Changes in inter- and intrahemispheric connectivity in patients with cardiovascular diseases and obstructive sleep apnea
Автор: Anna A. Orlova, Mikhail V. Agaltsov, Anton R. Kiselev, Maksim О. Zhuravlev, Oksana M. Drapkina
Журнал: Saratov Medical Journal @sarmj
Статья в выпуске: 4 Vol.5, 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Objective: to analyze the electroencephalographic (EEG) connectivity in patients with cardiovascular diseases and obstructive sleep apnea. Materials and Methods. A total of 133 polysomnograms in cardiology patients were analyzed. The patients were divided into 4 groups depending on the value of the apnea-hypopnea index (AHI). Based on the wavelet bicoherence method, the level of connectivity of the electrical activity in the brain between all pairs of EEG channels for the entire duration of the night sleep was independently calculated from the polysomnograms. Results. The mean value of interhemispheric connectivity decreased significantly with increasing severity of apnea syndrome almost in all frequency bands. The mean values of occipital interhemispheric connectivity exhibited an inversely proportional trend with an increase of AHI in ∆f6 [4.0-8.0 Hz]: 0.472 [0.391; 0.585], 0.439 [0.402; 0.509], 0.418 [0.384; 0.483], 0.395 [0.359; 0.433] (p=0.012). Intrahemispheric connectivity was superior to interhemispheric connectivity both in the left and right hemispheres and demonstrated heterogeneous dynamics. Conclusion. With increasing AHI, interhemispheric connectivity decreased and intrahemispheric connectivity increased selectively. At the same time, in the group of patients with AHI<10 events/h, this pattern was violated, and the level of EEG connectivity corresponded to the most severe grade of apnea.
Cardiovascular diseases, obstructive sleep apnea, polysomnography, wavelet analysis
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/149148542
IDR: 149148542 | DOI: 10.15275/sarmj.2024.0402
Текст научной статьи Changes in inter- and intrahemispheric connectivity in patients with cardiovascular diseases and obstructive sleep apnea
© This article is an open access publication. Russian Text. Published in Saratov Journal of Medical Scientific Research 2024; 20 (4): 419-424. ISSN 1995-0039.
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is the most common sleep-disordered breathing characterized by recurrent episodes of breathing cessation or significant reduction in respiratory flow while maintaining respiratory effort. The latter is caused by upper-airway collapse. Typically, an episode of OSA is accompanied by a reduction in blood saturation with oxygen and/or electroencephalographic (EEG) activation [1].
Intermittent hypoxemia leads to activation of proinflammatory cytokines and endothelial dysfunction, while fluctuations of an intrathoracic pressure and sympathetic hyperactivation increase pressure load [2]. Consequently, some cardiovascular diseases are associated with OSA, such as hypertension, cardiac arrhythmia, and chronic heart failure [3].
Various methods are employed to assess structural and functional changes in patients with OSA. One of them is a quantitative EEG analysis of polysomnographic recordings known as polysomnograms (PSGs), in particular, an assessment of the synchronization level between EEG channels [4, 5] calculated by nonlinear physics methods. Synchronization of EEG activity can point to interneuronal
functional communication in the brain and its disruption in case of a particular pathology [6].
According to the results of previous studies, the degree of interhemispheric synchronization decreases in patients with OSA vs. healthy individuals, while the degree of intrahemispheric synchronization selectively increases [7-9]. However, this pattern has not been studied yet in a cohort of patients with cardiovascular diseases, which are often associated with OSA.
Objective – analysis of the synchronization level between EEG signals in patients with cardiovascular pathology at various grades of OSA severity.
Materials and Methods
Our study was conducted in compliance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki and received approval from the independent Ethics Committee at the National Medical Research Center for Therapy and Preventive Medicine (NMRC TPM) of the Russian Federation Ministry of Healthcare (protocol # 02-03/22 of March 17, 2022). The informed consent was obtained from all study subjects prior to their participation in the study.
Our study involved 133 PSGs of cardiology patients who received inpatient or outpatient treatment at NMRC TPM. The study included patients aged 18 to 75 years with complaints of OSA / hypersomnia who agreed to participate in the study. Exclusion criteria were patient age over 75 years and the presence of concomitant diseases of the nervous system and cognitive impairment that could potentially affect the quality of nocturnal PSGs (Parkinson’s disease, complications after acute cerebrovascular accident, epilepsy, history of repeated traumatic brain injury, etc.). Patients were divided into 4 groups depending on the values of apnea-hypopnea index (AHI), which corresponded to the various severity grades of OSA: AHI> 50 events per hour (events/h) (n=23), 20≤AHI≤50 events/h (n=48), 10≤AHI≤20 events/h (n=13), AHI<10 events/h (n=49). The clinical characteristics of the groups are presented in the following table .
All patients underwent a comprehensive night sleep study using a stationary Comet-PLUS Grass Technologies PSG system (Astro-Med, Inc., USA). The PSG editing included an electrooculogram, six-channel EEG (O2, O1, C4, C3, F3, F4), chin electromyogram, electrocardiogram, as well as recordings of snoring, respiratory flow, chest and abdominal wall movements, and leg movements. Pulse rate, blood oxygen saturation, and body position in space were presented separately as digital values. Each recording was analyzed by an expert in sleep medicine in order to compile a final version of the study protocol and a conclusion on the severity of sleep-disordered breathing.
Based on the night recordings of EEG channels, the connectivity level of the electrical activity in the brain was independently calculated between all pairs of EEG channels for the entire duration of the night recording. The synchronization level was calculated for each of the following 14 frequency bands: ∆f1 [0.2; 1.0], ∆f2 [0.8; 1.6], ∆f3 [1.0; 2.0], ∆f4 [1.0; 4.0], ∆f5 [4.0; 6.0], ∆f6 [4.0; 8.0], ∆f7 [6.0; 8.0], ∆f8 [8.0; 10.0], ∆f9 [8.0; 12.0], ∆f10 [10.0; 12.0], ∆f11 [12.0; 14.0], ∆f12 [12.0; 20.0], ∆f13 [20.0; 30.0], and ∆f14 [30.0; 40.0] Hz.
To assess the connectivity of EEG signals, we used a method based on the calculation of wavelet bicoherence. This technique involves assessing the complex coefficients of the continuous wavelet transform for each EEG channel and consequent calculation of the mutual synchronization coefficient between two EEG signals. The synchronization coefficient takes any value from 0 to 1, which characterizes the synchronization level between the signals under study at a given point in time and at a certain frequency. The more synchronized or similar in a certain frequency band the dynamics of a certain pair of signals is, the closer the value of the synchronization coefficient is to 1, and vice versa. This method is discussed in detail in our earlier publication [9]. Accordingly, the higher the synchronization value is, the stronger is the connectivity between the considered pair of EEG channels.
In the nocturnal sleep study by M. Zhuravlev et al. [9] for patients with OSA and apparently healthy individuals, it was demonstrated that the variability of the synchronization estimated on the basis of wavelet bicoherence for different stages of sleep and over its entire duration is small. Taking into account this finding, in the present study, the synchronization of the electrical activity in the brain was studied in groups of patients with different severity of OSA.
This synchronization was recorded during the entire duration of the nocturnal sleep recording.
Statistical data processing was performed using the SPSS and STATISTICA software. Quantitative indicators are presented as the mean or median and interquartile range. For qualitative parameters, we indicate percentages and total counts of observations for each study group. The statistical significance of differences between study groups was assessed using the Mann-Whitney U test [10]. At p<0.05, the differences were considered statistically significant. When conducting multiple comparisons, the Bonferroni correction was taken into account [11], and differences were assumed statistically significant at p<0.012.
Results
The prevailing diagnosis of patients in all groups was hypertension (Table). In the group of patients with a low severity of OSA or its absence (AHI<10 events/h), the incidence of hypertension was the lowest, while the incidence of heart arrhythmia was the highest. Patients in this group were younger and less likely to suffer from type 2 diabetes. With an increase in AHI value, we observed a trend for BMI to increase in the groups.
Table. Clinical characteristics of study groups
|
Characteristics |
Apnea-hypopnea index (AHI), events/h |
p |
|||
|
>50 ( n =23) |
20≤AHI≤50 ( n =48) |
10≤AHI≤20 ( n =13) |
<10 ( n =49) |
||
|
Hypertension, stage, % |
<0.001 |
||||
|
I |
4.3 |
14.6 |
23.1 |
28.6 |
|
|
II |
30.4 |
31.3 |
7.7 |
14.3 |
|
|
III |
56.5 |
47.9 |
61.5 |
20.4 |
|
|
Heart arrhythmia, % |
29.6 |
25.0 |
16.7 |
40.8 |
|
|
Age, years |
56.2 [51.9; 60.6] |
59.2 [56.0; 62.3] |
56.4 [47.8; 65.0] |
47.6 [43.5; 51.7] |
|
|
Type 2 diabetes mellitus, % |
26.1 |
22.9 |
23.1 |
14.3 |
0.615 |
|
Female gender, % |
30.4 |
31.3 |
38.5 |
42.9 |
0.620 |
|
Smoking, % |
4.3 |
16.7 |
15.4 |
6.1 |
0.215 |
|
Body mass index, kg/m2 |
38.3 [32.7; 43.9] |
32.7 [30.5; 34.9] |
32.5 [29.5; 35.4] |
28.6 [25.9; 31.4] |
0.001 |
|
Total cholesterol, mmol/l |
5.3 [4.0; 6.6] |
5.0 [4.6; 5.5] |
5.3 [4.5; 6.0] |
5.2 [4.6; 5.7] |
0.941 |

Changes in inter- and intrahemispheric connectivity in patients with cardiovascular diseases and obstructive sleep apnea
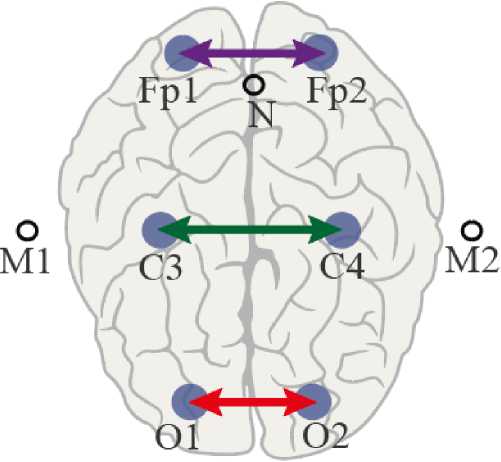
The mean values of the wavelet bicoherence, i.e., synchronization for each of the considered groups of patients in the specified frequency bands for all pairs of channels, are shown in figures below. Figure 1 presents the characteristics of interhemispheric synchronization of symmetrically located channels (O2–O1, C4–C3, and F4–F3). The compared channels are schematically shown in Figure 2 . Figures 3 and 4 are present the analysis of the connectivity of EEG activity within the right and left hemispheres, respectively.
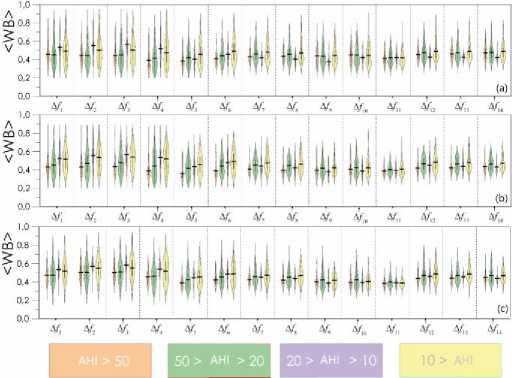
Figure 1. Mean values of the synchronization level estimated for symmetrical occipital (O2-O1) (a), central (C4-C3) (b) and frontal (F4-F3) (c) EEG signals presented for different groups of patients depending on the severity of sleep-disordered breathing. The horizontal black line shows the mean value of the distribution for each group of patients. The colors correspond to the following apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) values: orange >50 events/h, green 20≤AHI≤50 events/h, purple 10≤AHI≤20 events/h, yellow <10 events/h. WB – wavelet bicoherence.
frontal lobe
occipital lobe
Figure 2. EEG electrode placement diagram
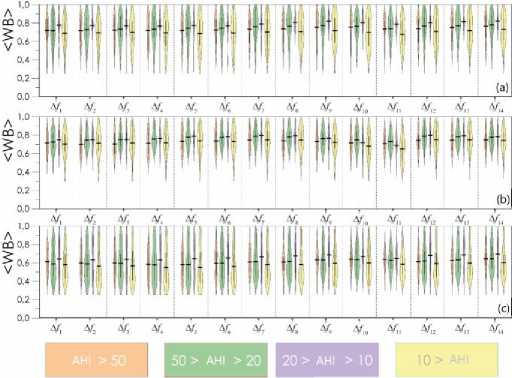
Figure 3. Mean values of the synchronization level estimated for EEG signals in the right hemisphere of the brain and presented for different groups of patients depending on the severity of sleep-disordered breathing: (a) O2-C4, (b) C4-F4, (c) O2-F4. The horizontal black line shows the mean value of the distribution for each group of patients. The colors correspond to the following apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) values: orange >50 events/h, green 20≤AHI≤50 events/h, purple 10≤AHI≤20 events/h, yellow <10 events/h. WB – wavelet bicoherence.
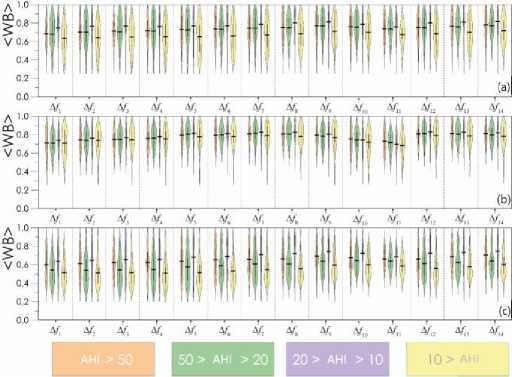
Figure 4. Mean values of the synchronization level estimated for EEG signals in the left hemisphere of the brain presented for different groups of patients depending on the severity of sleep-disordered breathing: (a) O1-C3, (b) C3-F3, (c) O1-F3. The horizontal black line shows the mean value of the distribution for each group of patients. The colors correspond to the following apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) values: orange >50 events/h, green 20≤AHI≤50 events/h, purple 10≤AHI≤20 events/h, yellow <10 events/h. WB – wavelet bicoherence.
Our study demonstrated that the mean value of interhemispheric synchronization in nearly all frequency bands significantly decreased with an increase in the severity of the OSA syndrome: with an increase in the number of apnea events per hour, the level of connectivity in the brain electrical activity was decreasing. However, this pattern was violated for the group of patients #3 characterized by AHI in the range of 10-20 events/h. For example, in the lowest frequency band, ∆f1, this group of patients demonstrated the maximum value for the connectivity between the O2-O1, C4-C3 and F4-F3 channels, similar to the ∆f2-4 bands. The mean values of the synchronization between the occipital EEG signals demonstrated an inversely proportional trend in ∆f6 with an increase of AHI: 0.472 [0.391; 0.585], 0.439 [0.402; 0.509], 0.418 [0.384; 0.483], 0.395 [0.359; 0.433] (p=0.012).
The right-hemispheric connectivity of the electrical activity in the brain is shown in Figure 3 . Intrahemispheric connectivity in both the left and right hemispheres exceeded interhemispheric connectivity in patients suffering from OSA.
When examining the O2–C4 connection within the right hemisphere, our attention was drawn to the extreme closeness of the characteristics in the groups of patients characterized by an OSA level of 20-50 events/h and over 50 events/h, which was significantly different from the groups with lower AHI values. With a reduction in AHI to 10-20 events/h, the level of connectivity increased significantly. Interestingly, with a minimum AHI value (less than 10 events/h), the level of connectivity in these leads significantly decreased. In C4-F4 and O2-F4 leads, the mean connectivity values calculated for the groups of patients with AHI greater than 50 events/h and less than 10 events/h were similar, being lower than for the other two groups of patients.
The left hemisphere ( Figure 4 ) also demonstrated the minimum connectivity values in the group of patients with AHI less than 10 events/h, and the maximum connectivity values for patients with a slightly higher number of OSA episodes (from 10 to 20 events/h). At the same time, higher AHI values (from 20 and from 50 events/h) significantly changed the connectivity solely in the O1-F3 leads (Figure 3c). The wavelet bicoherence value for this pair of EEG leads in the group with AHI exceeding 50 events/h was similar to the values in the group with AHI in the range of 10-20 events/h. For example, for the frequency band ∆f2, the mean connectivity values were 0.61 and 0.64 in the groups with AHI>50 events/h and 10-20 events/h, respectively (p=0.008). In addition, the connectivity for the pair of C3-F3 leads changed minimally in all four groups, varying significantly only in one frequency band (∆f11), decreasing on average from 0.71 in the group with AHI exceeding 50 events/h to 0.63 in the group with AHI under 10 events/h (p=0.874).
Therefore, the conducted analysis of changes in the connectivity of the electrical activity in the brain of patients with OSA demonstrated that at different AHI values, the changes occurred in a nonuniform and nonlinear manner. The synchronization for symmetrical EEG channels in the low-frequency bands in the groups of patients with AHI>50 events/h and 10-20 events/h differed statistically significantly (p<0.012). The other described qualitative changes, albeit quite noticeable, were difficult to quantitatively assess. The addition of the Bonferroni correction for the multigroup comparison was insufficient for reliable statistically significant separation of the different groups (p>0.012).
Discussion
As shown earlier, in patients without cardiovascular diseases [9], the level of interhemispheric connectivity of the electrical activity in the brain between symmetrical leads in patients with OSA decreases. The revealed trend also persists in the group of patients with cardiovascular pathology. This trend is aggravated by an increase in the number of apnea episodes. However, a group of patients with a minimum number of apnea episodes exhibits a somewhat different pattern. As the analysis of the clinical characteristics in the study groups shows, patients with an AHI of <10 events/h are statistically significantly younger and had a lower BMI. At the same time, the level of interhemispheric synchronization in this group demonstrates a decrease vs. the AHI group of 1020 events/h in various EEG frequency bands. Such dynamics of the interhemispheric synchronization is probably associated with significant disorders of the cardiovascular system observed in this group. In particular, over 40% of patients in this group demonstrate clinically significant heart arrhythmia. Thus, despite their young age, patients with AHI less than 10 events/h already suffered from cardiovascular pathology manifested by arrythmias of different etiologies. During polysomnography, they experienced sleep-disordered breathing, possibly aggravating the course of the underlying disease. It can be assumed that a decrease in the interhemispheric connectivity of the electrical activity in the brain is caused not only by disorders of the normal respiratory rhythm, but also by heart arrhythmia. If so, then this is a pattern similar to the group of patients with AHI less than 10 evebnts/h. However, this hypothesis requires further investigation.
Intrahemispheric synchronization reacts much less to the severity of OSA in the groups of patients. A notable difference is demonstrated by the central leads, C3-F3, in the left hemisphere in the mu-frequency band (12-14 Hz). Here, the mean connectivity increases with an increase in the number of OSA episodes. In general, this fact repeats the previously obtained results, which showed an increase in connectivity or synchronization in the left hemisphere of patients with apnea compared with the data of virtually healthy subjects [9].
Changes in the electrical activity of the brain in patients with OSA, based on the results of quantitative and qualitative EEG analyses, can be caused by various pathophysiological mechanisms. Hypoxemia observed in patients with OSA interferes with normal rest and restorative sleep, which causes chemical and/or structural damage to brain cells [12]. Currently, based on imaging and functional MRI studies, it was proven that the brain of patients suffering from OSA is characterized by a reduction in the volume of both gray and white matter, along with impaired activity of white matter at rest [13, 14].
Hence, the assessment of changes in the connectivity of the electrical activity in the brain of patients suffering from OSA and cardiovascular diseases (hypertension and heart arrhythmias) can become an additional tool for independent assessment of pathophysiological changes occurring in the patient’s central nervous system. The stability of these characteristics throughout the night allows us to hope for the possibility of developing a system of independent markers of disruption/change in the connectivity the electrical activity in the brain of patients also during their wakefulness, which will be helpful in the assessment of apnea severity.
Conclusion
We have established that, on average, with an increase in AHI values, interhemispheric connectivity decreased while intrahemispheric connectivity increased. At the same time, in
Changes in inter- and intrahemispheric connectivity in patients with cardiovascular diseases and obstructive sleep apnea the group of patients with AHI<10 events/h, this pattern was disrupted, and the connectivity of the electrical activity in the brain corresponded to the most severe grade of apnea. Perhaps this was due to the higher incidence of heart arrhythmia (>40%) in this group of patients.
Our study was performed in 2022-2024 within the framework of the Government Procurement, Development of Algorithms for Identification of Markers of Sleep-Disordered Breathing in Patients with Various Forms of Cardiovascular Pathology (No. 122013100209-5), at the Federal State Budgetary Institution of the Russian Federation Ministry of Healthcare, National Medical Research Center for Therapy and Preventive Medicine.
Author contributions. All authors made equal contributions to the preparation of the article.
Conflict of interest. None declared by the authors.


