Дерматофитозы животных в регионах России: этиологическая структура и чувствительность возбудителей к антимикотическим препаратам
Автор: Маноян М.Г., Гуршева А.С., Габузян Н.А., Панин А.Н.
Журнал: Сельскохозяйственная биология @agrobiology
Рубрика: Ветеринарная микробиология, микология
Статья в выпуске: 2 т.59, 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Систематическое изучение этиологической структуры дерматофитозов животных позволяет отслеживать распространенность этих заболеваний, изменения в видовом составе возбудителей, выявлять не встречавшихся ранее этиологических агентов. Мы сосредоточили свое внимание на социально значимых дерматофитах, вызывающих инфекции не только у животных, но и у человека, их распространение - важная социальная проблема, особенно с учетом устойчивости таких патогенов к антимикотическим препаратам. Сведения о заболеваемости сельскохозяйственных и домашних животных дерматофитозами в Российской Федерации и о чувствительности возбудителей этих инфекций к антимикотикам ограничены. В представленном исследовании определена распространенность основных этиологических агентов таких патологий и их чувствительность к часто используемым антимикотическим препаратам. Всего в результате изучения 851 образца патологического материала от сельскохозяйственных и домашних животных из 27 регионов России мы выделили 311 изолятов и охарактеризовали по чувствительности к антимикотикам 125 изолятов дерматофитов. В составе родов Microsporum и Trichophyton обнаружено шесть видов. Анализ проб клинического материала выявил высокую распространенность дерматофитов (36,54 % от общего количества исследованных образцов). Представлены данные о чувствительности 125 изолятов M. canis , M. gypseum, T. verrucosum, T. mentagrophytes, T. equinum к тербинафину, кетоконазолу и энилконазолу. Доля изолятов M. canis , устойчивых к тербинафину, достигла 6,4 %, к кетоконазолу и энилконазолу - 5,6 %. Доля изолятов M. gypseum , устойчивых к тербинафину, составляла 0,9 %, к кетоконазолу - 4,9%, к энилконазолу - 4,5 %. Доля изолятов T. verrucosum , устойчивых к тербинафину, равнялась 2,6 %, к кетоконазолу - 0,9 %, к энилконазолу - 0 %. Среди изолятов T. mentagrophytes 4,2 % были устойчивыми к тербинафину, 3,2 % - к кетоконазолу и к энилконазолу, среди T. equinum 0,7 % оказались устойчивыми к тербинафину, 0,4 % - к кетоконазолу и 0,2 % - к энилконазолу. Полученные данные будут использованы при разработке методики для оценки рисков распространения резистентных видов грибных патогенов, общих для человека и животных, которая должна проводиться на постоянной основе.
Дерматофиты, чувствительность, антимикотики, тербинафин, кетоконазол, энилконазол, сельскохозяйственные животные, домашние животные
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142242450
IDR: 142242450 | УДК: 619:579.62 | DOI: 10.15389/agrobiology.2024.2.342rus
Текст научной статьи Дерматофитозы животных в регионах России: этиологическая структура и чувствительность возбудителей к антимикотическим препаратам
Классическими микозами называют заболевания человека и животных, вызванные патогенными грибами — дерматофитами (1, 2). К дерматофитам относят три близкородственных группы микромицетов: роды Micro-sporum , Trichophyton и Epidermophyton . Последний встречается существенно реже и вызывает в основном дерматофитозы у человека. Дерматофитов объединяет выраженная кератинофильность и способность к протеолитической деградации кератина. Благодаря этому свойству дерматофиты проникают в кератинизированные ткани — роговой слой эпидермиса и его производные, вызывая их разрушение (1-4). Возбудители дерматофитозов распространены повсеместно. Основной ареал обитания — почва (5), особенно богатая субстратом, содержащим кератин (шерсть животных, птичьи перья), многие виды циркулируют в популяциях животных (грызуны, пушные звери, собаки, кошки и т.д.) (6-10).
Большинство животных, окружающих человека, создают потенциальный риск как источники заражения дерматофитозом. Наибольшую эпидемиологическую опасность представляют домашние животные-компаньоны (собаки, кошки, мелкие грызуны), имеющие наиболее длительные и тесные контакты с людьми (11-14). Сельскохозяйственные животные (крупный и мелкий рогатый скот) (15, 16,), пушные звери (песцы, норки, кро-
∗ Исследование выполнено за счет гранта Российского научного фонда ¹ 22-26-00206,
лики, нутрии) (13, 14) — это основные резервуары грибов-дерматофитов в сельской местности. Спортивные животные (прежде всего лошади) также могут стать источником заражения для человека, особенно при растущей популярности конного спорта (17). Важную роль в персистенции возбудителей и распространении дерматофитозов играют дикие животные при контакте человека с ними (17, 18).
Среди дерматофитов, обнаруживаемых на кожном покрове животных, доминируют зооантропофильные виды, представляющие опасность для человека (14, 19, 20). Microsporum canis может присутствовать на кожном покрове кошек, собак, лошадей, пушных зверей; Trichophyton mentagrophytes выявляют у собак, грызунов, пушных зверей, лошадей, T. verrucosum — у крупного и мелкого рогатого скота; патогенный для человека вид M. gypsеum встречается на шерстном покрове лошадей, кроликов и собак; M. nanum ( Nannizzia nana ) поражает свиней (19, 21-23).
С ХХ века можно проследить тенденции в изменении этиологической структуры микроспории. До середины прошлого столетия преимущественно регистрируемыми возбудителями на территории Европы были антропофилы ( Microsporum ferrugineum ). В 2010-х годах сообщалось, что М. canis — наиболее часто выделяемый гриб при микроспории волосистой части головы у детей в Европе, США, Южной Америке, Японии, Израиле, в ряде арабских стран (15, 23). В то же время, по некоторым источникам, среди возбудителей микроспории в США и Западной Европе доминирует Microsporum audouinii (24-26).
Самый распространенный возбудитель микроспории в России — зоофильный гриб М. canis , второй по частоте встречаемости — антропо-фильный гриб М. ferrugineum . Заболеваемость микроспорией в 2003 году в Российской Федерации составила 49 случаев на 100 000 человек населения (27). М. canis вызывает заболевания у собак, кошек, обезьян и реже у других животных (28). М. canis вызывает дерматофитозы животных чаще, чем другие виды рода Microsporum (61,1 % дерматофитозов у собак, 61,4 % — у кошек) (23). По сообщениям тех же авторов, второй по частоте встречаемости возбудитель микроспории у собак и кошек — М. gypseum (соответственно 22,8 % и 22,1 % случаев). М. gypseum распространяется преимущественно через почву.
Трихофития у человека в настоящее время по частоте встречаемости в мире и в России уступает микроспории даже в регионах с традиционно высокой заболеваемостью трихофитией (Дагестан, Башкортостан, Узбекистан, Таджикистан, Туркменистан, Казахстан, Армения) (29-31). Так, в 2006 году на территории Российской Федерации зарегистрировали 2,1 случаев трихофитии на 100 000 человек. Наиболее часто трихофития встречается в Южном федеральном округе (5,7 и 6,7 случаев на 100 000 человек соответственно в 2005 и 2006 году). К наиболее часто встречающимся возбудителям трихофитии относятся грибы Trichophyton verrucosum , Trichophyton mentagrophytes , Trichophyton tonsurans, Trichophyton violaceum (29).
Гриб T. verrucosum поражает преимущественно крупный рогатый скот (КРС), у других животных заболевания, вызванные этим видом, встречаются очень редко. Соответственно, основную группой риска трихофитии, вызванной T. verrucosum , составляют сотрудники животноводческих ферм или люди, имеющие контакт с КРС, также отмечается, что основным природным резервуаром T. mentagrophytes служат мышевидные грызуны (31).
В последние годы наблюдается беспрецедентный рост устойчивости к антимикотическим средствам у паразитических грибов, вызывающих у человека тяжелые заболевания (32, 33). В группу риска прежде всего попадают люди с ослабленным иммунитетом. Международные научные и медицинские организации, отмечая эту проблему, указывают на необходимость усилить изучение резистентности к антимикотическим средствам, в том числе в ветеринарной сфере, поскольку некоторые социально значимые микозы передаются человеку от животных. Есть данные об устойчивых Trichophyton rubrum, М. canis и М. gypseum к азоловым препаратам (флуконазол, итраконазол, вориконазол), некоторые штаммы T. rubrum, T. mentaro-phytes и М. canis могут быть устойчивы к кетаконазолу и тербинафину (3335). Резистентность дерматофитов, которые являются истинными патогенами человека и животных, затрудняет лечение таких инфекций, что создает социальные проблемы (36-38).
К сожалению, актуальных достоверных сведений о заболеваемости сельскохозяйственных и домашних животных инфекциями, которые вызваны дерматофитами, в Российской Федерации очень мало, отсутствуют данные о чувствительности возбудителей таких инфекций к антимикотическим препаратам.
Настоящее сообщение представляет результаты впервые проведенного в России систематического изучения видового состава (851 проба из 27 регионов) и определения чувствительности 125 изолятов к наиболее часто применяемым антимикотикам. На основании полученных данных будут разработаны методики для оценки рисков распространения резистентных видов грибных патогенов, общих для человека и животных, которая должна проводиться на постоянной основе.
Цель работы — выявить наличие дерматофитоза у сельскохозяйственных и домашних животных, определить этиологическую структуру основных возбудителей этой патологии и провести скрининг чувствительности выделенных изолятов к антимикотическим препаратам.
Методика . Объектом исследования служили образцы клинического материала (всего 851), отобранного от домашних и сельскохозяйственных животных (шерсть, струпья, мазки с ушей и кожного покрова) с клиническими признаками заболевания или с подозрением на дерматофитоз. Пробы отбирали в течение 2022-2023 годов в ветеринарных лабораториях в регионах Российской Федерации.
Для микроскопического исследования кератинизированного материала применяли общепринятый метод раздавленной капли с предварительным осветлением и размягчением материала в 10 % растворе КОН. Препарат не фиксировали и не окрашивали. Микроскопию проводили методами светлого поля и фазового контраста (микроскоп Olympus BX-43, «Olympus Corpю», Япония; система фотодокументирования изображений, увеличение ½40-100). Для выявления элементов грибов (мицелии, микро- и макроконидии) в любом материале использовали люминесцентный краситель каль-кофлуор белый 0,1 % (18909-100vl-f18909-100ML-F, «Sigma-Aldrich», США).
Выделение и идентификацию изолятов осуществляли методом посева на плотных питательных средах Сабуро с хлорамфениколом (40 мкг/мл) и циклогексемидом (0,05 %) (M664, Sabouraud dextrose agar, «HiMedia Laboratories Pvt., Ltd.», Индия), Сабуро с селективной модифицированной добавкой для дерматофитов (FD176, Dermasel Selective Supplement) в соотношении 5 мл на 500 мл среды, сусло-агаре (М129, «HiMedia Laboratories Pvt., Ltd.», Индия), среде Чапека-Докса (М075, «HiMedia Laboratories Pvt., Ltd.», Индия), картофельно-глюкозном агаре (М96, «HiMedia Laboratories Pvt., Ltd.», Индия.). При дифференциации изолятов рода Trichophyton использовали среды Трихофитон агары ¹1-7 (М531-536, М152, «HiMedia
Laboratories Pvt., Ltd.», Индия). Для получения отдельных колоний исследуемую культуру пересевали на каждую из перечисленных питательных сред методом укола в центр чашки и культивировали при температуре 28 ° С в течение 14-21 сут.
Для морфологической идентификации изолята изучали следующие признаки: цвет колонии и ее реверса, структуру колонии (складчатость, фактура поверхности), скорость роста, диаметр колонии. Строение колоний описывали при визуальном осмотре и с использованием стереоскопического микроскопа Olympus SZX-7 («Olympus Corp.», Япония) при увеличении ½8-56.
Для изучения особенностей строения вегетативного мицелия и репродуктивных органов готовили серии микропрепаратов методом скотч-от-печатка. Препараты не окрашивали, исследование проводили методами светлого поля и фазового контраста (микроскоп Olympus BX-43, «Olympus Corp.», Япония).
Выявленные особенности макро- и микроморфологии сопоставляли с указанными в определителе микроскопических грибов (28).
Чувствительность изолятов к основным применяемым субстанциям — кетоконазолу, тербинафину и энилконазолу («Sigma-Aldrich Chemie GmbH», Швейцария) определяли согласно стандарту EUCAST e.def. 9.3.1 . Использовали 24-луночные полистироловые культуральные планшеты (N-702002, «Wuxi NEST Biotechnology Co., Ltd.», Китай) с рабочим объемом лунки 500 мкл.
В качестве питательной среды для дерматофитов использовали среду RPMI-1640 без бикарбоната с содержанием глюкозы 2,0 % («Sigma-Aldrich Chemie GmbH», Швейцария), забуференную морфолинпропан-сульфоно-вой кислотой (MOPS) («Sigma-Aldrich Chemie GmbH», Швейцария). Среду готовили в двойной концентрации, стерилизовали фильтрованием (диаметр пор 0,22 мкм) и хранили при температуре +2,0-8,0 ° С.
Навеску фармацевтических субстанций массой 128 мг разводили в 10,0 мл диметилсульфоксида (DMSO для культур клеток, «Wuhan Servicebio Technology Co., Ltd.», Китай), получая таким образом двойную стоковую концентрацию. Затем, учитывая концентрацию препарата в субстанции, готовили стоковый раствор с концентрацией 6400 мг/л и разведения 3200, 1600, 800 и 400 мг/л (соответствуют концентрациям препаратов 32, 16, 8 и 4 мг/л после разведения в питательной среде и добавления суспензии исследуемой культуры).
Готовые стоковые растворы двойной концентрации разделяли на аликвоты по 1,0 мл и до применения хранили при температуре - 70 ° С в пробирках для заморозки. В соответствии со стандартами EUCAST допускается хранение растворов препаратов до 6 мес без потери их активности.
Изоляты культивировали на скошенной в пробирках среде Сабуро (M063, Sabourand dextrose agar, «HiMedia Laboratories Pvt., Ltd.», Индия) в течение 7 сут при +28 ° С. Затем споры смывали дистиллированной водой, содержащей 0,5 % Tween 80 (объем/объем), их концентрацию доводили до 2,0Е + 05 спор/мл, подсчитывая в камере Горяева. Приготовленную суспензию не хранили и использовали в течение 1 ч.
Все штаммы дерматофитов в концентрации 2,0Е + 05 спор/мл находились в среде RPMI 1640. В лунках К+ (положительный контроль жизнеспособности культуры дерматофита) к питательной среде антимикотики не добавляли, в лунки контроля стерильности среды (К-, отрицательный контроль) помещали только питательную среду. Определяли чувствительность изолятов к четырем концентрациям каждого из антимикотиков — 32, 16, 8 и 4 мг/л. Планшеты накрывали крышками, культивировали при 32 °С в течение 5 сут. Визуально учитывали рост (или его отсутствие) культур в лунке, интенсивность роста сопоставляли с контролем К+. Регистрировали такие признаки роста, как наличие мицелия в лунке, пристеночного кольца, осадка на дне лунки. За минимальную ингибирующую (МИК) принимали концентрацию препарата, которая ограничивала рост исследуемой культуры не менее чем на 90 % (при подсчете в камере Горяева). Изоляты считали устойчивыми (R), дозозависимыми (DD) или чувствительными (S) к терби-нафину при росте для концентраций соответственно > 32, 16-32 и <16 мг/л, к кетоконазолу — при концентрациях > 16, 8-16 и < 8 мг/л, к энилкона-золу — при концентрациях > 16, 8-16 и < 8 мг/л. Тесты проводили в двух повторностях.
Для всех протестированных изолятов рассчитывали среднее геометрическое значение МИК90. Значения МИК препаратов для разных видов сравнивали с помощью повторных измерений, однофакторного дисперсионного анализа и апостериорных тестов Шеффе с использованием программного обеспечения SPSS версии 16 . Значения p < 0,05 считали статистически значимыми.
Результаты . Представленные нами данные охватывают лишь малую часть дерматофитозов животных на территории Российской Федерации, подтвержденных в 2022-2023 годах. Систематическое изучение этиологической структуры зоодерматомикозов позволяет отслеживать распространенность этих патологий, изменения в видовом составе возбудителей, выявлять не встречавшихся ранее этиологических агентов.
Исследование охватывало 27 регионов России (рис. 1).
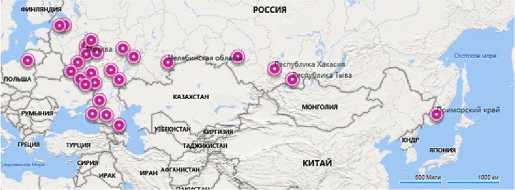
Рис. 1. Регионы Российской Федерации, из которых были получены образцы для исследования на наличие дермато-фитозов животных: Центральный регион — Белгородская область, Брянская область, Владимирская область, Воронежская область, г. Москва, Московская область, Калужская область, Курская область,
Липецкая область, Тверская область, Ярославская область (далее обозначены соответственно 1-11); Северо-Западный федеральный округ — Калининградская область, Ленинградская область, г. Санкт-Петербург (далее 12-14); Сибирский федеральный округ — Новосибирская область, Республика Тыва, Республика Хакассия (далее 15-17); Дальневосточный федеральный округ — Приморский край (далее 18); Южный федеральный округ — Краснодарский край, Ростовская область (далее 19, 20); Приволжский федеральный округ — Республика Марий Эл, Пензенская область, Саратовская область, Республика Татарстан (далее 21-24); Уральские федеральный округ — Челябинская область (далее 25); Северо-Кавказский федеральный округ — Республика Дагестан, Ставропольский край (далее 26, 27) (2022-2023 годы).
Выделение изолятов. Всего мы исследовали 851 пробу из 27 регионов России и выделили 311 изолятов дерматофитов (рис. 2).
Микроскопические грибы, относящиеся к дерматофитам (представители родов Microsporum и Trichophyton ), были выделены из 36,54 % полученных образцов и идентифицированы как Microsporum canis (M.c), Micro-sporum gypseum (M.g), Microsporum nanum (M.n), Trichophyton verrucosum (T.v), Trichophyton mentagrophytes (T.m), Trichophyton equinum (T.eq). Процентное соотношение, число и видовой состав основных выявленных нами дерматофитов представлены на рисунке 3.
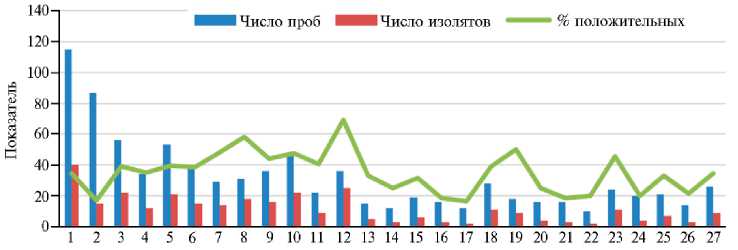
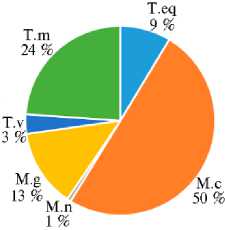
Рис. 3. Количественное соотношение идентифицированных видов дерматофитов (представителей родов Microsporum и Trichophyton ) среди 311 изученных изолятов (слева) и их распределение по регионам Российской Федерации (справа): 1-
Рис. 2. Число выделенных изолятов дерматофитов (по регионам Российской Федерации, 20222023 годы): 1-11 (см. рис. 1) — Центральный регион (число проб/число изолятов соответственно 115/40, 87/15, 56/22, 34/12, 53/21, 39/15, 29/14, 31/18, 36/16, 46/22, 22/9), 12-14 — СевероЗападный регион (36/25, 15/5, 12/3), 15-17 — Сибирский федеральный округ (19/6, 16/3, 12/2), 18 — Дальневосточный федеральный округ (28/11), 19, 20 — Южный федеральный окру (18/9, 16/4), 21-24 — Приволжский федеральный округ (16/3, 10/2, 24/11, 20/4), 25 — Уральский федеральный округ (21/7), 26, 27 — Северо-Кавказский федеральный округ (14/3, 26/9).
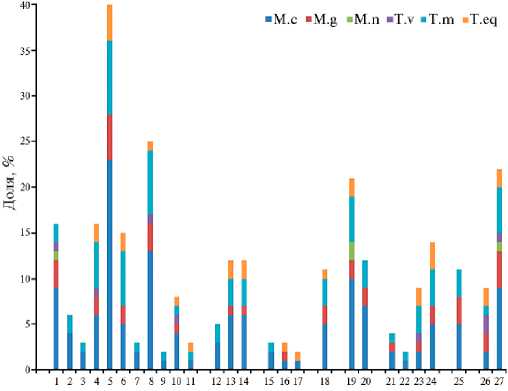
27 — регионы (см. рис. 1), в том числе 1-11 — Центральный регион, 12-14 — Северо-Западный регион, 15-17 — Сибирский федеральный округ, 18 — Дальневосточный федеральный округ, 19, 20 — Южный федеральный округ, 21-24 — Приволжский федеральный округ, 25 — Уральский федеральный округ, 26, 27 — Северо-Кавказский федеральный округ (2022-2023 годы).
Проведенный нами анализ проб клинического материала, отобранных от сельскохозяйственных и домашних животных, выявил высокую степень распространенности микроскопических грибов родов Microsporum и Trichophyton (как указано выше, 36,54 % исследованных образцов). Следует отметить, что данных о частоте регистрации клинических признаков дер-матофитозов у этих животных крайне мало, но такое количество выделяемых дерматофитных грибов указывает, как минимум, на высокий уровень миконосительства (39, 40). Переход от бессимптомного носительства к патологическому процессу возможен при определенных предрасполагающих факторах, таких как молодой возраст, иммуносупрессия, снижение естественной резистентности, дефицит питательных веществ, высокая температура окружающей среды при высокой влажности, травмы кожи. После проникновения через поврежденную кожу споры прорастают в роговом слое, а метаболиты грибов вызывают воспалительную реакцию в месте заражения (18, 41). Выделенные нами виды дерматофитов патогенны не только для животных, но и для человека (42-45).
Чувствительность к антимикотическим препаратам. Вы- бор препаратов при определении чувствительности 125 штаммов возбудителей дерматофитозов был обусловлен сведениями о зарегистрированных в Российской Федерации лекарственных средствах для ветеринарного применения (46).
Тиабендазол, энилконазол, миконазол и кетоконазол относятся к одной группе азоловых препаратов, обладают схожим механизмом действия, который заключается в инактивации одного из ферментов поздней стадии синтеза эргостерола — ланостерин-14 α -деметилазы (47, 48). Поэтому в настоящем исследовании мы использовали только энилконазол и кетоконазол. Тер-бинафин и нафтифин также представляют одну группу препаратов, это алли-ламины, которые инактивируют скваленэпоксидазу — фермент ранней стадии синтеза эргостерола (49, 50). Учитывая одинаковый механизм действия этих антимикотиков, мы ограничились изучением эффекта тербинафина.
1. Чувствительность к антимикотическим препаратам у изолятов дерматофитов, выделенных при исследовании патологического материала в 27 регионах Российской Федерации (2022-2023 годы)
|
Изолят |
Средние геометрические (GM) МИК 90 |
Концентрация субстанции, мг/л |
|
тербинафин кетоконазол энилконазол |
|
Microsporum canis ( n = 34 ) |
GM |
6,74 |
5,82 |
5,77 |
|
МИК 90 |
8 |
4 |
4 |
|
|
Диапазон |
4,0-32,0 |
4,0-32,0 |
4,0-32,0 |
|
|
Microsporum gypseum ( n = 30) |
GM |
6,52 |
5,70 |
5,78 |
|
МИК 90 |
8 |
4 |
4 |
|
|
Диапазон |
4,0-32,0 |
4,0-32,0 |
4,0-32,0 |
|
|
Microsporum nanum ( n = 2) |
GM |
2,71 |
2,10 |
0,00 |
|
МИК 90 |
8 |
4 |
0 |
|
|
Диапазон |
4,0-32,0 |
4,0-32,0 |
4,0-32,0 |
|
|
Trichophyton verrucosum ( n = 10) |
GM |
4,91 |
4,27 |
3,61 |
|
МИК 90 |
8 |
4 |
4 |
|
|
Диапазон |
4,0-32,0 |
4,0-32,0 |
4,0-32,0 |
|
|
Trichophyton mentagrophytes ( n = 28) |
GM |
6,51 |
5,63 |
5,59 |
|
МИК 90 |
8 |
4 |
4 |
|
|
Диапазон |
4,0-32,0 |
4,0-32,0 |
4,0-32,0 |
|
|
Trichophyton equinum ( n = 21) |
GM |
6,14 |
5,14 |
5,24 |
|
МИК 90 |
8 |
4 |
4 |
|
|
Диапазон |
4,0-32,0 |
4,0-32,0 |
4,0-32,0 |
Пр им еч ан и е. МИК — минимальная ингибирующая концентрация.
В нашем исследовании (табл. 1) средние геометрические значения МИК 90 по тербинафину для всех видов дерматофитов оказались существенно выше, чем полученные A.K. Gupta с соавт. (51) в 2003 году в аналогичных исследованиях. Отметим, что наибольшие средние геометрические значения МИК 90 по тербинафину выявлены для T. verrucosum и М. ca-nis — соответственно 6,51 и 6,74. Все изоляты продемонстрировали стабильно низкие средние геометрические значения МИК 90 (до 5,82) по энил-коназолу и кетоконазолу, а у М. nanum значение GM МИК 90 по энилкона-золу и кетоконазолу составило соответственно 0,00 и 2,10, что указывает на его чувствительность к препаратам. Среди изученных нами изолятов самую низкую чувствительность к энилконазолу продемонстрировали М. canis (GM МИК 90 = 5,77) и М. gypseum (GM МИК 90 = 5,78), самую высокую — T. equinum (GM МИК 90 = 3,61). Следует отметить, что M. gypseum и T. men-tagrophytes показали самую низкую чувствительность in vitro ко всем трем субстанциям (для M. gypseum GM МИК 90 от 5,70 до 6,52, для T. mentag-rophytes — от 5,59 до 6,51). У М. nanum GM МИК 90 по кетоконазолу и тер-бинафину были самыми низкими, что указывает на высокую чувствительность изолята к этим субстанциям.
Изоляты M. canis , M. gypseum , T. verrucosum , T. mentagrophytes , устойчивые к тербинафину, кетоконазолу и энилконазолу (имазилилу), были выявлены в 12 регионах России (табл. 2).
2. Регионы Российской Федерации с наибольшим числом изолятов дерматофитных грибов, устойчивых к основным антимикотическим препаратам, в отобранных образцах патологического материала (2022-2023 годы)
|
Регион |
M.c TBF |
M.c KET |
M.c EKZ |
M.g TBF |
M.g KET |
M.g EKZ |
T.v TBF |
T.v KET |
T.v EKZ |
T.m TBF |
T.m KET |
T.m EKZ |
T.e TBF |
T.e KET |
T.e EKZ |
|
г. Москва |
3 |
4 |
2 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
1 |
- |
- |
- |
|
Московская область |
- |
1 |
1 |
- |
1 |
1 |
1 |
- |
- |
1 |
1 |
1 |
- |
- |
- |
|
г. Санкт-Петербург |
2 |
1 |
3 |
- |
1 |
3 |
- |
- |
- |
4 |
1 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
Ленинградская область |
- |
2 |
- |
- |
2 |
- |
2 |
- |
- |
1 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
Краснодарский край |
3 |
3 |
2 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
2 |
3 |
2 |
- |
- |
|
|
Ростовская область |
3 |
1 |
- |
- |
2 |
3 |
1 |
- |
- |
- |
2 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
- |
|
Республика Татарстан |
1 |
2 |
3 |
- |
2 |
2 |
- |
- |
- |
2 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
Белгородская область |
1 |
1 |
1 |
- |
1 |
2 |
1 |
- |
- |
1 |
- |
- |
1 |
- |
|
|
Воронежская область |
2 |
1 |
3 |
- |
2 |
1 |
2 |
- |
- |
1 |
1 |
- |
- |
- |
|
|
Ставропольский край |
2 |
- |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
2 |
1 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
|
Саратовская область |
1 |
- |
1 |
1 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
1 |
- |
- |
- |
|
|
Курская область |
2 |
1 |
3 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
3 |
- |
1 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
- |
|
Всего |
20 |
17 |
20 |
3 |
13 |
14 |
8 |
3 |
- |
13 |
10 |
10 |
6 |
4 |
2 |
|
От числа изолятов вида, % |
58,8 |
50,0 |
58,8 |
10,0 |
43,3 |
46,7 |
80,0 |
30,0 |
- |
46,2 |
35,7 |
35,7 |
28,6 |
19,0 |
9,5 |
|
От числа выделенных изолятов, % |
6,4 |
5,6 |
5,6 |
0,9 |
4,9 |
4,5 |
2,6 |
0,9 |
4,2 |
3,2 |
3,2 |
0,7 |
0,4 |
0,2 |
П р и м е ч ани е. M.c — Microsporum canis , M.g — Microsporum gypseum , T.v — Trichophyton verrucosum , T.m — Trichophyton mentagrophytes , T.e — Trichophyton equinum ; TBF — тербинафин,
KET — кетоконазол, EKZ — энилконазол. Прочерки в таблице означают, что устойчивость не обнаружена.
Таким образом, проведенный нами системный анализ проб клинического материала, отобранных от сельскохозяйственных и домашних животных в разных регионах России (в Центральном, Северо-Западном, в Сибирском, Дальневосточном, Южном, Приволжском, Уральском и СевероКавказском федеральных округах) выявил высокую распространенность микроскопических грибов родов Microsporum и Trichophyton и рост числа устойчивых изолятов этих опасных возбудителей дерматофитозов. Например, М. canis — зооантропофильный вид, представляющий опасность для человека, имеет широкий круг потенциальных хозяев (15, 17). Среди изученных нами изолятов М. canis обладал самой высокой устойчивостью к антимикотическим препаратам. Аналогичные результаты были представлены в других публикациях (35, 52).
В современных условиях животные испытывают постоянное воздействие неблагоприятных внешних факторов, обусловливающих снижение естественной резистентности, в том числе из-за бессистемного, порой не оправданного применения противомикробных препаратов (53). Возросло число пород с врожденной дисфункцией иммунной системы; широкое распространение получили экзотические породы и даже виды животных, нетипичные для нашей климатогеографической зоны. Из-за интенсификации международных связей, климатических изменений, социально-экономических факторов существенно расширился ареал многих патогенных и потенциально патогенных грибов, в том числе эндемичных видов (53). Все это приводит к изменению этиологической структуры дерматомикозов животных, чем, в свою очередь, определяется актуальность ее мониторинга и оценки чувствительности возбудителей таких патологий, общих для человека и животных, к антимикотикам (с учетом тревожных данных о росте числа штаммов грибов, устойчивых к этим субстанциям). Устойчивые штаммы могут распространяться, передаваясь как от животного-носителя к другому животному напрямую при контакте, так и через почву в местах выгула, а также от животных к человеку. Этим определяется необходимость культурально-микологических исследований с выделением возбудителя в чистую культуру и определением его чувствительности к антимикотикам перед назначением фармакологической терапии. В большинстве случаев в ветеринарной практике препараты назначаются эмпирически, без определения чувствительности.
Итак, в образцах клинического материала (всего 851), отобранного в 27 регионах России от домашних и сельскохозяйственных животных (образцы шерсти, струпья, мазки с ушей и кожного покрова) с клиническими признаками или с подозрением на дерматофитоз, мы выявили высокую распространенность микроскопических грибов родов Microsporum и Trichophyton (обнаружено по три вида), что составило 36,54 %. Из 125 изолятов M. canis, M. gypseum, T. verrucosum, T. mentagrophytes, T. equinum доля чувствительных к основным субстанциям — тербинафину, кетоконазолу и энилконазолу составила более 6,0 % от общего числа выделенных. Доля изолятов M. canis, устойчивых к тербинафину, достигла 6,4 %, к кетоконазолу и энилкона-золу — 5,6 %. Доля изолятов M. gypseum, устойчивых к тербинафину, составляла 0,9 %, к кетоконазолу — 4,9 %, к энилконазолу — 4,5 %. Доля изолятов T. verrucosum, устойчивых к тербинафину, равнялась 2,6 %, к кетоконазолу — 0,9 %, к энилконазолу — 0 %. Среди изолятов T. men-tagrophytes 4,2 % были устойчивыми к тербинафину, 3,2 % — к кетоконазолу и к энилконазолу, среди T. equinum 0,7 % были устойчивыми к тер-бинафину, 0,4 % — к кетоконазолу и 0,2 % — к энилконазолу. Проведенный нами анализ клинического материала показал, что для эффективной и адекватной терапии дерматофитозов необходимо предварительно оценивать чувствительность выделенных культур возбудителей дерматофитозов животных к антимикотическим препаратам.
Список литературы Дерматофитозы животных в регионах России: этиологическая структура и чувствительность возбудителей к антимикотическим препаратам
- Moskaluk A.E., VandeWoude S. Current topics in dermatophyte classification and clinical diag-nosis. Pathogens, 2022, 11(9): 957 (doi: 10.3390/pathogens11090957).
- Moretti A., Agnetti F., Mancianti F., Nardoni S., Righi C., Moretta I., Morganti G., Papini M. Dermatophytosis in animals: epidemiological, clinical and zoonotic aspects. Giornale Italiano di Dermatologia e Venereologia, 2013, 148(6): 563-572.
- Paryuni A.D., Indarjulianto S., Widyarini S. Dermatophytosis in companion animals: а review. Veterinary World, 2020, 13(6): 1174-1181 (doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2020.1174-1181).
- Sylvén K.R., Bergefur A.L., Jacobson M., Wallgren P., Selling L.E. Dermatophytosis caused by trichophyton mentagrophytes complex in organic pigs. Acta Veterinaria Scandinavica, 2023, 65(1): 32 (doi: 10.1186/s13028-023-00695-w).
- Pontes Z.B., Oliveira A.C., Guerra F.Q., Pontes L.R., Santos J.P. Distribution of dermatophytes from soils of urban and rural areas of cities of Paraiba State, Brazil. Revista do Instituto de Me-dicina. Tropical de Sao Paulo, 2013, 55(6): 377-383 (doi: 10.1590/S0036-46652013000600002).
- Jartarkar S.R., Patil A., Goldust Y., Cockerell C.J., Schwartz R.A., Grabbe S,, Goldust M. Path-ogenesis, immunology and management of dermatophytosis. Journal of Fungi (Basel), 2021, 8(1): 39 (doi: 10.3390/jof8010039).
- Martinez-Rossi N.M., Peres N.T.A., Bitencourt T.A., Martins M.P., Rossi A. State-of-the-art dermatophyte infections: epidemiology aspects, pathophysiology, and resistance mechanisms. Journal of Fungi (Basel), 2021, 7(8): 629 (doi: 10.3390/jof7080629).
- Seyedmousavi S., Bosco S.M.G., de Hoog S., Ebel F., Elad D., Gomes R.R., Jacobsen I.D., Jensen H.E., Martel A., Mignon B., Pasmans F., Piecková E., Rodrigues A.M., Singh K., Vi-cente V.A., Wibbelt G., Wiederhold N.P., Guillot J. Fungal infections in animals: a patchwork of different situations. Medical Mycology, 2018, 56(suppl_1): 165-187 (doi: 10.1093/mmy/myx104).
- Cabañes F.J., Abarca M.L., Bragulat M.R., Castellá G. Seasonal study of the fungal biota of the fur of dogs. Mycopathologia, 1996, 133(1): 1-7 (doi: 10.1007/BF00437092).
- Boehm T.M.S.A., Mueller R.S. Dermatophytosis in dogs and cats — an update. Tierarztl Prax Ausg K Kleintiere Heimtiere, 2019, 47(4): 257-268 (doi: 10.1055/a-0969-1446).
- Cabañes F.J., Gallo M.G., Mancianti F., Tampieri M.P., Pinter L., Mignon B., Tomsíková A., Fabiková R., Weber A., Payá M.J., Cutuli M.T. Survey of cat and dog dermatophytosis in Europe. The ECMM working group report. “Trends in Medical Mycology”. Proceedings of the 9th Congress of the ECMM and 7th Trends in Invasive Fungal Infections. Bologna, 2003: 49-54.
- Moriello K.A., Coyner K., Paterson S., Mignon B. Diagnosis and treatment of dermatophytosis in dogs and cats: clinical consensus guidelines of the World Association for Veterinary Dermatol-ogy. Veterinary Dermatology, 2017, 28(3): 266-268 (doi: 10.1111/vde.12440).
- Kottferová L., Molnár L., Čonková E., Major P., Sesztáková E., Szarková A., Slivková M., Kott-ferová J. Fungal flora in asymptomatic pet guinea pigs and rabbits. Animals (Basel), 2022, 12(18): 2387 (doi: 10.3390/ani12182387).
- Chang C.C., Wechtaisong W., Chen S.Y., Cheng M.C., Chung C.S., Lin L.S., Lien Y.Y., Tsai Y.L. Prevalence and risk factors of zoonotic dermatophyte infection in pet rabbits in northern Taiwan. Journal of Fungi (Basel), 2022, 8(6): 627 (doi: 10.3390/jof8060627).
- Monod M., Fratti M., Mignon B., Baudraz-Rosselet F. Dermatophytes transmis par les animaux domestiques [Dermatophytes transmitted by pets and cattle]. Rev. Med. Suisse., 2014, 10(424): 749-753.
- Rambozzi L., Meneguz P.G., Molinar Min A.R., Pasquetti M., Peano A. Concurrent chorioptic mange and dermatophytosis in dairy goats: case report. Veterinary Sciences, 2022, 9(12): 677 (doi: 10.3390/vetsci9120677).
- Chermette R., Ferreiro L., Guillot J. Dermatophytoses in animals. Mycopathologia, 2008, 166(5-6): 385-405 (doi: 10.1007/s11046-008-9102-7).
- Weitzman I., Summerbell R.C. The dermatophytes. Clin. Microbiol. Rev., 1995, 8(2): 240-259 (doi: 10.1128/CMR.8.2.240).
- Nenoff P., Handrick W., Krüger C., Vissiennon T., Wichmann K., Gräser Y., Tchernev G. Der-matomycoses due to pets and farm animals: neglected infections? Hautarzt, 2012, 63(11): 848-858 (doi: 10.1007/s00105-012-2379-y).
- Moriello K.A. Dermatophytosis. In: Feline dermatology /C. Noli, S. Colombo (eds.). Springer, Cham, 2020: 265-296 (doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-29836-4_13).
- Nair S.S., Abhishek, Saini S., Chandana M.S., Sharun K., Athira V., Thomas P., Kumar B., Chaturvedi V.K. Dermatophytosis caused by Nannizzia nana (Microsporum nanum): a compre-hensive review on a novel pathogen. Brazilian Journal of Microbiology, 2023, 54(1): 509-521 (doi: 10.1007/s42770-022-00880-5).
- Carter M.E. Microsporum gypseum isolated from ringworm lesions in a horse. New Zealand Veterinary Journal, 1966, 14(7): 92-93 (doi: 10.1080/00480169.1966.33642).
- Murmu S., Debnath C., Pramanik A.K., Mitra T., Jana S., Dey S., Banerjee S., Batabyal K. Detection and characterization of zoonotic dermatophytes from dogs and cats in and around Kolkata. Veterinary World, 2015, 8(9): 1078-1082 (doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2015.1078-1082).
- Sacheli R., Adjetey C., Darfouf R., Harag S., Huynen P., Meex C., Descy J., Melin P., Arrese J., Hayette M.P. A one-year survey of Microsporum audouinii infections in Belgium: epidemiological and genotypic characterization. Clin. Microbiol. Infect., 2016, 22(3): 285.E9-285.E17 (doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2015.11.012).
- Kieliger S., Glatz M., Cozzio A., Bosshard P.P. Tinea capitis and tinea faciei in the Zurich area — an 8-year survey of trends in the epidemiology and treatment patterns. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology, 2015, 29(8): 1524-1529 (doi: 10.1111/jdv.12908).
- Donghi D., Hauser V., Bosshard P.P. Microsporum audouinii tinea capitis in a Swiss school: assessment and management of patients and asymptomatic carriers. Med. Mycol., 2011, 49: 324-328 (doi: 10.3109/13693786.2010.522602).
- Позднякова О.Н., Махновец Е.Н., Решетникова Т.Б., Немчанинова О.Б. Эпидемиология зооантропофильных дерматомикозов в городе Новосибирске. Проблемы медицинской микологии, 2003, 5(2): 64.
- de Hoog G.S., Guarro J., Gené J., Ahmed S., Al-Hatmi A.M.S., Figueras M.J., Vitale R.G. Atlas of clinical fungi, 4th edition. Hilversum, 2020.
- Фахретдинова Х.С., Медведева Е.А., Бурханова Н.Р., Гущина Р.Т. Динамика дерматомикозов в Республике Башкортостан в 1998-2003 гг. Проблемы медицинской микологии, 2004, 6(2): 124-125.
- Nussipov Y., Markabayeva A., Gianfaldoni S., Tchernev G., Wollina U., Lotti J., Roccia M.G., Fioranelli M., Lotti T. Clinical and epidemiological features of dermatophyte infections in Al-maty, Kazakhstan. Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences, 2017, 5(4): 409-413 (doi: 10.3889/oamjms.2017.124).
- Хисматуллина З.Р., Альхашаш С., Айдыбаева М.Г., Дагхамин И. Клинические проявления зооантропонозной трихофитии. Современные проблемы науки и образования, 2020, 5: 145 (doi: 10.17513/spno.30186).
- Fattahi A., Shirvani F., Ayatollahi A., Rezaei-Matehkolaei A., Badali H., Lotfali E., Ghasemi R., Pourpak Z., Firooz A. Multidrug-resistant Trichophyton mentagrophytes genotype VIII in an Ira-nian family with generalized dermatophytosis: report of four cases and review of literature. International Journal of Dermatology, 2021, 60(6): 686-692 (doi: 10.1111/ijd.15226).
- Gnat S., Łagowski D., Nowakiewicz A., Dyląg M., Osińska M. Complementary effect of mecha-nism of multidrug resistance in Trichophyton mentagrophytes isolated from human dermatophytoses of animal origin. Mycoses, 2021, 64(5): 537-549 (doi: 10.1111/myc.13242).
- Adimi P., Hashemi S.J., Mahmoudi M., Mirhendi H., Shidfar M.R., Emmami M., Rezaei-Matehkolaei A., Gramishoar M., Kordbacheh P. In-vitro activity of 10 antifungal agents against 320 Dermatophyte strains using microdilution method in Tehran. Iranian Journal of Pharmaceu-tical Research, 2013, 12(3): 537-545.
- Hsiao Y.H., Chen C., Han H.S., Kano R. The first report of terbinafine resistance Microsporum canis from a cat. Journal of Veterinary Medical Science, 2018, 80(6): 898-900 (doi: 10.1292/jvms.17-0680).
- Afshari M.A., Shams-Ghahfarokhi M., Razzaghi-Abyaneh M. Antifungal susceptibility and viru-lence factors of clinically isolated dermatophytes in Tehran, Iran. Iranian Journal of Microbiology, 2016, 8(1): 36-46.
- Hryncewicz-Gwóźdź A., Kalinowska K., Plomer-Niezgoda E., Bielecki J., Jagielski T. Increase in resistance to fluconazole and itraconazole in Trichophyton rubrum clinical isolates by sequential passages in vitro under drug pressure. Mycopathologia, 2013, 176(1-2): 49-55 (doi: 10.1007/s11046-013-9655-y).
- Manoyan M., Sololov V., Gursheva A., Panin A. Sensitivity of isolated dermatophyte strains to antifungal drugs in the Russian Federation. Journal of Fungi, 2019, 5(4): 95 9th Trends in Medical Mycology Held on 11-14 October 2019, Nice, France: P034 (doi: 10.3390/jof5040095).
- Ilhan Z., Karaca M., Ekin I.H., Solmaz H., Akkan H.A., Tutuncu M. Detection of seasonal asymptomatic dermatophytes in Van cats. Braz. J. Microbiol., 2016, 47(1): 225-230 (doi: 10.1016/j.bjm.2015.11.027).
- Hernandez-Bures A., Pieper J.B., Bidot W.A., O’Dell M., Sander W.E., Maddox C.W. Survey of dermatophytes in stray dogs and cats with and without skin lesions in Puerto Rico and confirmed with MALDI-TOF MS. PLoS ONE, 2021, 16(9): e0257514 (doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0257514).
- Segal E., Elad D. Human and zoonotic dermatophytoses: epidemiological aspects. Front Micro-biol., 2021, 12: 713532 (doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.713532).
- Beck W., Clark H.H. Zoophile Dermatophyten als Epizoonoseerreger und ihre Bedeutung in der Dermatologie [Zoophilic dermatophytes as epizoonoses pathogens and their significance to der-matology]. Hautarzt, 1998, 49(6): 457-461 (doi: 10.1007/s001050050770).
- Dworecka-Kaszak B., Biegańska M.J., Dąbrowska I. Occurrence of various pathogenic and op-portunistic fungi in skin diseases of domestic animals: a retrospective study. BMC Vet. Res., 2020, 16(1): 248 (doi: 10.1186/s12917-020-02460-x).
- Radentz W.H. Fungal skin infections associated with animal contact. Am. Fam. Physician., 1991, 43(4): 1253-1256.
- Dalis J.S., Kazeem H.M., Kwaga J.K.P., Kwanashie C.N. Prevalence and distribution of derma-tophytosis lesions on cattle in Plateau State, Nigeria. Veterinary World, 2019, 12(9): 1484-1490 (doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2019.1484-1490).
- Россельхознадзор. Государственная информационная система в области ветеринарии Ве-тИС. Режим доступа: https://vetrf.ru/. Без даты.
- Bhattacharya S., Esquivel B.D., White T.C. Overexpression or deletion of ergosterol biosynthesis genes alters doubling time, response to stress agents, and drug susceptibility in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. mBio, 2018, 9(4): e01291-18. (doi: 10.1128/mBio.01291-18).
- Pierson C.A., Eckstein J., Barbuch R., Bard M. Ergosterol gene expression in wild-type and ergosterol-deficient mutants of Candida albicans. Med. Mycol., 2004, 42(4): 385-389 (doi: 10.1080/13693780410001712016)
- Ryder N.S. Terbinafine: mode of action and properties of the squalene epoxidase inhibition. Br. J. Dermatol., 1992, 126(Suppl 39): 2-7 (doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1992.tb00001.x).
- Ryder N.S., Dupont M.C. Inhibition of squalene epoxidase by allylamine antimycotic com-pounds. A comparative study of the fungal and mammalian enzymes. Biochem. J., 1985, 230(3): 765-770 (doi: 10.1042/bj2300765.).
- Gupta A.K., Kohli Y. In vitro susceptibility testing of ciclopirox, terbinafine, ketoconazole and itraconazole against dermatophytes and nondermatophytes, and in vitro evaluation of combi-nation antifungal activity. Br. J. Dermatol., 2003, 149(2): 296-305 (doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2133.2003.05418.x).
- Aneke CI, Rhimi W, Hubka V, Otranto D, Cafarchia C. Virulence and Antifungal Susceptibility of Microsporum canis Strains from Animals and Humans. Antibiotics, 2021, 10(3): 296 (doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10030296).
- Маноян М.Г., Соколов В.В., Гуршева А.С., Габузян Н.А., Панин А.Н. Оценка рисков возникновения резистентности к антимикотическим средствам. Успехи медицинской микологии, 2019. 20: 431-436.


