Analysis and Design of Prefetching Framework for Mozilla Firefox
Автор: Neha Sharma, Sanjay Kumar Dubey
Журнал: International Journal of Information Engineering and Electronic Business(IJIEEB) @ijieeb
Статья в выпуске: 5 vol.7, 2015 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The presence of number of web sites has increased the user's attraction towards web objects. This tremendous use came up with the future requests prediction depending upon the current and past access behaviour. Use of Internet has boomed up a lot since the last decade. This use also came with the heavy load on the internet. In today's world, speed plays a significant role and hence the speed augmentation is one of the biggest issues. For this, web latency reduction by prefetching is one of the good ideas. For the same, web prefetching is performed, where user's next expected requests are prefetched in the web cache of the web browser. A browser is basically a GUI based application program, which provides a platform for running Internet. Mozilla Firefox is a web browser, which is in very much use these days. This paper provides an analysis of Mozilla Firefox prefetching technique (link and DNS prefetching) and then designs a new prefetching scheme for the same. The experimental results are performed in Matlab 5.0. The results show that the designed prefetching framework is more efficient in terms of the cache hit ratio.
Mozilla Firefox, Prefetching, Cache, Browser, Link, DNS
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/15013360
IDR: 15013360
Текст научной статьи Analysis and Design of Prefetching Framework for Mozilla Firefox
Published Online September 2015 in MECS DOI: 10.5815/ijieeb.2015.05.02
Communication has grown a lot in the last decade via Internet. The immense growth of web for sharing information and entertainment made the Internet lively. This liveliness came with lots of load on it. As a result, several issues arrived such as increase in web latency. Web cache is used to reduce web latency for short-term prefetching of web objects and to increase bandwidth. Recently and frequently used web pages are being stored in web cache. Reverse proxy is good technique to implement web cache. Instead of going to server, now client will request to the proxy. The web objects will directly be loaded from the proxy, resulting in the reduction in waiting time (web latency) and traffic in the network. Upon receiving a new object, the proxy server, provide a copy to the end-user and keep another copy to its local storage [1]. Web cache of browser, stores the web pages client is using. Now, the question is how to select the pages. For this, different prefetching techniques are used. These prefetching techniques are browser dependent. The browser with better prefetching scheme, is more efficient.
Web requests or better say, web surfing patterns of the user are almost same for the specific intervals. Even there is some similarity between set of users [2]. They might access the same pattern simultaneously.
Prefetching is the technique, where user’s next expected requests are loaded previously in the web cache, by applying some predictive methods. It basically improves the web performance and due to prefetched information, user can access the web objects faster and hence, user satisfaction towards the browser will improve. Prefetching can be performed on server-side as well as browser-side. The browser-side prefetching is the work to be performed by different organisations to reduce the load and to improve their work performance. A good prefetching technique at browser-side increases user’s satisfaction.
Numbers of browsers are present today but only few among them are famous in users. Users choose a browser depending upon its few services, i.e. facility of add-ons, extensions available, support and speed etc. If the browsing speed is good and the browser is user-friendly, then it meets the users expected requirements. Browsing speed depends upon the web latency, if web latency is less, it means waiting time for web objects fetching is less. Less waiting time means, faster access. In today’s scenario, everyone is short of time. So, run-time needs to be as short as possible. Hence, prefetching at the browserside is a good option for enhancing the browser capabilities and pleasing the users.
The paper works on the analysis of 2nd most popular web browser, Mozilla Firefox, prefetching scheme. Mozilla Firefox uses link prefetching technique and its few versions also uses DNS prefetching scheme. The paper provides a thorough study of the same and then, designs a new prefetching framework for the Mozilla Firefox browser. A comparative report on the cache hit ratio of the old and new prefetching techniques has been provided. The efficiency and effectiveness, depending upon the cache hit ratio, is represented in the forms of graphs, to clear the picture. The results found make it very much clear that new prefetching framework produces comparatively better results than the old one. Hence, it results in web latency reduction too.
The paper is divided into different sections for the ease. Section 2 provides an overview of primarily research done in this field. A lot of work has been done previously in this field and this part of paper explains the same. Section 3 gives an overview of the research methodology used for the paper. Section 4 focuses on the Mozilla Firefox prefetching techniques, i.e. link and DNS prefetching. Section 5 concentrates on the designing of new framework for Mozilla Firefox given in the paper. In section 6, comparative report provided for old and new prefetching designs. Finally, the conclusion of the paper has been written, explaining the work done in brief with the merits and scope of the work in the present scenario.
-
II. Literature Review
Kosala et al. provided a review in the area of web mining [3]. The paper examines the connection between different web mining types and correspondingly related agent paradigm. This paper focuses basically on representation issues, on the process, and on the learning algorithm, and the application of the recent works as the criteria in the field of web mining.
Pallis et al. explained the short-term prefetching problem on a web cache environment using an algorithm for clustering inter-site web pages [4]. The proposed scheme efficiently integrates web caching and prefetching. According to this scheme, each time a user requests an object, the proxy fetches all the objects which are in the same cluster with the requested object.
Sharma and Dubey proposed a framework for web traffic reduction [5]. The paper presented a framework for the prefetching and prediction in web. According to the framework, previous web requests of the user will be extracted from the proxy web log. From this web log, strong rules will be generated using FP Growth algorithm. These rules will be used to prefetch the upcoming requests of the current user.
Vijayan and Jayasudha addressed about the different prefetching and caching techniques, how they predict the web object to be pre-fetched. It also focused on what are the issues, challenges involved when these techniques are applied to a mobile environment [6].
Greeshma et al. analyzed web prefetching techniques and other directions of web prefetching [7]. The significance of these techniques is to reduce the network traffic and improve the user satisfaction. The authors gave an idea that web prefetching and caching can also be integrated to get better performance.
Kasthuri et al. explained that depending upon the past requests, future references can be deducted and implemented using predictive prefetching [8]. The prediction engine can be present either in the client or server side. The papers prediction engine resides at client side. It used the set of past references to find correlation and initiates prefetching that were finding out user’s future requests for web documents based on previous requests.
Wan et al. discovered latent factors of user browsing behaviours [9]. It was discovered on the basis of random indexes and detecting clusters of web users according to their activity patterns acquired from access logs.
Ramya and Sathiyamoorthi had re-evaluated principles and existing works of conventional and intelligent web caching [10]. Categorisation of prefetching techniques was also done and the main focus is history-based prefetching approach. This three step approach’s first step is data extraction from proxy web log. Then after, extracted data is preprocessed. Using clustering, this preprocessed data is mined and to know the patterns to be pre-fetched, sequence analysis is being performed.
Singh et al. proposed a framework for prediction of web requests of users and accordingly, prefetching the content from the server [11]. The proposed framework improved performance of web proxy server using web usage mining and prefetching scheme. They have clustered the users according to their access pattern and usage behaviour with the help of K-Means algorithm and then Apriori algorithm is applied to generate rules for prefetching pages. This cluster based approach was applied on proxy server web log data to test the results using LRU and LFU prefetching schemes.
Sharma and Dubey provided the literature survey in the area of web mining [12]. The paper basically focuses on the methodologies, techniques and tools of the web mining. The basic emphasis is given on the three categories of the web mining and different techniques incorporated in web mining.
-
III. Research Methodolgy
Mozilla Firefox is the second best browser these days[13]. Due to its speed problem, it is on second number, instead of being on the top. Its prefetching scheme somewhere lacked and as a result, web latency was quiet more as it was expected to be. While searching for Mozilla Firefox, so many relevant papers were found on this topic. The relevant material is referred from different journals, conferences, websites and Mozilla official web page too. The papers and database collected was analysed, depending upon the objective and then after, shortlisted accordingly. To provide relevant information for the Mozilla prefetching techniques, data collected form following sources:
Mozilla Firefox official web page
Scopus Database
Google Scholar
Elsevier
ACM
Springer
IEEE
-
IV. Mozilla Firefox Prefetching Scheme
Mozilla Firefox different versions use different prefetching techniques. Link prefetching and DNS prefetching are the two major techniques implemented in Mozilla Firefox browser and even in Netscape too.
-
A. Link Prefetching
A link prefetching mechanism is a technique used for modifications to both the browser and the server [14]. Fisher proposed a server-driven link prefetching technique in 2002 [15]. Fig. 1 presents the link prefetching method proposed by Fisher. It is designed to provide a solution to prefetching that is friendly to both client and server, specially addressing some of the shortcomings of existing ad-hoc methods. The browser follows special directives from the web server (or proxy server) that instruct it to prefetch specific documents. The server can inject these directives into an HTML document or into the HTTP response headers [16]. The browser responds to the prefetch directives after it finishes rendering the document (or HTTP response) containing the directives [17]. This mechanism allows servers to control precisely what is prefetched by the browser, and it allows the browser to determine when best to prefetch documents based on local network inactivity, browser idle time, etc.
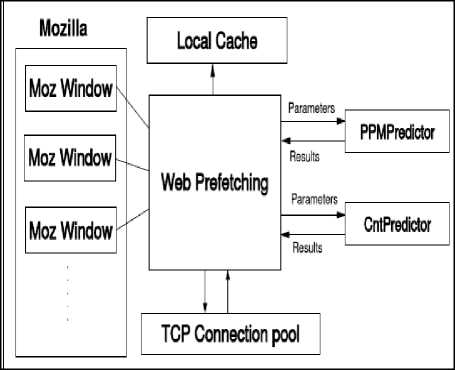
Fig. 1. Link Prefetching [15]
-
B. DNS Preftching
In DNS prefetching, depending upon the user’s request, DNS of the expected next requests has been prefetched. DNS prefetching only helps in prefetching the Domain Name of the Server (DNS) for which request can be made, so time to convert domain name into IP address has been saved. It means that web pages are not prefetched in actually, only the DNS h\as been prefetched [18]. Hence, the technique not actually accomplishes the task of prefetching. It just reduces the latency time to some extent. Mozilla Firefox also provides the facility to its users to control DNS prefetching [19]. Firefox 3.5 performs DNS prefetching. It performs only domain name resolution. Google chrome also has a prefetching feature similar to the DNS prefetching scheme [20].
-
V. Framework Design-Optimized Mozilla Prefetching Technique
Mozilla Firefox is a second most popular browser, according to a survey [13]. Its prefetching concern can be one of the reason of it’s not be on the top. The paper provides a prefetching framework design for the Mozilla Firefox browser. Caching with prefetching is a good option to improve prefetching capabilities. Prefetching helps in reducing the web latency and hence web objects can be prefetched at the client-side, i.e. browser-side prefetching. Fig. 2 represents process of prefetching. The prefetching framework for Mozilla Firefox has been provided in this section. The design of prefetching framework consists of number of steps, explained as below:
-
A. User Requests
Initially user puts the requests on the Mozilla Firefox browser. At a particular time number of requests can be put on the Mozilla windows. So, all requests need to be fulfilled by the browser for number of users.
-
B. Request Fulfillment
As the requests come to Mozilla, Mozilla will check for the requests on L2 cache. If cache hit, then request will be fulfilled from their only. Otherwise, for the cache miss, connection with the server will be created and requests will be transferred to the server. After TCP connection creation, server will respond to the client’s requests. The server listen the request and reverts back with response. The corresponding response is being transferred to the user.
-
C. Web Prefetch
Web prefetch is the module where the user’s future expected requests will be stored depending upon their past behavior. User’s history is stored in web log. User web log is also being maintained on the web. Initial requests of the users will be saved in the web log. Now, depending upon this web log (history of web objects used by different users) users upcoming requests will be prefetched. As the user logs in or requests web objects, depending upon its past behavior (stored in web log), its expected future requests are being prefetched and kept in the web cache.
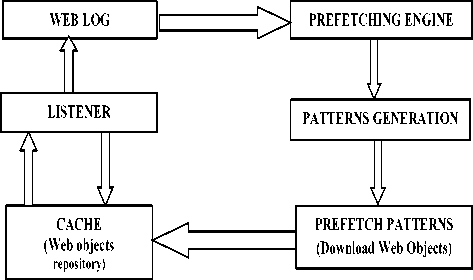
Fig. 2. Process of Prefetching
From web log data will be extracted and grouped according to the users and their access behavior. For prefetching, hints are being passed to the web prefetch module via L2 cache. These hints are basically the user information. Depending upon these hints, users past requested objects will be passed on to the DNS mapping module.
-
D. DNS Mapping Module
Users know about the domain names instead of IP addresses of the web objects. IP address is a 32-bit address used to define different networks in World Wide Web [21]. So, whenever user’s put any request to the browser, they use domain names and browser also stores the domain names. So, in this step, domain names will be converted into their corresponding IP addresses, before applying any of the association rule mining algorithm.
-
E. Prediction by Partial Matching (PPM)
PPM is one of the efficient association rule mining algorithm. On the hints passed by previous module, association rule mining will be applied to find out the sequence of the web objects to be prefetched, which are likely to be requested by the users. PPM algorithm is used for pattern finding. PPM will find out the patterns to be prefetched depending upon the comparison of current context with each Markov model [22].
-
F. Patterns
PPM results in the frequent patterns generation. These patterns are the expected future requests of the users, depending upon their access behavior. So, whenever a user re-enters in the browsing phase, their corresponding pattern is found and web objects are prefetched and kept in the browser cache. It’ll improve the chances of cache hit and reduce web latency too.
-
G. Inverse DNS Mapping Module
As in the DNS mapping module domain names were converted into the IP addresses, so now for the understanding of user and making matching of the request provided by the user, IP addresses of the web objects to be prefetched will be converted into their respective domain names. This is the task of reverse domain in the networking [22]. Now, these web pages will be prefetched and stored in the browser cache.
-
H. Optimal Page Replacemnet algorithm
L2 cache is used in the design and prefetched web objects are stored here. It has limited size. So, pages need to be replaced in it after sometime. For page replacement, optimal page replacement algorithm is used. Optimal page replacement algorithm has the lowest page fault rate. It works well in the cases where the system has prior knowledge of future requests. Hence, it is best for the prefetching case. In this algorithm, the pages that will be used the farthest in the future are replaced [23]. The algorithm works in two phases: firstly it runs to generate the reference traces and then to actually replace the web objects, that’ll be used farthest in the future. Following
Fig. 3 represents the OMPT (Optimized Mozilla Prefetching Technique).
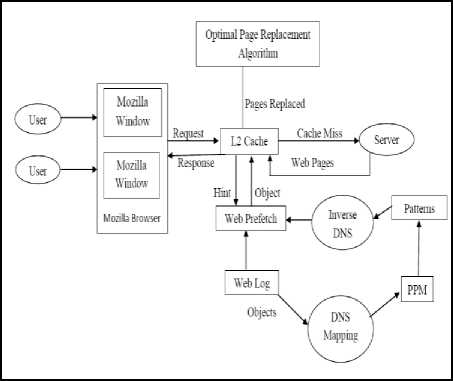
Fig. 3. Optimized Mozilla Prefetching Technique
-
VI. Result Analysis
Present section provides the result analysis of Mozilla prefetching scheme and OMPT. Depending upon the user’s scenario, prefetching capabilities of both the techniques has been analyzed graphically. There are two important parameters to compare the prefetching results of both the techniques: precision and recall. Precision in basic terms means number of web objects correctly found from the set of prefetched objects. Recall is the number of correctly fulfilled web objects requests from the number of user requests from the cache. Precision is shown in equation (1) and Recall is shown in equation (2).
Precision = Prefetch hits / Prefetches (1)
Recall = Prefetch hits / User requests (2)
Fig. 4 represents Precision vs. Threshold graph for Mozilla and OMPT, whereas Fig. 5 represents Recall vs. Threshold graph. Fig. 6 depicts the Latency vs. traffic graph and Fig. 7 show the energy vs. Cache size. Fig. 8 focused on Cache Hit Rate vs. Prefetch Threshold.
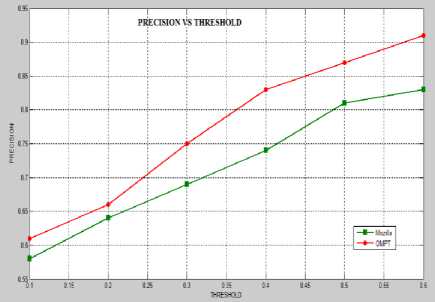
Fig. 4. Precision vs. Threshold
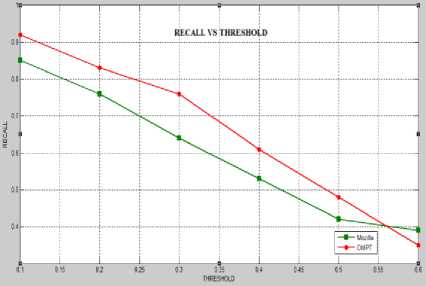
Fig. 5. Recall vs. Threshold
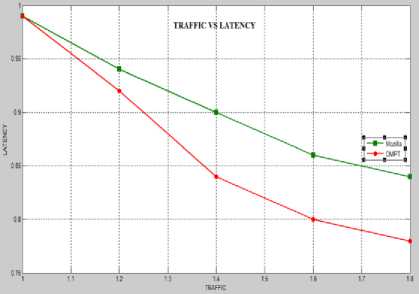
Fig. 6. Traffic vs. Latency
came into the picture in near about 2004 December. Its prefetching technique is the main focus of this paper. The paper presents an analysis of Mozilla Firefox prefetching technique. Two kinds of prefetching techniques are explained viz. link and DNS prefetching. The paper also designed a prefetching framework for the Mozilla Firefox browser. The design consists of L2 cache, web prefetch engine, DNS mapping, PPM, and inverse DNS mapping modules. PPM is used as association rule mining algorithm and it generates the patterns, which need to be prefetched. Accordingly, user requests will be saved in the browser cache. Optimal page replacement algorithm is used for page replacement in browser cache. Result analysis is being provided for both Mozilla prefetching technique and OMPT (proposed design). The result analysis came with the fact that OMPT provides better results than the Link prefetching technique of Mozilla. Web latency is reduced more in the OMPT and cache hit ratio is also comparatively better. Proxy server design and implementing the work are under the future scope.
Список литературы Analysis and Design of Prefetching Framework for Mozilla Firefox
- A. K. Chauhan, V. Chauhan and R. Gupta, "Exploring the Web Caching Method to Improve the Web Efficiency", International Journal of Computer Applications in Engineering Sciences,vol. 1, issue 4,2011.
- N. Sharma and S.K. Dubey, "Fuzzy C-means clustering based prefetching to reduce web traffic", International Journal of Advances in Engineering & Technology, vol. 6, issue 1, pp. 426-435, 2013, ISSN: 2231-1963.
- R. Kosala and H. Blockeel, "Web Mining Research: A Survey", ACM SIGKDD Explorations Newsletter, vol. 2 issue 1, June 2000.
- G. Pallis, Vakali and J. Pokorny, "A clustering-based prefetching scheme on a Web cache environment", Computers and Electrical Engineering 34, Elsevier,pp 309–323, 2008.
- N. Sharma and S.K. Dubey, "FP tree use in prefetching", Third International Conference on Advances in Computer Science (Elsevier Track), 2nd December, 2013.
- G. G. Vijayan and S. J. Jayasudh , "A survey on web pre-fetching and web caching techniques in a mobile environment", Natarajan Meghanathan, et al.. (Eds): ITCS, SIP, JSE-2012, CS & IT 04, pp. 119–136,2012.
- G. Vijayan Greeshma and J. S. Jayasudha, "A survey on web pre-fetching and web caching techniques in a mobile environment" Natarajan Meghanathan, et al.. (Eds): ITCS, SIP, JSE-2012, CS & IT 04, pp. 119–136,2012.
- I. Kasthuri, M.A. Ranjit Kumar , K. Sudheer Babu, and Dr. S. S. S. Reddy, " An Advance Testimony for Weblog Prefetching Data Mining", International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering, vol. 2, issue 4,2012.
- M. Wan, A. Jonsson, C. Wang, L. Li, and Y. Yang, "A Random Indexing Approach for Web User Clustering and Web Prefetching", pp. 40–52, Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2012.
- T.V. Sree ramya and V. Sathiyamoorthi, "Survey on Integrating Web Caching and Pre-Fetching" International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering, Volume 3, Issue 4, April 2013, ISSN: 2277 128X.
- N. Singh, A. Panwar and R. S. Raw, "Enhancing the Performance of Web Proxy Server through Cluster Based Prefetching Techniques", International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communications and Informatics (ICACCI), 2013, ISBN 978-1-4799-2432-5.
- N. Sharma and S.K. Dubey, "A Hand to Hand Taxonomical Survey on Web Mining", International Journal of Computer Applications, vol. 60, issue 3, 2012, ISSN 0975 – 8887.
- http://www.w3schools.com/browsers/browsers_stats.asp accessed last on December 2013.
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Link_prefetching accessed last on January 2014.
- D. Fisher and G. Saksena, "Link Prefetching in Mozilla: A Server-Driven Approach", Netscape/AOL, 2002.
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Talk%3ALink_prefetching accessed last on December 2013.
- https://support.mozilla.org/en-US/kb/Firefox-cant-load-websites-other-browsers-can accessed last on December 2013.
- https://developer.mozilla.org/en/docs/Controlling_DNS_prefetching accessed last on February 2014.
- http://bitsup.blogspot.in/2008/11/dnsprefetching-for-Firefox.html accessed last on March 2014.
- http://dev.chromium.org/developers/design-documents/dns-prefetching accessed last on December 2013.
- A. Tanenbaum, "Computer Networks", Prentice Hall Professional Technical Reference, 2002.
- J. Domenech , A. J. Gil, J. Sahuquillo, and A. Pont, "Evaluation, Analysis and Adaptation of Web Prefetching Techniques in Current Web", Universitat Politecnica de Valencia, 2007.
- A. Silberschatz, P. B. Galvin and G. Gagne," Operating System Concepts", Wiley Publishing, 2008.


