BSHOA: Energy Efficient Task Scheduling in Cloud-fog Environment
Автор: Santhosh Kumar Medishetti, Ganesh Reddy Karri
Журнал: International Journal of Computer Network and Information Security @ijcnis
Статья в выпуске: 4 vol.16, 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Cloud-fog computing frameworks are innovative frameworks that have been designed to improve the present Internet of Things (IoT) infrastructures. The major limitation for IoT applications is the availability of ongoing energy sources for fog computing servers because transmitting the enormous amount of data generated by IoT devices will increase network bandwidth overhead and slow down the responsive time. Therefore, in this paper, the Butterfly Spotted Hyena Optimization algorithm (BSHOA) is proposed to find an alternative energy-aware task scheduling technique for IoT requests in a cloud-fog environment. In this hybrid BSHOA algorithm, the Butterfly optimization algorithm (BOA) is combined with Spotted Hyena Optimization (SHO) to enhance the global and local search behavior of BOA in the process of finding the optimal solution for the problem under consideration. To show the applicability and efficiency of the presented BSHOA approach, experiments will be done on real workloads taken from the Parallel Workload Archive comprising NASA Ames iPSC/860 and HP2CN (High-Performance Computing Center North) workloads. The investigation findings indicate that BSHOA has a strong capacity for dealing with the task scheduling issue and outperforms other approaches in terms of performance parameters including throughput, energy usage, and makespan time.
Spotted Hyena Optimization, Butterfly Optimization Algorithm, Cloud Computing, Fog Computing, IoT
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/15019297
IDR: 15019297 | DOI: 10.5815/ijcnis.2024.04.06
Текст научной статьи BSHOA: Energy Efficient Task Scheduling in Cloud-fog Environment
In recent years, IoT (Internet of Things) has become increasingly important in many areas of modern life. In addition to conventional smart gadgets, the IoT and the associated technology have expanded internet access to a variety of other systems, such as wearable devices, machinery, automobiles, and sensors [1-3]. A few of the services that these gadgets offer include telemedicine, smart traffic management, intelligent sales and shipping, and vehicle networking. To extract data required for the Internet of Things applications, the information produced by these gadgets must be analyzed. Acquiring and interpreting IoT data is one of the uses of cloud computing. The cloud center receives diverse information from different IoT devices, evaluates the results, and then transmits the required control signals to these objects. Both cloud servers and the IoT have difficulties in this utilization. To address these issues and limitations, the fog computing strategy serves as a bridge between IoT devices and the cloud center [4-6]. The fog nodes are connected to the IoT devices on a local network, and they serve as the intermediary between all of the devices' connections and the cloud center. Fog nodes can gather all the data close to the IoT devices and only send useful data about the IoT devices to the cloud, thereby minimizing internet traffic and improving the efficiency of the network.
Since scheduling tasks in cloud computing has a wider management system, there are still several factors that affect job performance, including an uneven workload and high resource consumption [7-10]. Fog computing emergence is crucial because this process places a significant load and delay on the cloud data center. Task scheduling is a typical underlying issue in fog computing that affects demand and resource allocation [11-14]. The client requirements are high in IoT contexts, and the effectiveness of the fog computing network's performance is significantly greater than that of the cloud computing network's service. To achieve effective scheduling, it is crucial to allocate processes in fog and cloud computing by user requests. This is a serious issue that needs to be solved.
The makespan and energy consumption are not taken into consideration by conventional task scheduling methods [15-17]. The problem of scheduling the jobs amongst fog nodes has also been brought up since IoT devices frequently have little processing power and can make use of the processing capacity of the fog nodes. Researchers face a hurdle with job scheduling optimization in this situation because of the diversity of cloud and fog nodes as well as network latency among these computing systems and IoT [18-20]. Therefore, taking into account both makespan and energy usage is one of the main objectives of this research.
In this study, the energy-aware task scheduling problem is focused on processing large-scale IoT applications in the Cloud-Fog environment. To resolve this issue, the Butterfly Spotted Hyena Optimization Algorithm (BSHOA) is suggested. The important objective of the BSHOA technique is to successfully balance makespan and energy consumption to finish the jobs in the Cloud-Fog system. The proposed technique combines the benefits of the BOA and SHO algorithms to produce the best results.
The main contributions of this paper are stated below.
• In cloud-fog environments, a smart task scheduling approach is suggested based on the efficient Butterfly Spotted Hyena Optimization Algorithm (BSHOA) for IoT devices.
• To verify the Quality of Service (QoS) needs for IoT devices, the measurements of makespan, energy consumption, execution time, reaction time, and throughput time are taken into account.
• By completing a series of tests with varied numbers of tasks, the effectiveness of the proposed technique is validated in terms of the evaluation metrics.
2. Literature Review
The overall structure of this article is prepared as follows. The relevant articles are briefly described in Section 2. The job scheduling issue in the Cloud-Fog computing environment is described mathematically in Section 3. The suggested algorithm is thoroughly described in Section 4. The results of the experiment are presented in Section 5. The article is concluded and future works are discussed in Section 6.
For IoT task scheduling problems, Abd Elaziz et al. [21] suggested the hybrid technique depended on Salp Swarm Algorithm (SSA) and artificial ecosystem-based optimization (AEO). This version was created utilizing the SSA operators to improve AEO's capacity to exploit data while searching for the best result for the task scheduling issue in cloud-fog computing frameworks. To analyze the effectiveness of the suggested approach, various experiments were carried out by the authors.
According to time limitations, Najafizadeh et al. [22] suggested the multi-objective simulated annealing (MOSA) technique secure task distribution on fog and cloud nodes. The authors employed the Goal Programming Approach (GPA) to handle the trade-off between service cost and time. Moreover, they suggested a unique attribute known as access level to evaluate the performance of the approach. In this metric, the task client (IoT device) can use to define whether the task can be carried out by any node or just by nearby fog nodes.
For task scheduling in a cloud-fog environment, Abohamama et al. [23] presented the improved genetic algorithm (IGA) based framework. The task schedule was presented as a permutation-based optimization (POP) issue and the permutations were provided by the genetic algorithm. Then, the tasks were delegated to a virtual machine in the order determined by the optimal permutation.
Fatehi et al. [24] implemented the theory of Dynamic Voltage Frequency Scaling in fuzzy Non-dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm 2 (NSGA-II) for energy-efficient job scheduling in green data centers. Fuzzy crossover and mutation were used in this procedure to ensure the best possible convergence of the initial solution. To accomplish this, the authors suggested that the mean-variance function of objective values and the binary variance function of gene values be used to manage the crossover rate and increase variation in the ideal Pareto front.
A discrete Pathfinder Algorithm (DPFA) based scheduling algorithm was created by Zandvakili et al. [25]. The suggested scheduler takes into account five objectives as cost functions. They are resource use, tardiness, throughput, energy use, and makespan. To analyze the effectiveness suggested approach, the authors compared this algorithm with various techniques
Table 1 provides an overview of relevant task-scheduling techniques. The analysis of the currently used methodologies reveals that the majority of them concentrate on reducing the task scheduling's execution time or makespan without taking into account QoS metrics like throughput and energy usage of the cloud servers. This leads to an inconsistent load, and the users are dissatisfied. To overcome this, an effective hybrid optimization algorithm is used in this paper to determine the best virtual machine for each activity and increase efficiency.
Table 1. Comparison of related works
|
Article |
Technique |
Tool used to simulate |
Environment |
Makespan |
Energy consumption |
Throughput |
Execution time |
Response time |
Limitations |
|
Abd Elaziz et al. |
AEOSSA |
MATLA B R2018b |
Cloud-fog |
✓ |
× |
✓ |
× |
× |
The provided method has a single purpose and ignores other factors like energy consumption. |
|
Najafizade h et al. |
MOSA |
MATLA B |
Cloud-fog |
× |
× |
× |
× |
× |
Cost is the only factor taken into account; other crucial factors are ignored. |
|
Zandvakili et al. |
DPFA |
MATLA B |
Cloud |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
× |
× |
Take fewer tasks for analysis, yet more tasks are required so that the results can be more thoroughly evaluated. |
|
Proposed approach |
BSHOA |
CloudSim 3.0.3 |
Cloud-fog |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
- |
3. System Model and Problem Formulation
In this section, the system architecture of the proposed framework is explained, and then describes the energy-aware scheduling scenario.
-
3.1. System Model
-
3.2. Problem Formulation
Three layers make up the proposed structure of the system shown in Fig. 1. In three layers, the top surfaces are cloud servers, the heterogeneous nodes in fog are the second layer, and the third layers are IoT devices used by end users.
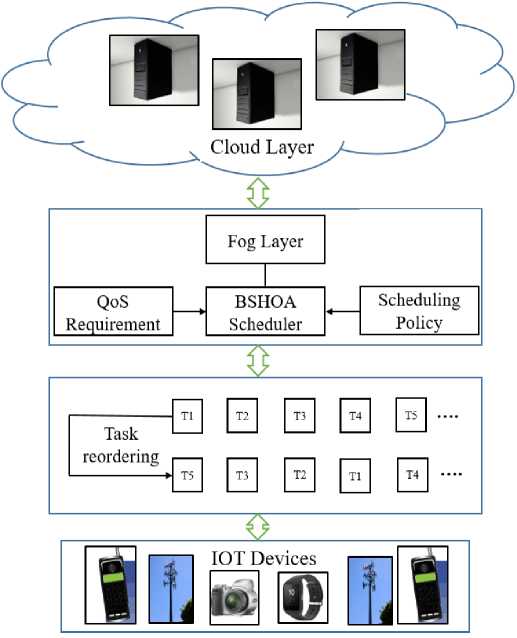
Fig.1. System architecture
The fog layer receives the IoT device's task to process. Every task can be divided into several smaller, autonomous, or interdependent activities. The broker is the element of the fog layer that is most important. There are three main sections: Resource Monitoring Service, Task Manager, and Task Scheduler. All task entries are sent to Task Manager and dispersed IoT devices. The attributes and resource demands of the submitted tasks are maintained by this module before they are sent to the Task Scheduler. The Resource Monitoring Service is in charge of gathering and keeping track of the resource availability reports. To aid in creating accurate schedule plans, it also exchanges cloud and fog nodes via Task Scheduler. By initializing the job requirements to the appropriate compute nodes, the Task Scheduler resolves task scheduling based on the details of the initialized work and the capabilities of the resources available. Afterward, the task proposals for execution are gathered and returned to the fog broker so that they can be delivered to the appropriate users. If the tasks must be completed quickly, they should be assigned to the nearest fog node to lessen the latency and boost processing effectiveness. On the other hand, since cloud nodes have greater computational power than fog nodes, it is best to send compute-intensive activities to them.
IoT application requests are divided into manageable, independent tasks and routed to the Fog layer where they are handled using the Cloud-Fog computing architecture. Considering that T k represents the kth task, the system receives a collection of n distinct tasks at each time, as shown below.
Here, N m denotes the mth processing node. Several properties are included in every processing node. They are energy EG m , computing capacity CC m and data storage S m . In this, the computational capacity is measured by Millions of Instructions per Second (MIPS). Using the aforementioned notations, the task scheduling issue is to distribute n tasks among m fog nodes in a manner that ensures the QoS parameters are ideal. The task t i assigned to the cloud node is represented by X icd and the task assigned to fog node f j is denoted by X ij.
To allocate the required tasks to the suitable fog node, the energy utilization, response time, transmission time, and execution time are statistically examined. Based on these constraints, the work is assigned to the appropriate node.
-
3.3. Execution Time
-
3.4. Response Time
-
3.5. Energy Consumption
To decide the schedule, the scheduler analyzes the ECT matrix which is n×m size. This matrix contains the estimated computation time of task requests. In this, the amount of possible computing nodes is denoted by m and the total amount of task requests is denoted by n. The following formula (3) can be used to determine the expected time that job T i will take to complete on computing node N j .
ETu=^ (3)
Here, in node N j , the execution speed is denoted by PS j and task length is denoted by TL i. It is determined that assigning work demands to the available network entities is an NP-hard issue. Finding the ideal schedule with the shortest makespan or completion time is the main goal of this work is to solve the cloud-fog system's task scheduling difficulty.
The execution time (ET) of a task at the specified node and the job's transmission time (TT) from the origin to the destination is added to determine the response time (RS) of a task that is handled in several layers. The following formula is used to determine how quickly task ti responds when handled by Nj:
RS^ = ET(Xj') + TT^) (4)
This approach involves two types of energy consumption: the energy used to transfer a job to a processing node and the energy used to complete the task. The transmission time (TT) is multiplied by a fixed coefficient to get the energy EGT (X ij ) necessary to transfer task t i to a fog or cloud node as follows:
EGT(X lj) = A^TT total (X lj ) (5)
Here λ is a wireless interface-related constant. It represents the energy cost per unit of time (TT) for transferring a task over a wireless network. By dividing the execution time by a fixed coefficient, the energy consumption EGP(X ij ) for carrying out task ti on fog node fj is represented in equation (6).
EGP(Xl^) = H*ET(Xlj)(6)
Here, μ is a coefficient indicating how much power is used during each CPU cycle. The sum of the processing energy and the transmission energy for the fog or cloud is determined in the following equation (7):
TotalEG(Xij) = EGT(Xtj) + EGP(Xtj)(7)
-
3.6. Makespan
-
3.7. Objective Function
-
4. Proposed Task Scheduling Algorithm
The highest duration for completing the task (completion time CT) of a resource is its makespan (MKS) which is computed in equation (8).
This section provides the objective function that will be utilized to assess the effectiveness of the task allocation problem solution. The important goal of this work is to reduce the overall energy consumption and makespan. The fitness function (OF) for this issue, which is regarded as a bi-objective issue, can be formalized in equation (9):
OF =qx TotalEG + (1—^)x MKS (9)
Here ^is the parameter that balances the two elements of the fitness function. Thus, minimizing OF is the goal of our job scheduling strategy.
The designed task scheduler method's primary stages are described in this section. The benefits of the Spotted Hyena Optimization (SHO) algorithm are used to enhance the behavior of the Butterfly Optimization Algorithm (BOA) in the proposed approach. The primary goal of employing SHO is to improve BOA's search capabilities. This results in less attraction to nearby points and faster convergence. The SHO offers significant exploration, which results in good accuracy, effective mitigation of the local minima issue, optimization of the initial parameters, and high convergence rates for the majority of problems.
Construction of the initial population X, which includes N solutions, is the first point in the newly designed task scheduler technique known as BSHOA. The optimum outcome (Xb) is then estimated along with the fitness value. Following that, the BOA and SHO operators are used to upgrade solutions X within the current population. This procedure of updating solutions is carried out repeatedly till the endpoint requirements are satisfied and return Xb. The next sections provide a detailed description of the proposed method.
-
4.1. Initialization
-
4.2. Updating Stage
Initializing the population's candidates is expressed in equation (10):
XP [j = floor(Lb tj + RA* (Ub tj — Lb^) j = 1,2...... n (10)
Here, the random number RA is between 0 and 1. When it comes to the search space's constraints, Lb and Ub are both set to 1. To transform the real numbers into discrete values, use floor (•). This is relevant for this distinct optimization issues like scheduling tasks.
Afterward, every butterfly (node) produces a certain fragrance (makespan and energy usage) using equation (11). Depending on its most significant fragrance it identifies as the best solution Xb. Then, other nodes are updated in line based on this.
FR , = c*Ia (11)
X b = min(FR i ) (12)
Here FR i represents the makespan and energy used by the ith processing node. I is the stimulation intensity, which is established by the ith node's function evaluation.
The proposed method computes which agent has the lowest fitness value (X b ) by analyzing each agent's fitness value (FR i ). After then, each agent's value (such as X i ) is updated using equation (13).
X i
f Update X i using BOA (t + ) {Update X i using SHO
if RA > 0.5 otherwise
Here, the BOA and SHO operators are switched according to a random number called RA.
At last, the update phase's actions are stopped and the best solution xb is returned after the stop conditions have been verified and satisfied. Algorithm 1 provides the pseudo-code for the BSHOA.
Input: N- total no. of solutions, T-total no. of repetitions, m- total no. of virtual machines, n- total no. of IoT tasks.
Initialize the primary solutions (X).
Assign t = 1.
while t <= t max do
Evaluate X i by calculating its fitness with equation (11).
Identify X b which has the least fitness with equation (12).
for i = 1 : N do
Improve X i with Equation (13).
t = t + 1.
4.3. Computational Complexity Analysis
5. Result and Discussion5.1. Experimental Settings
5.2. Datasets
Return X b .
The computational complexity assessment of the aforementioned algorithms is provided in this subsection. Assume that n stands for the number of tasks, m for the number of populations, and T for the number of iterations. BOA algorithm's complexity is O (m×n×m×T), while SHO's is O (n×T×m×n). As a result, O (n×m×T) is the overall computational complexity of BSHOA.
The contributions proposed in this work are evaluated experimentally in this section. Specifically, Section 5.1 introduces the simulation parameters and datasets. The assessment measurements are explained in section 5.2. Finally, Section 5.3 presents the investigation findings and related considerations.
A computer running Windows 10 with the CloudSim 3.0.3 toolkit and an Intel Core i5 processor operating at 2.40 GHz and 4 GB of RAM was used to perform all the experiments. Table 2 provides a full configuration of the cloud-fog framework that is being provided. CloudSim toolkit enables the modeling and simulation of vast and intricate computer environments. Therefore, it is selected for this research.
Table 2. Configuration details
|
Entity |
Value |
|
No. of datacenter |
2 |
|
No of Host |
4 |
|
Cloud nodes |
|
|
bandwidth |
0.5GB/s |
|
storage |
15GB |
|
No of VMs |
15 |
|
RAM |
1GB |
|
CPU power |
3000–5000 MIPS |
|
Fog nodes |
|
|
bandwidth |
1 GB/s |
|
storage |
10GB |
|
RAM |
500MB |
|
CPU power |
1000–2000 MIPS |
|
No of VMs |
20 |
The effectiveness of the suggested BSHOA algorithm was tested in the experiments using real datasets. The research uses real-world datasets created by the "Parallel Workload Archive [26]," which consists of NASA Ames iPSC/860 and HPC2N workloads. The educational sector is provided with these parallel workloads in the traditional workload style (.SWF). In this experiment, the cleaned forms of the HPC2N and NASA iPSC logs were used.
-
5.3. Performance Metrics
-
5.4. Comparison of Results
Various performance criteria were employed to assess the effectiveness of the suggested approach. They are the following: makespan, throughput, and power consumption. The most popular criteria for evaluating the effectiveness and reliability of scheduling techniques are Makespan which is computed using equation (8).
The entire amount of work that is completed successfully in a specific amount of time is referred to as throughput. To guarantee that the results of the provided work are produced in the shortest amount of time, the cloud-fog environment must achieve a high degree of throughput. Consequently, the following expression can be used to calculate the throughput:
ThrPt = ^ t.etasks ET(tl) (14)
The amount of energy used by system servers makes up the total amount of energy consumption (cloud or fog nodes). A practical system should use as little energy as possible. Equation (7) specifies the total energy that is estimated for a cloud or fog node.
This section compares the performance analysis of the suggested method using the four algorithms artificial ecosystem-based optimization with Salp Swarm Algorithm (AEOSSA) [21], conventional Butterfly optimization algorithm (BOA) [27], conventional Spotted Hyena optimization algorithm (SHO) [28], conventional chameleon swarm algorithm (CSA) [29], and conventional Salp Swarm Algorithm (SSA) [30]. This AEOSSA algorithm is implemented in NASA Ames iPSC/860 and HPC2N data workloads which are similar to the proposed framework. To provide accurate comparisons among these algorithms, every scenario is executed 100 times, recorded the outcomes, and then contrasted with the average outcome. As a consequence, the data in this subsection represents the average of 100 executions of each method.
Tables 3 and 4 compare the mathematical outcomes of the suggested strategy for the NASA iPSC workload and the HPC2N workload. The highest, average, and worst makespan values generated according to each technique are presented in these tables. In the majority of the evaluated examples, it can be determined from the findings in the tables that the suggested method outperforms the other five comparison techniques.
Table 3. Makespan using NASA workload
|
Task |
Statistics |
AEOSSA[21] |
BOA [27] |
SHO [28] |
CSA[29] |
SSA [30] |
Proposed BSHOA |
|
500 |
Best |
48.51 |
49.89 |
46.78 |
50.88 |
67.67 |
44.67 |
|
Average |
53.86 |
51.55 |
48.41 |
55.09 |
78.33 |
46.89 |
|
|
Worst |
69.94 |
53.56 |
52.77 |
58.34 |
89.68 |
49.12 |
|
|
1000 |
Best |
99.69 |
99.67 |
95.13 |
102.15 |
146.40 |
93.98 |
|
Average |
112.30 |
105.98 |
98.67 |
106.67 |
163.53 |
95.12 |
|
|
Worst |
128.77 |
110.87 |
105.89 |
112.31 |
178.62 |
109.23 |
|
|
1500 |
Best |
155.00 |
141.78 |
138.89 |
147.98 |
234.42 |
132.74 |
|
Average |
167.81 |
146.57 |
140.18 |
157.99 |
253.43 |
135.34 |
|
|
Worst |
192.23 |
150.21 |
149.90 |
167.97 |
266.68 |
144.19 |
|
|
2000 |
Best |
202.39 |
193.78 |
189.46 |
197.06 |
322.88 |
184.32 |
|
Average |
226.38 |
197.91 |
195.67 |
207.24 |
346.74 |
187.81 |
|
|
Worst |
256.85 |
210.89 |
208.17 |
215.31 |
370.27 |
199.11 |
|
|
2500 |
Best |
260.77 |
237.28 |
231.40 |
246.94 |
416.74 |
227.64 |
|
Average |
290.03 |
241.82 |
236.91 |
257.85 |
442.03 |
231.21 |
|
|
Worst |
327.24 |
248.31 |
242.11 |
267.50 |
475.52 |
249.91 |
|
|
3000 |
Best |
303.68 |
281.77 |
278.61 |
354.78 |
512.89 |
274.33 |
|
Average |
334.14 |
286.35 |
281.39 |
358.45 |
569.90 |
279.27 |
|
|
Worst |
397.45 |
293.12 |
292.98 |
379.56 |
583.15 |
291.49 |
The makespan of the algorithm rises according to the proportion of network demand. The makespan results presented in Figs. 2 and 3 demonstrate that the proposed method outperformed the baseline algorithms. Because the proposed approach considered the makespan throughout the optimization. When there are fewer tasks, BSHOA's makespan is almost equivalent to that of all the other techniques. When the number of tasks increases, the proposed BSHOA presented a significant performance than other algorithms. Because it ensures a fair allocation and employs the evaluation function to evaluate the effectiveness of the solution in each solution set.
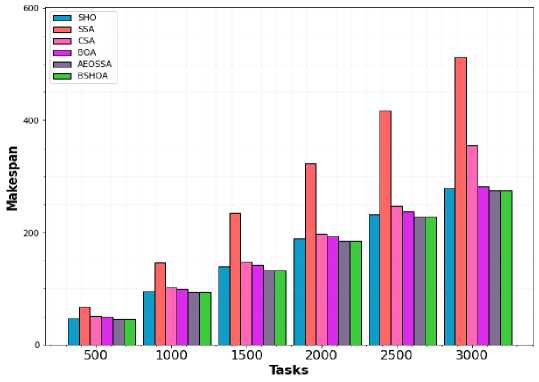
Fig.2. Makespan for NASA workload
Table 4. Makespan using HPC2N workload
|
Task |
Statistics |
AEOSSA [21] |
BOA [27] |
SHO [28] |
CSA [29] |
SSA [30] |
Proposed BSHOA |
|
500 |
Best |
5271.46 |
5128.91 |
4967.45 |
5347.63 |
8001.93 |
4728.91 |
|
Average |
6027.33 |
5342.88 |
5199.67 |
5654.95 |
8955.87 |
5042.88 |
|
|
Worst |
6755.25 |
5687.33 |
5543.26 |
5874.67 |
9978.12 |
5387.33 |
|
|
1000 |
Best |
12015.41 |
10,922.78 |
10,654.45 |
11,664.67 |
18496.02 |
9,923.67 |
|
Average |
13123.01 |
12,127.86 |
12,056.76 |
12,133.40 |
19965.24 |
11,756.89 |
|
|
Worst |
14811.80 |
13,012.89 |
12,412.98 |
12,467.56 |
21164.00 |
12,275.54 |
|
|
1500 |
Best |
18452.60 |
16,874.23 |
15,543.21 |
17,925.15 |
29824.93 |
14,871.67 |
|
Average |
20971.57 |
17,671,34 |
16,446.12 |
18,698.31 |
32586.68 |
15,989.12 |
|
|
Worst |
22899.44 |
18,721.22 |
17,921.98 |
19,361.54 |
34633.10 |
17,432.12 |
|
|
2000 |
Best |
26788.22 |
24,675.43 |
23,895.12 |
25,116.20 |
43808.80 |
22,167.88 |
|
Average |
30065.89 |
26,458.43 |
25,745.32 |
26,711.07 |
46803.83 |
24,452.12 |
|
|
Worst |
32584.23 |
27,134.21 |
26,732.44 |
27,662.21 |
49927.90 |
25,543.65 |
|
|
2500 |
Best |
33868.85 |
33,478.43 |
33,145.78 |
34,020.78 |
58845.85 |
30,421.74 |
|
Average |
39885.18 |
34,763.32 |
34,432.11 |
35,198.99 |
62437.16 |
32,332.34 |
|
|
Worst |
45334.08 |
36,125.43 |
35,987.91 |
36,756.72 |
65412.07 |
35,654.23 |
|
|
3000 |
Best |
46798.87 |
45,978.65 |
43,876.45 |
47,128.56 |
74,671.92 |
40,735.54 |
|
Average |
47,568.22 |
47,213.54 |
45,231.29 |
49,784.89 |
75,342.11 |
42,189.67 |
|
|
Worst |
50,104.22 |
49,871.34 |
48,489.41 |
52,834.67 |
77,825.44 |
45,823.55 |
The suggested approach surpasses all known heuristics consistently, especially in terms of the best makespan achieved. According to the graphical representation of best makespan results for the workloads on NASA iPSC and HPC2N with different task sizes, proposed BSHOA all had significantly better makespan results than the other peer algorithms such as SSA, BOA, SHO, and CSA on every single NASA iPSC and HPC2N instances. The AEOSSA technique achieves better results than SSA and CSA algorithms. However, it is stuck in local optima and has delayed convergence. Therefore, it can be said that BSHOA is a highly good strategy for resolving moderate to big cloud task allocation challenges.
-
5.5. Energy Consumption
According to Equation 5, the amount of energy needed to transfer the job to the cloud or fog node is determined during the investigation. Afterward, the energy usage for task execution on a cloud or fog node is computed once the task is sent. Finally, the total energy used during transmission and task execution will be determined by equation 7. Figs. 4 and 5 compare the overall consumption of energy of the SSA, BOA, SHO, CSA, and proposed BSHOA using the NASA iPSC workloads and the HPC2N workloads samples. Fig. 4 demonstrates that, for the NASA workload, the suggested BSHOA algorithm consumes the least energy when compared to the original BOA, SHO, and other competitive techniques. The SSA algorithm consumes the highest energy than other techniques. But in the AEOSSA algorithm, the advantage of the AEO algorithm leads the technique to perform well than SSA and CSA algorithms. In a similar vein, Fig. 5 demonstrates that the suggested methodology obtains the least power consumption when contrasted to the other comparable techniques in HPC2N workload.
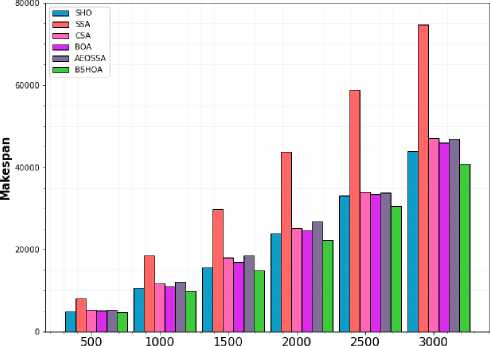
Tasks
Fig.3. Makespan for HP2CN workload
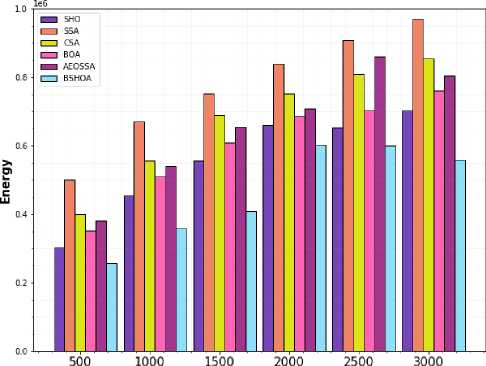
Tasks
Fig.4. Energy consumption for NASA workload
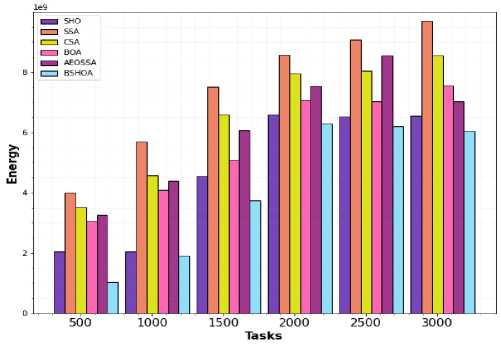
Fig.5. Energy consumption for HP2CN workload
-
5.6. Throughput
-
5.7. Execution Time
The throughput attained by the SSA, BOA, SHO, CSA, and proposed BSHOA algorithms utilizing real workloads is compared in Figs. 6 and 7. The amount of IoT tasks is shown on the horizontal plane in these charts, whereas the throughput metric is shown on the vertical plane.
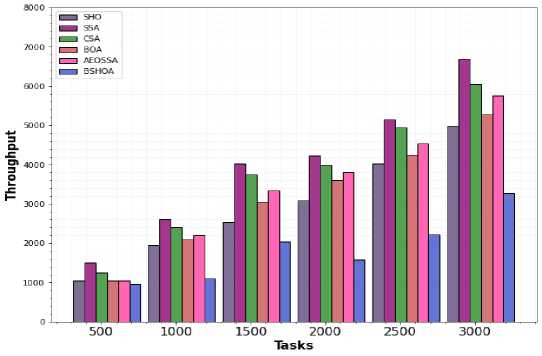
Fig.6. Throughput for NASA workload
With these figures, it can be seen that BSHOA outperforms all other examined evolutionary algorithms techniques in terms of throughput for all job dimensions and workloads. It demonstrates the BSHOA algorithm's consistency and reliability in locating nearly ideal results for actual tasks. Additionally, in the majority of test cases and workloads, the traditional SHO and BOA techniques also yield superior throughput than the SSA and CSA approach. The findings demonstrate that the SHO technique outperforms the BOA algorithm in terms of throughput for all task dimensions and workloads. SHO has a higher rate of convergence than BOA and other metaheuristic algorithms. This benefit makes the hybridization of the proposed BSHOA offer better throughput values than all the other methods.
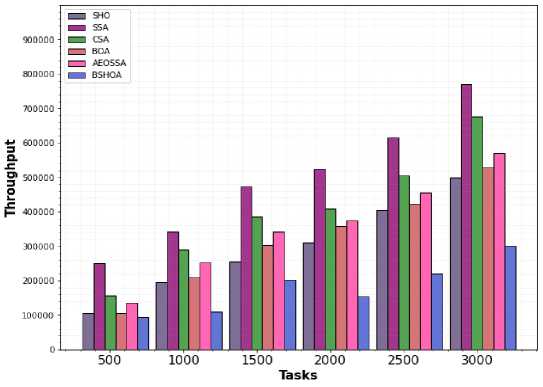
Fig.7. Throughput for H2PCN workload
Based on the rate of information processing, the overall execution time can be measured in millions of instructions per second. Equation (3) figures out the overall execution time. To ensure that the overall execution time is kept to a minimum, we want to choose the best resources that are available for carrying out activities. Figs. 8 and 9 show a comparison of the overall execution times for five task scheduling algorithms for the NASA workload and the HP2CN workload.
It demonstrates that the suggested approach (BSHOA), particularly for a high number of tasks, decreases the overall execution time. Because the BSHOA scheduler distributes tasks using a combination of the BOA and SHO algorithm, less time is spent searching and tasks will receive almost perfect VM. In comparison to BOA, BSHOA can lower total execution time by around 28.3%. SSA and CSA work efficiently when there are few jobs to do. But as the number of tasks increases, these algorithms' execution times grow significantly. The SSA method process jobs with delays of 8.6% and 9.12%, correspondingly, as compared to BOA and SHO.
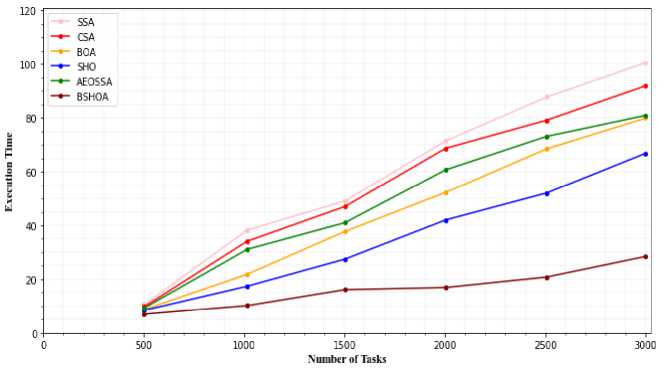
Fig.8. Execution Time for NASA workload
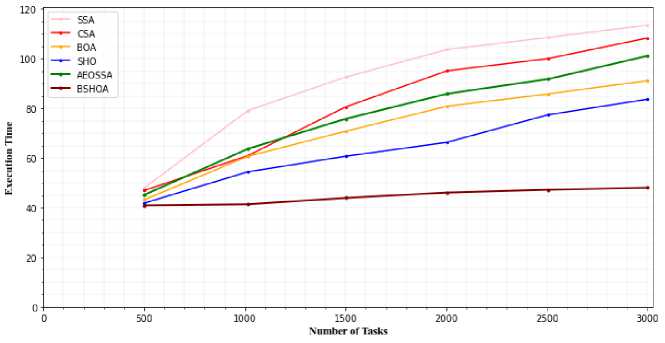
Fig.9. Execution Time for H2PCN workload
5.8. Response Time
6. Conclusion and Future Scope
IoT task response times are depicted in Figs. 10 and 11. Response time in this context refers to the interval between when an IoT device initiates a job and when the entry point receives the reply. For IoT jobs, SSA has the least reaction time (58.12 seconds) among existing approaches. BOA and SHO are given 35.32 and 19.56 seconds, respectively (better than SSA). The average response times with each job for the two workloads are displayed in Figs. 10 and 11. It is obvious that among the NASA and HP2CN workloads, SSA takes the longest and the suggested BSHOA technique simply requires the quickest response time. The SSA and CSA techniques get a significant SLO violations because of their long reaction times.
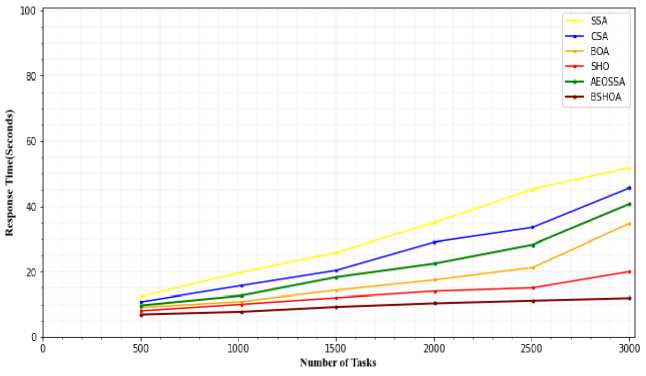
Fig.10. Response time for NASA workload
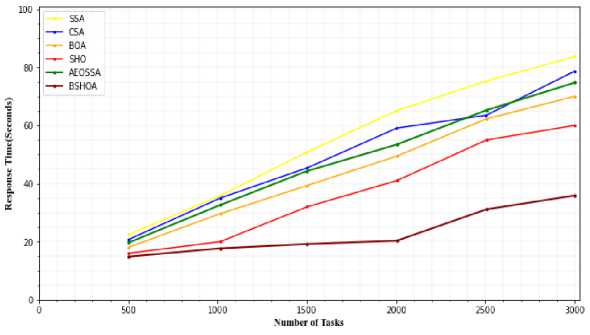
Fig.11. Response time for H2PCN workload
From all the above observations the results show that there has been a notable improvement in the overall throughput time and makespan when taking into account actual workloads. The BOA and SHO strategies have been integrated with the suggested algorithm, which is largely responsible for BSHOA's achievements. We conclude that the created BSHOA is the most efficient and effective approach for addressing cloud-fog Task Scheduling improvement challenges since it consistently delivers the finest solutions.
In a heterogeneous computing environment, cloud-fog computing is considered to obtain adequate cloud computing. This study suggests a trustworthy scheduling method for distributing demands from IoT devices that are linked to the cloud edge towards the available resources in a cloud-fog scenario. The Butterfly Spotted Hyena Optimization algorithm (BSHOA), a different job scheduling method, has been created in this research to enhance the service quality for the IoT in cloud-fog computing environments and compared with existing techniques to demonstrate the effectiveness of the approach. By observing all the results, it is found that the proposed technique is better than SSA by 55.7%, CSA by 50.76%, AEOSSA by 45.37%, BOA by 40.28% and SHO by 36.81% in terms of the average makespan and energy consumption in HPC2N workload. In NASA workload, the proposed technique is better than SSA by 58.14%, CSA by 54.35%, AEOSSA by 49.71%, BOA by 45.63% and SHO by 42.78% in terms of the average makespan and energy consumption. The experimental findings demonstrate that the proposed BSHOA surpasses all comparison algorithms in all of the studied cases and is superior to the conventional BOA and SHO. Hence, based on the algorithm's overall performance, it can be said that this algorithm will be a better choice for cloud-fog environment because it requires less energy and time. In the future, this work is extended with other optimization algorithms and considering other parameters such as transmission costs, budget and deadline.
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Acknowledgements
We declare that this manuscript is original, has not been published before, and is not currently being considered for publication elsewhere.
Availability of Data and Material
Not applicable
Code Availability
Not applicable
Список литературы BSHOA: Energy Efficient Task Scheduling in Cloud-fog Environment
- A. Najafizadeh, A. M. Salajegheh, Rahmani and A. Sahafi, “Privacy-preserving for the internet of things in multi-objective task scheduling in cloud-fog computing using goal programming approach,” Peer-to-Peer Networking and Applications, vol. 14, no. 6, pp. 3865-3890, 2021.
- Z. Yin, F. Xu, Y. Li, C. Fan, F. Zhang, G. Han and Y. Bi, “A Multi-Objective Task Scheduling Strategy for Intelligent Production Line Based on Cloud-Fog Computing,” Sensors, vol. 22, no. 4, pp. 1555, 2022.
- S. Azizi, M. Shojafar, J. Abawajy and R. Buyya, “Deadline-aware and energy-efficient IoT task scheduling in fog computing systems: A semi-greedy approach,” Journal of network and computer applications, vol. 201, pp. 103333, 2022.
- J. C. Guevara and N. L. Da Fonseca, “Task scheduling in cloud-fog computing systems,” Peer-to-Peer Networking and Applications, vol. 14, no. 2, pp. 962-977, 2021.
- J. F. Tsai, C. H. Huang and M. H. Lin, “An optimal task assignment strategy in cloud-fog computing environment,” Applied Sciences, vol. 11, no. 4, pp. 1909, 2021.
- M. Yadav, K. N. Tripathi and S. C. Sharma, “A bi-objective task scheduling approach in fog computing using hybrid fireworks algorithm,” The Journal of Supercomputing, vol. 78, no. 3, pp. 4236-4260, 2022.
- Z. Movahedi and B. Defude, “An efficient population-based multi-objective task scheduling approach in fog computing systems,” Journal of Cloud Computing, vol. 10, no. 1, pp. 1-31, 2021.
- H. Wadhwa and R. Aron, “Optimized task scheduling and preemption for distributed resource management in fog-assisted IoT environment,” The Journal of Supercomputing, pp. 1-39, 2022.
- Z. Yakubu, M. Aliyu, Z. A. Musa, Z. I. Matinja and I. M. Adamu, “Enhancing cloud performance using task scheduling strategy based on resource ranking and resource partitioning,” International Journal of Information Technology, vol. 13, no. 2, pp. 759-766, 2021.
- M. Sharma, M. Kumar and J. K. Samriya, “An optimistic approach for task scheduling in cloud computing,” International Journal of Information Technology, vol. 14, no. 6, pp. 2951-2961, 2022.
- V. Hurbungs, V. Bassoo and T. P. Fowdur, “Fog and edge computing: concepts, tools and focus areas,” International Journal of Information Technology, vol. 13, no. 2, pp. 511-522, 2021.
- H. Momeni and N. Mabhoot, “An Energy-aware Real-time Task Scheduling Approach in a Cloud Computing Environment. Journal of AI and Data Mining, vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 213-226, 2021.
- R. Madhura, B. L. Elizabeth and V. R. Uthariaraj, “An improved list-based task scheduling algorithm for fog computing environment,” Computing, vol. 103, no. 7, pp. 1353-1389, 2021.
- S. Ijaz, E. U. Munir, S. G. Ahmad, M. M. Rafique and O. F. Rana, “Energy-makespan optimization of workflow scheduling in fog–cloud computing,” Computing, vol. 103, no. 9, pp. 2033-2059, 2021.
- M. Keshavarznejad, M. H. Rezvani and S. Adabi, “Delay-aware optimization of energy consumption for task offloading in fog environments using metaheuristic algorithms,” Cluster Computing, vol. 24, no. 3, pp. 1825-1853, 2021.
- M. I. Khaleel, “Multi-objective optimization for scientific workflow scheduling based on Performance-to-Power Ratio in fog–cloud environments,” Simulation Modelling Practice and Theory, pp. 102589, 2022.
- R. Medara and R. S. Singh, “Energy-aware workflow task scheduling in clouds with virtual machine consolidation using discrete water wave optimization,” Simulation Modelling Practice and Theory, vol. 110, pp. 102323, 2021.
- D. Javaheri, S. Gorgin, J. A. Lee and M. Masdari, “An Improved Discrete Harris Hawk Optimization Algorithm for Efficient Workflow Scheduling in Multi-Fog Computing,” Sustainable Computing: Informatics and Systems, pp. 100787, 2022.
- H. K. Yugank, R. Sharma and S. H. Gupta, “An approach to analyse energy consumption of an IoT system. International Journal of Information Technology, pp. 1-10, 2022.
- A. A. Mutlag, M. K. Abd Ghani, M. A. Mohammed, A. Lakhan, O. Mohd, K. H. Abdulkareem and B. Garcia-Zapirain, (2021). Multi-Agent Systems in Fog–Cloud Computing for Critical Healthcare Task Management Model (CHTM) Used for ECG Monitoring. Sensors, vol. 21, no. 20, pp. 6923.
- M. Abd Elaziz, L. Abualigah and I. Attiya, “Advanced optimization technique for scheduling IoT tasks in cloud-fog computing environments. Future Generation Computer Systems, vol. 124, pp. 142-154, 2021.
- A. Najafizadeh, A. Salajegheh, A. M. Rahmani and A. Sahafi, “Multi-objective Task Scheduling in cloud-fog computing using goal programming approach. Cluster Computing, vol. 25, no. 1, pp. 141-165, 2022.
- A. S. Abohamama, A. El-Ghamry and E. Hamouda, “Real-Time Task Scheduling Algorithm for IoT-Based Applications in the Cloud–Fog Environment,” Journal of Network and Systems Management, vol. 30, no. 4, pp. 1-35, 2022.
- S. Fatehi, H. Motameni, B. Barzegar and M. Golsorkhtabaramiri, “Energy aware multi objective algorithm for taskscheduling on DVFS-enabled cloud datacenters using fuzzy NSGA-II,” International Journal of Nonlinear Analysis and Applications, vol. 12, no. 2, pp. 2303-2331, 2021.
- A. Zandvakili, N. Mansouri and M. M. Javidi, “Energy-aware task scheduling in cloud compting based on discrete pathfinder algorithm,” International Journal of Engineering, vol. 34, no. 9, pp. 2124-2136, 2021.
- Parallel workloads archive (2022). http://www.cse.huji.ac.il/labs/parallel/workload/logs.html
- S. Arora and S. Singh, “Butterfly optimization algorithm: a novel approach for global optimization,” Soft Computing, vol. 23, no. 3, pp. 715-734, 2021.
- G. Dhiman and V. Kumar, “Spotted hyena optimizer: a novel bio-inspired based metaheuristic technique for engineering applications. Advances in Engineering Software, vol. 114, pp. 48-70, 2017.
- M. S. Braik, “Chameleon Swarm Algorithm: A bio-inspired optimizer for solving engineering design problems,” Expert Systems with Applications, vol. 174, pp. 114685, 2021.
- S. Mirjalili, A. H. Gandomi, S. Z. Mirjalili, S. Saremi, H. Faris and S. M. Mirjalili, “Salp Swarm Algorithm: A bio-inspired optimizer for engineering design problems,” Advances in engineering software, vol. 114, pp. 163-191, 2017.


