Characterization of low velocity local impact of sandwich panels
Автор: Dolganina N.Yu., Sapozhnikov S.B.
Статья в выпуске: 4, 2014 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The present paper deals with analysis of local indentation and their energies in point loading of sandwich panel with thin orthotropic composite faces and honeycomb core as an introduction for low velocity impact loading and energy absorbing in sandwich structures. Energy is consumed in two stages: local indentation of sandwich panel skin and bending of sandwich panel. If the impact is located near support or clamping only first stage (indentation of sandwich panel) will be presented. Here the analytical model has been used assuming a rigid-perfectly plastic compressive behaviour of the honeycomb core and membrane behaviour of orthotropic skin for large indentation of sandwich panel. In experimental work were investigated two types of sandwich panels, which consisted of different laminated skins: cross-ply of unidirectional CFRP and AFRP (aramid fabric reinforced plastic) and core honeycomb materials (impregnated paper like Nomex and one layer of glass fabric reinforced plastic). Length of cell side is 2.5 mm. Skins were made with symmetrical lay-ups [0/90]s and [45/-45]s. For indentation test we used steel balls with radius 5-30 mm, speed of loading was 2 mm/min. The experimental results are in good agreement with the analysis. These results can be used in impact loading and energy absorption studies of laminated structures by integrating of “local load vs deflection” curve.
Sandwich panel, laminated structures, thin orthotropic composite faces, honeycomb core, low velocity impact, local load, bending, compressive behaviour of the honeycomb, energy absorbing, analytical model
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/146211540
IDR: 146211540 | УДК: 539.3 | DOI: 10.15593/perm.mech/2014.4.11
Текст научной статьи Characterization of low velocity local impact of sandwich panels
Sandwich structures are consisted of composite laminates as skins and low density honeycomb (or foam) core. These parts exhibit important role in local impact loading. Energy in this kind of loading is absorbed in two stages: indentation of sandwich panel and bending of sandwich panel. Here we will work with the first stage – local indentation.
The contact law between two isotropic elastic bodies was first developed by Hertz [1]. Willis [2] investigated the contact behaviour between a transversely isotropic half-space and a rigid sphere. Yang and Sun [3] have conducted several static indentation tests on glass/epoxy. Wu and Yen [4] have presented experimental results for contact and low velocity impact response of composite laminates by rigid spheres. Christoforou [5] has intro- duced a theory for indentation in composites too. In loading of sandwich structures, honeycomb core has a weak resistance. Much research effort has been given to this problem in order to model a response of sandwich structures to local load. Soden [6] also presented an analytical model for indentation of sandwich beam assuming plastic behaviour for core. Shuaeib and Soden [7] extended experimentally this work. Zenkert, et al [8] have studied indentation of sandwich beams. They presented an elastic-perfectly plastic compressive behaviour of core that elastic part of indentation is described by Winkler foundation model. Hazizzian and Cantwell [9] have investigated low velocity impact of sandwich structures and attended to absorbed energy in structures. Fer-aboly [10] and Olsson and McManus [11] have experimentally and numerically studied of damage resistance characteristics of honeycomb composite panels. For numerical research authors have used popular code ABAQUS [12] or LS-DYNA [13]. Numerical study of the low-velocity impact response of composite sandwich panels and beams has been given in [14-17].
In the present paper, indentations on sandwich panels have been done analytically and experimentally in case of quasi-static indentation by using rigid spherical indenter. Also results have been presented in terms of skin's in-plane elastic characteristics and core plastic behaviours, indenter diameter, energy absorbed, and length of contact area in the testing.
1. Theory
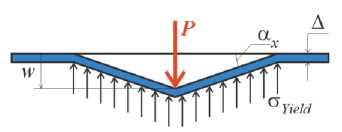
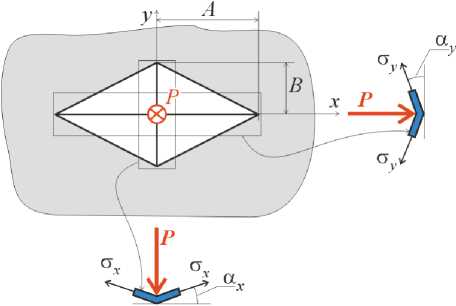
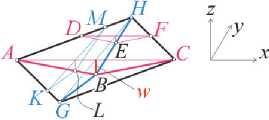
To get the formula for connection indentation load and deflection there are five assumptions: 1) indentation load is applied in one point; 2) thin skin is ortotropic elastic membrane (zero bending stiffness); 3) honeycomb core under transverse compression is rigid-perfectly plastic media that applies constant reaction to lower surface of skin; 4) skin surface into the indentation area is a pyramid with rhombus base; 5) out of the indentation skin area remains flat and stress-free. These assumptions are illustrated by fig. 1.
The pyramid shape of deformed skin is shown on fig. 1, where x and y – the main axes of orthotropic symmetry of skin laminate. Fig.1a illustrates constant vertical reaction of a core on the skin. Fig. 1c illustrates the 3D deflection of skin into deformed area: line AC became ABC, line DF became DEF. Because the triangle ABC is proportional DEF the strain along axis x (ε x ) is constant inside deformed area. The same situation is along y -axis: line GH became GBH, line KM became KLM. The strain along axis y (ε y ) is constant inside deformed skin area too.
a
b
c
Fig. 1. Simplified shape of deformed skin surface according the assumptions: a – constant vertical reaction of a core on the skin; b – zero-wide stripes of skin with x and y orientation; c – 3D deflection of skin into deformed area
It can be written the geometrical (1) and physical (2) equations according the assumptions:
w w ww
1 +^2 - 1; е у = а 1 +^2- 1; tg « х = ; tg « у =- ; (1)
A B AB
° х = Q11 ^ х + Q 12 ^ у ; ° у = Q 12 ^ х + Q22 ^ у , (2)
here σ x , σ y are the normal stresses of skin inside deformed area, Q ij are components of Hook's law matrix of orthotropic elasticity. According fig. 1b it can be written the equations of equilibrium (3) for all deformed skin and separate zero-wide stripes of skin with x and y orientation:
P = 2 AB oYield ; P = 4 g B A sin a ; P = 4 c, A A sin a, . (3)
Yield x x yy
There is full system of equation (1)–(3) to find size ( A , B ), depth ( w ) and energy ( W ) of deformed area if the load P is known. Of course, thickness of skin (Δ), 'yield' stress of core (σ Yield ) and matrix of skin laminate elasticity Q ( Q 11 , Q 12 and Q 22 ) should be known too for plane stress state.
If depth of indentation much less than lateral size ( w << A , B ) it can be written in quite simple formulas:
w = ( p / k )2/3; P = kw 3/2; W = 0,6 kw 5/2;
k = 27 a YkM A [( Q 11 Q > ' + Q 12 ];
P ;
2 0 Yield ( Q 22 / Q11 )
B =
P
7 2О№М( Q 11 / Q 22 )14 .
For quasi-static indentation of sandwich panel on testing machine it should be used spherical indenter with radius R ( R << A , B ). In this case indentation law P = kw 1,5 must work only up to failure of skin under indenter.
To predict skin failure load P* there are several additional assumptions: 1) only fibers are working in plies under indenter; 2) real elliptical contact area is substituted by rectangular area; 3) fracture of single fiber is brittle, but strain-driven stress-strain diagram of ply (billions of fibers) may have increasing and decreasing (softening) parts, see [18]. Thus, failure load P* can be find out by so called “limit analysis”, where local loading is deflection-driven process (fig. 2). For each deflection w it should be calculated load P ( w ). Here will be max P ( w ) = P* .
Under indenter the skin works as shown on fig. 2. Flat shape of skin under point loading (dot line) converts into curved shape on arc 2α x . In this case equilibrium of the indenter must be written in form:
a = R sin2 a ~ 2 Rw / A ; b = R sin2 a ~ 2 RwIB ; xy
8 R A w 2 ( 0^0 )
P „________ x x ____ y '
.
AB
Using eqs. (4) and (5) we will have eq. (6) for estimation of failure load P* :
_ = 16 ( 5 A )12[max( 5 x + 5 у ) R ] 32
= 6 ( Q 11 Q 22 )12 + Q 12 . (6)
For getting max( 5 x + 5 у ) in eq. (6) we have to make next assumption for strain ё under indenter - there is proportional deformation as it is out of indenter zone (eq.(7)) with parameter e :
e = ё , / ё у =e x / e , - B 2 / A 2 = ( Q 22 / Q „)12. (7)
For these conditions, plane stress state can be estimated as shown (eq. (8)):
-
5 x = Q 11 e x + Q 12 ё у = p ( Q n + Qu e );
-
5 у = Q 12 ё x + Q 22 ё у = p ( Q 12 + Q 22 e );
5 x +5 у = p[ Q 11 + Q 12 (1 + e ) + Q 22 e ], (8)
where p is independent parameter of deformation which can only increase during local loading, 5 is stress in the skin under indenter (fig. 2).
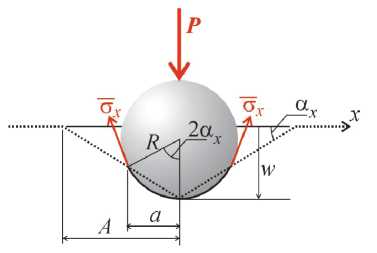
Fig. 2. Equilibrium of indenter on the skin
Due to monothropic behaviour of each ply
5 x +5 у = P
У E i ( p ) 8, (cos4 9 , + (1 + e ) cos2 Ф , sin2 Ф, + e sin4 ф , )
i = 1
where φ i is fiber orientation in i -ply, n is quantity of plies, Es ( p ) is secant modulus of i -ply along fiber direction (function of parameter p ), δ i is ply thickness.
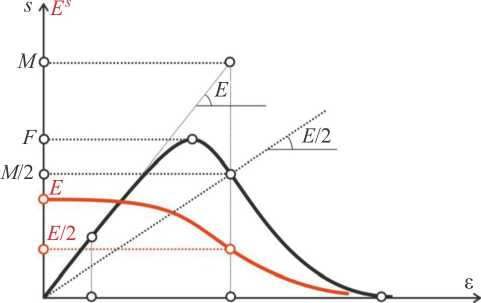
According [9] typical industrial fibers have strength distribution close to normal (Gaussian) law with known median M and variation coefficient k v ≈ 0,20. In this case M ≈ F /0,672. Strain driven diagram of ply is shown on fig. 3 (black line), secant modulus is shown by red line.
М(1-Зкх)ПЕ МНЕ М(Д+Зкда
Fig. 3. Strain driven diagrams of ply
For engineering calculations secant modulus can be written as
E i ( p ) = E i
Ep
1 - i exp
M i k v 2 π 0
( ζ- M i / E i )2
-
[ 2( M i k v / E i ) J
d Z ,
where ζ is an internal integration argument.
For calculation of fracture load P* all formulas (eqs. (5)–(10)) were coded in popular MathCAD processor for convenience of use.
For example, if the skin lay-up is balanced like [0/90]s or [+45/–45]s, Q 12 << Q 11 , A = B , a = b and max( σ x + σ y ) ≈ 2 F .
Thus fracture load is:
P * = 45,2
Δσ Yield F 3 R 3 Q 11 Q 22
It can be seen that the most valuable factors are radius R of indenter and tension strength F of the skin, i.e. increasing of radius in 1,5 times fracture load will increase in 1,84 times.
During loading up to skin failure the absorbed energy W can be written as eqs. (4), (11):
W ≈ 217
( σ Yield Δ F 5 R 5) 1 : 2 Q 11 Q 22
It can be noticed that the most valuable factors for absorbing energy without skin fracture are the strength of skin F and the radius of indenter R . Increasing radius in 10% we can increase energy upon 27%!
2. Experimental works
In this paper there are two sandwich panels, consisted of different laminated skins: cross-ply of unidirectional CFRP and AFRP (aramid fabric reinforced plastic) and core honeycomb materials (impregnated paper like Nomex and one layer of glass fabric reinforced plastic). Length of cell side is 2,5 mm. All mechanical behaviours were obtained from the tests on INSTRON 5882 (static testing machine) with using precise contact extensometer and software Bluehill2.
Skins were made with symmetrical lay-ups [0/90]s and [45/–45]s and carefully cut out from panel and tested by tension. Transverse uniform compression was provided for honeycomb cores without special preparation, i.e. with skins. All needed behaviours are shown in table 1: strength of skin F , modulus of elasticity E (or Q ), skin thickness Δ and compression 'yield' stress of the core σ Yield .
Table 1
Mechanical data of all tested materials
|
Sample |
Skin |
Core |
||
|
1 |
CFRP, [45/-45] |
2s |
Impregnated paper honeycomb |
|
|
F , GPa |
E , GPa |
Δ, mm |
σ Yield , MPa |
|
|
0,90 |
50 |
1,04 |
0,85 |
|
|
2 |
Aramid FRP, [0/90] (7 fabric) |
GFRP, one layer fabric honeycomb |
||
|
F , GPa |
E , GPa |
Δ, mm |
σ Yield , MPa |
|
|
1,20 |
25 |
0,98 |
1,65 |
|
Transverse uniform compression (stress-strain curves) of impregnated paper (1) and GFRP fabric (2) honeycomb cores are shown on fig. 4.
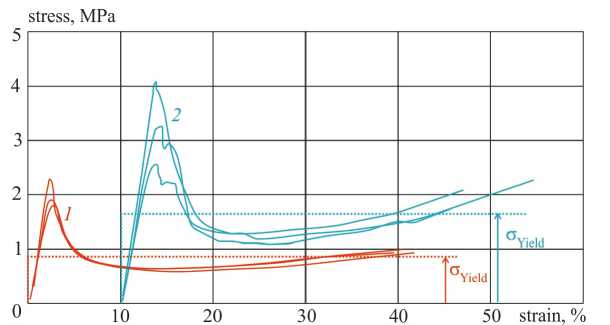
Fig. 4. Stress-strain curves under uniform compression of two different cores
Here up to 40% deformation 'yield' stresses of cores are 0,85 MPa for case (1) and 1,65 MPa for case (2). This is average stress for rigid-perfectly-plastic material.
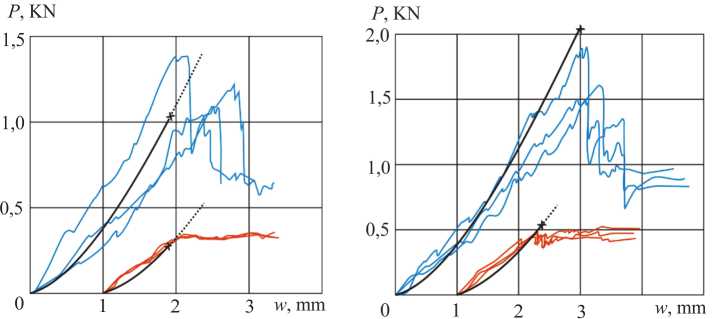
For indentation test there were used steel balls with radius 5–30 mm, speed of loading was 2 mm/min. The curves ‘load ( P ) vs ball displacement ( w )’ were displayed on the computer screen and measured values were written in *.csv file for rebuilding in MS Excel (fig. 5).
Local static indentation curves are shown on fig. 5. Black solid lines on fig. 5 – current theory (eq. 4) small cross – theoretical estimation of skin failure load (eq. 11).
a b
Fig. 5. Local indentation curves: a – R = 5 mm; b – R = 7,9 mm. Sample 1 (CFRP skin) – red lines, sample 2 (AFRP skin) – blue lines
To compare experimental and theoretical absorbed energy up to skin failure, see table 2.
Table 2
Absorbed energy
|
Sample # |
Indenter radius, mm |
Experimental energy, Joules |
Theoretical energy, Joules |
Error, % |
|
1 |
5 |
0,12±0,02 |
0,074 |
–38,3 |
|
7,9 |
0,305±0,02 |
0,232 |
–23,9 |
|
|
2 |
5 |
1,05±0,15 |
0,821 |
–21,8 |
|
7,9 |
2,42±0,14 |
2,58 |
+6,6 |
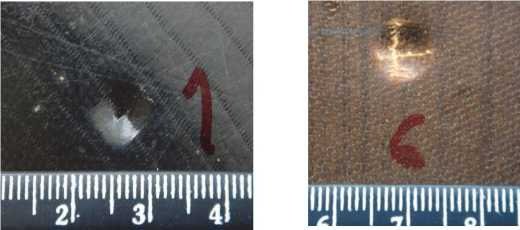
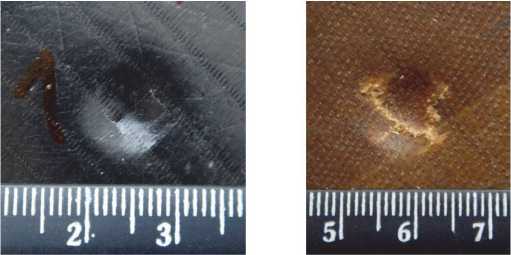
Fig. 6 illustrates the fact that the crack in the skin locates only under indenter and the residual cavity carries out the crack with length equal size of contact region ( a , b ) (eqs. 5, 6). Indenter R = 30 mm couldn't brake skins.
a
b
Fig. 6. Broken skin after indentation: a – R = 5 mm; b – R = 7,9 mm
3. Discussion
The theory developed in this work has a good agreement with experiment on local indentation by spherical indenters excepting initial part of indentation especially for small indenter radius and CFRP skin. It is true be- cause, at first, skin has bending stiffness, it is not pure membrane, secondly, initial part of compressive diagram of core has another form – not perfectly plastic. Moreover, honeycomb core, in contrast with foam core, is inhomogeneous media, point of loading may be located inside of honey cell or on the honey wall node. That is the reason to have different initial part of indentation curve. But in general, for absorbed energy up to skin failure, the theory is good enough for engineering applications because it gives the lowest bound of absorbed energy. Here will be an additional safety factor.
To predict residual in-plane strength of sandwich panel real cavity should be substituted by hole, not crack, because cracked skin surface is curved by indenter and its rigidity is near zero.
Conclusion
The simplification of the shape of deformed thin orthotropic skin of sandwich panel under local loading gave the ability to derive quite simple formulas to estimate contact behaviours and strength of panel even for large indentation. These formulas could be useful as 'first iteration' for structural design. Obviously, current approach will work for sandwich panel based on foam core too. However, sandwich panels with thick skins are not a good object for this theory.
This work was carried out in South Ural State University (National Research University) with a financial support of Russian Science Foundation (project № 14-19-00327).


