Body mass index associates with sleep phase delay and low daytime skin temperature despite similar 24-hour patterns of physical activity in adults
Автор: Gubin D.G., Petrov I.M., Khasanova Yu.V., Kolomeychuk S.N., Cornelissen G.
Журнал: Тюменский медицинский журнал @tmjournal
Статья в выпуске: 1 т.22, 2020 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Disruption of circadian rhythms was recently recognized as an important factor underlying metabolic disorders. Changes in the circadian rhythms of sleep, activity, temperature, and energy expenditure can thus serve as early markers of metabolic state and diabetes risk.
Body mass index, metabolism, monitoring, temperature, sleep, activity, energy expenditure, circadian rhythm
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/140303364
IDR: 140303364 | DOI: 10.36361/2307-4698-2020-22-1-35-41
Текст научной статьи Body mass index associates with sleep phase delay and low daytime skin temperature despite similar 24-hour patterns of physical activity in adults
Introduction. Circadian disruption is a complex state of desynchronized circadian rhythms, either due to external misalignment between the intrinsic clock and the environment, or to internal desynchronization. Examples of external misalignment are social jet lag, light at night, and shift-work (Roenneberg et al, 2012; Gooley et al, 2011; Vetter, 2020). Internal desynchronization is more likely to occur at an older age and in the presence of disease or pre-disease (Bass, 2012; Gubin, 2013; Gubin & Weinert, 2015; Gubin et al, 2016; Xie et al, 2019). In other words, disorganized circadian hygiene can be an underlying cause of disease, and a misaligned circadian phenotype can facilitate the onset and progression of pathology. Vice versa, disease can manifest itself as a deviant circadian pattern, alterations observed in terms of period, phase, amplitude, and/or overall pattern of variability.
Circadian disruption is considered a risk factor for numerous chronic diseases (Agadzhanian & Gubin, 2004; Arble et al, 2015). They include metabolic state (Maury, 2019; Noh, 2018; Panda, 2016; Park et al, 2019; Zimmet et al, 2019), obesity (Noh, 2018; Broussard & Van Cauter, 2016; McHill & Wright, 2017; Park et al, 2019; Zimmet et al, 2019), and diabetes (Arble et al, 2015; Gubin et al, 2017b; Javeed & Matveyenko, 2018; Mason et al, 2020). Excessive artificial light in the late evening or night disrupts melatonin production and signalling, sleep, thermoregulation, blood pressure, glucose homeostasis (Gooley et al, 2011; Qian & Scheer, 2016; Touitou et al, 2017; Gubin et al, 2017a; Poggiogalle et al, 2018), and lipid metabolism (Gooley, 2016; Poggiogalle et al, 2018).
Specific mechanisms of intrinsic vs. extrinsic circadian disruption, and genetic factors predisposing individual susceptibility of circadian clock to disrupting factors, however, remain largely unknown. For example, the over-50-fold individual difference in melatonin production sensitivity in response to the same evening light exposure remains unexplained (Phillips et al, 2019).
Modern monitoring techniques are useful tools for an in-depth analysis of circadian physiology, not just in the laboratory, but also in everyday life. In this study, we investigate overt circadian rhythms of physical activity, skin temperature and metabolism, simultaneously with sleep parameters, monitored during three consecutive days (72-hours) in adults followed-up for metabolic reasons in Tyumen University clinic.
Methods. Thirteen adults (seven women), followed-up for their risk of developing metabolic disorders at the Tyumen Medical University’s clinic, underwent a full 72-hour outpatient monitoring of sleep, activity, skin temperature and metabolism during the 2019-2020 winter season. All data were obtained with the same monitor Sense Wear, Arm Band Pro3 , Pittsburgh, USA, which
BMI <27; BMI >27
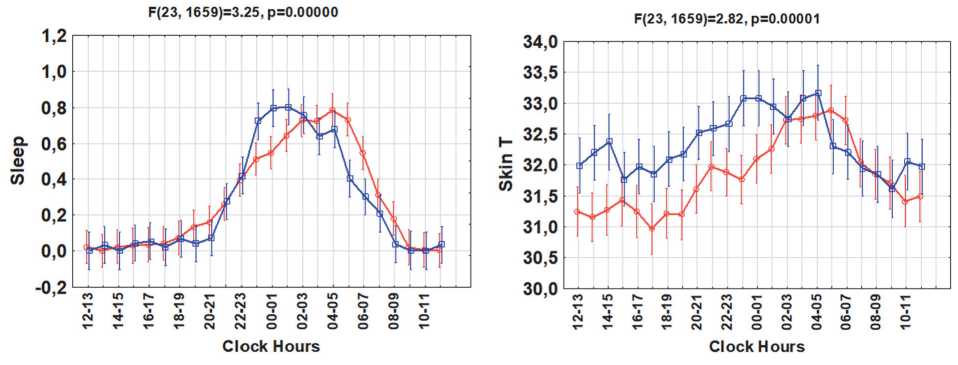
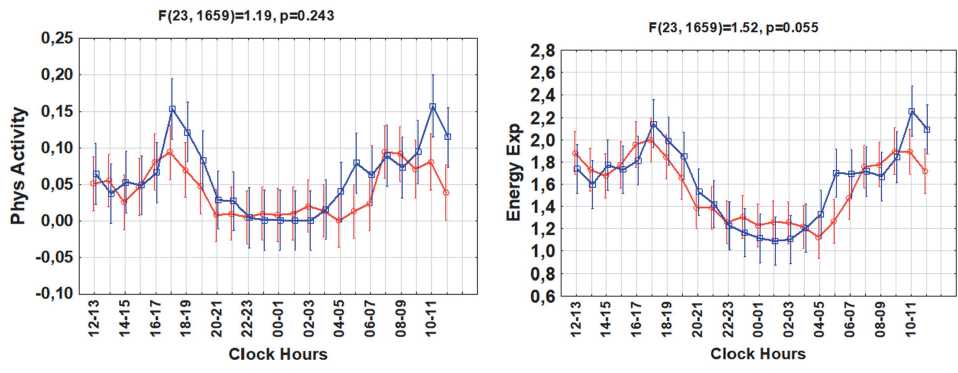
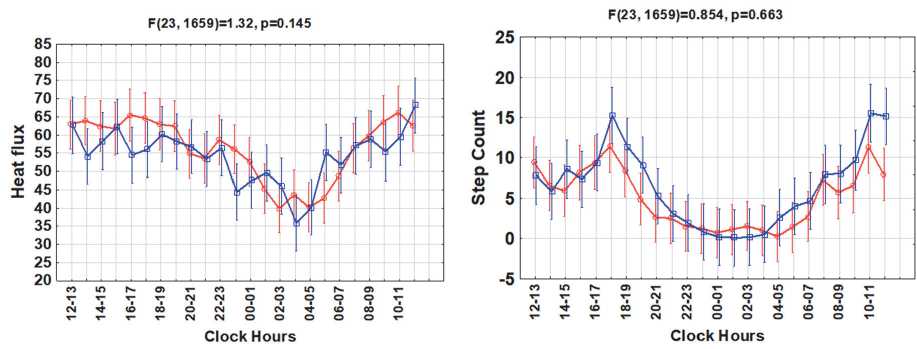
Figure 1. Circadian rhythms of sleep, skin temperature, physical activity, energy expenditure, heat flux and step counts in groups with higher or lower body mass index (BMI)
has proven to be a reliable device for scientific research on sleep physiology, activity, and metabolism (Almeida et al, 2011; Koehler et al, 2017). Only data from records (n=13) with more than 90% reliable measurements were analyzed. Patients were subdivided into two groups according to their body mass index (BMI): either >27 kg/m2 (n=6, 4 women) or <27 kg/m2 (n=7, 3 women). Patients in the two groups had a similar average age (60.8±3.3 vs. 55.4±2.9; p=0.250).
Hourly means and standard deviations of each patient were computed from the original data of sleep time, lying time, step counts, energy expenditure, physical activity, heat flux, and skin temperature. The circadian patterns between the two groups were compared by Cosinor and ANOVA analysis of the hourly mean values.
Statistical analyses were performed using the software packages Excel, STATISTICA 6 and SPSS 23.0. The Shapiro-Wilk’s W-test was applied to check for normality. When variables were normally distributed (W-test’s p-value >0.05), a 1-way ANOVA was used, with Tukey’s post hoc correction for multiple testing. Otherwise, the Kruskal-Wallis and the Mann-Whitney post hoc tests were used.
The level of statistical significance was set at 5%.
Each 72-hour time series was fitted with a 24-hour cosine curve by least squares to yield estimates of the MESOR (M, Midline Estimating Statistics Of Rhythm, a rhythm-adjusted mean), 24-hour amplitude (A) and acrophase (Φ phase angle of the peak of the cosine curve fitted to the data in reference to local midnight). Results were summarized by population-mean cosinor (Cornelissen, 2014). Rhythm parameters were compared using Bingham’s parameter tests (Bingham et al, 1982). Exact p-values are listed in the text.
Results. Groups with higher vs. lower BMI differed significantly in their 24-hour patterns of sleep (F(23,1659) =3.25; p<0.0001) and skin temperature (F(23,1659) =2.82; p<0.0001), Fig.1. The higher BMI group also tended to have a later sleep phase (cosinor-estimated mean phase delay of about 1h:44min, p=0.10) and a later circadian phase of skin temperature (by about 2h:40min, p=0.09), Fig.2. The higher BMI group had a lower daytime skin temperature, but a night-time skin temperature similar to that of the lower BMI group. No differences in mean value, MESOR, or circadian amplitude were found for either sleep amount or skin temperature. The circadian
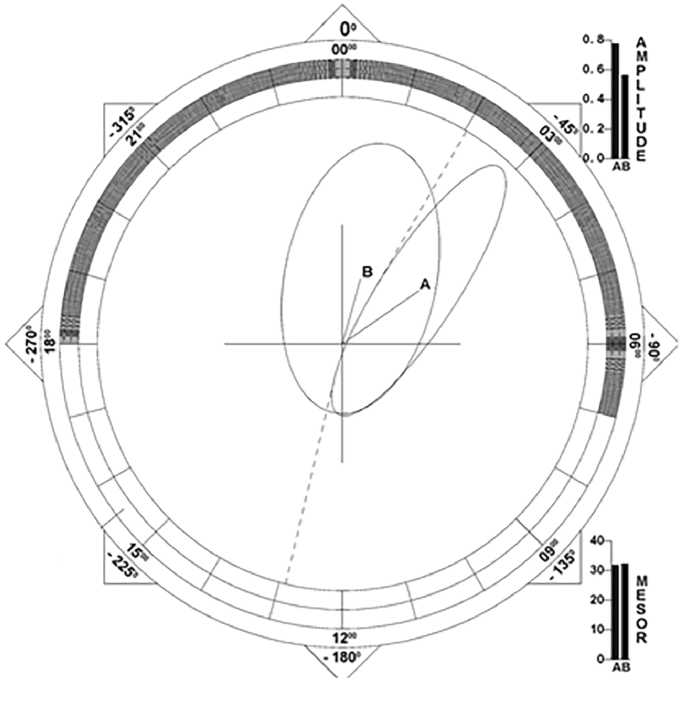
Figure 2. The group with a higher body mass index tended to have a delayed circadian phase of skin temperature. A: BMI > 27 kg/m2; B: BMI < 27 kg/m2.
Population-mean cosinor analysis:
BMI < 27 kg/m2: Mean phase = 01:00 hh: min;
BMI > 27 kg/m2: Mean phase = 03:40 hh: min;
Bingham-test for acrophase difference: F(1, 11) =3.316; p=0.09.
pattern of skin temperature differed between men and women.
Contrary to sleep and skin temperature, the two groups had similar 24-hour patterns of physical activity (p=0.243), step counts (p=0.663), heat flux (p=0.143), and energy expenditure (p=0.055), Fig.1. There were no differences in the mean values, amplitudes or corresponding circadian phases or in the hourly averages of these variables. A “gating” effect was apparent for physical activity and energy expenditure, as differences between the two groups were only present for a short time in the morning and evening, Fig.1.
Discussion. Until recently, research on the bidirectional relationship between BMI and sleep focused mainly on its association with sleep duration. Most studies concentrated on adolescents and young adults, which yielded results generally different from those found in adults. In adults, the relationship between BMI and sleep duration was close to be U-shaped. An increase in BMI could be linked to short and especially long sleep duration (Grandner et al, 2015).
Not only altered sleep duration, but also a shift in the circadian phase of sleep and temperature can serve as an indicator of metabolic risk, and can be specific for certain disorders. Herein we found that daytime skin temperature was lower in adults with a higher BMI. These results are in agreement with the previously reported gradual increase in body temperature in prediabetes and type 2 diabetes mellitus during the night (Gubin et al, 2017b), since the circadian patterns of skin temperature and body temperature are inversely related.
The main finding from this pilot study is the association between a phase-delayed circadian rhythm of temperature and sleep with a metabolic indicator, independently of any differences in their 24-hour mean values or in the circadian characteristics of physical activity or energy expenditure. Objective estimates of phase are often overlooked in currently undertaken surveys. Differences in 24-hour temperature in relation to BMI, however, may not be evident in the general population (Heikens et al, 2011). Differences in temperature have been attributed to gender and menopausal stage in women (Bastardot et al, 2019).
The circadian phase is a reliable and relatively stable endpoint, which can be used in prospective studies to detect early signs of metabolic disorders. Indeed, the circadian phase, the intrinsic circadian period, and chronotype were found to be fairly reproducible over several months (Kantermann & Eastman, 2018). A diminished circadian amplitude of body or wrist temperature can be used as a criterion of metabolic disorder (Gubin et al, 2017b; Harfmann et al, 2017). In cases when monitoring is performed during several consecutive days, a diminished temperature stability of the circadian temperature variation can serve the same purpose (Harfmann et al, 2017). These endpoints can also correlate with certain biochemical variables, such as triglycerides (Harfmann et al, 2017), leptin (Gubin et al, 2017b), or a disrupted 24-hour profile of fasting blood glucose (Gubin et al, 2017b).
A later chronotype (evening preferences in diurnal activity) has been repeatedly shown to be associated with a higher overall morbidity and mortality (Knutson & von Shantz, 2018). Specifically, a higher risk of overweight (Maukonen et al, 2016; Mazri et al, 2020; Sun et al, 2020), prediabetes and diabetes (Reutrakul et al, 2013; Knutson & von Shantz, 2018; Afroz-Hossain et al, 2019; Hudec et al, 2020) has been linked to an evening chronotype. A higher BMI in adult women correlates with an evening chronotype (Sládek et al, 2020). A later chronotype also associates with higher HbA1c determinations in patients with prediabetes, independently of social jetlag and other sleep disturbances in a Thai population (Anothaisintawee et al, 2017).
Since chronotype is a reflection of the intrinsic clock (Duffy et al, 2001; Emery et al, 2009; Gubin & Kolomeychuk, 2019) and has heritability of about 50% (Kalmbach et al, 2017), certain genetic factors are expected to be shared between specific circadian phases and the risk of metabolic disorder. For example, the melatonin receptor MTNR1B rs10830963 G-allele associates with reduced pancreatic beta-cell function and higher diabetes mellitus risk due to an increase in fasting blood glucose (Prokopenko et al, 2009; Sparsø et al, 2009). The MTNR1B G-allele also associates with prolonged endogenous melatonin secretion (Lane et al, 2016). The combination of an evening chronotype with the CG (though not GG) genotype potentiates diabetes risk (Tan et al, 2020). A personalized approach is thus recommended, since the association between evening chronotype and metabolic consequences may have genetic specifics, such as racial differences (Sun et al, 2020).
Social jet-lag is another established factor underlying the risk of metabolic disorder (Roenneberg et al, 2012), and can be associated with a decreased circadian amplitude of wrist temperature (Polugrudov et al, 2016). A multidirectional relationship exists among social jet lag, chronotype, photoperiod, mood, and food addiction (Borisenkov et al, 2020a, b).
Not only chronotype, sleep phase and duration, but also the habitual exposure to artificial light during the night may exert an independent effect leading to a higher BMI and an increased risk of obesity (Park et al, 2019). In mice, even relatively short-term exposure to low levels of light-at-night (LAN) alters metabolism and the circadian rhythm of core temperature, and increases body mass (Borniger et al, 2014). LAN not only leads to weight gain, but also increases glucose intolerance and insulin resistance, that can be reversed by return of darkness. LAN exposure also shortens survival of mice with type 2 diabetes (Russart et al, 2019). Thus, individual differences in diurnal vs. nocturnal exposure to light (deficient natural diurnal light / excessive artificial nocturnal light) and chronotype should be considered in research aimed at evaluating metabolic risk.
The timing of habitual food intake is another important factor that modulates both overt circadian rhythms and metabolic consequences. For example, skipping breakfast was recently reported to be an independent lifestyle habit associated with persistently increased arterial stiffness in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Japan (Mita et al, 2020). Diet-induced thermogenesis and the ability to maintain temperature homeokinesis can be subject to individual genetic-based differences (Reinhardt et al, 2016; Vinales et al, 2019). Therefore, future studies should include reliable tools to assess circadian patterns in food intake that estimate both the amount and timing of meals.
Conclusion. Profound changes in the circadian pattern and its phase of physiological functions may occur in the absence of any difference in mean value. This pilot study indicates that suboptimal metabolic state can be predicted in terms of specific changes in the circadian phase of sleep and temperature that are not observed in their 24-hour mean value or amplitude, and not in the circadian patterns of physical activity and energy expenditure. Further in-depth analyses of circadian rhythm parameters are needed to unmask undesirable behavioural factors and unravel metabolic risk in order to provide personalized recommendations for a healthy lifestyle and well-being.
Список литературы Body mass index associates with sleep phase delay and low daytime skin temperature despite similar 24-hour patterns of physical activity in adults
- Afroz-Hossain A, Dawkins M, Myers AK. Sleep and Environmental Factors Affecting Glycemic Control in People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Curr Diab Rep. 2019;19 (7):40. doi:10.1007/s11892-019-1159-9.
- Agadzhanian NA, Gubin DG. Desinkhronoz: mekhanizmy razvitiia ot molekuliarno-geneticheskogo do organizmennogo urovnia [Desynchronization: mechanisms of development from molecular to systemic levels]. Usp Fiziol Nauk. 2004;35 (2):57-72.
- Almeida GJ, Wasko MC, Jeong K, et al. Physical activity measured by the SenseWear Armband in women with rheumatoid arthritis. Phys Ther. 2011;91 (9):1367-1376. doi:10.2522/ptj.20100291.
- Anothaisintawee T, Lertrattananon D, Thamakaison S, Knutson KL, Thakkinstian A, Reutrakul S. Later chronotype is associated with higher hemoglobin A1c in prediabetes patients. Chronobiol Int. 2017;34 (3):393-402. doi:10.1080/07420528.2017.1279624.
- Arble DM, Bass J, Behn CD, et al. Impact of sleep and circadian disruption on energy balance and diabetes: a summary of workshop discussions. Sleep. 2015;38 (12):1849-1860.
- Bass J. Circadian topology of metabolism. Nature. 2012;491 (7424):348-356. doi:10.1038/nature11704.
- Bastardot F, Marques-Vidal P, Vollenweider P. Association of body temperature with obesity. The CoLaus study. Int J Obes (Lond). 2019;43 (5):1026-1033. doi:10.1038/s41366-018-0218-7.
- Bingham C, Arbogast B, Cornelissen-Guillaume GC, et al. Inferential statistical methods for estimating and comparing cosinor parameters. Chronobiologia 1982;9 (4):397-439.
- Borisenkov MF, Popov SV, Pecherkina AA, et al. Food addiction in young adult residents of Russia: Associations with emotional and anthropometric characteristics. Eur Eat Disord Rev. 2020;28 (4):465-472. doi:10.1002/erv.2731.
- Borisenkov MF, Popov SV, Tserne TA, et al. Food addiction and symptoms of depression among inhabitants of the European North of Russia: Associations with sleep characteristics and photoperiod. Eur Eat Disord Rev. 2020;28 (3):332-342. doi:10.1002/erv.2728.
- Borniger JC, Maurya SK, Periasamy M, Nelson RJ. Acute dim light at night increases body mass, alters metabolism, and shifts core body temperature circadian rhythms. Chronobiol Int. 2014;31 (8):917-925. doi:10.3109/07420528.2014.926911.
- Broussard JL, Van Cauter E. Disturbances of sleep and circadian rhythms: novel risk factors for obesity. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2016;23 (5):353-359. doi:10.1097/MED.0000000000000276.
- Cornelissen G. Cosinor-based rhythmometry. Theor Biol Med Model 2014;11:16.
- Duffy JF, Rimmer DW, Czeisler CA. Association of intrinsic circadian period with morningness-eveningness, usual wake time, and circadian phase. Behav Neurosci. 2001;115 (4):895-899. doi:10.1037//0735-7044.115.4.895.
- Gooley JJ, Chamberlain K, Smith KA, et al. Exposure to room light before bedtime suppresses melatonin onset and shortens melatonin duration in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011;96 (3): E463-E472. doi:10.1210/jc.2010-2098.
- Gooley JJ. Circadian regulation of lipid metabolism. Proc Nutr Soc. 2016;75 (4):440-450. doi:10.1017/S0029665116000288.
- Grandner MA, Schopfer EA, Sands-Lincoln M, Jackson N, Malhotra A. Relationship between sleep duration and body mass index depends on age. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2015;23 (12):2491-2498. doi:10.1002/oby.21247.
- Gubin DG. [Molecular Basis of Circadian Rhythms and Principles of Circadian Disruption]. Usp Fiziol Nauk. 2013;44 (4):65-87.
- Gubin DG, Weinert D. Temporal order deterioration and circadian disruption with age 1. Central and peripheral mechanisms. Adv Gerontol. 2015;5:209-218. https://doi.org/10.1134/S2079057015040086.
- Gubin DG, Weinert D, Bolotnova TV. Age-Dependent Changes of the Temporal Order – Causes and Treatment. Curr Aging Sci. 2016;9 (1):14-25. doi:10.2174/1874609809666151130215824.
- Gubin DG, Weinert D, Rybina SV, et al. Activity, Sleep and Ambient Light Have a Different Impact on Circadian Blood Pressure, Heart Rate and Body Temperature Rhythms. Chronobiology Int. 2017;34 (5):632-649. https://doi.org/10.1080/07420528.2017.1288632.
- Gubin DG, Nelaeva AA, Uzhakova AE, Hasanova YV, Cornelissen G, Weinert D. Disrupted circadian rhythms of body temperature, heart rate and fasting blood glucose in prediabetes and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Chronobiol Int. 2017; 34 (8): 1136-1148. doi:10.1080/07420528.2017.1347670.
- Gubin DG, Kolomeychuk SN. Circadian clock precision, chronotype, health and longevity. J. Chronomed. (Tyumenskij medicinskij zhurnal). 2019;21 (2):14-27. doi: 10.36361/2307-4698-2019-21-2-14-27.
- Harfmann BD, Schroder EA, England JH, et al. Temperature as a Circadian Marker in Older Human Subjects: Relationship to Metabolic Syndrome and Diabetes. J Endocr Soc. 2017;1 (7):843-851. doi:10.1210/js.2017-00086.
- Heikens MJ, Gorbach AM, Eden HS, et al. Core body temperature in obesity. Am J Clin Nutr. 2011;93 (5):963-967. doi:10.3945/ajcn.110.006270.
- Hudec M, Dankova P, Solc R, Bettazova N, Cerna M. Epigenetic Regulation of Circadian Rhythm and Its Possible Role in Diabetes Mellitus. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21 (8):3005. doi:10.3390/ijms21083005.
- Javeed N, Matveyenko AV. Circadian Etiology of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Physiology (Bethesda). 2018;33 (2):138-150. doi:10.1152/physiol.00003.2018.
- Kalmbach DA, Schneider LD, Cheung J, et al. Genetic Basis of Chronotype in Humans: Insights From Three Landmark GWAS. Sleep. 2017;40 (2): zsw048. doi:10.1093/sleep/zsw048.
- Koehler K, Drenowatz C. Monitoring Energy Expenditure Using a Multi-Sensor Device-Applications and Limitations of the SenseWear Armband in Athletic Populations. Front Physiol. 2017;8:983. doi:10.3389/fphys.2017.0098.
- Kantermann T, Eastman CI. Circadian phase, circadian period and chronotype are reproducible over months. Chronobiol Int. 2018;35 (2):280-288. doi:10.1080/07420528.2017.1400979.
- Knutson KL, von Schantz M. Associations between chronotype, morbidity and mortality in the UK Biobank cohort. Chronobiol Int. 2018;35 (8):1045-1053. doi:10.1080/07420528.2018.1454458.
- Lane JM, Chang AM, Bjonnes AC, et al. Impact of Common Diabetes Risk Variant in MTNR1B on Sleep, Circadian, and Melatonin Physiology. Diabetes. 2016;65 (6):1741-1751. doi:10.2337/db15-0999.
- Mason IC, Qian J, Adler GK, Scheer FAJL. Impact of circadian disruption on glucose metabolism: implications for type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2020;63 (3):462-472. doi:10.1007/s00125-019-05059-6.
- Maukonen M, Kanerva N, Partonen T, et al. The associations between chronotype, a healthy diet and obesity. Chronobiol Int. 2016;33 (8):972-981. doi:10.1080/07420528.2016.1183022.
- Maury E. Off the Clock: From Circadian Disruption to Metabolic Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20 (7):1597. doi:10.3390/ijms20071597.
- Mazri FH, Manaf ZA, Shahar S, Mat Ludin AF. The Association between Chronotype and Dietary Pattern among Adults: A Scoping Review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019;17 (1):68. doi:10.3390/ijerph17010068.
- McHill AW, Wright KP Jr. Role of sleep and circadian disruption on energy expenditure and in metabolic predisposition to human obesity and metabolic disease. Obes Rev. 2017;18 Suppl 1:15-24. doi:10.1111/obr.12503.
- Mita T, Osonoi Y, Osonoi T, et al. Breakfast skipping is associated with persistently increased arterial stiffness in patients with type 2 diabetes. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2020;8 (1): e001162. doi:10.1136/bmjdrc-2019-001162.
- Noh J. The Effect of Circadian and Sleep Disruptions on Obesity Risk. J Obes Metab Syndr. 2018;27 (2):78-83. doi:10.7570/jomes.2018.27.2.78.
- Panda S. Circadian physiology of metabolism. Science. 2016;354 (6315):1008-1015. doi:10.1126/science.aah4967.
- Park YM, White AJ, Jackson CL, Weinberg CR, Sandler DP. Association of Exposure to Artificial Light at Night While Sleeping With Risk of Obesity in Women [published online ahead of print, 2019 Jun 10]. JAMA Intern Med. 2019;179 (8):1061-1071. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2019.0571.
- Phillips AJK, Vidafar P, Burns AC, et al. High sensitivity and interindividual variability in the response of the human circadian system to evening light. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019;116 (24):12019-12024. doi:10.1073/pnas.1901824116.
- Poggiogalle E, Jamshed H, Peterson CM. Circadian regulation of glucose, lipid, and energy metabolism in humans. Metabolism. 2018;84:11-27. doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2017.11.017.
- Polugrudov AS, Panev AS, Smirnov VV, Paderin NM, Borisenkov MF, Popov SV. Wrist temperature and cortisol awakening response in humans with social jetlag in the North. Chronobiol Int. 2016;33 (7):802-809. doi:10.3109/07420528.2016.1168829.
- Prokopenko I, Langenberg C, Florez JC, et al. Variants in MTNR1B influence fasting glucose levels. Nat Genet. 2009;41 (1):77-81. doi:10.1038/ng.290.
- Qian J, Scheer FAJL. Circadian System and Glucose Metabolism: Implications for Physiology and Disease. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2016;27 (5):282-293. doi:10.1016/j.tem.2016.03.005.
- Reinhardt M, Schlögl M, Bonfiglio S, Votruba SB, Krakoff J, Thearle MS. Lower core body temperature and greater body fat are components of a human thrifty phenotype. Int J Obes (Lond). 2016;40 (5):754-760. doi:10.1038/ijo.2015.229.
- Reutrakul S, Hood MM, Crowley SJ, et al. Chronotype is independently associated with glycemic control in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2013;36 (9):2523-2529. doi:10.2337/dc12-2697.
- Roenneberg T, Allebrandt KV, Merrow M, Vetter C. Social jetlag and obesity [published correction appears in Curr Biol. 2013 Apr 22;23 (8):737]. Curr Biol. 2012;22 (10):939-943. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2012.03.038.
- Russart KLG, Chbeir SA, Nelson RJ, Magalang UJ. Light at night exacerbates metabolic dysfunction in a polygenic mouse model of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Life Sci. 2019;231:116574. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116574.
- Sládek M, Kudrnáčová Röschová M, Adámková V, Hamplová D, Sumová A. Chronotype assessment via a large scale socio-demographic survey favours yearlong Standard time over Daylight Saving Time in central Europe. Sci Rep. 2020;10 (1):1419. Published 2020 Jan 29. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-58413-9.
- Sparsø T, Bonnefond A, Andersson E, et al. G-allele of intronic rs10830963 in MTNR1B confers increased risk of impaired fasting glycemia and type 2 diabetes through an impaired glucose-stimulated insulin release: studies involving 19,605 Europeans. Diabetes. 2009;58 (6):1450-1456. doi:10.2337/db08-1660.
- Sun X, Gustat J, Bertisch SM, Redline S, Bazzano L. The association between sleep chronotype and obesity among black and white participants of the Bogalusa Heart Study. Chronobiol Int. 2020;37 (1):123-134. doi:10.1080/07420528.2019.1689398.
- Tan X, Ciuculete DM, Schiöth HB, Benedict C. Associations between chronotype, MTNR1B genotype and risk of type 2 diabetes in UK Biobank. J Intern Med. 2020;287 (2):189-196. doi:10.1111/joim.12994.
- Touitou Y, Reinberg A, Touitou D. Association between light at night, melatonin secretion, sleep deprivation, and the internal clock: Health impacts and mechanisms of circadian disruption. Life Sci. 2017;173:94-106. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2017.02.008.
- Vetter C. Circadian disruption: What do we actually mean? Eur J Neurosci. 2020;51 (1):531-550. doi:10.1111/ejn.14255.
- Vinales KL, Begaye B, Thearle MS, Krakoff J, Piaggi P. Core body temperature, energy expenditure, and epinephrine during fasting, eucaloric feeding, and overfeeding in healthy adult men: evidence for a ceiling effect for human thermogenic response to diet. Metabolism. 2019;94:59-68. doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2019.01.016.
- Xie Y, Tang Q, Chen G, et al. New Insights Into the Circadian Rhythm and Its Related Diseases. Front Physiol. 2019;10:682. Published 2019 Jun 25. doi:10.3389/fphys.2019.00682.
- Zimmet P, Alberti KGMM, Stern N, et al. The Circadian Syndrome: is the Metabolic Syndrome and much more!. J Intern Med. 2019;286 (2):181-191. doi:10.1111/joim.12924.


