Bioactive Components and Chemical Constituents of Some Important Legumes in Traditional Medicine
Автор: Mohamad Hesam Shahrajabian, Wenli Sun, Qi Cheng
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 4 т.16, 2021 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Legumes in traditional medicine play a key role in the world. In majority of countries, especially in Iran and China, western and traditional medicine has been practiced side by side of each other. The aim of this study is to review bioactive components and chemical constituents of some important legumes in East of Asia. All relevant papers in English language of researchers and scholars from various countries gathered. The soybean itself is composed of approximately 40% protein, 20% oil, 35% carbohydrates, and 5% trace minerals and other compounds. The most important functional components of soy are α-Linolenic acid, isoflavones, lecithins, lectins, linoleic acid, peptides, phytosterols, protein and saponin. Peanuts are considered an important source of oil, folate, antioxidants, protein, and essential fatty acids (linoleic), and it ranked fourth in oilseed crops in the world after soybeans, rapeseed, and cotton. Peanuts are considered an important source of oil, folate, antioxidants, protein, and essential fatty acids (linoleic), and it ranked fourth in oilseed crops in the world after soybeans, rapeseed, and cotton. It has been revealed the presence of flavonoids, tannins, terpenoids, saponins, steroids, alkaloids by positive reaction with the respective test reagent. Cow peas are valuable source of protein, carbohydrate, mineral and vitamins, and it also contain biologically active components including phenols, phytic acid, saponin, oligosaccharides, fiber and etc. Nutrition therapy according to traditional Asian medicine by considering tremendous benefits of legumes is quite effective at not only treating common diseases, but also its prevention.
Soybean, Peanuts, Cowpea, Bioactive Components, Legume, Traditional Medicine
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/143178312
IDR: 143178312
Текст научной статьи Bioactive Components and Chemical Constituents of Some Important Legumes in Traditional Medicine
Legumes are indispensable for human diet in respect to their valuable and nutritive bioactive molecules (Soleymani et al. , 2011a,b,c; Soleymani and Shahrajabian, 2012; Soleymani et al. , 2012a,b; Yong et al. , 2018). Among the species of medicinal plants, some are mainly confined to folk medicine and some are used as occasional or local substitutes for the main species listed in the Materia Medica (Soleymani and Shahajabian, 2018; Sun et al. , 2019a,b; Shahrajabian et al. , 2019a,b,c; Shahrajabian et al. , 2021a,b,c,d). Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has a history of thousands of years it is formed by summarizing the precious experience of understanding life, maintaining health, and fighting diseases accumulated in daily life, production and medical practice (Ogbaji et al. , 2013; Ogbaji et al. , 2018; Shahrajabian et al. , 2019d,e,f,g,h,I; Sun et al. , 2021a,b,c). Soybean has been one of the most important sources of vegetable-sourced proteins (Ziegler et al. , 2016). The soybean ( Glycine Max . (L.) Merrill ) is a leguminous which has been originated from China and has been cultivated for more than five thousand years and it has been considered as a stable food in many countries of East of Asia. Soybean are suggested to have many health benefits such as the healthy functioning of bowels, heart, kidney, liver, lowering of serum cholesterol levels and reduction in the risk for coronary heart disease (CHD), reduction in the risk for breast cancer, and osteoporosis in women, and alleviation of the disturbances caused by menopause (Oyvind et al. , 2006) [23]. Peanuts or groundnuts as they are known in some parts of the world are the edible seeds of a legume. Commercially, it is used mainly for oil production but apart from oil, the by-products of peanut contains many other functional compounds like proteins, fibers, polyphenols, antioxidants, vitamins and minerals which can be added as a functional ingredient into many processed foods (Arya et al. , 2016; Chukwumah et al. , 2007; Wu et al. , 2015; Zahran and Tawfeuk, 2019). Cow pea is commonly cultivated as a nutritious and highly palatable food source in Asia, the Middle East, the USA and throughout the tropics and subtropics. It can be used as forage, hay, and silage (Wu et al. , 2015).
SOYBEAN
Sitohy and Osman (2018) reported glycinin, basic subunit, and β-conglycinin isolated from soybean protein. Their results suggest that a soy protein fraction containing mainly β-conglycinin can be used as an effective environmentally friendly fungicidal agent against postharvest fungal infections. Isanga and Zhang (2008) in their research has implicated soybean phytochemicals as functioning in cholesterol reduction, cardiovascular disease prevention, diabetic symptoms prevention, bone loss prevention, and cancer prevention. However, some bioactive compounds in soybean are reported to have some adverse effects to health. Soybeans have various bioactive compounds such as saponins, protease inhibitors, phytic acid, and isoflavones (Setchell et al., 2003). The most important isoflavones in soy is genisteinl; and others are composed by daidzein and glycitein, and the metabolism of isoflavones is different from that of parent compounds (Markiewicz et al., 1993). Soy isoflavones have weak estrogens, and they can function as agonists, partial agonists, or antagonists to endogenous estrogens and xenoestrogens at estrogen receptors (Tikkanen et al., 1998; Ishii and Tanizawa, 2006). Filho et al. (2014) stated that the conversion of isoflavone was influenced directly by the characteristics of each sample, inhibiting or promoting the action of the enzyme. Silva and Perrone (2018) concluded that soybean meals presented 43% higher protein content, from 29% to 101% higher bioactive compounds contents and 52% higher antioxidant capacity than soybeans. High moisture thermal procedure employed during soybean meal processing led to a 13-fold increase in aglycone isoflavones contents, which could affect the bioavailability of isoflavones in the residue. They have concluded that dry soybean meal extracts are suitable materials for performing long-term in vivo studies, as these extracts were stable when stored at room temperature unprotected from light for 180 days. Vernaza et al. (2012) reported that consumption of soybean has been linked to cholesterol reduction and prevention of cardiovascular and gastrointestinal diseases, cancer, diabetes and obesity. They have found that the health benefits of soy are attributed to the presence of bioactive compounds such as isoflavones, saponins, lunasin and others. Lokuruka (2011) concluded that many of the chemical reactions affecting amino acid residues are often accompanied by proteinprotein interactions involving formation of covalent bonds, which may reduce their bioavailability. Excessive thermal denaturation and heat-induced interactions may from mutagenic and toxic compounds. Hydrogenation results in the formation of the hypercholesterolemic trans fatty acids isomers implying potential loss of the unsaturated essential fatty acids. He concluded processing can cause changes in the sensory appeal and the nutritive value of soybeans and soy products, and to minimize the adverse changes, minimal washing, fermentation and thermal processing below 100oC for short periods are suggested, although the higher temperatures used during soy oil hydrogenation will unavoidably introduce health-related adverse changes. Martino et al. (2019) found that a 50% substitution of casein with soybean protein reduced lipid peroxidation and liver fat, and improved intestinal morphology, while a 100% substitution reduced cholesterol and triglyceride levels; therefore, whole soybean, a source of vitamin E and isoflavone, is a functional food, which has cardioprotective effects and reduces cardiovascular disease risk associated with oxidative stress. Chatterjee et al. (2018) showed that some soy peptides like lunasin and soy morphins possess more than one of the properties and play a role in the prevention of multiple chronic diseases. Meghwal and Sahu (2015) revealed that isoflavones are the most abundant phytoestrogen in soybeans which are structurally similar with 17 β-estradiol. The antioxidant property of genistein and daidzein are well established in different experimental and clinical models. Isoflavones compounds have been found effective in the management of diabetes. It reduces low-density lipoprotein and triglycerides and hence minimizes the risk of coronary heart disease. Soy isoflavones was found useful for treatment of osteoporosis by inhibiting tyrosine kinase. In soy isoflavones, genistein is effective in the treatment of cancer by acting on androgen receptor and inhbiting tyrosine kinases. Many nutraceuitical and medicinal uses and applications of soy isoflavones have been investigated such as treatment and prevention of cardiovascular diseases, cholesterol lowering, osteoporosis, diabetes, cancer, cognitive decline, and menopausal symptoms. Content of vitamin E, total phenols and isoflavone of whole soybean flour is presented in Table 1. Comparison of levels of some bioactive compounds (%) from different saponified deodorizer distillate sources is shown in Table 2. Composition of unsaponified deodorizer distillates (%) obtained from chemical or physical refining of different soft oils is presented in Table 3. Various soybean fermented foods and their processing is presented in Table 4. Fatty acid composition of soybean oil (SO) and fully hydrogenated soybean oil is shown in Table 5. Sterols profile of the bioactive compounds loaded in the lipid nanoparticles is presented in Table 6.
|
Table 1. Content of vitamin E, total phenols, and isoflavone of whole soybean flour (Martino et al. , 2019). |
|
|
Phytochemical |
Amount |
|
Vitamin E (mg/100 g) |
3.84 |
|
α-tocopherol |
0.42 |
|
γ-tocopherol |
2.53 |
|
δ-tocopherol |
0.89 |
|
Total phenols (mg de EAG/100g) |
60 |
|
Isoflavones (mg/g) |
1,566.81 |
|
Daidzein |
658.23 |
|
Genistein |
753.34 |
|
Glicitein |
155.25 |
Table 2. Comparison of levels of some bioactive compounds (%) from different saponified deodorizer distillate sources (Winter, 1990).
|
Bioactive compounds |
Deodorizer Distillates |
|||
|
Sunflower |
Cotton |
Soybean |
Rapeseed |
|
|
Unsaponifiables matter |
39.0 |
42.0 |
33.0 |
35.0 |
|
Tocopherols |
9.30 |
11.40 |
11.10 |
8.20 |
|
α-Tocopherols |
5.70 |
6.30 |
0.90 |
1.40 |
|
Sterols |
18.0 |
20.0 |
18.0 |
14.60 |
|
Stigmasterol |
2.90 |
0.30 |
4.40 |
1.80 |
|
Mean values of replicate samples. |
||||
Table 3. Composition of unsaponified deodorizer distillates (%) obtained from chemical or physical refining of different soft oils (Verleyn et al. , 2001; Dumont and Narine, 2007).
**∆5 avenasterol, ∆7 avenasterol and ∆5 stigmasterol
Table 4. Various soybean fermented foods and their processing (Varnosfaderani et al. , 2019).
|
Name |
Definition and Production |
|
Doenjang |
Doenjang is a representative traditional Korean fermented food that has played an important role in providing protein in typically graincentered, protein-scarce diets. It is prepared by fermented soybean paste. |
|
Sufu |
Sufu is a traditional and highly flavored fermented tofu. Its preparation consists of a former fermentation by inoculation of tofu with Actinomucor elegans and incubation for 48 h to produce pehtze (pizi). Fermentation is usually performed between 20o C and 35o C. |
|
Miso |
Miso is commonly produced from koji. Soybean koji can be prepared by soaking soybeans in water and mixing with the conidia of A. oryzae or A. sojae and incubated at room temperature. |
|
Natto |
Natto is a B. subtilis fermented soybean. Its preparation consists of splitting, soaking, and boiling of soybeans, followed by fermentation with B. subtilis at 37o C for 48 h. |
|
Tempeh |
Tempeh is produced by soaking soybeans at room temperature for 10-12 h and dehulling them by hand. They are heated up to the boiling point and boiled for 20 min. After colling to 35-40oC, and inoculums of R. oligosporus for incubation in the dark at 37o C for 22 h. |
|
Douchi |
Douchi is prepared by soaking soybeans in water for 8 h at room temperature; after raining, soybeans are cooked (>100oC) and then inoculated either with Mucor, Bacteria, or Aspergillus strains at 30-35oC (pre-fermentation) |
|
Tofuyo |
Tofuyo is a traditional fermented tofu from Okinawa in Japan. |
|
Chunggugjang |
Chunggugjang is a traditional fermented Korean soybean product. |
|
Aspergillus= A, B. subtilis = Bacillus subtilis , R. oligosporus = Rhizopus oligosporus |
|
Table 5. Fatty acid composition of soybean oil (SO) and fully hydrogenated soybean oil (FHSO) (Santos et al. , 2019).
|
Fatty acids (%) |
SOa FHSOa |
|
C16:0- Palmitic acid C16:1- Palmitoleic acid C18:0- Stearic acid C18:1- Oleic acid C18:2- Linoleic acid C18:3- Linolenic acid C20:0- Arachidonic acid C22:0- Behenic acid Ʃ Saturated Ʃ Unsaturated |
10.70 ± 1.12 11.22 ± 0.50 0.09 ± 0.02 - 4.26 ± 0.26 87.11 ± 0.06 23.38 ± 0.96 - 53.32 ± 0.58 -
0.41 ± 0.03 0.60 ± 0.18
15.83 100 83.45 <1 |
a Average of three replicates ± Standard Deviation. Values 0.2% were omitted from the table.
Table 6. Sterols profile of the bioactive compounds loaded in the lipid nanoparticles (Santos et al. , 2019).
Kunitz-Trypsin inhibitor (KTI), Bowman-Birk inhibitor (BBI), and lunasin are three major and best characterized bioactive proteins/peptides of soybean seeds (Park et al. , 2005). KTI and BBI are serine protease inhibitors with molecular weights of 20.1 and 8 kDa, respectively [47]. Both of these proteins have been shown to exhibit anti-carcinogenic and/or anti-invasive metastatic activities (Isanga and Zhang, 2007; Dia et al. , 2012). Two essential fatty acid (EFAs) present in soy oil is presented in Figure 1. Functional components of soy and their impact is shown in Table 7. Soy phytosterols and their structural similarity with cholesterol are presented in Figure 2. Duenas et al. (2012) observed that fermentation process caused significant changes in the phenolic composition of soybean seeds, and
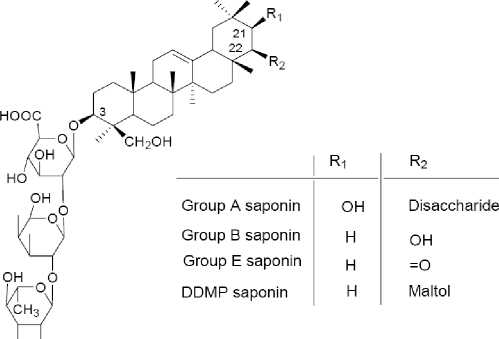
therefore, it could also affect the beneficial biological effects associated with these components. These changes could be due to enzymes production and activation by the microbiota used in order to perform the fermentation process, brining out complex biochemical metabolism of soybean during the process. In general, the fermentation process produced a significant increase in the levels of the phenolic acids and flavonoids, mainly aglycones isoflavones. The chemical structure and types of soy sapnins is shown in Figure 3. Bioactive peptide production from legume sources as anticancer agents is shown in Figure 4. Structure of genistein, daidzein and glycitein is shown in Figure 5. Structure of glyceollins is presented in Figure 6.
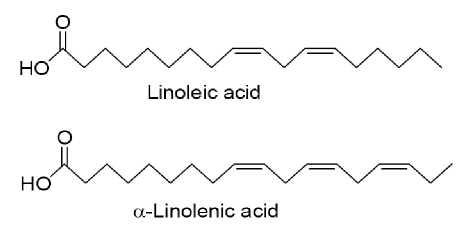
Fig. 1. Two essential fatty acid (EFAs) present in soy oil (Dixit et al. , 2011).
Table 7. Functional components of soy and their impact (Sugano, 2006).
|
α-Linolenic acid |
Essential fatty acid, hyptriglyceridemic, improves heart health |
|
Isoflavones |
Estrogenic, hypocholesterolemic, improves digestive tract function, prevents breast, prostate, and colon cancer, bone health, improve lipid metabolism |
|
Lecithins Lectins Linoleic acid Peptides Phytosterols Protein Saponin |
Improve lipid metabolism, improve memory and learning abilities Anti-carcinogenic, immunostimulator Essential fatty acid, hypocholesterolemic Readily absorbed, reduce body fat, anticancer Hypocholesterolemic, improves prostate cancer Hypocholesterolemic, antiatherogenic, reduces body fat Regulates lipid metabolism, antioxidant |
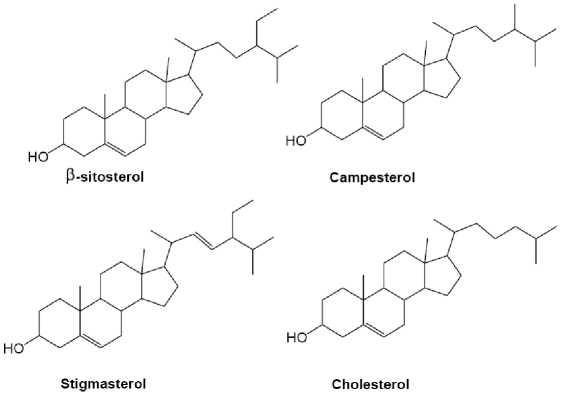
Fig. 2. Soy phytosterols and their structural similarity with cholesterol (Dixit et al. , 2011).
окон
Fig. 3. The chemical structure and types of soy saponins (Dixit et al. , 2011).
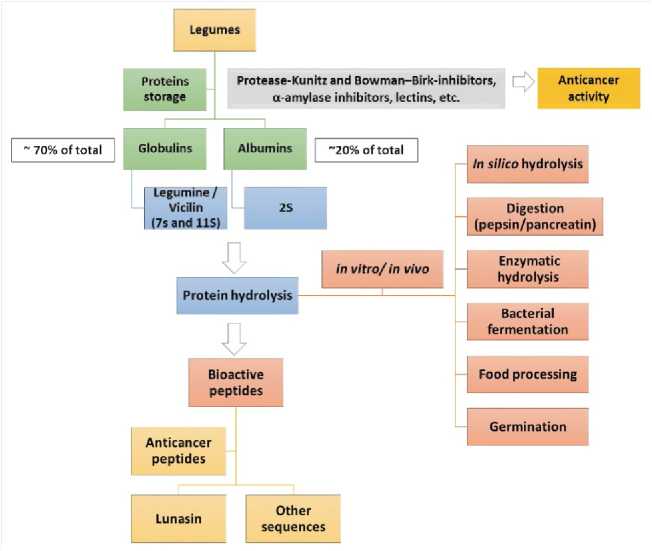
Fig. 4. Bioactive peptide production from legume sources as anticancer agents (Marcela et al. , 2017).
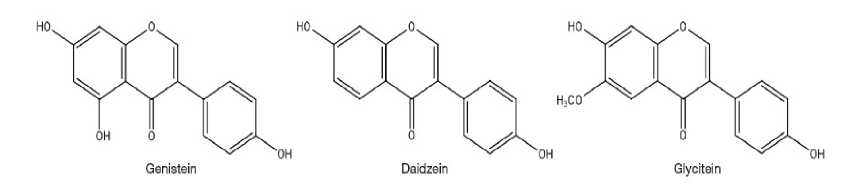
Fig. 5. Structure of genistein, daidzein and glycitein (Wu et al. , 2017).
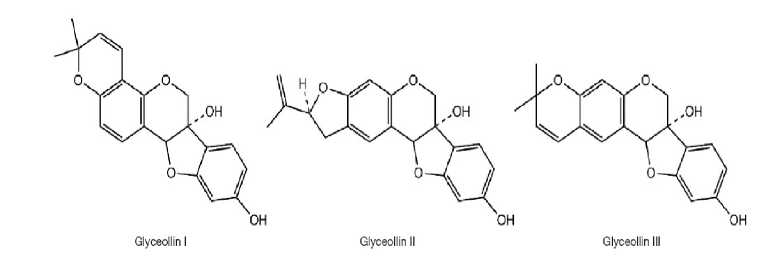
Fig. 6. Structure of glyceollins (Wu et al. , 2017).
PEANUTS
Peanut is one of the most widely used legumes due to its nutrition and taste, and it has been recognized recently as a functional food (Francisco and Resurreccion, 2008). The peanut industry ,s byproducts such as peanut hulls and shells, skins, and even leaves and roots have also been identified as possible sources of bioactive compounds (Bhat et al., 2019). Peanuts are also a source of helpful biologically active components found in plant foods, such as phytochemicals. Some of the phytochemicals in peanuts include flavonoids and phenolic compounds. This article discusses bioactive compounds and nutraceuticals in peanuts that could be used in prevention and management of illnesses such as cancer, cardiovascular disease, osteoporosis, and other degenerative diseases. The biological activity of anti-nutritional factors in peanuts is also briefly discussed (Isanga and Zhang, 2007). The most important bioactive compounds in s a hell of peanut is 1) arginine: an amino acid with high levels in peanuts, is a precursor to nitric oxide, which helps expand blood vessels and decrease blood pressure, 2) Resveratrol: also found in grapes and wine, improves longevity and performance and reduces inflammation, 3) Phytosterols: are well-known for their ability to reduce cholesterol levels and research shows they have cancer-preventing qualities, 4) Phenolic acids: are found in plants and act as a defense mechanism for environmental stress and pest attacks. They may also defend our bodies and keep the bodies healthy, 5) Flavonoids: are the class of compounds found in peanuts that reduce inflammation and inhibit platelets from sticking to arteries. Bhat et al. (2019) reported that peanut consists of different functional components such as coenzyme Q10 which secures the heart amid absence of oxygen, for example at high altitudes and in case of clogged veins. Also, peanut possess various health benefits beyond basic nutrition. Peanuts act as efficiency source of dietary fiber, and other essential nutrients that include few B complex group of vitamins, vitamin E, minerals such as iron, zinc, potassium, magnesium and antioxidant minerals such as selenium, manganese and copper. The antioxidant activity of peanut is because of vitamin E, caffeic, coumaric acid, flavonoids and stilbenes, and these bioactive compounds possess preventative properties (Yu et al., 2006). Akl et al. (2019) observed that the analysis of soluble and insoluble of peanut meal protein by native and SDS-PAGE showed peptide bands at low molecular weight in range (up to 25 kDa); which were extracted by acid and base treatments. These peptides were easily digested and were recommended as baby, sports people and geriatric food. The soluble extracts showed high contents of phenolic compounds especially that extracted by ethanol: 1N NaOH, and it also contains appreciable amounts of saponins and flavonoids that exhibited anti-oxidant activities especially DPPH scavenging activities 91% extracted by ethanol: 1N NaOH. The protein extract of 60% ethanol were the most effective on (MCF7) and 100% ethanol were the most effective on (HEPG2). Bioactive compounds in peanuts are shown in Figure 7. Groundnuts (Arachis hypogae), all types, nutritional value per 100 g is shown in Table 8. Components in nuts that are thought to be beneficial is presented in Table 9. The chemical structure of trans-resveratrol and trans-piceatannol is shown in Figure 8.
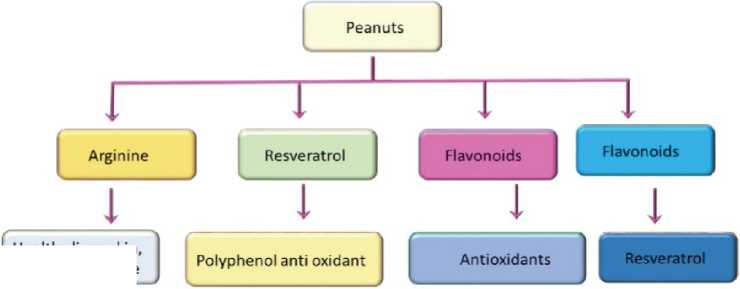
Healthy liver, skin, Jointsand muscle
Fig. 7. Bioactive compounds in Peanuts (Bhat et al. , 2019).
Table 8. Groundnuts ( Arachis hypogae ), all types, nutritional value per 100 g (Bhat et al. , 2019).
|
Principle |
Nutrient value |
Percentage of RDA |
|
Energy |
567 Kcal |
12 |
|
Carbohydrates |
16.13g |
12 |
|
Protein |
25.80g |
46 |
|
Total Fat |
49.24g |
165 |
|
Cholesterol |
0 mg |
0 |
|
Dietary Fiber |
8.5 g |
22 |
|
Vitamins |
||
|
Folates |
240 μg |
60 |
|
Niacin |
12.066 mg |
75 |
|
Pantothenic acid |
1.767 mg |
35 |
|
Pyridoxine |
0.348 mg |
27 |
|
Riboflavin |
0.135 mg |
10 |
|
Thiamin |
0.640 mg |
53 |
|
Vitamin A |
0 IU |
0 |
|
Vitamin C |
0 |
0 |
|
Vitamin E |
8.33 mg |
55.5 |
|
Electrolytes |
||
|
Sodium |
18 mg |
1 |
|
Potassium |
705 mg |
15 |
|
Minerals |
||
|
Calcium |
92 mg |
9 |
|
Copper |
1.144 mg |
127 |
|
Iron |
4.58 mg |
57 |
|
Magnesium |
168 mg |
42 |
|
Manganese |
1.934 mg |
84 |
|
Phosphorus |
76 mg |
54 |
|
Selenium |
7.2 μg |
13 |
|
Zinc |
3.27 mg |
30 |
Source: USDA National Nutrient data base.
Table 9. Components in nuts that are thought to be beneficial (Kris-Etherton et al. , 1999).
n-6 and n-3 Monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids
Fiber
Micronutrients
Vitamin E
Folic acid
Copper
Magnesium
Plant protein (arginine)
Phytochemicals
Plant sterols
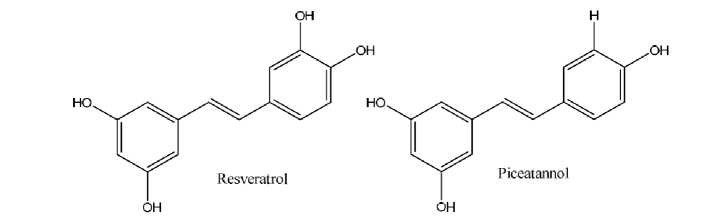
Fig. 8. The chemical structure of trans -resveratrol and trans -piceatannol (Lin et al. , 2007).
Table 10. Phytochemical screening of peel extracts of Arachis hypogeal (Velu et al. , 2015).
|
Secondary metabolites |
Chloroform |
Acetone |
Ethanol |
Methanol |
Aqueous |
|
Carbohydrates |
+++ |
+++ |
+++ |
+++ |
+++ |
|
Tannins |
- |
+++ |
+++ |
+++ |
- |
|
Saponins |
- |
- |
+++ |
+++ |
- |
|
Flavonoids |
- |
+++ |
+++ |
+++ |
+++ |
|
Alkaloids |
- |
+++ |
+++ |
+++ |
- |
|
Betacyanin |
- |
+++ |
+++ |
+++ |
+ |
|
Quinones |
- |
+ |
+++ |
+ |
- |
|
Glycosides |
- |
++ |
+++ |
+++ |
- |
|
Cardiac |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
Glycosides |
|||||
|
Terpenoids |
- |
+ |
+ |
++ |
- |
|
Triterpenoids |
- |
- |
- |
+ |
+ |
|
Phenols |
+ |
+++ |
+++ |
+ |
+ |
|
Coumarins |
- |
+++ |
+++ |
+++ |
+ |
|
Acids |
- |
+ |
+ |
+ |
- |
|
Protein |
- |
- |
- |
- |
+++ |
|
Steroids |
+ |
++ |
+++ |
+++ |
- |
Table 11. Fatty acid composition of the peanut powder extracts with and without skin (Silva and Perrone, 2015).
|
Fatty acids (mg 100g-1 of lipids) |
Peanut powder extract |
peanut powder extract |
|
With skin |
Without skin |
|
|
Saturated |
8.0000 ± 0.024 |
8.6203 ± 0.023 |
|
Palmitic C16:0 |
4.3346 ± 0.010 |
4.4486 ± 0.002 |
|
Stearic C18:0 |
1.2498 ± 0.003 |
1.2968 ± 0.005 |
|
Arachidic C20:0 |
0.6229 ± 0.002 |
0.6647 ± 0.005 |
|
Beenic C22:0 |
1.7927 ± 0.009 |
2.2102 ± 0.011 |
|
Monounsaturated |
26.0094 ± 0.017 |
28.6719 ± 0.008 |
|
Oleic C18:1 |
25.3536 ± 0.014 |
27.9162 ± 0.002 |
|
Eicosenoic C20:1 |
0.6558 ± 0.003 |
0.7557 ± 0.006 |
|
Polyunsaturated |
9.0854 ± 0.001 |
9.1751 ± 0.005 |
|
Linoleci C18:2 |
9.0854 ± 0.001 |
9.1751 ± 0.005 |
Note. Values expressed in mean ± standard deviation.
Velu et al. (2015) noted that phytochemical screening of the peel extract of Arachis hypogaea showed the presence of bioactive compounds such as tannins, saponin, flavonoids, alkaloids, glycosides, beta cyanin, coumarins, quinines and steroid. Silva and Perrone (2015) concluded that the bioactive compounds are found in larger amounts in the peanut powder extract with skin. The peanut powder extracts are classified as non-hygroscopic, have poor fluidity, intermediate cohesiveness in samples with skin and high cohesiveness in samples without skin. The peanut powder extracts have significant percentage of minerals like K, P, Mg, and Ca, and they are mainly composed of oleic and linoleic fatty acids. Lewis et al (2013) showed that peanut skin extracts contain high levels of procyanidins and other phenolic compounds, whether extracted with acetone or ethanol. Despite measureable differences in procyanidin and phenolic content between the two extraction systems studied, both possessed similar antioxidant activity as determined by chemical assays and anti-inflammatory activity in an in vitro model of inflammation. Fatty acid composition of the peanut powder extracts with and without skin in Table 11.
COW PEA
Lee et al. (2011) evaluated anti-inflammatory effects of methanol extract and solvent fractions of cowpea (Vigna sinensis L.) seeds and the isolated compounds. In their experiment, ethyl acetate and n-butanol fractions of VS seeds were found to strongly inhibit nitric oxide (NO) production, and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) mRNA and protein expressions in lipoplysaccharides (LPS)-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophage cells. Among the isolated compounds, Lna and LA were found to inhibit NO production significantly. Contents of LnA and LA in VS seeds were 2.034 and 1.162 mg/g on dry weight basis, respectively. LA suppressed the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α in LPS-induced macrophage cells. Cai et al. (2003) reported that the amount of protocatechuic acid increased from trace -3.6 to 9.3-92.7 mg/100 g of flour in the 17 varieties of cowpeas after hydrolysis. Six other phenolic acids, including, p-hydroxybenzoic acid, caffeic acid, p-coumaric acid, ferulic acids, 2,4-dimethoxybenzoic acid, and cinnamic acid, were also identified. Cowpea is an important food crop in tropical countries especially in west of Africa where it is a cheap source of dietary protein; the dry seed consists of about 25% protein and 67% carbohydrate, and it is also a good source of calcium, iron, vitamins and carotene. Dalaram (2015) stated that contains phenolic compounds and it is believed that it works synergistically to promote human health through their antioxidant properties and their ability to modulate the activity of various enzymes, and these phenolics are also potent inhibitors of α-amylase and α-glucosidase, the two important enzymes involved in the regulation of glucose homeostasis. Cowpeas are low in fat and high in protein, thus, the legume can prevent cardiovascular and metabolic diseases associated with high fats; furthermore, cowpeas are rich in thiamine, riboflavin, vitamins A and C, niacin, calcium, potassium, magnesium and carbohydrates (Chipurura et al., 2018). The major polyphenols common to all cowpea varieties are phenolic acids derivatives (148-1176 μg/g), and flavonol glycosides (27-1060 μg/g). Some varieties also contain anthocyanins (875-3860 μg/g), and flavan-3-ols (2155-6297 μg/g). The flava-3-ols (tannins) are dominated by monomers, mostly catechin-7-O-glucoside. Cowpea also contains beneficial bioactive peptides. Sombie et al. (2018) noticed that cowpea genotypes with colored seed coast showed the highest phenolic content, ferric reduction ability and anti-lipid peroxidation activities. In their experiment, it has been found that nitric oxide scavenging potential was found not be related to its total phenolic and total flavonoids content. 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) and hydroxyl radicals scavenging potentials were not correlated with the total flavooids content. Compound detected in the extracts of flours, porridge and digested porridge (μg/g) is shown in Figure 9. Traditional Chinese herbs and medicines play vital role in sustainable agriculture and food systems (Adelakun and Duodu, 2017; Khoshkharam et al., 2020; Shahrajabian et al., 2020a,b,c,d,e; Shen et al., 2020; Sun et al., 2020a,b,c).
CONCLUSION
Pulses make a major share of the human diet in many regions of the world and play a significant role in the human nutrition, especially as source of protein, vitamins, minerals, dietary fiber and folic acid. Grain pulses also contain certain biologically active components including enzyme inhibitors, lectins, phytates, oligosaccharides, and phenolic compounds. Soybean comprises isoflavones, phytosterols, saponins, and other basic nutritive constituents, such as lipids, vitamins, minerals, oligosaccharides, and biological active peptides, that are of strong therapeutic values. The soybean itself is composed of approximately 40% protein, 20% oil, 35% carbohydrates, and 5% trace minerals and other compounds. Soy protein isolates and concentrates have been used to develop a range of food products including beverages and meat alternatives and they can be processed to function similarly to the traditional sources of protein in meat and dairy products. The most important health benefits of soybean are bioactive components include protect heart health, anticancer, reduce the effects of menopause, promotes bone health, improve metabolism, and decrease the risk of diabetes. Peanut (Arachis hypogaea Linn.) belongs to the family of Rosales and is widely cultivated around the world as an important economical crop. Peanuts are considered an important source of oil, folate, antioxidants, protein, and essential fatty acids (linoleic), and it ranked fourth in oilseed crops in the world after soybeans, rapeseed, and cotton. It has been revealed the presence of flavonoids, tannins, terpenoids, saponins, steroids, alkaloids by positive reaction with the respective test reagent. The numerous bioactive components in peanut contribute to their antioxidant capacity. Cowpeas are legumes recognized as a good source of proteins in many countries especially developing countries. It contains high levels of polyphenols, and the major polyphenols commons to all cowpea varieties are phenolic acids derivatives, and flavonol glycosides. Some varieties also contain anthocyanins and flavan-3-ols. Cow peas are valuable source of protein, carbohydrate, mineral and vitamins, and it also contain biologically active components including phenols, phytic acid, saponin, oligosaccharides, fiber and etc. Growing of leguminous plants can also benefits both the plants and soils by yielding nitrogen in the compound form. Legumes in traditional Medicine are natural and organic health care system which views the body as a complex network of interconnected parts. The most important health benefits of legumes are improve metabolic activity, health weight gain, anti-cancer potential, boost heart health, relieve menopausal symptoms, boost digestion, improve bone health, prevent birth defects, improve circulation, control diabetes and relieve sleep disorders.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest.
Список литературы Bioactive Components and Chemical Constituents of Some Important Legumes in Traditional Medicine
- Adelakun, O.E., Duodu, G. (2017). Identification and quantification of phenolic compounds and bioactive properties of sorghum-cowpea-based food subjected to an in vitro digestion model. European Journal of Nutrition and Food safety, 7(1), 57-66.
- Akl, E.M., Wagdy, S.M., Taha, F.S., Samira, S.M., Omar, S.S. (2019). Effect of different solvent treatments on peanut meal protein fractions as 1 bioactive compounds. Asian Journal of Scientific Research, 12, 211-219.
- Arya, S.S., Salve, A.R., Chauhan, S. (2016). Peanuts as functional food: a review. J Food Sci Technol, 53(1), 31-41.
- Bhat, E.A., Sajjad, N., Manzoor, I., Rasool, A. (2019). Bioactive compounds in Peanuts and Banana. Biochemistry and Analytical Biochemistry, 8, 382. Cai, R., Hettiarachchy, N.S., Jalaluddin, M. (2003). Highperformance liquid chromatography determination of phenolic constituents in 17 varieties of cowpeas. J Agric Food Chem, 51(6), 1623-1627.
- Chatterjee, C., Gleddie, S., Xiao, C.W. (2018). Soybean bioactive peptides and their functional properties. Nutrients, 10, 1211. Chipurura, B., Baudi, J.S., Munodawafa, T., Benhura, C. (2018). Effect of soaking, dehulling and boiling on protein, polyphenolic and antinutrient content of cowpeas (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp). Nutrafoods, 17, 205-211.
- Chukwumah, Y., Walker, L., Vogler, B., Verghese, M. (2007). Changes in the phytochemical composition and profile of raw, boiled and roasted peanuts. J Agric Food Chem, 55, 9266-9273.
- Dalaram, I.S. (2015). Total polyphenol content and antioxidant capacity of cowpea effect of variet and locality. Potravinarstvo, 9(1), 358-364.
- Dia, V.P., Gomez, T., Vernaza, G., et al. (2012). Bowman-Birk and Kunitz protease inhibitors among antinutrients and bioactives modified by germination and hydrolysis in Brazilian soybean cultivar BRS 133. J Agric Food Chem, 60, 78867894.
- Dixit, A.K., Antony, J.I.X., Sharma, N.K., Tiwari, R.K. (2011). Soybean constituents and their functional benefits. Opportunity, Challenge and Scope of Natural Products in Medicinal Chemistry, 367-383. ISBN: 978-81-308-0448-4
- Duenas, M., Hernandez, T., Robredo, S., Lamparski, G., Estrella, I., Munoz, R. (2012). Bioactive phenolic compounds of soybean (Glycine max cv. Merit): modifications by different microbiological fermentations. Polish Journal of Food and Nutrition Science, 62(4), 241-250.
- Dumont, M.J., Narine, S.S. (2007). Soapstock and deodorizer distillates from North Americanvegetable oils: review on their characterization, extraction and utilization. Food Res Int, 40, 957-974.
- Filho, M.L.D.M., Hirozawa, S.S., Prudencio, S.H., Ida, E.I., Garcia, S. (2014). Petit Suisse from black soybean: bioactive compounds and antioxidant properties during development process. International Journal of Food Sciences and Nutrition, 65(4), 470-475.
- Francisco, M.L.D.L., Resurreccion, A.V.A. (2008). Functional components in peanuts. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 48(8), 715746.
- Isanga, J., Zhang, G.N. (2007). Biologically active components and nutraceuticals in peanuts and related products: Review. Food Reviews International, 23(2), 123-140.
- Isanga, J., Zhang, G.-N. (2008). Soybean bioactive components and their implications to health- a review. Food Reviews International, 24(2), 252276.
- Ishii, Y., Tanizawa, H. (2006). Effects of soyasaponins on lipid peroxidation through the secretion of thyroid hormones. Biol Pharm Bull, 29, 1759-1763.
- Khoshkharam, M., Shahrajabian, M.H., Sun, W., Cheng, Q. (2020). Sumac (Rhus coriaria L.) a spice and medicinal plant- a mini review. Amazonian Journal of Plant Research, 4(2), 517-523.
- Kris-Etherton, P., Shaomei, Y.P., Joan, S., Hope, E.R., Guixiang, Z., Terry, D.E. (1999). Nuts and their bioactive constituents: effects on serum lipids and other factors that affect disease risk. Am J Clin Nutr, 70(suppl), 504S-511S.
- Lewis, W.E., Harris, G.K., Sanders, T.H., Sanders, T.H., White, B.L., Dean, L.L. (2013). Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of peanut skin extracts. Food and Nutrition Sciences, 4, 22-32.
- Lee, S.M., Lee, T.H., Cui, E.J., Baek, N.I., Hong, S.G., Chung, I.S., Kim, J. (2011). Anti-inflammatory effects of cowpea (Vigna sinensis K.) seed extracts and its bioactive compounds. Journal of the Korean Society for Applied Biological Chemistry, 54(5), 710-717.
- Lin, L.L., Lien, C.Y., Chen, Y.C., Ku, K.L. (2007). An effective sample preparation approach for screening the anticancer compound piceatannol using HPLC coupled with UV and fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr., B: Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Science, 853(1-2), 175-182.
- Lokuruka, M.N.I. (2011). Effects of processing on soybean nutrients and potential impact on consumer health: an overview. African Journal of Food, Agriculture, Nutrition and Development. African Journal of Food, Agricuture, Nutrition and Development, 11(4).
- Marcela, G.-M., Eden, C.-S., Rosalva, M.-E. (2017). Bioactive peptides from legumes as anticancer therapeutic agents. International Journal of Cancer and Clinical Research, 4, 081.
- Markiewicz, L., Garey, J., Adlercreutz, H., Gurpide, E. (1993). In vitro bioassays of non-steroidal phytoestrogens. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol, 45, 399-405.
- Martino, H.S.D., Grancieri, M., Almeida, C.G., Andrade, G.F., Alves, N.E.G., Dias, D.M., SantAna, H.M.P., Ribeiro, S.M.R., Piovesan, N.D., Lucio, H.G., Benjamim, L.A. (2019). Whole soybean flour with high concentration of isolfavone and vitamin E modulates cardiovascular risk factors in Wistar rats. International Food Research Journal, 26(5), 15471556.
- Meghwal, M., Sahu, C.K. (2015). Soy isoflavonoids as nutraceutical for human health: an update. Journal of Cell Science and Therap, 6, 1.
- Ogbaji, P.O., Shahrajabian, M.H., Xue, X. (2013). Changes in germination and primarily growth of three cultivars of tomato under diatomite and soil materials in auto-irrigation system. International Journal of Biology, 5(3), 80-83.
- Ogbaji, P.O., Li, J., Xue, X., Shahrajabian, M.H., Egrinya, E.A. (2018). Impact of bio-fertilizer or nutrient solution on spinach (Spinacea Oleracea) growth and yeidl in some province soils of P.R. China. Cercetari Agronomice in Moldova, 2(174), 43-52.
- Oyvind, M., Kenneth, A., Markham, R. (2006). Flavonoids, chemistry, biochemistry and applications. CRC Press Taylor and Francis Group, USA.
- Park, J.H., Jeong, H.J., de Lumen, B.O. (2005). Contents and bioactivities of lunasin bowman birk inhibitor and isoflavones in soybean seed. J Agric Food Chem, 53, 7686-7690.
- Santos, V.D.S., Miyasaki, E.K., Cardoso, L.P., Ribeiro, A.P.B., Sanrana, M.H.A. (2019). Crystallization, polymorphism and stability of nanostructured lipid carriers developed with soybean oil, fully hydrogenated soybean oil and free phytosterols for food applications. Journal of Nanotechnology Research, 1(1), 001-022.
- Setchell, K.D., Brown, N.M., Desari, P.B., Zimmer-Nechimias, L., Wolfe, B. et al (2003). Bioavailability, disposition, and dose-response effects of soy isoflavones when consumed by healthy women at physiologically typical dietary intakes. J Nutr, 133, 1027-1035.
- Shahrajabian, M.H., Sun, W., Cheng, Q. (2019a). Sustainable agriculture and soybean, a legume in traditional Chinese medicine with great biological nitrogen fixation. Journal of Biological and Environmental Sciences, 13(38), 71-78.
- Shahrajabian, M.H., Sun, W., Cheng, Q. (2019b). Chinese star anise and anise, magic herbs in traditional Chinese medicine and modern pharmaceutical science. Asian Journal of Medical and Biological Research, 5(3), 162-179.
- Shahrajabian, M.H., Sun, W., Cheng, Q. (2019c). A review of astragalus species as foodstuffs, dietary supplements, a traditional Chinese medicine and a part of modern pharmcautical science. Applied Ecology and Environmental Research, 17(6), 13371-13382.
- Shahrajabian, M.H., Sun, W., Cheng, Q. (2019d). Tremendous health benefits and clinical aspects of Smilax china. African Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, 13(16), 253-258.
- Shahrajabian, M.H., Sun, W., Cheng, Q. (2019e). DNA methylation as the most important content of epigenetics in traditional Chinese herbal medicine. Journal of Medicinal Plant Research, 13(16), 357369.
- Shahrajabian, M.H., Sun, W., Cheng, Q. (2019f). The influence of traditional Iranian and Chinese medicine on western and Islamic countries. Asian Journal of Medical and Biological Research, 5(2), 94-99.
- Shahrajabian, M.H., Sun, W., Cheng, Q. (2019g). Modern pharmacological actions of longan fruits and their usages in traditional herbal remedies. Journal of Medicinal Plants Studies, 7(4), 179-185.
- Shahrajabian, M.H., Sun, W., Cheng, Q. (2019h) A review of ginseng species in different regions as a multipurpose herb in traditional Chinese medicine, modern herbology and pharmacological science. Journal of Medicinal Plant Research, 13(10), 213226.
- Shahrajabian, M.H., Sun, W., Cheng, Q. (2019i). Clinical aspects and health benefits of ginger (Zingiber officinale) in both traditional Chinese medicine and modern industry. Acta Agriculturae Scandinavica, Section B- Soil and Plant Science. DOI: 10.1080/09064710.2019.1606930
- Shahrajabian, M.H., Sun, W., Khoshkharam, M., Cheng, Q. (2020a). Rambutan, a tropical plant with ethno-pharmaceutical properties. Agrociencia, 54(1), 121128.
- Shahrajabian, M.H., Sun, W., Cheng, Q. (2020b). A short review of goji berry, ginseng and astragalus in traditional Chinese and Asian medicine. Black Sea Journal of Health Science, 3(2).
- Shahrajabian, M.H., Sun, W., Cheng, Q. (2020c). Chinese star anise (Illicium verum) and pyrethrum (Chrysanthemum cinerariifolium) as natural alternatives for organic farming and health care- A review. Australian Journal of Crop Sciences, 14(03), 517-523.
- Shahrajabian, M.H., Sun, W., Shen, H., Cheng, Q. (2020d). Chinese herbal medicine for SARS and SARS-CoV-2 treatment and prevention, encouraging using herbal medicine for COVID-19 outbreak. Acta Agriculturae Scandinavica, Section B-Soil & Plant Science. DOI: 10.1080/09064710.2020.1763448
- Shahrajabian, M.H., Sun, W., Cheng, Q. (2020e). Chinese jujube (Ziziphus jujube Mill.)- a promising fruit from traditional Chinese medicine. Annales Universitatis Paedagogicae Cracoviensis, 5, 194219.
- Shahrajabian, M.H., Chaski, C., Polyzos, N., Petropoulos, S.A. (2021a). Biostimulants application: A low input cropping management tool for sustainable farming of vegetables. Biomolecules, 11(698), 1-26.
- Shahrajabian, M.H., Sun, W., Khoshkharam, M., Cheng, Q. (2021b). Caraway, Chinese chives and cassia as functional foods with considering nutrients and health benefits. Carpathian Journal of Food Science and Technology, 13(1), 101-119.
- Shahrajabian, M.H., Sun, W., Cheng, Q. (2021c). Asafoetida, natural medicine for future. Current Nutrition and Food Science, 17, 1-5.
- Shahrajabian, M.H., Sun, W., Cheng, Q. (2021d). Improving health benefits with considering traditional and modern health benefits of Peganum harmala. Clinical Phytoscience, 7(18), 1-9.
- Shen, H., Shahrajabian, M.H., Li, C., Sun, H., Li, J., Sun, W., Cheng, Q., Chen, B., Wang, Z. (2020). Microbial contamination database and limit standards for herbal medicine. Agrociencia, 54(1), 107-120.
- Silva, F.D.O., Perrone, D. (2015). Characterization and stability of bioactive compounds from soybean meal. LWT-Food Science and Technology, 63(2), 992-1000.
- Silva, K.M.D., Almeida, F.D.A.C., Sousa, F.C.D., Castro, D.S.D., Moreira, I.D.S., Lima, J.P., Neto, A.F. (2018). Chemical and physical characterization of peanut powder extracts. Journal of Agricultural Science, 10(4), 323-334.
- Sitohy, M., Osman, A. (2018). Bioactive compounds in soybean proteins and its applications in food systems. In: Negm A.M., Abu-hashim M. (eds) Sustainability of Agricultural Environmental in Egypt: Part I. The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry, vol 76. Springer, Cham.
- Soleymani, A., Shahrajabian, M.H., Naranjani, L. (2011a). Changes in qualitative characteristics and yield of three cultivars of berseem clover intercropped with forage corn in low iunput farming system. Journal of Food, Agriculture and Environment, 9(1), 345-347.
- Soleymani, A., Shahrajabian, M.H., Naranjani, L. (2011b). The effects of nitrogen as starter fertilizer on ash percentage, important elements and solar radiation absorption of berseem clover cultivars intercropped by corn. Journal of Food, Agriculture and Environment, 9(1), 342-344.
- Soleymani, A., Shahrajabian, M.H., Naranjani, L. (2011c). Yield and yield components of berseem clover cultivars in low nitrogen fertilizer input farming. Journal of Food Agriculture and Environment, 9(2), 281-283.
- Soleymani, A., Shahrajabian, M.H. (2012). Forage yield and quality in intercropping of forage corn with different cultivars of berseem clover in different levels of nitrogen fertilizer. Journal of Food, Agriculture and Environment, 10(1), 599-601.
- Soleymani, A., Shahrajabian, M.H., Naranjani, L. (2012a). Evaluation the benefits of different berseem clover cultivars and forage corn intercropping in different levels of nitrogen fertilizer. Journal of Food, Agriculture and Environment, 10(1), 599-601.
- Soleymani, A., Shahrajabian, M.H., Khoshkharam, M. (2012b). Effect of different fertility systems on fresh forage yield and qualitative traits of forage. Research on Crops, 13(3), 861-865.
- Soleymani, A., Shahrajabian, M.H. (2018). Assessment of ET-HS model for estimating crop water demand and its effects on yield and yield components of barley and wheat in semi-arid region of Iran. Cercetari Agronomice in Moldova, 4(172), 37-49.
- Sombie, P.A.E.D., Compaore, M., Coulibaly, A.Y., Quedraogo, J.T., Tignegre, J.B.D.L.S., Kiendrebeogo, M. (2018). Antioxidant and phytochemical studies of 31 cowpeas (Vigna unguiculata (L. Walp.)) genotypes from Burkina Faso. Foods, 7(143).
- Sugano, M.Ed. (2006). Soy in health and disease prevention, CRC Press, FL, USA.
- Sun, W., Shahrajabian, M.H., Cheng, Q. (2019a). Anise (Pimpinella anisum l.), a dominant spice and traditional medicinal herb for both food and medicinal purposes. Cogent Biology, 5(1673688), 1-25.
- Sun, W., Shahrajabian, M.H., Cheng, Q. (2019b). The insight and survey on medicinal properties and nutritive components of shallot. Journal of Medicinal Plant Research, 13(18), 452-457.
- Sun, W., Shahrajabian, M.H., Cheng Q, (2020a). Traditional Iranian and Arabic herbal medicines as natural-anti-cancer drugs. Agrociencia, 54(1), 129142.
- Sun, W., Shahrajabian, M.H., Khoshkharam, M., Cheng, Q. (2020b). Adaptation of acupuncture and traditional Chinese herbal medicines models because of climate change. Journal of Stress Physiology and Biochemistry, 16(1), 85-90.
- Sun, W., Shahrajabian, M.H., Khoshkharam, M., Shen, H., Cheng, Q. (2020c). Cultivations of cotton in China and Iran with considering biological activities and its health benefits. Cercetari Agronomice in Moldova, 1(181), 105-120.
- Sun, W., Shahrajabian, M. H., Cheng, Q. (2021a). Fenugreek cultivation with emphasis on historical aspects and its uses in traditional medicine and modern pharmaceutical science. Mini-Review in Medicinal Chemistry, 21, 1-7.
- Sun, W., Shahrajabian, M.H., Cheng, Q. (2021b). Barberry (Berberis vulgaris), a medicinal fruit and food with traditional and modern pharmaceutical uses. Israel Journal of Plant Sciences. http://dx.doi.org/10.1163/22238980-bja10019
- Sun, W., Shahrajabian, M.H., Cheng, Q. (2021c). Schisandra chinensis, five flavor berry, a traditional Chinese medicine and a super-fruit from North Eastern China. Pharmacognosy Communications, 11(1), 13-21.
- Tikkanen, M.J., Wahala, K., Ojala, S., Vihma, V., Adlercreutz, H. (1998). Effect of soybean phytoestrogen instake on low density lipoprotein oxidation resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 95, 3106-3110.
- Varnosfaderani, S.M., Razavi, S.H., Fadda, A.M. (2019). Germination and fermentation of soybeans: two healthy steps to release angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitory activity compounds. Applied Food Biotechnology, 6(4), 201-215.
- Velu, K., Elumalai, D., Hemalatha, P., Babu, M., Najaki, A., Kaleena, P.K. (2015). Phytochemical screening and larvicidal activity of peel extracts of Arachis hypogaea against chikungunya and malarial vectors. International Journal of Mosquito research, 2(1), 01-08.
- Verleyen, T., Verhe, R., Garcia, L., Dewettinck, K., Huyghebaert, A., De Greyt, W. (2001). Gas chromatographic characterization of vegetable oil deodorization distillate. J Chromatogr A, 921, 277-285.
- Vernaza, M.G., Schmiele, M., Paucar-Menacho, L.M., Steel, C.J., Chang, Y.K. (2012). Brazilian soybean products: functional properties and bioactive compounds. Hispanic Foods: Chemistry and Bioactive Compounds. Chapter 16, pp 259-277.
- Winters, R.L. (1990). Edible fats and oils processing, basic principles and modern practices (Erickson, D.R. ed.). World Conference Proceedings, AOCS, Champaign, pp. 402-405.
- Wu, X., Wu, X., Xu, P., Wang, B., Lu, Z., Li, G. (2015). Association mapping for fusarium wilt resistance in Chinese Asparagus bean germplasm. The Plant Genome, 8(2).
- Wu, H., Zhang, Z., Huang, H., Li, Z. (2017). Health benefits of soy and soy photochemicals. AME Medical Journal, 2, 162.
- Yong, Y., Hu, Y.G., Shahrajabian, M.H., Ren, C.Z., Guo, L.C., Wang, C.L., Zing, Z.H. (2018). Changes in dry matter, protein percentage and organic matter of soybean-oat and groundnut-oat intercropping in different growth stages in Jilin province, China. Acta Agriculturae Slovenica, 111(1), 33-39.
- Yu, J., Ahmedna, M., Goktepe, I., Dai, J. (2006). Peanut skin procyanidins: composition and antioxidant activities as affected by processing. J Food Compos Anal, 19, 364-371.
- Zahran, H.A., Tawfeuk, H.Z. (2019). Physicochemical properties of new peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) varieties. OCL, 26, 19.
- Ziegler, V., Vanier, N.L., Ferreira, C.D., Paraginski, R.T., Monks, J.L.F., Elias, M.C. (2016). Changes in the bioactive compounds content of soybean as a function of grain moisture content and temperature during long-term storage. Journal of Food Science, 81(3), H762-H768.


