Assessment of Industrial Gas Content in the Yamal and Gydan Oil and Gas Bearing Areas
Автор: Shchegolkova A.A.
Журнал: Arctic and North @arctic-and-north
Рубрика: Social and economic development
Статья в выпуске: 54, 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
In accordance with the strategic planning documents of the Russian gas industry, the development of the Yamal and Gydan oil and gas bearing regions is one of the priority tasks, as they are associated with the formation of a strategic reserve of gas resources and the creation of new gas production centers. The article analyses the spatial distribution of natural gas reserves in the oil and gas bearing areas of the Arctic region and concludes that the distribution of free gas resources is uneven both by section and by area. Some oil and gas bearing areas are characterized by a weak degree of geological and geophysical study. Depletion of the base fields in the Pur-Taz and Nadym-Pur oil and gas bearing areas raises the question of shifting the raw material base of the gas industry to the hard-to-reach areas of Yamal and Gydan, including the waters of the Kara Sea, the Ob, Taz and Gydan Bays. The paper provides a quantitative assessment of the level of commercial gas content of the Yamal and Gydan oil and gas bearing areas, including in the context of oil and gas bearing regions. It was determined that based on the technology of field development, processing and transportation scheme when assessing the prospects of development and options for monetization of gas resources, a zone of pipeline transport and a zone of liquefied natural gas are distinguished. Taking into account the current economic conjuncture of Arctic natural gas reserves development, it is reasonable and promising at this point in time to expand the resource base by developing satellite fields in Yamal and Gydan oil and gas bearing regions, which already have developed production, processing, transport and social infrastructure, as well as through additional exploration of discovered and developed fields and deposits.
Yamal oil and gas bearing region, Gydan oil and gas bearing region, natural gas reserves, industrial gas content, monetization of natural gas, pipeline natural gas, liquefied natural gas
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/148329507
IDR: 148329507 | УДК: [338:622.27](571.121)(045) | DOI: 10.37482/issn2221-2698.2024.54.54
Текст научной статьи Assessment of Industrial Gas Content in the Yamal and Gydan Oil and Gas Bearing Areas
DOI:
In accordance with the strategic planning documents defining the strategic development of the oil and gas industry, the main parameters of the industry’s sustainable development have
-
∗ © Shchegolkova A.A., 2024
This work is licensed under a CC BY-SA License been defined, including the expansion and rational use of the hydrocarbon resource base. Under unfavorable conditions and considering the external sanctions pressure on the fuel and energy sector of Russia, it is necessary to revise the model of sustainable development of the oil and gas industry. In this situation, there is a risk of lack of chronological and spatial synchronization of prospecting and exploration work, commissioning of a complex of capacities in the production and development of fields, transportation, storage, processing of natural gas and its valuable components.
Scientists and practitioners have been studying the geological structure of productive deposits of gas fields in the Arctic zone of the West Siberian oil and gas province (WSOGP), improving geophysical methods for exploration of oil and gas resources, and the problems of their safe development [1, Kontorovich V.A., Kontorovich A.E.], [2, Ananenkov A.G., Mastepanov A.M.], [3, Laverov N.P., Bogoyavlenskiy V.I., Bogoyavlenskiy I.V.], [4, Skorobogatov V.A., Kabalin M. Yu.], [5, Lokhov A.S., Gubaidullin M.G., Korobov V.B., Tutygin A.G.], [6, Rakhmangulov R.R., Yusupov R.R., Rasskazov A. A.] and others.
Problems of spatial organization of the development of hydrocarbon resources in the Arctic zone of the Russian Federation (AZRF), analysis of the economic feasibility of implementing oil and gas projects, assessment of an effective scheme for transporting oil and gas resources from Arctic fields are the subject area of research in [7, Kozmenko S., Teslya A., Fedoseev S.], [8, Fadeev A.M., Cherepovitsyn A.E., Larichkin F.D.], etc.
The vector of strategic development of the gas industry is defined in the following documents: Energy Strategy of the Russian Federation until 2035 (2020) 1, which defines the priorities and targets of the state energy policy; Strategy for the development of the mineral resource base (MRB) until 2035 (2018) 2, which determines the directions for the development of geological exploration with the aim of sustainable provision of industry with mineral raw materials; Long-term LNG development program (2021) 3, which describes in detail the scenario and stages of development of the LNG industry in the Russian Federation; the General Scheme for the development of the gas industry until 2035 (2021), which provides details and elaboration of forecasts and directions for the development of the gas industry in order to ensure reliable gas supply, defines target guidelines for the strategic development of the industry, etc.
A significant, but not fully resolved problem in scientific research is the assessment of the industrial gas content of strategically important oil and gas regions from the perspective of spatial organization and directions of monetization of gas resources.
Research in the field of spatial organization of development and monetization of gas resources of deposits in the Arctic region is timely and relevant, since the energy development of the Yamal and Gydan oil and gas bearing areas (OGA) is highlighted as a priority in strategic documents defining the development scheme of the Russian gas industry in the future until 2035; these OGAs are associated with increasing the country’s gas potential.
The purpose of the study is to solve the scientific problem of assessing the level of industrial gas content of the Yamal and Gydan oil and gas fields, to study the spatial organization of the development and monetization of gas resources.
The factual and practical basis of the study is provided by data from the state balance of mineral reserves, official data from gas industry companies, industry strategic planning documents, the results of our own research, etc. During the study, comparative analytical methods were used to interpret geological and geophysical materials, collection and systematization of factual data, statistical methods of economic analysis.
Spatial distribution of natural gas reserves in the West Siberian oil and gas bearing province of the AZRF
According to experts, “the volume of recoverable hydrocarbon reserves in the Arctic fields of Russia is 245 billion tons of standard fuel” [9, Kontorovich V.A.], while about 66% falls on the WSOGP, the northwestern part of which is predominantly gas-bearing with high concentrations Aptian-Albian-Cenomanian deposits. The level of natural gas production in the Arctic regions of the WSOGP is currently at peak level. However, in order to achieve the planned strategic indicators, according to the General Scheme for the development of the oil and gas industry until 2035 (2021), it is necessary to compensate for the falling production of natural gas. The General Scheme’s planned indicators assume a level of natural gas production ranging from 838.3 billion m3 to 1048 billion m3 per year, depending on the scenario — low, medium and high, which are developed on the basis of the availability of potential industrial capacities of the oil and gas sector.
Table 1 presents an analysis of the spatial distribution of natural gas reserves in the Arctic region of the WSOGP.
-
Table 1
Spatial distribution of natural gas reserves in the Arctic region of the WSOGP 4
|
Oil and gas bearing areas of the Arctic part of the WSOGP |
Location of the oil and gas region |
Area of responsibility |
Degree of development / Prospects |
Volume of recoverable reserves, billion m3 |
|
Sverdrupskaya POGA |
Kara Sea shelf |
PJSC Rosneft |
Based on the results of exploration and appraisal drilling, |
>1 300 |
|
Prednovozemelskaya OGA |
PJSC Rosneft |
>500 |
|
South Kara OGA |
PJSC Gazprom |
commercial oil and gas potential was proven, eight OGCFs were discovered on the shelf within the limits of OGA / High production costs, lack of necessary infrastructure and production technologies |
>2 600 |
|
|
Yamal OGA |
Extreme northwest of WSOGP. Yamal Peninsula, water area of the Ob and Baydaratskaya bays |
PJSC Gazprom PJSC NOVATEK |
Degree of exploration - 70% / Resource strategic base of Yamal projects; Resource base of the complex for processing ethanecontaining gas (CPEG) in Ust-Luga; Kamennomyssk Sea using IRP - PJSC Gazprom. Resource strategic base of the Yamal LNG Project, as well as the planned projects: Arctic LNG 2, 3, Ob GCC and LNG - PJSC NOVATEK |
>16 000 |
|
Gydan OGA |
Northern part of the WSOGP. Gydan Peninsula, water area of the Ob, Yuratsk, Gydan and Taz bays |
PJSC Gazprom PJSC NOVATEK PJSC Rosneft |
Degree of exploration - 22% / Development of the Severo- Kamennomyskoe gas condensate field is underway - PJSC Gazprom, Semakovskoe GF - LLC RusGazAlli-ance. Resource strategic base of the Arctic LNG 1 project -PJSC NOVATEK |
>2 200 |
|
Nadym-Pur-Taz region |
Nadym-Purskaya OGA - northeastern part of the WSOGP Pur-Tazovskaya OGA - east of the central part of the WSOGP |
PJSC Gazprom PJSC NOVATEK PJSC Rosneft PJSC Lukoil |
70% of Russia’s natural gas is extracted / declining production, >75% of capacity. Development of projects for HTR extraction |
initial reserves: 32 000 |
|
Yenisei-Khatanga OGA, AZRF part |
Extreme northeast of the WSOGP, the waters of the Gydan Bay and the Yenisei Bay |
PJSC NOVATEK PJSC Rosneft LLC Ermak Neftegaz |
GPW is non-systematic, degree of exploration is <10% / GPW is underway to prepare the Vostok-Oil resource base (oil and LNG production) - PJSC Rosneft |
450 |
An assessment of the spatial distribution of natural gas reserves in the Arctic region of the WSOGP showed that despite the fact that the industrial development of Arctic natural gas deposits has been going on for more than 50 years, some OGAs are characterized by a poor degree of geological and geophysical knowledge.
The gas content of the Yamal and Gydan OGAs was identified as early as in the 1950s with the beginning of geological prospecting work (GPW). The actual implementation of geological exploration in Yamal began in the late 1950s, on the Gydan Peninsula — in the early 1970s. The first field of the Yamal OGA was discovered in 1964 — the Novoportovskoe oil and gas condensate field (OGCF), which is currently the largest in Yamal. In the area of the Gydan OGA, the first field was discovered on the coast of the Ob Bay in 1975 — the Geofizicheskoe OGCF, in 1978 — the Gydanskoe GF and Antipayutinskoe GF. In 1979, in the northern part of the Gydan Peninsula, with a partial location in the waters of the Ob Bay, the Salmanovskoe (Utrennee) OGCF was discovered, which belongs to the category of large ones (since 2012, in accordance with the zoning of oil and gas geological territories, the Salmanovskoe OGCF and the Shtormovoe GF are classified as Yamal OGA).
Industrial gas content of the Yamal oil and gas production area
Within the Yamal OGA, including the adjacent water area, 33 fields with total free gas reserves of over 16 trillion m3 have been discovered; the volume of promising and predicted resources, according to various estimates, is in the range of 7–10 trillion m3 [10, Lyugai D.V., Soin D.A., Skorobogatko A.N.]. Table 2 presents information on the state of free gas reserves and resources of the Yamal OGA in the context of oil and gas bearing regions (OGR), as well as the adjacent water area, based on the data of the State Balance Sheet, the Ministry of Natural Resources and the Federal State Budgetary Institution “Rosgeolfond”. A detailed assessment of the gas resources of the Yamal OGA is presented in the author’s previous works.
-
Table 2
Assessment of free gas reserves and resources of the Yamal OGA 5
|
Oil and gas bearing region, Field |
Free gas, billion m3 |
||
|
Reserves |
Resources |
||
|
А+В 1 +С 1 |
В 2 +С 2 |
D 1 +D 2 |
|
|
Malyginskiy OGR Malyginskoe GCF, Shtormovoe GF (onshore/offshore), Syadorskoe GF, Severo-Obskoe GCF (offshore) |
812.0 |
305.6 |
2 665.3 |
|
Tambeyskiy OGR Yuzhno-Tambeyskoe GCF (onshore/shelf), Severo-Tambeyskoe GCF, Tasiyskoe GCF, Zapadno-Tambeyskoe OGCF, Salmanovskoe (Utrennee) OGCF (onshore/shelf) |
4 044.3 |
743.2 |
558.6 |
|
Nurminskiy OGR Bovanenkovskoye OGCF, Kharasaveyskoe GCF (onshore/shelf), Kruzenshternskoe GCF (onshore/shelf), Yuzhno-Kruzenshternskoe GF, Severo-Bovanenkovskoe GF, Vostochno-Bovanenkovskoe GF, Arktikskoe OGCF, Verkhnetiuteyskoe GF, Zapadno-Seyakhinskoe GCF, Neutinskoe OGCF, Nurminskoe OGCF, Sredneyamalskoe OGCF, Khambateyskoe GCF. |
7 747.4 |
1 394.9 |
1 155.0 |
|
South Yamal OGR (onshore) Novoportovskoe OGCF, Kamennomysskoe GF (onshore), Malo- Yamalskoe GCF, Rostovtsevskoe OGCF, Ust-Yuribeyskoe GF, Blizhnenovoportovskoe GF, Baidaratskoe GCF, Nerstinskoe GF |
498.7 |
173.5 |
897.6 |
|
Yuzhno-Yamalsky OGR (water area) Kamennomysskoe GF (shelf), Kamennomysskoe GF - sea, Obskoe GF |
561.0 |
- |
1 836.6 |
|
Total for Yamal OGA |
13 663.4 |
2 617.2 |
7 113.1 |
As the analysis of Table 2 shows, commercial gas content has been established in all oil and gas bearing areas of the Yamal OGA, except for the potential Shchuchinskiy OGR (POGR), which is also a part of the Yamal OGA. Within the Yamal OGA, the most promising are the Tambeyskiy and Nurminskiy OGRs, they account for 85% of proven natural gas reserves, while in recent years the volumes of recoverable reserves have been revised upward for the Tambeyskoe group of fields, as well as the Kharasaveyskoe and Kruzenshternovskoe fields. Two major gas accumulation centres — the Bovanenkovo and Tambay clusters — were formed in these fields.
Natural gas exploration in the South Yamal OGR is uneven. The South Yamal OGR is considered to be predominantly oil-bearing. In 1964, the Novoportovskoe OGCF was discovered, which is the largest on the Yamal Peninsula with recoverable oil and condensate reserves of more than 250 million tons, natural gas — 320 billion m3. Among the regions of the Yamal OGA, the share of proven reserves and predicted resources of natural gas in the territory of the South Yamal OGR does not exceed 7% of the total volume, in contrast to the water area of this OGR, where LLC Gaz- prom Dobycha Yamburg is developing the Kamennomysskoe-Sea GF, discovered in 2000 and classified as unique with proven reserves of 555 billion m3.
The Malyginsky OGR is the least explored, the degree of exploration does not exceed 30%; geological and geophysical exploration of Neocomian and Jurassic deposits is being actively carried out here. In addition, in 2018, in the North Ob subsoil area in the northern part of the Gulf of Ob, LLC Arctic LNG-3 opened a new gas field, classified as a large field with proven reserves of over 320 billion m3.
The previously conducted analysis by type of deposits allows us to assess the nature and degree of prospects for the industrial development of a given oil and gas deposit. According to experts, the key dominant complex in Yamal is the Albian-Cenomanian and Aptian. “Natural gas, concentrated in the Aptian-Albian-Cenomanian formations, lies at a depth of 700–1500 meters. This is dry (energy) natural gas” [11, Shchegolkova A.A.], its composition is dominated by methane hydrocarbons. The main feature is that natural gas from these formations is used without preliminary processing.
-
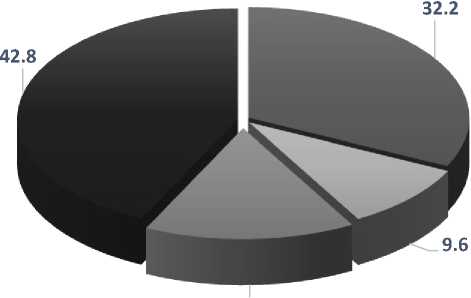
Figure 1 shows the nature of the productivity of the Yamal OGA by fields of the distributed fund (Fig. 1).
15.4
■ Albian-Cenomanian
- Jurassic
■ Neocomian
(Valanginian)
■ Aptian
Fig. 1. Natural gas deposits of the Yamal OGA (compiled by the author).
The largest accumulations in the Aptian-Albian-Cenomanian strata were identified in the Tambeyskoe and Nurminskoe OGRs. As for promising and prospective resources, according to experts, most (over 50%) of natural gas is concentrated in Jurassic and pre-Jurassic deposits. According to specialists from Gazprom, the resources of Jurassic deposits in the northwestern part of the WSOGP amount to 10–40 billion tons of fuel equivalent. In Jurassic formations, natural gas is at a depth of 3400–4000 m “... in the zone of anomalously high formation pressure” [9, Kontorovich V.A.]. In addition to high capital costs, drilling of such wells involves the development of a unique set of modern engineering and geological surveys and technological solutions.
Industrial gas content of the Gydan oil and gas production area
The Gydan OGA is an area of predominant gas accumulation. Large-scale development of these territories began at the beginning of the 21st century. Within the Gydan OGA, including the adjacent waters of the Ob and Taz bays, 16 fields with total free gas reserves of 2234.0 billion m3 have been discovered; the volume of promising and predicted resources is about 8 trillion m3. Table 3 presents information on the status of free gas reserves and resources in the Gydan OGA in terms of oil and gas bearing regions (OGR) based on the data of the State Balance Sheet, the Ministry of Natural Resources and the Federal State Budgetary Institution “Rosgeolfond”.
Table 3
Assessment of free gas reserves and resources of the Gydan OGA 6
|
Oil and gas bearing region, Field |
Free gas, billion m3 |
Degree of development |
Subsoil user |
|
|
Reserves АВС 1 +С 2 |
Resources D 0 +D 1л +D 2 |
|||
|
Severo-Gydanskiy POGR |
||||
|
Exploration drilling is underway in Severo-Gydanskiy POGR |
- |
1 244.3 |
prospect. |
LLC Arctic LNG 1 |
|
Total for Severo-Gydanskiy POGR |
- |
1 244.3 |
||
|
Gydanskiy OGR |
||||
|
Gydanskoe GF |
116.1 |
528.6 |
prospect. |
LLC Arctic LNG 1 |
|
Total for Gydanskoe GF |
116.1 |
528.6 |
||
|
Napalkovskiy OGR |
||||
|
Geofizicheskoe OGCF (onshore/shelf) |
413.0 |
100.0 |
prospect. |
LLC Arctic LNG 1 |
|
Soletsko-Khanaveyskoe GCF |
154.7 |
2 028.3 |
prospect. |
LLC Arctic LNG 1 |
|
Trekhbugornoe GF |
6.0 |
1 027.0 |
prospect. |
LLC Arctic LNG 1 |
|
Vostochno-Bugornoe GCF |
<10 |
n/d |
prospect. |
LLC Arctic LNG 1 |
|
Im. V.I. Giri GCF (including the entire Bukharinskiy sector) |
52.0 |
1 190.0 |
prospect. |
LLC Arctic LNG 1 |
|
Total for Napalkovskiy OGR |
631.7 |
4 345.3 |
||
|
Messovskiy OGR |
||||
|
Vostochno-Minkhovskoe GF Minkhovskoe GF |
210.0 |
330.0 |
prospect. |
PJSC Rosneft |
|
Tota-Yakhinskoe GF (on-shore/shelf) |
1.6 |
426.4 |
prospect. |
PJSC Gazprom |
|
Semakovskoe GF (onshore/shelf) |
320.5 |
30 |
develop. |
LLC RusGazAlliance (JV of PJSC Gazprom and JSC RusGazDobycha) |
|
Parusovoe OGCF Severo-Parusovoe OGCF Yuzhno-Parusovoe OGCF |
>100.0 |
208.7 |
prospect. |
LLC RusGazAlliance (JV of PJSC Gazprom and JSC RusGazDobycha) D/SRM for the NorthWestern Federal District, on the continental shelf and in the world ocean |
|
Severo-Kamennomysskoe GCF (shelf) |
432.0 |
- |
develop. |
LLC Gazprom Dobycha Yamburg |
|
Antipayutinskoe GF (onshore/shelf) |
340.4 |
800.0 |
prospect. |
PJSC Gazprom |
|
Chugoryakhinskoe GCF (shelf) |
81.7 |
- |
prospect. |
LLC Gazprom Dobycha Yamburg |
|
Total for Messovskiy OGR |
1 486.2 |
1 795.1 |
||
|
Total for Gydanskiy OGA |
2 234.0 |
7 913.3 |
||
The Gydan OGA belongs to the category of the least studied WSOGP; its development has been repeatedly postponed due to the high degree of inaccessibility [12, Kontorovich A.E.], “complete absence of industrial and social infrastructure” [11, Shchegolkova A.A.], as well as the environmental component, which is expressed in the weak susceptibility of the environment to technogenic loads, which can lead to a long period of its self-recovery [13, Agarkov S.A., Saveliev A.N., Kozmenko S.Y., Ulchenko M.V., Shchegolkova A.A.]. The problem is aggravated by complex natural and climatic conditions — the presence of perennial frozen rocks 7, the spread of permafrost, saline and heaving soils, thermokarst and thermo-erosion processes, a high degree of swamping, thick layers of underground monolithic ice in the lowlands, which reach 300–400 meters [14, Kok-ko K.T., Buanes A., Koivurova T., Masloboev V., Pettersson M.].
The industrial gas content of the Gydan OGA has been established in three OGRs: Gydan-skiy, Napalkovskiy and Messovskiy. The highest degree of exploration was recorded in the south- ern part of the Gydan Peninsula, as well as the waters of the Ob, Gydan and Taz Bays — the exploration coefficient reaches 0.45.
The overwhelming majority of industrial natural gas deposits of the Gydan OGA are concentrated in the Aptian-Albian-Cenomanian formations, as well as Neocomian (Valanginian) deposits. Unlike the Yamal, natural gas reserves in the Cenomanian reservoir of the Gydan OGA are not so significant. The best potential, according to expert estimates, is found in the Aptian reservoirs, which contain significant reserves of natural gas [15, Toropova T.N. Kontorovich V.A.], [16, Kontorovich V.A., Toropova T.N., Shcherbanenko V.M.]. The prospects for the gas content of the Gydan OGA are associated with the reservoir deposits of the Jurassic oil and gas complex.
Zonal development of natural gas resources of the Yamal and Gydan OGAs
The implementation of the strategic objectives of the gas industry in the Yamal and Gydan OGAs, enshrined in the General Scheme for the development of the gas industry and the Longterm LNG development program in the Russian Federation, allows us to distinguish two zones for the development of natural gas resources, based on options for their monetization:
-
1. Pipeline transport zone. It is the area of responsibility of PJSC Gazprom, JSC RusGazDobycha and their joint venture. It is represented in the Yamal OGA by the northwestern and southeastern coasts, as well as the southern part of Yamal; in the Gydan OGA — by the northern part of the Tazovskiy Peninsula, as well as the Yamal shelf, Ob and Taz bays.
-
2. Liquefied natural gas (LNG) zone. It is the area of responsibility of PJSC NOVATEK and its subsidiaries. The LNG cluster is located in the Yamal OGA in the eastern and northeastern parts of the Yamal Peninsula and the northern part of the Ob Bay; in the Gydan OGA — in the north of the Gydan Peninsula, including its coast with access to the waters of the Ob and Gydan bays.
Table 4 presents an assessment of the prospects for the development and monetization of natural gas resources located in the pipeline transport zone according to the data of PJSC Gazprom.
Table 4
Assessment of the prospects for the development and monetization of natural gas resources in the pipeline transport zone 8
|
Field |
Location |
Project description |
Gas transportation |
Timeframe |
|
Bovanekovo Industrial Group, projects of PJSC Gazprom (8.9 trillion m3) |
||||
|
Bovanenkovskoe OGCF |
North-western coast of the Yamal Peninsula |
Three gas fields were commissioned: 2012, 2014, 2018 (total annual production capacity of 115 billion m3/year) |
MGP Bovanenkovo — Ukhta — Torzhok 1, 2, 3 (2023) |
2012 |
|
Kharasaveyskoe GCF |
North-western coast of the Yamal Peninsula with access to the water |
|
|
2023 |
|
area of Bai-daratskaya Bay |
|
ern corridor of the Arctic GTS. |
||
|
Kruzenshternskoe GCF Yuzhno- Kruzenshternskoe GF |
A feasibility study is underway, which includes:
|
|
2028 |
|
|
Semakovskiy cluster, a joint venture project between PJSC Gazprom and JSC RusGazDobycha (420 billion m3). |
||||
|
Semakovskoe GF |
Northern coast of the Tazov-skiy Peninsula with access to the water area of the Taz Bay |
Development of the field from shore by means of an ERD well (horizontal well, design bottom hole -3663 m, vertical depth - 849 m, vertical offset - 3045 m, KERD 3.46) and an offshore production complex (14.2 billion m3/year). |
Semakovskoe - CGTU OGCF Severo-Parusovoe - GTU OGCF Parusovoe - Gas Compressor Station (GCS) Yamburgskaya (122 km), further along the central corridor of the Arctic GTS |
December 2022 |
|
Parusovoe OGCF |
Northern part of the Tazov-skiy Peninsula |
An investment decision on development has been made, and project documentation has been approved. |
2025 |
|
|
Severo-Parusovoe OGCF |
2027– 2029 |
|||
|
Southern industrial group (Novoportovsk oil and gas accumulation hub), projects of PJSC Gazprom (1.3 trillion m3) |
||||
|
Novoportovskoe OGCF (leading raw material - oil) |
South of the Yamal Peninsula |
“A complex of technological and auxiliary facilities has been introduced: for associated petroleum gas (APG) - 11.03 billion m3, natural gas - 5.07 billion m3. Associated petroleum gas (APG) is compressed at the gas treatment facility -8.59 billion m3 POG utilization - 95%, of which:
|
Yamal Gas - Yamburg -Tula I, II subsea GP connection (115.5 km, including subsea part of the GP - 58.4 km) |
October 2021 |
|
Kamennomysskoe GF |
South-eastern coast of the |
"Development of a technical and com- |
It is possible to connect the Semakovskoe and |
n/d |
|
Yamal Peninsula with access to the Gulf of Ob Bay |
mercial proposal for the implementation of FEED; preparation of a technical scheme for the development of the PK1 reservoir (Cenomanian layer)” [11] |
Pribrezhnoe clusters to the ETA, further along the central corridor of the Arctic GTS |
||
|
Blizhnenovo- Portovskoe GF |
South of the Yamal Peninsula |
“It is a pilot site of PJSC Gazprom for the extraction of minerals from Paleozoic sediments” [11] |
GP connection of the Khambateyskoe CGTU GCF - Malo-Yamalskoe GCF - Blizhnenovopor-tovskoe CGTU GCF -Novoportovskoe CGTU OGCF - Gaz Yamal GP -Yamburg MGP - Tula I, II MGP |
2023 |
|
Malo-Yamalskoe GCF |
Design and survey work on the arrangement has been completed |
2023– 2025 |
||
|
Khambateyskoe GCF |
South-eastern coast of the Yamal Peninsula with access to the Gulf of Ob Bay |
2023– 2025 |
||
|
Coastal cluster, projects of PJSC Gazprom, as well as joint ventures of PJSC Gazprom and JSC RusGazDobycha (> 1000 billion m3, 60 billion m3/year) |
||||
|
Kamennomysskoye GF — sea |
Ob Bay water area, Kamenny Cape area |
The development of GF is supposed to be carried out through an ice-resistant stationary platform (ISP) and satellite ice-resistant block conductors (30 billion m3/year). |
Two lines of the subsea GP and GP-connection: GP GF Kamenno-mysskoe-Sea / GF Severo- Kamennomysskoe -CGTU OGCF Severo-Parusovoe - GCS Yam-burgskaya, further along the central corridor of the Arctic GTS |
2025 |
|
Severo- Kamennomysskoe GCF |
Gulf of Ob water area, junction of the Ta-zovsky, Yamal and Gydan peninsulas |
2027 |
||
|
Tota-Yakhinskoe GF |
Southern coast of the Gydan Peninsula with access to the Taz Bay water area |
GF development projects are under development. Development of GF from the shore through an ERD well. |
|
2030 |
|
Antipayutinskoe GF |
||||
|
Chugoryakhinskoe GCF |
Junction of the Taz and Ob Bays |
GF development projects are under development. The development of GF is supposed to be carried out through ISP and satellite ice-resistant block conductors. |
Lines of the subsea GP and GP-connection from the GF to the ETA of the Semakovskoe and Pribrezhnoe clusters, — GCS Yamburgskaya |
|
|
Obskoe GF |
Gulf of Ob water area 20 km NW of Yamburg |
|||
The Arctic gas transportation system (GTS) includes field and main gas pipelines. “The specificity of the Arctic GTS lies in the fact that gas pipelines in this area are built and operated in difficult natural and climatic conditions — in permafrost zones, in the presence of numerous natural obstacles (rivers, lakes, wetlands, etc.)” [17, Shchegolkova A.A.]. The renewal of the Arctic gas transportation infrastructure began with the intensification of GPW and additional exploration of natural gas fields in the Yamal and Gydan OGAs, and the discovery of unique fields. “The formation of a comprehensive Arctic GTS includes the construction and increase in the capacity of existing main, field and distribution gas pipelines, compressor and gas distribution stations” [17].
Transportation of natural gas from the Arctic fields of the Yamal and Gydan OGAs is carried out in two directions:
-
• along the northern corridor from the fields of the Bovanenkovo industrial group, represented by the main gas pipeline (MGP) Bovanenkovo — Ukhta — Torzhok 1, 2, 3 (built in 2012-2023);
-
• along the central corridor from the fields of the Yuzhnaya industrial group, Semakovskiy and Pribrezhnyy clusters, represented by the MGP Progress (export) Yamburg — Western border; MGP system Yamburg — Tula I, II; MGP system Yamburg — Yelets I, II; MGP system Yamburg — Volga region (built in the 1980s - early 1990s).
Table 5 presents an assessment of the prospects for the development and monetization of natural gas resources in the LNG zone (according to PJSC NOVATEK).
Table 5
Assessment of the prospects for the development and monetization of gas resources in the LNG zone 9
|
Field |
Location |
Project description |
LNG transportation |
Timeframe |
|
Resource base of the Yamal LNG project, PJSC NOVATEK |
||||
|
Yuzhno- Tambeyskoe GCF |
North-eastern coast of the Yamal Peninsula with access to the Gulf of Ob water area |
The GCF is developed through the operation of 208 directional wells. Liquefaction technology "Arctic Cascade" has been developed, which is based on utilisation of the Arctic climate. Four LNG production lines with a capacity of 17.4 million tons (24 billion m3)/year, actually 21 million tons (29 billion m3) in 2022. Transport and infrastructure facilities: - Sabetta airport, - Sabetta terminal (port) |
A fleet of 15 Arc7 ice-class tankers was formed |
2017 |
|
Resource base of the Arctic LNG 2 project, PJSC NOVATEK |
||||
|
Salmanovskoe (Utrennee) OGCF (onshore/shelf) |
Northern part of the Gydan Peninsula, partly on the eastern shore of the Gulf of Ob with access under the |
LNG plant on gravity-fuelled bases (GFBs) Three LNG production lines PM 19.8 million tons (27.3 billion m3)/year - LNG; 1.6 |
A fleet of 21 Arc7 ice-class tankers is being formed: - SBC Zvezda - 15 tankers; - Daewoo Shipbuild- |
2023 (1st line), 2024, 2026 |
|
water area |
million tons/year of GC. Construction of transport and infrastructure facilities: - Utrenniy airport, - terminal (port) Utrenniy |
ing & Marine Engineering (DSME) - 6 tankers (after the contract was cancelled in 2022, the counter-agent was changed). Tanker delivery dates are synchronised with the launch of the lines |
||
|
Stormovoe GF (onshore/shelf) |
Northern part of the Gydan Peninsula, with access to the water area of the Ob and Gydan Bays |
|||
|
Resource base of the Ob MCC and LNG project, PJSC NOVATEK |
||||
|
Verkhnetiuteyskoe GF |
Eastern part of the Yamal Peninsula |
Engineering surveys are underway. LNG plant: in June 2022, a decision was made to use the Arctic Cascade liquefaction technology, three LNG production lines, 4.8 million tons (6.6 billion m3)/year MCC plant: production from LNG - 2.2 million tons of ammonia, 130.000 tons of hydrogen |
An investment decision is expected. |
possibly after 2024, in September 2022 the project was announced to be suspended |
|
Zapadno- Seyakhinskoe GCF |
||||
|
Arcticheskoe OGCF |
||||
|
Neutinskoe OGCF |
||||
|
Resource base of the Arctic LNG 1 project |
||||
|
Gydanskoye GF |
Northern part of the Gydan Peninsula |
GPW and additional field exploration is underway. Arctic LNG 1 will be realised under the Arctic LNG 2 project The project includes: - three LNG production lines, 19.8 million tons (27.3 billion m3)/year - LNG; 1.6 million tons/year of GC; - a cargo terminal in the Tazovskiy district in the area of responsibility of Arctic LNG 1 |
An investment decision on the Arctic LNG 1 project is expected at the end of 2023. Contractors and investors for the construction of tankers for the Arctic LNG 1 project have not been determined. |
possibly after 2027 |
|
Soletsko- Khanaveyskoe GCF |
||||
|
Geofizicheskoe OGCF |
North of the Gydan Peninsula on the eastern shore of the Gulf of Ob, with access under the water area of the Gulf of Ob (Geof-izicheskoe) |
|||
|
Trekhbugornoe GF |
||||
|
Vostochno- Bugornoe GCF |
||||
|
Im. V.I. Giri GCF (Bukharinskiy sector) |
||||
|
Resource base of the Arctic LNG 3 project, PJSC NOVATEK |
||||
|
Severo-Obskoe GCF |
Northern part of the Ob Bay water area |
Exploratory drilling is underway. Production parameters and LNG technology have not been approved. Estimated production capacity is 19.8 million tons (27.3 billion m3)/year - LNG. |
The parameters of the tanker fleet for the Arctic LNG 3 project have not been determined. |
resource base is being explored |
The LNG cluster is allocated in accordance with the projects for the construction of LNG plants of PJSC NOVATEK, as well as the Long-term program for the development of LNG in the Rus- sian Federation. The organization of LNG production and transportation makes it possible to differentiate supply directions, overcoming sanction restrictions on pipeline gas [18, Kozmenko S.Yu., Masloboev V.A., Matviishin D.A.], “is a tool for the economic development of the regional space, aimed at creating sustainable model of development of the Russian Arctic” [19, Agarkov S.A., Bo-goyavlenskiy V.I. et al.].
In addition to the above zones for the development of natural gas resources, a third zone can be distinguished (Table 6), which includes promising fields of the Tambeyskaya and Minkhovskaya industrial groups with an uncertain scheme of gas resources transportation.
Table 6
Assessment of the prospects for the development and monetization of gas resources of the Tambeyskaya and Minkhovskaya industrial groups 10
|
Field |
Location |
Project description |
LNG transportation |
Timeframe |
|
Tambeyskaya Industrial Group, JV projects of PJSC Gazprom and JSC RusGazDobycha (7.3 trillion m3) |
||||
|
Tambeyskoye OGCF (Severo-Tambeyskoe, Za-padno-Tambeyskoe, Tasiyskoe, Malyginskoe). EGPC resource base in Ust-Luga. |
North-eastern coast of the Yamal Peninsula |
GPW and additional exploration of the fields using directional drilling is underway. Development of a feasibility study for a vertically integrated PFS production, transportation and processing project |
Several transportation options are being considered:
|
2026 |
|
Minkhovskiy cluster, PJSC Rosneft project |
||||
|
Vostochno-Minkhovskoe GF Minkhovskoe GF |
Southern coast of the Gydan Peninsula |
GPW and additional exploration of the GF using the total depth method is underway, and the volume of reserves has been specified. In the course of GF development Jet Pump technology, which was previously used for oil facilities, was applied. Perspective objects were prepared, including those not accounted for on the state balance sheet of the Russian Federation |
Several transportation options are being considered: - gas supply to Gazprom's GTS based on the creation of a joint venture between Rosneft and Gazprom-Neft using the infrastructure of the Vos-tochno-Messoyakhskoe OGCF; - construction of an LNG plant |
resource base is being explored |
The Tambeyskaya industrial group is the area of responsibility of the joint venture between PJSC Gazprom and JSC RusGazDobycha. The fields of this group represent the resource base of the ethane-containing gas processing complex (EGPC) in Ust-Luga, however, the transportation scheme has not yet been approved, as well as for the Minkhovskiy industrial cluster, which is located in the area of responsibility of PJSC Rosneft, where several options for monetization of gas resources are being considered: gas supply to Gazprom’s GTS based on the creation of a joint venture between Rosneft and Gazpromneft using the infrastructure of the Vostochno-Messoyakhskoe oil and gas condensate field, construction of an LNG plant.
Conclusion
-
1. The assessment of the spatial distribution of gas resources in the AZRF of the WSOGP has shown that the least studied, but at the same time promising in terms of discovery of large natural gas fields, is the northern and north-western part of the WSOGP, which includes the Yamal and Gydan OGAs, including the adjacent waters of the Kara Sea, the Gulf of Ob, Taz and Gydan bays. The main prospects for growth of the natural gas resource base are associated with these OGAs against the background of declining production in the Pur-Taz and Nadym-Pur OGAs by all main parameters (number of discovered fields, explored hydrocarbon reserves, range of productivity, etc.).
-
2. Industrial gas content has been established in all oil and gas bearing areas of the Yamal and Gydan OGAs, but this indicator varies for individual OGRs. The degree of industrial “exploration of natural gas reserves in the Yamal OGA is quite high” [11, Shchegolkova A.A.], the exploration coefficient for the entire OGA reaches 0.7, which indicates that the oil and gas potential in this OGA has been established and studied quite thoroughly. The Gydan OGA is characterized by uneven distribution of free gas resources both in section and area. The degree of industrial exploration of natural gas reserves of the entire Gydan OGA is low, the exploration coefficient is 0.22. The main reason lies in the fact that geological exploration is predominantly local in nature, concentrated within the boundaries of the licensed areas of oil and gas companies at specific oil and gas promising sites and fields. The structure of reserves in these oil and gas bearing areas is quite complex and unequal: both in terms of the depth of occurrence and the nature of productivity, and because of the remoteness from the UGSS of Russia, areas with developed social and transport infrastructure.
-
3. The depletion of basic fields in the Pur-Tazovskaya and Nadym-Purskaya OGAs raises the question of shifting the raw material base of the gas industry to hard-to-reach areas of the Yamal and Gydan OGAs, including the waters of the Kara Sea, the Ob, Tazovskaya and Gydanskaya bays, which implies the creation of a production, transport and social infrastructure with mandatory synchronization in terms of: prospecting and exploration, commissioning of a complex of capacities in the production and development of fields, transportation, storage, processing of natural gas and its valuable components, distribution among consumers. The level of natural gas production at the level of 838.3–1048 billion m3 per year declared in strategic documents by 2035 in the context of geopolitical confrontation and unprecedented sanctions pressure requires the adoption of strategically calibrated decisions on the development of newly discovered natural gas fields and the development of gas business projects. Based on the mining and geological characteristics of the deposits, natural and climatic conditions, environmental safety, the presence of industrial and
-
4. Based on field development technology, processing and transportation schemes, when assessing the prospects for the development and monetization of gas resources, a pipeline transport zone and an LNG zone are distinguished. The pipeline transport zone of the Yamal and Gydan OGAs is represented by gas clusters located within the scope of operation of the northern and central corridors of the Arctic GTS. When building an optimal scheme for the monetization of natural gas through the Arctic GTS, it is promising to connect newly discovered wells and fields of the Yamal and Gydan OGAs to the UGSS using field pipelines. “For coastal fields, options are possible for deep drilling and development of gas resources from the shore using onshore drilling equipment through an ERD well with subsequent transportation of hydrocarbons to onshore technological complexes using a pipeline system, integration of offshore gas transportation infrastructure into existing or newly created ones, following the example of those being implemented gas projects in the Ob and Taz Bays” [17, Shchegolkova A.A.].
social infrastructure, as well as taking into account the current economic situation in the development of Arctic natural gas reserves, the most justified and promising at the moment is the expansion of the resource base through the development of satellite fields and a number of coastal fields in the Yamal and Gydan OGAs that already have a developed mining, processing, transport and social infrastructure, as well as through additional exploration of open and developing fields and deposits.
The LNG zone is represented by fields that are the resource base for both ongoing and potential LNG projects of PJSC NOVATEK, located in an area of high inaccessibility — the northeastern and eastern coasts of the Yamal Peninsula and the north of the Gydan Peninsula, including the water area. Proven liquefied natural gas production technologies will be optimal for the design of LNG projects in the AZRF: “Arctic Cascade”, which is based on the use of the characteristics of the Arctic climate, domestic technologies and equipment (Yamal LNG), as well as the production of liquefaction lines on gravity-type foundations (Arctic LNG 2) subject to synchronization with the construction of Arc7 ice-class tankers.
Список литературы Assessment of Industrial Gas Content in the Yamal and Gydan Oil and Gas Bearing Areas
- Kontorovich V.A., Kontorovich A.E. Geological Structure and Petroleum Potential of the Kara Sea Shelf. Doklady Earth Sciences, 2019, vol. 489, no. 1, pp. 1289–1293. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1028334X19110229
- Ananenkov A.G., Mastepanov A.M. Gazovaya promyshlennost' Rossii na rubezhe XX i XXI vekov: nekotorye itogi i perspektivy: monografiya [Russian Gas Industry at the Turn of the 20th and 21st Centuries: Some Results and Prospects]. Moscow, Gazoil Press Publ., 2010, 303 p.
- Laverov N.P., Bogoyavlensky V.I., Bogoyavlensky I.V. Fundamental Aspects of the Rational Develop-ment of Oil and Gas Resources of the Arctic and Russian Shelf: Strategy, Prospects and Challenges. Arktika: ekologiya i ekonomika [Arctic: Ecology and Economy], 2016, no. 2 (22), pp. 4–13.
- Skorobogatov V.A., Kabalin M.Yu. Zapadno-Arkticheskiy shel'f Severnoy Evrazii: zapasy, resursy i dobycha uglevodorodov do 2040 i 2050 gg. [West Arctic Shelf of Northern Eurasia: Reserves, Re-sources and Hydrocarbon Production up to 2040 and 2050]. Neftegaz.RU, 2019, no. 11 (95), pp. 36–51.
- Lokhov A.S., Gubaidullin M.G., Korobov V.B., Tutygin A.G. Geographical and Ecological Land Zoning of Onshore Oil Pipeline Location by Level of Hazard to Environment from Emergency Oil Spills in Arctic Region. Theoretical and Applied Ecology, 2020, no. 4, pp. 43–48. DOI: https://doi.org/10.25750/1995-4301-2020-4-043-048
- Rakhmangulov R.R., Yusupov R.R., Rasskazov A.A. Searching for the Jurassic Period: Drilling Deep Horizontal Wells under HPHT Conditions. Burenie i Neft'' [Drilling and Oil], 2019, no. 12, pp. 42–45.
- Kozmenko S., Teslya A., Fedoseev S. Maritime Economics of the Arctic: Legal Regulation of Environ-mental Monitoring. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2018, vol. 180 (1), art. 012009. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/1755 1315/180/1/012009
- Fadeev A.M., Cherepovitsyn A.E., Larichkin F.D. Strategicheskoe upravlenie neftegazovym kom-pleksom v Arktike [Strategic Management of the Oil and Gas Complex in the Arctic]. Apatity, KSC RAS Publ., 2019, 289 p. DOI: https://doi.org/10.25702/KSC.978.5.91137.407.5
- Kontorovich V.A. A Model of the Geologic Structure and the Oil and Gas Prospects of Neocomian (Berriasian-lower Aptian) Sediments of the West Siberian Arctic Regions and the Kara Sea Shelf. Ge-ologiya i Geofizika [Russian Geology and Geophysics], 2020, vol. 61, no. 12, pp. 1735–1755. DOI: https://doi.org/10.15372/GiG2020154
- Lyugay D.V., Soin D.A., Skorobogatko A.N. Features of Oil-Gas-Bearing Capacity of Yamal Peninsular in Respect to Estimation of Prospects for a Southern Part of Kara Sea. Nauchno-tekhnicheskiy sbornik. Vesti gazovoy nauki [Scientific and technical collection. News of gas science], 2017, no. 3 (31), pp. 29–35.
- Shchegolkova A.A. Spatial Organisation of Gas Resources Development in the Yamal Oil and Gas Bearing Region. Arktika i Sever [Arctic and North], 2021, no. 45, pp. 61–74. DOI: https://doi.org/10.37482/issn2221-2698.2021.45.61
- Kontorovich A.E. Ways of Developing Oil and Gas Resources in the Russian Sector of the Arctic. Her-ald of the Russian Academy of Sciences, 2015, vol. 85, no. 3, pp. 213 222. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1019331615030120
- Agarkov S.A., Kozmenko S.Y., Saveliev A.N., Ulchenko M.V., Shchegolkova A.A. Spatial Organization of Economic Development of Energy Resources in the Arctic Region of the Russian Federation. Journal of Environmental Management and Tourism, 2018, vol. 9, no. 3 (27), pp. 605 623. DOI: https://doi.org/10.14505/jemt.v9.3(27).21
- Kokko K.T., Buanes A., Koivurova T. et al. Sustainable Mining, Local Communities and Environmental Regulation. Barents Studies: Peoples, Economies and Politics, 2015, vol. 2 (4), no. 1, pp. 51 81.
- Toropova T.N., Kontorovich V.A. Structural History and Petroleum Potential of the Central Part of the Gydan Peninsula (Northeast of Western Siberia). Neftegazovaya Geologiya. Teoriya i Praktika [Petroleum Geology Theoretical and Applied Studies], 2019, vol. 14, no. 3, 25 p. DOI: https://doi.org/10.17353/2070-5379/28_2019
- Kontorovich V.A., Toropova T.N., Shcherbanenko V.M. Model of Geological Structure and Petroleum Perspective of Neocomian Strata Belonging to Gydan Area (Underpim Regional Clinoform). Nefte-gazovaya Geologiya. Teoriya i Praktika [Petroleum Geology Theoretical and Applied Studies], 2022, vol. 17, no. 4. DOI: https://doi.org/10.17353/2070-5379/37_2022
- Shchegolkova A.A. Spatial Organization of the Arctic Gas Transportation System. Regional'nye Prob-lemy Preobrazovaniya Ekonomiki [Regional Problems of Economic Transformation], 2022, no. 10 (144), pp. 11–18. DOI: https://doi.org/10.26726/1812-7096-2022-10-11-18
- Kozmenko S.Yu., Masloboev V.A., Matviishin D.A. Justification of Economic Benefits of Arctic LNG Transportation by Sea. Zapiski Gornogo Instituta [Journal of Mining Institute], 2018, vol. 233, pp. 554–560. DOI: https://doi.org/10.31897/PMI.2018.5.554
- Agarkov S.A., Bogoyavlensk V.I., Kozmenko S.Yu. et al., eds. Global'nye tendentsii osvoeniya energet-icheskikh resursov Rossiyskoy Arktiki. Chast'. I. Tendentsii ekonomicheskogo razvitiya Rossiyskoy Arktiki [Global Trends in the Development of Energy Resources in the Russian Arctic. Part. I. Trends in Economic Development of the Russian Arctic]. Apatity, KSC RAS Publ., 2019, 170 p.


