Численные методы анализа многокомпонентных газовых смесей с помощью инфракрасной лазерной спектроскопии
Автор: Голяк Игорь Семенович, Карева Елизавета Романовна, Фуфурин Игорь Леонидович, Анфимов Дмитрий Романович, Щербакова Анастасия Викторовна, Небритова Ольга Александровна, Демкин Павел Павлович, Морозов Андрей Николаевич
Журнал: Компьютерная оптика @computer-optics
Рубрика: Численные методы и анализ данных
Статья в выпуске: 4 т.46, 2022 года.
Бесплатный доступ
В настоящей работе рассматривается применение машинного и глубокого обучения в спектральном анализе многокомпонентных газовых смесей. Экспериментальная установка состоит из квантово-каскадного лазера с диапазоном перестройки 5,3 - 12,8 мкм пиковой мощностью до 150 мВт и астигматической газовой ячейки Эрриотта с длиной оптического пути до 76 м. В качестве тестовых веществ использовались ацетон, этанол, метанол и их смеси. Для обнаружения и кластеризации веществ, в том числе молекул-биомаркеров, предложены методы машинного обучения, такие как стохастическое вложение соседей с t-распределением, метод главных компонент и методы классификации, такие как случайный лес, градиентный бустинг и логистическая регрессия. Для спектрального анализа газовых смесей использована неглубокая свёрточная нейронная сеть на базе TensorFlow (Google) и Keras. В качестве обучающей выборки использовались модельные спектры веществ, а в качестве тестовой - модельные и экспериментальные. Показано, что нейронные сети, обученные на модельных спектрах (база данных NIST), могут распознавать вещества в экспериментальных газовых смесях. Предложено использовать нейронные сети для идентификации газовых смесей как единого целого. На экспериментальной установке зарегистрированы следующие минимальные концентрации: 80 ppb для ацетона и 100 - 120 ppb для этанола и метанола. Показана возможность применения предложенных методов для анализа спектров выдыхаемого человеком воздуха.
Газовый анализ, спектральный анализ, биофотоника, инфракрасная спектроскопия, квантово-каскадный лазер, биомаркер, машинное обучение, глубокое обучение
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/140295017
IDR: 140295017 | DOI: 10.18287/2412-6179-CO-1058
Текст научной статьи Численные методы анализа многокомпонентных газовых смесей с помощью инфракрасной лазерной спектроскопии
Спектральный анализ многокомпонентных газовых смесей является нетривиальной задачей из-за существенного пересечения спектральных линий веществ, а также различия на несколько порядков в интенсивности спектральных линий. Актуальной является разработка численных методов решения обратной задачи спектроскопии.
Известно, что выдыхаемый человеком воздух содержит более 3000 соединений [1], в т. ч. летучие неорганические [2] и органические соединения [3]. Существует связь между состоянием человеческого организма и химическим составом выдыхаемого воздуха [1, 2]. Определение состава выдыхаемого воздуха может дать существенную информацию о состоянии здоровья человека и исследовать взаимосвязи между различными физиологическими и биохимическими процессами в организме.
Количественный анализ для обнаружения количеств следовых газов на основе газовой хроматографии и масс-спектрометрии остается «золотым стандартом» идентификации летучих органических соединений (ЛOC) в газовых смесях. Сочетание этих методов позволяет быстро идентифицировать ЛOC с высокой селективностью и чувствительностью вплоть до уровней ppt [6]. Однако эти методы не подходят для измерений в реальном времени. Требование точной калибровки хроматографической колонки, ручные процедуры отбора проб [7] и пробоподготовки являются дополнительными ограничениями.
Разработка новых лазерных источников среднего инфракрасного диапазона, таких как квантовые каскадные лазеры (ККЛ) и межзонные каскадные лазеры, привела к заметному прогрессу в лазерной абсорбционной спектроскопии, что дает большие надежды на развитие метода в биомедицинских приложениях. Это обусловлено высокой селективностью метода лазерной инфракрасной спектроскопии относительно молекул-биомаркеров в среднем инфракрасном диапазоне, а также небольшим размером устройства, которое снижает стоимость «одного измерения» [8, 9].
Концентрации ЛОС обычно измеряются в диапазоне от ppm до ppb, и, следовательно, для обнаружения необходимо использовать наиболее чувствительные методы измерения поглощения. Чувствительность спектроскопических методов ограничена длиной оптического пути. В этом случае используются методы, позволяющие увеличить длину оптического пути до десятков или сотен метров, тем самым увеличивая минимальную чувствительность на уровнях ppm-ppb [10].
Компания Aerodyne Research, Inc. (США) начала промышленное производство компактного газоанализатора на основе ККЛ среднего инфракрасного диапазона для регистрации следовых количеств CH 4 , N 2 O, NO, NO 2 , CO, CO 2 , формальдегида, муравьиной кислоты, этилена, ацетилена, аммиака и т. д. (Mini Monitor [11]). Газоанализатор позволяет измерять концентрации CO и NO в режиме реального времени и со значительно более высокой чувствительностью, чем предлагаемые на рынке устройства, использующие диодные лазеры ближнего ИК-диапазона [12, 13].
Для решения обратной задачи спектроскопии, как правило, используются статистические подходы, основанные на корреляции Пирсона [14– 16] или методе наименьших квадратов [17], что позволяет найти наилучшие совпадения между экспериментальным спектром и эталонным спектром из базы данных. Обратная задача является некорректно поставленной, и описанные методы решения не дают универсального подхода для решения в случае большого числа компонентов.
Альтернативным подходом является анализ спектра смеси как единого целого (паттерна) [18] . В этом случае необходимо применение методов классификации, среди которых активное развитие получили методы машинного обучения.
Как правило, подходы машинного обучения для классификации используют комбинацию методов (LDA, Linear Discriminant Analysis) и (PCA, Principal Component Analysis). В работе [19] определялись и оптимизировались технические характеристики и диагностическая точность анализа выдыхаемого воздуха, связанного с рутинной спирометрией. Анализ спектров выдыхаемого воздуха включал обработку сигналов, коррекцию окружающей среды на основе альвеолярных градиентов и статистику на основе PCA с последующим дискриминантным анализом.
В дополнение к методам кластеризации используются также методы для классификации веществ. В этой связи следует упомянуть методы логистической регрессии, градиентного бустинга и случайного леса.
В работе [20] была исследована возможность анализа конденсата выдыхаемого воздуха с целью получения биомаркеров для ранней диагностики рака легких. Пробы были собраны у 192 человек. Авторы использовали алгоритм случайного леса для создания надежной модели с использованием данных о белках для диагностики пациентов с раком легких, где полученная площадь под кривой ROC указывала на хорошую классификацию (82%).
В работе [21] исследователи реализовали 11 алгоритмов классификации и их вариации, включая логистическую регрессию, k-ближайших соседей, метод опорных векторов, дерево решений, случайный лес, метод градиентного бустинга и наивный Байес, при обнаружении рака молочной железы на общедоступном наборе данных рака молочной железы Coimbra. Показано, что градиентный бустинг как алгоритм машинного обучения представляет собой лучший классификатор прогноза рака молочной железы с точностью 74,14 %.
Для визуализации данных используется метод стохастического вложения соседей с t-распределением (t-SNE, t-Distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding). В работе [22] сообщается об использовании инфракрасной термографии для надежного мониторинга чистоты дыхания бесконтактным и неинвазивным способом. Полученные параметры поступают в классификаторы k-NN и SVMs, которые определяют, имеют ли добровольцы аномальное или нормальное дыхание. Паттерн между точками данных, подаваемыми в классификаторы, просматривается с помощью алгоритма t-SNE. Графики t-SNE показали видимое разделение между точками данных, принадлежащих к разным классам.
Глубокое обучение – одна из самых передовых областей исследований в последние годы, ориентированная на изучение функций и построение моделей прогноза непосредственно из наборов данных. Оно дало отличные результаты во многих областях химии, биологии и спектроскопии, включая данные ИК- и рамановской спектроскопии, метаболомику и т.д. Эти приложения демонстрируют преимущества методов глубокого обучения в извлечении сигналов, изучении признаков и моделировании сложных взаимосвязей.
В работе [23] для повышения точности классификации происхождения табака с помощью метода спектроскопии в ближнем инфракрасном диапазоне (NIRS) использовался алгоритм, основанный на мультимодальных сверточных нейронных сетях (CNN, Convolutional Neutral Network), использующий преимущества сильной способности нейросети к извлечению признаков.
В статье [24] в качестве сетей глубокого обучения использовались CNN, полностью свёрточная сеть (FCN, Fully Convolutional Network) и сеть анализа главных компонентов для определения их способности распознавать наркотики в моче человека и изме- рять пиримифос-метил в экстракте пшеницы в двух входных формах одномерного вектора или двумерной матрицы. Наилучший результат распознавания лекарственных препаратов в моче с точностью 98,05 % в наборе предсказаний был получен с использованием CNN со спектрами комбинационного рассеяния в качестве входных данных в матричном виде. Оптимальное количественное определение пиримифос-метила было получено с использованием FCN со спектрами в матричном виде с коэффициентом обнаружения 0,9997 и среднеквадратичной ошибкой 0,1574 в наборе предсказаний.
В работе [25] применяют нейронную сеть с градиентным бустингом (GrowNet). Исследование проводится с целью изучения пределов нейронных сетей как слабых обучающихся в парадигме бустинга и анализа влияния каждого компонента GrowNet на производительность и сходимость модели. Авторы показывают, что предложенная модель обеспечивает лучшую производительность в регрессии, классификации и обучении ранжированию на нескольких наборах данных по сравнению с современными методами бустинга.
В наших предыдущих исследованиях [26–28] рассмотрены модели выдыхаемого воздуха с точки зрения основных соединений, где определены точность восстановления соединений с использованием метода байесовой оценки; возможность кластеризации спектров с различными отношениями сигнал / шум (SNR, Signal-to-noise Ratio) методами линейного дискриминантного анализа LDA и анализа главных компонент PCA; возможность использования сверточных нейронных сетей для анализа чистых веществ с различным отношением сигнал / шум.
В настоящей работе предложены методы анализа спектров смесей как единого целого (паттернов) с целью их классификации, что может найти применение для биомедицинских приложений. Мы использовали сочетание методов машинного обучения и методов классификации (случайный лес, градиентный бу-стинг, логистическая регрессия). Мы используем неглубокую CNN на основе TensorFlow (Google) и Keras для идентификации биомаркеров в газовых смесях. Модельные ИК-спектры, созданные на основе базы данных NIST, используются для обучения, а в качестве тестовых наборов – модельные и экспериментальные спектры. Процесс обучения на модельных спектрах позволяет существенно сократить время разработки программного обеспечения газоанализаторов.
Экспериментальная установка
Экспериментальная установка основана на методе инфракрасной лазерной спектроскопии и предназначена для высокочувствительного спектрального анализа многокомпонентных газовых смесей, чистых веществ и выдыхаемого человеком воздуха. Принципиальная схема установки представлена на рис. 1.
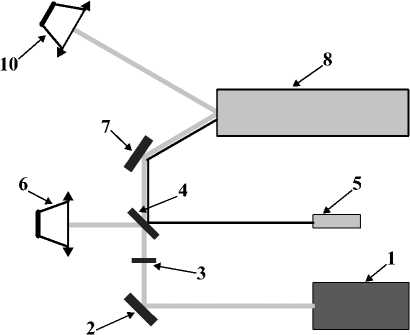
Рис. 1. Схема экспериментальной установки: 1 – ККЛ; 2 – плоское зеркало; 3 – фокусирующая линза; 4 – светоделитель 95/5; 5 – видимый лазер; 6 – референтный фотоприемник; 7 – плоское зеркало; 8 – многоходовая кювета; 9 – плоское зеркало; 10 – сигнальный фотоприемник
Экспериментальная установка состоит из инфракрасного квантово-каскадного лазера и кадмий-ртуть-теллурового фотоприемника, охлаждаемого каскадом ячеек Пельтье. Квантово-каскадный лазер (LaserTune, Block Engineering) излучает в импульсном режиме с пиковой мощностью до 150 мВт, длительностью импульса около 50 нс и частотой повторения около 1 МГц. Излучение происходит в спектральном диапазоне 5,3– 12,8 мкм с шагом перестройки 2 см –1. Размер лазерного луча в поперечном сечении составляет около 2×4 мм2. Расходимость не более 5 мрад, нестабильность мощности около 5 %.
Фотоприемник типа PVMI-4TE (Vigo, Польша) обладает обнаружительной способностью D∗∼6 –8×109 см*Гц1/2/Вт и временным разрешением не менее 4 нс.
ККЛ (рис. 1, поз. 1) излучает в ИК-диапазоне, луч попадает на зеркало (рис. 1, поз. 2), после чего проходит через фокусирующую линзу (рис. 1, поз. 3). Далее луч проходит через светоделитель (рис. 1, поз. 4), где отраженный луч попадает в опорный фотоприемник (рис. 1, поз. 6), а второй луч падает на зеркало (рис. 1, поз. 7) и, отразившись от него, попадает в кювету (рис. 1, поз. 8) под углом 3°. Луч выходит из кюветы под углом 6° относительно входного луча в той же плоскости и попадает на сигнальный фотоприемник (рис. 1, поз. 9). Для юстировки установки используется лазерная указка (рис. 1, поз. 5).
Для проведения экспериментов были использованы три схемы пробоподготовки. Первая схема (рис. 2, Путь Б) предназначена для получения спектров чистых веществ и измерения их минимальных концентраций. Схема состоит из пробы (рис. 2, поз. 2), из которой подается вещество на регулятор расхода газа 2 (РРГ, GE50A (Bronkhorst, Нидерланды)) (рис. 2, поз. 3). Затем вещество с заданной скоростью попадает в кювету (рис. 2, поз. 5). Вся система предвари- тельно вакуумируется с помощью насоса MVP 015-2 DC (Vacuumbrand GMBH and CO KG, Германия) (рис. 2, поз. 6). Давление в кювете отслеживается по вакуумметру (рис. 2, поз. 7), в том числе в системе имеется выход на атмосферу (рис. 2, поз. 8).
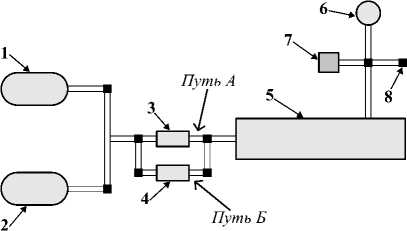
Рис. 2. Схема модуля для чистых веществ и многокомпонентных смесей: 1 – баллон с азотом;
2 – резервуар с тестовым веществом; 3,4 – регуляторы расхода газа; 5 – многоходовая газовая кювета Эрриота;
6 – насос; 7 – вакуумметр; 8 – выход на атмосферу
Вторая схема установки для получения спектров многокомпонентных газовых смесей (рис. 2, Путь А) включает в себя две пробы с веществами (рис. 2, поз. 2), из которых отдельно на РРГ1 (FC-201CV) (рис. 3, поз. 3) подаются вещества. Дальнейший эксперимент проходит аналогично описанной ранее первой схеме для чистых веществ.
Наконец, третья схема (рис. 3) предназначена для получения спектров выдыхаемого человеком воздуха. Для получения корректного спектра из пробы выдыхаемого воздуха (рис. 3, поз. 2) необходимо подать поток продувочного газа (рис. 3, поз. 1) на нафионовый осушитель серии MD (Perma Pure LLC, США) (рис. 3, поз. 3) через РРГ2 (рис. 3, поз. 5) с отношением пробы к продувочному газу, равным 1:2. Для этого на РРГ1 (рис. 3, поз. 1) и на РРГ2 выставляется скорость потока, соответствующая отношению объемных долей пробы к азоту. Затем осушенная проба попадает в кювету (рис. 3, поз. 6) и снимается спектр. Данная схема также включает в себя вакуумный насос, вакуумметр и выход на атмосферу (рис. 3, поз. 7, 8, 9 соответственно).
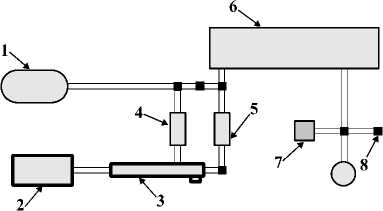
Рис. 3. Схема модуля для выдыхаемого воздуха:
1 – баллон с азотом; 2 – тедларовый пакет;
3 – нафионовый осушитель; 4,5 – регуляторы расхода газа;
6 – многоходовая газовая кювета Эрриота; 7 – насос;
8 – вакуумметр; 9 – выход на атмосферу
Для сбора и хранения пробы использовались тед-ларовые пакеты.
Эксперименты показали чувствительность разработанной установки на уровне 80 ppb по ацетону и 100–120 ppb по этанолу и метанолу.
Численные методы анализа экспериментальных данных
В настоящей работе используются следующие методы машинного обучения: метод главных компонент и стохастическое вложение соседей с t-распределением. Следующие алгоритмы применялись для оценки прогностической эффективности классификации: градиентный бустинг, случайный лес и логистическая регрессия.
Логистическая регрессия применяется для прогнозирования вероятности возникновения события на основе значений набора функций. Для этого вводится так называемая зависимая переменная y, которая принимает только одно из двух значений и набор независимых переменных – вещественных x1, x2,…, xn, на основании значений которых требуется вычислить вероятность принятия определенного значения зависимой переменной. Все регрессионные модели могут быть представлены как у = F(X1,x2,...,Xn), P = ———, 1 + e - y где P – вероятность того, что интересующее событие произойдет, y – стандартное уравнение регрессии.
Случайный лес – это непараметрический многомерный ансамблевый метод, введенный Breiman, 2001 [29]. Алгоритм случайного леса создает деревья решений для выборок данных, а затем получает прогноз по каждой из них и, наконец, выбирает лучшее решение посредством голосования. Это метод ансамбля, который лучше, чем единое дерево решений, потому что он уменьшает переобучение путем усреднения результата.
Классификатор градиентного бустинга – это агрегированный алгоритм начальной загрузки, основанный на нескольких деревьях решений. Функция дифференцируемых потерь минимизируется за счет оптимизации весов моделей и обучающих данных. В задаче оценки функции или «прогнозирующего обучения» имеется система, состоящая из случайной «выходной» или «ответной» переменной y и набора случайных «входных» или «объясняющих» переменных x = { x 1 ,…, x n }. Используя «обучающую» выборку { у , , x , •} N известных значений ( y , x ), целью является получение оценки или приближения F ˆ ( x ) к функции F *( x ), отображающей x в y , которая минимизирует ожидаемое значение некоторой заданной функции потерь L ( y , F ( x )) по совместному распределению всех ( y , x ) значений
F* = argmin E y_ x L(y,F ( x )) = argmin E x [ Ey ( L ( y , F ( x ))) | x ] .
FF
В качестве метода глубокого обучения применяется неглубокая свёрточная нейронная сеть (см. рис. 4).
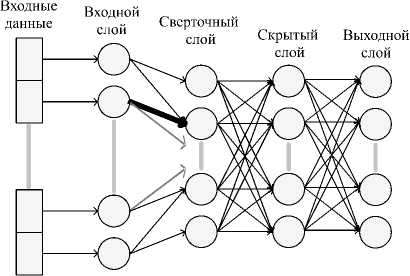
Рис. 4. Принципиальная схема неглубокой нейронной сети
Архитектура сети включает в себя входной, сверточный, скрытый полносвязный слой и полносвязный выходной слой. Количество слоев выходного слоя соответствует количеству определяемых классов. В качестве функции активации применяется функция ReLU для сверточного и скрытого полносвязного слоя, для выходного слоя – многомерная логистическая функция активации (Softmax). Для обучения нейронной сети применяется метод стохастического градиентного спуска. Модель нейронной сети построена с помощью библиотеки машинного обучения TensorFlow и библиотеки глубокого обучения Keras.
Результаты и обсуждения
Цель работы заключается в определении оптимального метода для анализа многокомпонентных газовых смесей. Для достижения цели были поставлены следующие задачи:
-
1. Подготовка модельной и экспериментальной выборки смесей для проведения эксперимента.
-
2. Применение методов машинного и глубокого обучения к подготовленным данным.
-
3. Сравнение эффективности полученных результатов.
-
4. Апробация оптимального метода идентификации на реальных спектрах выдыхаемого человеком воздуха.
Тренировочные, валидационные и тестовые выборки
Для создания модельных спектров из базы NIST [30] были взяты 5 спектров чистых веществ: ацетон, ацетальдегид, этанол, этилен и метанол. На рис. 5 приведены модельный и экспериментальный спектры этанола. Коэффициент корреляции Пирсона составляет значение 0,77.
Оптические плотности компонентов в смеси выбираются случайным образом от 10% до 70% от самой глубокой линии с использованием равномерного распределения. Так же ко всем модельным спектрам добавлен белый шум. Отношение сигнал / шум изме- няется от 6 до 14 с шагом 1 от глубины самой слабой линии в рассматриваемом спектральном диапазоне.
В результате чего получилась выборка, состоящая из 26 классов смесей (все комбинации из 5 веществ, описанных выше) и включающая в себя 11700 спектров. Данная выборка была разбита на тренировочную и валидационную в соотношении 50% на 50%.
Модельный и экспериментальный спектры этанола
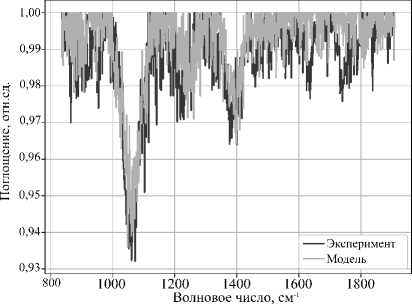
Рис. 5. Экспериментальный и модельный спектр этанола
Тестовая модельная выборка состоит из 200 модельных спектров смесей с различными отношениями сигнал / шум и глубинами оптических линий.
Тестовая экспериментальная выборка состоит из 829 спектров смесей и сформирована из 3 классов: ацетон и метанол, этанол и метанол, этанол и ацетон.
Созданные выборки применялись для методов машинного и глубокого обучения.
Методы машинного обучения
Разработанные численные методы предназначены для классификации газовых смесей и выявления биомаркеров. Данные преобразовывались таким образом, чтобы их распределение имело среднее значение 0 и стандартное отклонение 1. Число главных компонент для спектров смеси равно 2.
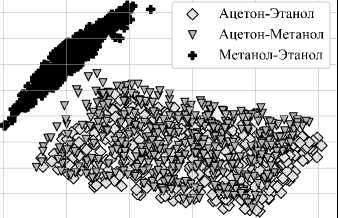
На рис. 6 а показан результат применения метода PCA, а на рис. 6 б – результат применения метода t-SNE для спектров смесей. Использовался метод PCA с 6 компонентами, и получен коэффициент дисперсии 0,95. На рис. 6 а показаны проекции данных на 2-мерное подпространство для удобства визуализации. Для читаемости отображение классов на рис. 6 ограничено 3 смесями.
Точности классификаторов, использованных для идентификации газовых смесей, приведены в табл. 1. Классификатор градиентного бустинга в совокупности с методами машинного обучения дает преимущественно более высокий результат.
Методы глубокого обучения
Свёрточная нейронная сеть – это один из видов нейронных сетей с использованием свёрточных слоев. Операция свертки является взвешенным суммированием в небольшом окне, которое называется свёрточным ядром. По мере того, как свёрточное ядро скользит по входному вектору, выходные векторы локальных признаков формируют так называемую карту признаков.
наборе смесей составила 99%. Данный результат существенно не отличается от результатов использования метода градиетного бустинга (табл. 1).
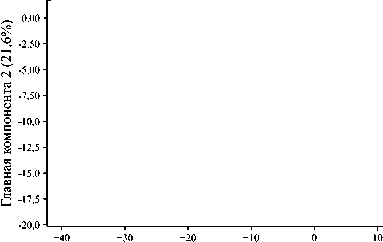
Главная компонента 1 (52,7%)
Метод РСА
а)
б)
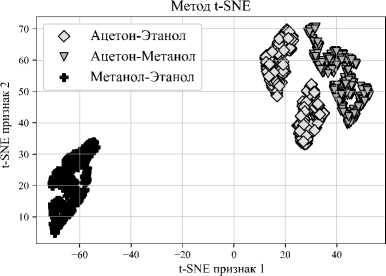
Рис. 6. Результаты кластеризации смесей веществ по методу PCA (а) и по методу t-SNE (б)
Табл. 1. Точность распознавания примененных классификаторов для модельных смесей веществ
|
Классификаторы |
Смеси |
|
|
PCA |
t-SNE |
|
|
Градиентный бустинг |
99 % |
74 % |
|
Случайный лес |
98 % |
70 % |
|
Логистическая регрессия |
97 % |
59 % |
Табл. 2. Зависимость точности обучения от количества эпох на тренировочной выборке
|
Число эпох |
Точность |
|
|
Медиана |
Среднее квадратичное отклонение |
|
|
200 |
0,512 |
0,480 |
|
300 |
0,982 |
0,018 |
|
400 |
0,993 |
0,001 |
|
500 |
0,993 |
0,003 |
Далее мы обучили созданную нейронную сеть на модельных спектрах смесей, а распознавание проводилось на 3 классах экспериментальных смесей: ацетон и метанол, этанол и метанол, этанол и ацетон. Точность распознавания на 829 тестовых смесях составила не более 89%. Для методов машинного обучения описанный эксперимент не дает положительный результат (точности каждого из них не превысили 5%).
Также был поставлен численный эксперимент, когда нейронная сеть обучалась и тестировалась исключительно на 3 классах экспериментальных смесей. Размеры выборок: обучающая – 649, тестовая – 170 спектров. Точность распознавания в данном случае составила 88 %.
Для определения оптимальных параметров нейронной сети была проведена оптимизация гиперпараметров сети с применением Random Grid Search Cross-Validation framework (RGS-CV) [31]. Для применяемой сети были получены следующие параметры: размер сета равен 10; количество эпох равно 400 (табл. 2); количество ядер свёрточного слоя равно 48; размер ядра свёрточного слоя равен 20; шаг свертки равен 1; параметр регуляризации равен 10 –10, момент для стохастического градиентного спуска равен 0,9; скорость обучения равна 10 –3. Характеристики выходного слоя нейросети для распознавания газовых смесей: количество классов равно 26; входная размерность массива данных равна 961.
Результаты обучения представлены на рис. 7. Точность распознавания на тестовом модельном
б)
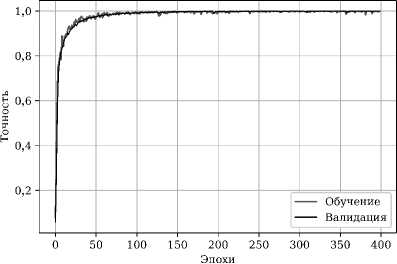
Рис. 7. Обучение нейронной сети на смесях: (а) функция потерь обучения на модельной выборке vs функция потерь на валидационной; (б) точность обучения на модельной выборке vs точность валидации
Таким образом, сверточная нейронная сеть, обученная как на модельных, так и на экспериментальных многокомпонентных смесях, способна разделять спектры по классам с довольно высокой точностью, используя спектр как единое целое (паттерн). Результат на модельных данных указывает на то, что нейронная сеть действительно работает по спектральным линиям, выделяя их как признаки.
Из полученных результатов можно сделать вывод, что полученная нейронная сеть может быть использована для анализа реальных спектров выдыхаемого человеком воздуха.
Анализ инфракрасных спектров выдыхаемого человеком воздуха
В эксперименте приняли участие четыре волонтёра, среди которых – две женщины и два мужчины в возрасте от 23 до 26 лет. На момент проведения лабораторных экспериментов у испытуемых отсутствовали хронические заболевания. Пробы выдыхаемого воздуха брались утром натощак и вечером на протяжении нескольких дней. Всего зарегистрировано 260 спектров. Матрица кросс-корреляции представлена на рис. 8.
Из представленной на рис. 8 матрицы кросскорреляций видно, что корреляция Пирсона не позволяет классифицировать испытуемых по спектрам выдыхаемого воздуха. Нейронная сети, обученная на экспериментальных спектрах, позволяет с точностью 99 % классифицировать испытуемых по инфракрасным спектрам выдыхаемого воздуха.
Полученный результат демонстрирует принципиальную возможность разработанных методов для кластеризации спектров больных и здоровых людей, что может найти применение в медицинской диагностике. Однако подробное рассмотрение задачи анализа выдыхаемого человеком воздуха выходит за рамки настоящей работы.
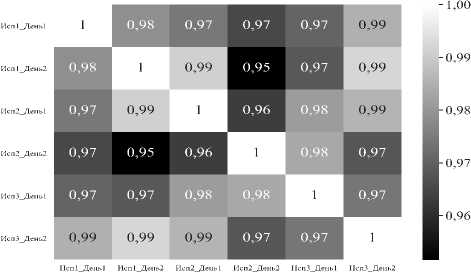
Рис. 8. Матрица кросс-корреляции
Заключение
В работе проведен анализ эффективности распознавания многокомпонентных газовых смесей методами машинного и глубокого обучения.
Установлено, что наиболее эффективным методом классификации многокомпонентных газовых смесей является сверточная нейронная сеть. Показано, что применение нейронной сети позволило классифицировать инфракрасные спектры выдыхаемого человеком воздуха с точностью 99%. Сверточные нейронные сети представляют собой эффективный метод обработки и анализа спектральных данных в биомедицине, где целесообразно исследовать весь спектр целиком без необходимости анализа отдельных компонент. Более того, нейронная сеть, обученная на модельных данных, с точностью не хуже 89 % распознает экспериментальные спектры, что позволяет существенно сократить время и затраты на сбор данных для обучения нейронной сети.
Работа выполнена в рамках реализации программы стратегического академического лидерства «Приоритет-2030», утвержденных постановлением Правительства Российской Федерации от 13 мая 2021 г. № 729.
Список литературы Численные методы анализа многокомпонентных газовых смесей с помощью инфракрасной лазерной спектроскопии
- Selvaraj R, Vasa NJ, Nagendra SMS, Mizaikoff B. Advances in mid-infrared spectroscopy-based sensing techniques for exhaled breath diagnostics. Molecules 2020; 25: 2227. DOI: 10.3390/molecules25092227.
- Vaks VL, Domracheva EG, Sobakinskaya EA, Chernyaeva MB. Exhaled breath analysis: physical methods, instruments, and medical diagnostics. Physics-Uspekhi 2014; 57: 684-701. DOI: 10.3367/ufne.0184.201407d.0739.
- van Mastrigt E, Reyes-Reyes A, Brand K, et al. Exhaled breath profiling using broadband quantum cascade laser-based spectroscopy in healthy children and children with asthma and cystic fibrosis. J Breath Res 2016; 10: 026003. DOI: 10.1088/1752-7155/10/2/026003.
- Pauling L, Robinson AB, Teranishi R, Cary P. Quantitative analysis of urine vapor and breath by gas-liquid partition chromatography. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1971; 68: 23742376. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.68.10.2374.
- Wallace LA, Pellizzari ED, D.Hartwell T, Sparacino CM, Sheldon LS, Zelon H. Personal exposures, indoor-outdoor relationships, and breath levels of toxic air pollutants measured for 355 persons in New Jersey. Atmospheric Environ 1985; 19(10): 1651-1661. DOI: 10.1201/9780367810870-15.
- Matthews DE, Hayes JM. Isotope-ratio-monitoring gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 1978; 50: 1465-1473. DOI: 10.1021/ac50033a022.
- Lu Z, Huang W, Wang L, Xu N. Exhaled nitric oxide in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis 2018; 13: 2695-2705. DOI: 10.2147/COPD.S165780.
- Nadeem F, Mandon J, Khodabakhsh A, Cristescu S, Harren F. Sensitive spectroscopy of acetone using a widely tunable external-cavity quantum cascade laser. Sensors 2018; 18: 2050. DOI: 10.3390/s18072050.
- Xia J, Zhu F, Kolomenskii AA, et al. Sensitive acetone detection with a mid-IR interband cascade laser and wavelength modulation spectroscopy. OSA Continuum 2019; 2: 640. DOI: 10.1364/OSAC.2.000640.
- Heinrich K, Fritsch T, Hering P, Murtz M. Infrared laser-spectroscopic analysis of 14NO and 15NO in human breath. Appl Phys B 2009; 95: 281-286. DOI: 10.1007/s00340-009-3423-1.
- Jimenez R, Herndon S, Shorter JH, Nelson DD, McManus JB, Zahniser MS. Atmospheric trace gas measurements using a dual quantum-cascade laser mid-infrared absorption spectrometer. Proc SPIE 2005; 5738: 318. DOI: 10.1117/12.597130.
- McManus JB, Nelson DD, Herndon SC, et al. Comparison of cw and pulsed operation with a TE-cooled quantum cascade infrared laser for detection of nitric oxide at 1900 cm-1. Appl Phys B 2006; 85: 235-241. DOI: 10.1007/s00340-006-2407-7.
- Wysocki G, McCurdy M, So S, et al. Pulsed quantum-cascade laser-based sensor for trace-gas detection of carbonyl sulfide. Appl Opt 2004; 43(32): 6040-6046. DOI: 10.1364/A0.43.006040.
- Vasil'ev NS, Vintaykin IB, Golyak IgS, Golyak IlS, Kochikov IV, Fufurin IL. Recovery and analysis of raman spectra obtained using a static fourier transform spectrometer. Computer Optics 2017; 41(5): 626-635. DOI: 10.18287/2412-6179-2017-41-5-626-635.
- Kochikov IV, Morozov AN, Svetlichnyi SI, Fufurin IL. Substance recognition in the open atmosphere from a single Fourier transform spectroradiometer interferogram. Opt Spectrosc 2009; 106: 666-671. DOI: 10.1134/S0030400X09050075.
- Li J, Hibbert DB, Fuller S, Vaughn G. A comparative study of point-to-point algorithms for matching spectra. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 2006; 82: 50-58. DOI: 10.1016/j.chemolab.2005.05.015.
- Samsonov DA, Tabalina AS, Fufurin IL. QCL spectroscopy combined with the least squares method for substance analysis. J Phys Conf Ser 2017; 918: 012034. DOI: 10.1088/1742-6596/918/1/012034.
- Skarysz A, et al., Convolutional neural networks for automated targeted analysis of raw gas chromatography-mass spectrometry data. 2018 Int Joint Conf on Neural Networks (IJCNN) 2018: 1-8. DOI: 10.1109/IJCNN.2018.8489539.
- de Vries R, Brinkman P, van der Schee MP, et al. Integration of electronic nose technology with spirometry: validation of a new approach for exhaled breath analysis. J Breath Res 2015; 9: 046001. DOI: 10.1088/1752-7155/9/4/046001.
- Löpez-Sänchez LM, Jurado-Gamez B, Feu-Collado N, et al. Exhaled breath condensate biomarkers for the early diagnosis of lung cancer using proteomics. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2017; 313: L664-L676. DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00119.2017.
- Austria YD, Goh ML, Maria LBSta Jr, Lalata J-A, Goh JE, Vicente H. Comparison of machine learning algorithms in breast cancer prediction using the coimbra dataset. International Journal of Simulation: Systems, Science & Technology 2019 Suppl 2; 20: 23. DOI: 10.5013/ijssst.a.20.s2.23.
- Jagadev P, Giri LI. Non-contact monitoring of human respiration using infrared thermography and machine learning. Infrared Phys Technol 2020; 104: 103117. DOI: 10.1016/j.infrared.2019.103117.
- Zhang L, Ding X, Hou R. Classification modeling method for near-infrared spectroscopy of tobacco based on multimodal convolution neural networks. J Anal Methods Chem 2020; 2020: 9652470. DOI: 10.1155/2020/9652470.
- Weng S, Yuan H, Zhang X, et al. Deep learning networks for the recognition and quantitation of surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Analyst 2020; 145: 4827-4835. DOI: 10.1039/D0AN00492H.
- Badirli S, Liu X, Xing Z, Bhowmik A, Doan K, Keerthi SS. Gradient boosting neural networks: GrowNet. arXiv Preprint 2020. Source: ¿https://arxiv.org/abs/2002.07971n.
- Fufurin IL, Golyak IS, Anfimov DR, et al. Machine learning applications for spectral analysis of human exhaled breath for early diagnosis of diseases. Proc SPIE 2020; 11553: 115531G. DOI: 10.1117/12.2584043.
- Tabalina AS, Anfimov DR, Fufurin IL, Golyak IS. Infrared quantum cascade laser spectroscopy as non-invasive diagnostic tests for human diseases. Proc SPIE 2020; 11359: 113591J. DOI: 10.1117/12.2555042.
- Fufurin IL, Anfimov DR, Kareva ER, et al. Numerical techniques for infrared spectra analysis of organic and inorganic volatile compounds for biomedical applications. Opt Eng 2021; 60(8): 082016. DOI: 10.1117/1.OE.60.8.082016.
- Breiman L. Random forests. Machine Learning 2001; 45: 5-32. DOI: 10.1023/A:1010933404324.
- Linstrom P. NIST Chemistry WebBook, NIST Standard Reference Database Number 69. Source: ahttps://webbook.nist.gov/chemistry/n.
- Bergstra J, Yoshua B. Random search for hyper-parameter optimization. J Mach Learn Res 2012; 13: 281-305.


