Церебральные микроэмболы и цереброваскулярные осложнения при хирургическом лечении стенозирующих поражений каротидных артерий
Автор: Батрашов В.А., Рыбалко Н.В., Боломатов Н.В., Виноградов О.И., Кузнецов А.Н.
Журнал: Вестник Национального медико-хирургического центра им. Н.И. Пирогова @vestnik-pirogov-center
Рубрика: Оригинальные статьи
Статья в выпуске: 2 т.11, 2016 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Каждая операция, выполняемая при окклюзионно-стенозирующих поражениях каротидных артерий, сопровождается церебральной микроэмболией. Наибольшее количество МЭС регистрируется при проведении эндоваскулярных вмешательств, за счет преобладания в структуре газовой микроэмболии. Отмечена статистически значимая связь между МЭС материальной природы и церебральными ишемическими событиями в периоперационном периоде.
Атеросклероз каротидных артерий, каротидная эндартерэктомия, каротидная ангиопластика со стентированием, церебральная эмболия, сосудистые церебральные осложнения, сarotid endarterectomy, сarotid angioplasty with stenting
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/140188546
IDR: 140188546 | УДК: 616.133-005.7:616.13/.14-089-06
Текст научной статьи Церебральные микроэмболы и цереброваскулярные осложнения при хирургическом лечении стенозирующих поражений каротидных артерий
Хирургические операции, выполняемые при стенозирующих поражениях брахиоцефальных артерий, наряду с антитромботической терапией, являются основой профилактики повторного ишемического инсульта, но сами могут быть источником периоперационных сосудистых осложнений [1–3].
В течение последних двух десятилетий было проведено большое количество рандомизированных контролируемых исследований, посвященных сравнительной оценке эффективности и безопасности каротидной эндартерэктомии (КЭЭ) и каротидной ангиопластики со стентированием (КАС) [4–11]. В связи с гетерогенностью обследуемых групп пациентов, различиями в дизайне исследований, медицинском оборудовании и уровне профессионализма в каждой конкретной клинике, результаты проведенных исследований не всегда были однозначны.
Основными периоперационными неврологическими сосудистыми осложнениями при данных вмешательствах являются эмболия в церебральные артерии, гипоперфузия и гиперперфузия. По данным Spencer, полученным на основании анализа 500 КЭЭ, из цереброваскулярных осложнений этой операции в 54% случаев причиной была эмболия, в 29% – гиперперфузия, в 17% – ишемия [12].
Транскраниальная допплерография применяется для интраоперационного мониторинга церебральной гемодинамики, начиная с 1980-х годов, и позволяет диагностировать в реальном времени все три основные причины осложнений: эмболию, гипоперфузию и гиперперфузию.
Микроэмболические сигналы (МЭС) газового и материального происхождения регистрируются практически при каждой КЭЭ и КАС [12–16]. Некоторые авторы обнаруживают связь между наличием микроэмболов в интракраниальных артериях и периоперационными со- судистыми осложнениями [2–3, 17–19], тогда как другие исследователи получают противоположные результаты [20–24]. Одна из причин неоднородности полученной информации – невозможность до последнего времени четко и достоверно выявить состав эмболического материала, что является необходимым условием оценки эффективности и безопасности проведенного сосудистого хирургического вмешательства. Внедрение в клиническую практику методов дифференцировки микроэмболов на газовые и материальные (двухчастотный метод, индекс модуляции частоты) позволило подойти к проблеме периоперационной эмболии на качественно новом уровне.
В исследовании принимал участие 41 пациент (средний возраст 65 ± 4,5 лет) с гемодинамически значимым стенозоми внутренней сонной артерии (ВСА), проходивших лечение в Пироговском Центре с 2012 по 2014 г. Двадцать шесть стенозов (63,5%) было прооперировано методом КЭЭ (1-я группа) и 15 (36,5%) – методом КАС (2-я группа).
Всем пациентам при поступлении проводили комплексное клиническое, лабораторное и инструментальное обследование, включая дуплексное сканирование интра – и экстракраниальных отделов брахиоцефальных артерий, трансторакальную эхокардиографию, ЭКГ, МРТ головного мозга. При возникновении острых сосудистых постоперационных осложнений пациенту дополнительно проводилось МРТ головного мозга в диффузионно-взвешенном режиме.
Допплеровский мониторинг средней мозговой артерии (СМА) на аппарате СОНОМЕД-300М фирмы Спектромед (Россия) выполнялся каждому пациенту при поступлении и в раннем послеоперационном периоде. Длительность процедуры составляла 1 час. Проводилась инсонация гомолатеральной СМА через височное аку-

Батрашов В.А., Рыбалко Н.В., Боломатов Н.В., Виноградов О.И., Кузнецов А.Н.
ЦЕРЕБРАЛЬНЫЕ МИКРОЭМБОЛЫ И ЦЕРЕБРОВАСКУЛЯРНЫЕ ОСЛОЖНЕНИЯ ПРИ ХИРУРГИЧЕСКОМ ЛЕЧЕНИИ СТЕНОЗИРУЮЩИХ ПОРАЖЕНИЙ КАРОТИДНЫХ АРТЕРИЙ стическое окно на глубине 50,3 ± 0,5 мм датчиком 2 МГ. Детекция МЭС проводилась в соответствии с критериями Consensus Committee of the Ninth International Cerebral Symposium [30].
Дополнительно всем пациентам интраоперационно проводили билатеральный допплеровский мониторинг СМА с анализом записи в режиме on-line. Дифференцировка состава МЭС на газовую и материальную проводилась с вычислением ИМЧ (индекса модуляции частоты). В качестве диагностических критерий принимался ИМЧ < 1000 Гц/с для материальных эмболов и ИМЧ ≥ 1000 Гц/с для микропузырьков газа.
Анамнестические и клинико-диагностические особенности пациентов двух групп были сопоставимы (табл. 1).
Стеноз определялся как гемодинамически значимый при значении его 70% и более. Поражение сонной артерии классифицировалось как симптомное, если у пациента ранее в течение шести месяцев был зафиксирован гомо-латеральный ишемический инсульт, подтвержденный результатами нейровизуализации. В соответствии с данной классификацией 51% (21) стенозов были симптомными (табл. 1). Хирургическое лечение им проводилось для вторичной профилактики инсульта.
Операции и манипуляции на каротидных артериях у пациентов с асимптомным стенозом (n = 20; 49%) проводились по следующим показаниям: профилактическое оперативное лечение перед проведением аортокоронарного шунтирования – в 3 (15%); гемодинамически значимый стеноз ВСА с недостаточным коллатеральным церебральным кровотоком – в 7 (35%); цереброваскуляр-
Табл. 1. Базовые анамнестические и клинико-диагностические характеристики пациентов
|
Анамнестические и клинико-диагностические характеристики |
1-я группа (n = 26) |
2-я группа (n = 15) |
|
Мужской пол |
18 (69%) |
12 (81%) |
|
Курение |
17 (65%) |
12 (81%) |
|
Гипертоническая болезнь |
23 (88%) |
13 (90%) |
|
Сахарный диабет |
5 (19%) |
4 (27%) |
|
Ишемическая болезнь сердца |
21 (80%) |
12 (81%) |
|
Фибрилляция предсердий |
3 (11%) |
3 (18%) |
|
Степень стеноза (по шкале NASCET): 70–79% |
15 (59%) |
5 (34%) |
|
80–89% |
9 (34%) |
10 (66%) |
|
90–99% |
2 (7%) |
0 (0%) |
|
Симптомный стеноз |
16 (61%) |
5 (33%) |
|
Бляшка осложненная изъязвлением и/или кровоизлиянием |
14 (53%) |
7 (46%) |
|
Контралатеральный стеноз >70% |
10 (35%) |
5 (36%) |
|
Наличие МЭС до операции |
2 (7%) |
0 (0%) |
|
Периоперационная антитромботическая монотерапия |
18 (69%) |
0 (0%) |
|
Периоперационная антитромботическая двойная терапия |
8(30%) |
15 (100%) |
Примечание : все различия не являются статистически значимыми, р > 0,05.
ная симптоматика в бассейне гомолатеральной ВСА более чем шесть месяцев назад – в 10 (50%) наблюдениях.
Антитромботическая терапия проводилась при КЭЭ следующим образом: как минимум один из антитромбо-цитарных препаратов (ацетилсалициловая кислота 100 мг и/ или клопидогрель 75 мг) ежедневно. Гепарин (5000 ед. внутривенно) вводился перед наложением зажима на каротидную артерию.
Пациенты перед КАС получали стандартную двойную антитромбоцитарную терапию (ацетилсалициловая кислота 100 мг и клопидогрель 75 мг) до КАС и не менее 3 месяцев после. Гепарин (5000 ед.) вводили внутривенно до установки стента. Трем пациентам операции выполняли без средств дистальной защиты. Перед началом и после стентирования проводили ангиографию сонных и позвоночных артерий с обязательной оценкой состояния интракраниального сосудистого русла.
Для оценки полученных результатов использованы методы статистического анализа: χ 2-критерий Пирсона (анализ таблиц сопряженности), t-критерий Стьюдента с применением программы SPSS 13. Различия считали статистически значимыми при уровне ошибки p < 0,05.
Результаты
Все операции сопровождались наличием МЭС в церебральном сосудистом русле. Всего было получено 352 МЭС детектируемых во время проведения КЭЭ, из них 76% были материальной природы, и 5432 МЭС, выявленных при проведении КАС, из них только 23% были материальной природы. Из табл. 2. следует, что среднее значение МЭС составляло 27 (18–52) во время КЭЭ и 200 (127–269) во время проведения КАС; среднее значение материальных эмболов 14 (10–20) для КЭЭ и 8 (6–9,5) для КАС соответственно (табл. 2.). Таким образом, общее количество МЭС значительно преобладало в группе пациентов, прооперированных методом КАС, когда как количество материальных МЭС – в группе КЭЭ.
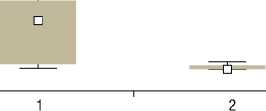
Далее был выполнен анализ частоты регистрации и типа МЭС во время основных этапов КЭЭ и КАС. Как видно из рис.1, наиболее эмбологенным этапом КЭЭ (55% всех зарегистрированных эмболов) был момент снятия зажима с ВСА и пуска кровотока. В этом периоде регистрировались преимущественно газовые микроэмболы, как следствие недостаточной деаэрации оперируемой
Табл. 2. Распределение частоты регистрации микроэмболических сигналов и осложнений эмболического характера из артериального источника в периоперационном периоде у пациентов с КЭЭ и КАС
|
Показатель |
1-я группа КЭЭ |
2-я группа КАС |
р |
|
МЭС общее количество, из них материальных |
27 (18–52) 14 (10–20) |
200 (127–269) 8 (6–9,5) |
0,00 0,00 |
|
Ипсилатеральный ишемический инсульт |
7,7% (n = 2) |
0% (n = 0) |
0,58 |
|
ТИА в ипсилатеральном бассейне |
3,8% (n = 1) |
6,6% (n = 1) |
0,32 |

Батрашов В.А., Рыбалко Н.В., Боломатов Н.В., Виноградов О.И., Кузнецов А.Н. ЦЕРЕБРАЛЬНЫЕ МИКРОЭМБОЛЫ И ЦЕРЕБРОВАСКУЛЯРНЫЕ ОСЛОЖНЕНИЯ ПРИ ХИРУРГИЧЕСКОМ ЛЕЧЕНИИ СТЕНОЗИРУЮЩИХ ПОРАЖЕНИЙ КАРОТИДНЫХ АРТЕРИЙ

□ Медиана ^™ 25-75%
I Мин. Макс.


□ Медиана
^™ 25-75%
| Мин. Макс.
1 2
количествоматериальные
количествоматериальные
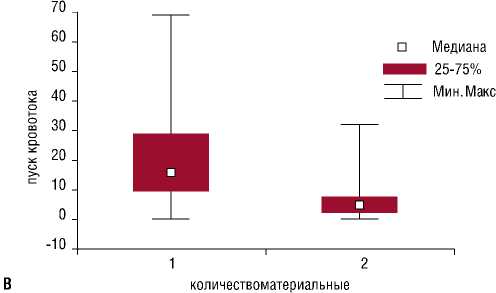
Рис. 1. Распределение частоты регистрации МЭС (общее количество и материальные) у пациентов группы КЭЭ по этапам операции

□ Медиана
^™ 25-75%
I Мин. Макс.
1 2
количествоматериальные
500_
200_
-100
A
24 _
20 _
18 _
14 .
12 _
10 _
8 _
6 _
4 _
2 .
0 _
-2 _.

количество-материальные
В
□ Медиана 25-75%
100 = 90 -| 80. S 70 _
X 60 _
| 50 _ f 40-
I зо _ °- 20 _ а ю_ 0.
-10
□ Медиана 25-75%
I Мин. Макс.
количество-материальные


□ Медиана ^™ 25-75%
140 _ 120.
„ 100.
I 80.
| 60.
S 40 _ “ 20.
-20 _.

□ Медиана
^™ 25-75%
I Мин. Макс.
количество-материальные
1 2
количество-материальные
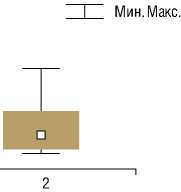
Рис. 2. Распределение частоты регистрации МЭС (общее количество и материальные) у пациентов группы КАС по этапам операции
Батрашов В.А., Рыбалко Н.В., Боломатов Н.В., Виноградов О.И., Кузнецов А.Н.
ЦЕРЕБРАЛЬНЫЕ МИКРОЭМБОЛЫ И ЦЕРЕБРОВАСКУЛЯРНЫЕ ОСЛОЖНЕНИЯ ПРИ ХИРУРГИЧЕСКОМ ЛЕЧЕНИИ СТЕНОЗИРУЮЩИХ ПОРАЖЕНИЙ КАРОТИДНЫХ АРТЕРИЙ
ВСА. Большинство материальных эмболов (до 62%) во время проведения КЭЭ были зарегистрированы до пережатия ВСА, во время выделения атеросклеротической бляшки, что может быть связано с погрешностью выполнения хирургических манипуляций (рис. 1а).
Выполнение интраоперационной ангиографии, как этапа КАС, провоцировало появление занавеса МЭС газового происхождения, что не всегда позволяло четко оценить истинное количество материальных МЭС. Наибольшее количество МЭС при проведении КАС отмечалось во время введения и удаления проводника (рис. 2а и рис. 2г). Основная доля материальных (до 80%) зарегистрированных МЭС во время КАС приходилась на этап раздувания стента – баллона и последующей дефляции, во время которого происходит отжатие атеросклеротической бляшки в стенку ВСА и последующее проникновение атероматозных микрочастиц в церебральный кровоток (рис. 2в). Не было обнаружено значимых различий в количестве регистрируемых материальных МЭС у пациентов, перенесших эндоваскулярное вмешательство на каротидных артериях с применением средств дистальной защиты и без применения церебральной протекции.
Ни одного летального исхода не было зарегистрировано в послеоперационном периоде (30 дней). У пациентов группы КЭЭ наблюдалось больше осложнений в раннем полеоперационном периоде (2 ишемических инсульта и 1 ТИА) (табл. 2). У одного больного группы КАС перенесшего ипсилатеральную транзиторную ишемическую атаку, во время проведения оперативного вмешательства был диагностирован субтотальный стеноз контралатеральной ВСА.
В случаях оперативного вмешательства, осложнившихся церебральными сосудистыми событиями, на допплерографической записи преобладали материальные МЭС, а на диффузионно-взвешенных снимках были диагностированы множественные «свежие» очаги в ис-пилатеральном каротидном бассейне.
Статистическая связь между наличием МЭС материального генеза в церебральном сосудистом русле и осложнениями эмболического характера в интра- и раннем послеоперационном периодах была подтверждена с применением теста Хи-квадрат (табл. 3).
Обсуждение
В медицинской литературе неоднократно говорилось о значении церебральных микроэмболов при проведении оперативных вмешательств на сердце и сосудах, как предиктора развития инсульта и ТИА, у пациентов с симптомным и асимптомным атеросклеротическим поражением каротидных артерий [17–21, 26–28]. С другой стороны, исследования, посвященные проблеме искусственных клапанов сердца – патологии, при которой массивная газовая микроэмболия является частым событием, подтверждют отсутствие связи между газовыми МЭС и острой цереброваскулярной симптоматикой [29, 30]. Наиболее вероятной причиной данного состояния
Табл. 3. Таблица сопряженности – наличие материальных МЭС и осложнений (p < 0,000). Частотный анализ в подгруппах – критерий Хи-квадрат
Проведенное исследование показало, что периоперационная эмболия материального характера, при проведении КЭЭ и КАС, является независимым фактором развития острых сосудистых церебральных осложнений. По результатам нашего исследования основными источниками материальных эмболов являются фрагменты морфологически «нестабильной» атеросклеротической бляшки при выполнении доступа к оперируемой артерии (в группе КЭЭ) и на этапе раздувания баллона (в группе КАС).
Каждая операция, выполняемая при окклюзион-но-стенозирующих поражениях каротидных артерий, сопровождается церебральной микроэмболией как газовыми, так и материальными частицами. Эффективная оценка риска развития церебральных нарушений может базироваться только на точном знании количества и состава эмболического материала. Определение наиболее «эмбологенных» этапов оперативного вмешательства позволяет оптимизировать работу хирургической бригады. Транскраниальная допплерография обладает возможностью эффективно детектировать микроэмболы в церебральном сосудистом русле и дифференцировать газовые и материальные микрочастицы. Массивная послеоперационная церебральная эмболизация, особенно материальными микрочастицами, требует безотлагательного проведения дополнительных диагностических методов (ультразвуковое дуплексное сканирование каротидных артерий и/или селективная церебральная ангио-
Батрашов В.А., Рыбалко Н.В., Боломатов Н.В., Виноградов О.И., Кузнецов А.Н. ЦЕРЕБРАЛЬНЫЕ МИКРОЭМБОЛЫ И ЦЕРЕБРОВАСКУЛЯРНЫЕ ОСЛОЖНЕНИЯ ПРИ ХИРУРГИЧЕСКОМ ЛЕЧЕНИИ СТЕНОЗИРУЮЩИХ ПОРАЖЕНИЙ КАРОТИДНЫХ АРТЕРИЙ графия), а также усиления антитромботической терапии или повторного оперативного вмешательства.
Выводы
-
1. Общее количество регистрируемых МЭС значительно преобладает при эндоваскулярных вмешательствах за счет массивной газовой эмболии, преимущественно связанной с внутриартериальным введением контрастного вещества.
-
2. Основная доля микроэмболов в церебральных артериях, выявляемых у пациентов, прооперированных открытым хирургическим доступом, относится к материальным.
-
3. Существует статистически значимая связь между МЭС материальной природы, и церебральными ишемическими событиями в интра- и послеоперационном периодах.
-
4. Наибольшее количество материальных эмболов регистрируется до пережатия ВСА при проведении КЭЭ, и на этапе раздувания стента-баллона при выполнении КАС.
Список литературы Церебральные микроэмболы и цереброваскулярные осложнения при хирургическом лечении стенозирующих поражений каротидных артерий
- Shevchenko Yu.L., Odinak M.M., Kuznetsov A.N., Erofeev A.A. Cardiogenic and angiogenic cerebral embolic stroke: Moscow. Geotar-Media; 2006: 63-75.Russian. (Шевченко ЮЛ, Одинак ММ, Кузнецов АН, Ерофеев АА. Кардиогенный и ангиогенный церебральный эмболический инсульт: Mocквa. ГЭОТАР -Медиа, 2006: 63-65).
- Ackerstaff RGA, Moons KGM, van de Vlasakker CJW, Moll FL, Vermeulen FE, Algra A, Spencer MP. Association of intraoperative transcranial Doppler monitoring variables with Stroke from carotid endarterectomy. Stroke. 2000; 31(8): 1817-23.
- Ackerstaff RGA, Suttorp MJ, van den Berg JC, Overtoom TT, Vos JA, Bal ET, Zanen PА. Prediction of early cerebral outcome by transcranial Doppler monitoring in carotid bifurcation angioplasty and stenting. J Vasc Surg. 2005; 41(4):618-24.
- Bonati LH, Ederle J, McCabe DJ. for the CAVATAS Investigators Long-term risk of carotid restenosis in patients randomly assigned to endovascular treatment or endarterectomy in the Carotid and Vertebral Artery Transluminal Angioplasty Study (CAVATAS): long-term follow-up of a randomised trial. Lancet Neurol. 2009; 9(3): 297-305.
- Bonati LH, Dobson J, Featherstone RL, Ederle J., van der Worp HB, de Borst GJ, Mali WP, Beard JD, Cleveland T, Engelter ST, Lyrer PA, Ford GA, Dorman PJ, Brown MM. International Carotid Stenting Study investigators. Long-term outcomes after stenting versus endarterectomy for treatment of symptomatic carotid stenosis: the International Carotid Stenting Study (ICSS) randomized trial.Lancet.20-15; 385(9967): 529-38.
- Brott TG,Hobson RW, Howard G. Stenting versus endarterectomy for treatment of carotid-artery stenosis.N Engl J Med. 2010; 363(1):11-23.
- Calvet D, Dobson J, Algra A. Long term outcome after stenting versus endarterectomy for symptomatic carotid stenosis: a preplanned meta-analysis of individual patient data. Cerebrovasc Dis.2014; 376(9746):1062-73.
- Eckstein HH, Ringleb P, Allenberg JR. Results of the Stent-Protected Angioplasty versus Carotid Endarterectomy (SPACE) study to treat symptomatic stenosis at 2 years: a multinational, prospective, randomized trial. Lancet Neurol. 2008; 7(10): 893-902.
- Mas JL, Chatellier G, Beyssen B. Endarterectomy versus stenting in patients with symptomatic severe carotid stenosis. N Engl J Med. 2006; 355(16):1660-71.
- Mas JL, Trinquart L, Leys D, Albucher JF. for the EVA-3S investigators Endarterectomy Versus Angioplasty in Patients with Symptomatic Severe Carotid Stenosis (EVA-3S) trial: results up to 4 years from a randomized, multicenter trial. Lancet Neurol. 2008;7(10): 885-92.
- Silver FL, Mackey A, Clark WM. for the CREST Investigators. Safety of stenting and endarterectomy by symptomatic status in the Carotid Revascularization Endarterectomy Versus Stenting Trial (CREST). Stroke.2011; 42(3): 675-80.
- Spencer MP. Transcranial Doppler monitoring and causes of Stroke from carotid endaretrectomy. Stroke.1997; 28(4): 685-91.
- Lasek-Bal A, Urbanek T, Puz P, Ziaja D, Ziaja K. Cerebral embolism in the perioperative period in patients post interventional treatment of carotid artery stenosis: a preliminary report. Kardiol Pol. 2014; 72(9):783-9.
- Macdonald S. Strategies for reducing microemboli during carotid artery stenting. J Cardiovasc Surg. 2012; 53(1 Suppl 1): 23-6.
- Skjelland M, Krohg-Sorensen K, Tennoe B, Bakke SJ, Brucher R, Russell D. Cerebral microemboli and brain injury during carotid artery endarterectomy and stenting. Stroke. 2009; 40(1): 230-4.
- Wolf O, Heider P, Heinz M, Poppert H, Sander D, Greil O, Weiss W, Hanke M, Eckstein HH. Microembolic signals detected by transcranial Doppler sonography during carotid endarterectomy and correlations with serial diffusion-weighted imaging. Stroke. 2004; 35(11): 373-5.
- Cantelmo NL, Babikian VL, Samaraweera RN, Gordon JK, Pochay VE, Winter MR. Cerebral microembolism and ischemic changes associated with carotid endarterectomy. J Vasc Surg. 1998; 27(6): 1024-30.
- Faraglia V, Palombo G, Stella N, Taurino M, locca ML, Romano A, Bozzao A. Cerebral embolization in patients undergoing protected carotid-artery stenting and carotid surgery. J Cardiovasc Surg. 2007; 48(6): 683-8.
- Muller M, Reiche W, Langenscheidt P, Hassfeld J, Hagen T. Ischemia after carotid endarterectomy: comparison between transcranial Doppler solography and diffusion-weighted MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2000; 21(1): 47-54.
- Bossema ER, Brand N, Moll FL, Ackerstaff RGA, van Doornen LJP. Perioperative microembolism is not associated with cognitive outcome three months after carotid endarterectomy. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2005; 29(3): 262-8.
- Crawley F. Comparison of microembolism detected by transcranial Doppler and neuropsychological squealer of carotid surgery and percutaneous transluminal angioplasty. Stroke. 2000; 31(6): 1329-34.
- Van Heesewijk HPM, Vos JA, Louwerse ES, van den Berg JC, Overtoom TT, Ernst SM, Mauser HW, Moll FL, Ackerstaff RG; Carotid PTA and Stenting Collaborative Research Group. New brain lesions at MR imaging after carotid angioplasty and stent placement. Radiology. 2002; 224(2): 361-5.
- Piorkowski M, Kläffling C, Botsios S, Zerweck C, Scheinert S, Banning-Eichenseher U, Bausback Y, Scheinert D, Schmidt A.Postinterventional microembolism signals detected by transcranial Doppler ultrasound after carotid artery stenting. Vasa. 2015; 44(1): 49-57.
- Poppert H, Wolf O, Resch M, Theiss W. Differences in number, size and location of intracranial microembolic lesions after surgical versus endovascular treatment without protection device of carotid artery stenosis. J Neurol. 2004; 251(10): 1198-203.
- Consensus Committee of Ninth International Cerebral Hemodynamics Symposium/Basic identification criteria of Doppler microembolic signals. Stroke.1995; 26(6): 1123.
- Markus HS, King A, Shipley M, Topakian R, Cullinane M, Reihill S, Bornstein NM, Schaafsma A. Asymptomatic embolisation for prediction of stroke in the Asymptomatic Carotid Emboli Study (ACES): a prospective observational study. The Lancet Neurology.2010; 9(7): 663-71.
- Ritter MA, Dittrich R, Thoenissen N, Ringelstein EB, Nabavi DG. Prevalence and prognostic impact of microembolic signals in arterial sources of embolism: a systematic review of the literaturey. Journal of Neurology. 2008; 255(7): 953-61.
- Valton L, Larrue V, Pavy le Traon A, Geraud G. Cerebral microembolism in patients with stroke or transient ischemic attack as a risk factor for early recurrence. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1997; 63(6): 784-7.
- Kofidis T, Fischer S, Leyh R, Mair H, Deckert M, Haberl R, Haverich A, Reichart B. Clinical relevance of intracranial high intensity transient signals in patients following prosthetic aortic valve replacement. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2002; 21(1): 22-6.
- Nadareishvili ZG, Beletsky V, Black SE, Fremes SE, Freedman M, Kurzman D, Leach L, Norris JW. Is cerebral microembolism in mechanical prosthetic heart valves clinically relevant? J Neuroimaging. 2002; 12(4): 310-5.


