Changes in jasmonic and salicylic acids levels in barley challenged with cochliobolus sativus
Автор: Aldaoude A., Jawhar M., Al-shehadah E., Shoaib A., Moursel N., Arabi M.I.E.
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 1 т.18, 2022 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Spot blotch (SB), caused by Cochliobolus sativus is a common foliar disease of barley worldwide. The phytohormones jasmonic acid (JA) and salicylic acid (SA) play important functions in plant defense systems. However, the changes in JA and SA pathways in response to SB disease have been poorly documented. In the current work and to better understand the mechanisms of barley resistance to this disease, JA and SA pathways were evaluated in resistant ‘Banteng’ and susceptible ‘WI2291’ cultivars across four time points post pathogen challenge. The data showed that JA and SA contents were elevated in fungus-inoculated and non-inoculated leaves in both resistant and susceptible interactions 24h post inoculation. However, although JA signaling was activated in parallel with SA signaling up to 72h in both cultivars, JA had no significant differences across four time points as compared with non-inoculated controls. Furthermore, the resistant cultivar ‘Banteng’ constitutively contained higher levels of SA (956.2 ng/g) comparing with the susceptible one ‘WI2291’ (192.5 ng/g) 96h post inoculation, whereas, JA pathway was weakly activated over time. We thus hypothesized that SA signaling has an important function in resistance mechanisms against SB disease, whereas JA signaling has a contrasting role in this defense system, which might prove crucial information concerning barley signaling events induced by C. sativus invasion.
Barley, defense signaling, jasmonic acid, salicylic acid, cochliobolus sativus
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/143178337
IDR: 143178337
Текст научной статьи Changes in jasmonic and salicylic acids levels in barley challenged with cochliobolus sativus
Plants possess a complex defense responses activated upon pathogen detection through elaborating signaling networks regulated by phytohormones including JA and SA. Therefore, discovery of targets and the understanding JA and SA molecular modes in physiological processes could help in the dissection of the complex JA and SA signalling networks, confirming their functional role in plant defenses against fungal diseases (Brouwer et al. , 2020).
A number of woks have demonstrated that SA usually activates defense mechanisms against both biotrophic and hemi-biotrophic pathogens (Bari and Jones 2009), whereas JA activates resistance towards necrotrophic phathogens (reviewed in Thaler et al. , 2012). JA and SA defense signaling pathways are commonly antagonistic in dicotyledonous species (Koornneef and Pieterse 2008), whereas this antagonistic crosstalk between JA and SA-dependent defense signaling is unclear in monocotyledonous species, and barley can serve as a model for molecular studies of other monocotyledonous species.
Cochliobolus sativus (Ito & Kurib.) Drechsl. ex Dast. (anamorph: Bipolaris sorokiniana (Sacc. in Sorok.) Shoem.) is a hemi-biotroph fungus that causes SB of barley, a disease responsible for large economic losses in barley-growing areas (Clark 1979; Rehman et al. , 2020). The fungus has an early biotrophic growth phase that needs living cells followed by a necrotrophic phase involving programmed cell death leading to activate various signalling pathways including plant hormones such as JA and SA (Kumar et al. , 2002 ). Our previous results suggest that SA signaling may have a function in barley defense against C. sativus ( Al-Daoude et al. , 2019 ), however, the interaction between JA and SA signaling pathways of barley defense mechanism(s) against this pathogen is still not clear.
In the present study, we focused on the defense responses of two barley cultivars Banteng and WI 2291, which are incorporated in international breeding programs for improving barley resistance to SB disease. Banteng was described as highly resistant to C. sativus over 15 years of field and greenhouse experiments
(Arabi and Jawhar 2004), i.e. had a lower level (compared with WI2291) of SB symptom development. We thus hypothesized that JA and SA-triggered defenses could drive contrasted levels of resistance in Banteng and WI2291, inoculated by the same C. sativus isolate. Thus, the aim of the present study was therefore to obtain a more comprehensive view of JA- and SA-dependent barley leaves responses to C. sativus infection in resistant and susceptible cultivars, during four time points of pathogen infection.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Barley genotypes
After 15 years of greenhouse and field screening, the German cv. Banteng has demonstrated to be the highly resistant genotype to all C. sativus isolates available so far (Arabi and Jawhar 2003), therefore, it was used in this work. The highly susceptible control for these diseases, the cv.‘WI2291’ from Australia was also used in the experiments. Seeds were sown in 20-cm pots filled with sterilized peat moss and arranged in a randomized block design with three replicates for each cultivar/disease at 20°C, with a 16 h-light/8 h-dark cycle.
Inoculation with C. sativus
The inoculum used in all the tests was the ‘selected’ Cs 41 isolate (Arabi and Jawhar 2004) which belongs to the P4 pathotype according to Arabi and Jawhar (2003). Seedlings of each genotype were manually inoculated with Cs 41 isolate by spraying plants with a conidial suspension of 2 ×104 conidia mL-1 in pure water. Plants were kept in the same greenhouse at 22°C/18°C (day/night) with 12-h photoperiod and 90% relative humidity. Non-inoculated control plants were sprayed with pure water and surfactant.
Quantification of JA in plant samples
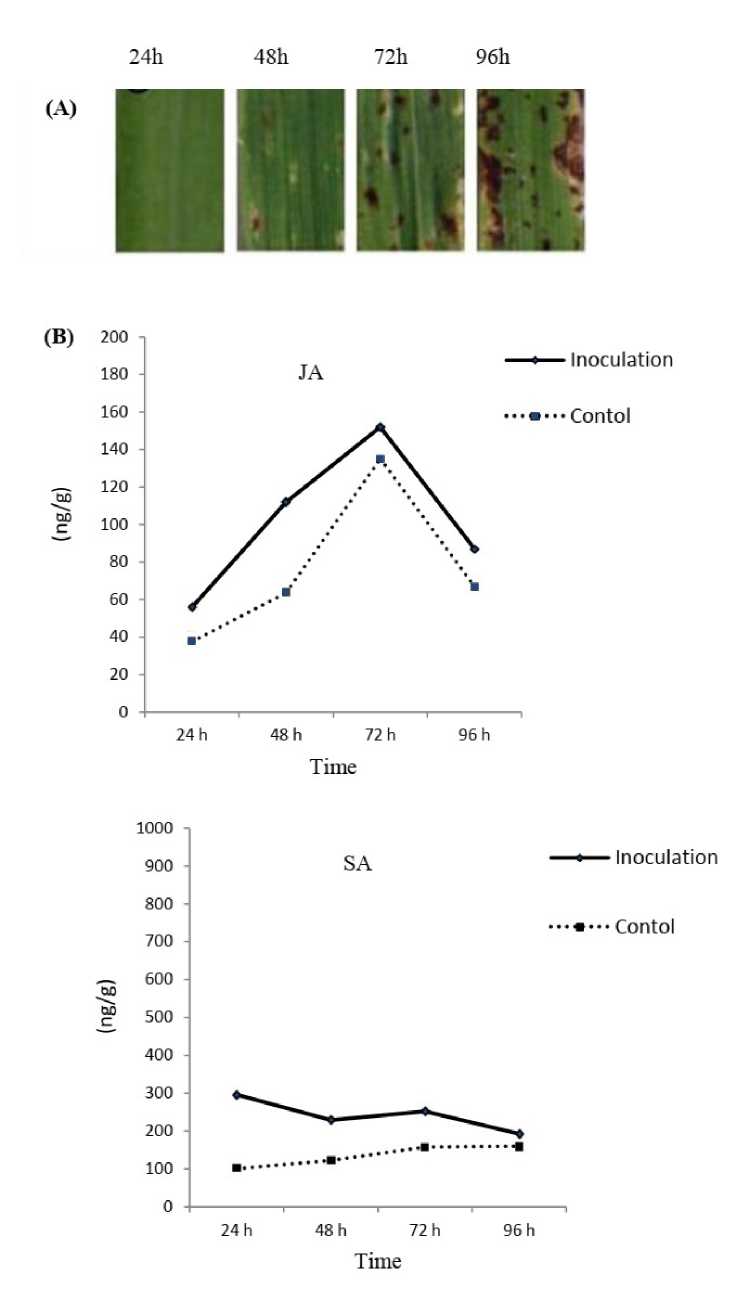
JA was analyzed at different time points 24, 48, 72 and 96 hours post inoculation (hpi) using the protocol described by Trapp et al. (2014). Briefly, 100 mg of plant material was ground in a liquid nitrogen. The extraction was performed by adding 1.0 mL of ethyl acetate, dichloromethane, isopropanol, MeOH:H2O into each tube containing dry plant material. Samples were centrifuged at 16,000 g for 5 min. The supernatant phase was transferred into a new 1.5 micro-centrifuge tube and was passed through carbon-packed solid phase extraction tubes (Supelclean ENVI-Carb SPE tubes), dried in speed vac. After drying, 1000μL of MeOHwere added to each sample, homogenized under vortex and centrifuged at 16,000 g for 10 min. The supernatant was applied on a thin layer chromatography plate (Silica gel on TLC Al foil with fluorescence indicator 254 nm SA quantification SA was quantified in barley third leaf tissues at 24, 48, 72 and 96 hours post inoculation (hpi) (Table 1). Three replicates were achieved for each time point. SA was measured according to Trapp et al. (2014. Extraction was done by adding 1.0 ml of ethylacetate, dichloromethane, isopropanol and MeOH: water (8:2) into each. The extract was centrifuged at 4°C at 16,000 g for 5 min and the supernatants were transferred to a new 1.5 micro-centrifuge tubes and dried in speed vac. Then, 100 μl of MeOH was added to each sample, homogenized under vortex and centrifuged at 4°C at 16,000 g for 10 min. SA was analyzed by a high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) system (Agilent Technologies, Germany). The data of JA and SA were statistically evaluated using the standard deviation and t-test methods. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION SB infection symptoms (presence of solid, dark necrotic lesions) were more severe on the susceptible genotype ‘WI2291’ as compared with the resistant one Banteng (Fig 1 and 2). Four different stages were chosen to cover early barley responses to SB which leads within 96h to a visible hypersensitive cell death on the susceptible genotype by considering the observations of Wisniewska et al. (1998) with barley susceptibility to Bipolaris sorokiniana. In this study, we aimed to investigate the involvement of JA and SA pathways in the resistant and susceptible barley cultivars at four time points after C. sativus inoculation. Overall, our data supply a more detailed view of JA- and SA-triggered defenses induced by C. sativus in barley leaves. The results showed that both hormonal pathways were activated after infection, and JA signaling was activated in parallel with SA signaling up to 72 h of infection (Fig 1 and 2). JA signaling promoted disease by constraining the activation of SA signaling. The higher content of SA in comparison to JA in barley leaves, suggests that SA most likely attenuates JA mediated defenses by limiting JA accumulation in the C. sativus inoculated leaves. JA accumulation is similarly restricted by the activation of SA signaling in tobacco leaves (Niki et al., 1998). Our results are also in line with Ellis et al. (2002) who suggested that both JA and SA signaling pathways increased after infection of Arabidopsis by Pseudomonas syringae but SA appeared to be more effective than JA. The mechanism of interactions between the SA and JA signaling pathways remains unknown. In the case of SB infection in this study, the SA pathway appears to be more efficient than the JA pathway in SB resistance because Banteng is more resistant to SB disease than WI2291. Tamaoki et al. (2013) hypothesized that plant species have evolved the technique of suppressing or weakening JA-inducible plant defenses by activating the SA-inducible pathway. However, the role of JA signaling in monocotyledonous species interaction with fungal pathogens has not been genetically validated. Future experiments to discern the role of JA signaling during this interaction should consider the results presented here on the monocotyledonous role of JA signaling in barley interaction with C. sativus. Overall, our findings suggest that SA signaling has an important role in resistance mechanisms against C. sativus disease, and JA signaling has contrasting role in this defense system. This study provides new insights concerning the role of both JA and SA pathways in monocotyledons such a barley against the hemi-biotroph fungus C. sativus. In addition, we highlighted the fact that two different hormonal responses may be induced in response to the same isolate of C. sativus in different barley cultivars Figure 1. (A); SB symptoms, B: Changes in JA and SA in barley resistant (Banteng) seedlings inoculated C. sativus. The data represents mean of three replicates SE. Figure 2. (A); SB symptoms, B: Changes in JA and SA in barley susceptible (WI 2291) seedlings inoculated C. sativus The data represents mean of three replicates SE. Table 1. Developmental stages of C. sativus on barley leaves during the selected time points Sampling time point Hours after inoculation (hpi) Young haustorium formed and host cytoplasm becomes granular 24 Small, dark brown lesions without chlorotic margin 48 Medium, dark brown lesions with chlorotic margin 72i Large, dark brown lesions with chlorotic margin 96 The developmental stages of the fungus as described by Bisen and Channy (1983) ACKNOWLEDGMENTS The authors thank the Director General of AECS and the Head of Molecular biology and Biotechnology Department for their support this research. CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest.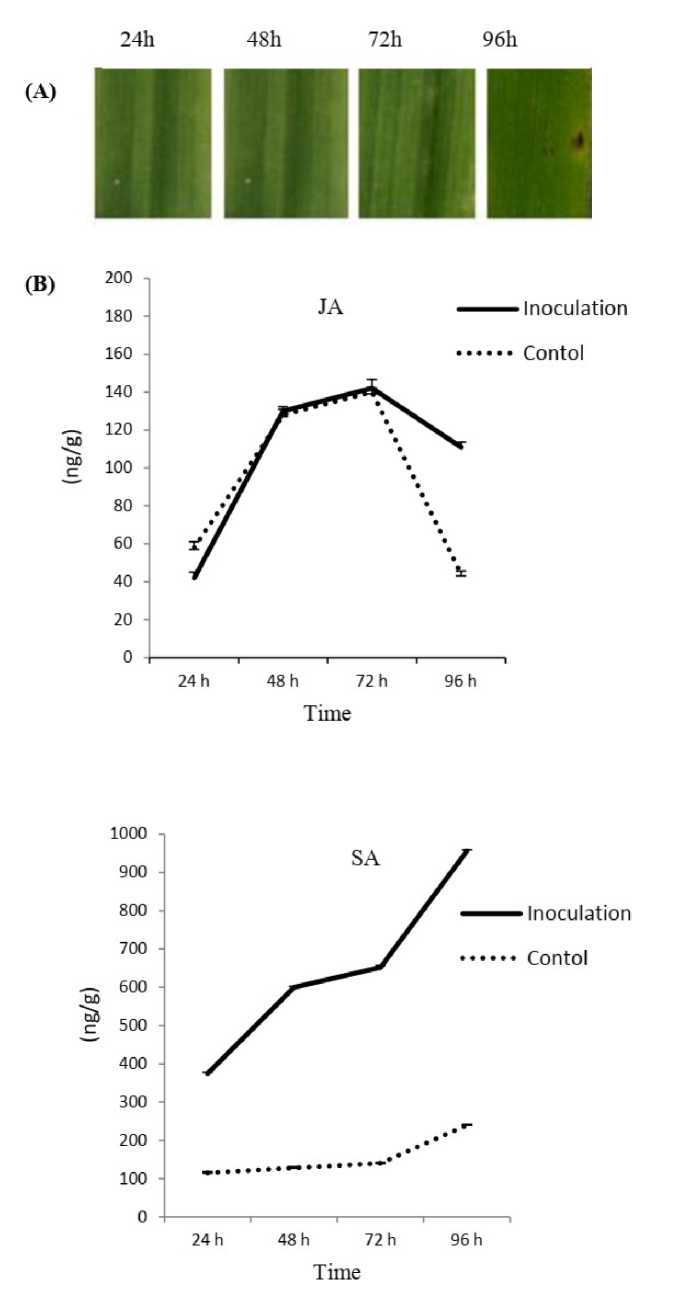
Список литературы Changes in jasmonic and salicylic acids levels in barley challenged with cochliobolus sativus
- Al-Daoude A., Al-Shehadah E., Shoaib A., Jawhar M., Arabi M.I.E. 2019. Salicylic Acid pathway changes in barley plants challenged with either a biotrophic or a necrotrophic pathogen. Cereal Res. Comm. 47:1-8.
- Antico, C.J., Colon, C., Banks, T. et al. Insights into the role of jasmonic acid-mediated defenses against necrotrophic and biotrophic fungal pathogens. Front. Biol. 7, 48-56 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007
- Arabi M.I.E., Jawhar M., 2003. Pathotypes of Cochliobolus sativus (spot blotch) on barley in Syria. Journal of Plant Pathology 85: 193-196.
- Arabi MIE, Jawhar M, 2004. Identification of Cochliobolus sativus (spot blotch) isolates expressing differential virulence on barley genotypes in Syria. J. Phytopathol., 152: 461-464.
- Bari R, Jones JD. Role of plant hormones in plant defence responses. Plant Mol Biol. 2009;69:473-88.
- Brouwer, S.M., Odilbekov, F., Burra, D.D. et al. Intact salicylic acid signalling is required for potato defence against the necrotrophic fungus Alternaria solani. Plant Mol Biol 104, 1-19 (2020).
- Clark RV (1979) Yield losses in barley cultivars caused by spot blotch. Canadian J Plant Pathol 1:113-117.
- Ellis C, Karafyllidis I, Turner JG (2002. a) Constitutive activation of jasmonate signaling in an Arabidopsis mutant correlates with enhanced resistance to Erysiphe cichoracearum, Pseudomonas syringae, and Myzus persicae. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 15: 1025-1030
- Koornneef A, Pieterse CM. Cross talk in defense signaling. Plant Physiol. 2008;146:839-44.
- Kumar J, Schafer P, Huckelhoven R, Langen G, Baltruschat H, Stein E, Nagarajan S, Kogel HK. Bipolaris sorokiniana, a cereal pathogen of global concern: cytological and molecular approaches towards better control. Mol Plant Pathol 2002; 3: 185-195.
- Leon-Reyes A, Van der Does D, De Lange ES, Delker C, Wasternack C, et al. (2010) Salicylate-mediated suppression of jasmonate-responsive gene expression in Arabidopsis is targeted downstream of the jasmonate biosynthesis pathway. Planta 232: 1423-1432.
- Niki, T., Mitsuhara, I., Seo, S., Ohtsubo, N. and Ohashi, Y. (1998) Antagonistic effect of salicylic acid and jasmonic acid on the expression of pathogenesis-related (PR) protein genes in wounded mature tobacco leaves. Plant Cell Physiol.39: 500-507.
- Rehman S, Gyawali S, Amri A, Verma RPS (2020) First report of spot blotch of barley caused by Cochliobolus sativus in Morocco. Plant Dis 104:3
- Tamaoki D, Seo S, Yamada S, et al. Jasmonic acid and salicylic acid activate a common defense system in rice. Plant Signal Behav. 2013;8(6):e24260. doi:10.4161/psb.24260
- Thaler JS, Humphrey PT, Whiteman NK. 2012. Evolution of jasmonate and salicylate signal crosstalk. Trends in Plant Science 17, 260-270.
- Trapp M.A., De Souza G.D., Filho E.R., Boland W., Mithofer A., 2014. Validated method for phytohormone quantification in plants. Front Plant Sci 5:417.
- Wisniewska, H., Wakulinski, W. and Chelkowski, J., Susceptibility of barleys to Bipolaris sorokiniana seedling blight determined by disease scoring and electrolyte. J. Phytopathol., 1998, vol.146, pp. 563566.


