Condition Factor, Haematology and Serumbiochemistry of Adult African Carp (Labeo coubie. Ruppell, 1832) from the Benue River Basin, Nigeria
Автор: Adeyemo Bolade Thomas, Enefe Glory Ndidi
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 2 т.17, 2021 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Study evaluated for two seasons (July 2018 and August 2019), the relationship between fish biometry, fish haematology, serum biochemistry and the environmental conditions in 243 apparently healthy adult African Carp fish (Labeo cubie) sampled from three locations along the Benue River and its adjoining wetlands. Fish length, weight and condition factor differed significantly (p 0.05) between seasons with fish sampled in the raining season being significantly (p 0.05) heavier ( 470 g). The erythrocytes counts, leucocytes count and packed cell volume varied significantly (p 0.05) with sapling sites and season. Serum glucose concentration, transaminases and alkaline phosphatase activity were significantly (p 0.05) higher in the dry season. Total protein, albumin and urea nitrogen concentrations were significantly higher in the raining season. Water temperature, turbidity and electrical conductivity were significantly higher in the dry season and varied significantly between seasons and sampling sites. This is the first study to document the biometry, haematology and serum biochemistry and the physico-chemical parameters of water needed for the culture and management/conservation of L. cubie. This data set could serve, as benchmark for future investigation of the zootechnical requirements for the culture and or management of feral populations of Labeo cubie.
Benue River, African carp, Labeo cubie, haematology, serum biochemistry, seasonal variation
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/143173895
IDR: 143173895
Текст научной статьи Condition Factor, Haematology and Serumbiochemistry of Adult African Carp (Labeo coubie. Ruppell, 1832) from the Benue River Basin, Nigeria
The African Carp ( Laboe cubie . Ruppell, 1832) is a bentho-pelagic potadromuos fish that is widely distributed within the drainage basins of most major river systems of Nigeria (Leveque, 2003; De Weirdt et. al., 2007). Laboe cubie is reported to display a high degree of behavioral food plasticity due to its ability to feed on aquatic invertebrates, plants and decaying organic matter (Ugwumba, 1988; Adeyemi and Akombo, 2012). These attributes has enable it to occupy and colonize various fresh water habitats (Froese and Pauly, 2018). Further, Labeo cubie is reported to have a high growth rate and has been reported to attain 10 kg body weight, 700 mm standard length. This fish is a highly valued fish food in several African countries where it is acclaimed for its sweet teste (Ayotunde et al., 2007). For these reasons, L. cubie has been proposed as a candidate fish species for aquaculture (Olaosebikan and Raji, 1998).
Information needed for the successful culture of this fish species can be gleaned from data obtained from healthy feral stocks in their natural environments (Pius and Benedict, 2002). These data includes length weight relationships, the Fulton condition factor, haematology and serum biochemical data, nutritional requirements and the physico-chemical parameters of the culture water required for the survival and longevity of the fish (Froese, 2006).
The Fulton’s condition factor, derived from the length-weight data, is a term used to compare the condition of plumpness or wellbeing of a fish (Shinkafi et. al., 2013). It is a usefull index for the monitoring of the feeding intensity, age and growth rate in fish (Oniye et. al., 2006). Hematological and serum biochemical parameters are key clinical tools required for the diagnosis and prognostication of health statuses under culture or natural conditions (Dacie and Lewis, 2006; Roberts et. al., 2010). Hematological assessment is a rapid approach for the determination of the state of homeostasis of the fish while serum biochemical assessments provides information on physio-pathological changes in the organs and or systems of the fish (Gul et. al., 2011). The haematological and serum biochemical parameters of some fish species have been investigated and reported with the purpose of establishing reference intervals with respect to age, sex, size and the influence of environmental variables on these parameters (De Pedro et. al., 2005; Adeyemo et. al., 2012; Fazio et. al., 2012; Pradhan et. al., 2012).
Haematological and biochemical studies help in understanding the relationship of blood characteristics to the habitat and adaptability of the species to the environment (Fazio et. al., 2012). Asides from the reports of Adadu et. al., (2014) and Olufeagba et. al., (2016) that dwelled on some aspects of the biology of Labeo cubie, there is a paucity of information on the effects of seasonal variations in water quality parameters on the weight-length relationship and on the haematology and serum biochemical parameters of this fish . The present study therefore, aims to evaluate the effects of seasonal variations in water quality parameters on condition factor, haematology and sembiochemistry of feral Laboe cubie sampled from natural habitats of this fish species.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This study was carried out at fishing sites along the Benue River and its wetlands (Figure 1). For the purposes of this study the seasons were divided into two clear periods marked by distinct precipitations patterns as Raining and Dry seasons following Jedere et al. (2007).
Fish and sample preparations:
243 adult Labeo cubie fish (407.5- 580.9 g) were sampled bimonthly between July 2018 and August 2019 from the Lower Benue River basin using seine and cast nets.
Sampling site A (Benue River 70 44′ N, 80 32′ E); Sampling site B (Discharge of Wase river into the Benue River 8026′N, 10005′E) and Sampling site C (Discharge of the Mada river into Benue River 7059′N, 7055′E) (Figure1). At the times of fish sampling, corresponding water samples were also taken from the sites for water quality assessments. Environmental conditions in all sampling sites were deemed to be similar (depth > 2 m and < 5 m; water temperature 28.84 0C to 29.16 0C). An average of six water samples were obtained per site. All sampling were effected in the early hours (0600- 0900 hrs.) of the morning.
To ensure sampled fishes were analyzed under approximately the same environmental conditions, all fish samples were collected in a single catch at same time of the sampling trips. Captured fish appeared healthy (and swam aggressively).
Following capture, fish were sedated in MS 222 (250 mg/L) for 10 to 15 minutes as described by (Neiffer and Stamper, 2009) and screened for the presence of lacerations, parasites and disease causing organisms following the methods of Roberts (2010). Then, 4 ml of blood was collected (using 5 ml syringe and 19 gauge needles) via caudal veine puncture. The collected blood were shared into two aliquots. The first aliquot was emptied into tubes (previously moistened with 10 % EDTA solution) and utilized for haematological evaluations and the other portion were emptied into clean narrow bored glass test tube (where they were allowed to clot for about an hour). The test tubes containing the clotted blood were then centrifuge at 18187 x g and the clear serum eluted (and stored at -20 0C) for use in serum biochemical evaluations.
Length- Weight Measurements
The standard lengths of each fish sample was measured in centimeters (cm) using a meter rule and the fish weight was taken in grams (g) using an electronic weighing balance.
The condition factor (K) was derived according to Pauly (1983) using the formula:
K = 100W/L3. Where K is the Fulton condition factor, W = fish weight in grams and L = length of fish.
Haematological evaluations
Erythrocytes enumerations was achieved using the Neubaeur counting chamber following the methods of Dacie and Lewis (2006). Briefly, 0.02 ml of anticoagulated blood was added to 3.98 ml Natt and Herrick dilution fluid to produce a 1:200 dilution; a drop of the diluted blood was then charged onto the counting chamber for erythrocytes enumeration. Erythrocytes counts were effected in the five groups of 16 small squares on the chamber using the high dry objectives (x 40) lens of a light microscope. Results obtained were then multiplied by 10,000 to obtained the total number of erythrocytes per microliter of blood (Prasad and Charles, 2010).
Leucocytes enumeration was determined using the method of Dacie and Lewis (2006). Briefly, 0.02 ml of blood was diluted in 0.38 ml of white blood diluting fluid (giving a dilution of 1:20). Then a drop of the blooddiluent mixture was charged onto the Neubauer counting chamber, and the leucocytes were enumerated on the four corner squares of the chamber using the x 100 objectives lens of the microscope. The number of cells thus counted was multiplied by 50 to obtain the total leucocytes count per microliter of blood (Prasad and Charles, 2010).
Hemoglobin concentration was determined using the cyanomethaemoglobin method of (Campbell, 2012). Briefly, 0.02 ml of anticoagulated blood was added to 5 ml of Drabkins reagent and after allowing to stand for 5 minutes, this was thoroughly mixed using a vortex mixer. The mixtures were then centrifuged at low speed and the supernatant eluted and placed in clean test tubes where absorbance of the samples and standards were read against a working reagent blank at a wavelength of 540 nM using a Statfax 4500 Chemistry analyzer (Awareness Technology, FL USA). Haemoglobin concentration was obtained by multiplying the absorbance of the sample with a calibration factor derived from the absorbance and concentration of the standard.
Packed cell volume was determined by the micro hematocrit method (Campbell, 2012). Briefly, micro capillary were almost filled with blood and then one end of the tubes were sealed with plasticine. The filled tubes were then spun at 10,000 revolution per minute for 5 minutes using a micro hematocrit centrifuge (Hawksley, Hematospin 1400, United Kingdom). The packed cell volume was then read off as a percentage on the micro hematocrit reader. The erythrocytic indices were determined using the following formulae as described by (Campbell, 2012).
i Mean corpuscular hemoglobin (Pg) = Hemoglobin (g/dL) X 10/Erythrocytes number (x 106/mm3).
ii Mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration
(%) = Hemoglobin (g/dL) X100/Packed cell volume (%).
iii Mean corpuscular volume = Packed cell volume (%) x 10/Erythrocytes number (x 106/mm3).
Serum biochemical evaluations
Clinical biochemistry analysis were performed to obtain serum concentrations of glucose, total protein, albumin, urea, uric acid, creatinine kinase and serum activities of alkaline phosphatase and the transaminases on the serum obtained from the blood samples using a multichannel automatic chemistry analyzer (Chemwell 4800, Awareness Technology FL. USA) and Dialab clinical chemistry colorimetric diagnostic kits (Dialab Produktion Astria) following the manufacturers instructions. Globulin was obtained mathematical by the deduction of values obtained for albumin from values obtained for serum total protein (Fazio et. al., 2013).
Water Quality assessments
The water quality parameters namely, temperature, dissolved oxygen concentration, pH and turbidity were assessed on site. Water temperature and dissolved oxygen concentrations were measured with an hand held oximeter (Hanna HI9147 oximeter Hanna Instruments, Romania), water pH was measured with an hand held pH meter (Hanna Instruments, Romania); electrical conductivity was determined with a portable conductivimeter (Hanna Instruments, Romania) and turbidity with a secchi disc. The other water quality parameters namely nitrite, nitrate and ammonia concentrations were determined in the laboratory using specific colorimetric methods and a chemistry analyzer. The water quality determinations followed the methods of APHA (1998).
Statistical Analysis
Data obtained for the haematological and serum biochemistry parameters were tested for normality using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. The assessed variables were subjected to the analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by a separation of the variant means by the Duncan’s multiple range (Duncan, 1955) with p set at ≤ 0.05. The results are presented as Mean ± SE. All data obtained in the study were analyzed using the SPSS 23 software (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA).
RESULTS
A total of 243 adult specimens of Labeo cubie were caught during five (5) different sampling periods of the study. The results from sampling site B was pooled with the results of sampling site C (and are subsequently regarded as results for site B).
The sampled fishes have a mean weight of 493.7 ± 21.44 g. The result obtained from the biometric evaluations of the sampled fish from Site A are depicted in Table 1. The standard length of fish sampled in the 2018 Raining season is 35.68 ± 7.24 with a body weight of 520.57 ± 11.81 g. These values were not significantly different (p > 0.05) from the corresponding values obtained for fish sampled in the 2019 Raining season. Further, these values differed significantly (p < 0.05) from the corresponding values obtained for fish sampled during the Dry season.
A seasonal comparison of the Fulton condition factor of the sampled fish shows that fish sampled in the 2018 Raining season were not significantly different (p > 0.05) from those sampled in the 2019 Raining season, but differed significantly (p < 0.05) from those of fish sampled in the Dry season of 2019 (Table 1).
The Length-weight and Fulton condition factor obtained for fish sampled from Sites B and Site C are shown in Table 2. There was no difference (p > 0.05) in the mean length of fish sampled in the 2018 Raining season compared to those sampled in the 2019-Raining season. However, the fish sampled in the 2018 Raining season were significantly (p < 0.05) heavier than those sampled in the 2019 Raining season. Further, the fish sampled in the 2018 raining season had a significantly (p < 0.05) higher Fulton condition factor compared to fish sampled during the 2019 raining season. A comparison of the biometric data of these fish further shows, that whereas the Fulton condition factor of fish sampled in the 2018 Raining season were not significantly (p > 0.05) different from those of fish sampled in the 2019 Dry season, they differed significantly from those of fish sampled in the early Dry season of 2019.
The data obtained for the haematological evaluations of fish sampled from the sampling sites are as presented in Table 3. The erythrocytes count, leucocytes count, packed cell volume and the haemoglobin concentrations varied significantly (p < 0.05) with sampling season and between the sampling sites.
In all the sampling sites, the total erythrocytes count were significantly (p < 0.05) higher in the raining season compared with values obtained in the dry season. In addition, the packed cell volume obtained for the sampled fishes were significantly (p < 0.05) higher in the dry season compared with the values obtained for the raining season. Further, Table (3) also shows that in fish sampled from Site A, the hemoglobin concentration was significantly higher in the raining season compared with the hemoglobin concentrations of fishes in the dry season. This was not the case in sampling site B, where there was no significant difference (p > 0.05) in the hemoglobin concentration of fishes sampled in the raining season compared with those sampled in the dry season (Table 3).
For both sampling sites, the total leucocytes counts were significantly (p < 0.05) higher in the dry season compared with values obtained in the raining season. Except for the lymphocytes count, the differential leucocytes (Neutrophil, Monocytes, Eosinophil and Basophil) counts, exhibited a similar trend. As the values obtained in the dry season were significantly (p < 0.05) higher than values obtained in the raining season.
The results obtained from the serum biochemistry assessments of the sampled fish are presented in Table 4. It shows the assayed parameters varied between seasons and sampling sites. In both sampling sites, the serum glucose concentration was significantly (p < 0.05) higher in the dry season compared with the results of the raining season while the serum total protein and the albumin concentrations were significantly (p < 0.05) higher in the raining season compared with the values obtained in the dry season. Further, a site-by-site comparison shows that fish sampled in Site A had significantly (p < 0.05) lower glucose concentrations compared with fish sampled in the corresponding seasons from Site B.
Table 4 also shows that the serum AST, ALT and ALP activities were significantly (p < 0.05) higher in the dry season compared with values obtained from fish sampled in the Raining season while the serum concentrations of urea nitrogen and creatinine were in the raining season compared with values obtained in the dry season. Further, a site-by-site comparison of the serum biochemical data shows that values obtained for Site B were significantly lower than the corresponding values obtained for fishes sampled from Site A.
Table 5. Shows data obtained for the water quality assessments of the water collected from the sampling sites. It shows that asides from water temperature, turbidity and electrical conductivity, the results obtained for the other measured parameters were not significantly (p > 0.05) different from one another.
Table 1: Length-weight values and Fulton condition factor of Labeo cubie sampled from Site A.
|
Period |
Season |
N |
Length (cm) |
Weight (g) |
Condition factor (K) |
|
May 2018-Sept 2018 |
Rain |
22 |
31.68 ± 7.24a |
520.57 ± 11.81a |
1.74 ± 0.57a |
|
Oct. 2018- Dec. 2019 |
Dry |
20 |
30.61 ± 3.65a |
465.09 ± 13.49b |
1.72 ± 0.63a |
|
Jan. 2019- March 2019 |
Dry |
23 |
27.93 ± 9.38a |
453.71 ± 6.11b |
2.08 ± 1.04b |
|
Apr. 2019- May 2019 |
Dry |
33 |
30.09 ± 5.10a |
570.24 ± 10.07c |
2.11 ± 0.97b |
|
Jun. 2019- Sept. 2019 |
Rain |
22 |
32.78 ± 2.77a |
417.19 ± 10.06a |
1.18 ± 0.44c |
N = Number of fish sampled. Columns with different superscripts differs significantly from one another (p < 0.05).
Table 2: Length-weight values and Fulton condition factor of Labeo cubie sampled from Site B and C.
|
Period |
Season |
N |
Length (cm) |
Weight (g) |
Condition factor (K) |
|
May 2018-Sept 2018 |
Rain |
36 |
30.68 ± 7.24a |
517.57 ± 21.81a |
1.79 ± 0.63a |
|
Oct. 2018- Dec. 2019 |
Dry |
22 |
34.22 ± 3.65a |
405.09 ± 10.49b |
1.01 ± 0.72b |
|
Jan. 2019- March 2019 |
Dry |
20 |
26.61 ± 4.03b |
310.38 ± 5.31c |
1.65 ± 0.79a |
|
Apr. 2019- May 2019 |
Dry |
27 |
30.59 ± 8.49a |
515.09 ± 4.17a |
1.80 ± 0.41a |
|
Jun. 2019- Sept. 2019 |
Rain |
18 |
32.00 ± 1.48a |
434.00 ± 3.11b |
1.35 ± 0.92c |
N = Number of fish sampled. Columns with different superscripts differs significantly from one another (p < 0.05).
Table 3: Seasonal hematological parameter of Labeo cubie sampled from the lower Benue River.
|
Parameters |
Sampling site A |
Sampling site B and C |
||
|
Raining Season |
Dry season |
Raining Season |
Dry season |
|
|
RBC (x106. µL-1) |
3.01 ± 0.02a |
2.97 ± 0.10b |
2.82 ± 0.11b |
2.79 ± 0.01b |
|
PCV (%) |
22.19 ± 2.31a |
27.03 ± 4.75b |
23.41 ± 1.66a |
31.18 ± 4. 66b |
|
HB (g.L-1) |
8.17 ± 1.07a |
6.04 ± 1.55b |
8.29 ± 1.00a |
8.00 ± 2.10a |
|
MCV (fL) |
99.47 ± 4.68a |
195.7 ± 7.09b |
94.19 ± 2.77a |
190.3 ± 1.11b |
|
MCH (pg) |
20.83 ± 3.29a |
27.92 ± 6.02b |
17.41 ± 1.09c |
23.68 ± 4.21b |
|
MCHC |
17.09 ± 2.21a |
10.44 ± 1.73b |
16.88 ± 1.74a |
13.27 ± 1.19a |
|
Thrombocyte (x103. µL-1) |
2.04 ± 1.07a |
3.11 ± 1.01a |
2.10 ± 0.67a |
4.07 ± 1.20a |
|
WBC (x103. µL-1) |
4.43 ± 0.78a |
6.07 ± 0.95b |
3.98 ± 1.65a |
5.92 ± 1.01b |
|
Lym (x103. µL-1) |
3.01 ± 0.02 a |
3.58 ± 0.01a |
2.71 ± 0.10b |
3.97 ± 0.02a |
|
Neut (x103. µL-1) |
0.36 ± 0.01a |
0.63 ± 0.02b |
0.29 ± 0.03a |
0.97 ± 0.11c |
|
Mono (x103. µL-1) |
0.85 ± 0.03a |
1.43 ± 0.01b |
0.80 ± 0.01a |
0.93 ± 0.10b |
|
Eos (x103. µL-1) |
0.06 ± 0.0a |
0.12 ± 0.01b |
0.06 ± 0.01a |
0.08 ± 0.01a |
|
Bas (x103. µL-1) |
0.11 ± 0.01a |
0.31 ± 0.01a |
0.10 ± 0.0a |
0.05 ± 0.00b |
RBC = Total erythrocyte; PCV = Packed cell volume; HB = Haemoglobin concentration; MCV = Mean corpuscular volume; MCH = Mean corpuscular haemoglobin; MCHC = Mean corpuscular haemoglobin concentration; WBC = Total leucocytes count; Lym = Lymphocytes count; Neut = Neutrophils count; Mono = Monocytes count; Eos= Eosinophils count; Bas = Basophils count. Rows with different superscripts differs significantly from one another (p < 0.05).
Table 4: Seasonal serum biochemical parameter of Labeo cubie sampled from the lower Benue River.
|
Parameters |
Sampling site A |
Sampling site B and C |
||
|
Raining Season |
Dry season |
Raining Season |
Dry season |
|
|
Glucose (mg/dL) |
94.85 ± 6.11a |
100.2 ± 8.02b |
72.04 ± 2.87c |
98.70 ± 2.14b |
|
Total protein (g/dl) |
88.06 ± 3.11a |
83.60 ± 1.94a |
96.02 ± 5.09b |
83.51 ± 3.13a |
|
Albumin (g/dl) |
65.92 ± 4.12a |
60.74 ± 2.90b |
70.29 ± 1.23a |
37.94 ± 1.03c |
|
Globulin (g/dl) |
22.14 ± 4.01a |
22.86 ± 3.08a |
25.73 ± 1.90a |
45.57 ± 1.50b |
|
AST (I.U. L-1) |
89.73 ± 3.67a |
103.43 ± 7.09b |
90.54 ± 5.27a |
119.07 ± 3.44c |
|
ALT (I.U. L-1) |
44.81 ± 2.83a |
67.12 ± 4.27b |
47.00 ± 1.94a |
61.03 ± 6.09b |
|
ALP (I.U. L-1) |
64.29 ± 2.18a |
93.05 ± 6.55b |
70.51 ± 3.56c |
101.44 ± 2.71b |
|
UN |
20.82 ± 4.69a |
13.56 ± 1.93b |
27.19 ± 6.54a |
15.94 ± 2.00b |
|
Creatinine |
77.02 ± 3.77a |
83.41 ± 10.57a |
70.00 ± 1.74b |
95.5 ± 3.74c |
|
Uric acid |
2.81 ± 0.10a |
2.17 ± 0.22a |
1.98 ± 0.02a |
3.14 ± 0.01b |
AST = Aspartate amino transferase; ALT = Alanine amino transferase; ALP = Alkaline phosphatase; UN = Serum urea nitrogen. Rows with different superscripts differs significantly from one another (p < 0.05).
Table 5: Seasonal water quality parameters at the sampling site
|
Sampling site A |
Sampling site B and C |
|||
|
Parameter |
Dry season |
Raining season |
Dry season |
Raining season |
|
Dissolve oxygen (mg.L-1) |
7.5 |
8.0 |
7.5 |
7.8 |
|
Temperature (0C) |
32.0 |
27.6 |
29.7 |
28.1 |
|
pH |
7.5 |
6.9 |
7.5 |
7.0 |
|
Turbidity (cm) |
23.7a |
28.4b |
25.6a |
27.0b |
|
Electrical conductivity (µS/cm) |
27.4a |
15.6b |
29.1a |
17.4b |
|
Total Ammonia (mg.L-1) |
0.42 |
0.33 |
0.44 |
0.33 |
|
Nitrite (mg.L-1) |
0.01 |
0.01 |
0.01 |
0.01 |
|
Nitrate (mg.L-1) |
0.10 |
0.00 |
0.10 |
0.11 |
|
Phosphates (mg.L-1) |
0.046 |
0.031 |
0.039 |
0.042 |
Rows with different superscripts differs significantly from one another (p < 0.05).
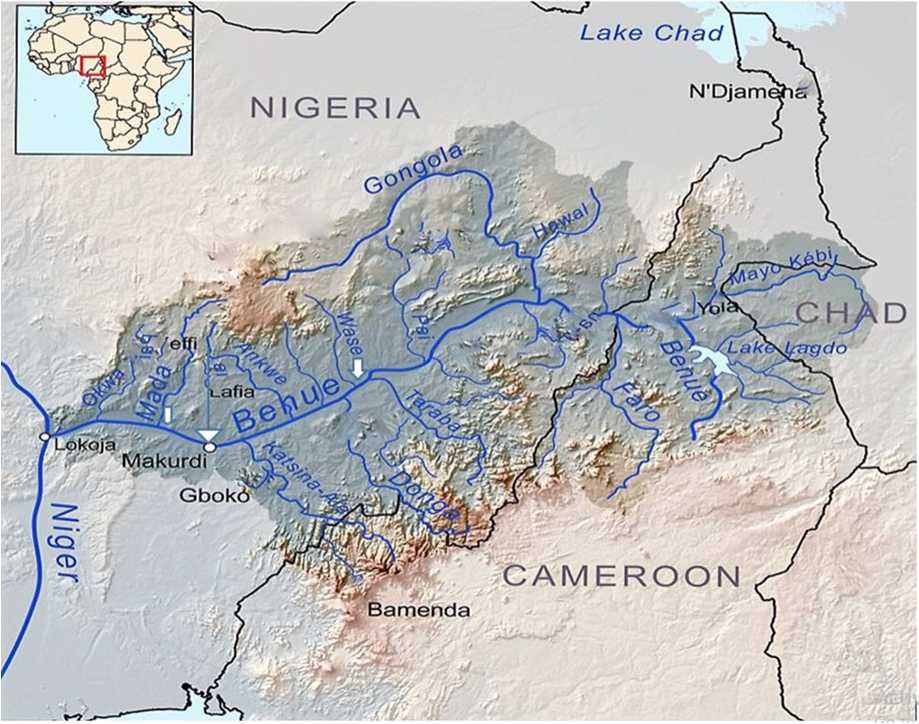
Figure 1. Benue River Basin showing sampling sites for Laboe cubie. Sampling site A (7044′N, 8032′E) Benue River. Sampling site B (8026′N, 10005′E) Discharge of Wase river into the Benue River and Sampling site C (7059′N, 7055′E) Discharge of the Mada river into Benue River. Source google maps 2019.
DISCUSSION
The sustainable management and conservation of the biodiversity of a fishery and other aquatic resources is strongly correlated with the availability of reliable and robust data of the length-weight and condition factor of the assessed stock (FAO, 2003; Poelen et. al., 2014). The results of the present study shows the sampled fish were longer and heavier in the raining season compared with their lengths and weights in the dry season. Further, the lengths, weights and condition factors of Laboe cubie obtained in our study were higher than the values reported by Adadu et. al., (2014) and Olufeagba et. el., (2016). This may be due to the fact that we sampled from near pristine locations, and therefore, we might have sampled from less fished stocks as fish length, weight and size are factors that has been reported to be influenced by genetic composition, health status, age, location (availability of food), and fishing intensity
(Wimberger, 1992; Fromentin and Fonteneau, 2001). Hence, the fish samples in the present study may be of a different age and or strain compared with the samples of the previous studies.
Although the results of the present study shows the condition factor of the sampled fishes to be generally greater than 1.0 in both sampling sites (which implies the sampled fish are in good conditions). The results also, reveals that fish sampled from site A were longer, heavier and had higher condition factor values compared with fish sampled from site B. This implies the availability of abundant food composition, excellent environmental variables and excellent feeding intensity and fish growth rate in site A compared with sampling site B (Akagbeso-Samson et. al., 2003; Monentcham et. al., 2009; Adeyemi and Akombo, 2012).
The influence of environmental variables on the haematological and serum biochemical parameters of some fish species have been reported (De Pedro et. al.,
2005; Fazio et. al., 2012; Pradhan et. al., 2012). The results of the present study shows that the, heamatological and serum biochemical parameters of Labeo cubie sampled from the Lower Benue river was significantly affected by environmental conditions present at the sampling sites. The values obtained for the total erythrocytes counts and haemoglobin concentrations were highest in the raining seasons, (a period when the sampled fish also exhibited the highest biometric parameters). This is similar to the report of Jewad et. al. (2004), who had reported that the erythrocytes count and haemoglobin contration increases with increase in fish size. Labeo cubie is a bentho-pelagic fish that require a high amount of energy for its feeding life style.
The erythrocytes are specialized cells that transport digested food and other metabolites around the body. Erythrocytes are also packed with heamoglobin. The haemoglobins are molecules needed for the transport of oxygen, carbon dioxide and other dissolved gases between the gills of fish and its environment. The difference in values for the total erythrocytes count and the heamoglobin concentration of the fish sampled from site A compared to those of sampling site B, may be a result of the variations in the physico-chemical parameters of the river water (Lahodey et. al., 2013). Hence the fish in site A due to their larger sizes, may need more erythrocytes and haemoglobin to meet their increased demand for oxygen and energy transports in agreement with the findings in Gabius niger (Fazio et. al., 2012), and Catla catla (Pradhan et. al., 2012).
The packed cell volume (pcv) is the percentage quantity of the cellular components per unit volume of blood. The pcv is reported to increase in periods of stress occasioned by low dissolved oxygen concentration of the culture water, high environmental (water) temperature and disease situations (Tavares-Dias and Moraes 2004; De Pedro et. al., 2005). The results of this study shows the values to be higher in the dry season compared with the raining season (in both sampling sites). Further, the pcv in fish sampled from site B were higher than those sampled from site A, suggesting the temperature and or the dissolved oxygen concentration in site A may be more favourable for the longevity of L. cubie. The eryhtrocytic indices (mcv, mch and mchc) are clinically relevant tools needed for the diagnosis of the state/type of anemia. These values are mathematical derived from the values reported for total erythrocytes count, haemoglobin concentration and the packed cell volume. Hence, they will also vary as already described for the already mentioned parameters.
The cells of the leucocytic series, also called the white blood cells are specialized cells involves in various aspects of the immune response. The relative increase or decrease in number of these cells therefore, reflects the presence of pathogens and or response of the fish host to the disease pathogen (Campbell, 2012). Further, leucocyte counts have been noted to increase under conditions of stress (Cataldi et. al., 1998). The total leucocytes count in the present study was higher in the dry season compared with the raining season in the sampling sites. This may be attributable to the changes in the physico-chemical parameters of the river as reported by (Fazio et. al., 2012; Fazio et. al., 2013; Pradhan et. al., 2012).
The serum chemical evaluations are essential in the assessments of the organ-systems in an animal. The results obtained from this evaluations in aquatic organisms, have been noted to vary with season due to intrinsic factors (like age, sex, maturity and health/disease status) and extrinsic factors such as the physico-chemical parameters of the water (Bullis, 1993). Serum glucose concentration is a common measure of the secondary stress response needed to meet the increased energy demands in flight or flee response to potential threats. The findings in the present study shows that, in both sampling sites, serum glucose concentration was higher in the dry season compared with the raining season. This may be indicative of stress conditions occasioned by poor physico-chemical parameters of the river waters (Fazio et. al., 2013).
Proteins are important molecules needed for the proper functioning of the body and its cells. The proteins are involved in specific immune defenses of the body and contributes to the maintenance of the acid-base balance and the protection of cellular integrity. According to Campbell (2012), the serum total protein concentration decreases under conditions of extreme food shortages due to its utilization as a source of energy. Serum total protein concentration may also decrease in disease conditions such as protein losing enteropathy and or severe parasitic infections. The serum total protein and albumin concentrations are reported to increases with increase in age and body weight/size (Fazio et. al., 2012; 2013). The serum total protein and serum albumin concentrations in this study were higher in the raining season compared to the dry season; this may suggest protein sparing due to abundant food availability in the raining season compared to the dry season (Fazio et. al., 2012). A similar explanation may account for the higher serum total protein values in fish sampled from site A compared to fish sampled from site B.
The transaminases (alanine aminotransferase ALT and aspartate aminotransferase AST) are protein metabolic enzymes needed for amino acid transamination. These enzymes are widely considered as useful biomarkers for hepatic disruptions in aquatic animals (Bullis, 1993; Roberts et. al., 2010). ALT catalyzes the transfer of amino group between L -alanine and α-ketoglutarate, while AST is responsible for the irreversible catalytic transfer of amino group between aspartate and glutamate. The presence of ALT and AST in higher than normal ranges in serum is indicative of hepatocellular degeneration and dysfunction (Robert et. al., 2010). The ALT and AST values obtained for fish sampled in the present study were higher in the raining season compared to the dry season, and due to the absence of serum chemistry data for healthy L. cubie in literature, we could not justifiably infer the reason for these increases.
Serum urea nitrogen is a product of protein catabolism and hence, a form for the excretion of protein nitrogen. Serum urea nitrogen is reported to increase following episodes of feeding; it reflects the plane of nutrition in fish (Bullis, 1993). The serum urea concentrations in the blood of fish sampled in the raining season were higher than those of fish sampled in the dry season. Fish sampled in the raining season exhibited higher weights and condition factor, signifying abundant feed and better feeding. This is in agreement with the report of Fazio et. al. (2012), who observed an increase in serum urea concentrations in actively feeding Grey mullet (Mugil cephalus).
Variations in the physico-chemical factors of the river (especially water temperature, turbidity and electrical conductivity) across seasons and sampling sites markedly affected the haematology and serum biochemistry of L. cubie in the Benue River, a similar finding by De Pedro et. al., (2005) in Tench ( Tinca tinca ). Further, these variations also affected the growth and condition factor of the fish as reported by Jawad et. al., (2004) in Indian Shad ( Tenualosa ilisha ).
CONCLUSION
The results of this study provide a knowledge of the haematological and serum biochemical parameters of Labeo cubie from two different natural habitats. It shows that fluctuations in some physico-chemical factors influence the haematology and serum biochemistry of this fish. The study represents the first attempt at providing a comprehensive data set for the health assessment of Labeo cubie . As such, the values reported in this study may serve as a valid point for future investigations gared towardsthe establishment of haematology and serum biochemistry reference range for Labeo cubie .
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors are thankful to Ms. Nancy Atsua (our local guide to the fishing sites and communities) and to Mr. John Ochete, Richard Oguche and Paulinus Idachaba for their technical support in fish catching and handling.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The Authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Список литературы Condition Factor, Haematology and Serumbiochemistry of Adult African Carp (Labeo coubie. Ruppell, 1832) from the Benue River Basin, Nigeria
- Adadu M.O., Omeji S. and Oyeniyi M.E. (2014) Food and feeding habits of condition factor of Labeo cubie (African Carp) in Lower River Benue. J. Glob. Bios. 3, 890- 894.
- Adeyemi S.O. and Akombo P.M. (2012) Diet and dietary habits of Labeo senegalensis in a tropical freshwater ecosystem. Animal Research Int. 9, 1502-1505.
- Akegbejo-Samsons F.O., George A. and Agbon A.O. (2003) Growth, reproduction and aquaculture potential of the African bonytonque fish (H niloticus) in ponds and reservoirs in coastal southwest states of Nigéria. In: International Conference of the Panafrican Fish and Fisheries Association, Cotonou, Benin, 10-14 November 2003.
- APHA (American Public Health Association). (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. 20th ed. Washington, DC: APHA.
- Ayotunde E.O., Stephen N. and Okey I. B. (2007) Parasitological examinations and food composition in the gut of feral African carp, Labeo coubie in the Cross River, Southeastern, Nigeria. Afr. J. Biot. 6(5), 625-630.
- Bullis R.A. (1993) Clinical pathology of temperate freshwater and Estuarine fish. In: Stoskopf MK (ed.), Fish Medicine. Saunders Company, USA. 232–323
- Campbell T.W. (2012). Haematology of fish. In: Thrall, M.A., Weiser, G., Allison, R., (eds.), Veterinary haematology and clinical chemistry. Ames (IA): John Wiley and Sons United Kingdom, pp. 293-312.
- Cataldi E., Di Marco P., Mandich A. and Cataudella S. (1998) Serum parameters of Adriatic Sturgeon Acipenser naccarii (Pisces: Acipenseriformes): Effects of temperature and stress. Comp. Bioch. Physiol. 20, 273–278.
- De Pedro N., Guijjaro A.I., Lopez-Patino M.A., Martinez-Alvarez R., Delgado M.J. (2005) Daily and seasonal variations in hematological and biochemical parameters in the tench, (Tinca tinca Linnaeus, 1758). Aqua. Res. 36, 1185-1196.
- De Weirdt D., Getahun A., Tshibwabwa S and Teugels G.G. (2007) Cyprinidae. Pages 466-572. in M. L. J. Stiassny, G. G. Teugels, and C. D. Hopkins (eds.), The fresh and brackish water fishes of Lower Guinea, West-Central Africa. Volume I. Collection Faune et Flore tropicales 42. Institut de Recherche pour le Développement, Paris, France, Muséum National d’Histoire Naturelle, Paris, France, and Musée Royal de l’Afrique Centrale, Tervuren, Belgium.
- Decie S.I.V. and Lewis S.M. (2006). Practical Hematology. 10th Ed., Churchill Livingstone, London. ISBN: 13: 978- 443, pp: 736.
- Duncan D. (1955) Multiple range and multiple F-tests. Biometrics, 11, 1-42. FAO Inland Water Resources and Aquaculture Service, Fishery Resources Division 2003. Review of the state of world fishery resources: inland fisheries. Food and Agriculture Organization Fisheries Circular No. 942: 1–60.
- Fazio F., Faggio C., Marafioti S., Torre A., Sanfilippo M., Piccione G. (2012) Comparative study of haematological profile on Gobius niger in two different habitat sites: Faro Lake and Tyrrhenian Sea. Cahiers De Biologie Marine 53, 213-219. Available: https://iris.unime.it/handle/11570/1953625.
- Fazio F., Marafioti S., Torre A., Sanfilippo M., Panzera M. and Faggio C. (2013) Haematological and serum protein profiles of Mugil cephalus: effect of two different habitat. Ichth. Res. 60, 36–42.
- Froese R. (2006) Cube law, condition factor and weight– length relationships: history, meta-analysis and recommendations. J. App. Icht. 22, 241–253. DOI 10.1111/j.1439-0426.2006.00805.x
- Froese R. and Pauly D. (eds.), (2018). Labeo coubie (Rüppell, 1832). FishBase. Available: http://www.fishbase.org/summary/Labeocoubie. html. (Accessed March 2018).
- Fromentin J.M. and Fonteneau A. (2001). Fishing effects and life history traits: a case study comparing tropical versus temperate tunas. Fish. Res. 53, 133–150. DOI 10.1016/S0165-7836(00)00299-X
- Gul Y., Gao Z.X., Qian X.Q. and Wang W.M. (2011). Haematological and serum biochemical characterization and comparison of wild and cultured northern snakehead (Channa argus Cantor, 1842). J. App. Icht. 27, 122–128. DOI: 10.1111/jai.2011.27.issue-1.
- Jawad L.A., Al-Mukhtar M.A. and Ahmed H. K. (2004) The relationship between haematocrit and some biological parameters of Indian shad, Tenualosa ilisha (family Clupeidae). Ani. Biod. Con. 27, 47–52.
- Jidere C.M., Okeke F.I. and Mohammed S.O. (2007) Determination of Agro-Ecological zones of Nigeria using current satellite information. Nig. J. Space Res. 4, 29-36.
- Lehodey P., Senina I., Calmettes B., Hampton J. and Nicol S. (2013). Modelling the impact of climate change on Pacific skipjack tuna population and fisheries. Clim. Change 119, 95-109. DOI 10.1007/s10584-012-0595-1
- Lévêque C. (2003) Cyprinidae. Pages 322-436 in Pauly D., Lévêque C and Teugels G.G (eds.), The fresh and brackish water fishes of West Africa Volume 1. Coll. faune et flore tropicales 40. Institut de recherche de développement, Paris, France, Muséum national d'histoire naturelle, Paris, France and Musée royal de l'Afrique Central, Tervuren, Belgium.
- Monentcham S.E., Kouam J., Pouomogne V. and Kestemont P. (2009) Biology and prospect for aquaculture of African bonytongue, Heterotis niloticus (Culvier, 1829): a review. Aquac. 289, 91-198.
- Neiffer D.L. and Stamper M.A (2009) Fish sedation, anesthesia, analgesia and euthanasia: considerations, methods and types of drugs. ILAR Journal. 50(4), 343-360. https://doi.org/10.1093/ilar.50.4.343
- Olaosebikan B.D., and Raji A. (1998). Field guide to Nigerian freshwater fishes. Federal College of Freshwater Fisheries Technology, New Bussa, Nigeria.
- Olufeagba S.O., Okomoda V.T. and Benny A.A (2016). Some Aspects of the Biology of Labeo Coubie Ruppell, 1832 and Labeo senegalensis Valenciennes, 1842 from Lower River Benue. J. Fish. Sc. 10(2), 049-054.
- Oniye S.J., Adebote D.A., Usman, S.K. and Makpo, J. K. (2006) Some aspects of the biology of Protopterus annectens (Owen) in Jachi Dam near Katsina, Katsina state, Nigeria. J. Fish. Aqua. Res. 1, 136-141.
- Pauly, D. (1983) Some simple methods for the assessment of tropical fish stocks. FAO Fisheries Technical Paper, (234), FAO Rome, Italy. Pius M.O. and Benedict, O. O. (2002) Food and Feeding inter-relationship. A preliminary indicator to the formulation of the feed of some Tilapine fishes. Trop. J. Anim. Sci. 5, 35-41.
- Poelen J.H., Simons J.D. and Mungall C.J (2014) Global Biotic Interactions: an open infrastructure to share and analyze species-interaction datasets. Ecol. Inform. 24, 148-159.
- Pradhan S.C., Patra AK., Sarkar B. and Pal A. (2012) Seasonal changes in hematological parameters of Catla catla (Hamilton 1822). Comp. Clin. Pathol. A 21, 1473-1487. DOI: 10.1007/s00580-011-1316-2.
- Prasad G. and Charles S. (2010) Haematology and leucocyte enzyme cytochemistry of a threatened yellow catfish Horabagrus brachysoma (Gunther, 1864). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 36, 435- 443.
- Roberts H.E (2010). Physical examination of fish. In: Roberts H E (ed.), Fundamentals of ornamental fish health. Ames (IA): John Wiley and Son; p 161-165.
- Roberts H.E., Scott Weber II E. and Smith S.A. (2010) Nonlethal Diagnostic Techniques. Chapter 17, PP: 172-184, of Fish Medicine, in: Roberts, H.E. (ed.). Fundamentals of Ornamental Fish Health. A John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., Publication, USA.
- Shinkafi B.A., Ukoha L.N. and Tukur N.A. (2013) Some Aspects of Growth and Reproduction in the Nile Perch (Lates niloticus, Linne 1762) From River Rima, Northwestern Nigeria. Nig. J. Fish. Aquac. 1, 31–41
- Tavares-Dias M and Moraes F.R (eds.) (2004): Hematology of Teleost Fish. Villimpress, Ribeirao Preto, Sao Paulo.
- Ugwumba A.A.A. (1988) Food and feeding habits of some culturable fish species in Nigeria. Technical Paper, Nigeria Institute for Oceanography and Marine Research, Lagos, Nigeria.
- Wimberger P.H. (1992). Plasticity of fish body shape, the effects of diet, development, family and age in two species of Geophagus (Pisces: Cichlidae). Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 45, 197-218.


