Currency risk management at companies of agro-industrial complex
Автор: Platonova Yu.Yu., Bondarenko T.N.
Журнал: Экономика и бизнес: теория и практика @economyandbusiness
Статья в выпуске: 3-1 (61), 2020 года.
Бесплатный доступ
This article examines the economic relations arising in the process of managing and minimizing currency risks. There was presented a comprehensive classification of currency risks and systematic methods of managing them. The commodity structure of Russian exports was analyzed and there was determined the current state of Russian exports of agricultural products. Moreover, based on the study and analysis of foreign and Russian experience in currency risk management, proposals were developed for comprehensive optimization of hedging methods and currency risk management on the example of an export-oriented enterprise in the field of agriculture.
Risks, currency risks, assessment tools, risk hedging, management optimization
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/170182491
IDR: 170182491 | DOI: 10.24411/2411-0450-2020-10190
Текст научной статьи Currency risk management at companies of agro-industrial complex
The actuality of this article due to the problem of optimization of hedging methods of currency risks of company`s that engaged in foreign economic activity. These companies are influenced by currency risk and the influence on them is no less than on large corporations.
Currency risk can have both positive and negative consequences, with the greatest impact on its appearance at the present time is the economic and political situation in the world. Therefore, a continuous assessment is essential to company's currency exposure, since the application of existing methods, techniques and tools is not able to completely rid the company's currency risk. It follows that, when any factors affect the currency risk, whether external or internal they are, it is advisable for economic entities to resort to the development of integrated management to reduce the currency risk by using a combination of methods and tools [1].
Currency risks have a significant impact on businesses at the micro and macro levels, as well as on the global scale.
So in figure 1, we show that from February 2019 to January 2020, the dollar and euro exchange rates declined moderately against the ruble. The most change in the value of the dollar occurred in August 2019 and October 2019, when exchange rate fluctuations exceeded 2,33 rubles, and the weakest one occurred in November. The most gain of euro rate was in October 2019, when it grew by 3,7%, and lost – in September 2019, when its value decreased by 3,45%.
In relation to the ruble rate and the Russian financial market as a whole, 2019 can be called a good year for the ruble. The reason of the strengthening of the national currency and the growth of stock quotes was the reduction of sanction risks and the inflow of foreign capital into ruble assets [2].
While in Russia, the main elements of hedging remain the use of derivatives, however, in China to control capital outflows of the yuan and to insure the national currency against the prospect of a strengthening of the strengthening of the US dollar.
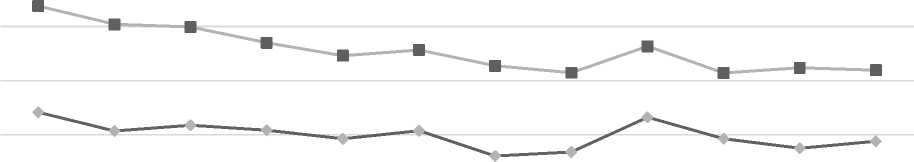
— — The US dollar ■ The Euro
Figure 1. Dynamics of the exchange rate of the dollar-ruble and the euro-ruble exchange rate from February 2019 to January 2020 [3]
According to table 1, we monitored the dynamics of the China's national currency, and noted that during February-December
2019, the Chinese currency weakened against the dollar by 4,86%, which will have a positive impact on exports.
Table 1. Dynamics of changes in yuan-dollar exchange rate for June 2019 – April 2020 [3]
|
Period |
Rate |
Change |
|
February 2019 |
6,7012 |
- |
|
March 2019 |
6,6936 |
-0,0076 |
|
April 2019 |
6,7114 |
0,0178 |
|
May 2019 |
6,7362 |
0,0248 |
|
June 2019 |
6,9053 |
0,1691 |
|
July 2019 |
6,8651 |
-0,0402 |
|
August 2019 |
6,8847 |
0,0196 |
|
September 2019 |
7,155 |
0,2703 |
|
October 2019 |
7,1318 |
-0,0232 |
|
November 2019 |
7,0396 |
-0,0922 |
|
December 2019 |
7,0269 |
-0,0127 |
Table 2. Analysis of solvency coefficients of Petrokhleb-Kuban L.L.C. for 2017-2018
|
Indicators |
The beginning of 2017 |
The beginning of 2018 |
The end of 2018 |
Change in 2017 |
Change in 2017-2018 |
|
1. Current assets, thousands of rubles |
241 430 |
309 047 |
406 497 |
67 617 |
165 067 |
|
2. Noncurrent Assets, thousands of rubles |
85 908 |
58 877 |
45 186 |
-27 031 |
-40 722 |
|
3. Short-term debt receivable, thousands of rubles |
167 640 |
118 549 |
174 127 |
-49 091 |
6 487 |
|
4. Cash and short-term financial investments, thousands of rubles |
1 673 |
5 132 |
3 521 |
3 459 |
1 848 |
|
5. Equity, thousands of rubles |
19 748 |
25 594 |
28 335 |
5 846 |
8 587 |
|
6. Current liabilities, thousands of rubles |
247 773 |
297 832 |
429 442 |
50 059 |
181 669 |
|
7. Cash ratio |
0,00675 |
0,01723 |
0,00820 |
0,01048 |
0,00145 |
|
8. Liquidity ratio |
0,68334 |
0,41527 |
0,41367 |
-0,26807 |
-0,26967 |
|
9. Current ratio |
0,97440 |
1,03766 |
0,94657 |
0,06326 |
-0,02783 |
|
10. Working capital financed by equity to total assets ratio |
-0,27403 |
-0,10770 |
-0,04145 |
0,16634 |
0,23258 |
|
11. Net current assets, thousands of rubles |
-6 343 |
11 215 |
-22 945 |
17558 |
-16 602 |
Table 3. Suggestions for the currency risk management system optimization of Petrokhleb-
|
Proposal |
Result |
|
Application of the VaR method to assess the impact of foreign exchange risk |
Preservation of a certain percentage of the proceeds due to fluctuations of the ruble and ensuring further development of Petrokhleb-Kuban L.L.C. |
|
Restriction of currency risks` concentration |
Setting of internal financial rules ensures the reduction of the risk of insolvency of enterprise Petrokhleb-Kuban LLC and reduces foreign exchange risk when performing transactions in foreign currency. |
|
Hedging foreign exchange risk through derivatives (options and forwards) |
Benefits from increasing floating interest rates, while the maximum losses from applying a currency option are limited by the premium In application of the forward contract unfavorable change of exchange rate will ensure maximum expenses of enterprise Petrokhleb-Kuban L.L.C. |
|
Application of the currency terms and conditions of a contract |
There is no financial cost involved. There is a possibility of the most comprehensive management of foreign exchange risk. There was flexibility with regard to payment terms. |
|
Placement of foreign exchange accounting in a company |
Simplifying the procedure for including exchange rate differences in the financial report. Obtaining objective information on the effectiveness of foreign exchange transactions. |
Table 4. Methodology of minimization of currency risks of Petrokhleb-Kuban L.L.C. based on the VaR method
|
Date |
Exchange rate, dollar/ruble |
Natural logarithm rate relation |
|
01.02.2019 |
67,0795 |
|
|
01.03.2019 |
65,3577 |
-0,026003223 |
|
01.04.2019 |
65,8895 |
0,008103836 |
|
01.05.2019 |
65,4176 |
-0,007187761 |
|
01.06.2019 |
64,6314 |
-0,012090975 |
|
01.07.2019 |
65,3834 |
0,011568043 |
|
01.08.2019 |
63,0541 |
-0,036275316 |
|
01.09.2019 |
63,4172 |
0,00574203 |
|
01.10.2019 |
66,6235 |
0,04932225 |
|
01.11.2019 |
64,6407 |
-0,030213125 |
|
01.12.2019 |
63,7748 |
-0,013486115 |
|
01.01.2020 |
64,4097 |
0,009906115 |
|
Volatility |
— |
0,000536177 |
|
VaR (with probability of 95%), rubles (k=1,65) |
— |
2,562878609 |
Futhermore, we focused on the impact of currency risks on companies engaged in foreign economic activity in the agricultural sector, namely, the company Petrokhleb-Kuban L.L.C.
The main activity of this organization is wholesale trade of agricultural products. To date, Petrokhleb-Kuban L.L.C shows successful interaction with both russian and foreign major partners [4].
Our focus was on the main foreign partners, among which we identified and marked the leader in terms of the number of transactions with Petrokhleb-Kuban L.L.C. – the Swiss company Aston FFI (Suisse) S. A. The
total value of contracts exceeds 16 million dollars, and this is only for the last 6 months.
To assess the impact of currency risks on Petrokhleb-Kuban L.L.C., we analyzed its financial condition.
In table 2, we analyzed the solvency coefficients of the analyzed enterprise, which showed a slight decrease in solvency, which is not critical, since some coefficients are within the norm, and a slight deviation from the norm does not affect the overall financial result. However, the company should pay more attention to the repayment of short-term obligations in order to maintain the positive dynamics of the company's solvency.
We also analyzed the dynamics and structure of indicators of the report on the financial results as a percentage of sales revenue of Petrokhleb-Kuban L.L.C. We noted that during the two analyzed periods, the company's revenue decreased by 1 830 552 thousand rubles, which was a change of 42,97%. This sharp decline in revenue was influenced by the adoption in May 2017 of the "Charter on agricultural products turnover" with the active participation of the Internal Revenue Service (IRS).
In order to assess the impact of currency risk of Petrokhleb-Kuban L.L.C., we analyzed the turnover balance sheet for 2019 and noted that there were 87 427, 87 dollars on the
company's currency account, which already shows the presence of currency risk. Speaking about the volume of currency in settlements with foreign partners, we have highlighted that the largest share of foreign currency is accounted for in 57.21, 57.22 and 62.21 subaccounts, where shares of 23,6%, 32,12% and 27,14% are concentrated on debits, respectively.
According to the analyzed information about Petrokhleb-Kuban L.L.C., we have been formulated the following proposals, presented in table 3, which will help to optimize the structure of currency risk management [5].
Table 4 shows the calculation of the value of VaR indicator, through which we got the amount of losses, which with a probability of 2.56 % does not exceed the established limit of 5 %. Moreover, we noted that it is necessary to control the VaR indicator at an ac-
ceptable level just like regular values of the dollar exchange rate update on the website of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation in real mode. This is the way to protect the company from 2.56 % of revenue losses only due to fluctuations of the ruble.
Further, we have shown the effectiveness of using derivatives to hedge currency risks on the example of an option, which is shown
in table 5. By applying this method, risk min imization amounted to 760 919,876 rubles.
Table 5. Effectiveness of currency risk insurance on the example of Petrokhleb-Kuban L.L.C. under various scenarios (purchase price – 529,760 dollars)
|
The way of settlement of foreign currency transactions |
Indicator |
Current rate |
Exchange rate of the ruble against the dollar |
|
Without hedging currency risk |
Exchange rate RUB/USD. |
58,5318 |
55,6717 |
|
Expenses, rubles |
0 |
0 |
|
|
Contract value, rubles |
31 007 806,37 |
29 492 639,79 |
|
|
Profit/loss, rubles |
— |
-1 515 166,58 |
|
|
Using currency risk insurance (foreign exchange option) |
Exchange rate RUB/USD. |
— |
58,9518 |
|
Expenses, rubles |
— |
976 745,90 |
|
|
Contract value, rubles |
— |
32 207 051,47 |
|
|
Profit/loss, rubles |
— |
760 919,88 |
Table 6. Detailed structure of the “Currency risk management policy for Petrokhleb-Kuban L.L.C.”
|
№ |
Structure |
Key aspects |
The content |
|
1 |
The general provisions |
|
|
|
2 |
The terms and definitions |
Systematization of terms used in the Policy and disclosure of their definitions. |
|
|
3 |
The objectives of the company |
Determing the direction of setting risk management objectives for the company. |
|
|
Key objectives in the area of risk management. |
ronments;
its stability on the international market;
|
||
|
Objectives of the integrated risk management framework |
eign exchange risk management framework;
business planning;
change risks;
consequences from already implemented currency risks. |
||
|
4 |
Principles of risk management |
Determination the principles for the development of a mechanism for managing currency risks. |
|
|
5 |
Stages of currency risk management |
Identification of stages of currency risk management, as well as direct implementation of risk management mechanisms |
|
|
I stage. Quantitative risk assessment and macroeconomic analysis. |
of currency risk;
carrying out macroeconomic analysis. |
||
|
II stage. Determining the appetite for currency risk. |
the highest structural level of the company;
efficiency;
goals and objectives at the lowest level of internal organization;
for managing currency risks;
employees). |
||
|
III stage. Development of hedging strategies. |
results;
currency risks;
|
||
|
6 |
Restrictions on currency risk man agement |
Identifying restrictions that affect risk management decision-making. |
- - lack of impact of integrated risk management on other existing functional areas; - - compliance with the complex management of the given set of tasks and requirements by the senior management; - - adaptation of the company to geopolitical, political, eco nomic environmental and legislative conditions. |
Список литературы Currency risk management at companies of agro-industrial complex
- Dmitrieva M.A. Valyutnyj risk: ot opredeleniya k klassifikacii // Rossijskoe predprinimatelstvo. - 2015. - T. 16. №15. - S. 2423-2436.
- Trends (Hedging currency risks) Marketing Core Investments & MACS. - [Electronic resource]. - URL: https://www.credit-suisse.com/pwp/am/downloads/marketing/trends_0203_en.pdf/ -March 2016
- Official website "WorldBankGroup". - [Electronic resource]. - URL: http://www.vsemirnyjbank.org/ (date 26.02.2020).
- Non-commercial partnership of professionals and participants of foreign economic activity "PROVED". - [Electronic resource]. - URL: http://proved-np.org/services/novosti/novosti_ved/ (date: 27.02.2020).
- Nikulina O.V., Krivosheina A.O. Razrabotka meropriyatij po minimizacii valyutnyh riskov predpriyatij APK v sfere zakupki importnyh materialov i oborudovaniya // Ekonomika i predprinimatelstvo. - 2014. - №24.


