Comparative analysis on performance emission test of single cylinder engine and multi cylinder engine
Автор: Shi Yuanyuan, Niu Xiaoxiao, Zhang Xiangchen, Wang Zhilei
Журнал: Бюллетень науки и практики @bulletennauki
Рубрика: Технические науки
Статья в выпуске: 11 т.6, 2020 года.
Бесплатный доступ
In the research and test of diesel engine, because the performance test of multi cylinder engine with different configuration needs to be replaced, and there is a certain risk in the first test, while the single cylinder engine is more suitable for the research and test of different configurations because of its simple structure and convenient replacement of components. Therefore, by comparing the differences of combustion state between single cylinder engine and multi cylinder engine with the same configuration, the change law of performance characteristics of single cylinder engine and multi cylinder engine under different working conditions is confirmed. By analyzing the difference of emission performance of single cylinder engine with different configuration, the emission performance of multi cylinder engine under different configuration is predicted. The research in this paper has important significance for further research and test of diesel engine.
Diesel engine, single cylinder engine, multi cylinder engine, performance test
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14117673
IDR: 14117673 | УДК: 621.431 | DOI: 10.33619/2414-2948/60/32
Текст научной статьи Comparative analysis on performance emission test of single cylinder engine and multi cylinder engine
Бюллетень науки и практики / Bulletin of Science and Practice
UDC 621.431
Introduction of test methods
A common rail diesel engine (1800r / min) produced by China Henan Diesel Engine Industry Co, Ltd. (HND) is selected The single cylinder diesel engine was tested with 25%, 50%, 75%, 90% and 100% propulsion performance tests and 10%, 25%, 50%, 75% and 100% load characteristic tests, respectively. Through the comparative analysis of the test results (explosion pressure, exhaust temperature, smoke, mechanical efficiency, fuel consumption), the variation rules of single cylinder diesel engine and multi cylinder diesel engine under the same working condition were verified.
Calibration of single cylinder engine
Due to the structural differences between single cylinder engine and multi cylinder engine, including the differences of intake and exhaust system, fuel system, oil system and cooling system of single cylinder engine, it is necessary to calibrate single cylinder engine and multi cylinder engine before verification test. By adjusting the single cylinder power, controlling the injection signal and intake pressure, the consistency of combustion state between single cylinder engine and multi cylinder engine is ensured [1–2].
By adjusting the control fuel injection signal to make the combustion start point consistent; by adjusting the intake pressure to make the intake air consistent; by adjusting the single cylinder power to make the indicated work the same. (Note: only 100% working condition comparison chart is reserved).
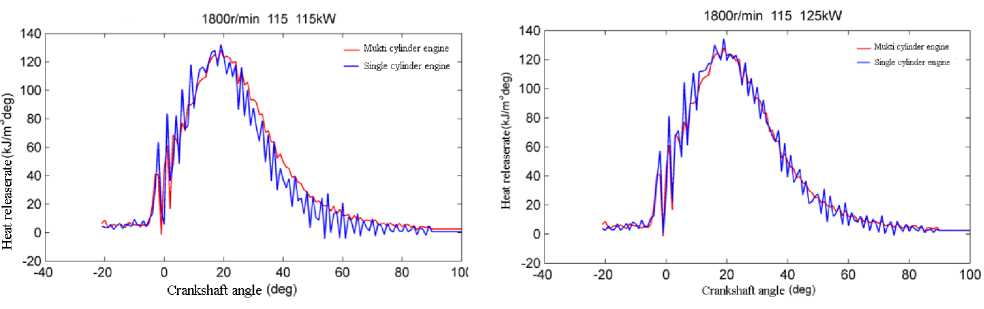
a) Comparison chart of combustion heat release
a) Comparison chart of combustion heat release rate.
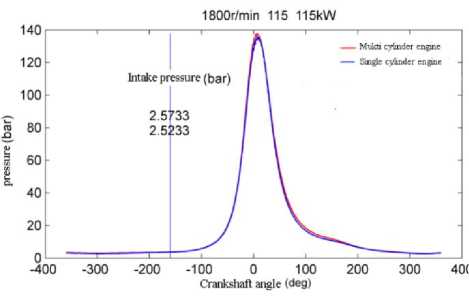
b) Comparison chart of cylinder pressure curve.
rate.
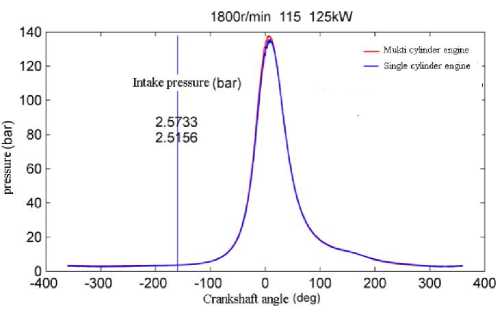
b ) Comparison of cylinder pressure curves.
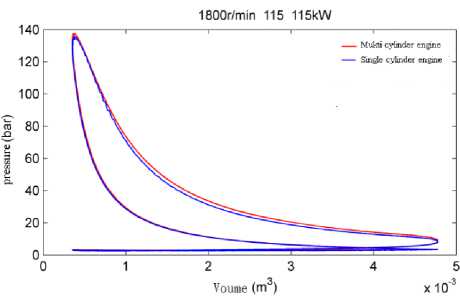
c ) Indicator diagram.
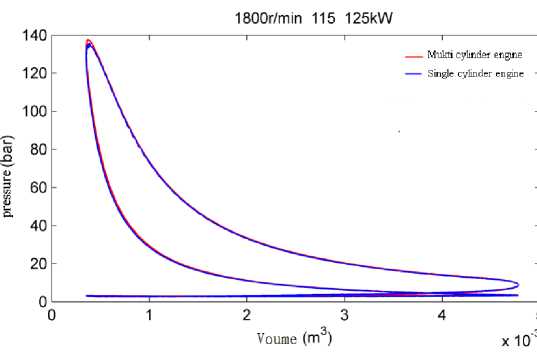
Figure 1. 1800rpm/115kW(same output work) combustion in cylinder.
c ) Indicator diagram.
Figure 2. 1800rpm/115kW (same indication work) combustion in cylinder.
By comparing the heat release rate and cylinder pressure curves of multi cylinder engine and single cylinder engine, it is concluded that the combustion state of single cylinder engine and multi cylinder engine is basically the same when the fuel injection state is consistent with the intake and exhaust state. Therefore, the single cylinder engine test can be used as the basis for piston verification.
Comparison of test data
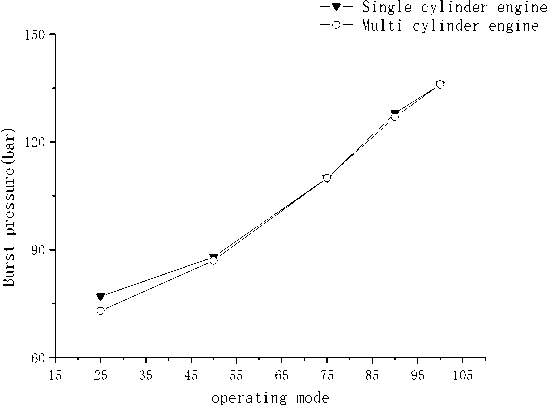
Through the test of a single cylinder engine and a multi cylinder engine, the comparison curves of explosion pressure, exhaust temperature, smoke, mechanical efficiency and fuel consumption are obtained (see the figure below for details).
(a) Explosion pressure of propulsion line
-
(b) Explosion pressure of load line
—▼— Single cylinder engine
—О — Multi cylinder engine
operating mode
-
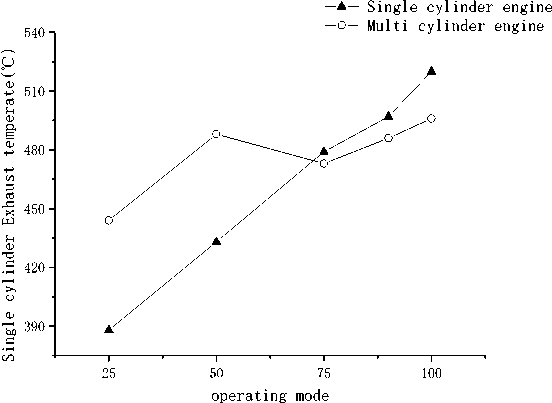
(c) Exhaust temperature of propulsion line
—▼— Single cylinder engine — О — Multi cylinder engine
E
operating mode
-
(d) Exhaust temperature of load line
—A—Single cylinder engine — О —Multi cylinder engine
E
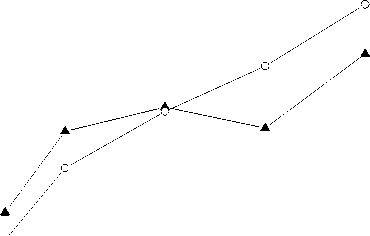

(e)Single cylinder exhaust temperature of propulsion line
(f) Single cylinder exhaust temperature of load line
-
—▼— Single cylinder engine
-
—о— Multi cylinder engine
50 75
operating mode
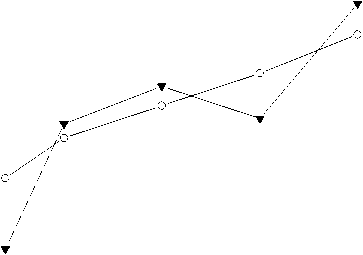
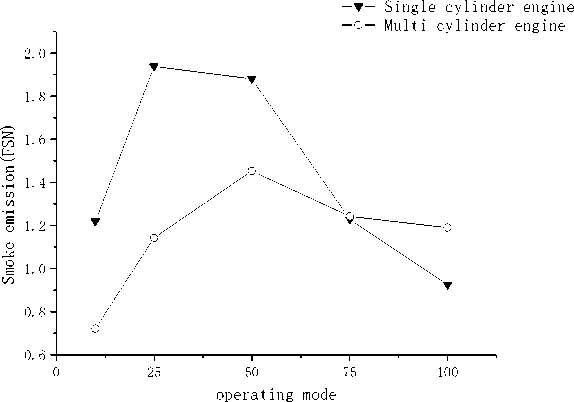
(g) Smoke intensity of propulsion line
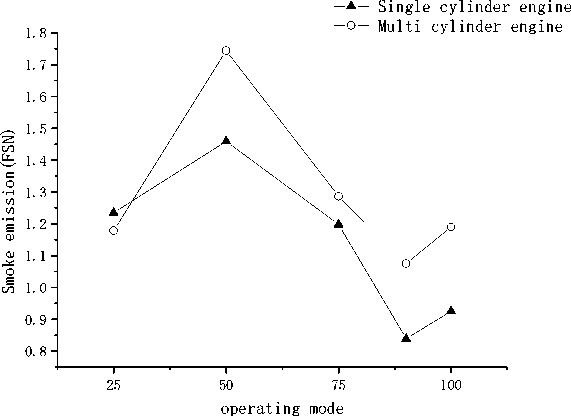
(h) Smoke intensity of load line
(i) Mechanical efficiency of propulsion line
—▼— Single cylinder engine
—о— Multi cylinder engine
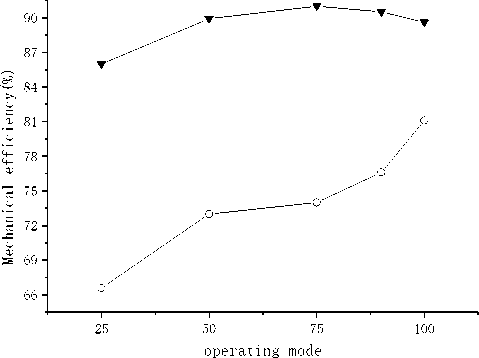
(j) Mechanical efficiency of load line
-
—Л— Single cylinder engine
-
—о— Multi cylinder engin

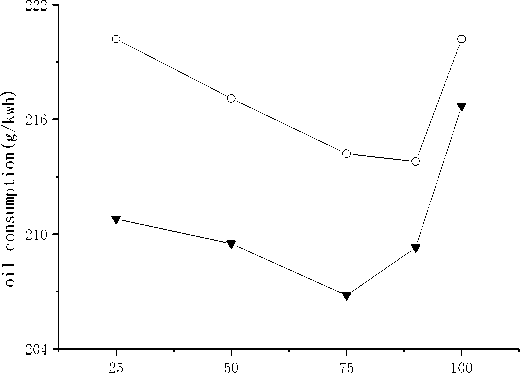
(k) Fuel consumption of propulsion line
—▼— Single cylinder engine
—о— Multi cylinder engine
operating mode
(l) Fuel consumption of load line
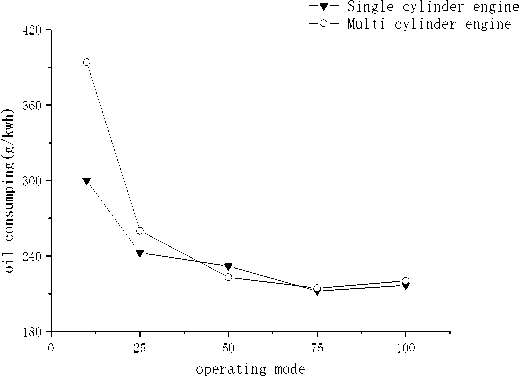
Table 1.
COMPARISON TABLE OF SINGLE CYLINDER ENGINE/MULTI CYLINDER ENGINE TEST DATA (PROPULSION CHARACTERISTICS)
|
Working condition |
Model |
Single cylinder power |
Oil consumption |
Explosion pressure |
Smoke intensity |
Mechanica l efficiency |
|
25% |
Single cylinder |
37 |
210.8 |
77 |
1.235 |
86 |
|
Multi cylinder |
29 |
220.2 |
73 |
1.178 |
66.6 |
|
|
50% |
Single cylinder |
63 |
209.5 |
88 |
1.459 |
89.9 |
|
Multi cylinder |
58 |
217.1 |
87 |
1.744 |
73 |
|
|
75% |
Single cylinder |
102 |
206.8 |
110 |
1.198 |
91 |
|
Multi cylinder |
86 |
214.2 |
110 |
1.286 |
74 |
|
|
90% |
Single cylinder |
118 |
209.3 |
128 |
0.839 |
90.5 |
|
Multi cylinder |
104 |
213.8 |
127 |
1.075 |
76.6 |
|
|
100% |
Single cylinder |
125 |
216.7 |
136 |
0.925 |
89.6 |
|
Multi cylinder |
115 |
220.2 |
136 |
1.19 |
81.1 |
Table 2.
COMPARISON OF SINGLE CYLINDER ENGINE/MULTI CYLINDER ENGINE TEST DATA (LOAD CHARACTERISTICS)
|
Working condition |
Model |
Single cylinder power |
Oil consumption |
Explosion pressure |
Smoke intensity |
Mechanical efficiency |
|
100% |
Single cylinder |
125 |
216.7 |
136 |
0.925 |
89.6 |
|
Multi cylinder |
115 |
220.2 |
136 |
1.19 |
81.1 |
|
|
75% |
Single cylinder |
98 |
212.1 |
114 |
1.228 |
86.9 |
|
Multi cylinder |
86 |
214.4 |
116 |
1.242 |
74.7 |
|
|
50% |
Single cylinder |
72 |
231.9 |
93 |
1.88 |
85.2 |
|
Multi cylinder |
58 |
223.1 |
96 |
1.453 |
67.7 |
|
|
25% |
Single cylinder |
40 |
242.5 |
72 |
1.938 |
75.1 |
|
Multi cylinder |
29 |
260.1 |
77 |
1.143 |
51.4 |
|
|
10% |
Single cylinder |
22 |
300 |
64 |
1.219 |
59.4 |
|
Multi cylinder |
12 |
394 |
62 |
0.721 |
31.3 |
Through the analysis and comparison of the above test results, the following conclusions are obtained:
-
(1) When the intake state and combustion state are the same, the burst pressure of single cylinder engine and diesel engine is basically the same.
-
(2) The fuel consumption rate of multi cylinder engine is about 3–7 g/kWh higher than that of single cylinder engine.
-
(3) The temperature difference between multi cylinder engine and single cylinder engine is about ± 20 ℃.
-
(4) The smoke values of multi cylinder engine and single cylinder engine are different.
-
(5) Due to the different piston types of single cylinder engine and multi cylinder engine, there is a certain difference in smoke and fuel consumption rate, but the performance and burst pressure of single cylinder engine can basically reflect the performance changes of the whole engine.
Conclusions
-
1. After completing the single cylinder emission test, it can be concluded that the performance of the single cylinder engine can basically reflect the performance of the whole machine, and no other emission performance tests can be carried out in the future.
-
2. The combustion state of the single cylinder engine is basically consistent with that of the whole engine, and the single cylinder engine test can be used as the basis for piston verification.
Список литературы Comparative analysis on performance emission test of single cylinder engine and multi cylinder engine
- Zhijian Huang, Zhou Yuan Heat pump industry energy saving application. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2014. 9. P. 123-131.
- Zheng X. The refrigeration principle and device. 2008.


