Analysis on current situation and existing problems of water resources utilization in Yellow River basin of Inner Mongolia, China
Автор: Fan C.
Журнал: Теория и практика современной науки @modern-j
Рубрика: Основной раздел
Статья в выпуске: 3 (117), 2025 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The Yellow River basin in Inner Mongolia is an important part of the ecological barrier in northern China. With the rapid economic development, continuous population growth and the impact of climate change, the imbalance between supply and demand of the Yellow River water resources and the contradiction between water use are more prominent. This study analyzes the current situation of water resources utilization in the Yellow River Basin of Inner Mongolia in recent ten years, and comprehensively analyzes the current situation of water resources utilization in the Yellow River Basin of Inner Mongolia through the changes of total water supply, water supply type, water consumption, water consumption industry, water consumption and other indicators. On this basis, it is found that the contradiction between supply and demand of water resources is prominent, the reuse rate of recycled water is low, the basin collaborative protection mechanism is not perfect, and the social participation in water resources management is weak. This paper tries to provide reference for solving the dilemma of water resources protection and sustainable development in the Yellow River Basin of Inner Mongolia.
Inner mongolia yellow river basin, water resources utilization, water supply, problem analysis
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/140311188
IDR: 140311188
Текст научной статьи Analysis on current situation and existing problems of water resources utilization in Yellow River basin of Inner Mongolia, China
The Yellow River, the mother river of the Chinese nation, is the largest surface water source in northwest and North China. With 2% of the country's surface runoff, it undertakes 15% of the country's arable land irrigation, 12% of the population's water diversion, and the production and living water supply tasks of more than 50 large and medium-sized cities. Long-term high-intensity water resources development and utilization make the Yellow River basin's own system weak ability to withstand external stress. In addition, the basin is located in arid and semi-arid climate zone, with less river water and more sand, water and sand imbalance, water and soil loss and flood and drought disasters in the basin are serious, and the ecological environment is fragile. The Mongolian section of the Yellow River Basin is located in northwest China, with a unique physical location, vast basin area, rich resources and energy, concentrated urban industries, and extremely important ecological, economic and strategic status. It is an important energy base, grain production base and an important ecological barrier in China. With the rapid development of economy, the continuous growth of population and the impact of climate change, there are many problems in the development and utilization of water resources in the Yellow River Basin of Inner Mongolia, including the shortage of water resources in the basin, the contradiction between supply and demand, and the prominent problems of water ecological environment. At present, the exploitation and utilization of water resources along the Yellow River in Inner Mongolia is as high as 80%, which is close to critical overload, far exceeding 40% of the common river basins in China. Water resources shortage has become the main bottleneck restricting the economic and social development of the river basin. Therefore, to study the current situation and existing problems in the development and utilization of water resources in the Yellow River Basin of Inner
Mongolia, take water resources as the biggest rigid constraint, strengthen the optimal allocation and rational utilization of water resources, fully implement water-saving and water control actions, and continuously promote the conservation and intensive use of water resources are the key to solving the shortage of water resources and the imbalance between supply and demand in the Yellow River Basin of Inner Mongolia.
Current situation of water resources utilization in theYellow River Basin of Inner Mongolia
1. Present situation of water supply in Yellow River basin of Inner Mongolia
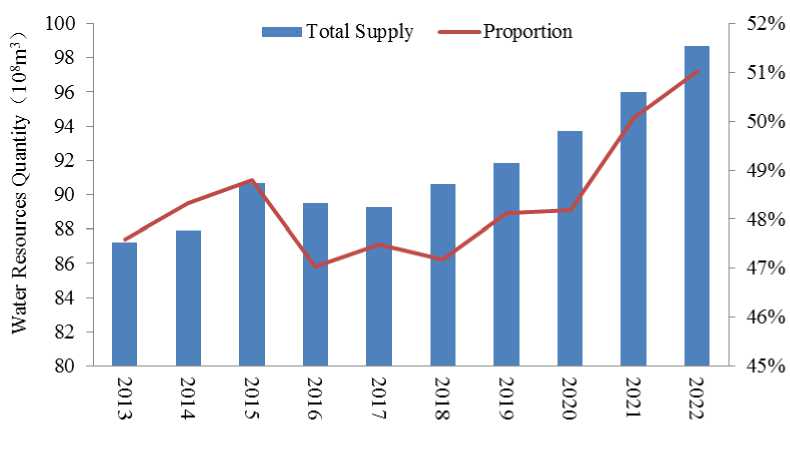
Fig1 Water resources supply in the Yellow River Basin of Inner Mongolia in recent 10 years
The Yellow River Basin in Inner Mongolia is located in the northern arid and semi-arid climate zone, and its main water supply sources are surface water and groundwater, both of which provide a large amount of water resources for production and life at the same time. Surface water resources are susceptible to climate change and abundant and low water years, and the quantity of water resources has increased greatly. Groundwater, as a stable water supply source for regional water, is less affected by climate change and abundant and low water changes. In dry years, it can provide water for production and life stably. According to the analysis of water resources supply in the Yellow River Basin of Inner Mongolia in the past 10 years, it can be seen from Figure 1 that the total water supply is relatively stable, and the overall trend is increasing year by year. The average annual water supply is 9.154 billion m3, and the coefficient of variation is 004. The Yellow River basin accounts for a relatively high proportion of water supply in the whole region, reaching 51.02% in 2022, contributing half of the water resources in the whole region, and the annual average is 48.38%.
All water supply sources in the Yellow River Basin of Inner Mongolia are analyzed. As shown in Figure 2, the water supply sources are composed of surface water, groundwater, other water and intermediate water. The average water supply of surface water from 2013 to 2022 is 6.226 billion m3, and the maximum supply year is 2021, which can reach 6.868 billion m3. The minimum supply year was 2013, which was 5.540 billion m3. The overall surface water supply showed an increasing trend year by year, and the proportion of surface water supply in the total water supply also increased from 63.53% in 2013 to 71.56% in 2021 and 68.04% in 2022. It can be seen that surface water is the main source of water resources supply in the cities of the Yellow River basin in Inner Mongolia. The average annual water supply of groundwater resources is 2.652 billion m3, and the coefficient of variation is 0.06. The maximum supply year is 2013, which can reach 29.45m3, accounting for 33.77% of the total water supply in that year; the minimum supply year is 2021, which is 2.321 billion m3, accounting for 21.18% of the total water supply. The average annual supply of groundwater is 42.60% of surface water, and the overall groundwater supply shows a decreasing trend year by year, but its water supply proportion is maintained at about 30% all year round, with a fluctuation range of 24.18% ~ 33.77%.
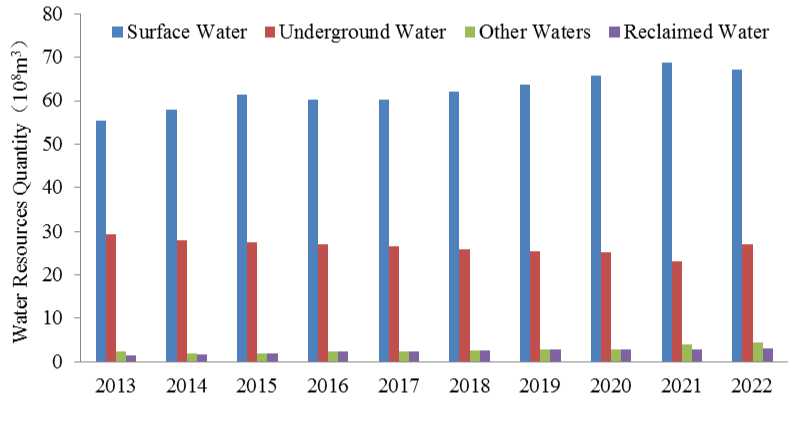
Fig2 Water resources supply types in the Yellow River Basin of Inner Mongolia from 2013 to
The supply of other types of water resources mainly includes sewage treatment reuse water, mine drainage water, rainwater recycling and brackish water. According to the water supply of other types of water sources in the Yellow River Basin, the average annual water supply is 276 million m3, accounting for 3.02% of the total water supply, which is relatively small. The proportion of other types of water supply has increased year by year, from 2.18% in 2014 to 4.49% in 2022, an increase of about two times. In other types of water supply, the main water is medium water, which can be used after sewage treatment, is a relatively stable water source, and is also the focus of attention of water resources conservation and efficient use. In recent years, the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region has vigorously developed reclaimed water reuse projects, and the reclaimed water reuse amount of the cities in the Yellow River Basin has shown an upward trend year by year, and the reclaimed water reuse amount in 2022 is nearly double that in 2013, showing a significant increase trend as a whole.
2. Current situation of water use in Yellow River basin of Inner Mongolia
As the center of economic development in the central and western regions of Inner Mongolia, the Yellow River Basin in Inner Mongolia is a major area for agriculture, industry and population, and also an important part of the ecological security barrier in northern Xinjiang. According to the "eight-seven water division" plan, the annual available Yellow River water resources in the Yellow River Basin in Inner Mongolia are 5.86 billion m3, but with the passage of time and rapid economic development, The original "eighty-seven water" program has been unable to fully adapt to the new development requirements, and needs to be optimized and adjusted according to the actual situation.
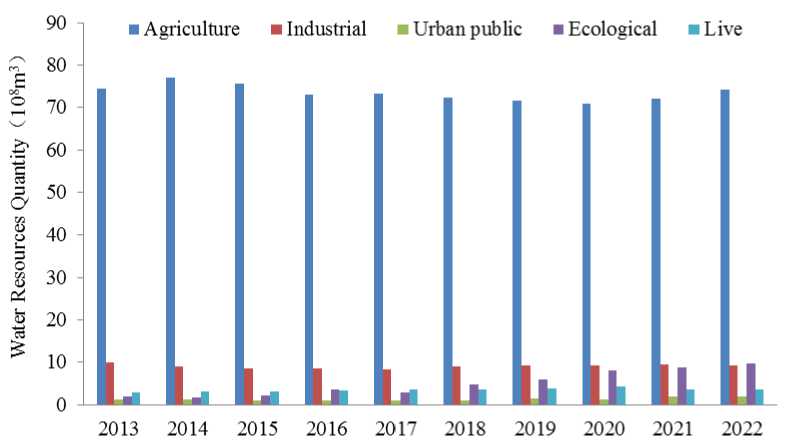
Fig3 Water consumption by industry in the Yellow River Basin, Inner Mongolia from 2013 to 2022
Based on the analysis of water use in the Yellow River Basin of Inner Mongolia in recent 10 years, as shown in Figure 3, it can be seen that the main water use of the Yellow River Basin of Inner Mongolia is agricultural water, and agricultural water consumption is much higher than that of other industries. The annual average value of agricultural water consumption is 7.343 billion m3, and the coefficient of variation is 0.025, indicating stable water consumption. It is maintained between 7.091 billion m3 and 7.702 billion m3 throughout the year, showing a fluctuating trend as a whole, and the annual water consumption of agriculture is 8.07 times that of the highest water consumption industry. The average annual water consumption of industrial water is 909 million m3, the coefficient of variation is 0.056, the maximum water consumption year is 1.006 billion m3 in 2012, and the minimum annual water consumption fee is 840 million m3 in 2017. Compared with agricultural water consumption, industrial water consumption as a whole shows a downward trend of fluctuation. Urban public water consumption and residential water consumption are relatively stable, showing an overall increasing trend year by year. Urban public water consumption mainly includes construction, greening and service water consumption, with an average annual value of 1.27 and a coefficient of variation of 0.25. Urban public water consumption and residents' life mainly depend on urban construction and social development. With the expansion of urban development scale, water consumption increases significantly. Compared with other industries, water consumption for ecological environment has increased significantly in recent years, from 182 million m3 in 2013 to 978 million m3, with an extreme value ratio of 6.0, indicating that with the popularization of ecological civilization and the construction of ecological security barrier in northern Xinjiang, all regions attach importance to the improvement of ecological environment and strengthen the construction of ecological environment, and water consumption has doubled.
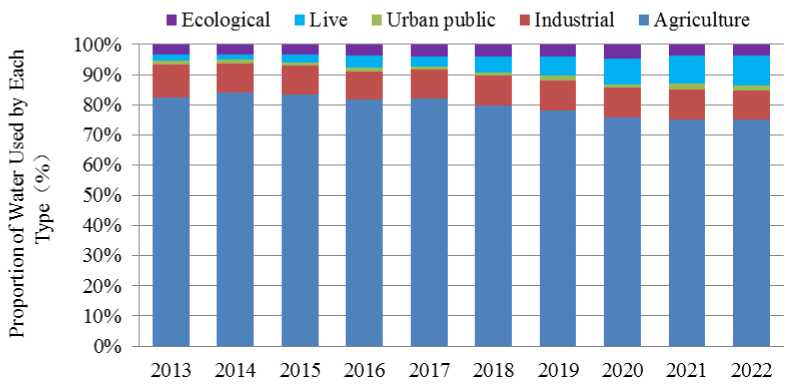
Fig4 Proportion of water use by various industries in the Yellow River Basin of Inner Mongolia from 2013 to 2022
The proportion of water used by various industries in the Yellow River Basin of Inner Mongolia in the past 10 years is analyzed. As can be seen from Figure 4, the Yellow River Basin is the main area for agricultural planting in Inner Mongolia, and the proportion of agricultural water use has been high for a long time, staying at 75.09% ~ 87.58%. However, the proportion of agricultural water use as a whole shows a downward trend. However, the increase in agricultural water consumption is not obvious, and the second reason is that the proportion of water used in ecological environment has increased, resulting in a decline in the proportion of water used in other industries. The proportion of supply water is relatively stable, with an average of 9.94% for many years, and a long-term maintenance between 9.37% and 11.60%. The proportion of urban public water and residential water consumption is at a low level, the long-term proportion of urban public water is 1.40%, and the proportion of residential water consumption is 3.81%. The proportion of ecological environment water consumption has risen rapidly, from 1.85% to 9.91%, which is close to industrial water consumption. It can be seen that the key difficulties in the comprehensive and efficient utilization of water resources in the Yellow River Basin are to improve the efficiency of agricultural water use, reduce the proportion of agricultural water use, and free up more water resources to be allocated to other industries.
The Yellow River is rich in water resources, and there are various ways of using water in the basin. However, some water resources cannot be returned to the surface and underground water bodies in the water transport and water use routes, which belong to the process of water resources consumption, such as transpiration and evaporation, soil absorption, product adsorption, human and animal utilization, etc. Therefore, controlling water resources consumption and reducing the proportion of water consumption can effectively improve water resources reserves in the basin. Based on the analysis of water resources consumption in the Yellow River Basin of Inner Mongolia, as shown in Figure 5, it can be seen that the average annual water consumption is 5.599 billion m3, accounting for 61.19% of water consumption; the maximum water consumption year is 2022 (6.455 billion m3, accounting for 65.40%); the minimum water consumption year is 2013 (5.194 billion m3). Accounting for 59.35%, the overall showed an increasing trend year by year.
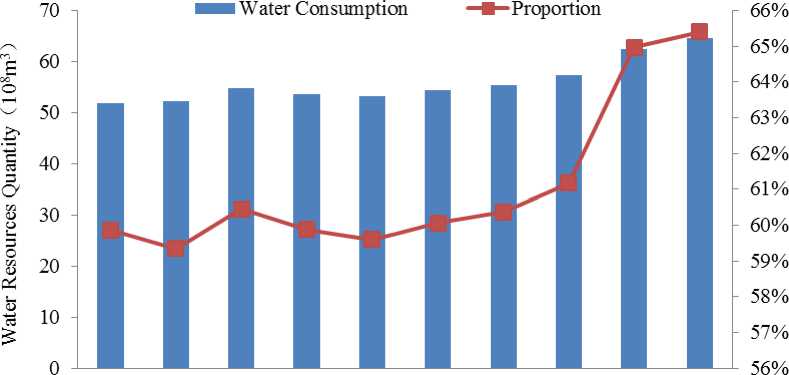
2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022
Fig 5 Water consumption in the Yellow River Basin, Inner Mongolia from 2013 to 2022
There are problems in the utilization of water resources in the Yellow River basin of Inner Mongolia
-
1. The contradiction between supply and demand of water resources is prominent
The Yellow River basin in Inner Mongolia is located in the semi-arid region. The shortage of water resources has long been a problem, and the contradiction between supply and demand is increasingly prominent, which has become an important bottleneck restricting the sustainable development of regional economy and society. This contradiction is mainly reflected in the limited total water resources, uneven distribution of time and space, and continuous growth of demand. According to the "Water Resources Bulletin of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region 2022", the total amount of conventional water resources available in the Yellow River basin of Inner Mongolia is 9.072 billion m3, but the actual total water resources in 2022 are only 5.038 billion m3, and the per capita water resources are only 460m3, less than one-fifth of the average level of the autonomous region. The distribution of Yellow River runoff is very uneven in time, and the natural runoff in flood season (July to October) accounts for about 58% of the whole year, while the water supply is tight in non-flood season. In terms of spatial distribution, the annual runoff of the river above Lanzhou accounted for 62% of the whole river, while the area between Lanzhou and Hekou town accounted for only 0.3%, indicating a serious imbalance in water resources distribution among regions. With the development of economy and society, the demand for water in agriculture, industry and domestic use is increasing. Agriculture is a major water user in the Yellow River Basin of Inner Mongolia, and irrigation water accounts for a large proportion. However, due to the backward irrigation technology, the utilization efficiency of water resources is low, and the waste phenomenon is serious. The rapid advancement of industrialization and urbanization has also led to a sharp rise in industrial and domestic water demand, further aggravating the contradiction between supply and demand of water resources. Ecological water demand has been paid more and more attention, but in the case of limited total water resources, ecological water is often crowded out, leading to the deterioration of ecological environment.
-
2. The reuse rate of reclaimed water is low
-
3. The basin cooperative protection mechanism is not sound enough
-
4. Social participation in water resources management is weak
Recycled water refers to the water that can be used beneficially after wastewater or rainwater is properly treated and reaches certain water quality indexes to meet certain requirements for use.
From an economic point of view, the cost of recycled water is the lowest, and from an environmental point of view, the recycling of sewage helps to improve the ecological environment and achieve a virtuous cycle of water ecology. According to the data of Inner Mongolia Water Resources Bulletin, the utilization rate of seawater desalination and rainwater in the Yellow River Basin is zero, and the amount of recycled water recycling and treatment is small. From 2013 to 2022, although the amount of recycled water reuse has increased, with an added value of 297 million m3 in 2022, the proportion of recycled water reuse is still low. In recent 10 years, the highest is 26.49%, but compared with the developed areas in China, the level of recycled water reuse is generally low, only reaching the national average level, and there is still room for further use. However, as the collection, treatment and utilization of recycled water is a complex systematic project, the construction of the project requires a large amount of capital investment, resulting in high water prices, and then lead to the low utilization rate of recycled water, resulting in waste of water resources. The National Development and Reform Commission jointly issued the "Guidance Document on Promoting the Utilization of sewage Resources" on January 11, 2021, taking water shortage and water-sensitive areas as key areas to encourage the establishment of pilot demonstration cities, with the overall goal of achieving more than 25% water reuse in waterscarce cities, which will form a corresponding market. The reuse rate of water in the developed areas of northern China will exceed 35%, and a systematic, safe, environmentally friendly, economically feasible and efficient wastewater resource utilization model will be established.
Water resources have fluidity and water cycle has spatial characteristics. These attributes of water resources make it necessary to cooperate and coordinate with each other in water conservancy, agriculture and animal husbandry, natural resources, emergency management and other departments. There are significant differences in economic development level, policy coordination and technology sharing in the east and west regions of the Yellow River Basin in Inner Mongolia, which limit the coordinated development of the overall regional economy and water resources protection. The lack of effective regional and sectoral cooperation mechanisms makes it difficult to achieve optimal results in resource allocation and policy implementation in the Yellow River Basin. Promoting the protection of water resources in the Yellow River Basin is a systematic project involving cross-region, multi-department, main and tributaries, upstream and downstream, left and right banks, etc. At present, the management system and working mechanism of unified and integrated integration and overall linkage have not been established, and the capacity of each city and department to coordinate the utilization and protection of water resources in the Yellow River Basin is weak. The phenomenon of multi-management and crossmanagement among departments still exists, and the system of efficient use of water resources is not perfect, and it is urgent to form a working pattern of jointly grasping large-scale protection and jointly promoting large-scale governance.
Water resources have ecological, economic and social multi-dimensional attributes. The multidimensional nature of water resources also leads to the involvement of multiple stakeholders, and the complexity of water resources management is relatively high. The weakness of social participation has become an important factor restricting the sustainable use of water resources. The weakness of social participation is mainly reflected in the lack of public awareness, limited participation channels, and insufficient play of the role of social organizations, etc. These problems directly affect the efficiency and effect of water resources management. Public awareness and participation in water resources management are generally low. The general public lacks a deep understanding of the scarcity, importance and role of water resources, and many people believe that water resources are "inexhaustible" public resources, resulting in the waste of water resources in daily life. Social participation channels are limited, and it is difficult for the public to effectively participate in the decision-making and implementation process of water resources management. At present, the decision-making power of water resources management is mainly concentrated in government departments, and public participation is mostly at the formal level, lacking substantive participation mechanisms. As a bridge between the government and the public, social organizations should play an important role in monitoring, promoting and coordinating water resources management. However, due to insufficient policy support, lack of funding and professional limitations, many social organizations have limited scope and influence in the field of water resources management.
Conclusion
Taking the current situation of water resources utilization in the Yellow River Basin of Inner Mongolia as the research object, this paper briefly analyzes the situation of water resources utilization in the Yellow River Basin of Inner Mongolia from 2013 to 2022 and the problems existing in the conservation of water resources. The annual average water supply of the Yellow River basin in Inner Mongolia is 9.154 billion m3, with surface water as the main source. The groundwater supply showed a decreasing trend year by year, and the proportion of the total water supply from unconventional sources was 3.02%, which was relatively small, but showed an increasing trend year by year. The largest water consumption in the Yellow River Basin of Inner Mongolia is mainly agricultural water, with an annual average of 7.343 billion m3. Irrigation water accounts for 84.49% ~ 95.82% of the total agricultural water consumption, industrial water and urban public water consumption remain relatively stable, and ecological water consumption shows an increasing trend year by year. Through analysis, it is found that there are some problems in the Yellow River Basin of Inner Mongolia, such as prominent contradiction between supply and demand of water resources, low reuse rate of reclaimed water, imperfect collaborative protection mechanism of the basin, and weak social participation in water resources management.


