Current state and development trends of the global institutions of the environmental sustainability of economy
Автор: Savkin V.I.
Журнал: Вестник аграрной науки @vestnikogau
Рубрика: Экономические науки
Статья в выпуске: 6 (99), 2022 года.
Бесплатный доступ
An ecological component in modern society becomes a basic one, since it provides fundamental foundations for the existence of each person. The methodological basis of the research is based on the synthesis of various approaches, methods and tools within the framework of the development of global institutions of environmental sustainability of the economy. The object of this research is the economic processes and phenomena that determine formation of global institutions of the environmental sustainability of the economy. The purpose of the research is to work out directions for the development through the formation of institutions for the environmental sustainability of the economy. The scientific novelty is in the author's characterization of the features of modern environmentally oriented development, as well as the proposed directions for the development of global institutions of environmental sustainability of the economy. The practical significance of the study is in the possibility of applying the developed directions of environmental development by government authorities in the formation of state policy ensuring sustainable development of the economy. The environmental component has not been and still is not a limiting factor in the economic growth. At the same time, the technological development has dramatically increased the negative impact on the environment. It is also important for the social development to be aimed at shaping ecological behavior using new transformational changes leading to managing and restoring ecosystems, while simultaneously promoting human well-being. The development of modern society takes place against the background of fundamental dysfunctions in key components that ensure the harmonious existence of mankind. The institutions of environmental sustainability of the economy can be considered as a new foundation in the management of socio-economic processes, which determines not only the growth of economic and social well-being. The solution of environmental problems in modern society should be a key factor, and its compliance with new living standards depends exactly on it. The transition to a new concept for the development of world institutions of environmental sustainability of the economy, taking into account the special role of ecology, can meet the needs of society without endangering future generations.
Sustainable development, social and ecological and economic development, human development, environmental sustainability institutions, environmental management
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147239359
IDR: 147239359 | УДК: 631.155.12 | DOI: 10.17238/issn2587-666X.2022.6.126
Текст научной статьи Current state and development trends of the global institutions of the environmental sustainability of economy
Introduction . The current stage of society’s development is characterized by many various processes, among which it is worth noting those that systemically affect the structures of society. The most vulnerable from the point of view of the prospects of any economy are the directions that ensure sustainable development, i.e., the social and environmental direction. The specificity of modern society also is in the fact that globalization is superimposed on the contradictory process of transformation, accompanied by deepening social inequality and the expanding environmental threats. The processes taking place in Russian society nowadays indicate the need for further research of the approaches that provide a synthesis of social and economic and environmental development. At the same time, the ecological component in modern society becomes principal, since it provides the fundamental foundations for the existence of every person, society and states.
The emergence of the concept of sustainable development is associated with the English economist Thomas Robert Malthus, who at the beginning of the 18th century expressed the hypothesis that population growth occurs exponentially, and the growth of food and resource production is arithmetic progression, and this can lead to negative consequences in the long term [1-4].
The ecological situation both in the world and in the Russian Federation is characterized by a high level of anthropogenic impact on the environment and significant environmental consequences of the economic activity [5]. Therefore, the formation of new trends in the development of the institutions of the environmental sustainability of economy, in our opinion, should be associated with an adequate subordination of the environmental component - the economic and social development of the society.
Conditions, materials and methods. The methodological base of the study is based on the synthesis of various approaches, methods and tools in the framework of the development of environmental sustainability institutions. The study used methods - analysis, synthesis, deduction and analogy. The object of research is the economic processes and phenomena that determine the formation of environmental sustainability institutions. The purpose of the work is to develop directions for the formation of world institutions for the environmental sustainability of the economy.
The scientific novelty is in the author's characterization of the features of modern environmentally oriented development, as well as the proposed directions for the development of world institutions of environmental sustainability of the economy.
The practical significance of the study is the possibility of using the worked out methodology for the ecological development of the economy by the economic management authorities in the formation of the state policy ensuring sustainable growth.
Results and discussion. The main organizational and management factor that affects negatively the environment is full absence or weak development of the institutions of the environmental sustainability of the economy. The system of the modern economy does not contribute to protection and sustainable use of natural resources and measures against pollution [6, 7]. The dynamics of the coefficient of environmental sustainability policies and institutions (one of the World Bank criteria that assesses the degree to which environmental policy contributes to the protection and sustainable use of natural resources and pollution control) shows that, it has been in the range of 3.1-3 .2 units since 2005 (Fig. 1). In this regard, the global concern about the negative impact of production on the environmental situation remains largely declarative and does not reach any real change in environmental policy and the development of sustainable development institutions. The ecological component of sustainable development in this case should be dominant in the ecological and economic system.
3,220
3,200
3,180
3,199
3,180
3,160
3,140
3,120 3,1123,110
3,115
3,100
2004 2006 2008 2010 2012 2014 2016 2018 20202022
years
The coefficient assesses the degree to which environmental policy contributes to the protection and sustainable use of natural resources and pollution control, from 1 - low to 6 - high.
Figure 1 3 Dynamics of the global coefficient of policies and institutions of environmental sustainability1
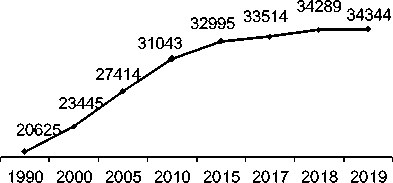
The economic development of the society has changed rapidly in recent decades. From 1960 to 2021, the global GDP increased from 1.39 to 96.1 billion US dollars, i. e. more than 50 times over 60 years (Fig. 2). Until recently, such a rapid boom had been largely limited only by the availability of resource potential (natural) and by the innovations that ensure the growth of labor productivity. The environmental component was not and still is not a limiting factor of the economic growth. At the same time, the technological boom has dramatically increased negative impact on the environment. According to the World Bank, from 1990 to 2019, CO2 emissions alone increased from 20625272.9 kt to 34344006.1 kt (Fig. 3). Comparing the dynamics of changes in world GDP with CO2 emissions into the atmosphere, one can observe a direct dependence of these indicators. This was especially evident in the period 1999-2015.
Modern social development as another important component of sustainable development implies an increase in the possibilities for the consumption of material, intellectual, spiritual and other resources by the population. In this regard, the most important condition is social development aimed at a qualitative change in human life. In many ways, the socio-economic development of the society in the twentieth century was associated with economic growth, which gave rise to an unprecedented impact on the environment. Humanity has faced contradictions between growing social needs and negative pressure on the environment.
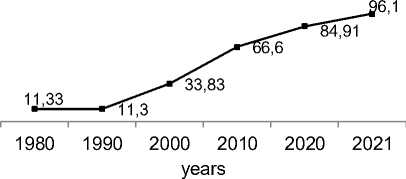
Figure 2 3 Dynamics of world GDP, billion US dollars2
years
Figure 3 3 Dynamics of global CO2 emissions, kt*10003
Overcoming dysfunctions in the "social development - ecology" system, as well as in the "economy - ecology" system, is possible only with a systematic representation of the processes taking place in the society. The Human Development Index (HDI), which measures average achievements in three main dimensions of human development (a long and healthy life, knowledge and a decent standard of living), to a greater extent reflects the dynamics of the social development of the society. According to the World Bank, for the period from 1990 to 2019, its value increased from 0.598 to 0.737 (the average annual increase in HDI for 1990-2019 was 123%) (Fig. 4). To a greater extent, this is determined by the fact that social incentives are associated with the needs of the economic nature, and their satisfaction is an internal incentive motive for the system of economic relations. I. Schumpeter wrote that “needs are both the cause and the guiding principle of economic behavior, and represent its driving forces” [8].
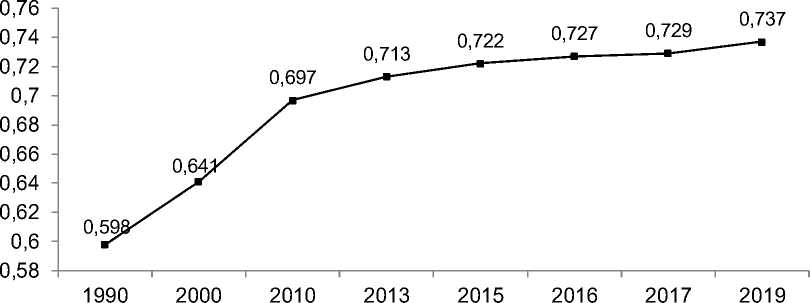
Human Development Index (HDI): A composite index that measures average achievement in three main dimensions of human development: a long and healthy life, knowledge and a decent standard of living. Average Annual HDI Growth: The smoothed annual HDI growth over a given period, calculated as an annual compound growth rate.
Figure 4 3 Dynamics of the world human development index (HDI *)4
Social development should focus on shaping ecological behavior using new transformational changes aimed at managing and restoring ecosystems, while at the same time promoting human well-being. The trend of social manifestation should be formed “from the bottom up”, since in this case many new environmentally oriented responsible initiatives are manifested in the economy.
The directions for the development of world institutions of environmental sustainability of the economy proposed by us are based on the fact that environmental development (the state of the environment) is a dynamic constant that determines the possibility (feasibility) and boundaries of economic and social growth. Understanding the existence of the problem of sustainable development, as shown above, does not lead to positive changes in solving environmental problems. In this regard, there is a need to restructure the perception of the dominant role of environmental problems. There are three main directions for the development of world institutions of the environmental sustainability of the economy: 1. recognition of the need to solve environmental problems, 2. development of environmentally- oriented vectors and alternatives, 3. implementation of decisions. The activities of world institutions of environmental sustainability of the economy should be based on the following principles: continuity, planning, consistency and efficiency. The interrelation of these principles ensures the development of optimal solutions and the adequate use of resource potential.
Conclusions. The development of modern society takes place against the background of fundamental dysfunctions in key components that ensure the harmonious existence of mankind. The development of global institutions for the environmental sustainability of the economy can become a new approach to the management of social and economic processes. The development of global institutions is framed by the existing gap in the components of sustainable development, which today determine only the growth of economic and social well-being with the simultaneous increase in the pressure on the environment. Understanding environmental problems in the modern society should be a key factor and its compliance with new living standards depends exactly on it. The transition to a new concept of the development of world institutions of environmental sustainability of the economy, taking into account the special role of ecology, can meet the needs of society without endangering future generations.
Список литературы Current state and development trends of the global institutions of the environmental sustainability of economy
- Anikin A.V. Malthus and Malthusianism // Youth of Science: Life and Ideas of Economic Thinkers before Marx. 2nd ed. M.: Politizdat, 1975. P. 266-274.
- Blaug M., Malthus Th.R. 100 great economists before Keynes: An introduction to the lives & works of one hundred great economists of the past. St. Petersburg: Economics, 2008. P. 187-190.
- Blaug M. Population, waning fertility and rent. Economic thought in retrospect. Economic Theory in Retrospect. M.: Delo, 1994. P. 62-81.
- Blaug M. Theory of overproduction. Economic thought in retrospect. Economic Theory in Retrospect. M.: Delo, 1994. P. 150-160.
- Fundamentals of state policy in the field of environmental development of the Russian Federation for the period up to 2030. Official website of the President of the Russian Federation // http://kremlin.ru/events/president/news/15177.
- Savkin V.I. Environmental management: solving the problem of sustainable development of rural areas // Management in Russia and abroad. 2018. No. 2. P. 64-68.
- Savkin V.I. Environmental management: the formation of a new methodology // Problems of theory and practice of management. 2015. No. 10. P. 84-89.
- Schumpeter I. Theory of economic development: translation from German. M.: Progress, 1982. P. 69.


