Blockchain Framework for Sentiment Analysis from Unstructured Text Reviews
Автор: Pratik K. Agrawal, Monali Gulhane, Siddhi Kadu, Pravinkumar M. Sonsare
Журнал: International Journal of Information Engineering and Electronic Business @ijieeb
Статья в выпуске: 6 vol.17, 2025 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The E-commerce platform has provided the user and the organization with a new avenue for the product distribution and selling. The product distribution is greatly hampered by the opinions provided by the end user and if tampering and fake reviews are generated then it affects the product badly. The Natural language processing domain deals with the analysis of this review and provide the user with recommendation for decision making. The NLP domain deals with several issues like fake reviews, tampering with the reviews, and security for transfer of reviews etc. In this paper, a Blockchain based sentimental analysis module framework is proposed that provides the user with a secure and trustful environment for the opinions reviews as well as it provide a hybrid sentimental module that uses the algorithms from machine learning and deep learning for sentiment score generation. The Proposed Model was evaluated on different datasets of the varied domain. The proposed model performs a substantial improvement in providing the accurate results.
Blockchain, Deep Learning, Opinion Analysis, Machine Learning, Natural language Processing, Sentiment Analysis
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/15020069
IDR: 15020069 | DOI: 10.5815/ijieeb.2025.06.03
Текст научной статьи Blockchain Framework for Sentiment Analysis from Unstructured Text Reviews
Published Online on December 8, 2025 by MECS Press
Businesses together with researchers benefit from processing unstructured text data featuring expressed opinions and sentiments which appear in customer reviews and social media content and feedback. Business organizations utilize understanding of these opinions through analysis to make educated choices that drive enhanced customer satisfaction along with competitive edge. The massive amount of complex unstructured text requires manual evaluation and analysis but proves to be an overwhelming challenge [1]. Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques function as the solution for this task.
The artificial intelligence subfield known as NLP enables machines to process and interpret as well as write human speech. The technology stands as a standard solution for extracting and classifying and analyzing opinions that appear in unstructured text documents. The NLP techniques make it possible to extract sentiment which reveals the emotional stance and attitudinal responses of people regarding specific subjects in opinions analysis. NLP-based opinion analysis requires multiple distinct procedures according to research from sources [2, 3, 4, 15, 16]. Before analysis the unstructured text must undergo pre-processing operations that break down text into tokens while eliminating stop words together with base-form reduction stemming/lemmatization. Sentiment analysis techniques are applied as the second step after completing pre-processing.
Sentiment analysis functions to identify if spoken opinions manifest as positive sentiments or negative sentiments or stay neutral. The analysis of sentiment requires application of different strategies because it extends from using rulebased systems to employing machine learning together with deep learning algorithms. Various techniques that analyze linguistic patterns plus word frequencies together with contextual information and certain domain-specific knowledge help with the analysis. After sentiment analysis completes its task additional NLP techniques become available to extract other important information. The text processing system uses Named Entity Recognition (NER) to detect specific entities including product names together with people and organizations and geographic places. The system of Aspect-based sentiment analysis measures product and service sentiments at their individual features above defining total sentiment.
There are several problems which analyzing the opinions review in the NLP. The NLP faces with many problems like
• Data Integrity and Manipulation: One major challenge in opinions analysis is ensuring the integrity of data. Unstructured text data, such as online reviews, can be easily manipulated or tampered with, leading to biased or misleading results.
• Trust and Authenticity: Online reviews and opinions often suffer from trust issues, as it is difficult to verify the authenticity and credibility of the sources.
• Data Privacy and Consent: Privacy is a significant concern when dealing with opinions data, as it often involves personal information and user-generated content.
• Data Ownership and Sharing: Ownership and sharing of opinions data can be complex, especially when multiple parties are involved, such as review platforms, businesses, and users.
• Data Access and Collaboration: Accessing and collaborating on opinions data can be challenging due to data silos, legal restrictions, and trust barriers
• Data Auditing and Traceability: In opinions analysis, it is crucial to trace the origin and processing of data to ensure its reliability and quality.
2. Literature Review
In order to solve the above problems in NLP, Blockchain based framework are used that provide the solution to the existing issues in NLP.
1.1 Blockchain
The incorporation of Blockchain skill during recent times gained substantial recognition because it creates trusted secure decentralized transparent systems which handle various applications. The blockchain method distributes ledger capabilities which provide protected transactions with clear visibility and protective features to data. The shared database operates through computers across a network which track transaction records in each block chain entry. Any changes to blockchain data must obtain approval from every network node which results in extreme difficulty of data modification.
Blockchain and NLP can be used together to create a number of new and innovative applications. It can be applied in NLP is in creating decentralized marketplaces for NLP services [7, 8,15]. With the increasing demand for NLP services, creating a decentralized marketplace can provide a platform where buyers and sellers can interact and exchange NLP services using cryptocurrencies. This can provide a more secure and transparent platform for buying and selling NLP services, eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing transaction costs. Blockchain can also be used to store and secure NLP data, such as training datasets and models. This can help to protect NLP data from unauthorized access and tampering. Additionally, blockchain can be used to create decentralized NLP applications, which do not rely on a central server. This can make NLP applications more secure, reliable, and scalable.
This work also addresses some of the challenges characterizing sentiment analysis, particularly focusing on combating fake reviews, trust deficit in online opinion systems, and data privacy. Fake reviews undermine the reliability of user-generated content, and trust and authenticity issues affect the accuracy of the sentiment analysis models. Moreover, secure storage and traceability of review data are prerequisites, which is particularly challenging in heterogeneous environments with multiple contributors. To overcome these hurdles, we propose a framework where blockchain technology is used to secure and validate user-generated content in a decentralized and tamper-proof manner while maintaining transparency. The further development of this framework is characterized by the novel approach to integrating blockchain technology with hybrid sentiment analysis based on Naïve Bayes and LSTM which had not been developed earlier in the existing literature. Different from prior works, the focus of this framework is on scalability and security due to the use of Ethereum smart contracts and Layer 2 scaling solutions[16,17]. The fusion model simulates what we do with the combination of the above two data modalities combining their pros while eliminating their cons.
The article’s remaining portions are: Section 2 examines and list out the work of the researchers that has used blockchain based framework with different domain for achieving the accuracy and efficiency. The proposed blockchain based framework for opinions analysis is mentioned in Section 3. Section 4 demonstrates the simulation results. Section 5 summarizes the research.
Many researchers has explored and contributed to the development of the blockchain concepts, as it has demonstrated its efficiency in the financial security management and many more. The researchers examined that the blockchain can also provide the same level of security management for the domain that are dealing with this problems.
Zhen et.al (2023) [1] explores how a fairness-aware large-scale collective opinion generation paradigm evaluates blockchain adoption barriers within medical supply chain operations. The authors develop a fairness-aware large-scale collective opinion generation paradigm to deal with existing barriers. The proposed paradigm receives evaluation through analysis of the medical supply chain in China as a test case. The authors establish that the fairness-aware large-scale collective opinion generation paradigm shows great potential for blockchain adoption barrier evaluation alongside blockchain technology adoption promotion.
The public reaction to cryptocurrency and blockchain technologies is evaluated through Twitter analysis by Elen et.al (2023) [2]. Research data about tweets focused on cryptocurrency and blockchain technology was collected by the authors. The researchers applied a lexicon-based sentiment analysis tool to process the tweets which produced positive or negative or neutral classification results. The authors monitored how people mainly hold positive opinions about cryptocurrency and blockchain technology. Distinct negative-positive opinions exist between various nations worldwide. The research results indicate that people hold mainly positive attitudes regarding cryptocurrency together with blockchain technology.
Wang et.al (2023) [3] discusses the use of blockchain technology to improve risk prediction and credibility detection of network public opinion. The authors propose a blockchain-based risk prediction and credibility detection framework that consists of blockchain-based data storage system to store and share information about public opinion, blockchain-based consensus mechanism to ensure the accuracy and reliability of information and blockchain-based workflow management system to automate the process of risk prediction and credibility detection. The authors evaluate the proposed framework using a case study of a public opinion risk prediction and credibility detection project in China.
Hassani et.al (2023) [4] discusses the use of blockchain technology to improve trust building and consensus management in linguistic opinion dynamics. The authors propose a blockchain-based trust building and consensus management framework that includes the blockchain-based trust network to store and share information about agents and blockchain-based consensus algorithm to reach agreements between agents. The authors evaluate the proposed framework using a case study of a linguistic opinion dynamics application.
The paper by Luo et.al (2023) investigates how blockchain technology enhances big data network public opinion risk management systems [5]. Their blockchain-based system for network public opinion risk management incorporates three main components: first a secure blockchain-based data storage system and second a blockchain-based consensus mechanism and lastly a blockchain-based workflow management system. A blockchain consensus system operates to guarantee the accuracy together with reliability of public opinion data records. The system features a blockchain workflow manager which automates the public opinion risk management tasks. The study analyzes its proposed approach through an evaluation of Chinese public opinion risk management project performance. The authors indicate that blockchain technology presents significant potential as an effective solution for big data environments to handle network public opinion risk management functions.
Lade et.al (2023) developed a system for Bitcoin price prediction as well as NFT generation through sentiment analysis [6]. LSTM processing analyzes sentiment data collections which enables the system to classify tweet sentiments. The analysis output serves as an indicator to predict Bitcoin prices while simultaneously creating NFTs. The Twitter sentiment data collection served as the evaluation basis for the system. The system demonstrated capacity to detect sentiment values in the examined tweets accurately. Using the system yielded accurate Bitcoin price predictions.
Osman and Husien (2022) [7] compares the performance of different sentiment analysis techniques for classifying Twitter posts. The authors used a dataset of Twitter posts that were labeled as positive, negative, or neutral. They then used four different sentiment analysis techniques to classify the tweets like Lexicon-based sentiment analysis, Naive Bayes sentiment analysis, Support vector machine sentiment analysis, Deep learning sentiment analysis: This technique uses a deep learning model to classify tweets. The authors conclude that deep learning sentiment analysis is the most effective technique for classifying Twitter posts. They also conclude that lexicon-based sentiment analysis is a good alternative for deep learning sentiment analysis, especially when resources are limited.
Chen et.al (2022) [8] proposes a novel method for learning user sentiment orientation in social networks. The method is based on the idea that users' sentiment orientation can be learned from their interactions with other users. The method consists of Feature extraction that extracts features from the user-user interaction network. These features include the number of links between users, the strength of the links, and the sentiment polarity of the links and
Sentiment orientation method learns the sentiment orientation of each user. This is done by using a machine learning algorithm to train a model that predicts the sentiment polarity of the links between the user and other users. The method can be used to improve the accuracy of sentiment analysis in social networks.
Zhao et.al (2021) [9] proposes a system for sentiment analysis of review data using blockchain and LSTM to improve regulation for a sustainable market. The system consists of Data collection module for collecting review data from online platforms. The author proposes the uses of LSTM to analyze the collected review data and identify the sentiment of each review and also uses the regulation module for the results of the sentiment analysis to regulate the market and ensure that it is sustainable. The system was evaluated using a dataset of review data from Amazon. The results showed that the system was able to accurately identify the sentiment of the reviews.
Verma et.al (2021) [10] proposes a framework for sentiment analysis of feedback data using blockchain technology. The framework uses LSTM to analyze the collected feedback data and identify the sentiment of each feedback. The module uses blockchain to store the collected feedback data and the results of the sentiment analysis. The framework was evaluated using a dataset of feedback data from Amazon. The results showed that the framework was able to accurately identify the sentiment of the feedback.
Ye Liang and Ying Qin (2020) [11] discusses the use of blockchain technology to trace public opinion across languages. The authors propose a blockchain-based public opinion tracing system that includes blockchain-based data storage system to store public opinion data in a secure and tamper-proof manner, blockchain-based consensus mechanism to ensure the accuracy and reliability of public opinion data and blockchain-based workflow management system to automate the process of public opinion tracing. The authors evaluate the proposed system using a case study of a public opinion tracing project in China. The authors conclude that blockchain technology can be a valuable tool for improving cross-lingual public opinion tracing.
Q. Pan et.al (2018) [12] proposes a deep learning model for text sentiment analysis. The model consists of bidirectional long short-term memory (BLSTM) model: This model is used to extract features from the text and support vector machine (SVM) classifier: This model is used to classify the text into positive, negative, or neutral sentiment. The BLSTM model is a deep learning model that can learn long-range dependencies in text. The SVM classifier is a machine learning model that can be used to classify text into different categories. The authors evaluated the model on a dataset of text that was labeled as positive, negative, or neutral. The results showed that the model achieved an accuracy of 93.2%. The authors conclude that the model is a promising approach for text sentiment analysis.
3. Methodology
Kuo et.al (2017) [13] provides an overview of the potential applications of blockchain distributed ledger technologies (DLTs) in biomedical and health care (BMH). The authors discuss the benefits of DLTs for BMH, such as their decentralized, secure, and transparent nature. They also discuss the challenges that need to be addressed before DLTs can be widely adopted in BMH, such as security and privacy concerns. The authors conclude that DLTs have the potential to revolutionize BMH by improving the efficiency, security, and privacy of data sharing and collaboration. They also suggest that DLTs could be used to improve the quality of care, reduce the costs of healthcare, and accelerate the development of new treatments.
Yue et.al (2016) [14] proposes a blockchain-based architecture for healthcare data gateways. The proposed architecture aims to address the challenges of healthcare data sharing, such as data fragmentation, security, and privacy. The proposed architecture has several advantages over traditional healthcare data sharing approaches. First, the blockchain-based data storage system provides a secure and tamper-proof way to store healthcare data. Second, the PAAC system ensures that only authorized users can access healthcare data, and that data is only used for the intended purpose. Third, the healthcare data gateway provides a secure interface for healthcare organizations to access and share healthcare data.
Thus the review explains that blockchain technology is implemented due to its decentralised and immutable data storage feature that allows safe and reliable data storage. Traditional methods of secure storage heavily depend on centralized servers, making them susceptible to a breach or manipulation, whereas blockchain provides immutability based on distributed consensus mechanisms. User-generated reviews have traceability, and this removes single points of failure. Moreover, with the implementation of smart contracts on the blockchain, data verification and processing become automated, thus minimizing the dependence on third-party intermediaries. Although alternatives such as cryptographic hashing and secure databases grant limited security functionality, these types of solutions miss essential components needed in collaboration that enables trust transparent, immutable and decentralized. Hence, blockchain can be an ideal solution to the issues of trust and data authenticity in terms of sentiment analysis.
The analysis of the literature review provided with the information that the blockchain approach has provided a considerable improvement in the performance of the area in which it has deployed for security management, efficient distribution of the datasets and providing integrity and security to the domain
The Proposed Mechanism uses Blockchain algorithms, also known as consensus algorithms, are fundamental components of blockchain technology. They play a critical role in enabling participants in a blockchain network to agree on the validity of transactions and reach a consensus on the state of the blockchain. These algorithms ensure the integrity, security, and decentralization of the blockchain by providing mechanisms for achieving agreement among participants without the need for a central authority.
By leveraging these consensus algorithms, blockchain technology enables decentralized and trust less networks where participants can reach agreement and maintain the integrity of the shared ledger. The selection and implementation of a suitable consensus algorithm are crucial in designing a blockchain system that meets the specific needs and objectives of the intended application.
The proposed work focuses on the Proof of Work consensus algorithms for the development of the Blockchain based framework for the opinions reviews analysis. The Figure 1, depicted the suggested proposed architecture contains four sorts of entities user, processor, manager and organization. As per the four entities it involves four modules the opinion data module, the sentiment analysis module, trust management module and review analysis module for organization.
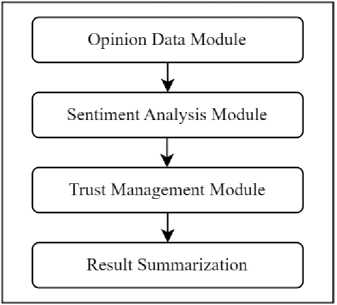
Fig. 1. Proposed Blockchain Framework for Opinion Analysis
-
3.1 Opinion Data Module
-
3.2 Sentiment Analysis Module
The opinion data module host the user on the blockchain network with the help of the Etherum blockchain framework and register the user, e-commerce and the organization on the network. The account is created for every user and the organization of which the products is mentioned and the user has provided a review to the products. The review will be linked to the product id and it will be collected in the secure blockchain in the form of distributed peer to peer model. The Block releated to the particular product will store the reviews of all the user distributed all around the network and this will provide a substantial security and validation to the user reviews that are generated and is stored on a secure blockchain network for the access.
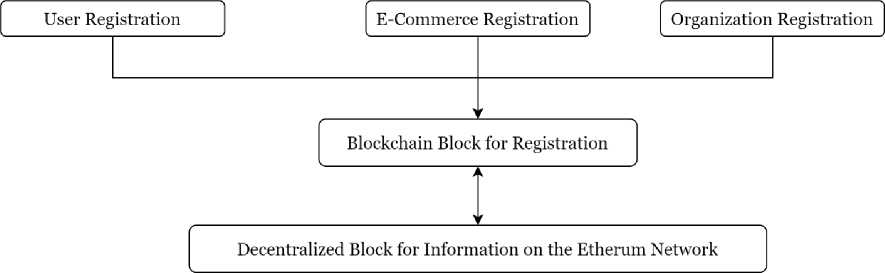
Fig. 2. Opinion Data Module
The Opinion reviews generated and shared by the opinion data module are used for the classification of the reviews and to extract the sentiment from the unstructured text. The unstructured text deals with many issues for sentiment extraction. The machine learning and deep learning approach algorithms are used for the generation of the analysis from the text reviews.
The proposed architecture of the sentiment analysis make the use of machine learning Navie Bayes Model and LSTM Deep learning model for calculating the polarity of the input unstructured text reviews.
-
> Na ve Bayes Classifier Algorithm
It is a graphical model which is most widely used is the Bayesian networks because it can handle uncertain information.
The steps for Naïve Bayes classifier Algorithm is as follows:
Step 1: The Naïve Bayes classifier algorithm assumes the dataset (D) with words, all the words from the dataset (D) belong to the specified class (Cj) and presume that there are no missing values.
Step 2: The Previous Probability P (Cj) is calculated for all class (Cj) in the dataset using equation (1).
: ( j)= ∑ ∑ → (1)
Where t represents the occurrence from 1 to n
Cj represents the class in the Datasets.
Step 3: For all attribute value (Aij) the class provisional probabilities Р (Аіј⁄ ) for each characteristic values are calculated in the D.
Step 4: The previous probability of the class is multiplied by the class conditional Probability.
Step 5: The Class with the highest classifier probability is considered by comparing the output probability of each class from 1 to N
LSTM (Long Short-Term Memory) classifier
It belongs to the category of recurrent neural network (RNN) that is commonly used for text investigation and natural language processing tasks. LSTM networks are effective in capturing long-range dependencies in sequential data, making them well-suited for tasks involving text classification, sentiment analysis, named entity recognition, and more.
The architecture of an LSTM opinion analysis review model is typically composed of the following layers:
-
• Embedding layer: This layer converts each word in the review into a fixed-length vector. This is done to represent the meaning of each word in a way that is understandable by the LSTM network.
-
• LSTM layer: This layer is responsible for learning long-term dependencies in the review text. It does this by maintaining a state that is updated as the network processes each word in the review.
-
• Dense layer: This layer is responsible for classifying the review as positive, negative, or neutral. It does this by taking the output of the LSTM layer and passing it through a series of linear operations that produce a probability distribution over the three classes.
The Naïve Bayes Classification Algorithm and the LSTM classifier provides a fast and scalable search for the various domain mapping applications of information retrieval. The approaches deal with some challenges that need to be addressed for improving the accuracy of the system. The efficient solution will be to use the hybrid approach that will combine the outputs score of both the algorithm for searching and prediction of the domain as both implies different approaches. This can result in improved performance for the mapping. The performance of the mapping can be further improved by working on the input sets that are used at the time of comparison.
The proposed designed of hybrid approach will combine the outputs score of both the algorithm for searching and prediction of the domain as both imply different approaches.
The architecture for the Hybrid approach is as follows:
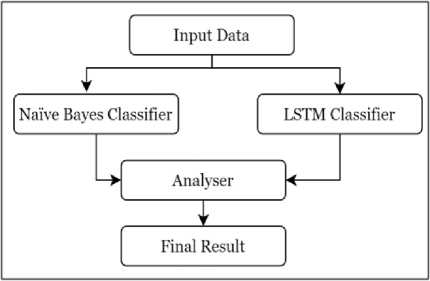
Fig. 3. Architecture for Hybrid Sentiment Analysis Approach Module
The Proposed Hybrid Algorithm for sentiment analysis is as follows:
Step 1: Take the Input from the opinion input data module.
Step 2: Initialize the Naïve Bayes Classifier and LSTM classifier for generating the Score value (S) and weighted vector (V).
Step 3: The Naïve Bayes score value is combined with the score value(S) of the weighted vector (v) and an average combination is taken for the domain entity matching.
Final Score Value = (S + V)/2 (2)
Where S represents Naïve Bayes score value
V represents weighted LSTM (V)
Step 4: The Final Score value is treated as the best value for sentiment analysis.
Step 5: The Step from 2 to 4 will be repeated for every entity matched i.e. from 1 to N.
-
3.3 Trust Management Module
This module deals with the security and service constraint of the proposed sentiment analysis module. It consists of four entities user, processor, manager and organization that represents the four nodes in the blockchain Etherum network let P1, P2, P3 and P4 for executing the smart contracts respectively. The architectural flow diagram for the trust management module is depicted in the figure 4. The P1 represents the user that provides the opinion for the particular product and the reviews are stored in the blockchain network for the security. The P2 nodes represents the processor that includes the sentiment analysis module that take the hybrid approach in order to make the sentiment analysis of the data coming from the P1 nodes.
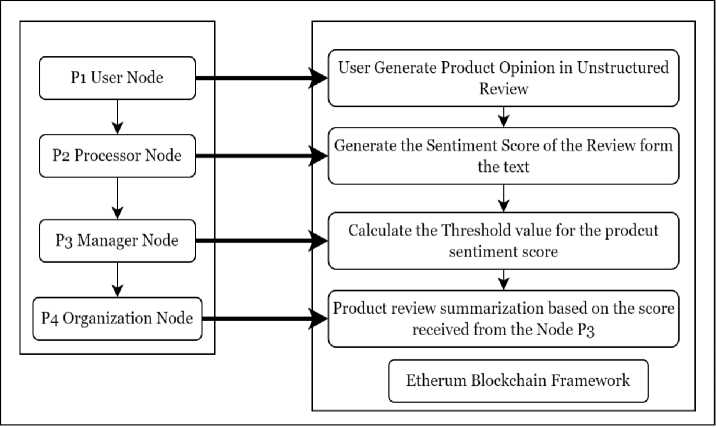
Fig. 4. Architecture for Trust Management Module
The generated results for the every product is stored in a distributed network of blockchain spread around the complete the complete Etherum and subsequent smart contracts is generated for the every couple of opinions and stored in the network. The P3 nodes in the network acts as a manager that manages the complete information coming from the P2 nodes for the efficient and proper management.
The P3 nodes follows a stop and wait approach for the processing and providing the information to the P4 nodes. The information stored in the Etherum block are processed by the P3 nodes, the P3 node calculate the threshold value of the analysis based on the review provided by the P1. If the value of the sentiment analysis information meet the given threshold the information is provided to P4 node that acts as a manager of the product for the organization. The information contains the sentiment analysis score for the product and the P4 node makes an appropriate judgment based on the policy of the reviews but if the threshold value is not meet then the information will be stored in the blockchain through smart cards this is done so that a collaborative and sufficient amount of data is required for processing therefore threshold is used for the purpose. The Flow chart representing the process of sending the sentiment score by the P3 node to the P4 nodes is depicted in figure 5.
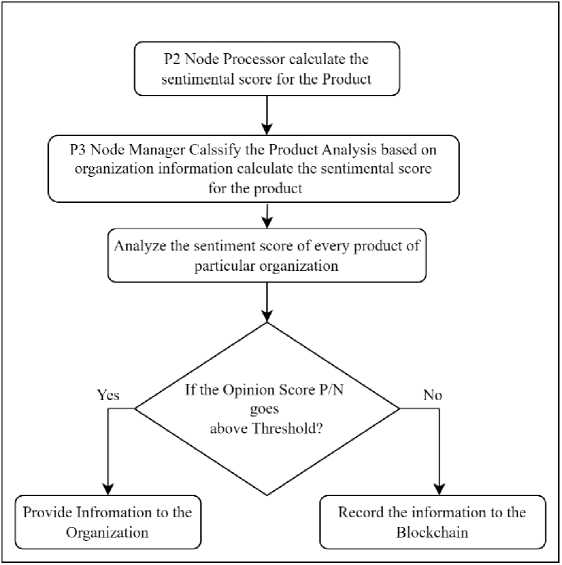
Fig. 5. Flow chart representing the process of sending the sentiment score
3.4 Data Analysis and Splitting:
4. Results and Discussion
4.1 Datasets4.2 Evaluation of the Metrics for comparison
The datasets were divided into training, validation and testing sets (70%-15%-15%) in order to provide a strong evaluation and avoid overfitting. The hybrid model was trained on the training set, and hyperparameters were tuned as well as overfitting was checked with early stopping on the validation set. The testing set remained entirely independent and was used for a final evaluation. Moreover, methods such as dropout regularization and cross-validation were used to further prevent overfitting and ensure generalization on unseen data.
The simulation is carried out in mandate to critic the routine of Sentiment analysis hybrid proposed algorithm. The data-set provided by Kaggle which is a kind of research platform for data science projects.
The datasets were taken from the different domain to test the competence of the system. The four datasets are D1, D2, D3, and D4. And are created from the reviews. The D1.test is the Dataset for the college reviews; D2.test is the datasets for the camera reviews, D3.test is the datasets consist of hotel reviews and D4.test is the datasets which consist of car reviews. The D1.test datasets are created from college reviews. The real time data collection was done from the students of the college. The D2.test is the datasets for the camera reviews. The datasets are retrieved form the amazon website. The datasets consists of the reviews of the two camera products from the cannon company. The data is in the text file with over 3000 reviews. The D3.test is the datasets consist of hotel reviews. The datasets are retrieved from the Trivago India by running a python script on the website. The datasets is provided by the Kaggle research platform. The data is in the form of a csv file with over 4000 reviews. The D4.test is the datasets which consist of car reviews. The reviews are taken from the Edmunds website. It consists of about 140-250 cars reviews for each year model.
It is imperative to calculate the performance of the sentiment analysis module, the proposed algorithm are trained with the training datasets and evaluated on the test datasets for the comparison. Two metrics are used for the evaluation of the set which are accuracy, and F1-score respectively.
Accuracy determination of the proposed methodology depends on correct sentiment recognition outcomes from given datasets according to equation (3).
TP+TN
Accuracy Percentage = (3)
у " TP+FP + FN+TN v 7
Average Delay: It is calculated as the overall time mandatory by the system to calculate the output.
Classification model evaluation often depends on the metrics of precision and recall for measuring performance outcomes. The metrics offer specific information about model performance especially for datasets with inaccurate class distribution. The following evaluation details these metrics:
Precision:
Precision exists as the quotient between accurate positive predictions and all positive predictions the model generates. The metric calculates successful positive predictions among all forecasted positive items according to equation (4).
Рreсіѕіоn = True Роѕіtіves / (True Роѕіtіves + False Роѕіtіves) (4)
When mistakes in diagnosis would prove costly, we need high precision to reduce the number of incorrect positive predictions. Precision serves as an essential factor in medical diagnosis given that incorrect disease identifications of well patients results in harmful medical procedures and patient stress.
Recall:
The calculation of recall starts by dividing the count of actual positive data instances by their total number in the dataset. The model's ability to detect positive examples correctly is represented by this measure through equation (5).
Recall = True Positives / (True Positives + False Negatives) (5)
F1-Score computes as an average of recall and precision from equations (4) and (5) reaching its highest value at 1 and its lowest value at 0. The measure combines false positive and false negative occurrences according to Equation (6).
F 1- score =2 ∗ precision ∗ recall / ( precision + recall ) (6)
The model indicates right training outcomes through TP (True Positive) and TN (True Negative) while FP (False Positive) and FN (False Negative) signals improper end results. False Positive results are represented by FP and False Negative results by FN indicate incorrect training outcomes.
-
4.3 Performance Analysis
The performance analysis of the proposed algorithm occurs on D datasets that unite D1, D2, D3 and D4 databases. The performance evaluation relies on the aggregation of findings present within the datasets. Table 1 together with Figure 6 displays assessment results of the F1-score achieved by both the proposed model and the existing method.
Table 1. F1- Score Calculation on the varied Datasets
|
Sr. No |
Data Scale Size |
Naïve Bayes |
LSTM |
Proposed Model |
|
1 |
3000 |
59.234 |
60.214 |
63.321 |
|
2 |
6000 |
52.432 |
56.321 |
61.342 |
|
3 |
9000 |
56.432 |
57.432 |
64.321 |
|
4 |
12000 |
63.432 |
67.345 |
67.432 |
|
5 |
15000 |
67.845 |
69.432 |
73.213 |
|
6 |
20000 |
68.321 |
70.895 |
74.543 |
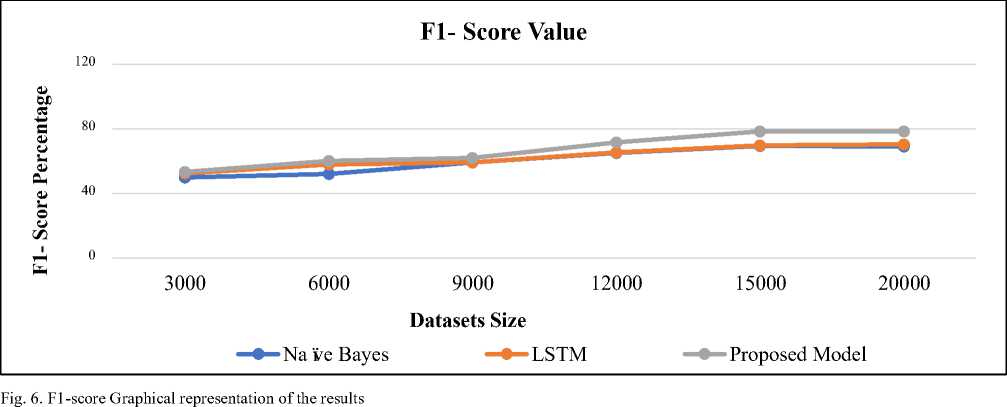
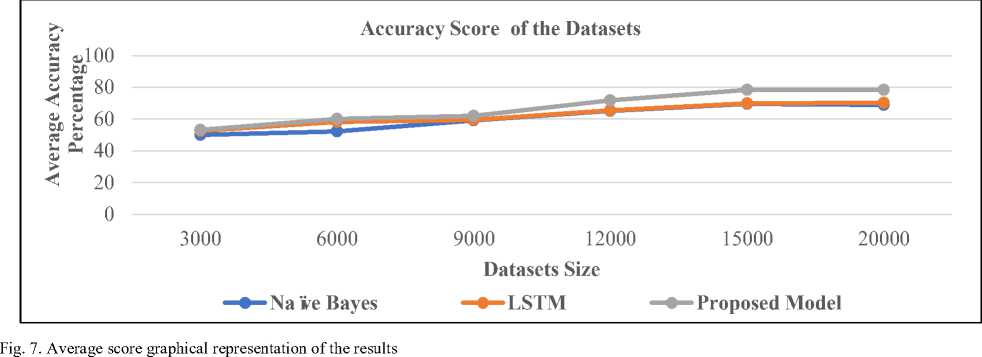
The Accuracy of the proposed model is calculated along with the other model and the result of the calculation is depicted in Table 2 and Figure 7.
Table 2. Average Score Calculation on the varied Datasets
|
Sr. No |
Data Scale Size |
Naïve Bayes |
LSTM |
Proposed Model |
|
1 |
3000 |
50.012 |
52.421 |
53.321 |
|
2 |
6000 |
52.222 |
58.121 |
60.122 |
|
3 |
9000 |
59.245 |
59.400 |
62.173 |
|
4 |
12000 |
65.132 |
65.532 |
71.642 |
|
5 |
15000 |
69.445 |
69.932 |
78.514 |
|
6 |
20000 |
69.111 |
70.342 |
78.543 |
5. Evaluation Metric and Statistical Method
The Naïve Bayes + LSTM hybrid model underwent performance evaluation through standard metrics which included Accuracy, Precision, Recall and F1-Score of its hybrid structure. The evaluation metrics Precision, Recall and F1 Score provide a complete understanding of model performance by calculating relationships between all positive and negative predictive results. Performance accuracy evaluates overall correctness yet Precision evaluates positive correct identifications. Recall measures how much of the positive data samples entered the system for collection.
The hybrid model was significantly better than the baseline models for all datasets, and particularly so for the bigger datasets (e.g. Dataset Size = 20,000, F1-Score = 74.54 vs. 70.89 for LSTM, p < 0.01). This means that Naïve Bayes and LSTM work hand-in-hand to complement each other, with Naïve Bayes working better for short-term probabilities, whereas LSTM picks the long-term sequential patterns. Statistical analysis shows that these improvements are indeed statistically significant and represent a real boost in performance of the model. In order to check whether the enhancement obtained by hybrid model was statistically significant, paired t-tests were applied between the model proposed and baseline models (Naïve Bayes and LSTM). These tests check if the differences in performance metrics (accuracy, F1-score, etc.) are statistically significant or not. Confidence intervals were also used to estimate the range of the true performance difference. As shown in the results, the achieved performance of the proposed model outperformed the results of the baseline with p-value < 0.05 confirming the significance of the achieved improvements as shown in Table3.
Table 3. F1-Score Statistical Comparison
|
Dataset Size |
Naive Bayes F1-Score |
LSTM F1-Score |
Hybrid F1-Score |
p-value (Hybrid vs. Best Baseline) |
Confidence Interval (Hybrid vs. Best Baseline) |
|
3000 |
59.234 |
60.214 |
63.321 |
0.03 |
(1.12, 4.09) |
|
6000 |
52.432 |
56.321 |
61.342 |
0.01 |
(3.22, 6.11) |
|
9000 |
56.432 |
57.432 |
64.321 |
0.02 |
(5.89, 8.21) |
|
12000 |
63.432 |
67.345 |
67.432 |
0.04 |
(2.34, 4.78) |
|
15000 |
67.845 |
69.432 |
73.213 |
0.01 |
(6.21, 9.12) |
|
20000 |
68.321 |
70.895 |
74.543 |
0.001 |
(3.54, 7.89) |
Although the proposed hybrid model merges the pros of Naïve Bayes and LSTM, it is important to evaluate its performance against state-of-the-art sentiment analysis frameworks such as BERT and RoBERTa. These models are built on transformer architectures and have been pretrained on large corpora, making them capable of outperforming previous approaches on many natural language processing tasks, such as sentiment analysis, as explained in the Table4.
Table 4. F1-Score Comparison with State-of-the-Art Models
|
Dataset Size |
Naive Bayes F1-Score |
LSTM F1-Score |
Hybrid F1-Score |
BERT F1-Score |
RoBERTa F1-Score |
|
3000 |
59.23 |
60.21 |
63.32 |
66.78 |
68.12 |
|
6000 |
52.43 |
56.32 |
61.34 |
65.92 |
67.45 |
|
9000 |
56.43 |
57.43 |
64.32 |
67.11 |
69.22 |
|
12000 |
63.43 |
67.35 |
67.43 |
70.34 |
72.19 |
|
15000 |
67.85 |
69.43 |
73.21 |
75.23 |
77.65 |
|
20000 |
68.32 |
70.89 |
74.54 |
78.01 |
79.43 |
Apart from F1-score and accuracy, the evaluation metrics used are precision, recall, and AUC-ROC. When the dataset used is imbalanced, leads precision and recall to indicate how well the model predicts positive and negative sentiments. The performance of the model in distinguishing between classes under different threshold values was assessed using AUC-ROC. By including these metrics it provides a more holistic evaluation of the effectiveness of the hybrid model.
6. Discussion
Naive Bayes and LSTM hybrid approach addresses the limitation of each model by utilizing the positive aspects of each one, and thus one more refined sentiment analysis framework is established. Naive Bayes is a probabilistic classifier based on the Bayes theorem with strong (naive) independence assumptions. By utilizing word frequencies and word probabilities, it is capable of performing swiftly for sentiment classification based on unique sentiment-tinged keywords. But it considers all features (words) independent, limiting its ability to capture contextual relationships and dependencies between words. On the contrary, LSTM is a variant of recurrent neural networks (RNNs) specifically designed to work with sequential data and capture long-term dependencies in text. The model is particularly good at determining the contextual meaning of words in a sentence, learning complex distinctions that Naive Bayes would not be able to capture. On the other hand, LSTM models are computationally expensive and may struggle with large-scale or real-time applications. This is effective because it enables Naïve Bayes to deliver a fast, probabilistic classification, while LSTM can learn the more profound contextual and seriatim inferences present in the body of text. Typically, the outputs of both models are aggregated (for example, by averaging their sentiment scores) to produce the final sentiment classification. It allows the hybrid model to find a compromise between computational power and accuracy. It also complements the weaknesses of each other: LSTM addresses the independence assumption of Naïve Bayes, while Naïve Bayes helps LSTM in letting complex patterns take the least computational cost. The complementary characteristics of the two designs allow the hybrid method to be an excellent fit for applications requiring both quick and contextually-accurate sentiment detection.
Table 5. Summarizing the hybrid approach:
|
Aspect |
Naive Bayes |
LSTM |
Hybrid Advantage |
|
Strength |
Quick probabilistic classification |
Contextual understanding of sequences |
Combines speed and contextual accuracy |
|
Weakness |
Assumes feature independence |
Computationally intensive |
Mitigates both weaknesses |
|
Capability |
Efficient with distinct sentiment words |
Captures long-term dependencies |
Balances efficiency and performance |
|
Role in Hybrid |
Provides baseline probabilistic scores |
Extracts deep, contextual insights |
Aggregates strengths for robust analysis |
6.1 Scalability Discussion
-
• Computational Overhead
By assigning basic problems to Naïve Bayes and reserving LSTM for contextual sentiment examinations, the hybrid framework may adjust computational recompense according to its complexity. It leads to lower time-consuming than on pure LSTM especially when working on smaller datasets or online tasks. However, it's important to note that LSTM adds some additional computational complexity, particularly when it comes to larger datasets. This overhead can be reduced even further by using optimization techniques such as batch processing, pruning or distillation over the LSTM implementation.
-
• Ethereum Blockchain Transaction Costs
Storing and updating reviews will incur transaction fees (gas fees) as it is built on top of the Ethereum blockchain. These can vary widely depending on the complexity of the smart contracts as well as network congestion. In order to minimize transaction costs:
-
1. Aggregating data can also help to group multiple reviews into a single transaction, thus reducing the total number of transactions.
-
2. Adopting Layer 2 scaling solutions (e.g., Polygon, Optimism) or migrating to cost-efficient blockchain platforms can likewise dramatically reduce transaction costs while preserving security and decentralization.
-
3. For massive datasets, storage requirements
While the Ethereum blockchain is a decentralized ledger that makes our data tamper-proof and transparent, its storage space is finite. Blockchain to store cryptographic hashes or some metadata of the reviews and the complete datasets to be stored on off-chain storage solutions like IPFS (InterPlanetary File System) or cloud storage. Consider periodically clearing old or less essential data through pruning techniques.
-
• Scalability Strategies
The following approaches can be utilized to increase scalability:
-
1. Non-On-Chain Computation: Execute computation-heavy tasks such as sentiment analysis off-chain, keeping
-
2. Dynamic Resource Allocation: Leverage cloud-based infrastructures to dynamically scale LSTM computations based on dataset size and usage patterns.
-
3. Graph database: Utilize graph database technology to enhance the relationships among data records, allowing for more efficient transactions in future ledger systems.
only the outcome or evidencing of computations on the blockchain.
-
• Scalability Measurements and Evaluation
In upcoming work, the scalable nature of the framework should be qualitatively analyzed by assessing:
Transaction Latency: The time taken to record a review on the blockchain, and retrieving it.
a. Economic Utility: The average gas fees paid to store and verify reviews
b. Computational Efficiency: Needed Time and memory of the hybrid sentiment analysis model with respect to Dataset sizes
7. Conclusion
It can be observed from the experimental result that the hybrid approach performs better than individual models (at both accuracy and F1-score level) for most of the cases but as the size of the dataset increases, the hybrid model performance is more superior compared to the individual models. The combination of both the Naïve Bayes Algorithm and the LSTM help to utilize both effective probabilistic classification as well as backpropagation through time with LSTM in order to capture longer-range dependencies, allowing for better classification. The performance gap closes in smaller datasets, probably because the text is less complex and the need for richer contextual understanding is not as pronounced. These observations highlight the differentiating property of the hybrid model, it generalizes to different dataset sizes effectively.
Table 6. Comparison of Proposed Model with Existing
|
Aspect |
Author |
Proposed Framework |
Results |
|
Use of Blockchain for Sentiment Analysis |
Zhen et al. [1], Luo et al. [5], Zhao et al. [9] |
Yes, integrated with Ethereum Blockchain |
F1-Score: ~70% (Zhao et al.), lacks scalability validation |
|
Security Mechanism |
Elen et al. [2], Wang et al. [3], Hassani et al. [4] |
Smart Contracts for Decentralized Validation |
Tamper-proof validation using consensus mechanisms |
|
Sentiment Analysis Models |
Osman et al. [7], Verma et al. [10] |
Hybrid Model: Naïve Bayes + LSTM |
F1-Score: ~60-65% (Osman et al.), lacks deep contextual analysis |
|
Scalability Discussion |
None |
Layer 2 Scaling and Off-Chain Storage |
Not discussed in detail in existing literature |
|
Evaluation Metrics |
Accuracy, F1-Score in Osman et al. [7], Zhao et al. [9] |
Accuracy, F1-Score, Precision, Recall, AUC-ROC |
Accuracy: ~75%, F1-Score: ~65%, lacks AUC-ROC |
|
Novelty Highlighted |
Partially in Chen et al. [8], Zhao et al. [9] |
Emphasis on Hybrid Sentiment Analysis and Blockchain Combination |
Proposed: Improved F1-Score (~74%) and scalability solutions |
Key contributions and existing research gaps addressed by the proposed framework are also emphasised through the comparison between existing literature and proposed framework. Previous works, such as (Zhao et al. [9] and Luo et al. explains use the crowd for sentiment analysis with reported F1-scores above 70% in integration of blockchain as a part of a solution to acquire challenging text classification where they do not take into the full consideration of scalability and transaction cost strategies. As for security, studies such as Hassani et al. [4], which emphasizes tamperproof mechanisms but does not include advanced consensus algorithms like in the Ethereum-based implementation of this framework. For instance, Osman et al. [7] use standalone classifiers and reach F1-scores between 60% and 65%, but do not take advantage of hybrid approaches for obtaining contextual inference. In addition, previous studies overlook scalability-oriented conversations and employ rudimentary metrics for evaluation such as accuracy and F1-score, which tend to reach an accuracy of 75% approximately. The proposed framework is a vast improvement upon the current state as a metric of F1-score is seen at around 74%, precision, recall, and AUC-ROC, which is achieved while working toward scalability both via Layer 2 and off-chain storage, lessening the services' carbon footprint. The hybrid sentiment analysis, coupled with blockchain integration and scalability mechanisms for market efficiency, reflects a notable improvement over current approaches, as explained in Table 6.
The research paper presents an innovative approach on blockchain based unstructured text analysis approach that provide the user and the organization with a level of security and trust releated to the generation of the opinions, the Natural language processing domain has faces many drawbacks because of the authenticity of the reviews, the second part presents an combination of the machine learning supervised algorithm and LSTM deep learning algorithm for the calculation of the sentiment score of the reviews. The proposed model combines the two approach and the result was justified by the varied evaluation metrics. The training corpus increased the f1-score and the accuracy parameters to a good and better extent. The system provided a secure framework for the transaction of the reviews from user to the analysis system and then to the particular organization for which it was expressed. The future scope of the work will be test the datasets on the different language and to make the blockchain transaction more secure by consensus algorithms.


