Antiseizure and neuroprotective effects of citrus maxima l fruit components in pentylentetrazole-induced epilepsy in Wistar albino rats
Автор: Jasminvinitha S., Agnel Arul john N., Deepika
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 3 т.19, 2023 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Objective: The frequent neurological condition epilepsy disrupts the brain's regular electrochemical processes. Similar to a seizure, epilepsy is a sign of aberrant brain activity. The developed world has an epilepsy prevalence of 0.5-1%, whereas the underdeveloped world has a larger prevalence due to more risk factors. There are several antiepileptic medications on the market, but their therapeutic efficacy is severely limited by their adverse effects and drug interactions. Owing to their widespread acceptance and beneficial efficiency with few side effects, herbal medicines are used extensively throughout the world. The current study's purpose is to ascertain whether different fruit components, such as fruit juice, residue, and pericarp of Citrus maxima Linn, have anti-seizure properties when used to treat rats with pentylenetetrazole (PTZ)-induced seizures. Methods: To test the antiepileptic potential in pentylenetetrazole-induced epileptic rats, the aqueous extract of fruit pericarp, an aqueous solution of lyophilized powdered fruit juice, and residues of Citrus maxima L were each administered at varying doses of 200 and 400 mg/kg body weight. The experimental animals' physical actions, such as immobility, swimming, and motor activity, were evaluated. By measuring and analysing Neurotransmitter levels, including those of GABA, glutamate, norepinephrine, serotonin, and dopamine, as well as the effects of PTZ on the animal's brain, were examined. Result: The results of the phytochemical screening showed that tannin, coumarin, quinine, glycosides, sugar, and phenols were present. On the thirty-day mark, acute PTZ injection at a dose of 75 mg/kg body weight resulted in seizures that lengthened immobility and reduced swimming time. The PTZ enhanced levels of lipid peroxidation, oxidative stress, and degeneration of neural and non-neural cells (glial cells), while the aqueous extract of various portions of the fruit of Citrus maxima Linn restored levels of glutamate, dopamine, serotonin, norepinephrine, and GABA. Conclusion: According to the findings, convulsions can be treated with Citrus maxima Linn, a traditional source.
Citrus maxima linn, convulsions, epilepsy, gaba, neurotransmitters, pentylenetetrazole (ptz)
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/143180570
IDR: 143180570
Текст научной статьи Antiseizure and neuroprotective effects of citrus maxima l fruit components in pentylentetrazole-induced epilepsy in Wistar albino rats
The nervous system's two main parts are the peripheral nervous system, which is made up of ganglia and peripheral nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord, and the central nervous system, which is made up of the brain and spinal cord. “A permanent propensity to have epileptic seizures as well as the neurological, cognitive, psychological, and social effects of the illness describe the brain disorder known as epilepsy.” (Syeda Nishat Fathima et al., 2015). It is a neuropsychological disorder that develops as a result of excessive neurotransmitter discharge. (Hasan et al., 2012). Recurrent convulsions of cerebral origin, as well as bouts the occurrence, with or without consciousness loss, of sensory, motor, or autonomic symptoms are additional characteristics. (Manas Kumar Das et al., 2015). Almost 50 million people worldwide have epilepsy, and 80 percent of them reside in poor nations. It is the third most prevalent condition worldwide. It is more serious than the combined effects of multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, and cerebral palsy. Antiepileptic medications may stabilise the neuronal membrane by preventing the focused discharge from detonating healthy brain cells. These medications only affect neurons that are firing often. The present crop of AEDs frequently cause disabling side effects and neither treat the disease nor stop relapse. Epilepsy continues to pose a substantial therapeutic challenge despite the basic advancements gained in the treatment of neurological illnesses. A key area of focus in the search for novel, all-natural medications to combat this crippling neurological illness is the plant kingdom. Thus, Many therapeutic plants have been discovered by the traditional medical systems to cure these issues. These treatments have no side effects and are becoming more and more popular in the majority of developing nations. (Umachigi et al., 2007). The World Health Organization claims that around 75 percent of people worldwide use conventional medicines, mostly herbal remedies. (Gilani and Rahman, 2005; Rahmati et al., 2013). Among these, the Tirupura plant, itrus maximum Linn (Rutaceae), has the Tamil name Pambalimasu, and the Northeastern region is up to 1,500 m in Assam. Since 100 years ago, Asia has employed Citrus maxima Linn in traditional medicine. In situations of epilepsy, chorea, and acute cough, the decoctions of the leaves, flowers, and rind are used for their calming effects. An application of the hot leaf decoction is made on ulcers and swells.
onsuming fruit juice acts as a febrifuge. The sarcocarps are used to treat lumbago, dyspepsia, and coughing. The pulp is regarded as a helpful therapy option for urinary issues. Antibiotic activity has been observed in leaf extractions. From ancient times, medical professionals and laypeople have used traditional medicinal plants with a variety of active ingredients and qualities to treat illnesses like epilepsy. The current study's objective was to look at the antiseizure and neuroprotective effects of Citrus maxima L. fruit on Wistar albino rats that had been given pentylenetetrazole to produce epilepsy.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Plant Collection
Citrus maxima L. was chosen as the plant resource for this study. Fruit from Citrus maxima L was gathered recognised, and verified at the RAPINAT Herbarium, St Joseph's ollege, Trichy, Tamil Nadu.

Extraction of plant material
Citrus maxima L. fresh fruit was taken, the juice was squeezed out, and the juice and its residue were gathered. The juice and leftovers were freeze-dried for five hours in a blast freezer. It was then stored in a lyophilizer for 4 days to eliminate the water content. The fruit's pericarp was removed and ground into a coarse powder using an electric blender. 1200 ml of water were used to boil 220 g of dry powder until it was reduced by one-third. It was filtered and dried using evaporation. The extracted paste was screened for phytochemical content and pre-clinical effects.
Parameter studied
The physicochemical and preliminary phytochemical screening were established by the conventional textual approach. (Anonyms, 2001; Brindha et al ., 1981).
Induction of epilepsy
Six groups of six albino rats, one of each sexual category, each weighing between 80 and 100 g, were created. I was the control group for the group and I got PTZ (75 mg/kg) intraperitoneally. For thirty days straight, the aqueous solution of Citrus maxima Linn was administered to groups III and IV (Fruit Juice), IV and V (Fruit Pulp), and groups VII and VIII (Fruit Pericarp) together with the common medication diazepam (4 mg/kg i.p./group IX). On 30th administered subcutaneously 30 minutes after diazepam was administered intravenously and 60 minutes after the extract was given orally. Each animal was then placed into its own plastic cage and kept under observation for a minimum of 30 minutes and a maximum of 24 hours.
Experimental Animals
Unharmed adult When the Wistar strain of albino rats aged between two and three months and weighed 90 to 120 g, we bought them from Biogen in Bangalore. Before the experiment, the animals were given five days to acclimatize to the lab environment. The rats were housed in typical polypropylene cages. Animals were provided unlimited access to water and regular rat chow pellets from Bangalore, India's Sai Durga Foods and Feed, Bangalore. After gaining the necessary approval from the committee (Approval No. 790/03/ac/ P SEA), the research was conducted in compliance with P SEA ethical norms.
Experimental Design
Physical behaviors like the “Hole cross test” (Takagi et al., 1971) and the Forced swimming test (Tong-Un et al., 2010) were performed. Then, the animals were cervical dislocated and slaughtered after the treatment period. The brain tissue was removed and homogenized was used to examine neurotransmitters, as well as neurotransmitters like glutamat (Raju 2004), GABA (Lowe et al., 1958), Serotonin (Margret Schlumfjf et al., 1974), Noradrenaline (Dilip Kumar Pal, 2009) and Dopamine (Atack., 1973).
Statistical Analysis
The result was expressed using S.E.M. means. The data was statistically analyzed using one method of variance analysis (ANOVA), and P values under 0.05 were considered significant.
RESULTS
Citrus maxima L fruit pericarp, fruit residual, and lyophilized powder samples all included tannin, glycosides, sugar, alkaloids, and coumarin, according to a preliminary phytochemical examination. Glycosides, sugars, quinines, phenols, tannins, and coumarin are present in the aqueous extract of Citrus maxima L's lyophilized fruit juice, fruit residue, and fruit pericarp. It has been discovered that plants containing flavonoids and alkaloids have anticonvulsant properties.
Citrus maxima L's fruit juice, fruit residue, and pericarp were found to have loss on drying values of 2.67%, 2.82%, and 1.38, respectively. These values fall within the acceptable range of 1-3% for the edible medicine. This suggests that there is reduced chance of microbial attack during long-term storage of the plant. Ashing sought to eradicate any signs of organic material. Indicating the level of caution required when preparing the plant for pharmaceuticals, to identify adulteration and alien organic matter with sand and dirt, the total ash value might be used.
Citrus maxima L's fruit juice, fruit residue, and pericarp extractive values for various solvents were calculated and are shown in Table 2. Citrus maxima L's fruit residue has extractive values for hexane, chloroform, ethyl acetate, alcohol, and water of 0.15, 0.40, 0.43, 15.15, and 20.50, respectively. Similar results were found for Citrus maxima L's fruit pericarp, which had extractive values of 0.24, 1.36, 1.57, 13.20, and 22.45 for Hexane, hloroform, Ethyl acetate, Alcohol, and Water, respectively, and the fruit juice, which had extractive values of 0.74, 0.41, 1.38, 6.20, and 12.8 for each of these solvents. Citrus maxima L's pericarp, fruit residue, and juice all had higher water extractive values, demonstrating that water permeates the fruit's cells and facilitates better extraction than ethanol, which has a lower extractive value.
In Vivo Antiepileptic activity
Physical Behavior
Onset and Duration of Seizure
PTZ administration led to both mortality and tonic-clonic convulsions in rats. An aqueous extract of fruit juice, fruit remnants, and Citrus maxima Linn's pericarp was used as a pretreatment for rats, and it significantly and dose-dependently (200 & 400 mg/kg body weight) protected against PTZ-induced convulsion. In comparison to PTZ control rats (16.5 sec), it greatly postponed the onset of convulsions (186.3,172.3 &165.4 sec for group IV, VI & VIII respectively). An aqueous extract of fruit juice, fruit remnants, and the pericarp of itrus maxima Linn. Treated animals also shown a significant and dependent on dose decrease in the duration (12.31,21.28 & 42.12 seconds for group IV, VI &VIII respectively) of tonic convulsion as compared to PTZ control rats (280.12 seconds). (Fig. 1)
Immobility Test
Neurotransmitter
Citrus maxima L.'s impact on the glutamate levels in rats with epilepsy brought on by PTZ
Citrus maxima L's impact on the levels of GABA in rats with PTZ-induced epilepsy
Citrus maxima L's impact on the levels of serotonin in rats with epilepsy brought on by PTZ
Serotonin levels in the forebrain of PTZ-induced epileptic control rats (0.13 ng/g tissue) were found to be greater (p˂0.05) in comparison to normal rats (0.45 ng/g tissue) in PTZ models. Rats treated with the common medicine diazepam and the aqueous extract of lyophilized powdered fruit juice, fruit residue, and fruit pericarp of Citrus maxima L showed a substantial
Citrus maxima L's impact on rats with epilepsy induced by PTZ and nor-epinephrine levels
Citrus maxima L's impact on dopamine levels in rats with PTZ-induced epilepsy
Dopamine levels in the forebrain of PTZ-induced epileptic control rats (0.62 pg/g tissue) were found to be greater (p˂0.05) in comparison to normal rats (1.67 pg/g tissue) in PTZ models. Rats treated with the common drug diazepam (1.42 pg/g tissue) and the aqueous extract of lyophilized powdered fruit juice, fruit residue, and fruit pericarp of Citrus maxima L showed a substantial (p˂0.05) drop in dopamine levels (1.41, 1.25 & 1.06 pg/g tissue for IV, VI & VIII groups respectively). (Fig. 7)
Table 1 Citrus maxima L. fruit total ash, water soluble ash, acid soluble ash, and loss on drying
|
S.No |
Parameters |
VALUE % W/W |
||
|
Lyophilized Powder of Fruit Juice |
Lyophilized Powder of Fruit Residue |
Dry Powder of Fruit Pericarp |
||
|
1 |
Loss or drying |
2.67 |
2.82 |
1.38 |
|
2 |
Total ash content |
4.17 |
5.76 |
6.46 |
|
3 |
Water soluble ash |
3.12 |
4.12 |
4.55 |
|
4 |
Acid insoluble ash |
0.33 |
1.14 |
1.57 |
Table 2 Extractive Values of fruit of Citrus maxima L
|
S.No |
Parameters |
VALUE % W/W |
||
|
Lyophilized Powder of Fruit Juice |
Lyophilized Powder of Fruit Residue |
Dry Powder of Fruit Pericarp |
||
|
1 |
Hexane |
0.15 |
0.24 |
0.74 |
|
2 |
hloroform |
0.40 |
1.36 |
0.41 |
|
3 |
Ethyl acetate |
0.43 |
1.57 |
1.38 |
|
4 |
Ethanol |
15.15 |
13.20 |
6.20 |
|
5 |
Water |
20.50 |
22.45 |
12.8 |
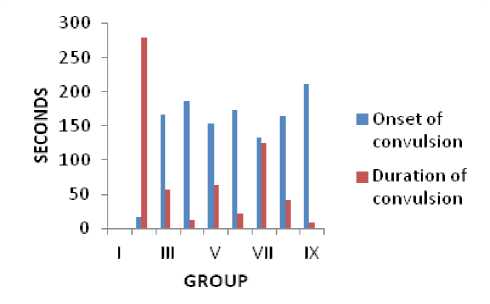
Figure 1: Onset and Duration of Seizure
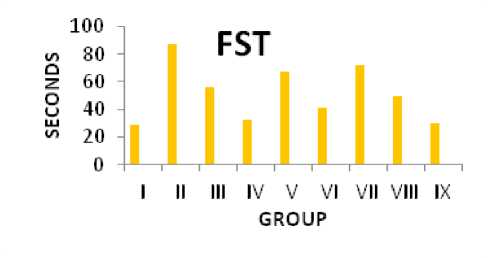
Figure 2: Swimming Behavior (Immobility)
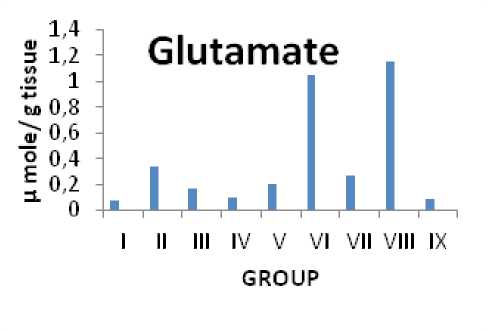
Figure 3: Impact on the glutamate level in rats
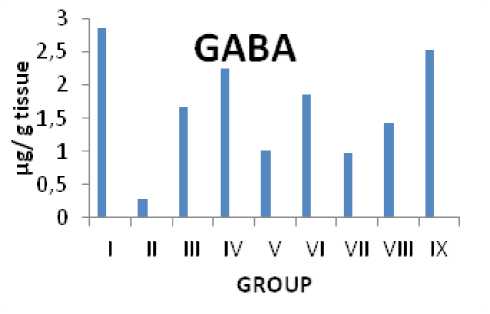
Figure 4: Impact on the levels of GABA in rats
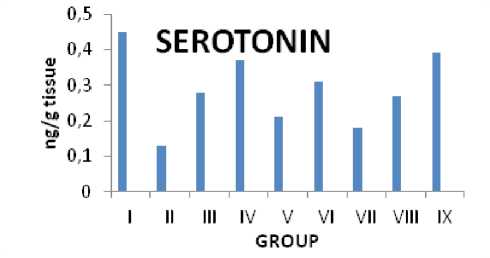
Figure 5: Impact on the level of serotonin in rats
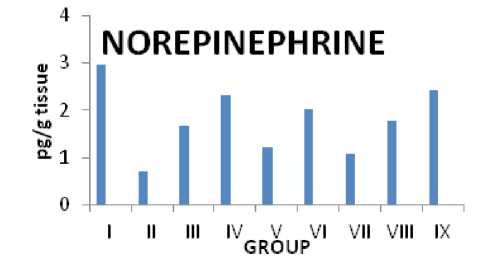
Figure 6: Impact on the level of nor epinephrine in rats
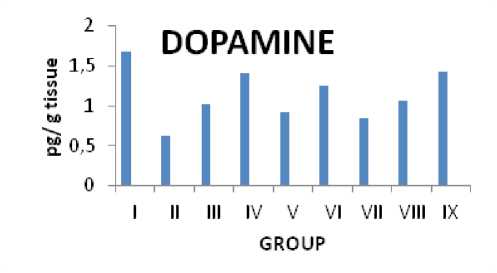
Figure 7: Impact on the levels of dopamine in rats
DISCUSSION
Glycosides, sugars, quinines, phenols, tannins, and coumarin were found in the aqueous extract of the lyophilized juice from the fruit pericarp of Citrus maxima L. limate, altitude, and rainfall are just a few examples of the environmental elements that affect how many different phytochemicals the plant has. (Kokate et al ., 2004) These many phytochemical components the plant appeared to have the capacity to serve as a source of beneficial medicines and to enhance the users' state of health due to the presence of numerous substances that are essential to maintaining good health. (Bhumi et al ., 2014)
The existence of bioactive chemicals in significant amounts and with fever impurity is indicated by the high extraction value. When evaluating crude pharmaceuticals, the extractive value that is water soluble is crucial. A reduced extractive value indicates adulteration, the inclusion of expired material, incorrect drying, or improper storage techniques.
Patients with generalised epilepsy have hippocampus-specific neurotransmitter alterations, such as GABA hypoactivity is a presynaptic inhibitor, and hyperactivity of glutamate, a presynaptic inhibitor and excitotoxin at the postsynaptic level. There have also been reports of the neuroactive chemicals noradrenaline and dopamine, which are hyperactive, and serotonin, which is hypoactive, both of which act excitatory at the postsynaptic level. Here, we discuss the neurotransmitters (GABA, glutamate, noradrenaline, dopamine, and serotonin) that are changed in generalized epilepsy as well as the receptors on which these neurotransmitters act.
Long thought to be the main mammalian brain neurotransmitter that inhibits activity is gammaaminobutyric acid (GABA). A wide family of traditional and modern antiepileptic medications are GABAergic transmission enhancers. ( zuczwar et al., 2001). The enzyme GABA transaminase catabolizes GABA intracellularly, and its inhibition significantly raises GABA levels in brain tissue, which is correlated with a higher seizure threshold. Ionotropic GABAA and metabotropic GABAB receptors are the mechanisms by which GABA works. “The combination of pentameric GABAA receptors, which is made up of two a, two b, one g, or one d subunit, forms a hloride channels that are ligand-gated and mediates tonic or phasic inhibition based on the receptor's subunit composition.” (Mula, 2009). The agonist, antagonist, and allosteric modulator affinities of the GABAA receptor are also influenced by its configuration. Fast inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSP) are produced when the GABAA receptor in the brain is activated, and it is widely acknowledged that this receptor complex is essential for the prevention and suppression of seizures (apart from the lack of non-convulsive seizures). (Depaulis et al., 1997). Some of the strongest convulsants are bicuculline, picrotoxin, and pentelyenetrazole, whereas benzodiazepines, barbiturates, and a number of neurosteroids are Agonists or positive modulators of the GABAA receptor, preventing seizures in both experimentation on humans and animals. Synaptic excitation and inhibition in balance appears to be important for maintaining a healthy level of brain excitability. According to the current study, GABA levels significantly increased during PTZ-induced seizures.
Glutamic acid serves as the central nervous system's main excitatory amino acid neurotransmitter. “It activates metabotropic glutamate receptors as well as the agonists of ionotropic receptors, NMDA (N-methyl-D-aspartic acid), AMPA (a-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-isoxazole propionic acid), and Kainate receptors. These receptors influence intracellular functions and ion channel activities via G-proteins”. (Urbanska et al., 1998) Agonists of the ionotropic glutamate receptor show strong proconvulsant effects and are frequently utilised in seizure experimentation. Excess glutamate builds up in the synaptic space as a result of restricted glutamate transport, which increases NMDA receptor activation, additional glutamate release, and seizures. Additionally, it's possible that certain infantile epilepsy is partly caused by glutamate transporter failure. The demonstration that improved glutamate transporter performance can shield mice from seizures is a crucial next step. (Demarque, 2004). In the current investigation, glutamate levels in both animal models were significantly reduced by aqueous extracts of Citrus maxima's fruit, fruit remnants, and pericarp. These findings lead to the hypothesis that an aqueous extract of Citrus maxima's fruit, fruit residue, and pericarp may have operated on glutamate transporters and diminished excitatory effects of glutamate by inhibiting NMDA receptors.
Serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine [5-HT]), an essential postsynaptic excitatory neurotransmitter that is disseminated throughout the nerve system of the body, is produced by serotonergic forebrain neurons in the brainstem. (Buchanan et al ., 2010). In those with generalised epilepsy, serotonin levels in the brain are shown to be lower. (Dailey et al ., 1989). Reduced brain serotonin levels in pentylenetetrazole-induced rats increase the susceptibility to seizures. (Wenger et al ., 1973). When In order to manage seizures, human brain tissue was surgically removed, it was shown that vigorously spiking temporal cortex had higher levels of 5-hydroxy indole acetic acid (5-HIAA), a serotonin breakdown product, than normal tissue. (Louw et al ., 1989). In epileptic animal brain tissue extracted for the purpose of treating epilepsy, enhanced serotonin immunoreactivity has been seen after treatment with an aqueous extract of fruit juice, fruit leftovers, and the pericarp of Citrus maxima Linn. (Trottier et al ., 1996).
Serotonin and norepinephrine both have postsynaptic excitatory effects, while glutamate and GABA both have presynaptic inhibitory effects. These substances are also changed in generalised epilepsy and severe depression. (Kanner, 2008), Norepinephrine has a protective impact on seizures at high dosages, but at low quantities it can intensify an epileptic seizure. (Jurgens et al ., 2005).
One among the most significant the brain's neuromodulators, dopamine has a significant impact on the excitability of neurons. It possesses receptors, dopamine. D1 and D2 receptive elements are the two subfamilies that make up this receptor. D2-like receptors have been found to be highly expressed in a variety of brain areas, mRNA study revealed that these regions included the frontal cortex, olfactory bulbs, nucleus accumbens, hippocampus, and amygdala.. Via D2-like receptors, dopamine inhibits the excitability of hippocampus neurons. (Starr, 1996; Starr, 1993). Dopamine production rises during epilepsy. Dopamine thus has the ability to reduce seizure activity via stimulating hippocampus D2-like receptors. Dopamine levels dropped in animals given pentylenetetrazole. The fruit was then treated with an aqueous extract of fruit juice, fruit scraps, and Citrus maxima Linn's pericarp. For the regulation of epilepsy, an elevated dopamine level in the brain tissue of epileptic animals is respected.
CONCLUSION
PTZ is a powerful chemical agent that caused convulsions in rats, according to the findings of the present investigation. Citrus maxima L. fruit pericarp extract and lyophilized fruit juice and residue extract both displayed anticonvulsant and antiseizure effects against PTZ-induced oxidative seizure in rats. Alkaloids, coumarin, and phenol were found in the lyophilized fruit juice and fruit residue as well as the aqueous extract of the fruit pericarp of Citrus maxima L. Citrus maxima L.'s lyophilized fruit juice and fruit residue, as well as the aqueous extract of the fruit pericarp, both include alkaloids and phenols that may help explain the plant's anticonvulsant properties.
This study also shows that levels of neurotransmitters such glutamate, GABA, serotonin, dopamine, and noradrenaline are considerably altered in the forebrain and that they play a part in the regulation of pentylenetetrazol-induced seizures in rat models. The root causes of epilepsy include inhibition of GABA and increase of glutamate activity. After PTZ induction and treatment with aqueous extracts of lyophilized fruit juice and fruit residue and an aqueous extract of the fruit pericarp of Citrus maxima L. at doses of 200 and 400 mg/kg, which had anticonvulsant activity in PTZ-induced epileptic rats by either blocking sodium channels or by enhancing GABA receptor-mediated inhibitory activity, which decreased the level of glutamate and increased the level of GABA. In light of these findings, it is possible that the anti-seizure effects of an aqueous extract of lyophilized fruit juice and fruit residue and an aqueous extract of Citrus maxima L. fruit pericarp are attributable to the presence of neurotransmitters that have been restored in the rat brain. These findings back up the plant's traditional medical applications for treating convulsions.
ETHICAL APPROVAL
After receiving the required approval from the committee, the study's methodology was approved by the P SEA's ethical standards (Approval No. 790/03/ac/ P SEA).
CONFLICT OF INTERESTS
The authors declare lack of conflict of interest
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The Dean of Life Sciences, Head, and faculty members who teach and don't teach in the biochemistry department at Srimad Andavan Arts and Science ollege (Autonomous) in Tiruchirappalli, Tamil Nadu, India, are acknowledged by the authors for providing research facilities. generous guidance to finish this research venture.
Список литературы Antiseizure and neuroprotective effects of citrus maxima l fruit components in pentylentetrazole-induced epilepsy in Wistar albino rats
- Anonyms., (2001) The ayurvedic pharmacopeia of India, Government of India, Ministry of health family welfare. Department of Indian system of medicine and Homeopathy, New Delhi, 1, 142- 143.
- Atack C.V., (1973) The determine of dopamine by a modification of the dihyroxyindolefluorimetric assay. Br. J. Pharmac. 48, 699-714.
- Bhumi G, Savithramma N. (2014) Screening of pivotal medicinal plants for qualitative and quantitative phytochemical constituents. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci, 6, 63-5.
- Brindha P, Sasikala and Bhima Rao., (1981) Pharmacognostic studies on Coleus Aromaticus Benth. Indian Borage B.M.E.B.R, 7, 17-31.
- Buchanan GF, Richerson GB., (2010) Central serotonin neurons are required for arousal to CO2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 107, 16354–9.
- Czuczwar SJ, Patsalos PN., (2001) The new generation of GABA enhancers. Potential in the treatment of epilepsy. CNS Drugs, 15, 339–350.
- Dailey JW, Reigel CE, Mishra PK, Jobe PC., (1989) Neurobiology of seizure predisposition in the genetically epilepsy-prone rat. Epilepsy Res. 3, 317–320.
- Demarque M., (2004) the role of glutamate transporters in developmental epilepsy. A concept in flus glutamate transporters prevent the generation of seizures in the developing rat Neocortex. The Journal of Neuroscience, 24(13), 3289-3294.
- Depaulis A, Deransart C, Vergnes M, Marescaux C., (1997) GABAergic mechanisms in generalized epilepsies: the neuroanatomical dimension. Rev Neurol (Paris), 153, Suppl 1, S8–13.
- Dilip Kumar pal., (2009) Determination of Brain Biogenic Amines in CynodonDactylon Pers. And CyperusRotundus L.Treated Mice, International Journal Of Pharmacy And Pharmaceutical Sciences, 1(1), 190-197.
- Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Anders U, Feather stone RM., (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol. 7, 88- 95.
- Gilani, A. H., and Rahman, A., (2005) Trends in ethnopharmacology. J. Ethnopharmacol. 100, 43–49. doi: 10.1016/j.jep; 06.001
- Hasan, S., Dwivedi, V., Misra, M., Singh, P. K., Hashmi, F., & Ahmed, T. (2012). Anti-epileptic activity of some medicinal plants. Int J Med Arom Plants, 2(2), 354-60.
- Jurgens CW, Boese SJ, King JD, Pyle SJ, Porter JE., (2005) Adrenergic receptor modulation of hippocampal CA3 network activity. Epilepsy Res, 117-128.
- Kanner AM., (2008) Mood disorder and epilepsy; A neurobiological perspective of their relationship, Dialogues, Clin Neuroscience. 10, 39-45.
- Kokate CK, Purohit AP, Gokhale P. (2004) Pharmacognosy. 2nd ed. New Delhi: Vallabh Prakashan, p. 466-70.
- Louw D, Sutherland GB, Glavin GB, Girvin J., (1989) A study of monoamine metabolism in human epilepsy. Can J Neurol Sci. 16, 394–397.
- Lowe IP, Robins E, Eyerman GS., (1985) The fluorimetric measurement of glutamic decarboxylase measurement and its distribution in the brain. Journal Neuro chem. 3, 8-18.
- Manas Kumar Das., (2015) Antiepileptic Activity of Methanol Extract of Butea monosperma (Lam.)
- Kuntze and its Isolated Bioactive Compound in Experimentally Induced Convulsion in Swiss Albino Mice, J. Pharm. Sci. & Res. Vol. 7(12), 1066-1072
- Schlumpf, M., Lichtensteiger, W., Langemann, H., Waser, P. G., & Hefti, F. (1974). A fluorometric micromethod for the simultaneous determination of serotonin, noradrenaline and dopamine in milligram amounts of brain tissue. Biochemical pharmacology, 23(17), 2437-2446.
- Mula M., (2009) New antiepileptic drugs: molecular targets. Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem, 2, 79–86.
- Rahmati, B., Mohsen, K., Mehrdad, R., and Parisa, A., (2013) Anti-epileptogenic and antioxidant effect of Lavandula officinalis aerial part extract against pentylenetetrazol-induced kindling in male mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 148, 152–157.
- Raju TR, Kutty BM, Sathyaprabha TN, Shankarnarayana Rao BS., (2004) Brain and behavior. National Institute of Mental Health and neurosciences, Bangalore, 134-138.
- Starr MS., (1993) Regulation of seizure threshold by D1 versus D2 receptors. New York: Academic Press, 235-69.
- Starr MS., (1996) The role of dopamine in epilepsy. Synapse, 22, 159-94.
- Fathima, S. N., Vasudevamurthy, S., & Rajkumar, N. (2015). A review on phytoextracts with antiepileptic property. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research, 7(11), 994.
- Takagi K, Watanabe M, Saito H., (1971) Studies on the Spontaneous Movement of Animals by the Hole Crosse Test: Effect of 2- dimethylaminoethanol, its acylates on the central nervous system. The Japanese J of Pharmacology. 21, 293.
- Tong-Un, T., Wannanon, P., Wattanathorn, J., & Phachonpai, W. (2010). Quercetin liposomes via nasal administration reduce anxiety and depression-like behaviors and enhance cognitive performances in rats. American Journal of Pharmacology and Toxicology, 5(2), 80-88.
- Trottier S, Evrard B, Vignal JP, Scarabin JM, Chauvel P., (1996) The serotonergic innervation of the cerebral cortex in man and its changes in focal cortical dysplasia. Epilepsy Res. 25:79–106.
- Umachigi, S. P., Kumar, G. S., Jayaveera, K. N., & Dhanapal, R. (2007). Antimicrobial, wound healing and antioxidant activities of Anthocephalus cadamba. African journal of traditional, complementary and alternative medicines, 4(4), 481-487.
- Urbanska, E. M., Czuczwar, S. J., Kleinrok, Z., & Turski, W. A. (1998). Excitatory amino acids in epilepsy. Restorative neurology and neuroscience, 13(1-2), 25-39.
- Wenger GR, Stitzel RE, Craig CR., (1973) The role of biogenic amines in the reserpine – induced alteration of minimal electroshock seizure thresholds in the mouse. Neuropharmacology. 12, 693–703.


