Collaborative Question Answering System Using Domain Knowledge and Answer Quality Predictor
Автор: Kohei Arai, Anik Nur Handayani
Журнал: International Journal of Modern Education and Computer Science (IJMECS) @ijmecs
Статья в выпуске: 11 vol.5, 2013 года.
Бесплатный доступ
With the rapid development of E-Learning, collaborative learning is important for teaching, learning methods and strategies. Studies over the years shown that students had actively and interactively involved in a classroom discussion to gain their knowledge. Collaborative learning is able to accommodate the situation, where student can exploit and share their resources and skills by asking for information, evaluating, monitoring one another’s information and idea. Therein, the activity allowing one question has many answer or information that should be selected. Every answer has a weighting and very subjective to select. In this paper, we introduce question answering for collaborative learning with domain knowledge and answer quality predictor. By using answer quality predictor, the quality of answers could be determined. On the other side, domain knowledge could be used as knowledge about the environment in which the target information operates as a reference. Through the process of collaborative learning, the usage knowledge base will be enriched for future question answering. Further, not only the student could get answers form others but also provided by the system.
E-Learning, Collaborative Learning, Question Answer, Domain Knowledge, Answer Quality Predictor
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/15014600
IDR: 15014600
Текст научной статьи Collaborative Question Answering System Using Domain Knowledge and Answer Quality Predictor
The concept of Collaborative Learning is two or more people learn or attempt to learn something together than independent. Different with individual learning, in collaborative learning student can exploit and share their resources and skills by asking, evaluating, monitoring one another’s information and idea, etc [1]. Collaborative Learning is a model that knowledge can be created by sharing experiences within a population where members actively interact [2] [3]. In the Collaborative Robotic Instruction (A Graph Teaching Experience Computers and Education), the goal of collaborative learning is methodologies and environments which students or student where each depends on and is responsible to each other [4]. Including both directly with face-to-face conversations [5] or using computer discussions (online forums, chat rooms, etc.) [6].
In [3] authors indicate that when they found some problem, students learn better when they learn together more frequently than working individually as members in a group. Indeed, the effectiveness of collaborative learning on the internet has been identified by various studies. Interaction among students is fostered as communication over the internet is unpretentious and convenient when addressing to a single user or multiple users. By posting questions for other participants to answer, students could obtain several answers to their question. The problem is sometimes the answer chosen by student as the best answer is not necessarily the best quality answer. The decision of an asker is influenced by subjective reasoning such as the relations between students, the asker’s own point of view, his lack on the subject and others [7]. Therefore, an automatic answer quality predictor system may improve these situations as it will choose the best answer objectively. On the other side, in the implementation of collaborative learning, in addition to sharing information, sometimes students also need a reference which relevant with the topic. In this study, besides providing answer quality predictor as a recommender, the system also provides an answer that is taken from the domain knowledge as a reference.
Question answering system is a discipline area in the field of information retrieval (IR). The QA systems are concerned with providing relevant answers in response to questions proposed in natural language [8] [9] [10]. A QA implementation may construct its answers by querying a structured database of knowledge or information (knowledge base) usually using some computer program. QA systems can pull several answers from an unstructured collection of natural language documents, include a local collection of reference text, internal organization documents and web pages, compiled news wire reports, a set of Wikipedia pages, a subset of World Wide Web pages. There are three main components in the QA system, including question processing, information processing and answer processing [8] [9].
In this paper, we proposed question answering system for collaborative learning environments (CQA) with domain knowledge and answer quality predictor. With the proposed system, after questions provided, all available resources and responses from other students will be gathered and finally using domain knowledge and answer quality predictor will be provided an answer. The paper is organized as follows. First is the motivation for the question and answering system. Section 2 presents the related works on collaborative learning. Section 3 explains about the collaborative question answering mechanism proposed and architecture. In section 4, present the implementation and result of the system. Finally, section 5 is summary and conclusion of this paper.
-
II. RELATED WORK
Collaborative learning is one of the study groups. Some studies show that students get the most current learning through group rather than independently [11] [12]. Studies by the OTTER Group [13] have shown that the ideal class is organized around 50/50 rule. At least 50% of the time students spend is spent interacting with and learning about the other student in the virtual classroom. The social aspect of the classroom is an important factor. If social aspect missing, than student dissatisfaction rises dramatically, as does the attrition rate. In this learning mode, which is a collaborative learning, students who are interested in sharing their knowledge from a learning group to communicate and discuss all kinds of questions, asking one another for information, evaluating one another’s idea for help and teach each other. Therefore, learning is both a group activity and a social process and thus learning performance is strongly affected peers [14].
In the development of networks, comprise all forms of electronically supported learning and teaching that could eliminate the obstacles of time and space. In the collaborative learning, students could take part by computer at anyplace, at the same time or different time (synchronous and asynchronous). Researchers have used activity theory to analyze Computer Supported Collaborative Work (CSCW) system [15]. Group communication relationship [16] refers to the intra-group relationships determined by the interactions among members. However, how to form a learning group after the group is a problem in collaborative learning. Several study about QA for collaborative learning had been done. An application of question answering system for collaborative learning has been designed. [17] Wang et al. (2006) proposes a semantic-based automated question-answering system that responds to online questions of students. Their method can solve the problem of low interaction degree between students and instructor to gain knowledge. In fact, the question-answering knowledge-base can be enriched in the future question-answering process.
Hwang et al. (2008) [18] describe an e-learning system that is able to automatically answer the students' questions on the fly based on the training cases given by the teacher. It also weights the keywords for each candidate's answer according to the feedbacks provided by the students. Therefore, the system is able to generate better answers than existing approaches because of employing the self-adjusting method.[19] describe a multi agent system for building a question answering system in learning management systems and collaborative learning environments.
In [20] [21] we have developed question answering for collaborative learning with quality predictor. By posting questions for other participants to answer, students can obtain several answers to their question. The problem is sometimes the answer chosen by student as the best answer is not necessarily the best quality answer. The decision of an asker is influenced by subjective reasoning such as the relations between students, the asker’s own point of view, his lack on the subject and others. By using several non-textual features, an automatic best answer recommendation system may improve these situations as it will choose the best answer objectively. On the other side, in the implementation of collaborative learning, in addition to sharing information sometimes students also need a reference which relevant with the topic. In this study, besides providing answer quality predictor as a recommender, the system also provides an answer that is taken from the domain knowledge as a reference.
-
III. PROPOSED COLLABORATIVE QUESTION ANSWER SYSTEM
The collaborative question answer system based on closed-domain question answering deals with questions under a specific domain (internet and computer domain). Fig. 1 shows the complete overview proposed of Collaborative Question Answering Mechanism.
-
A. Proposed Collaborative Question Answering System
When the student needs some information, they can ask a question through a designed interface. When a new asked question enters the system, query is created. Then other students will response the question with answering and evaluating one another’s ideas by vote. After questions provided, all available resources and responses from other students will be gathered and finally using answer quality predictor, the most appropriate answer with respect to several criteria such as star, student’s history activity, the word length of student’s answer, and the candidate will be suggested. In the same time, the question will be analyzed through question processing, information processing and answer processing to extracting information from domain knowledge.
Besides making questions when to collaborate with others, even when having no difficulties, students could still browse the knowledge base to see what problems have encountered in collaborative question answer.
Through student activity the knowledge in the usage database continuous accumulating. This accumulated knowledge will then be shared with other through questions or browsing the usage knowledge base. In these systems all of user activity stored in the usage knowledge database.
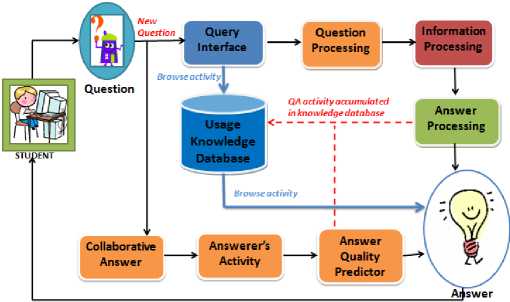
Figure 1. Collaborative Question Answering Mechanism
-
B. Architecture of Question and Answering Tool System
The architecture of the Question and Answering Tool System is shown in Fig. 2. There are three main components in the system, including question processing, information processing and answer processing.
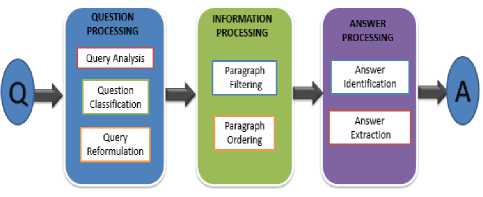
Figure 2. Architecture of Question Answering Tool System
The functions of the components are briefly described as follows,
-
• Question Processing
The function of Question processing is to identifies the focus of the question, classifies the question type, derives the expected answer type, and reformulates the question into semantically equivalent multiple questions. There are three kind of sub processing in the question processing, including query analysis, question classification and query reformulation. Question processing consists of question analysis, question classification, and question reformulation.
-
• Information Processing
Information processing also we could call document processing in QA system is also commonly referred to as a paragraph indexing module, where the reformulated question is submitted to the information retrieval system, which is turn retrieves a ranked list of relevant documents. Information processing consists of paragraph filtering and paragraph ordering.
-
• Answer Processing
The answer and validating modules is responsible for identifying, extracting and validating answer from the set of ordered paragraphs passed to it from the document processing module. Answer processing consists of answer identification and answer extraction.
-
C. Architecture of Collaborative Answer
When the student needs some information, they can ask a question through a designed interface. When a new asked question enters the system, query is created. Then other student wills response the question with answering and evaluating one another’s ideas by vote. After questions provided, all available resources and responses from other students will be gathered and finally using answer quality predictor, the most appropriate answer with respect to several criteria such as star, student’s history activity, the word length of student’s answer, and the candidate will be suggested. The architecture of the collaborative Answer is shown in Fig. 3.
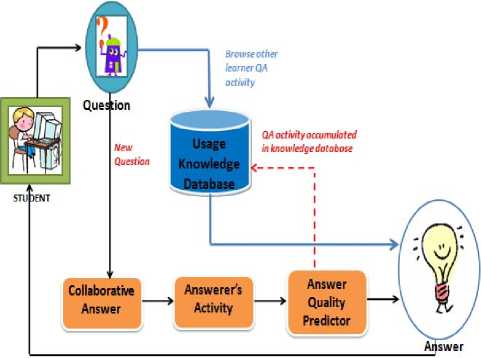
Figure 3. Architecture of Collaborative Answer System
-
IV. Implement and Result
According to the method described above and the structure of the collaborative question answering system, we build an implementation and experimental system.
-
A. Question Processing Tool
As mentioned before, question, document and answer processing are three main parts of a QA system. Important components of question processing are classification of question and reformulation.
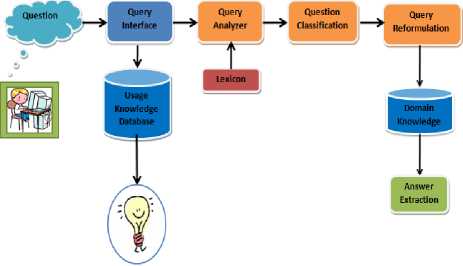
Answer
Figure 4. Block Diagram of Question Processing Tool
Design algorithm of question processing tool (as Fig.4) as follow:
-
1. Question: Student’s question.
-
2. Query Interface: Students posts a question through Query Interface. If the question is similar with the previous questions which are in the knowledge database, the answer of previous question will be displayed.
-
3. Query Analyzer: The function of the query analyzer is to determine a word or sequence words which indicate what information is being asked in the question. Type of the words and synonyms of them (if is existed) were defined in Lexicon Database.
-
4. Lexicon: Lexicon is used as vocabulary (dictionary) and contains all words that are related in domain. Fig. 5 showing the lexicon database of the system. We used Indonesian Thesaurus that get it from http://bse.depdiknas.go.id
-
5. Question Classification :
Devide as:
-
** Question Type: 5W + H. what, when, where, who, why + How
-
** Answer Type: Based on the question type. For the example money/number/definition/tittle are answer type for what question
-
6. Query Reformulation: In this part main question (Q) with using rules change to a question with new format. In this part question words and punctuation which make no difference in question and answer are deleted and the root of words will be specified.
-
7. Domain Knowledge : Information Domain, in this system we used id.wikipedia.com
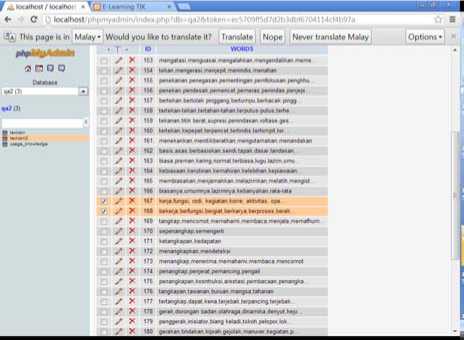
Figure 5. Database of Lexicon
TABLE I. QUESTION CLASSIFICATION
|
Question Classification |
Prepositionconjunctive |
Type of Answer |
|
What ~ Apa |
- kah dari- |
money/number/ definition/tittle |
|
Who ~ Siapa |
- kah dari-dengan-untuk- |
person |
|
When ~ Kapan |
- kah |
date |
|
Where ~ Dimana |
- kah dike-dari- |
place |
|
Why ~ Mengapa |
reason |
|
|
How ~ Bagaimana |
- kah |
explanation |
B. Information Processing
The information processing module in QA systems is also commonly referred to as paragraph indexing module. The document processing module usually relies on one or more information retrieval systems to gather information from a collection of document. In this system, we used a set of Wikipedia pages.
The principle of paragraph filtering is based o the most relevant documents should contain the question keywords in a few neighboring paragraphs, rather than dispersed over the entire document. Paragraph filtering can be used to reduce the number of candidate documents, also to reduce the amount of candidate text from each document. The aim of paragraph ordering is to rank the paragraphs according to a plausibility degree of containing the correct answer. We used same word sequence score to order paragraphs. In this radix sort, the number of words from the question that are recognized in the same sequence within the current paragraph window. Fig.6 showing the block diagram of Information processing tool.
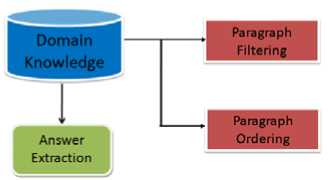
Figure 6. Block Diagram of Information Processing Tool
C. Answer Processing
Answer processing tool consist of two main components answer identification and answer extraction. In the answer identification, the answer type which was determined during question processing is crucial to the identification of the answer. Since usually the answer type is not explicit in the question or the answer, it is necessary to rely on a parser to recognize named entities (e.g. names of persons and organizations, monetary units, dates, etc.) In the answer extraction, the parser enables the recognition of the answer candidates in the paragraphs. So, once an answer candidate has been identified, a set of heuristics is applied in order to extract only the relevant word or phrase that answers the question. Fig. 7 showing the block diagram of answer processing tool.
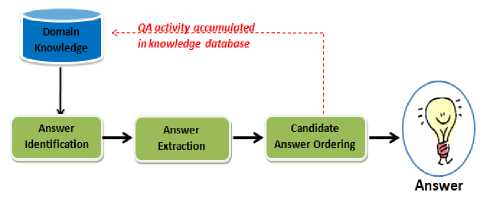
Figure 7. Block Diagram of Answer Processing Tool
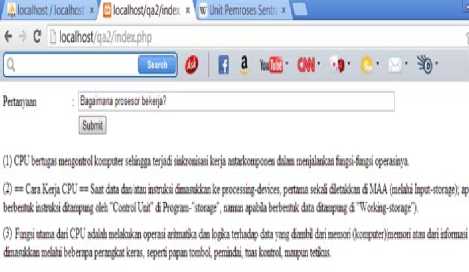
ЙЬ(10Я|ЮЮД^ 0 £ ■ l ItKdlhoit ,v . .л iXtj :. . J s96 k156 сач kep crosses» mermre utter ataj penryn masi* t^^mj^ »еч6зг1асм*г «# ptnxtu.M» K E . LEARNING wrgtarlemilinmBre^m*fcn*jmmvroaei penrtihersetUirt*kemrtanmeiy WtUr wxj keruWI merteferTHrturi d* tfsHxl JO nwnsu*ank»rw*ew*iu«*wvwng** Iu*k(M>2000646 R*JH 3061 6° 9° M*twM«*(le *И*>аг1 UM tmetiU UU «хареi Figure 8. CQA Interface Providing Domain Knowledge and Answer Quality Predictor Figure 9. Answer Processing Interface Providing List of Candidate Answers Worn CPU [suntingj Kompoiwi CPU ttrbip men|Mi Mfipi micim. yiitu itbogt btfikul Figure 10. Domain Knowledge Providing Candidates Paragraphs Unit kontrol yang mampu mengaiurjabnnya program Komponen ini sudah pasli iffdayl Mini tomui CPU CPU Мирта mongcmrol komputff athingp (ерт* Я1ктоп^вз51 kerja antawnponen tilam menjalankan fungsi-iungsi орегв^пуа lermasuh ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^) ^P П ^ tou(^' cara kerja CPU 1 of 21 л 1 ^ x | * register-register dan juga dengan bus-bus eksternal CPU yang menghubungkan dengan sistem lainnya, seperti memori utama, piranti masukan /keluaran. Cara Kerja CPU [s unting] = Saat data dan/atau instruksi dimasukkan ke processing-devices, pertama sekali diletakkan di MM (melalui Input-storage); apabila berbentuk instruksi ditampung oleh Control Unit di Program-storage, namun apabila berbentuk data ditampung di Working-storage). Jika register siap untuk men erima pengerjaan eksekusi, maka Control Unit akan mengambil instruksi dari Program-storage untuk алкьа1> ditampungkan ke Instruction Register, sedangkan alamat memori yang berisikan instruksi tersebut ditampung di Program Counter. Sedangkan data diambil oleh Control Unit dari Working-storage untuk ditampung di General-purpose register (dalam hal ini di Operandregister). Jika berdasar instruksi pengerjaan yang dilakukan adalah arithmatika dan logika, maka ALU akan mengambil alih operasi untuk mengerjakan berdasar instruksi yang ditetapkan. Hasilnya ditampung di Akumulator. Apabila hasil pengolahan telah selesai, maka Control Unit akan mengambil hasil pengolahan di Accumulator untuk ditampung kembali ke Working-storage. Jika pengerjaan rg keseluruhan telah selesai, maka Control Unit akan menjemput hasil pengolahan dari Working-storage untuk ditampung ke Outputstorage. Lalu selanjutnya dari Output-storage, hasil pengolahan akan ditampilkan ke output-devices. Figure 11. Domain Knowledge Providing Candidates paragraphs
D. Result According to the method described above and the structure of question and answering system, we build an experimental system in Indonesian collaborative question answer system specifically in the Computers and Internet Subject. We choose 20 questions and 60 answers, and there are two indexes measurement in this experimental. Beginning with measure, the domain knowledge performance continued with calculation the accuracy of answer quality predictor. Table ii. Result of Experiment Question 20 Answer 60 Domain Knowledge (DK) Answer extracted 18 Answer not extracted 2 Answer Quality Predictor (AQP) Accuracy 88.3% Inaccuracy 11.7% In the answer extraction for the domain knowledge, the parser enables the recognition of the answer candidates in the paragraphs. So, once an answer candidate has been identified, a set of heuristics is applied in order to extract only the relevant word or phrase that answers the question. Measuring the relevant word or phrase or a set of sentence with the keyword of question are conducted for domain knowledge result. From 20 question, 18 information could provided by the domain knowledge and 2 question are not. The QA tool could not provide information because there isn’t information on the domain knowledge. For the answer quality predictor, we use two parameter measurement accuracy and inaccuracy. From the 20 question and 60 answers, we got accuracy 88.3% and 11.7% for inaccuracy. Table 2 showing result of the experiment. V. CONCLUSION In this paper, a system for question answering system in the collaborative learning environment has been designed. The system operated upon the collaborative question answer system using domain knowledge and answer quality predictor. In the collaborative question answer, the activity allowing one question has many answer or information that should be selected. Every answer has a weighting and its very subjective to select it. By using answer quality predictor the quality of the information could be determined. On the other hand, domain knowledge could be used as knowledge about the environment in which the target information operates. We showing and testing our quality predictor measurement to a collection of question and answer pairs. From 20 question, 18 information could provided by the domain knowledge and 2 question are not. The QA tool could not provide information because there isn’t information on the domain knowledge. For the answer quality predictor we use two parameter measurement accuracy and inaccuracy. From the 20 question and 60 answers, we got accuracy 88.3% and 11.7% for inaccuracy. These models could be useful to complete a collaborative learning. Acknowledgment The authors wish to thank to the students of Electrical and Information Technology State University of Malang Indonesia, who contributed and supported to the experiments.
Список литературы Collaborative Question Answering System Using Domain Knowledge and Answer Quality Predictor
- Dillenbourg, P. (1999). Collaborative Learning: Cognitive and Computational Approaches. Advances in Learning and Instruction Series. New York, NY: Elsevier Science, Inc.
- Chiu, M. M. (2000). Group problem solving processes: Social interactions and individual actions. Journal for the Theory of Social Behavior, 30, 1, 27-50.600-631.
- Chiu, M. M. (2008).Flowing toward correct contributions during groups' mathematics problem solving: A statistical discourse analysis. Journal of the Learning Sciences, 17 (3), 415 – 463.
- Mitnik, R., Recabarren, M., Nussbaum, M., & Soto, A. (2009). Collaborative Robotic Instruction: A Graph Teaching Experience. Computers & Education, 53(2), 330-342.
- Chiu, M. M. (2008). Effects of argumentation on group micro-creativity. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 33, 383 – 402.
- Chen, G., & Chiu, M. M. (2008). Online discussion processes. Computers and Education, 50, 678 – 692.
- Kohei A. Anik Nur Handayani, 2013, Predicting Quality of Answer in Collaborative Q/A Community, IJARAI Journal Volume 2 Issue 3.
- Nabil Allam. A.M, Mohamed Hassan Haggag. The Question Answering Systems: A Survey. International Journal of Research and Reviews in Information Sciences (IJRRIS) Vol. 2, No. 3, September 2012, ISSN: 2046-6439.
- Muthukrishnan Ramprasath, Shanmugasundaram Hariharan. A Survey on Question Answering System. International Journal of Research and Reviews in Information Sciences (IJRRIS) Vol. 2, No. 1, March 2012, ISSN: 2046-6439.
- Mohammad Reza Kangavari, Samira Ghandchi, Manak Golpour. A New Model for Question Answering Systems. World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology. 2008.
- Johnson, D.W. and Johnson R.T. (1999) Cooperation and competition: Theory and research. Edina. MN: Interaction Book Company.
- Slavin, R. (1996) Research on cooperative learning and achievement: what we know, what we need to know. Contemporary Educational Pshchology, 21, 1, pp. 43-69.
- Gilrory, K.(2001). Collaborative e-learning: the right approach ([Online].Available at : http://www.ottergroup.com/otter-with-comments/ right_approach.html).
- Lave, J., and Wenger, E. (1991) Situated Learning: LegitimatePeripheral Participation. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
- Kuutti, K. (1991) The concept of activity as a basic unit of analysis for CSCW research. Proceedings of the Second European Conference on Computer-Supported Co-operative Work: EC-CSCW’91 (eds. L.J. Bannon, M. Robinson &K. Schmidt) pp. 249-264, Kluwer, Dordrecht.
- Watzlawick, P. (1967) Pragmatics of Human Communications: A Study of Interactional Patterns. Pathologies and Paradoxes. W.W. Norton, New York.
- Wang, C.C., Hung J.C., Yang C.Y., Shih T.K. (2006). An Apllication of Question Answering System for Collaborative Learning. IEEE Conference on ICDCSW’06.
- Hwang GJ, Yin PY, Wang TT, Judy TR, Hwang GH, 2008, An enhanced Genetic Approach to Optimizing Auto-reply Accuracy of an E-learning System, Elsevier Journal, Computers and Education 51 (2008) 337-353.
- Bahreininejad A, Alinaghi Tanaz, 2011, A Multi Agent Question Answering System for E-Learning and Collaborative Learning, nternational Journal of Distance Education Technologies, 9(2), 23-39, April-June 2011.
- Kohei A. Anik Nur Handayani, 2013, Predicting Quality of Answer in Collaborative Q/A Community, IJARAI Journal Volume 2 Issue 3.
- Kohei A. Anik Nur Handayani, 2013, Question Answering for Collaborative Learning with Answer Quality Predictor, I.J.Modern Education and Computer Science, 2013, 5, 12-17. Published Online June 2013 in MECS (http://www.mecs-press.org/).
- Kohei Arai, Anik Nur Handayani, 2012, Question Answering System for an effective Collaborative Learning, IJACSA Journal Vol.3 No.1.


