Биоинформатический анализ генома штамма Bacillus velezensis КР-2 с целью выявления биотехнологически важных свойств
Автор: Лаптев Г.Ю., Йылдырым Е.А., Дуняшев Т.П., Ильина Л.А., Тюрина Д.Г., Филиппова В.А., Бражник Е.А., Тарлавин Н.В., Пономарева Е.С., Дубровин А.В., Калиткина К.А., Новикова Н.И., Платонов А.В.
Журнал: Сельскохозяйственная биология @agrobiology
Рубрика: Микробиология
Статья в выпуске: 4 т.57, 2022 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Представители рода Bacillus активно используются при создании биопрепаратов для сельского хозяйства в связи со способностью продуцировать широкий спектр биологически активных молекул, обладающих антимикробной активностью, стимулирующих рост растений и восстанавливающих баланс микроорганизмов в пищеварительной системе животных. В представленной работе у штамма Bacillus velezensis КР-2 впервые был выявлен уникальный путь внутриклеточного синтеза осмопротектора глицин-бетаина при участии генов BetA , BetВ , BetT , BetC , о котором у бактерий рода Bacillus ранее не сообщалось. Обнаруженная нами особенность генома B. velezensis КР-2, связанная с синтезом сидерофора миксохелина A, вероятно, также уникальна для этого штамма в отличие от других изученных штаммов, относящихся к виду B. velezensis , поскольку не описана в литературе. Целью исследования был молекулярно-биологический анализ и биоинформатическая аннотация генома штамма Bacillus velezensis КР-2 для выявления генетических детерминант, определяющих возможность биосинтеза разнообразных биологически активных веществ, важных для создания биопрепаратов для сельского хозяйства. Материалом служил штамм B. velezensis КР-2 из коллекции ООО «БИОТРОФ+», выделенный из рубца молочной коровы. Антимикробную активность штамма бактерии исследовали методом отсроченного антагонизма. ДНК выделяли по стандартным методикам с использованием набора Genomic DNA Purification Kit («Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.», США). Библиотеку ДНК для полногеномного секвенирования готовили с помощью набора Nextera XT («Illumina, Inc.», США). Нуклеотидные последовательности определяли с использованием прибора MiSeq («Illumina, Inc.», США). Отфильтрованные по длине не менее чем от 50 до 150 п.н. парноконцевые последовательности собирали de novo с использованием геномного сборщика SPAdes-3.11.1 с соответствующими ключами. Сравнительный анализ генома штамма B. ve-lezensis КР-2 с нуклеотидными последовательностями других микроорганизмов проводили при использовании баз данных NCBI (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/). Для филогенетического анализа последовательность гена 16S рРНК передавали на веб-сервис Nucleotide BLAST (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov). Для перевода нуклеотидной последовательности контигов в аминокислотную использовали PROKKA 1.12 (https://bioweb.pasteur.fr/packages/pack@prokka@1.12). Функциональную аннотацию генома проводили с помощью веб-сервиса RAST 2.0 (https://rast.nmpdr.org). Для оценки пула генов, связанных с биотехнологически ценными свойствами, и построения метаболических карт использовали базу данных KEGG Pathway (http://www.genome.jp/kegg/). В результате полногеномного секвенирования получили 16 контигов с общей длиной 3936398 п.н., содержащих 46,6 % ГЦ-пар, с качеством N50 2109194 п.н. и N75 844068 п.н. В состав хромосомы входили 3854 кодирующие последовательности (CDS), связанные с синтезом полипептидов. Были выявлены 464 метаболические подсистемы, наиболее представленными из которых оказались подсистемы метаболизма аминокислот и их производных (431) и метаболизма углеводов (416). У штамма B. velezensis КР-2 обнаружен комплекс потенциальных свойств, включая синтез антимикробных пептидов, жирных кислот, витаминов, сидерофоров, ауксинов, способность к адгезии, устойчивость к токсическим соединениям, моторику и хемотаксис, возможность противостоять стрессовым факторам, стимулировать рост растений и участвовать в метаболизме фосфатов. В частности, в геноме B. velezensis КР-2 показано присутствие генов ( BacA , BacB , BacG , BacF , BacD ), вовлеченных в образование бацилизина - нерибосомно синтезируемого антимикробного бактериоцина. Данные о возможности синтеза этого дипептида согласуются с фенотипической характеристикой штамма - наблюдаемым in vitro антагонизмом в отношении Staphylococcus aureus , Escherichia coli , Fusarium oxysporum и Clostridium butyricum . У B. velezensis КР-2 нами выявлен уникальный путь внутриклеточного синтеза осмопротектора глицин-бетаина при участии генов BetA , BetВ , BetT , BetC , о наличии которого у бактерий рода Bacillus ранее не сообщалось. Выявлена способность синтезировать ауксины - индол-3-этанола, с продукцией которого ассоциированы гены IAR , TO , индол-3-ацетальдегида ( IAD , AAD , AO ) и индол-3-ацетонитрила ( N3 ). В геноме B. velezensis КР-2 мы также идентифицировали несколько кластеров генов, ассоциированных с синтезом сидерофоров ( DhbA , DhbB , DhbC , FeuA , FeuB , FeuC , FeuD ). Судя по данным лабораторных исследований и полногеномного секвенирования, штамм бактерии B. velezensis КР-2 - это один из бактериальных ресурсов, полезных для использования в сельском хозяйстве. Обнаруженные нами уникальные пути синтеза глицин-бетаина при участии генов BetA , BetВ , BetT , BetC важны для клеточной адаптации штамма B. velezensis КР-2 к высокоосмолярному стрессу, который создается в средах, подверженных частым колебаниям содержания воды, например в подвяленной растительной массе силоса и верхних слоях почвы.
Полногеномное секвенирование, bacillus velezensis, биологически активные вещества, антимикробная активность, бацилизин, глицинбетаин, пробиотики, pgpr, стартерные культуры
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142236352
IDR: 142236352 | УДК: 579.6:577.2 | DOI: 10.15389/agrobiology.2022.4.762rus
Текст научной статьи Биоинформатический анализ генома штамма Bacillus velezensis КР-2 с целью выявления биотехнологически важных свойств
Представители рода Bacillus активно используются при создании биопрепаратов для сельского хозяйства в связи со способностью продуцировать широкий спектр биологически активных молекул, обладающих антимикробной активностью, стимулирующих рост растений и восстанавливающих баланс микроорганизмов в пищеварительной системе животных. В представленной работе у штамма Bacillus velezensis КР-2 впервые был выявлен уникальный путь внутриклеточного синтеза осмопротектора глицин-бетаина при участии генов BetA, BetВ, BetT, BetC, о котором у бактерий рода Bacillus ранее не сообщалось. Обнаруженная нами особенность генома B. velezensis КР-2, связанная с синтезом сидерофора миксохелина A, вероятно, также уникальна для этого штамма в отличие от других изученных штаммов, относящихся к виду B. velezensis, поскольку не описана в литературе. Целью исследования был молекулярно-биологический анализ и биоинформатическая аннотация генома штамма Bacillus velezensis КР-2 для выявления генетических детерминант, определяющих возможность биосинтеза разнообразных биологически активных веществ, важных для создания биопрепаратов для сельского хозяйства. Материалом служил штамм B. velezensis КР-2 из коллекции ООО «БИОТРОФ+», выделенный из рубца молочной коровы. Антимикробную активность штамма бактерии исследовали методом отсроченного антагонизма. ДНК выделяли по стандартным методикам с использованием набора Genomic DNA Purification Kit («Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.», США). Библиотеку ДНК для полногеномного секвенирования готовили с помощью набора Nextera XT («Illumina, Inc.», США). Нуклеотидные последовательности определяли с использованием прибора MiSeq («Illumina, Inc.», США). Отфильтрованные по длине не менее чем от 50 до 150 п.н. парноконцевые последовательности собирали de novo с использованием геномного сборщика SPAdes-3.11.1 с соответствующими ключами. Сравнительный анализ генома штамма B. ve-lezensis КР-2 с нуклеотидными последовательностями других микроорганизмов проводили при использовании баз данных NCBI . Для филогенетического анализа последовательность гена 16S рРНК передавали на веб-сервис Nucleotide BLAST . Для перевода нуклеотидной последовательности контигов в аминокислотную использовали PROKKA 1.12 . Функциональную аннотацию генома проводили с помощью веб-сервиса RAST 2.0 . Для оценки пула генов, связанных с биотехнологически ценными свойствами, и построения метаболических карт использовали базу данных KEGG Pathway . В результате полногеномного секвенирования получили 16 контигов с общей длиной 3936398 п.н., содержащих 46,6 % ГЦ-пар, с качеством N50 2109194 п.н. и N75 844068 п.н. В состав хромосомы входили 3854 кодирующие последовательности (CDS), связанные с синтезом полипептидов. Были выявлены 464 метаболические подсистемы, наиболее представленными из которых оказались подсистемы метаболизма аминокислот и их производных (431) и метаболизма углеводов (416). У штамма B. velezensis КР-2 обнаружен комплекс потенциальных свойств, включая синтез антимикробных пептидов, жирных кислот, витаминов, сидерофоров, ауксинов, способность к адгезии, устойчивость к токсическим соединениям, моторику и хемотаксис, возможность противостоять стрессовым факторам, стимулировать рост растений и участвовать в метаболизме фосфатов. В частности, в геноме B. velezensis КР-2 показано присутствие генов (BacA, BacB, BacG, BacF, BacD), вовлеченных в образование бацилизина — нерибосомно синтезируемого антимикробного бактериоцина. Данные о возможности синтеза этого дипептида согласуются с фенотипической характеристикой штамма — наблюдаемым in vitro антагонизмом в отношении Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Fusarium oxysporum и Clostridium butyricum. У B. velezensis КР-2 нами выявлен уникальный путь внутриклеточного синтеза осмопротектора глицин-бетаина при участии генов BetA, BetВ, BetT, BetC, о наличии которого у бактерий рода Bacillus ранее не сообщалось. Выявлена способность синтезировать ауксины — индол-3-этанола, с продукцией которого ассоциированы гены IAR, TO, индол-3-ацетальдегида (IAD, AAD, AO) и индол-3-ацетонитрила (N3). В геноме B. velezensis КР-2 мы также идентифицировали несколько кластеров генов, ассоциированных с синтезом сидерофоров (DhbA, DhbB, DhbC, FeuA, FeuB, FeuC, FeuD). Судя по данным лабораторных исследований и полногеномного секвенирования, штамм бактерии B. velezensis КР-2 — это один из бактериальных ресурсов, полезных для использования в сельском хозяйстве. Обнаруженные нами уникальные пути синтеза глицин-бета-ина при участии генов BetA, BetB, BetT, BetC важны для клеточной адаптации штамма B. velezensis КР-2 к высокоосмолярному стрессу, который создается в средах, подверженных частым колебаниям содержания воды, например в подвяленной растительной массе силоса и верхних слоях почвы.
Бактерии рода Bacillus находят широкое применение в сельском хозяйстве в качестве основы пробиотиков, стимуляторов роста растений, биопестицидов и инсектицидов, стартерных культур для силосования, поскольку, обладая широкими метаболическими возможностями, служат важным источником для синтеза биологически активных молекул с полезными свойствами (1, 2). Такая востребованность прежде всего связана с присутствием в геноме микроорганизмов этой таксономической группы большого числа хромосомных локусов, определяющих синтез антимикробных соединений (3). Это одно из самых важных функциональных свойств, учитываемых при селекции потенциальных продуцентов биопрепаратов (4-6). P. Piewngam с соавт. (4) продемонстрировали, что один из штаммов рода Bacillus , продуцирующих фенгицин, проявлял активность в отношении золотистого стафилококка у мышей. E. Lara с соавт. (2) наблюдали снижение количества плесневых микромицетов и дрожжей при интродукции в силосную экосистему стартерной культуры на основе штамма B. subtilis .
Кроме того, возможность Bacillus spp. осуществлять метаболизм по пентозофосфатному пути делает их эффективными продуцентами витаминов, среди которых наиболее значимы кобаламин, рибофлавин, фолиевая кислота и биотин (7-9). Спектр ценных метаболитов включает также вещества с противовоспалительной активностью (10). T.-Y. Lee с соавт. (10) показали, что штамм бактерии B. subtilis , способный к синтезу поли-γ-глута-миновой кислоты, проявлял эффективность при лечении дерматита у мышей за счет подавления Th2-смещенного иммунного ответа и синтеза IL-17A. Способность штаммов бацилл синтезировать поверхностно-ассоциированные белки, в том числе белки S‐слоя, аминопептидазы, флагеллин и металлопротеазы, обеспечивает возможность специфически связываться с муцином и фибронектином, что может играть важную роль в адгезии в желудочно-кишечном тракте и обеспечивать пробиотический эффект (11). Высокой емкостью секреторных систем бактерий рода Bacillus предопределяется и потенциал для продукции множества гидролитических внеклеточных веществ. Среди ферментов, представляющих интерес для животноводства, — амилазы ( α - и β-амилазы), β-глюканазы (1), целлюлазы и ксиланазы (12), которые важны для усиления деградации сложных полисахаридов при интродукции штаммов в пищеварительную систему. Еще один пример ферментов Bacillus spp., имеющих биотехнологическое значение, — это инсектицидные метаболиты хитиназы, продуцируемые B. thuringiensis (1, 13), которые действуют совместно с δ -эндотоксинами (Cry или Cyt) (14).
Ряд бактерий рода Bacillus принадлежат к так называемой группе PGPR (plant growth promoting rhizobacteria) (15). Эти микроорганизмы, синтезируя фитогормоны, такие как ауксины (индол-3-уксусная кислота), способствуют интенсификации роста растений и благотворно влияют на их питание, солюбилизируя фосфаты и хелатируя железо сидерофорами (16).
Современные успехи в секвенировании геномов различных микроорганизмов позволяют открывать множество новых кластеров генов, которые кодируют новые или альтернативные варианты уже описанных путей синтеза биологически активных молекул (4, 17). В качестве экспериментальной модели в молекулярной биологии, в частности в геномных исследованиях, традиционно используется бактерия Escherichia coli (18, 19). Однако на сегодняшний день накоплен значительный объем данных по геномике многих других микроорганизмов, в том числе B. velezensis , признанного эффективным антибактериальным агентом и важным средством биологического контроля на сельскохозяйственных угодьях в качестве альтернативы химическим антибиотикам (20). В ряде работ проведены исследования геномов штаммов B. velezensis с целью установить безопасность, антимикробный и пробиотический потенциал этого микроорганизма для его применения в медицине (21), выявить промышленно значимые характеристики для производства ценного сырья (22), изучить способность синтезировать антибактериальные и антифунгальные метаболиты (23), активные против фитопатогенов.
В представленной работе у штамма B. velezensis КР-2 мы впервые выявили уникальный путь внутриклеточного синтеза осмопротектора гли-цин-бетаина при участии генов BetA , BetВ , BetT , BetC , который ранее не был известен у бактерий рода Bacillus . Обнаруженная нами особенность генома B. velezensis КР-2, связанная с синтезом сидерофора миксохелина A, вероятно, также уникальна для этого штамма в отличие от других изученных представителей вида B. velezensis , поскольку не описана в литературе.
Целью исследования был молекулярно-биологический анализ и биоинформатическая аннотация генома штамма Bacillus velezensis КР-2 для выявления генетических детерминант, определяющих возможность биосинтеза разнообразных биологически активных веществ, важных для создания биопрепаратов для сельского хозяйства.
Методика . Материалом служил штамм B. velezensis КР-2 из коллекции ООО «БИОТРОФ+», выделенный из рубца молочной коровы.
Антимикробную активность штамма исследовали методом отсроченного антагонизма (метод перпендикулярных штрихов) в соответствии с рекомендациями (24). Для этого взвесь испытуемой культуры (107 КОЕ/мл) высевали штрихом по диаметру чашки Петри на подсушенную в течение 24-48 ч агаризованную среду ГРМ (ФБУН ГНЦ ПМБ Оболенск, Россия) с добавлением глюкозы (7 г/л). После 24 ч инкубации при 37±1,0 ° С к выросшей культуре перпендикулярно направлению ее роста подсевали культуры тест-штаммов Staphylococcus aureus , E. coli , Fusarium oxysporum и Clostridium butyricum . Через 24 ч инкубации при 37±1,0 ° С оценивали угнетение роста тест-штаммов по расстоянию до штриха испытуемой культуры.
ДНК выделяли по стандартным методикам с использованием набора Genomic DNA Purification Kit («Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.», США) согласно прилагаемой инструкции (25). Метод основан на селективном детергентно-опосредованном осаждении ДНК из субстрата с применением растворов для лизиса клеточных стенок и осаждения ДНК, 1,2 М хлорида натрия, хлороформа.
Библиотеку ДНК для полногеномного секвенирования готовили с помощью набора Nextera XT («Illumina, Inc.», США). Нуклеотидные последовательности определяли, используя NGS-систему MiSeq («Illumina, Inc.», США) с комплектом реактивов MiSeq Reagent Kit v3 (300-cycle) («Illumina, Inc.», США). Недостоверные последовательности и адаптеры удаляли в программе Trimmomatic-0.38 (26).
Отфильтрованные по длине не менее чем от 50 до 150 п.н. парноконцевые последовательности собирали de novo с использованием геномного сборщика SPAdes-3.11.1 (27) с соответствующими ключами. Хромосомные и плазмидные контиги различали по информации в описании (контиги, собранные как плазмидные, имели соответствующую пометку — «-plasmid»). Качество сборки оценивали при помощи QUAST Version: 5.0.2 (А. Gurevich, 2017; .
Для сравнения генома штамма B. velezensis КР-2 с нуклеотидными последовательностями других микроорганизмов использовали базу данных NCBI . Для филогенетического анализа последовательность гена 16S рРНК передавали на веб-сервис Nucleotide BLAST . Настройки для поиска были установлены по умолчанию. Нуклеотидные последовательности контигов транслировали в аминокислотные в программе PROK-KA 1.12 (28). Функциональную аннотацию генома проводили с помощью веб-сервиса RAST 2.0 (29). При оценке пула генов, связанных с биотехнологически ценными свойствами, и построении метаболических карт использовали базу данных KEGG Pathway (30, 31). Для этого полученную транслированную последовательность белков передавали на сервер базы данных KEGG-KAAS . В качества критерия поиска были установлены алгоритмы GHOSTX и bidirectional best hit (BBH). Дополнительно использовали базу данных UniProt .
Математическую и статистическую обработку результатов проводили с помощью программных пакетов Microsoft Office Excel 2003.
Результаты . Штамм B. velezensis КР-2 обладал выраженным антагонистическим действием (рис. 1) в отношении исследованных тест-культур S. aureus , E. coli , F. oxysporum , C. butyricum : ширина зоны задержка их роста составляла соответственно 13,0±0,75; 5,0±0,30; 19,0±0,75 и 14,0±0,70 мм ( n = 5). Это позволяет предположить присутствие в составе культуральной жидкости B. velezensis КР-2 антимикробных веществ, диффундирующих в агар.
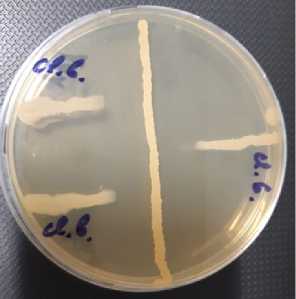
Рис. 1. Антагонистическое действие Bacillus velezensis КР-2 в отношении тест-культуры Clostridium butyricum . Взвесь B. velezensis КР-2 высеяна штрихом по диаметру чашки Петри. В перпендикулярном направлении подсеяна культура тест-штамма C. butyricum. Ближе к центральной части визуализируется зона отсутствия роста C. butyricum.
Полученные данные имеют важное практическое значение, поскольку S. aureus представляет опасность для сельскохозяйственных животных, так как может вызывать заболевания крупного рогатого скота, прежде всего мастит (32). C. butyricum способен выступать как основной инициатор клостридиального брожения при ферментации в силосе, что приводит к потере качества корма (33). Поэтому B. velezensis КР-2 перспективен при разработке биоконтролирующих средств для подавления патогенной микробиоты, в частности при интродукции в силосную массу и в пищеварительную систему сельскохозяйственных животных.
В связи с этим мы провели полногеномное секвенирование и последующую аннотацию генома штамма B. velezensis КР-2 с помощью вебсервиса RAST 2.0. При проведении BLAST анализа в базе NCBI контиг NZ_JAILSD010000003.1 определялся как участок 16S C Bacillus velezensis (штамм FZB42). Совпадение составляло 99,81 % (1547/1550 п.н., 3 мисмэтча). Геномная последовательность была депонирована в коллекции BioProjects (NCBI, под номером PRJNA756418.
Для загрузки на сервер использовали 16 полученных контигов с общей длиной 3936398 п.н., долей ГЦ-пар 46,6 % и показателями качества сборки N50 2109194 п.н. и N75 844068 п.н. Несоответствий и нестыковок в полученной сборке мы не установили.
В состав хромосомы входили 3854 кодирующие последовательности (coding sequence, CDS), связанные с синтезом полипептидов, число генов для тРНК — 93, для рРНК — 9. Плазмидная ДНК (8162 п.н.) содержала 52,1 % ГЦ-пар. Наибольший из аннотированых белков по длине состоял из 5434 аминокислотных остатков, наименьший — из 37 (рис. 2). Доминирующее количество белков имело длину от 37 до 500 аминокислотных остатков.
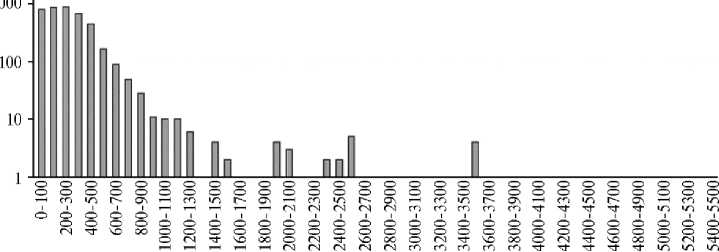
Диапазон количества аминокислотных остатков в белке
Рис. 2. Профиль длин аннотированных белков штамма Bacillus velezensis КР-2, полученный в результате полногеномного секвенирования и последующей аннотации генома штамма с помощью веб-сервиса RAST 2.0 .
Сравнение генома B. velezensis КР-2 с нуклеотидными последовательностями других микроорганизмов при использовании базы данных NCBI Microbial Genomes выявило высокую степень его сходства с геномом Bacillus velezensis (штамм FZB42), а также с геномами других представителей рода Bacillus ( B. subtilis QB928, B. subtilis subsp . subtilis str. AUSI98, B. subtilis subsp . subtilis str. 168). Кроме того, штамм B. velezensis КР-2 был близко связан с кластерами B. amyloliquefaciens и B. atrophaeus .
Штаммы бактерии B. amyloliquefaciens представляют интерес своей способностью стимулировать рост растений-хозяев благодаря продукции ауксинов, подавлять почвенные патогены, синтезируя антибактериальные и антифунгальные метаболиты, а также индуцировать резистентность растений к неблагоприятным факторам окружающей среды (34). Среди штаммов B. atrophaeus также нередко встречаются промышленно важные, в том числе активные продуценты антимикробных веществ, применяемые в качестве средств биологической защиты (35). Ранее A. Niazi с соавт. (34) при полногеномном секвенировании выявили у B. amyloliquefaciens UCMB5033 высокую идентичность генетического материала с B. atrophaeus и B. subtilis .
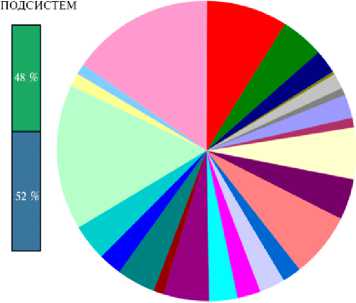
На следующем этапе исследования по результатам анализа генома B. velezensis КР-2 с помощью веб-сервиса RAST мы выявили 464 метаболи-766
ческие подсистемы — группы белков, которые совместно обеспечивают реализацию определенного биологического процесса (рис. 3). Среди категорий подсистем, присутствующих в геноме, наиболее представленными были подсистемы метаболизма аминокислот и их производных (431 подсистема) и метаболизма углеводов (416 подсистем).
ПОКРЫТИЕ РАСПРЕДЕЛЕНИЕ КАТЕГОРИЙ ПОДСИСТЕМ
НАИМЕНОВАНИЕ ПОДСИСТЕМ
Я Синтез кофакторов, витаминов, простстических групп, пигментов (255)
-
■ Клеточная стенка, синтез капсулы (131)
-
■ Адгезия и устойчивость к токсичным соединениям (65)
-
■ Системы, определяющие баланс калия (10)
Прочие метаболические пути (46)
-
■ Транспозирусмыс элементы, плазмиды, профаги, фаги (21)
-
■ Системы транспорта через клеточную мембрану (71)
Я Метаболизм железа (30)
Метаболизм РНК (157)
-
■ Метаболизм нуклеозидов и нуклеотидов (122)
-
■ Белковый обмен (191)
-
■ Клеточное деление и клеточный цикл (53)
Моторика и хемотаксис (84)
-
■ Регуляция и сигнальные системы (63)
Вторичный метаболизм (5)
-
■ Метаболизм ДНК (87)
Я Синтез жирных кислот, липидов и изопреноидов (138)
Я Обмен азота (32)
Я Состояние покоя и споруляции (116)
Я Дыхание (73)
Я Ответ на стрессовые факторы (106)
Метаболизм ароматических соединений (11)
Метаболизм аминокислот и их производных (431)
Обмен серы (39)
Я Обмен фосфора (29)
Я Метаболизм углеводов (416)
Рис. 3. Распределение категорий подсистем клеточного метаболизма у штамма Bacillus velezensis КР-2 на основе результатов функциональной аннотации генома с помощью веб-сервиса RAST . Круговая диаграмма представляет процентное содержание белков для каждой категории подсистем. Категории подсистем перечислены в легенде сверху вниз согласно направлению движения по круговой диаграмме по часовой стрелке. Цифры в скобках — число метаболических путей в соответствующей категории подсистемы. Покрытие подсистем — соотношение известных белков, которые могут быть помещены в существующие подсистемы (зеленый цвет), и неизвестных белков, которые не могут быть помещены ни в одну существующую подсистему (синий цвет).
У штамма B. velezensis КР-2 мы обнаружили комплекс потенциальных свойств, включая синтез антимикробных пептидов, жирных кислот, витаминов, сидерофоров, ауксинов, способность к адгезии, моторике и хемотаксису, устойчивость к токсическим соединениям, возможность противостоять стрессовым факторам, стимулировать рост растений и участвовать в метаболизме фосфатов (рис. 3).
В геноме B. velezensis КР-2 мы выявили гены ( BacA, BacB, BacG, BacF , BacD ), участвующие в образовании бацилизина. Бацилизин — это не-рибосомно синтезируемый антимикробный дипептид, который был обнаружен у одного из штаммов B. subtilis еще в 1946 году как вещество, вызывающее частичный лизис растущих культур Staphylococcus aureus (36). Позже M. Kenig и E. Abraham (37) отмечали высокую активность бацилизина (10 - 3 мг•мл - l) против E. coli . Данные о возможности синтеза этого пептида согласуются с наблюдаемым нами явлением антагонизма B. velezensis КР-2 в отношении S. aureus и E. coli . Известно (38), что бацилизин (L-аланин-[2,3-эпоксициклогексано-4]-L-аланин) состоит из остатка L-аланина на N-конце и небелковой аминокислоты L-антикапсина на С-конце. Несмотря на свою достаточно простую химическую структуру, он активен в отношении широкого спектра бактерий, дрожжей, микромицетов (37).
Интересно, что в результате аннотации в программе PROKKA 1.12 и базе данных UniProt у B. velezensis КР-2 были выявлены гены ComA и ComP, которые ответственны за «чувство кворума» (quorum sensing) у бактериальных популяций, то есть возможность координировать индивидуальное поведение за счет секреции молекулярных сигналов (38). Предпола- гают, что выработка бацилизина у бактерий рода Bacillus регулируется кво-рум-чувствительным путем с участием этих генов (38).
Описанные системы синтеза антимикробных пептидов не новы для бактерий рода Bacillus и довольно широко распространены среди них (39). Так, ранее на примере B. subtilis BAB-1 установлено, что около 5,2 % генома штамма связано с синтезом антимикробных продуктов, в том числе антибиотиков, продуцируемых нерибосомными пептидсинтетазами и полике-тидсинтазами, лантибиотиков, а также бациллибактина. C. Luo с соавт. (17) провели полногеномное секвенирование штамма B. subtilis 916 и обнаружили четыре кластера генов ( srf , bmy , fen и loc ), связанных с синтезом ли-попептидов — сурфактинов, бацилломицина, фенгицина и локилломици-нов, активных в отношении плесневых грибов. Ранее (21) при полногеномном секвенировании штамма B. velezensis KMU01 было показано, что его геном содержал оперон лантибиотического мерсацидина, включая гены пре-мерсацидина (IM712_RS05205), белка модификации (IM712_RS05195) и белка экспорта бактериоцина (IM712_RS05185).
Кроме того, мы обнаружили, что штамм B. velezensis КР-2 способен к синтезу и накоплению осмопротекторов (см. рис. 3). Один из важнейших осмопротекторов — глицин-бетаин, который присутствует в окружающей среде, например синтезируется растениями (40). У B. velezensis КР-2 имеется потенциал к аккумуляции глицин-бетаина напрямую из окружающей среды через три осмотически регулируемые системы поглощения, которые контролируются генами OpuD, ОpuAA, ОpuAB . Связь этих генов с аккумуляцией глицин-бетаина, а также их наличие в геноме Bacillus spp. была описана и в других исследованиях (41). Ранее C. von Blohn с соавт. (42) секве-нировали фрагмент ДНК плазмиды pORT4 B. subtilis длиной 2781 п.н. Показано, что эта область связана с синтезом белка OpuE, который важен для поглощения пролина в средах с высокой осмолярностью. Пролин служит у B. subtilis осмопротектором. При этом система поглощения пролина, контролируемая OpuE , функционирует независимо от известных транспортных систем для осмопротектора глицин-бетаина. S. Heo с соавт. (21) показали, что геном штамма B. velezensis KMU01 содержал две осмопротек-торные системы поглощения — для глицин-бетаина и пролин-бетаина (соответственно гены OpuA и OpuD ).
Оказалось, что в дополнение к прямому получению глицин-бетаина из окружающей среды B. velezensis КР-2 обладает потенциалом для накопления этого осмопротектора посредством его внутриклеточного синтеза, что требует присутствия в среде предшественников — холина или глицин-бетаинового альдегида (43). Выявленный в геноме B. velezensis КР-2 ген BetA связан с синтезом флавинадениндинуклеотид-зависимой холиндегидрогеназы (ЕС 1.1.99.1), которая окисляет холин до глицин-бетаинового альдегида. Ген BetB ассоциирован с продукцией дегидрогеназы бетаинового альдегида (ЕС 1.2.1.8), которая превращает глицин-бетаиновый альдегид в осмопротекторный глицин-бетаин, имея при этом высокую субстратную специфичность. Использование холина (молекулы-предшественника) обусловлено высоким сродством к ней транспортера BetT (43). При этом опе-рон betIBA находился под транскрипционным контролем регулятора кворума AnoR . Ранее сходный путь синтеза глицин-бетаина при участии генов BetA , BetВ , BetT , BetC был обнаружен у E. coli (43) и Acinetabacter nosocomialis (44), но не продемонстрирован для бактерий рода Bacillus , поэтому служит уникальной характеристикой изученного нами штамма.
Традиционно условия повышенного осмотического давления в средах рассматриваются как лимитирующие для развития микроорганизмов, 768
поскольку высокая соленость связана со снижением активности воды (45). Обнаруженные нами пути не только поглощения, но и синтеза глицин-бе-таина важны с точки зрения клеточной адаптации штамма B. velezensis к высокоосмолярному стрессу (45), который создается в средах, подверженных частым колебаниям содержания воды, например в подвяленной растительной силосной массе и верхних слоях почвы (46). Считается, что синтез и накопление осмопротекторов — наиболее гибкий ответ микроорганизмов на ограниченную доступность воды (47).
Помимо этого, у B. velezensis КР-2 был выявлен потенциал для синтеза производных индола, таких как индол-3-этанол, с продукцией которого ассоциированы гены IAR , TO , индол-3-ацетальдегид (гены IAD, AAD, AO ) и индол-3-ацетонитрил (ген N3 ). Обнаружена и возможность синтеза триптофана — важного предшественника ауксина индолил-3-уксусной кислоты (48), обусловленная генами PRAI , IGS , TSa , TSb, APRT. Известно, что ауксины положительно влияют на скорость вегетативного роста, время цветения и плодоношения растений, на процессы фотосинтеза, продукцию различных метаболитов и резистентность к стрессовым факторам окружающей среды, а также регулируют экспрессию генов (49). Поэтому синтез ауксинов рассматривается как важное преимущество для ассоциативного взаимодействия PGPR-бактерий с растениями (50). Проведенные биохимические исследования доказали, что штаммы рода Bacillus могут продуцировать ауксины, в частности индол-3-уксусную кислоту (51). При полногеномном секвенировании B. subtilis EA-CB0575 предсказан потенциал синтеза некоторых ауксинов (метаболизм индола через триптофан, а также возможность продукции индолацетата и индолацетамида) (52). Анализ генома B. velezensis BS89 выявил наличие кластеров генов, ответственных за синтез индол-3-уксусной кислоты (53).
При функциональной аннотации генома B. velezensis КР-2 мы также выявили потенциальные пути синтеза витаминов, в том числе биотина, тиамина, рибофлавина, менахинона. В частности, мы показали присутствие генов, связанных с синтезом биотина, — BPL , BR , BioF , BioA , BioD , BioB , BioW, BioC , BioN , BioG , BioK , BioZ . Возможность синтеза витаминов ранее была обнаружена у многих штаммов рода Bacillus (41, 54). Так, при полногеномном секвенировании B. subtilis UBBS-14 (55), выделенного из ферментированных продуктов питания, были детектированы гены, связанные с биосинтезом биотина, рибофлавина, витамина К, кобаламина, витамина В б и фолиевой кислоты. Витамины играют важную роль во многих обменных процессах в организме животных, оказывая влияние на продуктивность (56). Сообщалось, что эти вещества могут повышать стрессоустой-чивость растений, а также резистентность к заболеваниям при заражении фитопатогенами (57).
В геноме B. velezensis КР-2 мы идентифицировали несколько кластеров генов (DhbA, DhbB, DhbC, DhbE, DhbF, YuiI, FeuABCD), ассоциированных с синтезом сидерофоров и ассимиляцией фосфора (PstS, PstC, PstA, PstS hal, PstS С, PhoP, PhoR, PhoB). Были обнаружены практически все гены, необходимые для осуществления процесса связывания железа при участии бациллибактина (DhbA, DhbB, DhbC, DhbE, DhbF). Выявлен кластер генов DhbA, DhbB, DhbC, ассоциированных с продукцией ферментов 2,3-дигидро-2,3-дигидроксибензоатдегидрогеназы (ЕС 1.3.1.28), изохорисматазы (ЕС 3.3.2.1) и изохорисматсинтазы (ЕС 5.4.4.2), которые ответственны за синтез прекурсора бациллибактина. Кластер генов FeuA, FeuB, FeuC и FeuD ассоциирован с синтезом субстрат-связывающих белков системы транспорта железа. В геноме B. velezensis КР-2 также были обнаружены гены, вовлеченные в синтез других сидерофоров — энтерохелина (EntE, EntB) и миксохе-лина A (MxcE, MxcF). Вероятно, бактерии рода Bacillus для повышения своей конкурентоспособности могут синтезировать несколько сидерофоров, действующих в синергизме, что ранее было показано для других микроорганизмов (58).
Сидерофоры бактерий представляют большой интерес для применения в сельском хозяйстве (59). Дело в том, что для обеспечения жизнедеятельности многих бактерий, прежде всего патогенных, необходимы ионы металлов, в частности катионы железа, участвующие в переносе электронов и служащие кофакторами ферментов, контролирующих синтез ДНК и РНК (60, 61). Поэтому у микроорганизмов в процессе эволюции сформировались сидерофоры — специфические молекулярные структуры (низкомолекулярные хелатирующие агенты), которые позволяют усваивать ионы железа, находящегося в связанном состоянии (62). Применение пробиотических препаратов на основе полезных микроорганизмов, продуцирующих сидерофоры, которые снижают концентрации ионов железа, доступных для патогенов, могут оказать позитивный эффект на здоровье животных (63). Благодаря продукции сидерофоров и успешной конкуренции за ионы железа, присутствующие в почве, PGPR-ризобактерии способны ингибировать фитопато-генные микроорганизмы (64). Ранее при полногеномном секвенировании штамма B. subtilis EA-CB0575 (52) был выявлен потенциал для производства таких сидерофоров, как бациллибактин, энтерохелины и вибриобацины.
Обобщая, следует отметить, что, судя по данным лабораторных исследований, а также по совокупности полезных потенциальных свойств, выявленных методом полногеномного секвенирования, штамм B. velezensis КР-2 — это один из бактериальных ресурсов, перспективных для использования в сельском хозяйстве. Обладая потенциалом для синтеза целого комплекса метаболитов, он может адаптироваться к специфической среде в пищеварительной системе хозяина, в ризосфере или в кормах в процессе ферментации, успешно конкурировать с другими членами автохтонной микробиоты, а также проявлять функции, которые опосредуют позитивное влияние штамма на микробиологические процессы при его интродукции в различные среды.
Таким образом, в результате полногеномного секвенирования штамма Bacillus velezensis КР-2, выделенного нами из рубца молочной коровы, получено 16 контигов с общей длиной 3936398 п.н., содержащих 46,6 % ГЦ-пар, с качеством N50 2109194 п.н. и N75 844068 п.н. В состав хромосомы входили 3854 кодирующие последовательности (CDS), связанные с синтезом полипептидов. Обнаружены 464 метаболические подсистемы, наиболее представленными из которых были подсистемы метаболизма аминокислот и их производных (431 подсистема) и метаболизма углеводов (416 подсистем). Функциональная аннотация выявила комплекс потенциальных свойств, включая синтез антимикробных пептидов, жирных кислот, витаминов, сидерофоров, ауксинов, способность к адгезии, моторике и хемотаксису, устойчивость к токсическим соединениям, возможность противостоять стрессовым факторам, стимулировать рост растений и участвовать в метаболизме фосфатов. В частности, в геноме штамма B. velezensis КР-2 обнаружены гены, вовлеченные в продукцию бактериоцина бацилизина ( BacA , BacB , BacG , BacF , BacD ). Также выявлен уникальный путь внутриклеточного синтеза осмопротектора глицин-бетаина при участии генов BetA , BetВ , BetT , BetC . Показан потенциал синтеза ауксинов, таких как индол-3-этанол
(гены IAR , TO ), индол-3-ацетальдегид ( IAD, AAD, AO ) и индол-3-ацетонит-рил ( N3 ). Кроме того, в геноме B. velezensis КР-2 идентифицированы несколько кластеров генов, ассоциированных с синтезом сидерофоров ( DhbA , DhbB , DhbC , FeuA , FeuB , FeuC , FeuD ). Выявленная нами особенность генома B. velezensis КР-2, связанная с синтезом сидерофора миксохелина A, вероятно, уникальна, поскольку у других штаммов, относящихся к виду B. vele-zensis , подобное не обнаружено . Пути синтеза глицин-бетаина при участии идентифицированных нами генов BetA , BetВ , BetT , BetC имеют важное значение для клеточной адаптации штамма B. velezensis КР-2 к высокоосмолярному стрессу, который создается в средах, подверженных частым колебаниям содержания воды, например в подвяленной растительной массе силоса и в верхних слоях почвы. У штамма B. velezensis КР-2 аннотирована возможность синтезировать бактериоцины, что согласуется с наблюдаемым in vitro антагонизмом в отношении Staphylococcus aureus , Escherichia coli , Fusarium oxysporum и Clostridium butyricum. В дальнейшем, используя различные методы (жидкостная хроматография, масс-спектрометрия, спектроскопия ядерного магнитного резонанса), мы планируем сопоставить полученные молекулярные характеристики с эмпирически наблюдаемыми биохимическими и физиологическими паттернами продукции полезных метаболитов у B. velezensis КР-2. Это позволит получить новые фундаментальные знания о генетическом контроле и регуляции синтеза биоактивных веществ у бацилл и определить перспективы применения B. velezensis КР-2 в сельском хозяйстве.
Список литературы Биоинформатический анализ генома штамма Bacillus velezensis КР-2 с целью выявления биотехнологически важных свойств
- Schallmey M., Singh A., Ward O.P. Developments in the use of Bacillus species for industrial production. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 2004, 50(1): 1-17 (doi: 10.1139/w03-076).
- Lara E., Carvalho Basso F., Assis F., Souza F., Berchielli T., Reis R. Changes in the nutritive value and aerobic stability of corn silages inoculated with Bacillus subtilis alone or combined with Lactobacillus plantarum. Animal Production Science, 2015, 56(11): 1867-1874 (doi: 10.1071/AN14686).
- Guo Q., Li S., Lu X., Zhang X., Wang P., Ma P. Complete genome sequence of Bacillus subtilis BAB-1, a biocontrol agent for suppression of tomato gray mold. Genome Announcements, 2014, 2(4): e00744-14 (doi: 10.1128/genomeA.00744-14).
- Piewngam P., Zheng Y., Nguyen T.H., Seth W. Dickey, Joo H.-S., Villaruz A.E., Glose K.A., Fisher E.L., Hunt R.L., Li B., Chiou J., Pharkjaksu S., Khongthong S., Cheung G.Y.C., Kira-tisin P., Otto M. Pathogen elimination by probiotic Bacillus via signalling interference. Nature, 2018, 562(7728): 532-537 (doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0616-y).
- Bartolini M., Cogliati S., Vileta D., Bauman C., Ramirez W., Grau R. The stress-responsive alternative sigma factor SigB plays a positive role in the antifungal proficiency of Bacillus subtilis. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2019, 85(9): e00178-19 (doi: 10.1128/AEM.00178-19).
- Swartzendruber J.A., Incrocci R.W., Wolf S.A., Jung A., Knight K.L. Bacillus subtilis exopoly-saccharide prevents allergic eosinophilia. Allergy, 2019, 74(4): 819-821 (doi: 10.1111/all.13674).
- Kariluoto S., Edelmann M., Herranen M., Lampi A.-M., Shmelev A., Salovaara H., Korhola M., Piironen V. Production of folate by bacteria isolated from oat bran. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 2010, 143(1-2): 41-47 (doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2010.07.026).
- Duan Y.X., Chen T., Chen X., Zhao X.M. Overexpression of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase enhances riboflavin production in Bacillus subtilis. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2010, 85(6): 1907-1914 (doi: 10.1007/s00253-009-2247-6).
- Biedendieck R., Malten M., Barg H, Bunk B., Martens J.-H., Deery E., Leech H., Warren M.J., Jahn D. Metabolic engineering of cobalamin (vitamin B12) production in Bacillus megaterium. Microbial Biotechnology, 2010, 3(1): 24-37 (doi: 10.1111/j.1751-7915.2009.00125.x).
- Lee T.-Y., Kim D.-J., Won J.-N., Lee I.-H., Sung M.-H., Poo H. Oral administration of poly-y-glutamate ameliorates atopic dermatitis in Nc/Nga mice by suppressing Th2-biased immune response and production of IL-17A. The Journal of Investigative Dermatology, 2014, 134(3): 704711 (doi: 10.1038/jid.2013.389).
- Sánchez B., Arias S., Chaignepain S., Denayrolles M., Schmitter J.M., Bressollier P., Ur-daci M.C. Identification of surface proteins involved in the adhesion of a probiotic Bacillus cereus strain to mucin and fibronectin. Microbiology, 2009, 155(5): 1708-1716 (doi: 10.1099/mic.0.025288-0).
- Aizawa T., Urai M., Iwabuchi N., Nakajima M., Sunairi M. Bacillus trypoxylicola sp. nov., xy-lanase-producing alkaliphilic bacteria isolated from the guts of Japanese horned beetle larvae (Trypoxylus dichotomus septentrionalis). International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 2010, 60(1): 61-66 (doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.005843-0).
- Rairakhwada D., Seo J.-W., Seo M., Kwon O., Rhee S.-K., Kim C.H. Gene cloning, characterization, and heterologous expression of levansucrase from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2010, 37(2): 195-204 (doi: 10.1007/s10295-009-0664-2).
- Chandler D., Bailey A.S., Tatchell G.M., Davidson G., Greaves J., Grant W.P. The development, regulation and use of biopesticides for integrated pest management. Philosophical transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological sciences, 2011, 366(1573): 1987-1998 (doi: 10.1098/rstb.2010.0390).
- Raddadi N., Belaouis A., Tamagnini I, Hansen B.M., Hendriksen N.B., Boudabous A., Che-rif A., Daffonchio D. Characterization of polyvalent and safe Bacillus thuringiensis strains with potential use for biocontrol. Journal of Basic Microbiology, 2009, 49(3): 293-303 (doi: 10.1002/jobm.200800182).
- Raddadi N., Cherif A., Boudabous A., Daffonchio D. Screening of plant growth promoting traits of Bacillus thuringiensis. Annals of Microbiology, 2008, 58: 47-52 (doi: 10.1007/BF03179444).
- Luo C., Liu X., Zhou H., Wang X., Chen Z. Nonribosomal peptide synthase gene clusters for lipopeptide biosynthesis in Bacillus subtilis 916 and their phenotypic functions. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2015, 81(1): 422-431 (doi: 10.1128/AEM.02921-14).
- Cooper G.M. The cell: a molecular approach. Sinauer Associates, 2000.
- Reid C.J., Blau K., Jechalke S., Smalla K., Djordjevic S.P. Whole genome sequencing of Escherichia coli from store-bought produce. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2019, 10: 3050 (doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.03050).
- Xu P., Xie S., Liu W., Jin P., Wei D., Yaseen D.G., Wang Y., Miao W. Comparative genomics analysis provides new strategies for bacteriostatic ability of Bacillus velezensis HAB-2. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2020, 11: 594079 (doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.594079).
- Heo S., Kim J.-H., Kwak M.-S., Sung M.-H., Jeong D.-W. Functional annotation genome unravels potential probiotic Bacillus velezensis strain KMU01 from traditional Korean fermented kimchi. Foods, 2021, 10(3): 563 (doi: 10.3390/foods10030563).
- Li Y., Lei L., Zheng L. Xiao X., Tang H., Luo C. Genome sequencing of gut symbiotic Bacillus velezensis LC1 for bioethanol production from bamboo shoots. Biotechnol. Biofuels, 2020, 13: 34 (doi: 10.1186/s13068-020-1671-9).
- Silva F.J., Ferreira L.C., Campos V.P., Cruz-Magalhaes V., Barros A.F., Andrade J.P., Roberts D.P., de Souza J.T. Complete genome sequence of the biocontrol agent Bacillus velezensis UFLA258 and its comparison with related species: diversity within the commons. Genome Biology and Evolution, 2019, 11(10): 2818-2823 (doi: 10.1093/gbe/evz208).
- Нетрусов А.И., Егорова М.А., Захарчук Л.М., Колотилова Н.Н. Практикум по микробиологии: уч. пос. для студентов высших учебных заведений. М., 2005.
- Ильина Л.А. Изучение микрофлоры рубца крупного рогатого скота на основе молекулярнобио-логического метода T-RFLP с целью разработки способов ее оптимизации. Канд. дис. Дубро-вицы, 2012.
- Bolger A.M., Lohse M., Usadel B. Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics, 2014, 30(15): 2114-2120 (doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu170).
- Nurk S., Bankevich A., Antipov D., Gurevich A.A., Korobeynikov A., Lapidus A., Prjibel-ski A.D., Pyshkin A., Sirotkin A., Sirotkin Y., Stepanauskas R., Clingenpeel S.R., Woyke T., McLean J.S., Lasken R., Tesler G., Alekseyev M.A., Pevzner P.A. Assembling single-cell genomes and mini-metagenomes from chimeric MDA products. Journal of Computational Biology : a Journal of Computational Molecular Cell Biology, 2013, 20(10): 714-737 (doi: 10.1089/cmb.2013.0084).
- Seemann T. Prokka: rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics, 2014, 30(14): 20682069 (doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu153).
- Aziz R.K., Bartels D., Best A.A., DeJongh M., Disz T., R Edwards.A., Formsma K., Gerdes S., Glass E.M., Kubal M., Meyer F., Olsen G.J., Olson R., Osterman A.L., Overbeek R.A., McNeil L.K., Paarmann D., Paczian T., Parrello B., Pusch G.D., Reich C., Stevens R., Vass-ieva O., Vonstein V., Wilke A., Zagnitko O. The RAST Server: rapid annotations using subsystems technology. BMC Genomics, 2008, 9: 75 (doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-9-75).
- Kanehisa M., Goto S. KEGG: kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Research, 2000, 28(1): 27-30 (doi: 10.1093/nar/28.1.27).
- Kanehisa M., Goto S., Sato Y., Furumichi M., Tanabe M. KEGG for integration and interpretation of large-scale molecular data sets. Nucleic Acids Research, 2012, 40: 109-114 (doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr988).
- Zaatout N., Ayachi A., Kecha M., Kadlec K. Identification of staphylococci causing mastitis in dairy cattle from Algeria and characterization of Staphylococcus aureus. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 2019, 127(5): 1305-1314 (doi: 10.1111/jam.14402).
- Li R., Jiang D., Zheng M. Tian P., Zheng M., Xu C. Microbial community dynamics during alfalfa silage with or without clostridial fermentation. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10: 17782 (doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-74958-1).
- Niazi A., Manzoor S., Bejai S., Meijer J., Bongcam-Rudloff E. Complete genome sequence of a plant associated bacterium Bacillus amyloliquefaciens subsp. plantarum UCMB5033. Standards in Genomic Sciences, 2014, 9(3): 718-725 (doi: 10.4056/sigs.4758653).
- Sella S.R.B.R., Vandenberghe L.P.S., Soccol C.R. Bacillus atrophaeus: main characteristics and biotechnological applications — a review. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 2015, 35(4): 533-545 (doi: 10.3109/07388551.2014.922915).
- Abraham E.P., Callow D., Gilliver K. Adaptation of Staphylococcus aureus to growth in the presence of certain antibiotics. Nature, 1946, 158(4023): 818-821 (doi: 10.1038/158818a0).
- Kenig M., Abraham E.P. Antimicrobial activities and antagonists of bacilysin and anticapsin. Journal of General Microbiology, 1976, 94(1): 37-45 (doi: 10.1099/00221287-94-1-37).
- Özcengiz G., Ögülür 1. Biochemistry, genetics and regulation of bacilysin biosynthesis and its significance more than an antibiotic. New Biotechnology, 2015, 32(6): 612-619 (doi: 10.1016/j.nbt.2015.01.006).
- Milner J.L., Silo-Suh L., Lee J.C., He H., Clardy J., Handelsman J. Production of kanosamine by Bacillus cereus UW85. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1996, 62(8): 3061-3065 (doi: 10.1128/aem.62.8.3061-3065.1996).
- Rhodes D., Hanson A. Quaternary ammonium and tertiary sulfonium compounds in higher plants. Annual Review of Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology, 2003, 44: 357-384 (doi: 10.1146/annurev.pp.44.060193.002041).
- Kappes R.M., Kempf B., Bremer E. Three transport systems for the osmoprotectant glycine betaine operate in Bacillus subtilis: characterization of OpuD. Journal of Bacteriology, 1996, 178(17): 5071-5079 (doi: 10.1128/jb.178.17.5071-5079.1996).
- von Blohn C., Kempf B., Kappes R.M., Bremer E. Osmostress response in Bacillus subtilis КР-2: characterization of a proline uptake system (OpuE) regulated by high osmolarity and the alternative transcription factor sigma B. Molecular Microbiology, 1997, 25(1): 175-187 (doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1997.4441809.x).
- Lamark T., Styrvold O.B., Stmm A.R. Efflux of choline and glycine betaine from osmoregulating cells of Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 1992, 96(2-3): 149-154 (doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(92)90395-5).
- Subhadra B., Surendran S., Lim B.R., Yim J.S., Kim D.H., Woo K., Kim H.-J., Oh M.H., Choi C.H. The osmotic stress response operon betIBA is under the functional regulation of BetI and the quorum-sensing regulator AnoR in Acinetobacter nosocomialis. Journal of Microbiology, 2020, 58(6): 519-529 (doi: 10.1007/s12275-020-0186-1).
- Кашнер Д. Баросс Д., Морита Р. Жизнь микробов в экстремальных условиях. М., 1981.
- Miller K.J., Wood J.M. Osmoadaptation by rhizosphere bacteria. Annual Review of Microbiology, 1996, 50: 101-136 (doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.50.1.101).
- Galinski E.A., Trüper H.G. Microbial behaviour in salt-stressed ecosystems. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 1994, 15(2-3): 95-108 (doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.1994.tb00128.x).
- Кравченко Л.В., Азарова Т.С., Макарова Н.М., Тихонович И.А. Роль триптофана корневых экзометаболитов при фитостимулирующей активности ризобактерий. Микробиология, 2004, 73(2), 195-168.
- Дерфлинг К. Гормоны растений. Системный подход. М., 1985.
- Кацы Е.И. Молекулярные основы взаимоотношений ассоциативных микроорганизмов с растениями. М., 2005.
- Swain M.R., Naskar S.K., Ray R.C. Indole-3-acetic acid production and effect on sprouting of yam (Dioscorea rotundata L.) minisetts by Bacillus subtilis OT-2isolated from culturable cowdung microflora. Polish Journal of Microbiology, 2007, 56(2): 103-110.
- Franco-Sierra N.D., Posada L.F., Santa-María G., Romero-Tabarez M., Villegas-Escobar V., Álvarez J.C. Bacillus subtilis EA-CB0575 genome reveals clues for plant growth promotion and potential for sustainable agriculture. Functional & Integrative Genomics, 2020, 20: 575-589 (doi: 10.1007/s10142-020-00736-x).
- Chebotar V.K., Voshol G.P., Malfanova N.V., Chizhevskaya E.P., Zaplatkin A.N., Koma-rova O.V., Baganova M.E., Lazarev A.M., Balakina S.V. Draft genome sequence of plant growth-promoting Bacillus velezensis BS89. Microbiol. Resour. Announc., 2021, 10(1): e01294-20 (doi: 10.1128/MRA.01294-20).
- Sato T., Yamada Y., Ohtani Y., Mitsui N., Murasawa H., Araki S. Production of menaquinone (vitamin K2)-7 by Bacillus subtilis. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 2001, 91(1): 16-20 (doi: 10.1016/S1389-1723(01)80104-3).
- Sulthana A., Lakshmi S.G., Madempudi R.S. Genome sequencing and annotation of Bacillus subtilis OT-2UBBS-14 to ensure probiotic safety. Journal of Genomics, 2019, 7: 14-17 (doi: 10.7150/jgen.31170).
- Frye T.M., Williams S.N., Graham T.W. Vitamin deficiencies in cattle. The Veterinary Clinics of North America. Food Animal Practice, 1991, 7(1): 217-275 (doi: 10.1016/s0749-0720(15)30817-3).
- Chandrasekaran M., Paramasivan M., Chun S.-C. Bacillus subtilis CBR05 induces Vitamin B6 biosynthesis in tomato through the de novo pathway in contributing disease resistance against Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9(1): 6495 (doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-41888-6).
- Barona-Gómez F., Lautru S., Francou F.-X., Leblond P., Pernodet J.-L., Challis G.L. Multiple biosynthetic and uptake systems mediate siderophore-dependent iron acquisition in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) and Streptomyces ambofaciens ATCC 23877. Microbiology, 2006, 152(11): 33553366 (doi: 10.1099/mic.0.29161-0).
- Baghaee-Ravari S., Heidarzadeh N. Isolation and characterization of rhizosphere auxin producing Bacilli and evaluation of their potency on wheat growth improvement. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science, 2014, 60(7): 895-905 (doi: 10.1080/03650340.2013.856003).
- Абатуров А.Е., Крючко Т.А. Медикаментозное ограничение доступности ионов железа для патогенных бактерий (часть 1). Здоровье ребенка, 2018, 13(4): 416-425 (doi: 10.22141/22240551.13.4.2018.137030).
- Capdevila D.A., Edmonds K.A., Giedroc D.P. Metallochaperones and metalloregulation in bacteria. Essays in Biochemistry, 2017, 61(2): 177-200 (doi: 10.1042/EBC20160076).
- Johnstone T.C., Nolan E.M. Beyond iron: non-classical biological functions of bacterial sidero-phores. Dalton Transactions, 2015, 44(14): 6320-6339 (doi: 10.1039/c4dt03559c).
- Balakrishna A., Kumar N.A. Preliminary studies on siderophore production and probiotic effect of bacteria associated with the Guppy, Poecilia reticulata Peters, 1859. Asian Fisheries Science, 2012, 25: 193-205 (doi: 10.33997/j.afs.2012.25.2.008).
- Rout M.E., Chrzanowski T.H., Westlie T.K., DeLuca T.H., Callaway R.M., Holben W.E. Bacterial endophytes enhance competition by invasive plants. American Journal of Botany, 2013, 100(9): 1726-1737 (doi: 10.3732/ajb.1200577).


