Biochemical response of Glycine max (L.) Merr. to cobalt and lead stress
Автор: Imtiyaz Sofi, Agnihotri Rajneesh K., Ganie Showkat A., Sharma Rajendra
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 3 т.10, 2014 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Background: Heavy metal pollution of soil has become a global concern, largely due to the fact that the heavy metals accumulated in plants may either directly or indirectly find their way into animals and human beings. Present study was carried out on the phytotoxicity of cobalt (Co) and lead (Pb) on biochemical constituents viz. chlorophyll a, b, carotenoids, proline, protein and carbohydrate content of three different varieties of Glycine max viz. SL-688, PS-1347, DS-9712 treated with 50, 100 and 150 µM concentrations. Results: The exposure of soybean varieties to Pb and Co resulted in the reduction of chlorophyll, carotenoids, carbohydrate and protein content and addition in proline content. Test plants were more sensitive to lead in comparison to cobalt. PS-1347 variety was found to be more susceptible to both the heavy metals. Maximum deleterious effect was observed at higher concentrations (100 & 150µM). However, an additional supply of nitrogen not only minimized the inhibitory effect of these two heavy metals but also decreased the proline content of plants. Conclusions: The findings of the present study indicate that effect of heavy metals with different treatments on biochemical content was significantly different at 0.05 level of probability. Soils contaminated by heavy metals probably lead to substantial losses in seed yield of soybean plant.
Biochemical parameters, glycine max, heavy metal stress, phytotoxicity
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14323892
IDR: 14323892
Текст научной статьи Biochemical response of Glycine max (L.) Merr. to cobalt and lead stress
Pollution by heavy metals is one of the key environmental problems in the world today. Heavy metals make a significant contribution to environmental pollution as a result of human activities such as mining, smelting, power transmission and intensive agriculture (Nedelkoska and Doran, 2000). Heavy metals can affect plant’s growth and production by inhibiting physiological (Garg and Singla, 2011) and morphological and biochemical (Ozdener and Kutbay, 2011) processes. They are shown to cause disturbance in plant ion concentration (Barcelo et al ., 1986; Wallace et al ., 1992) and water balance to interfere with protein metabolism by influencing nitrate and sulphate reduction (Nussbaum et al ., 1988). A major environmental concern due to dispersal of urban and industrial waste generated by human activities is the contamination of soil with heavy metals. Polluted soil poses a severe problem to both health and land (Akhionbare et al ., 2010). The discharge of heavy metals as a byproduct of various human activities has been accompanied by large scale soil pollution (Shivhare and Sharma, 2012).
Cobalt is usually described as "beneficial" to the plant, however, it can be a contaminant in soils due to agricultural additives or metal refineries (Nies, 1999; Simon 2001). Cobalt is known to cause irreversible damage to a number of vital metabolic constituents and plant cell and cell membrane. Toxic concentration of cobalt inhibits active ion transport and greening and reduces shoot weight in plants (Jayakumar and Vijayrengan, 2006).
Lead (Pb), a potentially toxic heavy metal has attracted considerable attention of scientists due to its widespread distribution and potential risk to the environment. Lead contamination in soils not only aroused the changes of soil microorganism and its activities and resulted in soil fertility deterioration but also directly affected the change of physiological indices and, furthermore, resulted in yield decline (Majer et al., 2002).
Soybean ( Glycine max ) is a species of legume which is native to East Asia, widely grown for its edible bean. The plant is classed as an oilseed rather than a pulse by the UN Food and Agricultural Organization (FAO). The main producers of soy are the United States (35%), Brazil (27%), Argentina (19%), China (6%) and India (4%). Soybean production constitutes around 55% of the total world production of oilseeds and figures around 170-185 million tons. It is favoured by wide variety of climates and soils and thus considered to be the most economical crop. It contains about 20 % oil and 40 % high quality protein (as against 7.0 % in rice, 12 % in wheat, 10 % in maize and 20-25 % in other pulses). Soybean protein is rich in valuable amino acids (5%) in which most of the cereals are deficient. In addition, it contains a good amount of minerals, unsaturated fats, salts and vitamins (thiamine and riboflavin) and its sprouting grains contain a considerable amount of Vitamin C. Besides, Vitamin A is present in the form of precursor carotene, which is converted into vitamin A in the intestine.
Using chemical products as nutrients, fertilizers and pesticides, it is believed that safety gets compromised. Therefore, it is necessary to study the effects of heavy metals from these compounds. In this work we tried to present the effects of the two heavy metals (Pb and Co) on biochemical processes of three different varieties (SL-688, PS-1347 and DS-9712) of soybean plant.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
In the present investigation the chemicals used were obtained from Qualigen and Merck companies. Distilled water was used for preparation of all the solutions.
The seeds of different varieties of experimental plant, Glycine max (SL-688, PS-1347 and DS-9712) were procured from Indian Agricultural Research Institute, Pusa, New Delhi, India
The seeds were surface sterilized with dilute solution of sodium hypochlorite to prevent any fungal contamination and then rinsed three times with distilled water. The sand was thoroughly washed with water and then treated with 2% sodium hypochlorite and dried. The seeds were sown is earthen pots containing equal quantities (2kg) of washed and acid treated loamy sand soil. The soil was treated with Evans and Nason nutrient solution. Co and Pb (control, 50, 100 and 150µM) were provided along with nutrient solution twice a week. Nitrogen was also provided along with nutrient solution. Three identical sets were maintained during the whole experiment and experiments were conducted in green house to provide controlled conditions.
Metal treatments of Co and Pb was prepared using cobalt chloride and lead chloride solutions with concentrations of 50, 100 and 150 µM/L. Nitrogen was prepared using calcium nitrate at 5mM/L concentration. The samples were taken from three week old seedlings for biochemical analysis.
Biochemical analysis
Determination of chlorophyll and carotenoid content
Chlorophyll and carotenoids were extracted from leaves and estimated by the method of Arnon (1949). In this method 1g sample of green tissues was weighed and grinded in pestle and mortar with mixture of acetone and ethyl alcohol (3:1) by repeated homogenization. Supernatant was filtered and was made up to 100 ml. The amount of chlorophyll ‘a', ‘b' and carotenoid was determined by measuring the optical density on (UV-VIS spectrophotometer) at 663, 645 and 470nm.The chlorophyll and carotenoids were calculated by using standard formula.
Total carotenoids (mg g-1 fw) =A/(196xLxW), where:
A = OD of acetone extract at 440 nm
L = diameter of calorimeter tube (quartz)
W = gm sample per total volume
Proline determination
Proline content was measured according to the method of Bates et al. (1973). Fresh leaves were ground in 1.5ml of 3 % (w/v) and proline was estimated by ninhydrin reagent. The ninhydrin reaction mixture was partitioned against toluene and absorbance of the toluene phase was read at 520nm .Proline concentration was determined by plotting a standard curve and as expressed in mg/g proline.
Protein estimation
Protein was quantified according to Lowry (1951) method. Samples were homogenized in 0.1M phosphate buffer (pH=6.8). After adding reagent absorbance was recorded at 750nm and protein was calculated using the standard curve prepared with different concentration of Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA, Sigma: 20 – 200 µg).
Estimation of carbohydrates
Dried powder (50 mg) was extracted with 80% ethanol at room temperature for 1 hour and centrifuged at 1000 rpm at 250C for 60 minutes. The pellet was re-extracted with 80% ethanol for 10 minutes and centrifuged at 10,000 rpm at 250C. The two supernatants were cooled and the volume was reduced to 25 ml, which was used for the analysis of total soluble sugars, reducing sugar and non-reducing sugars.
The pellet was used to estimate starch. It was washed with 80% ethanol and then with water. To this 2 ml of water and 2 ml of 52% Perchloric acid (v/v) were added and the solution was left to hydrolyze at room temperature for 20 minutes. The mixture was then centrifuged at 10,000 rpm at 25ºC for 30 min and the supernatant was made up to 40 ml with distilled water. This was used for estimation of starch.
Total soluble sugars
Total soluble sugars were estimated by following Dubois et al. (1956). To 2 ml of extract, 0.5 ml phenol reagent was added. The colour was developed by rapidly adding 5 ml conc. H2SO4 and the solution was allowed to stand at room temperature for 30 minutes. The absorbance was recorded at 485 nm. The sugar concentration was calculated using a standard curve prepared by different concentrations (20-200 mM/L) of D-glucose.
Reducing sugars
For the estimation of reducing sugars Sumner (1935) method was followed. To 0.5 ml of ethanolic extract, 0.5 ml of water and 1 ml of Dinitrosalicylic acid (DNSA) reagent were added. The reaction mixture was boiled for 10 min and allowed to cool at room temperature. The absorbance was recorded at 560 nm. The concentration of reducing was calculated using standard curve prepared by taking different concentrations (20-200 mM/L) of D-glucose.
Starch
Starch was extracted from leaves by following Mc Cready et al. (1950). To 0.1 ml of the extract 0.9 ml of distilled water was added followed by the addition of chilled anthrone reagent (5 ml). The mixture was heated in a boiling water bath for 10 min and allowed to cool at room temperature. The absorbance was recorded at 630 nm against anthrone as blank. The concentration of starch was calculated using a standard curve prepared by taking different concentration (20-200 mM/L) of D-glucose.
The data was analyzed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) to determine the statistical significance of the differences between means of treatments.
RESULTS
Pigment composition (chlorophyll and carotenoids)
The deleterious effect of Co and Pb on pigment composition in all the three varieties of soybean is presented in Table 1-3. Both cobalt and lead reduced the chlorophyll ‘a', ‘b' and carotenoids content in all the three varieties. Plants were more susceptible to lead than cobalt. At 150µM concentration of both heavy metals chlorophyll a showed reduction of 0.640 and 0.320 (SL-688), 0.653 and 0.213 (PS-1347) and 0.511 and 0.226 (DS-9712) mg g-1 f.w, respectively. Maximum reduction in chlorophyll 'b' (0.692 and 0.350 f.w.) was found in DS-9712 variety. The carotenoids of PS-1347 plants were found to be most susceptible to both the heavy metals with maximum reduction up to 0.981 and 0.587 f.w, when compared to control (1.262 f.w) Application of nitrogen (Ca2 (No3)2) at 05 mM in the nutrient medium somehow minimized the effect of heavy metals. Increase in chlorophyll 'b' was more than the chlorophyll 'a' (Table 1-3 and Fig. 1-3). Carotenoids appear to be more tolerant to heavy metals as compared to other pigments thus showed an increase in the presence of the nitrogen (Table1-3 and Fig. 4).
Plants treated with the different concentrations (50, 100 and 150 µM) of Pb and Co showed high accumulation of proline and again the effect was more due to lead then cobalt. At 150 µM concentration of Co and Pb, enhancement was found to be 1.395 and 1.790, 0.441 and 1.080 and 1.052 and 1.575 mg g-1 in variety SL-688, PS-1347 and DS-9712, respectively. However with the application of nitrogen the proline content was reduced to some extent. Plants showed1.328 and 1.756 (SL-688), 0.441 and 1.080 (PS-1347) and 1.040 and 1.555 mg g-1 f.w. (DS-9712)
decline in proline content when treated with the media supplemented with additional source of nitrogen (Table 4).
The results pertaining to the effect of Co and Pb on protein content in all the three varieties is presented in Table 5. Plants showed reduction in protein content when exposed to Pb and Co at different concentrations. This detrimental effect was more by Pb as compared to Co at all the three concentrations. The protein content of DS-9712 plants was found to be more sensitive to both the heavy metals with maximum reduction up to 58 and 90% when compared to control (1.065 mg/g) at 150 µM concentration of Co and Pb, respectively. Addition of nitrogen in nutrient medium increased protein content and proved to be beneficial for plants (Table 5 and Fig. 1-4)
metals (Table 6 and Fig. 1-4).
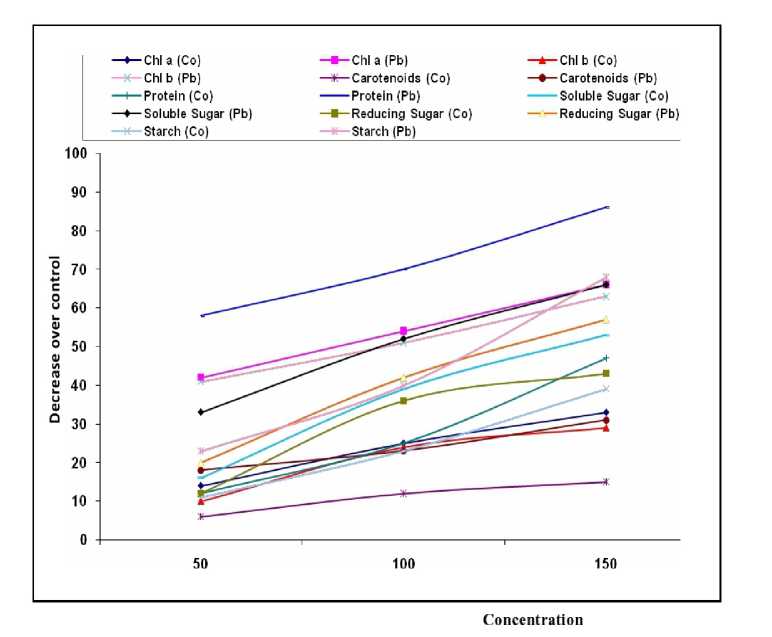
Figure 1. Co and Pb induced heavy metal stress on some biochemical parameters in SL-688 variety of Glycine max
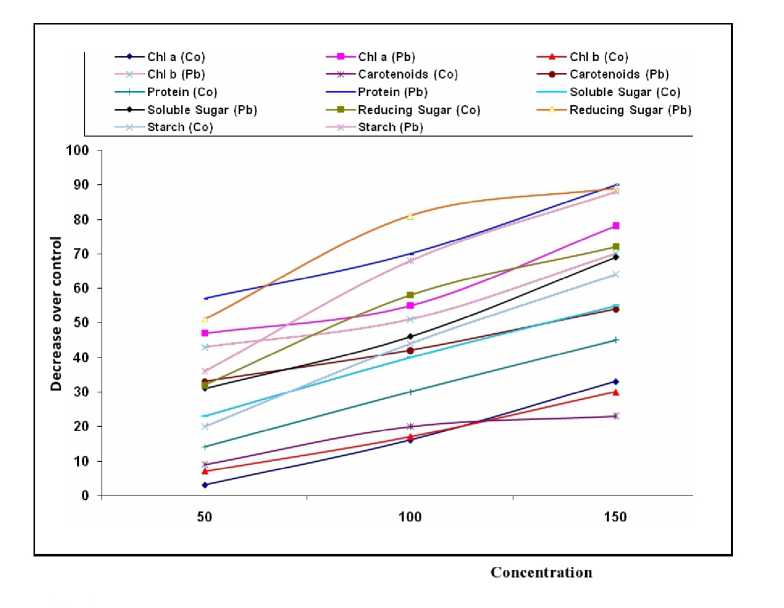
Figure 2. Effect of heavy metals on some biochemical parameters in PS-1347 variety of Glycine max
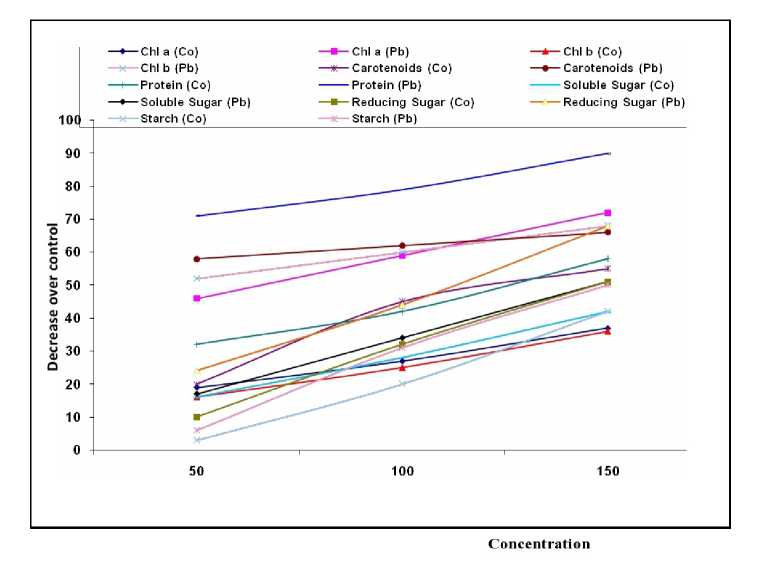
Figure 3. Effect of cobalt and lead on some biochemical parameters in DS-9712 variety.
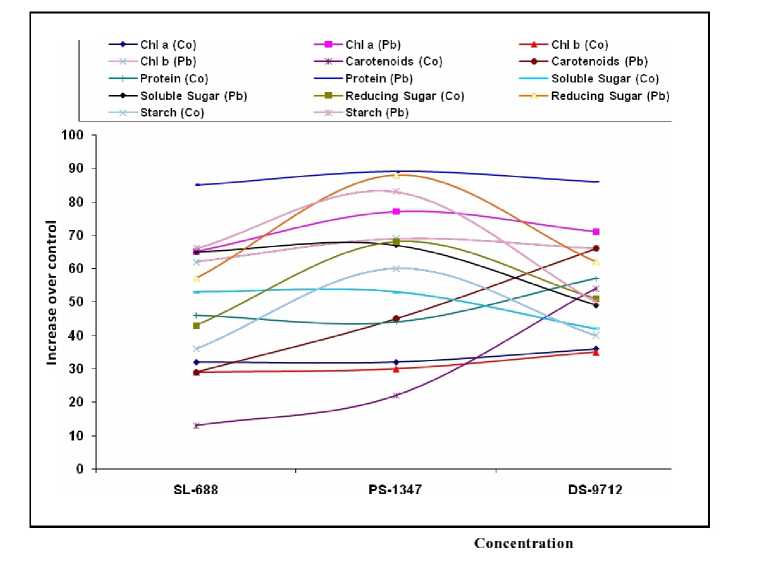
Figure 4. Percentage increase over control in biochemical parameters in different varieties of Glycine max on
application of nitrogen.
Table 1. Effect of cobalt and lead on pigment composition (mg g-1 f.w ) in SL-688 variety of soybean
Caroten
|
Metals |
Concentration (µM) |
Chlorophyll a |
Chlorophyll b |
Total Chlorophyll |
oids |
||||
|
0 mM N |
5 mM N |
0 mM N |
5 mM N |
0 mM N |
5 mM N |
0 mM N |
5 mM N |
||
|
Control |
0 |
0.955 |
0.965 |
1.069 |
1.070 |
2.035 |
2.035 |
2.205 |
2.190 |
|
50 |
0.818ns |
0.830 |
0.956ns |
0.970 |
1.774ns |
1.800 |
2.079* |
2.097 |
|
|
Co |
100 |
0.718ns |
0.729 |
0.805ns |
0.822 |
1.523ns |
1.551 |
1.946* |
1.960 |
|
150 |
0.640ns |
0.658 |
0.745ns |
0.759 |
1.385ns |
1.417 |
1.870* |
1.899 |
|
|
50 |
0.551ns |
0.567 |
0.633ns |
0.647 |
1.184ns |
1.214 |
1.795* |
1.812 |
|
|
Pb |
100 |
0.440ns |
0.556 |
0.520ns |
0.635 |
0.960ns |
1.191 |
1.680* |
1.696 |
|
150 |
0.320ns |
0.336 |
0.390ns |
0.408 |
0.710ns |
0.744 |
1.520* |
1.541 |
|
|
Data are average of 3 replicates, N – Nitrogen, ns = Non |
significant *= |
Significant at 5% level of probability. |
|||||||
|
Table 2. Effect of heavy metals on pigment composition (mg g-1 |
f.w) in PS-1347 variety of soybean |
||||||||
|
Metals |
Concentration (µM) |
Chlorophyll a |
Chlorophyll b |
Total Chlorophyll |
Caroten oids |
Carote noids |
|||
|
0 mM N |
5 mM N |
0 mM N |
5 mM N |
0 mM N |
5 5mM N |
0 mM N |
5 mM N |
||
|
Control |
0 |
0.970 |
0.976 |
1.180 |
1.190 |
2.150 |
2.166 |
1.262 |
1.275 |
|
50 |
0.944ns |
0.960 |
1.097ns |
1.110 |
2.041ns |
2.070 |
1.150* |
1.165 |
|
|
Co |
100 |
0.815ns |
0.828 |
0.980ns |
0.995 |
1.795ns |
1.823 |
1.010* |
1.045 |
|
150 |
0.653ns |
0.660 |
0.822ns |
0.830 |
1.475ns |
1.490 |
0.981* |
0.997 |
|
|
50 |
0.526ns |
0.535 |
0.676ns |
0.690 |
1.202ns |
1.225 |
0.851* |
0.864 |
|
|
Pb |
100 |
0.435ns |
0.442 |
0.580ns |
0.590 |
1.015ns |
1.032 |
0.731* |
0.742 |
|
150 |
0.213ns |
0.220 |
0.357ns |
0.370 |
0.570ns |
0.590 |
0.587* |
0.695 |
|
Data are average of 3 replicates, N – Nitrogen, ns = Non significant *= Significant at 5% level of probability.
Table 3. Effect of Cobalt and lead induced heavy metal stress on pigment composition (mg g-1 f.w) in DS-9712 variety of soybean.
|
Chlorophyll a Chlorophyll b Total Chlorophyll Carotenoids 0 mM N 5 mM N 0 mM N 5 mM N 0 mM N 5 mM N 0 mM N 5 mM N |
|
|
Control 0 |
0.815 0.828 1.080 1.095 1.895 1.923 2.098 2.110 |
|
50 |
0.661ns 0.684 0.905ns 0.933 1.556ns 1.581 1.675* 1.692 |
|
Co 100 |
0.595ns 0.623 0.810ns 0.846 1.405ns 1.469 1.146* 1.660 |
|
150 |
0.511ns 0.530 0.692ns 0.715 1.203ns 1.245 0.953* 0.970 |
|
50 |
0.439ns 0.460 0.514ns 0.538 0.953ns 0.998 0.890* 0.915 |
|
Pb 100 |
0.331ns 0.355 0.433ns 0.455 0.764ns 0.810 0.801* 0.817 |
|
150 |
0.226ns 0.240 0.350ns 0.373 0.576ns 0.613 0.709* 0.725 |
Data are average of 3 replicates, N – Nitrogen, ns = Non significant *= Significant at 5% level of probability.
Table 4: Effect of cobalt and lead on proline content in different varieties of Glycine max .
|
Proline content (mg g-1 f.w.) |
||||
|
Metals |
Concentration (µM) |
SL-688 |
PS-1347 |
DS-9712 |
|
0 Mmn |
5 mMN |
0 mMN |
5 mMN |
0 mMN |
5 mMN |
||
|
Control |
0 |
0.226 |
0.201 |
0.097 |
0.080 |
0.273 |
0.260 |
|
Co |
50 µM |
0.780* |
0.750 |
0.235* |
0.205 |
0.446* |
0.439 |
|
100 µM |
1.295* |
1.270 |
0.327* |
0.316 |
0.669* |
0.656 |
|
|
150 µM |
1.359* |
1.328 |
0.459* |
0.441 |
1.052* |
1.010 |
|
|
Pb |
50 µM |
1.593** |
1.565 |
0.565** |
0.551 |
1.262** |
1.250 |
|
100 µM |
1.650** |
1.627 |
0.783** |
0.769 |
1.386** |
1.365 |
|
|
150 µM |
1.780** |
1.756 |
1.101** |
1.080 |
1.575** |
1.555 |
|
Data are average of 3 replicates, N – Nitrogen, ns = Non significant *= Significant, **= Highly Significant at 5% level of probability.
Table 5: Effect of cobalt and lead on protein content in different varieties of soybean.
|
Protein content (mg/g) |
|
|
Metals Concentration (µM) |
SL-688 PS-1347 DS-9712 DS-9712 0 mMN 5 Mmn 0 mMN 5 mMN 0 mMN 5 Mmn |
|
Control 0 |
0.971 0.985 0.933 0.940 1.065 1.092 |
|
50 |
0.850ns 0.865 0.801ns 0.810 0.725ns 0.748 |
|
Co 100 |
0.725ns 0.737 0.657ns 0.670 0.620ns 0.650 |
|
150 |
0.517ns 0.530 0.516ns 0.528 0.443ns 0.465 |
|
50 |
0.405ns 0.424 0.401ns 0.418 0.310ns 0.335 |
|
Pb 100 |
0.287ns 0.305 0.280ns 0.301 0.225ns 0.252 |
|
150 |
0.133ns 0.151 0.090ns 0.099 0.105ns 0.125 |
Data are average of 3 replicates, N – Nitrogen, ns = Non significant at 5% level of probability.
Table 6: Effect of heavy metals (Co and Pb) on carbohydrate composition in different varieties of soybean.
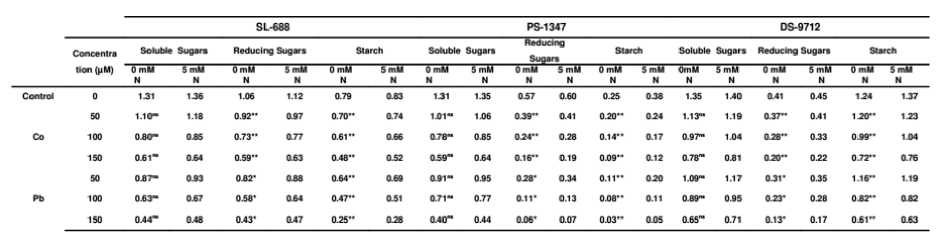
Data are average of 3 replicates, N – Nitrogen, ns = Non significant, *= Significant, **= Highly Significant at 5% level of probability
DISCUSSION
The present investigation showed that both heavy metals (Co and Pb) caused marked reduction in pigment composition, protein content and carbohydrate composition in all the test varieties of soybean. Decrease in pigment composition under heavy metal stress has been reported by several workers on various crops (El-Sheekh et al., 2003; Jayakumar et al., 2007; Jayakumar et al., 2009; Jaleel et al., 2009). Dubey and Pandey (2011) also observed decrease in pigment composition, plant growth and yield of chick pea when exposed to nickel and cobalt stress. Similar results were found by Shakir et al. (2010) in Triticum aestivum. Heavy metal severely inhibits plant growth and even causes plant death by disturbing the uptake of nutrients and inhibiting photosynthesis through degradation of chlorophyll (Zhang et al., 2007). Nagajyoti et al. (2008) reported the reduction in chlorophyll ‘a’, chlorophyll ‘b’ and total chlorophyll in groundnut by industrial effluents containing heavy metals.
Results indicated that increasing levels of cobalt and lead treatment markedly increased the proline content of all the test varieties of soybean. The findings of our study are in agreement with other workers (John et al., 2009; Singh et al., 2012). Under stress proline is a source of nitrogen and energy in metabolism for the plants. Associated with the stress, the accumulation of proline or some other organic solute may be serving as a compatible solute for maintaining the osmotic balance between the cytoplasm and vacuoles (John et al ., 2009; Dar, 2009; Tantary, 2009; Shakir et al., 2010; Asgharipou et al ., 2011) In response to the heavy metal stress from different sources, proline has also been observed to accumulate in (Fatima et al ., 2007).
In the present study, it was observed that the protein content get reduced in the test plants when exposed to both lead and cobalt. Our results are in agreement with the findings of other workers (Balestrasse et al ., 2003; Bavi et al ., 2011) in different crop plants. The reduction in the amount of protein could be due to decrease in protein synthesis or an increase in protein degradation (Balestrasse et al ., 2003). Heavy metals are known to promote protein denaturation (Gadd and Griffth, 1978) and increase the activities of proteases, RNAase and DNAase enzymes (Lee et al ., 1976).
In our study metal toxicity reduced the carbohydrate content like soluble sugars, reducing sugar, non reducing sugar and starch of three tested varieties of soybean. These results are in concern with the findings of several other workers. Salch and Al-Garni (2006) reported that the total carbohydrates may get inhibited if cadmium concentration in soil is more than 5mg/kg. Considerable reduction in the carbohydrate content of Lemna polyrrhiza L. was observed when treated with different concentrations of cadmium and lead (John et al., 2009). Similar results were also reported by (Gaweda, 2007) in vegetables and Hamid et al. (2010) in Phaseolus vulgaris when treated with different concentrations of lead. Carbohydrates are the polyhydroxy aldehydes or polyhydroxy ketones which are widely distributed in plants as changes in the carbohydrate fractions during growth and development are consistent with the changes in photosynthetic pigments. Pb toxicity caused a marked reduction in carbohydrate content. Hemaltha et al. (1997) observed that Pb2+ exposed old seedlings of rice (Oryza sativa) showed a marked decrease in carbohydrate content.
CONCLUSION
Findings of the present study revealed that imposition of both metals viz. cobalt and lead induced considerable changes in all the biochemical parameters studied in all the three varieties of Glycine max . Lead proved more toxic than cobalt which is more consistent in its effect on various plant parameters studied. The effect of cobalt and lead was comparably more at higher concentrations (100 and 150 mM). Carotenoids were less affected as compared to total chlorophyll. Carbohydrate content was also reduced under the exposure of cobalt and lead in the tested plants. Starch was more reduced as compared to other carbohydrates. Additional supply of nitrogen minimized the inhibitory effect of lead and cobalt with varying degree. Exceptionally, proline content in plant tissues increased under cobalt and lead induced stress. In contrast to other parameters, additional supply of nitrogen repressed the proline content. The deadly effects of heavy metals may be reduced in plants if provided with appropriate concentration and form of nitrogen. However, the extent of minimization or reduction depends on the type and concentration of metals and crop used. Thus cultivation of soybean in metal polluted soils should be avoided or appropriate control measures should be adopted to maintain the heavy metal content of soil below the damage threshold level.
Список литературы Biochemical response of Glycine max (L.) Merr. to cobalt and lead stress
- Abdul-Jaleel, C., Jayakumar, K., Chang-Xing, Z., Iqbal, M. (2009). Low concentration of cobalt increases growth, biochemical constituent’s, mineral status and yield in Zea mays. J. Sci. Res., 1, 128-137
- Akhionbare, S., Ebe, T., Akhionbare, W., Chukwuocha, N. (2010). Heavy metal uptake by corn (Zea mays L.) grown in contaminated soil. Res. J. Agric. Biol. Sci., 6, 993-997
- Asgharipour, M.R., Khatamipour, M., Razavi-omrani, M. (2011). Phytotoxicity on seed germination, early growth, proline and carbohydrate content in two wheat varieties. Adv. Env. Biol., 3, 786-792
- Azooz, M.M., Youessef, M.M., Al-Omair, M.A. (2011). Cooperative evaluation of zinc and lead and their synergistic effects on growth and some physiological response of Hassawi Okra (Hibiscus esculentus) seedlings. Am. J. Plant Physiol., 6 (6), 269-282
- Balestrasse, K.B., Benavides, M.P., Gallego, S.M., Tomaro, M.L. (2003). Effect of cadmium stress on nitrogen metabolism in nodules and roots of soybean plants. Funct. Plant Biol., 30, 57-64
- Barcelo, J., Cabot, C., Poshenrieder, C. (1986). Cadmium-induced decrease of water stress resistance in bush bean plants (Phaseolus vulgaris L. cv. Contender) II. Effects of Cd on endogenous abscisic acid levels. J. Plant Physiol., 125, 27-34
- Bavi, K., Kholdebarian, B., Moradshahi, A. (1988). Effect of cadmium on growth, protein content and activity in pea plants. Pak. J. Bot., 43 (3), 1467-1470
- Dar, S.H. (2009). Impact of lead and nickel on some physiological and biochemical activities of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). M. Phil. Dissertation submitted to Dr. B.R. Ambedkar University, Agra, India, pp. 71
- Dubey, P.K. and Pandey, A. (2011). Effect of nickel on chlorophyll, lipid peroxidation and antioxidant enzyme activities in black gram (Vigna radiata) leaves. Int. J. Sci. Nat., 2 (2), 395-401
- El-sheekh, M.M., El-Naggar, A.H., Osman, M.E.H., El-Mazaly, E. (2003). Effect of cobalt on growth, pigments and the photosynthetic electron transport in Monoraphidium mimutum and Nitzehia perminuta. J. Plant Physiol., 15 (3), 159-166
- Fatima, T., Khan, M.A. and Choudhary, M. (2007). Impact of environmental pollution on cynobacterial proline content. J. Appl. Phycol., 19 (6), 625-629
- Gadd, G.M. and Griffith, A.J. (1978). Microorganisms and heavy metal toxicity. Microb. Ecol., 4, 303-317
- Gaweda, M. (2007). Changes in the contents of some carbohydrates in vegetables cumulating lead. Pol. J. Environ. Stud., 16, 57-62
- Hamid, N., Bukhari, N., Jawaid, F. (2010). Physiological responses of Phaseolous vulgaris to different lead concentrations. Pak. J. Bot., 42 (1), 239-246
- Hemalatha, S., Anburaj, A., Francis, K. (1997). Effect of heavy metals on certain biochemical constituents and nitrate reductase activity in Oryza sativa L. seedlings. J. Environ. Biol., 18, 313-319
- Jaleel, A.C., Jayakumar, K., Chang-Xing, Z., Azooz, M.M. (2009). Antioxidant potentials protect Vigna radiata (L) Wilczek plants from soil cobalt stress and improve growth and pigment composition. Plant Omics J., 2 (3), 120-126
- Jayakumar, K, and Vijayrengan, P. (2006). Alteration in carbohydrate metabolism of Vigna mung (L.) Hepper as affected by cobalt stress. J. Eco Toxicol. Environ. 3, 18-21
- Jayakumar, K., Abdul-Jaleel, C., Vijayarengan, P. (2007). Changes in growth, biochemical constituents and antioxidant potentials in radish (Raphanus sativus L.) under cobalt stress. Turk. J. Biol., 31,127-136
- Jayakumar, K. and Vijayarengan, P. (2009). Effect of different concentration of cobalt on pigment contents of soybean. Bot. Res. Int., 2 (3), 153-156
- John, R., Amhad, P., Gadgil, K., Sharma, S. (2009). Heavy metal toxicity: Effect on plant growth, biochemical parameters and metal accumulation by Brassica juncea L. Int. J. Plant Prod., 3 (3), 65-76
- Lee, K.C., Cunningham, B.A., Chung, K.H., Baulsen, G.M., Liang, G.H., Moore, R.B. (1976). Effects of cadmium on respiration rate and activities of several enzymes in soybean seedlings Physiol. Plant., 36, 4-6
- Majer, B.J., Tscherko, D., Paschke, A. (2002). Effects of heavy metal contamination of soils on micronucleus induction in Tradescantia and on microbial enzyme activities: a comparative investigation. Mut. Res., 515, 111-124
- Nagajyoti, P. C., Dinakar, N, Prasad, T.N., Suresh, C., Damodharam, T. (2008). Heavy metal toxicity: industrial effluent effect on groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.) seedlings. J. Appl. Sci. Res., 4 (1), 110-121
- Nedelkoska, T. and Doran, M. (2000). Characteristics of heavy metal uptake by plant species with potential for phytoremediation and phytomining. Min. Engin., 13, 549-561
- Nies, D.H. (1999). Microbial heavy metal resistance. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 52, 730-750
- Nussbaum, S., Schmutz, D., Brunold, C. (1988). Regulation of assimilatory sulfate reduction by cadmium in Zea mays L. Plant Physiol., 88 (4), 1407-1410
- Salch, M. and Al-Garni, S. (2006). Increased heavy metal tolerance of cowpea plants by dual innoculation of an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and nitrogen-fixer Rhizobium bacterium. Afr. J. Biotechnol., 5, 133-142
- Shakier, D., Rajneesh, A., Sharma, R., Showkat, A. (2010). Effect of nickel and lead induced variations in pigment composition of Triticum aestivum L. Res. J. Agric. Sci., 1 (2), 128-131
- Shivhare, L. and Sharma, S. (2012). Effect of toxic heavy metal contaminated soil on an ornamental plant Georgina wild. Toxicol., 2, 2-7
- Simon, L. (2001). Effect of natural zeolite and bentonite on the phytoavailability of heavy metal in chicory. In environmental restoration of metals contaminated soil ed; Iskander, I.K Chapter 13, Lewis Pubishers Boca Raton, pp. 261-271
- Singh, G., Agnihortri, R.K., Sharma, R., Ahmad, M. (2012). Effect of lead and nickel toxicity on chlorophyll and proline content of Urd (Vigna mungo L.) seedlings. Int. J. Plant Physiol. Biochem., 10 (10), 30-32
- Tantrey, M.S. (2009). Studies on effect of Cd and Hg on some physiological and biochemical activities of Gram (Cicer arietinum L.). M. Phil. Dissertation submitted to Dr. B.R. Ambedkar University, Agra, pp. 71
- Wallace, A., Wallace, G.A., Cha, J.W. (1992). Some modifications in trace metal toxicities and deficiencies in plants resulting from interactions with other elements and chelating agents-the special case of iron. J. Plant Nut., 15, 1589-1598
- Zhang, P., Zhou, Q., Sun, X., Wang, F., Jiang, H. (2008). The alleviative effects of AsA on the growth of rape seedlings under Cd stress. J. Agro-Env. Sci., 10 (06), 2362-2366


