Cardio-toxicity of zinc oxide nanoparticles and Senecio glaucus L. with the prospective therapeutic impact of gallic acid in albino rats
Автор: El-Shafey Nouran Mohamed, Moustafa Nabil Hassan, El Sheikh Ali Abdel Aziz
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 3 т.21, 2025 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) are the utmost innovative nanoparticles used in the imperative claims. Senecio glaucus L. plant (SP) is an ordinary plant found in warm places. Gallic acid (GA) displays as a dynamic antioxidant against the innumerable pollutants. The existing study was intended to appraise the lethal influences of either alone or combined treatments of ZnO NPs and SP in the cardiac tissue and to dissect the cytoprotective effect of GA via biochemical and histopathological evaluations for 30 days in the albino rats. Rats were allocated into 8 groups with orally inoculated: Control, GA (100 mg/kg), ZnO NPs (150 mg/kg), SP (400 mg/kg), GA+ZnO NPs (100,150 mg/kg), GA+SP (100,400 mg/kg), ZnONPs+SP (150,400 mg/kg), and GA+ZnO NPs+SP (100,150,400 mg/kg). Our study signposted that ZnO NPs and SP significantly changed in the activity of creatine kinase enzyme (CK-MB) and the level of total lipids (TL) compared to the control group, (p
Zinc oxide nanoparticles, senecio glaucus l, gallic acid, biochemical indices, histopathological investigation
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/143184743
IDR: 143184743
Текст научной статьи Cardio-toxicity of zinc oxide nanoparticles and Senecio glaucus L. with the prospective therapeutic impact of gallic acid in albino rats
Nowadays, nanomaterials have an extended standing in the forward-looking evolutions due to their definite physicochemical topographies used in the sundry arenas (Kanaoujiya et al ., 2023). Due to its noteworthy feature of very minor diameter (1-100 nm) with a wide-ranging surface zone of nanoparticles (N s), they can combine to intracellular partitions, causing apoptosis (A O ) manner ( etroni et al., 2023; El-Sheikh et al ., 2024). Numerous studies have renowned that N s have already provoked reactive oxygen species (ROS) formation that may convince an inequality in the redox homeostasis and liberalize the physiological demeanors in the living cells (Yang et al ., 2023). Zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO N s) are used to fabricate various profitable claims. ZnO N s motivate several unfavorable influences in some beings (Juan et al ., 2021).
Using usual noxious plants as substitute insecticides parades lesser mortal effects towards the living entities found in the milieu. Middle the documented tangible plants, Senecio glaucus L. (S ) pageants as one of the individuals of Senecio species (Asteraceae Family). It grows in the deserts all over the world, containing abundant phytochemical amalgams that instigated cytotoxicity effects (Moustafa et al ., 2023a). Besides, Senecio plants produce several complaints and cellular dysfunctions, activated A O appliance in the living cells (Moustafa et al ., 2023b).
The heart is a dynamic pump that transfers blood to create energy into the body. The mechanism of cardiac work depends on the energy transfer alleyway (Son et al ., 2021). Cardiac function can be impaired by oxidative demolition (Guo et al ., 2020). Exclusively, the crucial biomarker for estimating energy-demanding cells, such as skeletal and cardiac muscles, is creatine kinase (CK). CK-MB is an isoenzyme of CK found in cardiac muscle and serves as almost 20% of total CK. It may be grown through a chronic necrotic state of the muscle fiber. Besides, it is a perilous biomarker in the diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction (Warrington, Mahajan, 2020).
The copious extent of cardiotoxic agents and their detailed effect on the heart utilities promote awareness in emerging stratagems through using various antioxidants. Gallic acid (GA), (3,4,5-tribenzoic acid) is a nutritional phenolic acid found in tea, raspberry, lemon, mango, and others. Numerous studies indicated that GA pageants anti-oxidative and anti-cancer properties that inhibit DNA fragmentation and protein modification driven by the diverse noxious composites (El-Shafey et al., 2023; EL-Shafey et al., 2024) To clarify the assembly between the structure of GA and its cardioprotective outcome, GA has an aromatic ring with three hydroxyl groups and one carboxyl group that can hunt ROS and deter the cellular injury (Yan et al., 2019).
To accomplish, a goal of the modern study was to estimate the lethal impacts of single or combined treatments of ZnO N s and S through examining biochemical factors and histopathological analyses in the cardiac muscle and to assess the auspicious protective impact of GA against cardiac-toxicity triggered by ZnO N s and S in albino rats.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO N s), sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (Na-CMC) salt, and gallic acid (GA) were subscribed from (Sigma Aldrich). 70% of ethanol solvent was procured from (EL-Naser). Creatinine kinase (CK-MB) enzyme was gotten from (Dialab). The total lipids kit was credited from (Diagnostic). Other chemicals were used from highgrade elements.
Full portions of S were collected from Cairo-Ismailia Road, Egypt. Exactly, it was extracted in 70% ethanol solvent for three days in gar, filtered, and vaporized at 60°C at a rotary evaporator to give greenish extract. The yield was retained at -20°C (Naema et al ., 2018).
The experiment was piloted on forty albino male rats weighing (180-220 g). The rats were housed in a special room at a controlled temperature (23±1°C) and humidity (55±5%), with a 12h dark/light cycle and ad libitum access. After a week of acclimation, the rats were allocated into eight groups, five rats in each one as follows: Control group: rats were taken (0.5% Na–CMC at 5 ml/kg) as a vehicle (Dhiyaaldeen et al., 2014). GA-treated group: rats were taken (100 mg/kg) (Mansouri et al., 2013). ZnO N s-treated group: rats were taken (150 mg/kg) (Srivastav et al., 2016). S -treated group: rats were taken (400 mg/kg) (El-Sheikh et al., 2021). GA+ZnO N s-treated group: rats were taken (100, 150 mg/kg). GA+S -treated group: rats were taken (100, 400 mg/kg). ZnO N s+S -treated group: rats were taken (150, 400 mg/kg). GA+ZnO N s+S -treated group: rats were taken (100, 150, 400 mg/kg) for one month via the gavage scheme.
After this time, the rats were slaughtered by cervical dislocation. The serum was collected for TL analysis and heart tissues were divided to two slices: The first slice of cardiac tissue was homogenized and centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 10 min to estimate CK-MB enzyme and the surplus slice was retained at 10% neutral buffered formalin for histological studies.
Assessment of biochemical indices of cardiac creatine kinase activity (CK-MB): The cardiac CK-MB activity was estimated to obtain a color at an absorbance (340 nm) (David, Robert, 1999). Estimation of serum total lipids level (TL): TL examination was evaluated in serum and measured at absorbance 545 nm (Zollner,Kirsch,1962).
Statistical analysis: Indicators were chosen as a mean±standard deviation (mean±SD) using statistical software package S SS for Windows 20.0 to prepare a comparison between the biochemical studies using a one-way ANOVA trial, followed by Tukey's post hoc analysis for comparison between the numerous groups. The level of significance was deliberated at <0.0522 (IBM Corp S SS. 2011).
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Determination of the effect of ZnO NPs, SP, and GA on biochemical parameters: (Table 1) revealed that TL level of ZnO N s-treated group, S -treated group and ZnO N s+S -treated group caused a significant increase in serum TL level compared to the control group, ( <0.001). The adverse effect of the combined treatment was stronger than the effect of the alone treatment. Further, the contrary impact of ZnO N s-treated group was more than the impact of S -treated group.
On the other hand, TL level of GA+ZnO N s-treated group produced a significant decrease relative to ZnO N s-treated group, GA+S -treated group provoked a significant drop relative to S -treated group, and GA+ZnO N s+S -treated group incited a significant diminution relative to ZnO N s+S -treated group, ( <0.001).Trendily, there was an improvement in the groups that treated with GA in the values of TL level relative to alone or combined treatments of ZnO N s and S , ( <0.001).
Table (1) displayed that ZnO N s-treated group, S -treated group and ZnO N s+S -treated group caused a significant difference in cardiac CK-MB activity compared to the control group, ( <0.001). Nevertheless, GA+ZnO N s-treated group made a significant decrease relative to ZnO N s-treated group, GA+S -treated group incited a significant reduction relative to S -treated group, and GA+ZnO N s+S -treated group incited a significant increase relative to ZnO N s+S -treated group, ( <0.001). Discerningly, there was an increase in the treatments, treated with GA in the values of CK-MB activity relative to the alone or combined treatments of ZnO N s and S . Besides, the lethal effect of the combined treatment was higher than the effect of the alone treatment of them. Further, the contrary impact of ZnO N s-treated group was more than the impact of S -treated group, ( <0.001). Thus, our records revealed that ZnO N s and S act as cardiotoxic and hyperlipidemic agents; nonetheless, GA acts as a cardioprotective and anti-hyperlipidemic agent.
Histopathological outcomes: Our histopathological records on cardiac tissue about ZnO N s, S , and GA affected all treated groups. As shown in (Figure 1:A-H), our records perceived an illustrative structure of muscle fibers: normal parallel longitudinal cardiomyocytes with acidophilic cytoplasm, oval central nuclei, interstitial spaces, and interstitial nuclei appeared in the control group, (Figure 1A). A healthy structure of cardiomyocytes was observed in GA-treated group (Figure 1B). On a hand, a wide interstitial hemorrhage and degeneration were observed in ZnO N s-treated group (Figure 2C). An extensive interstitial hemorrhage area and degeneration area were alleged in S -treated group (Figure1D). On the other hand, a mild degeneration was noticed in GA+ZnO N s-treated group (Figure1E). A mild degeneration found in GA+S -treated group (Figure 1F). Regrettably, an extensive interstitial hemorrhage and a great area of degeneration were detected in ZnO N s+S -treated group (Figure 1G). Finally, a small interstitial hemorrhage area, a mild degeneration, and few inflammatory cells appeared in GA+ZnO N s+S -treated group (Figure 1H). Hereafter, these clarifications found that a combined group of ZnO N s and S triggered more cardio-damage events than the alone group. Likewise, GA amended cardiomyocytes degeneration of ZnO N s and S treatments.
Currently, N s and poisonous plants regard as alternative insecticides used in many regions all over the world (Kumar et al ., 2021). N s treatments convinced numerous changes in the cardiac fibers and provoked the production of free radicles in the heart organ, leading to cell death. It produced a disturbance in CK-MB activity (Hozayenab et al ., 2019; Cheng et al .,2021). Likewise, N s management initiated cell damage in the cardiac tissue, inducing cell death pathway (Olugbodi et al ., 023). Senecio plant provoked a vasodilation in the cardiac artery, endothelial cell infiltration, and cardiac function disturbance in the living organisms, driven A O process ( aredes et al ., 2016; Cifuentes et al ., 2016).
Any elevation in the activity of CK-MB results from the myocardium complaints. Consistently, a risk in the rise of CK-MB activity can be induced myocardial degeneration (Basit,Huecker, 2023). Admitting to the dissolution of ZnO N s after metabolism, the accumulated zinc metals cause a fracas in the concentrations of ions. Henceforth, calcium channel blockers destruction instigates endothelial dysfunction for direct and indirect vasodilation. Thus, cardiac damage affects in the secretion of CK-MB activity (Strassheim et al., 2019). A supply of oxygen and nutrients via the coronary circulation to the myocardium was affected, leading to necroptosis (Kostov, Halacheva, 2018). NF-κB (nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells) activation is essential for an expression of the pro-inflammatory cytokines that assists in migration and infiltration of the inflammatory cells (Lin et al., 2018). Tunefully, the elevation of serum TL is the mark of cardiovascular problems, which prompts hypercholesterolemia (Yousef et al., 2019).
In contrast, the existing study confirmed that GA acts as a cardio-protective agent against the cardiovascular injury produced by the alone or both treatments of ZnO N s and S . To elucidate the capability of GA to ameliorate against the diverse noxious compounds, it has antioxidant assets of the phenolic structure that persuades to control in the apoptotic damage. It contracts a level of the cardiac function indicators (Hsieh et al. , 2017).GA improved cardiac markers, antioxidant biomarkers, and histological findings through myocardial infarction (Jin et al. , 2018; Ola-Davies, Olukole, 2018).
Table 1 : Influence of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO N s), Senecio glaucus L. (S ), and gallic acid (GA) on Total lipids level (TL) (mg/dl) and cardiac creatine kinase enzyme activity (CK-MB) (mU/g protein).
|
Groups |
TL level |
CK-MB Activity |
|
Control |
400.16 ±2.45 a |
44.00±1.22 b |
|
ZnO NPs |
1164.43±3.71***f |
57.95±2.46 ***d |
|
SP |
792.64 ±1.89***d |
95.62±2.46*** f |
|
GA+ZnO NPs |
845.03±2.89***e |
51.14±1.74 ***c |
|
GA+SP |
552.58±2.18***b |
56.78±2.57***d |
|
ZnO NPs+SP |
1341.81 ±7.23***g |
15.31± 2.75***a |
|
GA+ZnO NPs+SP |
772.04 ±2.89***c |
63.27±2.90 ***e |
Compared to the control group, highly significant:***( < 0.001). a,b,c,d,e,f,g letters represent the relations between treated groups at < 0.05:[aZnO N s relative to S , bZnO N s+S relative to ZnO N s, cZnO N s+S relative to S , dGA+ZnO N s relative to ZnO N s, eGA+S relative to S , fGA+ZnO N s+S relative to ZnO N s+S , g GA relative to control].
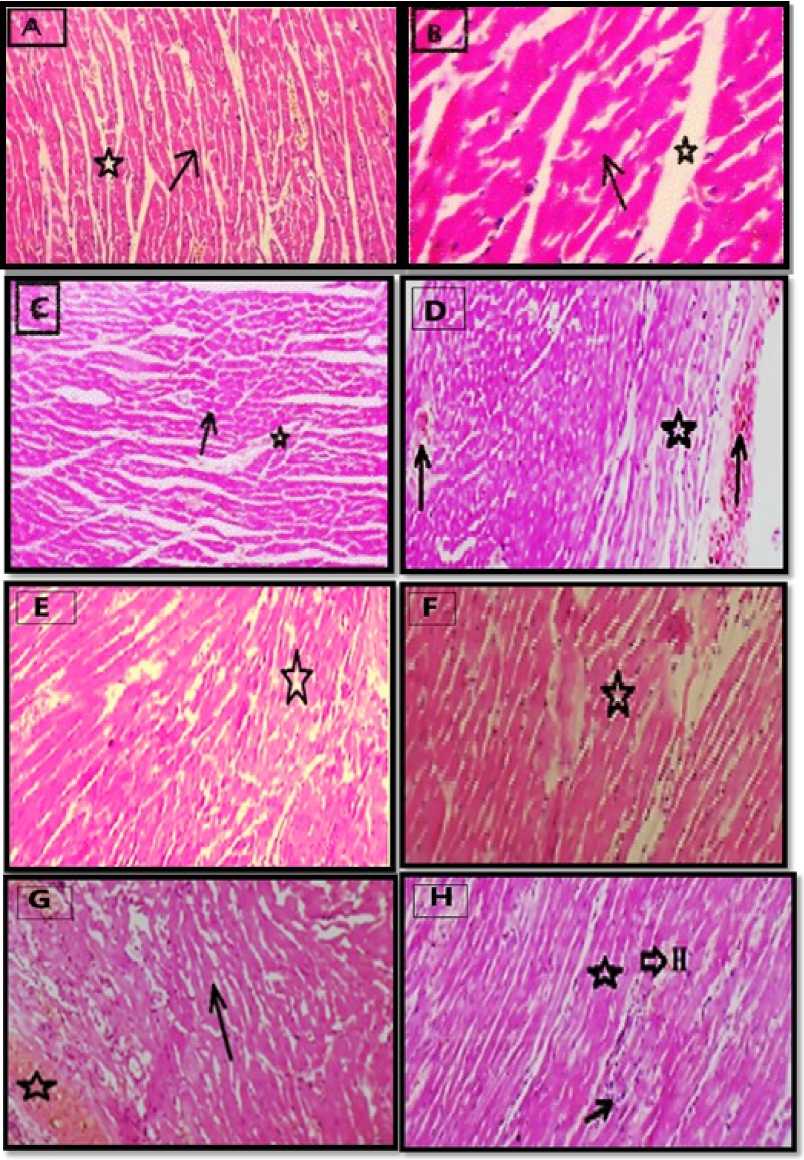
Figure 1. (A-H). hotomicrograph of the histological structure of the effect of Zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO N s), Senecio glaucus L. (S ), and Gallic acid (GA) on cardiac tissue. 1A ) Control group showing the typical structure of muscle fibers: normal parallel longitudinal cardiomyocytes with acidophilic cytoplasm, oval central nuclei (arrow), narrow interstitial spaces with few interstitial nuclei (star). 1B ) GA-treated group showing a healthy structure of muscle fibers. 1C ) ZnO N s-treated group showing an abnormal structure of muscle fibers: interstitial hemorrhage (star) and cardiomyocytes degeneration (arrow). 1D ) S -treated group showing more interstitial hemorrhage (arrow) and cardiomyocytes degeneration (star). 1E ) GA+ZnO N s-treated group showing medium degeneration of cardiomyocytes (star). 1F ) GA+S -treated group showing moderate degeneration of cardiomyocytes (star). 1G ) ZnO N s+S -treated group showing extensive interstitial inflammatory hemorrhage (arrow) and cardiomyocytes degeneration (star). 1H ) GA+ZnO N s+S -treated group showing the small interstitial hemorrhage area (H), cardiomyocytes degeneration (star), and few inflammatory cells appearance (arrow).
CONCLUSION
Finally, our study concluded that either alone or both treatments of ZnO N s and S prompted several variations in the cardiac function biomarkers and produced histological injury in the cardiac tissue. Thus, ZnO N s and S may exhibit as cardiotoxic agents. In dissimilarity, our records confirmed that GA incited a mitigation of their adverse variances. Hereafter, this research validated that GA exhibits a cardio-protective agent against myocardial damage of ZnO N s and S . CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest.
ABBREVIATIONS
ZnO N s Zinc oxide nanoparticles
S Senecio glaucus L. plant
CK-MB Creatine kinase enzyme
TL Total lipids level
A O Apoptosis


