Chromatographic Residue Analysis of Profenofos and Carbosulfan in Indian Major Carp, Labeo rohita (Hamilton)
Автор: Nagaraju Bantu
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 3 т.16, 2020 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Fish live in the aquatic column; they are facing challenge for surviving from pollutants, particularly from various chemical fertilizers and pesticides used in or adjacent paddy fields or flood lands. They can be exposed to animals in a number of ways. Hence, an attempt has been made to know the presence of profenofos and carbosulfan residues in different tissues viz., liver, muscle, gill and kidney of Labeo rohita exposed to sublethal and lethal concentrations for 15 days. The results of the present study revealed that, prolonged exposure to sublethal concentrations of profenofos and carbosulfan in Labeo rohita leads to increased accumulation of residue. Thus repeated or continuous exposure to low concentrations of pesticides can lead to high residue concentrations without mortalities. Thus the uptake and persistence of profenofos and carbosulfan depends not only on a number of physical and chemical conditions but also varies according to the biological conditions.
Labeo rohita, Profenofos, Carbosulfan, Chromatographic Residue analysis
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/143173843
IDR: 143173843
Текст научной статьи Chromatographic Residue Analysis of Profenofos and Carbosulfan in Indian Major Carp, Labeo rohita (Hamilton)
Aquatic organisms are affected by the pesticides and pollutants through irrigation drains leaching from agriculture fields into freshwater bodies, even though often the aquatic environment is not the primary site of application of pesticides. Two factors mainly contribute to the concentration of the pesticides in the aquatic ecosystem; persistence of pesticides in the soils and long-range transport of the pesticides in the atmosphere of which soils receive the major part of the globally used pesticides, the process of pesticide residual are transport is eventually to the water bodies and deposit in the soil ultimately constitutes a threat to the aquatic environment (Arjmandi et al., 2010).
The persistent nature of pesticide residues in the environment may pose the problem of chronic toxicity to animals and human being through air, water and foods intake. Many of these pesticides and their metabolites have been implicated in a wide range of adverse effects on environment as well as human beings. Because they can accumulate in aquatic organisms, especially fish, and cause disturbances to the aquatic ecosystem. The accumulation of chemical compounds in fish can also be dangerous for consumers (Gbylik et al ., 2013).
Animals intended for human food may absorb pesticides from residues in their feed, water or during direct/indirect exposure in the course of pest control. The most widely used pesticide extraction techniques from the foods of animal samples was solid-liquid extraction (SLE) and liquid-liquid extraction (LLE). The SLE procedure consists in grinding chopped samples or extracted fats several times at high speed in selected different organic solvents. This technical procedure has been applied to meat and meat products animal fat, offal, eggs and fish for extracting different kinds of pesticides. Similarly, LLE procedure consists in shaking liquid samples several times in selected organic solvents for extracting pesticide residues (LeDoux, 2011).
Fish are used extensively for environmental monitoring because they uptake contaminants directly from water and diet (Kafilzadeh et al., 2012).Fish live in the aquatic column; they are facing challenge for surviving from pollutants, particularly from various chemical fertilizers and pesticides used in or adjacent paddy fields or flood lands. They can be exposed to animals in a number of ways. Hence, an attempt has been made to know the presence of profenofos and carbosulfan residues in different tissues viz., liver, muscle, gill and kidney of Labeo rohita exposed to sublethal and lethal concentrations for 15 days.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Freshwater f ish , Labeo rohita of size 6±7 cm and 6.5±7.5 g weight were brought from a local fishfarm, Nandivelugu, Guntur district of Andhra Pradesh, India and acclimated at 28±20C in the laboratory for 15 days. Such acclimated fish were exposed to sublethal and lethal concentrations (1/10th 96 hr LC 50 i.e.10 µg l-1; 0.12 mg l-1 and 96 hr LC 50 i.e. 100 µg l-1; 1.2 mg l-1) of profenofos and carbosulfan for 15 days.
In the present investigation two kinds of chromatographic methods were employed. They are Column chromatography for clean up and Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC) for the confirmation of pesticide residues, whereby the residue is made free from coextractives or impurities by differential adsorption running through a column containing different lengths of adsorbents and identification of the residue content in gill, liver, kidneys and muscle tissues of the fish L. rohita exposed to profenofos and carbosulfan.
Extraction
After exposure to sub lethal concentration the fish were sacrificed and analysed for residues. The control fish were treated with pure acetone. The residues from the fish tissue of brain, liver, muscle, gill and kidney were extracted by the modified method of Mills and Olney (1977). 1 g of muscle and gill tissue was blended separately with 4 g of anhydrous sodium sulphate (Na 2 SO 4 ) (Pre-extracted in a Soxhlet column with analytical grade hexane); to get a free flowing powder.
This powder was extracted with 5 ml of hexane and acetone in ratio of 2:1 for each gram of powder. Soft tissues like liver, brain and kidney were homogenized in a tissue homogenizer with minimal quantity of all glass triple distilled water. The homogenized tissue was extracted with 2:1 hexane: acetone at a ratio of 5 ml for each gram of tissue. When very small quantity of tissue was available, a minimum of 6 ml of extracting solvent was used. Extraction was carried out for one hour in horizontal shaker bath, at gentle speed to avoid spillage. Clean-up and removal of the co-extractives
After extraction, acetone was washed out and the hexane extract was dried out over Na 2 SO 4 (AR grade). The extract was stored in stoppered glass vials and kept in the refrigerator for further processing.
The hexane extract was concentrated to about 1 ml (when the volume of extract was 4 ml or more) and transferred directly on to a florisil column prepared according to the Pesticide Residue (PR) grade and was heated overnight at 1300C and after cooling, it was deactivated with grades of increasing polarity using hexane and acetone.
ThinLayer Chromatographic analysis (TLC)
The method of Moats (1966) was followed and is as follows: The Silica gel was cleaned with triple distilled water to remove inorganic phosphate and other contaminants. The slurry was prepared and spread on the plates to give 250 thick TLC plates. The plates were dried for one hour and activated at 80oC in hot air oven for 15 minutes, taken out of the oven, cooled and stored.
The concentrated extract and technical pesticide standard were spotted with a sample spotter and micropipettes (5-20 µl) on thin layer chromatographic plates (5x20 cm size). The spotted plates were developed in a TLC chamber until the solvent front reached 10 cm mark from the original point. The plates were removed from the chamber, air dried and exposed to short-wave-length UV light, with intermittent exposure to stream to locate the spots. The exposure to steam improved the resolution of the spots. The appearance of blue spot on the TLC plates was taken as confirmation of the presence of residue in the particular tissue.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Results of the appearance of blue spot on the thin layer chromatography (TLC) plates in different tissue at different time period of exposure was presented in Table 1 and Figure 1-3, residue are in the following order of tissue weight; Gill>Muscle>Kidney>Liver for profenofos and Gill>Kidney>Liver>Muscle for carbosulfan respectively.
After 15days of exposure period the residue spots appeared prominently in brain and liver tissues for profenofos, muscle and brain for carbosulfan pesticides. In other tissues the residue spots were traced very little, in the other tissues, such as gill, muscle and kidney, little amount of residues were traced. Present study, it was observed that the prominence in residue spots increased steadily throughout the investigation period. This may be due continuous bathing of the fish in the toxicant medium. Though the excretion and metabolism processes are continuous, the uptake will lead to the maintenance of residue load.
Hence, the residues were found to appear throughout the study period whereas in terrestrial organisms, the dose will be given intraperitoneally and the residue levels decrease, with the increase in the duration of exposure. This may depend on the metabolism of the animal or degradation of the pesticide. Bradbury and Coats (1986) reported high levels of fenvalerate residues in bile, followed by gill and kidney tissues after a 48 hr exposure in rainbow trout. Mumtaz and Menzer (1986) reported that residues of 14C labelled fenvalerate are highest in fat, followed by skin, liver, heart, kidney, lung and brain in Japanese quail.
Studies with permethrin, cypermethrin and fenvalerate have established that rates of metabolism and elimination in rainbow trout are significantly lower than those reported toxicity of cypermethrin was studied by Miyamoto (1976).
The peaks eluted in tissue samples after 15 days of exposure showed that as the concentration of pesticide applied increased, the residues present also were found to increase. Continuous exposure of fish to the profenofos and carbosulfan resulted in bioaccumulation of the pesticide in the body of the organism and the accumulation was found to be more in gill than other tissues. The variations in the residue analysis are attributed to factors like difference in uptake rate and lipid content of respective animal tissue. The chemical structure, solubility, fish interaction and metabolic pattern are responsible for pesticide uptake. According to Tilak et al. (2004) and Aruna Sao (2008), residues of organophosphate and carbamate insecticides in the fish species and depend on the physiochemical characteristics of water, time of consumption, pH of water and the ambient temperature. These pesticides leave residues in the soil and water for several days after their application, and pose a constant threat to nontarget organisms, especially fish (Magare and Patil, 2000).
The results of present study revealed that prolonged exposure to sublethal concentrations led to increase in the accumulation of residue. This is in agreement with the earlier reports by (Bradbur et al., 1987; Tilak et al ., 2004) the accumulation is a factor responsible for changes in biochemical actions or pathological changes and also disturbance of overall biochemical cyclic reactions which are cumulative causing lethal actions even when the concentrations are sub lethal. According to Bagheri (2007), residues of OPs insecticides in the fish species.
The carbamate pesticides are more resistant to the microbial degradation and have a propensity to concentrate in lipid rich tissues of aquatic species and terrestrial mammals. Persistence of carbosulfan and accumulated effects by bioaccumulation, bioconcentration and biomagnification through food chain. The organophosphorus and carbamate pesticides and other class of pesticides were significantly higher in the gills and liver of the all fish studied than other organs like muscle etc. Such high levels in gills due to the fact that freshwater fish’s gills might be expected to be primary rout for the uptake of water along with chemicals, pollutants; while liver serves as a storage organ for vast different types of nutrients. Gills are in fish, are the prime target for waterborne toxicants and possess a detoxification system, although not as robust as that of liver (Li et al., 2010; Kubrak et al., 2012). Being an indicator of physiological conditions in animals in performing their gas-exchange function, gills are permanently in contact with environmental water and blood, providing path for aquatic pollutants entrance into the blood stream and hence further distribution to all organs (Pandey et al., 2008; Kubrak et al., 2012).
Table 1. A) Pesticide Standard Confirmation and the Tissue Chromatogram
|
Absorbent |
: Silica gel |
|
Solvent |
: Hexane + Acetone (90+10, 75+25 V/ V ) |
|
Front |
: 10 cm |
|
Spray reagents |
: Molybdate antimony tartrate; 2% Ascorbic acid |
|
Time |
: 30 minutes |
|
UV light exposure |
: 10 minutes |
|
Period of Exposure |
: 15 days |
|
Colour of the spot |
: Blue |
B) Rf Values of standard in different solvent systems
|
Solvent System |
Ratio v/v |
100x Rf |
|
|
Hexane +Acetone |
9.1 |
62.5 |
|
|
Hexane + Benzene |
1.1 |
88.4 |
|
|
Hexane + Acetone |
1.1 |
81.6 |
|
|
Benzene + Hexane |
4.6 |
42 |
|
|
Tissue |
100x Rf |
100xRf |
|
|
Brain |
84.9 |
74.2 |
|
|
Gill |
75.2 |
66.9 |
|
|
Liver |
87.6 |
76.3 |
|
|
Kidney |
82.4 |
22.5 |
|
|
Muscle |
86.5 |
54.7 |
|
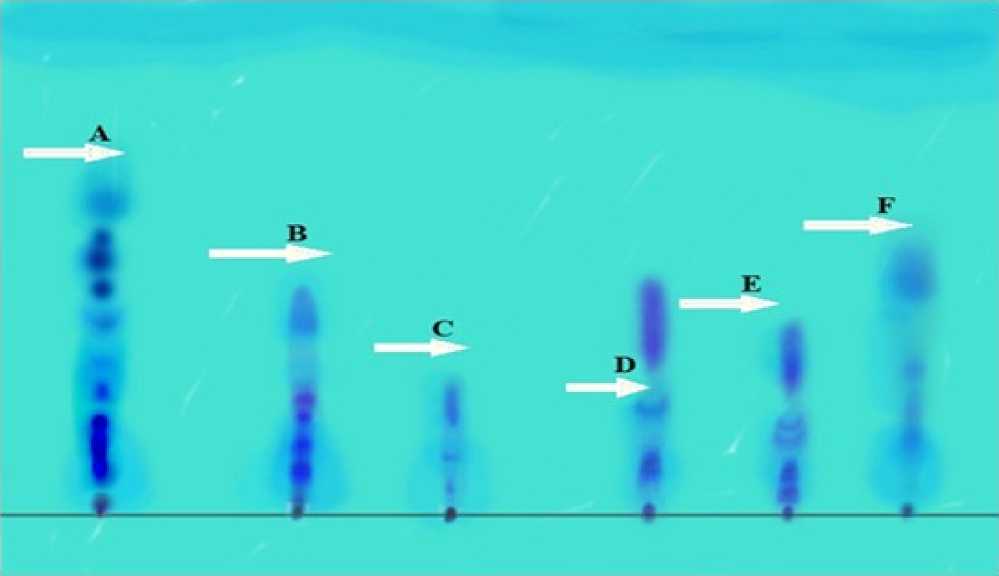
Figure 1: Chromatogram showed comparison of Rf values of profenofos and carbosulfan with standard (A&F), lethal (C&D) and sub lethal (B&E) concentrations of 15 days. The highest value of profenofos pesticide residues was detected in the gill of Labeo rohita , while the smallest value was detected in liver.
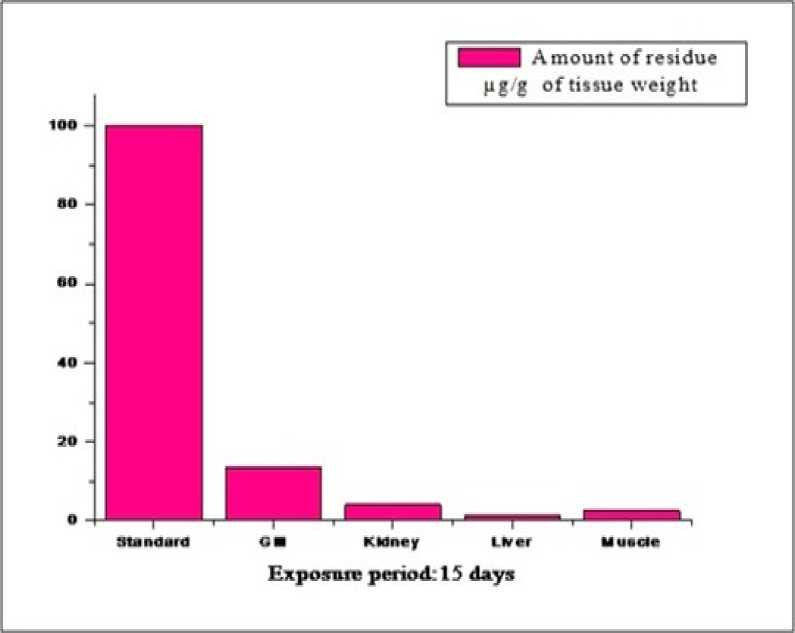
Figure 2: The residual concentrations over the standard, in different tissue of the freshwater fish, Labeo rohita , exposed to sub lethal concentrations of profenofos for 15 days.
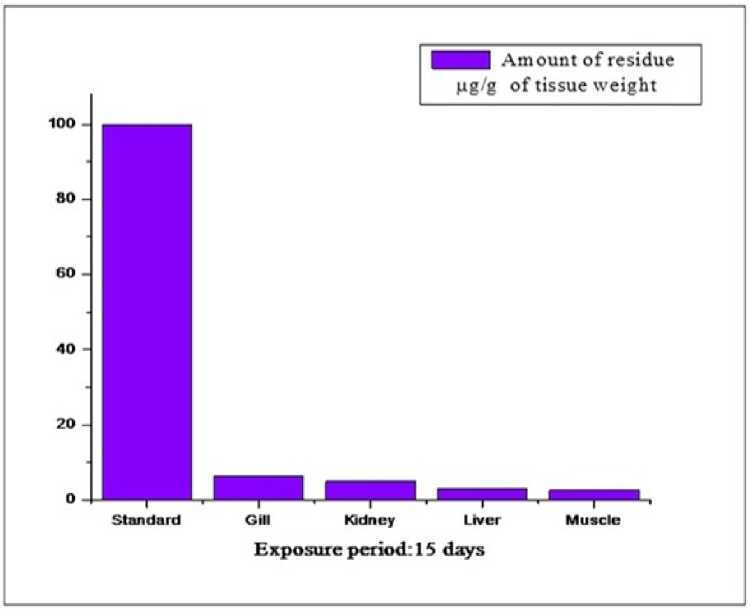
Figure 3: The residual concentrations over the standard, in different tissue of the freshwater fish, L. rohita exposed to sub lethal concentrations of carbosulfan for 15 days.
The correlation of the residue of profenofos and the AChE activity in Oreochromis niloticus and Labeo rohita by (Boran et al., 2007; Pathiratne and Chandrasekera, 2008; Coppage et al ., 1975) also supports the present study. The earlier studies (Tilak et al ., 2004 David, 2009) showed that the residues of chlorpyrifos accumulated more in brain than liver in Catla catla , Labeo rohita and Cirrhinus mrigala. Accumulation of the pesticides in different type of aquatic organisms is the function of their membrane permeability system and enzyme system, because of this fact carbosulfan accumulated in different tissues of the fish L. rohita as observed in the study. This is in corroboration with the reports of Ogunfowokan et al . (2012).
Liver is the main detoxifying tissue containing relatively high levels of detoxifying enzymes. It is also the first organ to face the effect of pesticides being carried through the portal circulation which might have been the cause of the greater accumulation of profenofos and carbosulfan.
CONCLUSION
The results of the present study revealed that, prolonged exposure to sublethal concentrations of profenofos and carbosulfan in Labeo rohita leads to increased accumulation of residue. Thus repeated or continuous exposure to low concentrations of pesticides can lead to high residue concentrations without mortalities. Thus the uptake and persistence of profenofos and carbosulfan depends not only on a number of physical and chemical conditions but also varies according to the biological conditions.
Список литературы Chromatographic Residue Analysis of Profenofos and Carbosulfan in Indian Major Carp, Labeo rohita (Hamilton)
- Arjmandi, R., Tavakol, M., and Shayeghi, M. (2010). Determination of organophosphorus insecticide residues in the rice paddies. International Journal Environmental Science Technology, 7(1): 175-182.
- Aruna Sao, Ajai K Pillai and Gupta, V.K. (2008). Spectrophotometric determination of carbosulfan in environmental samples. Journal of Scientific and Industrial Research, 67: 1088-1091.
- Bagheri, F. (2007). Study of pesticide residues (Diazinon, Azinphosmethyl) in the rivers of Golestan province (GorganRoud and Gharehsou), M. Sc. Thesis, Tehran University of Medical Science. Tehran, Iran.
- Bradbury, S.P., McKim J.M., Coats J.R. (1987). Physiological response of Rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri) to acute fenvalerate intoxication. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol, 27: 275-288.
- Bradbury, S.P., and Coats, J.R (1989). Toxicokinetics and toxicodynamics of pyrethroid insecticides in fish. Environ. Toxicol. Chem, 8: 373-380.
- David, M., Patil, V.K, Chebbi, S.G., Marigoudar, S.R., Chittaragi, J.B., Halappa, R. (2009). Gas-liquid chromatography for fenvalerate residue analysis: in vivo alterations in the acetylcholinesterase activity and acetylcholine in different tissues of the fish, Labeo rohita (Hamilton). Toxicology mechanisms and methods, 19(6-7), 410-415.
- Kafilzadeh F., Shiva A.H., Malekpour R. and Azad H.N. (2012). Determination of Organochlorine Pesticide Residues in Water, Sediments and Fish from Lake Parishan, Iran. World Journal of Fish and Marine Sciences 4(2): 150-154.
- Gbylik, M., Posyniak, A., Mitrowska, K., Bladek,T., and Zmudzki, J. (2013). Multi-residue determination of antibiotics in fish by liquid chromatographytandem mass spectrometry, Food Additives and Contaminants: Part A, 30(6): 940-948.
- Kubrak O.I., Atamaniuk T.M., Husak V.V., Drohomyretska I.Z., Storey J.M., Storey K.B., Lushchak V.I. (2012). Oxidative stress responses in blood and gills of Carassiusauratus exposed to the mancozeb-containing carbamate fungicide Tattoo. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 85: 37-43.
- LeDoux, M (2011). Analytical methods applied to the determination of pesticide residues in foods of animal origin. A review of the past two decades. J. Chromatogr. A, 1218, 1021-1036.
- Li, Z.H., Zlabek, V., Velisek, J., Grabic, R., Machova, J and Randak, T., (2010). Modulation of antioxidant defence system in brain of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) after chronic carbamazepine treatment. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, Part C, 151: 137-141.
- Magare, S.R., Patil, H.T (2000).Effect of pesticides on oxygen consumption.Red blood cell count and metabolites of fish, Pontius ticto. Environ. Ecol. 18: 891-894.
- Mills, J.A and Olney, P.A.,(1977). Pesticidal Analytical Manual, Food and Drug administration, Washington D.C. pp1- 5.
- Mumtaz, M.M., and Menzer R.E. (1986). Comparative Metabolism and Fate of Fenvalerate in Japanese quail (Coturnixcoturnix japonica) and Rats (Rattus norwegicus). Journal of Agriculture and food chemistry, 34(6): 929–936.
- Ogunfowokan, A.O., Oyekunle, J.A.O., Torto, V. and Akanni, M.S (2012). A study on persistent organochlorine pesticide residues in fish tissues and water from an agricultural fish pond. Emir. J. Food Agric, 24(2): 165-184
- Pandey, S., Parvez, S., Ansari, R.A., Ali, M., Kaur, M., Hayat, F., Raisuddin, S. (2008). Effects of exposure to multiple trace metals on biochemical, histological and ultrastructural features of gill of a freshwater fish, Channapunctata (Bloch). Chem-Biol. Interact, 174: 183-192.
- Pathiratne, A.L.W.H.U and Chandrasekera (2008). Effects of Biological and Technical Factors on Brain and Muscle Cholinesterases in Nile Tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus: Implications for Biomonitoring Neurotoxic Contaminations. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol, 54: 309–317.
- Tilak, K.S., Veeraiah, K., Rao, D.K (2004). Toxicity and bioaccumulation of chlorpyrifos in Indian carp Catla catla (Hamilton), Labeo rohita (Hamilton), and Cirrhinus mrigala (Hamilton). Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 73: 933–941.


