание (см. Рисунок 3). Предлагаемая методика осуществляет первичную оценку динамики обсуждаемых тем и выделение актуальных тем.
Для более точного ранжирования тем мы предлагаем учитывать как вес n -граммы, так и ее приведенную частотность для расчета показателя употребимости (формула (5), Рисунок 3). Используя вышеприведенную методику, учитывая приведенную частотность терминов и веса для тематических групп, получаем, что тематическая группа «Борьба с коронавирусом» становится наиболее популярной в июле, тогда как в апреле это была тема «Вакцинация».
Обсуждение
Социальные сети очень динамичны, обсуждение фактов и их интерпретация могут быстро меняться [8]. Новые факты или инциденты могут быстро сместить фокус твитов в другом направлении, так что происходит чрезмерное представление определенных тем в определенный период. В нашем случае такими фактами, на которых было акцентировано внимание пользователей, стали подозрение на заболевание коронавирусом после прививки вакциной «Спутник V» президента Аргентины Альберто Фернандеса (апрель), госпитализация в тяжелом состоянии известного российского музыканта Петра Мамонов (июль). Таким образом, анализ контента социальных сетей всегда следует интерпретировать с учетом сроков создания корпуса текстов.
Тематическое моделирование на основе n -грамм выявило следующие основные темы: «Вакцинация», «Тестирование», «Распространение болезни», «Борьба с коронавирусом», «Выявление коронавируса» и «Прогрессирование заболевания».
Авторы предлагают методику оценки значимости тем при анализе текстовых сообщений (твитов) с учетом весов выделенных n-грамм и их приведенной частотности. В Таблице 4 представлены результаты оценок популярности тем, связанных с коронавирусом, на основе учета веса топовых терминов и на основе показателя употребимости.
Анализ социальных сетей и статистическая обработка твитов о COVID-19
Таблица 4
Общие оценки популярности тем в апреле и июле, рассчитанные на основе весов n -грамм ( W x )
|
Тема |
Апрель |
Июль |
|
Вакцинация |
76 |
26 |
|
Тестирование |
40 |
31 |
|
Распространение болезни |
50 |
42 |
|
Борьба с коронавирусом |
2 |
78 |
|
Выявление коронавируса, прогрессирование заболевания (далее – Выявление коронавируса) |
27 |
29 |
Результаты расчета употребимости (формула (5)) представлены на Рисунке 3, из которого видно, что снижение частоты употребимости не изменило динамику снижения интереса к обсуждению тем «Вакцинация», «Тестирование». Учет показателя употре-бимости позволил количественно оценить всплеск интереса к обсуждению тем «Борьба с коронавирусом» и «Выявление коронавируса» (увеличились в 214 и 4 раза соответственно). Показатель употребимости выявил незначительное увеличение интереса к теме «Распространение болезни» (в отличие от расчетов, основанных на учете только веса терминов).
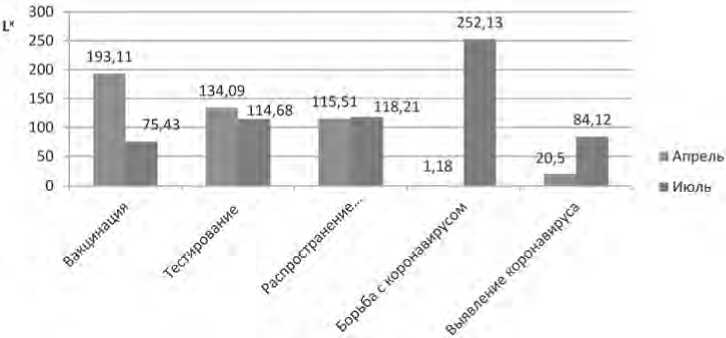
Рисунок 3. Оценка популярности обсуждаемых тем по тегу #коронавирус в русскоязычном «Твиттере» по предложенному параметру ( L x )
Для качественного анализа предложено использовать обособленные от корпуса наборы часто употребляемых терминов, которые мы предлагаем называть терминологическим портретом общественного мнения пользователей «Твиттера». В данном случае терминологический портрет характеризует общественное мнение русскоязычных пользователей о коронавирусе. Такие терминологические портреты могут помочь выявить наиболее обсуждаемые темы, оценить преобладающее настроение пользователей при обсуждении таких тем.
Выводы
Чтобы учесть изменение словарного запаса пользователей с течением времени, мы предлагаем выполнять срезы пользовательских сообщений в «Твиттере» через разные промежутки времени. В каждом срезе выделялись значимые термины и словосочетания, формировавшие терминологический портрет темы обсуждения в данный период времени. Сравнение терминологических портретов выявляет следующее: 1) основные темы для обсуждения; 2) термины, представляющие тему; 3) появление новых терминов.
На основе сравнения терминологических портретов за разные периоды активности пользователей можно сделать следующие выводы. С апреля по июль 2021 года активно обсуждались темы «Вакцинация», «Тестирование», «Распространение болезни», «Борьба с коронавирусом», «Выявление коронавируса».
С апреля по июль произошли изменения в теме вакцинации. В апреле только 41 % n -грамм относились к конкретной вакцине «Спутник V», и все n -граммы были только о вакцинации. В июле появились новые термины, такие как «антиваксеры», «ревакцинация», «прививочный сертификат», «поддельные сертификаты вакцинации» и «пропаганда вакцинации».
В теме «Тестирование2 в апреле обсуждались обязательства и необходимость тестирования. Если в апреле обсуждались только положительные результаты тестов, то в июле – положительные, отрицательные и ложноположительные результаты.
Третья волна коронавируса, мутации и новые штаммы в теме «Распространение заболевания» обсуждались в апреле. В июле также обсуждались новые штаммы, в том числе дельта-штамм. Активно обсуждались возрастные аспекты распространения инфекции.
В апреле о способах победы над коронавирусом мало говорили (упоминали только масочный режим). В июле словарный запас темы стал богаче. Названы такие способы борьбы, как карантин, реанимация, самоизоляция, кислородная поддержка.
В теме «Выявление коронавируса» как в апреле, так и в июле большое внимание уделялось обнаружению коронавируса. В апреле обсуждались последствия и осложнения коронавируса, в том числе детская смертность и неврологические проблемы, в июле – излечение от коронавируса.
В дальнейшей работе планируется создание тональных терминологических словарей с участием экспертов на основе выделенных тематических групп. Ограничением данного исследования стал анализ данных русскоязычного сегмента «Твиттера». В дальнейшем планируется рассмотреть и сравнить русско- и англоязычный сегменты социальных сетей.
Список литературы Анализ социальных сетей и статистическая обработка твитов о COVID-19
- Aljameel S.S., Alabbad D.A., Alzahrani N.A., Alqarni S.M., Alamoudi F.A., Babili L.M., Aljaafary S.K., Alshamrani F.M. (2020) A Sentiment Analysis Approach to Predict an Individual’s Awareness of the Precautionary Procedures to Prevent COVID-19 Outbreaks in Saudi Arabia. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 18(1):218. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18010218.
- Argentina’s President who was vaccinated tests positive for COVID-19. https://english.alarabiya.net/coronavirus/2021/04/04/Argentina-s-President-who-was-vaccinated-tests-positive-for-COVID-19.
- Bhat M., Qadri M., Noor-ul-Asrar Beg M.K., Ahanger N., Agarwal B.J.B. (2020) Behavior, & immunity. sentiment analysis of social media response on the Covid19 outbreak. Brain, Behavior and Immunity.
- Brand D., Kroon S., van der Merwe B., Cleophas L. (2015) N-Gram Representations For Comment Filtering. In Proceedings of the 2015 Annual Research Conference on South African Institute of Computer Scientists and Information Technologists (SAICSIT ‘15). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, Article 6, 1–10. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1145/2815782.2815789.
- Choi S., Lee J., Kang M.-G., Min H., Chang Y.-S., Yoon S.J.M. (2017) Large-scale machine learning of media outlets for understanding public reactions to nation-wide viral infection outbreaks. Methods, 129:50–59.
- ConnerC., Samuel J., Kretinin A., Samuel Y., Nadeau L. (2019) A Picture for The Words! Textual Visualization in Big Data Analytics,. Northeast Business and Economics Association (NBEA ) Annual Proc. (46), pp. 37–43.
- de las Heras-Pedrosa C., Sánchez-Núñez P., Peláez J.I. (2020) Sentiment Analysis and Emotion Understanding during the COVID-19. Pandemic in Spain and Its Impact on Digital Ecosystems. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, 17, 5542.
- Falzon L., McCurrie C., Dunn J. (2017) Representation and Analysis of Twitter Activity: A Dynamic Network Perspective. In Proc. of the 2017 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Advances in Social Networks Analysis and Mining 2017 (ASONAM ‘17). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, USA, 1183–1190. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1145/3110025.3122118.
- Hassan N.Y., Gomaa W.H., Khoriba G., & Haggag M.H. (2020) Credibility Detection in Twitter Using Word N-gram Analysis and Supervised Machine Learning Techniques. International J. of Intelligent Engineering and Systems, 13, 291-300.
- https://wordcloud.pro/ru/studio/editor?v=11
- Iglesias-Sánchez P.P., Witt G.F.V., Cabrera F.E., Jambrino-Maldonado C. (2020) The Contagion of Sentiments during the Covid-19. Pandemic Crisis: The Case of Isolation in Spain. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, 17, 5918.
- Khakimova A., Yang X., Zolotarev O., Berberova M., Charnine M. (2020) Tracking Knowledge Evolution Based on the Terminology Dynamics in 4P‐Medicine. International J. of Environmental Research and Public Health, vol. 17, No. 20, pp. 1–19. DOI: 10.3390/ijerph17207444.
- Khakimova A.Kh., Zolotarev O.V., Berberova M.A. (2020) Coronavirus Infection Study: Bibliometric Analysis of Publications on Covid-19 Using Pubmed and Dimensions Databases. Scientific Visualization, vol. 12, No. 5, pp. 112–129. DOI: 10.26583/sv.12.5.10.
- Kim G., Fukui K., Shimodaira H. (2018) Word-like character n-gram embedding. In Proceedings of the 2018 EMNLP Workshop W-NUT : The 4th Workshop on Noisy User-generated Text, pages 148–152, Brussels, Belgium. Association for Computational Linguistics.
- Mahdikhani M. (2022) Predicting the popularity of tweets by analyzing public opinion and emotions in different stages of Covid-19 pandemic, International Journal of Information Management Data Insights, vol. 2, Iss. 1:100053. ISSN 2667-0968, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jjimei.2021.100053.
- Manguri K.H., Ramadhan R.N., Rasul P., Amin M. (2020) Twitter Sentiment Analysis on Worldwide COVID-19 Outbreaks. Kurd. J. Appl. Res.
- Nasser N., Karim L., El Ouadrhiri A., Ali A., & Khan N. (2021). n-Gram based language processing using Twitter dataset to identify COVID-19 patients. Sustainable cities and society, 72, 103048. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2021.103048
- Nieuwenhuis M., Wilkens J. (2018) Twitter text and image gender classification with a logistic regression n-gram model. In Proc. of the Ninth International Conference of the CLEF Association (CLEF 2018).
- Rinker T.W. Sentimentr: Calculate Text Polarity Sentiment. Buffalo, New York, 2019, version 2.7.1.
- Samuel J., Ali G.G.M.N., Rahman M.M., Esawi E., Samuel Y. (2020) COVID-19 Public Sentiment Insights and Machine Learning for Tweets Classification, 11, 314. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11060314.
- Shi W., Liu D., Yang J., Zhang J., Wen S., Su J. (2020) Social Bots’ Sentiment Engagement in Health Emergencies: A Topic-Based Analysis of the Covid-19 Pandemic Discussions on Twitter. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, 17, 8701.
- Singh R., Singh R., Bhatia A. (2018) Sentiment analysis using Machine Learning technique to predict outbreaks and epidemics. International Journal of Advanced Science and Research, 3:19–24.
- Vicinitas. 2018 Research on 100 Million Tweets: What it Means for Your Social Media Strategy for Twitter. https://www.vicinitas.io/blog/twitter-social-media-strategy-2018-research-100-milliontweets. Accessed April 7, 2022.
- Vicinitas. https://www.vicinitas.io/
- World Health Organization. 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV): Strategic Preparedness and Response Plan, World Health Organization, Geneva, 2020.
- World Health Organization. 2020 Mental Health and Psychosocial Considerations during the COVID-19 Outbreak. Available online: WH O/2019-nCoV/MentalHealth/2020.
- Worldometer. COVID-19 CORONAVIRU S PAN DEMIC. https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/
- Zolotarev O., Solomentsev Y., Khakimova A., Charnine M. (2019) Identification of Semantic Patterns in Full-text Documents Using Neural Network Methods. Graphi Con 2019. Computer Graphics and Vision. Proc. of the 29th International Conference on Computer Graphics and Vision. Bryansk, Russia, September 23–26. http://ceur-ws.org/Vol-2485/paper64.pdf


