Application of high-speed hydrodynamic technology for the production of graphene nanosuspensions from natural graphites
Автор: Stebeleva O.P., Kashkina L.V., Vshivkova O.A., Minakov A.V.
Журнал: Siberian Aerospace Journal @vestnik-sibsau-en
Рубрика: Technological processes and material science
Статья в выпуске: 4 vol.25, 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Carbon nanostructures have been in the focus of world science for more than 25 years, since the discovery of fullerenes in 1985, single-walled carbon nanotubes in 1993, graphene in 2004, graphene quantum dots in 2004. Graphene is a monocrystalline graphite films (2D material) with a thickness of several atoms that are stable under environmental conditions and they have excellent electronic, mechanical, chemical, thermal and optical properties. All over the world, research and development of new methods of using graphene in various fields such as energy, oil production, materials science, and electronics are actively carried out. Currently, the use of graphene-containing materials as modifiers for the creation of durable and effortless materials in aviation, automotive and other branches of engineering is an urgent problem. It is advisable to introduce graphene particles into the composition of composite materials using their stable dispersions in a liquid medium. The production of colloidal graphene suspensions is effective in many cases using the method of liquid phase exfoliation of graphite. The paper presents the results of studying the physico-chemical properties of aqueous graphene suspensions obtained by liquid-phase exfoliation of natural graphites using high-speed hydrodynamic technology. Graphite grades GK-1 and GAK-2 (Grafitservice, Chelyabinsk, Russia) are crystalline graphites obtained by enrichment of graphite ores and joint enrichment of natural graphite ores and graphite-containing waste from metallurgical industries, respectively. Graphite suspensions were prepared in distilled water with 1 wt.% graphite, surfactant was added to some samples, processing time (3–120 min), rotor rotation speed (4 000–11 000 rpm). The resulting graphene suspensions were investigated by XRD, by electron microscopy and sedimentation analysis methods. The particle size was determined using the DT-1202 electroacoustic spectrometer. The presence of multilayer graphene is confirmed by comparing the results of XRD with the literature data. Along with multilayer graphene, the presence of graphene dots was detected. Aqueous graphene suspensions for graphites with different sedimentation times have been obtained. For graphite GAK-2 – six days, for graphite GK-1 – 90 days, for graphite GK-1 + surfactant – 6 months.
Graphene, liquid phase exfoliation, hydrodynamic treatment
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/148329763
IDR: 148329763 | УДК: 620.3 | DOI: 10.31772/2712-8970-2024-25-4-521-530
Текст научной статьи Application of high-speed hydrodynamic technology for the production of graphene nanosuspensions from natural graphites
Two-dimensional (2D) materials garnered significant attention in 2004 when it was demonstrated that a single layer of carbon atoms – graphene – could be stably isolated from graphite [1]. In 2017, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) established the nomenclature for graphene as a monocrystal consisting of a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice structure (lattice symmetry p3m1 , cluster of points D 3 ):
-
– graphene: a single layer of carbon atoms;
-
– bilayer graphene: two well-defined layers of graphene;
-
– multilayer graphene: consisting of three to ten well-defined layers of graphene;
-
– graphene nanoplatelets: thickness from 1 to 3 nm and lateral dimensions from ≈100 nm to 100 µm [2].
Graphene has captured the interest of researchers across various scientific disciplines due to its unique physical, chemical, electrical, and optical properties. Graphene is composed of carbon atoms bonded together in a honeycomb structure and exists in an sp2-hybridized state. A graphene sheet, with an atomic thickness, was first synthesized through mechanical liquid-phase exfoliation of graphite as reported in [3]. The synthesis of graphene involves two main approaches: the “bottom-up” methods, such as chemical vapor deposition [4] and molecular epitaxy [5], and the “top-down” methods, such as mechanical exfoliation of graphite [6–8]. However, the exfoliation methods suffered from a major drawback – lack of scalability [9]. The transition from laboratory-scale production to practical commercial applications necessitated the development of cost-effective methods for obtaining graphene.
High-shear exfoliation has emerged as a promising candidate for addressing the scalability challenge. In their seminal work, Paton et al. [10] demonstrated that high-quality graphene can be produced in large quantities using high shear (a hydrodynamic technology). Exfoliation was shown to occur when local shear rates exceeded 104 s-1, and the graphene production rate was 1.44 g h-1, which is high compared to other ultrasonic-based methods. Since the high-shear mixing method is widely available, the authors claim that their hydrodynamic shear exfoliation technology for graphene can be easily transferred to industrial processes, thereby making defect-free graphene widely available for various applications.
The development and optimization of processes for producing graphene suspensions through high shear rates (liquid-phase exfoliation, LPE) [11] require a comprehensive approach. This includes the exploration of natural resources, the development of technologies and equipment, and consideration of environmental and economic factors. This area of research holds significant potential for innovation across various industries.
The LPE method involves the delamination of graphite into individual graphene layers through mechanical forces in the presence of a suitable solvent [12]. This approach enables the production of colloidal graphene suspensions, which can subsequently be utilized in diverse applications. The method is straightforward to implement, scalable, and capable of yielding high-quality graphene. Furthermore, it allows for precise control over the size and the number of graphene layers.
It is essential to identify sources of high-quality graphite with minimal impurities and high crystallinity, as these properties are critical for efficient exfoliation. This technology requires specialized equipment, including hydrodynamic generators (mixers), centrifuges for separating nano- and microparticles, and systems for product quality control.
The use of environmentally benign solvents is crucial, alongside the development of methods for waste management and minimizing production waste. Optimal exfoliation conditions must be established with a focus on minimizing energy, solvent, and processing time costs. The possibility of reusing solvents and other materials is also under consideration.
The aim of this work was to obtain graphene suspensions by the LE method in a high-speed mixer and to study their properties.
Samples and experimental procedure
Two samples of graphite were selected as starting materials: GK-1 grade graphite and GAK-2 grade graphite. GK-1 graphite is intended for the production of pencil leads, with its characteristics regulated by GOST 4404-78. GK-1 is crystalline graphite obtained through the beneficiation of graphite ores, featuring a layered crystalline structure. The graphite is black with a grayish tint. GAK-2 grade graphite is intended for the production of electrodes for batteries, with its characteristics regulated by GOST 10273-79. GAK-2 is crystalline graphite obtained through the separate or combined beneficiation of natural graphite ores and graphite-containing waste from metallurgical processes.
It has a layered crystalline structure and exhibits a gray color with a characteristic metallic sheen (Table 1). In some samples, a surfactant, polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP), was added. Distilled water, regulated by GOST R 58144-2018: «Distilled Water. Technical Specifications», was used as the dispersion medium.
Table 1
Characteristics of graphite
|
Parameter |
Graphite GK-1 |
Graphite GAK-2 |
|
Ash content, %, not more than |
1,0 |
0,5 |
|
Mass fraction of moisture, % no more than |
0,5 |
1 |
|
Impurity content %, not more than |
Volatile matter release 0,5 Arsenkum 0,0025 |
Chlorine ions 0,1 Iron 0,5 %. |
The design features of the IKA T25 mixer (Germany) and the JRJ300D-1 mixer (China) are shown in Fig. 1, with their technical specifications provided in Table 2. The operating principle of the mixers can be described as follows: the liquid being processed enters the working zone of the disperser from below through openings. The rotor blades set the liquid into rapid motion. The liquid exits the openings at high velocity, generating intense flows that exert shear forces on the liquid.
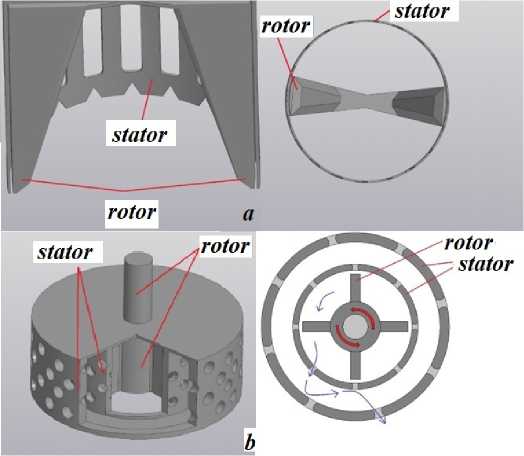
Fig. 1. Rotor-stator design in the mixer I KAT 25 ( a ) and JRJ300D-1 ( б )
Table 2
Technical characteristics of mixers
|
Parameter |
Mixer IKA T-25 |
Mixer JRJ300D-1 |
|
Engine output power, W |
400 |
300 |
|
Rotation range, rpm |
3000–25000 |
200–11000 |
|
Working volume, ml |
1–2000 |
500–40000 |
|
Rotor diameter, mm |
13,4 |
29 |
|
Stator diameter, mm |
18 |
Inner: 30 External: 70 |
The suspensions were processed using two mixers: IKA T25 and JRJ300D-1. Aqueous suspensions of the initial graphite samples were prepared using a magnetic stirrer. Each sample was prepared with a graphite concentration of 1 wt% in the suspension. Sedimentation analysis was conducted visually for 25 samples prepared under varying conditions. Samples that remained stable in suspension for a week were selected for further study. The sedimentation behavior varied among the samples; some settled immediately, such as sample 3, while others remained stable for several days or even months (Fig. 2).
To prepare samples (samples 1–7), 125 ml of water and 1.25 g of graphite were mixed on an IKA T25 mixer. Surfactant weighing 1.25 g was added to samples 4, 6, and 7. To prepare samples 8–16, the minimum permissible volume of liquid for the mixer of 500 ml and graphite weighing 5 g were taken on a JRJ300D-1 mixer. Surfactant weighing 5 g was added to samples 15 and 16. The processing parameters and type of graphite are presented in Table 3.
Table 3
Graphite processing parameters
|
Sample number |
Mixer speed, rpm |
Processing time, min |
Graphite brand |
Surfactant |
Mixer type |
|
1 |
9500 |
120 |
GAK-2 |
– |
IKA T25 |
|
2 |
9500 |
60 |
GK-1 |
– |
IKA T25 |
|
3 |
9500 |
120 |
GK-1 |
– |
IKA T25 |
|
4 |
9500 |
60 |
GK-1 |
+ |
IKA T25 |
|
5 |
9500 |
60 |
GAK-2 |
– |
IKA T25 |
|
6 |
9500 |
60 |
GAK-2 |
+ |
IKA T25 |
|
7 |
9500 |
30 |
GAK-2 |
+ |
IKA T25 |
|
8 |
9500 |
60 |
GAK-2 |
– |
JRJ300D-1 |
|
9 |
4000 |
10 |
GAK-2 |
– |
JRJ300D-1 |
|
10 |
7000 |
10 |
GAK-2 |
– |
JRJ300D-1 |
|
11 |
7000 |
10 |
GK-1 |
– |
JRJ300D-1 |
|
12 |
9500 |
3 |
GK-1 |
– |
JRJ300D-1 |
|
13 |
11000 |
5 |
GAK-2 |
– |
JRJ300D-1 |
|
14 |
11000 |
5 |
GK-1 |
– |
JRJ300D-1 |
|
15 |
11000 |
5 |
GK-1 |
+ |
JRJ300D-1 |
|
16 |
11000 |
5 |
GAK-2 |
+ |
JRJ300D-1 |
The work was carried out using a DT-1202 spectrometer. Bimodal and normal functions were used to describe the particle distribution function.
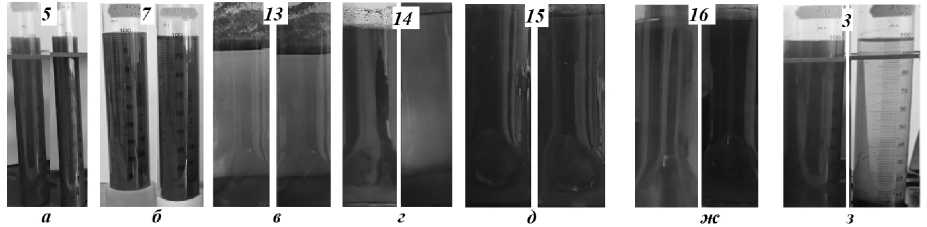
Fig. 2. Sedimentation of suspension samples immediately after preparation (left) and after 6 days:
5 ( а ), 7 ( б ), 13 ( в ), 14 ( г ), 15 ( д ), 16 ( ж ) and 3 ( з ) immediately after preparation and the next day
The preparation for X-ray phase analysis on the DRON-3 diffractometer involved drying the suspensions in a drying oven at 70 °C for 2 hours. The microstructure of graphene was studied using a JEOL JEM-2100 transmission electron microscope (at an accelerating voltage of 200 kV) equipped with an Oxford Inca x-sight energy-dispersive spectrometer.
Results and discussion
During mixer operation, the liquid exits the openings at high velocity, generating intense flows. This flow provides enough energy to overcome Van der Waals forces between graphite layers, leading to their exfoliation. According to [13], the dispersion process likely involves cavitation effects. Cavita- tion bubbles form at various points, introducing additional energy into the dispersion process and promoting more uniform and finer exfoliation. Furthermore, hydrodynamic dispersion involves active collisions between solid particles, which significantly contribute to the overall dispersion outcome.
The particle size of the initial graphites is a bimodal distribution (Fig. 3, a ). The sizes of the dispersed phase in the obtained graphene colloids (samples 15 and 16) are described as having both a normal distribution and a bimodal distribution (samples 13 and 14).
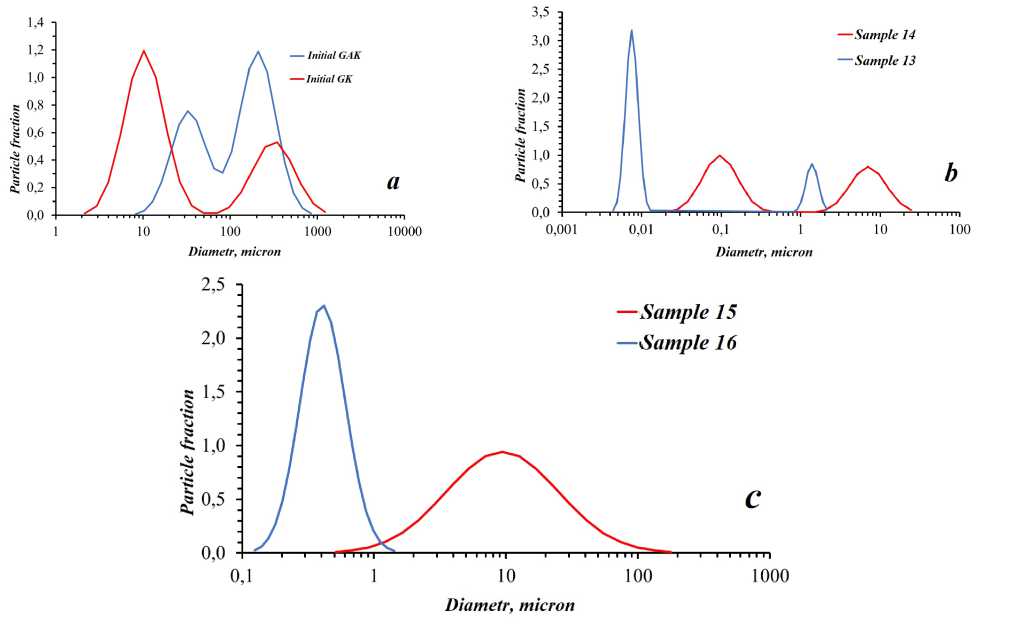
Fig. 3. Particle distribution in the initial samples of graphite ( а ) and graphene suspension after hydrodynamic treatment in a mixer ( b , c )
The parameters of the analyzed samples, obtained through acoustic spectroscopy, are summarized in Table 4. Processing with the JRJ300D-1 mixer (sample 13) significantly reduces particle size, achieving reductions by a factor of 100 or more compared to the initial graphite. The addition of a surfactant does not lead to a substantial decrease in particle size compared to samples without its addition. However, it enhances particle size uniformity. Moreover, using a surfactant increases the zeta potential of the suspension, thereby improving its stability. Graphene phases of nanometer-scale dimensions were identified in samples 13 and 14, measuring 10 nm and 100 nm, respectively. These structures, referred to as graphene dots, can be transformed into graphene quantum dots under specific conditions. Oxidation of graphene dots by reactive oxygen species, generated during cavitation processes in water, enhances the stability of the graphene suspension. Oxidized graphene dots inhibit the coagulation of graphene components, positively affecting the stability of graphene colloids. Sample 14 exhibits greater stability (90 days) compared to sample 13 (6 days). Additionally, the impurities present in the initial graphite samples influence the stability of the suspensions.
Table 4
Results of acoustic spectroscopy of the studied samples
|
Parameter |
Initial GAK-2 |
Sample 13 |
Sample 16 |
Initial GK-1 |
Sample 14 |
Sample 15 |
|
Particle size range, µm |
10–600 |
0,007–3 |
0,34–0,39 |
2–1000 |
0,02–12 |
0,8–100 |
|
Peak particle size values, µm |
30,6 and 204 |
0,01 and 2 |
0,36 |
10,2 and 324 |
0,1 and 7 |
8,5 |
|
Zeta potential, mV |
–4,5 up to – 9,5 |
0,2 up to – 0,96 |
0,7 up to – 1,79 |
–1 up to –8,8 |
5 up to –16 |
–5 up to – 1,16 |
|
Ratio of particle distribution at the right and left peaks, % |
65 and 35 |
20 and 80 |
– |
30 and 70 |
40 and 60 |
– |
The X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern (Fig. 4 a ) exhibits sharp graphite peaks at 2θ values of 11°, 26.5°, and 55°, corresponding to interplanar spacings of 6.8, 3.38, and 1.683 Å, respectively. The XRD spectrum of sample 7, also shown in Fig. 4 a , reveals that the graphite-related peaks are retained but with reduced intensity. The formation of a broad halo in the XRD spectrum of sample 5 (Fig. 4 a ) may indicate the presence of a fine-dispersed, X-ray amorphous phase. Additionally, the peak at 2θ = 11° is absent. A similar XRD pattern was reported in [14], where graphene was synthesized via ammonia reduction and characterized using powder X-ray diffraction. The diffraction lines corresponding to C(002) appeared at 2θ = 26.5°, with an interplanar spacing of 3.35 Å. The authors attribute this to a typical graphite structure and the presence of multilayer graphene.
The graphite peaks in X-ray phase analysis always demonstrate extremely high intensity, which makes it difficult to determine additional phases in the samples under study (Fig. 4, b ). X-ray amor-phism is not characteristic of the graphene suspension samples after processing in a mixer for 5 min. However, the peak intensity is significantly reduced by 40% for sample 13 and by 26% for sample 14 from the initial value. The effect of high shear rates affects the reflectivity of the samples under study and increases their dispersion. Samples 13 and 14 do not demonstrate a wide halo in the spectra (Fig. 4, b ) [15].
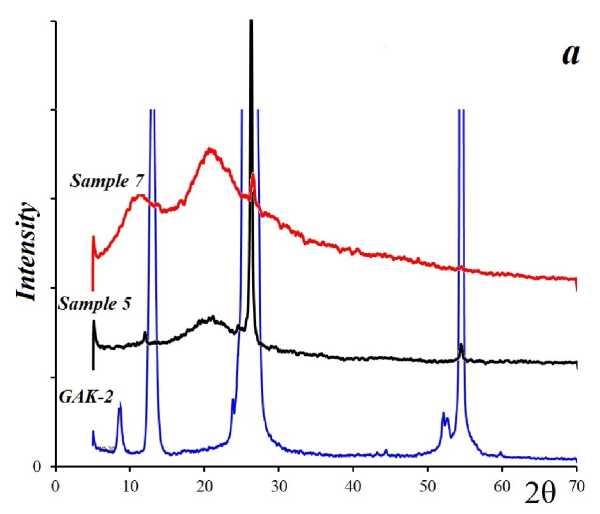
Fig. 4. X-ray spectra of graphite samples and solid fraction of graphene suspension samples
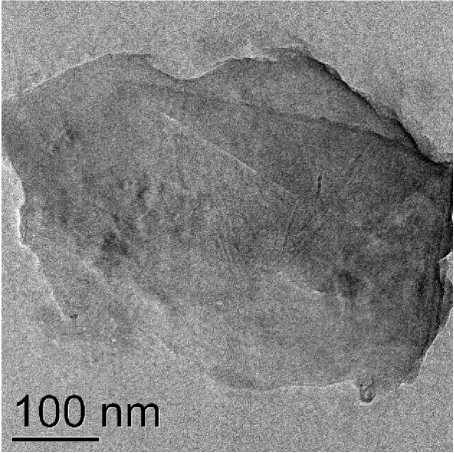
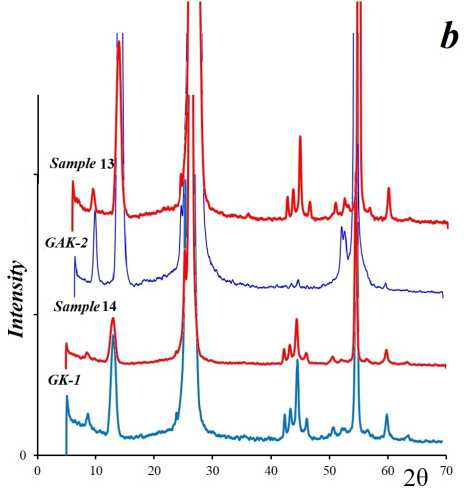

Fig. 5. Solid fraction of graphene suspension
The electron microscope image shows transparent layers of graphene (Fig. 5), which once again proves the XRD data and the possibility of obtaining a graphene suspension using liquid-phase exfoliation from natural graphites.
Conclusion
-
1. The application of high-speed hydrodynamic technology utilizing high-shear hydrodynamic devices enables the production of multilayer graphene particles with lateral dimensions of up to 12 µm.
-
2. Operating modes were selected for two hydrodynamic devices: high-speed mixers IKA T25 (Germany) and JRJ300D-1 (China). The industrial graphites GK-1 and GAK-2, derived from natural graphite, were investigated and demonstrated potential for successful use in the production of multilayer graphene through liquid-phase exfoliation.
-
3. When graphites are dispersed, graphene dots (graphene particle fragments) ranging in size from 10 to 100 nm are formed.
-
4. The oxidation of graphene quantum dots by reactive oxygen species generated during cavitation processes in water enhances the stability of graphene suspensions. Oxidized graphene quantum dots inhibit the coagulation of graphene particles.
-
5. Water-based graphene suspensions were obtained for the graphites GK-1 and GAK-2 with different sedimentation times. For GAK-2 graphite, the sedimentation time was six days, for GK-1 graphite it was 90 days, and for GK-1+surfactant graphite it was six months.
-
6. The presence of impurities in the graphite suspension negatively affects the liquid-phase exfoliation process of graphite and the stability of the resulting graphene suspensions.
Исследование выполнено за счет гранта Российского научного фонда № 24-29-00593,
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported by the grants the Russian Science Foundation № 24-29-00593,
Список литературы Application of high-speed hydrodynamic technology for the production of graphene nanosuspensions from natural graphites
- Novoselov K. S. et al. Electric Field Effect in Atomically Thin Carbon Films. Science. 2004, Vol. 306, No. 5696, P. 666–669.
- Kauling A. P. et al. The Worldwide Graphene Flake Production. Advanced Materials. 2018, Vol. 30, No. 44, P. 1803784.
- Chen J., Duan M., Chen G. Continuous mechanical exfoliation of graphene sheets via three-roll mill. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, Vol. 22, No. 37, P. 19625.
- Kamel M. S. A., Oelgemöller M., Jacob M. V. Chemical vapor deposition-grown graphene transparent conducting electrode for organic photovoltaics: Advances towards scalable transfer-free synthesis. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews. 2024, Vol. 203, P. 114740.
- Nanda V. Heterogeneous Epitaxy: Designed Peptides Scale Graphene’s Surface. Biophysical Journal. 2016, Vol. 110, No. 11. P. 2291–2292.
- Rasyotra A. et al. A review of low-cost approaches to synthesize graphene and its functional composites. J Mater Sci. 2023, Vol. 58, No. 10, P. 4359–4383.
- Backes C. et al. Production and processing of graphene and related materials. 2D Mater. 2020, Vol. 7, No. 2, P. 022001.
- Johner J. C. F. et al. Sonication-enhanced microfluidization for low-cost graphite exfoliation. Emergent mater. 2024.
- Yi M., Shen Z. Kitchen blender for producing high-quality few-layer graphene. Carbon. 2014, Vol. 78, P. 622–626.
- Paton K. R. et al. Scalable production of large quantities of defect-free few-layer graphene by shear exfoliation in liquids. Nature Mater. 2014, Vol. 13, No. 6, P. 624–630.
- Hernandez Y. et al. High-yield production of graphene by liquid-phase exfoliation of graphite. Nature Nanotech. 2008, Vol. 3, No. 9, P. 563–568.
- Yang R. et al. Synthesis of atomically thin sheets by the intercalation-based exfoliation of layered materials. Nat. Synth. 2023, Vol. 2, No. 2, P. 101–118.
- Liu L. et al. A green, rapid and size-controlled production of high-quality graphene sheets by hydrodynamic forces. RSC Adv. 2014, Vol. 4, No. 69, P. 36464–36470.
- Siburian R. et al. New Route to Synthesize of Graphene Nano Sheets. Orient. J. Chem. 2018, Vol. 34, No. 1, P. 182–187.
- Wang Z. et al. Scalable high yield exfoliation for monolayer nanosheets. Nat Commun. 2023, Vol. 14, No. 1, P. 236.


