Application of Biometric Security in Agent based Hotel Booking System - Android Environment
Автор: Wayne Lawrence, Suresh Sankaranarayanan
Журнал: International Journal of Information Engineering and Electronic Business(IJIEEB) @ijieeb
Статья в выпуске: 3 vol.4, 2012 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The process of finding the finest hotel in central location is time consuming, information overload and overwhelming and in some cases poses a security risk to the client. Some of the more advanced web sites allow for a search of the destination via a map for example hotelguidge.com and jamaica.hotels.hu. Booking of hotels is secured by the standard Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) to confirm the identity of a website or server, encrypt data during transmission, and ensure the integrity of transmitted data. Even with this in place, hackers have broken the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) by targeting weaknesses in the MD5 algorithm. Recently good amount of work been carried in the use of Intelligent agents towards hotel search on J2ME based mobile handset which still has some weakness. So taking the weakness in the current agent based system, smart software agents been developed that overcomes the weakness in the previous system In addition to smart agent based system been developed and published elsewhere, we here propose to extend the system with the booking capability that allows the user to book a hotel of choice where the authenticity of the client may be determined securely using biometric security and information transmitted using Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) (Server-Gated Cryptography (SGC)) on the internet which is novel and unique. This will be facilitated on Android 2.2-enabled mobile phone using JADE-LEAP Agent development kit.
Agents, SSL, MD5, JADE-LEAP, Android
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/15013130
IDR: 15013130
Текст научной статьи Application of Biometric Security in Agent based Hotel Booking System - Android Environment
Hotel search and booking [1][2] is something which is done by everyone who wishes to travel and stay. This process of finding the finest hotel in central location is time consuming, information overload and overwhelming and in some cases poses a security risk to the client. Various webs sites allow a user to select a destination from a pull-down list along with several categories to suit one’s preference. Some of the more advanced ones allow for a search of the destination via a map. Web sites such
-
II. INTELLIGENT AGENT TECHNOLOGIES
Hotel booking systems (HBS) have been around for decades and over the years have become more interactive, providing clients of hotels worldwide to book a reservation without having to physically walk into the facility. The need for providing HBS that are intelligent in nature is therefore inevitable. So with this in mind, we will review about Intelligent Agent.
Agent based technology falls within the field of Artificial Intelligence. An agent should be autonomous in nature, having the ability to control its own action. Agents in principle are self-reliant software programs [10]. It is critical that agents are intelligent in nature. This means they should possess the ability to sense the environment that they are in and adapt accordingly. Reference [11] discussed the flexible nature of agents. They are of the view that the agent should be adaptive, knowing how to adjust to its environment. Whilst Agent technology is not relatively new to the study of AI, the need to have a clear understanding of its capabilities is important. Agents usually require several inputs before they can arrive at an action which is outlined in [12].
Another point to note about agent is their mobility. Agents should be able to move from environment to environment. The portability of agents is crucial to facilitate information exchange [13]. To effectively develop or program intelligent agents, several agent development kits have been developed. Agent toolkits help programmers of agent–base systems to have an environment in which they can develop, simulate, test or monitor agent’s performances before actual deployment of the application. Reference [14] identified at least four categories of agent toolkits used today. They are generalpurpose agent toolkits, multi-agent toolkits, internet agent toolkit and mobile agent toolkits. Each of the preceding categories of agent toolkit has been used in agent-base solutions.
-
A. Agent based Mobile Hotel Search system
There has been some work been done in the use of intelligent Agents in Hotel search on mobile handsets. [5][6] .In all these Agent based system [5][6], there has been no GMAP facility included for searching the hotels and retrieving the results. Also these agents possess no learning capability i.e. past search experience to search the hotels. Finally no security implemented towards booking the hotel by giving financial information. So Smart agent based system have been implemented towards GMAP and learning capability and published elsewhere [7][8]. The smart agent based system developed possesses no booking facility which has been implemented in this paper using biometrics. But before we go into those details, we will review some of security technologies towards hotel booking.
-
B. Secure Socket Layer (SSL)
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) has been the standard used for many years to secure systems over the internet. Primarily Web Browsers and Web servers rely on Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocol to provide a channel that is securely encrypted for private communication over the public domain of the internet.. When the Web browser indicates that it is using a secure domain, a certain degree of encryption is employed which is dictated by the type of SSL Certificate. Thereafter the server sends a copy of its SSL [3] Certificate to the browser which will check with the certificate authority to determine if it can be trusted. If trust is successful, the server would send an acknowledgement to start an encrypted data session. A special type of greeting called an SSL handshake between the browser and server is initiated. There are currently eight different types of SSL on the market which are : Self-signed certificate, Domain Validated Certificate, fully authenticated SSL Certificate, ServerGated Cryptography (SGC), Wildcard Certificate, SAN (Subject Alternative Name) , SSL Certificate, Code Signing Certificates and Extended Validation (EV) SSL Certificates. However for our purposes SSL Certificates called Server-Gated Cryptography (SGC) [3] with 128-or 256-bit encryption would be used. It has been seen that up to 99.9% of web site visitors seems best suited for our intended purpose using SGC certificates. By making it mandatory version of browsers that support 128- or 256-bit encryption, we will achieve the highest level of protection to protect information being passed through our data channel.
-
C. Certificate Authority and Certificates
A Certificate Authority (CA), issues a certificate that is used to affirm people’s identity. Certificates are a combination of the users’ identification information and their public keys. Only after successful verification of the user’s identity, the Certificate Authority will be attached to its digital signature. Before the first transaction can be initiated, the user of the certificate has to distribute the public key to other users. The public key from the sender will be compared with the one in the matching certificate.
-
D. Vulnerability of Secure Socket Layer (SSL)
MD5 is a standard that is widely used, primarily to verify the integrity of data using 128-bit message digest from the input of message which can be of variable length. It is claimed to be as unique as a finger print. The algorithm was developed by MIT Professor Ronald L. Rivest. The algorithm was intended to be used in digital signature applications. The algorithm facilitates the secure compression of large files before being encrypted with a secret key under public key cryptosystem. MD5 is an extension of the MD4 algorithm which offers increase assurance of data security. [4] .However, weaknesses have been discovered in MD5 which allow for collisions in output which translates to attackers creating cryptographic tokens that appear to be genuine [19]. Currently there are no forthright fixes unless the Certificate Authorities stop using MD5 and switch to a more secure SHA-1 algorithm. [15].
-
E. Biometric Security
Biometric authentication [16][17] has been widely regarded as the hardest to forge or spoof. Since the early 1980s, systems of identification and authentication based on physical characteristics have been available to enterprise IT. Because of its convenience and ease of use, fingerprint authentication is becoming prominent. Computer peripherals are coming to market with built-in fingerprint readers and most of these units are relatively inexpensive. Recently Motorola released a mobile phone running Android 2.3 operating system. The Motorola ATRIX 4G features biometric fingerprint smart sensor ensures security. The unique fingerprint recognition
technology allows only authorized person to what’s on your phone. This smart sensor feature allows for faster, enhanced security and personal data privacy that surpasses password or PIN locks. [18]
-
F. Biometric Credit Card
The introduction of the world’s first card less payment service was launched by Citibank in Singapore on November 9, 2006[19]. The service employed technology used by a biometric authentication vendor Pay-By-Touch. This meant at the time of purchase Citibank Clear Platinum Card holders no longer need to present their plastic card. They are now required to simply scan their finger on a biometric scanner and enter a seven digit "Personal Search Number".
Biometrics credit card manufacturer’s assertion is that processing of these cards versus traditional credit cards is more secure [20]. The merchant will install a biometric reader at his register. The customer’s ID data would be entered once only, along with payment information and picture ID. The scanner reads the finger print [21] capturing 40 points of information, encrypting and then store this information. This delivers higher security, due to the fact that no two fingerprints are alike. Fingerprint pictures are eliminated, once ID and payment information are recorded to the scanning processor. For future transactions all you need is to swipe your finger to complete transactions. Payment by touch systems facilitates shorter processing time for transactions.
Biometric payment technology enables the consumer to pay by the touch of a finger on scanner linked to a payment wallet. The fingerprint is transmitted through a linked router and media required to approve the transaction through an automated process. Providers of biometric payment solutions require the completion of a pre-enrollment process, which captures necessary information such as personal identification, fingerprint and banking information. So taking all these into consideration we here have developed an Agent based system towards booking hotel using Biometric information which is secured and trustable. The development been carried out on latest Android handset that is been explained in forthcoming sections.
-
III. INTELLIGENT AGENT BASED HOTEL BOOKING SYSTEM
There has been quite amount of work carried out in the use of intelligent agents in hotel search systems which is been discussed before. So taking those into consideration, an improvised Agent based system towards hotel search been developed which used the intelligence to search for hotels using the GMAP facility [7][8]. Also the agent possesses intelligence to search hotels based on previous search experience of the agent which is Agent learning feature. The system however had no booking module incorporated which has now been implemented that possesses Biometric features to book hotel without needing to provide card information. The architectural details of the system are discussed below
-
A. Architecture of SAL-HSB
The Smart Agent Learning for Hotel Search System (SAL-HSB) [7][8] consist of the five agents which has been published elsewhere [8] . The details of these agents would not be discussed. We here would look into agents pertaining to booking which are Booking Agent, Card Agent, Trusted Third Party as shown in Fig.1
-
B. Hotel Agent (HA)
The hotel agent equips the central database agent with all the information regarding the hotel operation and services that is offered by the hotel. This is collected and stored by the central database agent for future use. Each hotel would host an agent that is registered with SAL-HSB application. Booking and cancellation information is also passed between the booking agent and the hotel agent to ensure that the hotel reservation system is updated and available for access by representatives of the hotel staff.
-
C. Booking Agent (BA)
The main function performed by this agent is to keep track of matters relating to bookings and cancellations while liaising with the central database agent and security agent. This involves capturing booking and cancellation information from the mobile GUI, room availability checks and resolve date conflicts and the presentation of booking information to the end user. The functions are summarized below. This agent is hosted by the mobile device.
-
• Liaise with the security agent.
-
• Liaise with the hotel agent.
-
• Presentation of booking information
-
D. Card Agent (CA)
The main roles are as follows which is hosted by the Card Data Centre
-
• Provides a secure connection to charge accounts from the administration end.
-
• Establishes a secure connection with the card center in order to verify the clients account during the booking process and liaise with the security agent.
-
E. Security Agent (SA)
The security agent is vital to booking process and performs the following functions.
-
• Creates a secure https connection with third party to verify hotel using trusted third party API’s.
-
• Securely transfer biometric data for verification to trusted third party.
-
• Liaise with card agent.
-
• Liaise with the booking agent.
-
F. Central Database Agent (CDA)
The Central Database Agent is one of the major players in the overall architecture that enables communication, accumulating and dispatching information and situated on the central repository of the system. Among the main functions of this agent is to capture and store information relating to the feedback feature implemented, collect information from all hotel agents about respective hotels which include data such as address, pricing and facilities, process query submitted by the search agent against data stored in the central database, querying the Directory Facilitator (DF) to know the registered hotel agents and executing popularity index calculations.
-
G. Trusted Third Party (TTP)
The trusted third party is a trust entity that is external and has the following responsibilities in the architecture of the system.
-
• Securely via an encrypted channel liaise with the hotel agent and booking agent for the purpose of authenticating the hotel booking and cancellation process.
-
• Securely liaise with card agent to validate hotels certificates.
-
• Securely verify client’s identity using biometric data-finger print matching techniques.
-
• Securely liaise with the security agent to obtain biometric information for authentication.
-
H. Directory Facilitator (DF)
The directory facilitator provides four methods for developers to interface with namely register, modify, deregister and search to aid in agent development and yellow page lookup of services for registered agents. All authorized agents are eligible for the services that are provided by the directory facilitator once registered. This includes a precise up-to-date list of all agents and services they provide. Agents can afterwards request the deregistration of a description at which time there is no longer an obligation on behalf of the directory facilitator to broker information on behalf of that agent. The agent is also able to request the directory facilitator to modify its agent description at any point in time for any reason. Agents can issue search requests to the directory facilitator to ascertain descriptions matching supplied search parameters.
-
I. Mobile Device
An android 2.2 smart phone with would be required by the end user for interfacing with our SAL-HSB application supported by a mobile network with reliable internet access and data services in order to allow for uninterrupted communication with the agent platform and other services on the internet for example Google maps API. This can also be supplemented with the use of an android emulator that mimics the mobile device when being developed. Having discussed the various agents in the SAL-HSB system developed from booking system point of view, we will see in detail the Hotel Booking and Cancellation process.
A pre-requisite to this process is completion of search operation where the desired hotel would have been identified by means of Hotel Search Agent. Acceptance of hotel policy and security rules and procedures is necessary for all parties involved when transmitting sensitive information over the internet. The biometric finger print of the user is captured and encrypted using bouncy castle API for secure transfer over https protocol via the mobile device. This is done once the secure Third Party gives permission to proceed that the hotel is trusted and if not the process would not be allowed to continue and alert displayed to end user. The security agent and VeriSign the trusted third party carry out this verification in the background. The user’s identity is authenticated using biometric security and credit card selection made. This information is once again sent to the security agent who in turns relays it to the card agent to be confirmed. Once confirmation is obtained this is relayed to the hotel agent and end user on his mobile device. The same is presented in Fig.1.
K. Hotel cancellation
Hotel policies will be enforced as guests would have agreed to this before booking was done. Once application is loaded and ready the user would select the cancellation option from the menu. Information will be transferred securely over https and biometric data encrypted from the mobile device. Additionally the hotel will be checked for third party certification via the hotel agent contacting the security agent. Once successful the receipt number and finger print would be acquired and the biometric information will be passed on to the card agent along with amount to be charged. The user will be notified whether they are charged and the amount being charged subject to hotel policy. This operation will also be done from the administration side to facilitate cancellations that are called in and also in cases where guest do not turn-up.
-
IV . ALGORITHMS IN SAL-HSB
The guest configures his or her required booking details based on the length of stay, arrival date, departure date, number of persons including children and number of rooms needed as shown in Fig. 5. All these fields are mandatory and must be filled out by the user before the process can be allowed to continue. The user can exit this process by clicking the hotel search result which will navigate back to the search listing and chose another hotel to book if so desired. The Booking Agent at this stage of the process has to ensure that the dates requested are available by the prospective hosting hotel and occupancy level will be adequate with respect to rooms and facilitie. All this has to be negotiated among the Hotel Agent and Central Database Agent via the Booking Agent. Once these dates are available and all other conditions are met, the summary screen will be displayed below for the guest to review and proceed as shown in
J. Hotel booking
Fig. 6. On reviewing the booking summary and agreeing to continue, Hotel’s cancellation policy is displayed for
The process of hotel booking and cancellation are presented in the algorithmic fashion whereas Hotel search been published elsewhere [7][8].
-
> Based on the results presented the user can select a hotel and view location on Google map, view ratings in detail and check facilities offered after which the hotel that best suits his/her needs may be chosen for booking.
-
> When the booking process is initiated, the hotel is authenticated by a Trusted Third Party which is achieved by the submission of the hotel information by the booking agent to the security agent to check trust with the trusted third party.
-
> If hotel is trusted, the booking process would continue otherwise it ends prematurely indicating that the hotel is not trusted.
-
> Once hotel is trusted, booking information and room selection would be made by the guest via the mobile device.
-
> Now the prospective guest identity is authenticated using biometric security and credit card selection i.e VISA, MASTERCARD made for payment. This information is once again sent to the security agent who in turns relays it to the card agent to be authenticated.
-
> Once confirmation is obtained from the card agent, this is relayed to the hotel agent and end user. The prospective guest at this point would not be charged instead booking be confirmed with booking Reference number
-
> Cancellation can be carried out on the mobile device where the user will be keying the booking number obtained from the booking process along with finger print which is encrypted for transmission.
-
> On submission, the hotel is checked for third party certification and once cleared the biometric information and booking receipt information is passed to the security agent.
-
> The security agent in turn communicates with the card agent to check its certification and charge the amount to the guest account if needed. The result is passed on to the hotel agent to effect the cancellation.
-
> Hotel agent sends the cancellation to user’s mobile device.
-
V. IMPLEMENTATION USING JADE-LEAP
SAL-HSB [7][8] Implementation was done using android SDK 11.0 and java development kit 1.6.0_25 (Jdk1.6.0_25) as the runtime environment using Eclipse Indigo release build id: 20110615-0604 with Android plug-in enabled as the integrated development environment IDE. This is an open source IDE which is freely available for download with a lot of features for java developers. JADE 4.0.1 was used for the agent platform to develop, control, manage and host all agents. Jade Android 1.0 enabled JADE-LEAP agents on the mobile device. The system’s cryptographic security
requirements were handled by the Bouncy Castle jdk16-146 lightweight JCE extensions for lightweight cryptography functions including symmetric encryption, public key encryption, and certificate based authentication Android mobile devices. This allowed for the creation and signing of public key certificates used for the security of sensitive information transmitted over the internet. VeriSign’s VIP Android [22-24] 1.4 was used to simulate the trusted third party for mobile devices.
GRFingerJava 4.5 fingerprint matching API provided a means to simulate the fingerprint matching that would have been carried out by a third party. Android platform 2.2, API level 8 with Google APIs was used to build the application with Google maps capabilities. Our data needs were all met by Microsoft SQL Server 2008 [25] developer edition. This was used to create all databases needed for our centralized hotels and card data center database. The system i.e. SAL-HSB is created using Android 2.2 [26] with Google API 8 and Java Agent Development Toolkit (JADE) with Lightweight Extensible Authentication Protocol (LEAP)[27].The list of agents in the JADE environment is shown in Fig. 2 The Central Database Agent resides in the main container and is labeled HSBDBAgentden. All other agents reside in separate split container and are identified by their names. The intelligence possess by Hotel search agent for varying scenarios been published elsewhere and is not the part of this paper [7][8]. We will substantiate agent intelligence with biometric security towards Hotel Booking and Cancellation.
-
A. Hotel Booking
Now that the search is completed and Hotel Search Agent presents user with list of hotel, the customer would go about booking the hotel of his choice as shown in Fig. 3. On completion of displaying the search result, the guest is allowed to select a hotel of choice for booking from the listing in Fig. below. As illustrated, the Guest is about to book hotel highlighted Wyndam, Kingston, Jamaica from the result listing shown in Fig. 3. Each hotel desired for booking is checked for verification with VeriSign before continuation of the booking process. This means their existence is validated based on third party certificates obtained from the third party, which in our case is VeriSign as shown in Fig. 4. The logo depicted in Fig. below indicates the trusted third party logo that we are using in SAL-HSB. When the user continues by clicking on “Book Now” security checks are made after which if successful, user will be allowed to continue with the booking process. The security agent connects over HTTPS using third party APIs to check if certificates used by booking agent are authentic and still valid. Only then are users allowed to book the hotel.
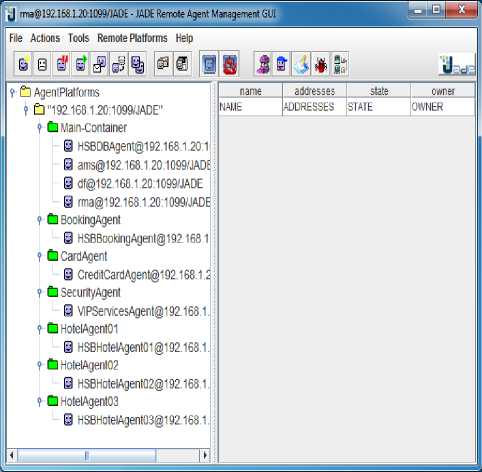
Figure 2 Agents in JADE Container
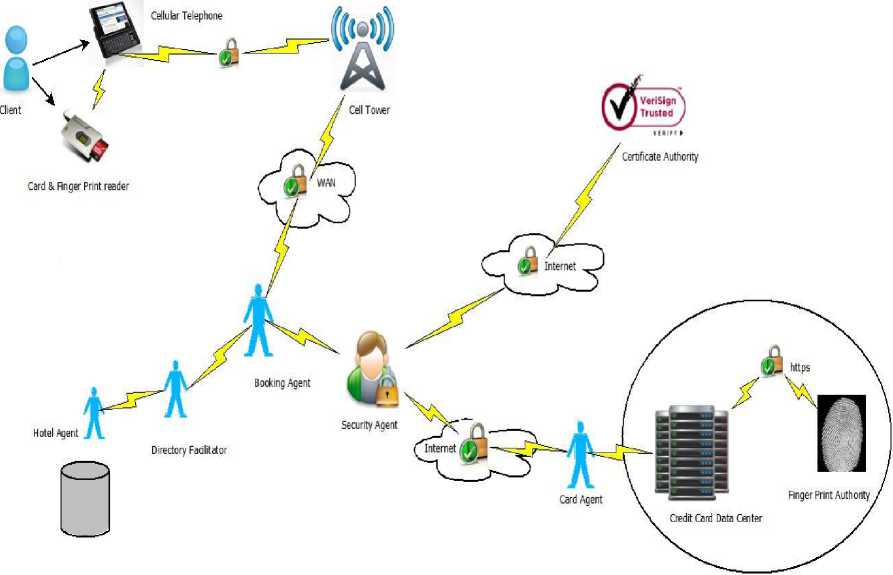
Figure.1 Hotel Booking
The guest configures his or her required booking details based on the length of stay, arrival date, departure date, number of persons including children and number of rooms needed as shown in Fig. 5. All these fields are mandatory and must be filled out by the user before the process can be allowed to continue. The user can exit this process by clicking the hotel search result which will navigate back to the search listing and chose another hotel to book if so desired. The Booking Agent at this stage of the process has to ensure that the dates requested are available by the prospective hosting hotel and occupancy level will be adequate with respect to rooms and facilitie. All this has to be negotiated among the Hotel Agent and Central Database Agent via the Booking Agent. Once these dates are available and all other conditions are met, the summary screen will be displayed below for the guest to review and proceed as shown in Fig. 6. On reviewing the booking summary and agreeing to continue, Hotel’s cancellation policy is displayed for prospective guest. The guest must agree to continue or discontinue to Hotel Cancellation policy before proceeding to book the hotel. On accepting the Hotel cancellation, Guest is required to provide basic personal information such as Name, Address, Telephone Number, E-mail etc.. This information protected over HTTPS connection. Once the Guest personal information is submitted, Guest is required to place right index finger for scanning on mobile device in order to obtain finger print. In addition credit card type is selected from the options displayed as shown in Fig. 7. The guest’s finger print will be acquired and later will encrypted using AES 128 bit encryption and verified as shown in Fig. 8. The guest’s finger print along with credit card type is used by the Security Agent to Authenticate and verify the prospective guest identity by contacting the Card Agent. This of course occurs also within an encrypted channel (HTTPS) to protect the party’s involved and to ensure integrity of our client’s data while entrusted in our care. Fig.8 depicts one such scenario where the finger print was verified with server and encrypted. When the Card Agent (CA) returns a reply to the Security Agent (SA), the Booking agent will be notified of the results so that the Central Database Agent (CDA), Hotel Agent (HA)
can make the necessary actions/changes related to the booking. The final step would be to notify the end user of his/her booking outcome on the mobile device as is illustrated clearly in Fig. 9. Once booking completed, Prospective guest is given receipt along with guest name, hotel and receipt number. Guest has now successfully completed a booking with Wyndham, Kingston Jamaica. The payment from the credit card is taken once the Guest checks in and not while booking the hotel. The booking here makes a hold on the amount on the credit card only
-
B. Hotel Booking Cancellation
Having made the booking, there are situations where the user might cancel the hotel booking or administrator might if the guest does not turn up. So this was implemented from two perspective; one from the mobile device and two from the hotel administration side. We will explore cancelling a booking in the following scenarios.
Let us consider a scenario where the hotel booking is cancelled a day before check-in date. The entry point is from the Home screen to select cancel booking and the option is loaded. When the screen loads, the hotel’s cancellation policy will be displayed and the user will be required to scan finger print and enter receipt number of the booking to be cancelled. User is reminded once more what the hotels policy is on towards cancellation. The user will enter the receipt number that was issued when booking was completed and to scan there finger print to ensure no one tampers with the system as shown in Fig. 10. When the user submits the cancellation policy screen, the Trusted Third party (TTP) will be triggered into action where the hotel will be verified once the user chooses to continue. The Security Agent (SA) is responsible for communicating with the third party entity. The Trusted Third Party (TTP) being used is VeriSign. The finger print and receipt number that was acquired in the first step will be processed for verification with the server by the Card Agent (CA) via the Security Agent (SA) as shown in Fig. 11. The amount being used in the activity i.e. deemed to be charged would be supplied by the Central Database Agent (CDA) for the Booking Agent (BA) to be forwarded to the Card Agent (CA) to be deducted from the client’s account as shown in Fig. 12. When process is successful “Approved” is displayed or “declined” when failed. After which when the user clicks continue, the Security Agent (SA) will notify the Booking Agent (BA) of the results which in turn update the Central Database Agent (CDA) and Hotel Agent (HA) that will carry out the necessary changes to the databases. The user is then updated on the mobile device by the Booking Agent (BA) as shown below in Fig. 13 about the status of his/her booking cancellation. This completes cancellation. Hotel policy is being enforced where a person is charged for one night’s stay for cancelling a day before check-in date. In case the guest have cancelled well in advanced adhering to hotel cancellation, the amount will not be charged from the user as shown in Fig. 14.
Let us consider final scenario in cancellation which allows the Hotel Administration interface for cancelling bookings. The Hotel administrator would cancel the booking if the Guest doesn’t turn up. The administrator would key-in the receipt number for a booking. This information is retrieved by the Hotel Agent using the Booking ID supplied by the administrator which is displayed in read only mode. Confirmation prompt gives the user the option to confirm in order to reduce user errors and to improve overall user interaction as shown in Fig. 15. This allows for an intelligent interaction between the Desktop Graphical User Interface (GUI) and the end user. The verified Hotel Agent contacts the Card Agent (CA) which connects over HTTPs to verify and charge the amount against the card holder’s account as shown in Fig. 16. This ends a successful cancellation by a member of the hotel administrative staff as shown in Fig. 17
-
C. Guest Feedback Implementation
Guest provides feedback using SAL-HSB which forms a part of the data that is displayed for each hotel. This information can prove very help full for all parties involved. This information can be selected over periods of three months, six months to a year. This option is obtained by selecting rating from the Fig. 18. Key features of hotel operation and facilities form the core areas of interest for guest feedback. Each area depicted in figure below is rated from one to five as shown in the Fig. 18.
The ratings popup menu lists all the possible grades that can be assigned to the area being rated. It ranges from a low of one which is rated poor to a high of five rated excellent. The potential guest is expected to make one selection of the available five options. The guest would fill out a typical screen just like the one shown in Fig. 19. Once this is done for all areas of input our Feedback Agent (FA) is now ready to collect all this information so that it can be properly stored by our Central Database Agent (CDA) for analysis at later date. The areas covered are:
-
• Infrastructure
-
• Environment
-
• Ambience
-
• Facilities
-
• Customer service
-
• Room Service
-
• Security
-
• Disability access
-
• Price
This will prove immensely valuable and helpful to our clients and the users of this application when carrying out future bookings. One must note that the information provided for rating is exclusive to the Feedback Agent (FA) and cannot be modified by any hotel. When the form is submitted, a confirmation screen is shown as in the Fig. 20.
Trust factor of conducting electronic commerce when some of the entities themselves cannot provide or even are aware of the pros and cons of conducting online transactions is important.. The proposed system features a security layer to the booking and cancellation process which seeks to protect both the guest and hotel from different levels of potential fraud or misrepresentation that could leave any of the participants involved with some financial loss or other ill-fated forms of inconvenience.
In order to corroborate the soundness of the planned system, we developed a functional prototype integrating with JADE-LEAP on Android, and bouncy castle API to create our required agents that would communicate in a multi-agent environment with external trusted third party via HTTPS and API to provide smart services. The proposed Agent based Hotel Booking System can be improved by integrating finger print scanners in all mobile handsets
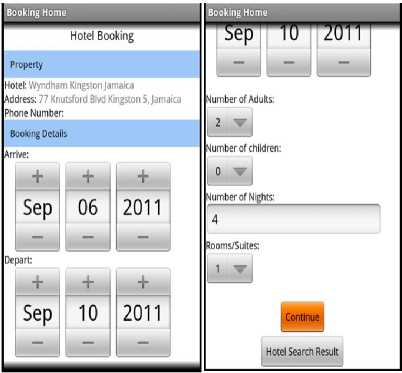
Figure 5 Booking Details
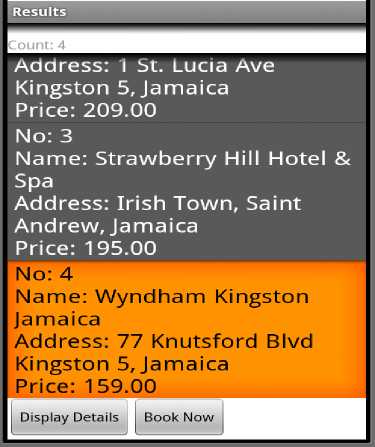
Figure 3 Hotel selected for booking
Figure 4 VeriSign Trusted
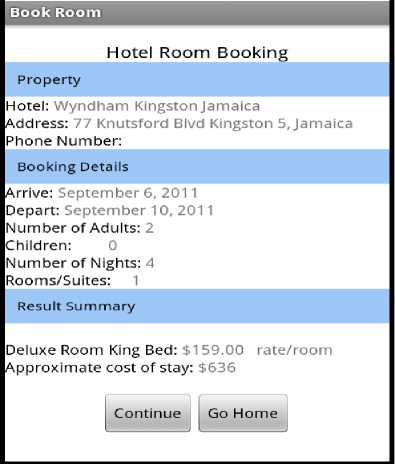
Figure 6 Summary of booking
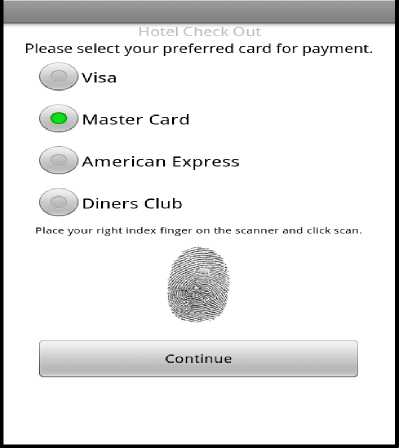
Figure 7 Biometric
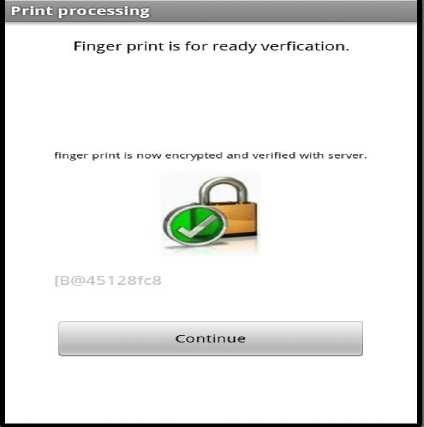
Figure 8 Encrypted Fingerprint Verification
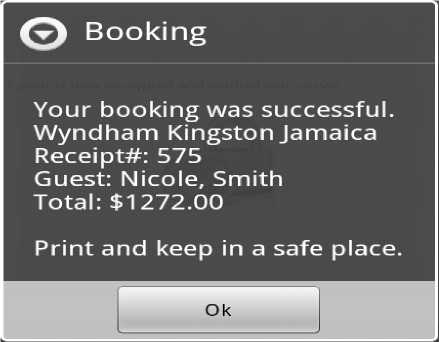
Figure.9 Booking Complete
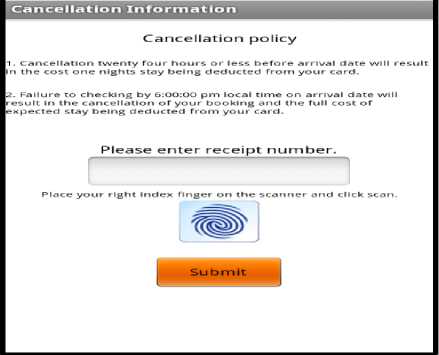
Figure 10 Cancellation policy and user input
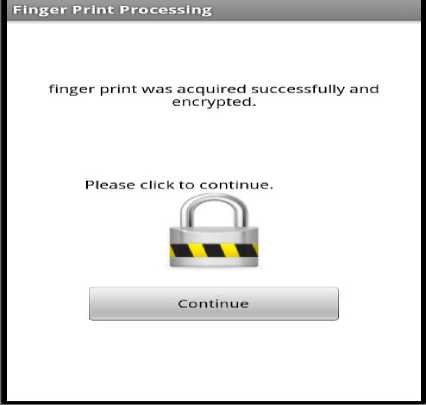
Figure 11 Fingerprint Verification
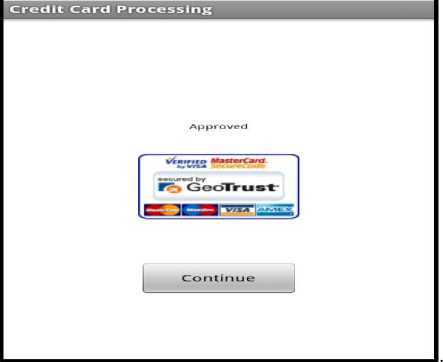
Figure 12 Credit Card Processing
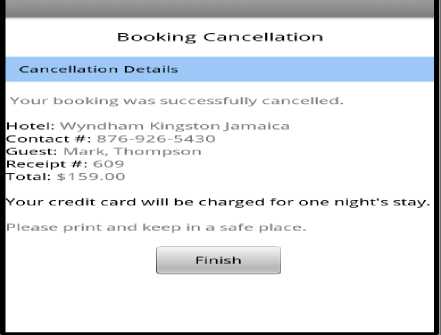
Figure 13 Hotel Booking Cancelled
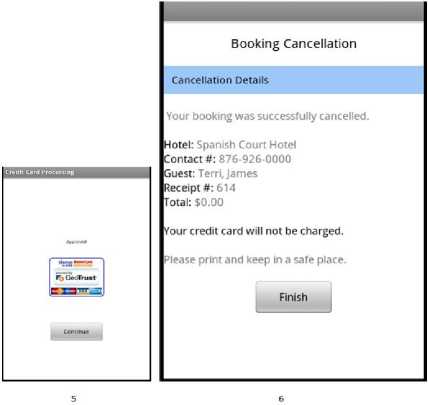
Figure 14 Final Steps in Cancellation Process
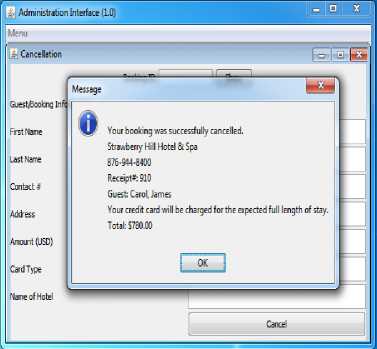
Figure 17 Hotel Cancellation Complete
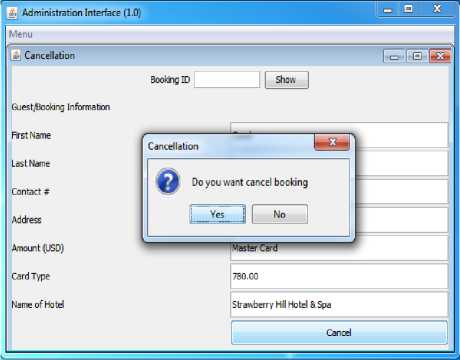
Figure 15 Cancellation- Confirmation Prompt

Figure 16 Charge being processed
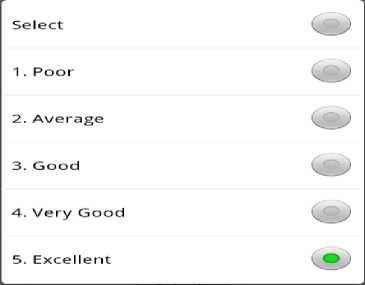
Figure 18 Ratings Options
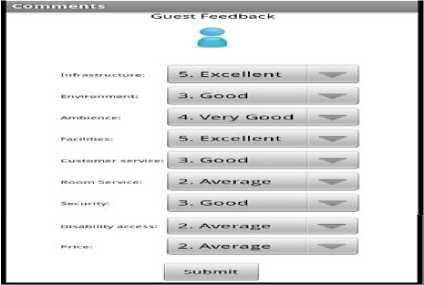
Figure 19 Guest Feedback User Interface
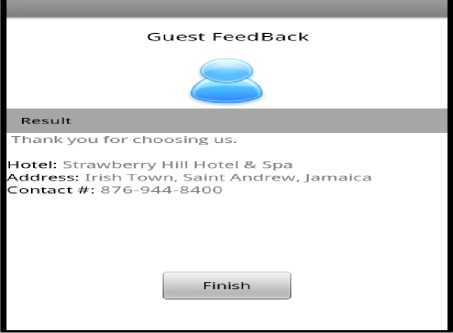
Figure 20 Feedback Confirmation
Список литературы Application of Biometric Security in Agent based Hotel Booking System - Android Environment
- Baleleng, T (2011). Hotel Reservation Techniques Retrieved from http://artificialintelligenceseo.info/2011/09/hotel-reservation-techniques
- Baloch, H (1999). Online Intelligent Hotel Reservation (IHR) using WAP Enable Mobile Phones. Retrieved from http://www.pardis.ir/articles/pdf/p06139.pdf
- SSLGUARD (2010). Server-Gated Cryptography .Retrieved from http://www.sslguard.com/datasheets/Thawte-sgc.pdf
- SearchSecurity (2001). MD5. Retrieved from http://searchsecurity.techtarget.com/definition/MD5
- Bailey, L S and Suresh, S(2009). Intelligent Agent based Mobile Tour Planner. Proceedings of First Caribbean Conference on Information and Communication Technology, Kingston, Jamaica. Pp 8-13.
- McTavish, C A and Suresh, S (2010). Intelligent Agent based Hotel Search & Booking System. Proceedings of 2010 IEEE International conference on Electro/Information Technology, Chicago, USA, May 20-22, 2010.pp.331-336
- Lawrence, W (2011). Application of Agents in Hotel Search and Secured Booking System. M.sc computer Science Dissertation, Department of Computing, University of WestIndies, Jamaica
- Lawrence, W and Suresh, S (2012)" Smart Agent Learning Hotel Search System- Android Environment", Accepted in International Journal of Information Technology and Computer Science , MECS Publishers.
- Ding et al, (2003), "On Programming Information Agent Systems - An Integrated Hotel Reservation Service as Case Study". Proceedings of First German Conference on Multiagent System Technologies, MATES 2003, Erfurt, Germany.
- Gobin, B A and Subramanian R K (2007). Knowledge Modeling for a Hotel Recommendation System, World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology, Vol.25. pp 244-248.
- Franklin, S. and Graesser, A. (1996). Is it an Agent, or just a Program? A Taxonomy for Autonomous Agents. Retrieved from http://www.msci.memphis.edu/~franklin/AgentProg.html
- Jennings, N. R., and Wooldridge, M. (1998). Applications of Intelligent Agents. Retrieved from http://agents.umbc.edu/introduction/jennings98.pdf
- Poole et al. (1998). Computational Intelligence. New York: Oxford University
- Reilly, D. (1998). Mobile Agents - Process migration and its implications. Retrieved from http://www.davidreilly.com/topics/software_agents/mobile-agents
- Naraine, R (2008). SSL broken! Hackers create rogue CA certificate using MD5 collisions. Retrieved from http://www.zdnet.com/blog/security/ssl-broken-hackers-create-rogue-ca-certificate-using-md5-collisions/2339
- Russell, K (2005). "QuickStudy: Biometric authentication." Computer World. Retrieved from http://www.computerworld.com/s/article/print/100772/Biometric_Authentication?taxonomyName=Security&taxonomyId=17
- Kumar, D and Ryu, Y (2009). A Brief Introduction of Biometrics and Fingerprint Payment Technology Retrieved from http://www.sersc.org/journals/IJAST/vol4/4.pdf
- Motorola (2011). Answers – Fingerprint Smart Sensor Retrieved from http://motorola-global-portal.custhelp.com
- Lynn, T (2006). Citibank S'pore launches biometric payment service. Retrieved from http://www.zdnetasia.com/citibank-spore-launches-biometric-payment-service_print-61965886.htm
- Ziemba, J (2004). Credit Card Processing: Biometrics Retrieved from http://business.lovetoknow.com/wiki/Credit_Card_Processing:_Biometrics
- Bocoum, M. (1999). Acceptance Threshold's Adaptability in Fingerprint-Based Authentication Methods. Master of Science Thesis, School of Computer Science, McGill University, Montreal, Canada.
- VeriSign (2011a). Beginner's Guide to Digital SSL Certificates. Retrieved fromhttp://www.verisign.com/ssl/ssl-information-center/ssl- resources/guide-ssl-beginner.pdf
- VeriSign (2011b). Secure Sockets Layer (SSL): How It Works. Retrieved from https://www.verisign.com/ssl/ssl- information-center/how-ssl- security-works/index.html
- VeriSign (2011c). SGC: True 128-Bit SSL Encryption Retrieved from http://www.verisign.com/ssl/sslinformation center/strongest-ssl-encryption/
- Microsoft (2007). Microsoft SQL Server 2008 Top New Features. Retrieved from www.microsoft.com/sqlserver/en/us/editions.aspx
- Google (2011). What is Android. Retrieved from http://code.google.com/android/what-is-android.html
- Bellifemine, F et al (2006). Developing Multi-Agent Systems with JADE. Wiley Publishing


