Changes in USA trade policy and their role in economic transformation
Автор: Yu.O. Kitaeva
Журнал: Экономика и бизнес: теория и практика @economyandbusiness
Статья в выпуске: 5 (123), 2025 года.
Бесплатный доступ
This article examines changes in USA trade policy and their impact on the transformation of the country's economy. Key aspects are analyzed, such as the introduction of tariff restrictions, the shift from free trade to protectionist strategies, and the effect of these changes on the structure of both external and internal trade. The role of tariff policy in redistributing trade flows, stimulating production localization, and changing consumer preferences is emphasized. The consequences for USA companies and the role of analytical tools in adapting to the new conditions are also discussed.
Trade policy, tariffs, USA. economy, foreign trade, production localization, analytical tools.
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/170209215
IDR: 170209215 | DOI: 10.24412/2411-0450-2025-5-162-167
Текст научной статьи Changes in USA trade policy and their role in economic transformation
American trade policy in the past few decades has undergone radical changes on the basis of both domestic economic necessities as well as global necessities. Tariff reorientation on foreign merchandise has also become powerful instruments for the purpose of influencing economic activity in order to stimulate domestic production as well as protect national interest. Such actions have gained new importance in the face of intensifying international competition as well as increased trade tension.
The relevance of this study stems from the necessity to understand how the impact of policy alterations in tariffs affects domestic supply and demand structure. The introduction of new tariffs creates the redistribution of trade flows, changes in consumer behavior, and the alteration of pricing mechanisms. In such a situation, one of the primary objectives is not only the substitution of imported goods but also the establishment of a sustainable local raw materials market capable of offering economic independence to the nation.
The aim of this study is to analyze the impacts of changes in import tariffs on the economic change of the USA, with specific reference to behavioral and structural changes in the economy.
Particular stress is laid on the use of data analytics as a strategic planning tool in the successful transition to the use of American raw materials, enabling businesses to adapt to new situations with minimal cost and maximum efficiency.
Main part. Evolution of USA trade policy: transition from free trade to protectionist strategies
The trade policy of the USA has faced significant change in recent decades, from a faithful commitment to ideals of free trade to the practice of protectionism. This process reflects profound shifts both in the domestic economy and in the world trade and economic system [1].
During the latter half of the twentieth century and early twenty-first century, the USA was among the world's leading drivers of trade liberalization, promoting the establishment of the World Trade Organization (WTO) and free trade agreements. But from the mid-2010s, under the pressure of change in the world competitive environment and the growing trade balance deficit, trade policy priorities began to change in the direction of the protection of national interests.
One of the principal steps in this direction was the application of tariffs to steel, aluminum, and an enormous list of Chinese products in the eponymous USA – China trade war of 20182019. It is estimated that by the end of 2019 the USA had imposed tariffs on some $350 billion worth of Chinese imports and China had hit back by imposing tariffs on some $100 billion worth of American exports [2].
The most important milestones in the rebalancing of USA trade policy include the renegotiation of the terms of membership in the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) and its replacement with the new USA – Mexico – Canada Agreement (USMCA) in 2020. In 2022, the USA introduced tariff barriers on a wide range of technologically sophisticated goods. Additionally, nationwide programs aimed at promoting production in the most vital industries were initiated in 2023-2024. They are evidence of the USA' aspiration to not only deny access to its domestic market to foreign-based producers but to acquire technological and industrial leadership with respect to international competitiveness.
The impact of the outside economic environment, which included the escalation of trade tensions with China, was among the driving factors behind the reshaping of USA trade policy. China's countermeasures, aimed to cut the supply of certain types of raw materials and technological goods, increased the demand for diversification of supplies and accelerated the formation of the national industrial complex. When international supply chains were in a period of instability, USA was forced to build up national support programs for key infrastructure, create its own raw materials base, and encourage high-technology industries.
Another milestone in the development of USA trade policy was the alteration of tariff schedules in 2025, a step towards increasingly blatant protectionism. The policies instituted were base tariff increases on an across-the-board range of imported goods, as well as selective tariff increases on imports from specific countries, like China, Canada, and Mexico (table 1).
Table 1. New USA tariffs introduced in 2025 [3]
|
Category of goods / country of origin |
Tariff rate |
Remarks |
|
Base tariff on all imported goods |
10% |
Applies to all countries, except for certain specified exemptions. |
|
Imports from China |
145% |
Includes «foundational tariff» (20%) and «retaliatory tar-iff» (125%). |
|
Imports from Canada and Mexico |
25% |
Goods under the USMCA agreement are exempt from tariffs. |
|
Steel and aluminum (all countries) |
25% |
Applies to all steel and aluminum products. |
|
Automobiles and auto parts (all countries) |
25% |
Parts compliant with USMCA rules are exempt from tariffs. |
|
Imports from 57 countries |
11–50% |
Introduction delayed by 90 days, excluding China. |
|
Imports from the EU |
20% |
Introduction delayed by 90 days, excluding China. |
Among the reasons cited for the enforcement of tariffs was that the persistent annual trade deficit in merchandise had a crippling impact on USA economic growth. The deficit brought about the decline of the country's manufacturing base, limited the potential for the development of sophisticated production capacity in the country. It also increased the reliance of the defenseindustrial base on other countries. The huge deficit and its longevity were explained to a great extent by a lack of reciprocity in the foreign trade relations of the USA: American companies faced higher tariffs and non-tariff foreign market barriers, making export operations more challenging.
In addition, some trading partners' economic policies, aimed at holding down wages and domestic consumption, reduced demand for USA goods abroad while artificially boosting the competitiveness of their exports.
Thus, the evolution of USA trade policy is a continuous process of adaptation to both external and internal changing circumstances, during which the free trade doctrine gave way to a more flexible and selective protectionist policy. These reforms paved the way for the large-scale restructuring of the domestic demand and supply structure, cumulatively raising the role of analytical tools in strategic planning of economic development.
Tariff measures and the transformation of consumer behavior
The imposition of tariff measures during 2018-2019 and the strengthening of USA trade policy further in 2025 directly influenced the action of consumers domestically. The tariff hikes on an expansive list of items led to an increase in prices for goods being imported, changed consumption trends, and directed demand towards the home market as well as other overseas markets.
For example, according to the USA Department of Commerce, following the imposition of tariffs on steel imports at 25% in 2018, America's steel industry capacity utilization was more than 80%. That is a phenomenal increase in the activity level in the industry. The report also says that these measures led to a reduction in imports, stimulated investment and growth by domestic steel producers, and assisted in enhancing USA national security.
The introduction of new tariffs in 2025 also significantly reshapes the economic agenda. On one hand, according to data from The Budget Lab at Yale University, the new tariffs led to a shortterm increase in consumer prices by 3%, equivalent to a reduction in purchasing power of $4,900 per household at 2024 price levels. After accounting for substitution effects, the net increase in prices amounted to 1,6%, or approximately $2,600 per household.
On the other hand, it is estimated that the application of the new tariffs, even considering the effect of import substitution, raises the USA' av- erage effective tariff rate by 15,6 percentage points. This is largely because of the widespread substitution of imports from China – the primary target of the tariff measures – with other sources from other countries [4]. With the share of Chinese imports falling from 14% to 3%, the impact of increased Chinese tariffs on the overall mix of USA imports decreased. Thus, tariff protection for USA producers has been strengthened, as consumers increasingly opt for goods that are less tariff-affected or produced locally. After all the adjustments, the average effective USA tariff rate reaches 18,0%, the highest since 1934, thereby creating favorable conditions to prefer domestic production and stimulate the localization of supply chains (fig. 1).
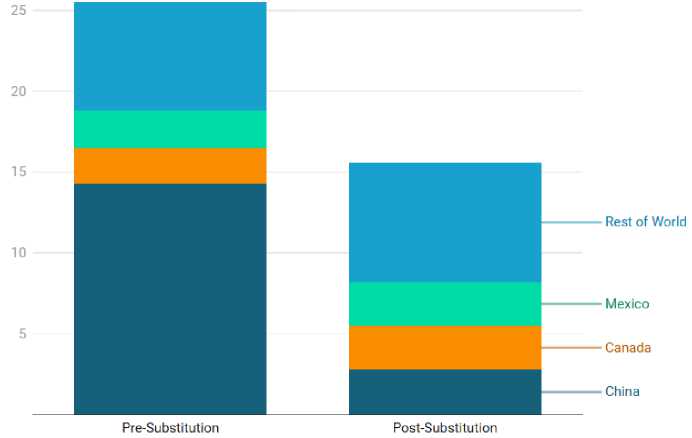
Figure 1. Change in average affective USA tariff rate, new 2025 policy through April 15 [5]
A rise in universal tariffs is estimated to reap $3,9 trillion extra revenue for the USA federal budget for the years from 2025 to 2034, states PIIE estimates. Increasing domestic production is considered to be one of the critical components of American national security.
The rising cost of a wide range of imported goods, including electronics, home appliances, apparel, and auto parts, has made foreign products more costly to USA consumers. For instance, a study by the Consumer Technology Association (CTA) and the National Retail Federation (NRF) found that the proposed tariffs would raise the cost of televisions imported from China by as much as 23%.
In response to inflation, a substantial shift has been noticed among consumers in the direction of locally manufactured goods as well as goods imported from countries exempt from tight tariff restrictions. The local manufacturers have been able to recover their position within the domestic market through price advantages and reducing the competition offered by exporters. The pattern of consumption has shifted increasingly towards more localized goods, signaling a continued adaptation of consumer behavior to the new trade environment and changes in pricing strategies.
According to a study conducted by Attest in April 2025, American consumers are increasingly turning to domestic markets in response to the new tariff measures. Approximately 50,1% of respondents reported switching to cheaper or local brands in an effort to offset price increases driven by tariffs (fig. 2).
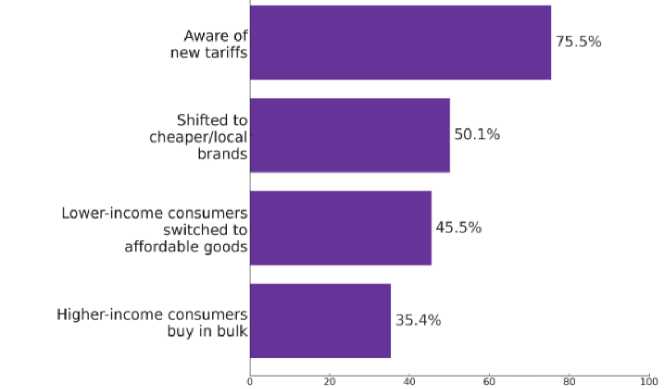
Figure 2. Results of the attest survey among American consumers [6]
Thus, the introduction of new tariff policies in 2025 emerged as the major driver for altering consumer behavior in the USA. The rise in prices of the imported commodities caused a shift in demand to domestically produced goods and products from countries with minimal tariff restrictions. The precipitous decline in the share of Chinese imports, the change in consumer preference in favour of domestic brands, and the pressure to redefine consumption strategies in conformity with the altered economic environment all indicate a profound structural realignment in the economy. These tendencies support the observation that tariff policy not only has a direct bearing on foreign trade but also acts positively in shaping new patterns of consumption at home.
The impact of changes in USA trade policy on the activities of American companies
Conversely, with rising inflation, some companies, particularly those in the trade, automobile, and electronics sectors, felt the impact of the increase in the cost of production. This was mainly due to the fact that most of the parts and finished goods in these industries had been imported previously by countries that are now facing new tariff limitations, particularly China. Hence, the cost of production rose, leading businesses to ei- ther increase end-consumer retail prices or offset part of the increased cost, thereby cutting operating profit.
At the same time, though, for companies that focus on the domestic market, the situation opened up new opportunities. For instance, Steel Dynamics recorded a 39% increase in revenue in metal operations during the first quarter of 2025 compared to the previous quarter due to growing demand for domestically manufactured products.
The USA largest home appliance producer, Whirlpoo l, reported that the tariffs would level the playing field for American producers [8]. With ten domestic plants producing 80% of its products in the USA, Whirlpool believes that tariffs will compensate for the initial advantages Asian producers had with cheaper raw materials and no tariffs. Despite the rising cost of components, Whirlpool maintained its net sales estimate at $15,8 billion and projected an adjusted earnings per share of $10, indicating its confidence with the beneficial effect that the tariffs have on its business.
TK Mold & Engineering , Inc. also had a positive assessment of the impact of the new tariff policies on economic activity in the USA. The demand for local production brought about an increase in orders for mold making and injection molding products that were previously outsourced abroad.
The recent tariffs will also impact the labor market. Despite concerns about the possible rise in unemployment, certain industries are expected to experience positive trends. As companies are adapting to the new conditions of trade, demand for specialists in logistics, customs brokerage, and trade data analysis is growing, creating additional job opportunities in these sectors of the economy. Besides, the tariff policy increases the competitiveness of USA agriculture: producers of dairy products, fruits, and other items that used to face stiff competition from imported goods are likely to benefit most from the shift in demand in favor of domestic goods, fostering employment in the agricultural and allied sectors.
Data analytics has become a vital instrument for business companies operating with the new terms of trade policies. It enables companies to reduce risks, optimize supply chains, and foresee changes in demand. According to the latest worldwide survey organized by McKinsey, more than 72% of USA companies utilize data analytics and artificial intelligence in at least one business function, which indicates considerable progress over the last few years.
The use of data analytics allows companies not only to respond to short-term changes but also to develop forward-looking strategies in an environment of growing trade uncertainty. Predictive analytics and supply chain optimization models assist companies in better assessing the probable impact of tariff rate adjustments, selecting the most resilient logistics routes, and readjusting pricing strategies to new market realities [9]. The effective marriage of data science and artificial intelligence is quickly emerging as a core competitive differentiator, not just guaranteeing short-term adjustment but long-term business resilience in the face of an increasingly dynamic external economic environment.
Hence, the new direction of USA trade policy in 2025 has become a chance as well as a challenge for American companies. Those firms which are able to excel in applying analytical tools and making their business models more elastic have gained the opportunity to consolidate their home market positions and obtain leverage against foreign shocks.
Conclusion
The changes in USA trade policy, implemented through the introduction of new tariff measures, have played a significant role in transforming the national economy. The increase in tariffs was a response to long-standing challenges related to the trade deficit and the weakening of the domestic manufacturing base. The introduction of both universal and targeted tariffs stimulated a reduction in imports, particularly from China, promoted the development of local production, and shifted consumer behavior in favor of domestically produced goods. These measures simultaneously strengthened internal supply chains and laid the foundation for enhancing the economic independence of the USA.


