Destruction of stable emulsions using nanodispersed fullerenes
Автор: Vakhitova R.I., Saracheva D.A., Kiyamov I.K., Sabitov L.S., Oleinik V.Iv.
Журнал: Нанотехнологии в строительстве: научный интернет-журнал @nanobuild
Рубрика: Исследование свойств наноматериалов
Статья в выпуске: 6 т.14, 2022 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Introduction. This article describes the results of the destruction processes studies of stable emulsion suspension sludge systems, conducted by the authors. Destruction processes are achieved by adding nanoparticles to demulsifying compositions. Currently, there is no universal composition demulsifier that effectively destroys emulsions formed in oil sludges. Research methods. To deal with this issues, the authors have conducted research on the creation of an effective demulsifier containing nanosized particles of fullerenes. The studies were carried out with dispersed oil-slurry emulsion-suspension systems, selected from open storage ponds of enterprises of JSC «Tatoilgaz» and JSC «TAIF-NK». For the destruction of the oil-containing system of the emulsion-suspension type, a composite mixture of complex action has been developed, which includes anionic wetting agents, nonionic surfactants, flotation reagents, detergents and alkaline buffer solutions that provide the required value of a constant indicator of the acid-base balance of the aqueous medium. Results and its discussion. A composite demulsifying mixture of complex action, which increases the effectiveness of the wetting washing action of surfactants, namely, the diphilic structure of the dispersed medium changes to hydrophilic, that is, the contacts of particles having a monophilic surface with the hydrocarbon phase of the emulsion medium are broken. When particles pass into the water volume from the phase separation boundary, the layer on the surface of the emulsified water is destroyed. The dehydration time of petroleum products is reduced by almost 2 times. Conclusion. During the research, the intensification and increase of the efficiency have been successfully reached.
Emulsion, demulsifier, fullerene, oil sludge
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142236271
IDR: 142236271 | УДК: 620.3: | DOI: 10.15828/2075-8545-2022-14-6-444-448
Текст научной статьи Destruction of stable emulsions using nanodispersed fullerenes
Original article
Currently, with the improvement and development of reagent technologies, there is a wide application of demulsifiers, surfactants, multifunctional reagents of complex action, demulsifying composites in systems for the collection, transport and preparation of superviscous oils, in the field of petrochemical technologies, in petroleum and gas processing plants during the technological processes of desalination and deep dehydration of oil field raw materials [1 - 9]. Nevertheless, researchers and scientists have failed to develop a demulsifier of a universal composition that provides enough efficiency in the destruction of emulsion water-oil systems, especially stable ones, formed by natural bitumen and super-viscous oils in various oilfields.
It is common practice to try to choose the most effective demulsifiers, to compose synergistic composite mixtures from various industrial reagents, but most often the required demulsification effect is not obtained.
The research is aimed at increasing the efficiency and intensity of the demulsification of oil-containing mixtures by dewatering stable oil-water emulsions, which include a large amount of mechanical impurities). As an object for research, we have selected emulsion-dispersed suspensions from oil sludge taken from open storage ponds at an oil sludge plant, and areas for dehydration of oil products, cleaning from silt) [10–12].
THE STUDY OF PROPERTIES OF NANOMATERIALS
The oil sludge sample in Unit 1 is a waste of oilfield preparation in various small oil companies and oil and gas production departments. The intermediate stable emulsion layers separated from the settling tanks are temporarily stored in the form of storage or slop oils in large volumes of tanks, open or closed containers. The volumes of stable emulsions are sent for further preparation and processing. (Oil sludge accumulates in large volumes at industrial plants, therefore, specific open-type storage ponds are built, where oil sludge is stored and settled. During the settling period, drainage of separated solids and water to the bottom of the pond also occurs).
It is found as a result of the research that the aggregate state of the emulsion is abnormally stable to the possibility of destruction, as well as a change in the pour point of the hydrocarbon volume, i.e. the state of oil sludge depends on the low salinity of bound water, high content of mechanical impurities, high-molecular and refractory paraffins and ceresins, resinous-asphaltene substances in the oil sludge.)
Changes in the mechanical properties of the oil sludge emulsion (pumpability, mobility) in blocks for supplying raw materials to oil sludge plants in winter contributes to equipment malfunction. According to the technological regulations, the operation of oil sludge plants is seasonal (spring, summer and autumn seasons), which limits the time of disposal of oil sludge waste.
In the oil sludge storage ponds, substandard products are collected in the desalination processes, oily waste from the deep processing of oil production wells and emergency oil spills. Samples were taken from storage ponds at various enterprises.
To destroy the oil-containing system of the emulsionsuspension type, a composite mixture of complex action (KMKA) has been developed, which includes anionic wetting agents, nonionic surfactants, flotation reagents, detergents and alkaline buffer solutions, which provide a constant indicator of acid-base equilibrium pH = 7/8 of the water environment (separated and emulsified water).
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE
When adding KMKA with a 250 g/t dosage to oil waste from oil sludge unit No. 1, the dehydrated oil sludge had the following composition: oil – 96.5% wt., Mechanical impurities – 1.2% wt., Water – 2.8% wt. Previously, oil sludge demulsification was carried out using various demulsifiers, such as Demulsifer, Reapon, Disolvan, Doufax, and Separol. All other things being equal, the oil sludge treated with demulsifiers had the following composition: mechanical impurities – not less than 2% wt., Water – more than 5% wt.
To increase the efficiency of oil sludge preparation, the authors propose to add nanodispersed carbon particles to the surfactant composition, which have a spatial spherical structure (fullerenes) and unique properties.
The C60 nanoparticle is the most widespread among fullerenes. This nanoparticle forms a closed spherical surface from regular polygons (pentagons and hexagons) [13–20].
After studying fullerenes of various industries, two control samples have been taken. At the initial stage of comparing identification fullerenes by the method of determining the mass concentrations of nanodispersed fullerenes as compositions. In this method, dilution is performed using high performance liquid chromatography. Toluene was used as an eluent. The photometric detection process was carried out in the range up to 324 nm.
Chromatographic analysis determined the composition of the samples. Sample No. 1 had the composition: fullerene С60 – 99.5%, С120О – partial presence, sample No. 2 had the composition: С60, С60О nanoparticles and heavy nanoparticles – С70, С70О, С76, С78, С84. The compositions of the samples under study are presented in Table.
According to their properties, fullerenes С70–С120 do not particularly differ from fullerene С60. However, they differ in the size of nanoparticles and in the spatial shape
Table 1
The composition of the control samples
|
Sample №1 |
||
|
Compounds |
Time, min |
Composition, % |
|
С60 |
8.500 |
99.520 |
|
С60О |
0.000 |
|
|
С70 |
0.000 |
|
|
С70О |
0.000 |
|
|
С120О |
20.270 |
0.480 |
|
Sample №2 |
||
|
Compounds |
Time, min |
Composition, % |
|
С60 |
7.690 |
61.240 |
|
С60О |
8.590 |
1.170 |
|
С70 |
12.530 |
34.710 |
|
С70О |
14.730 |
0.100 |
|
(С 76 , С 78 , С 84 ) |
17.420; 18.770; 19.570; 23.590 |
2.780 |
THE STUDY OF PROPERTIES OF NANOMATERIALS of a spherical structure, which tends to acquire an elliptical shape. The ability to easily capture atoms from other substances is at the heart of the processes of preparation, dosing and exposure to surface-active nanodispersed demulsifiers.
The preparation of nanodispersed surfactants was carried out using an acoustic rotor pulsating apparatus. To achieve maximum efficiency in the process of homog- enization of the nanodispersed medium, the optimal conditions for the operation of the acoustic apparatus were selected. It was found that for 10 days the aggregate stability of the studied nanodispersed mixture (0.5% fullerene was added to the KMKA) was 100%. In samples No. 1 and No. 2, spontaneous separation of the nanodispersed system was not observed even during centrifugation at a rotational speed of 3500 rpm and for 5 minutes.
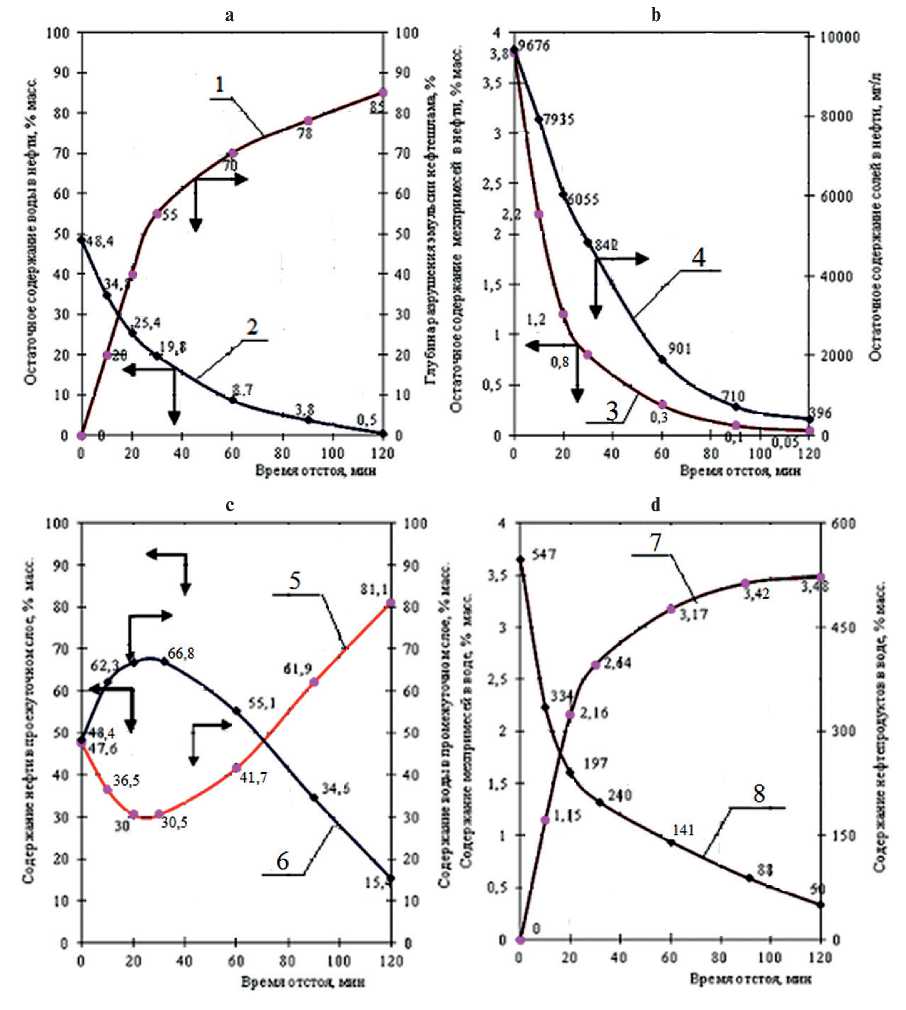
Fig. The process of destruction of oil sludge emulsion: graph 1 – the depth of destruction of the emulsion of oil sludge, %; graph 2 – residual water content in oil, % mass.; graph 3 – residual content of solids in oil, %; graph 4 – residual salt content in oil, mg/l; graph 5 – oil content in the studied layer, % mass.; graph 6 – water content in the studied layer, % mass.; graph 7 – the content of solids in water, % mass.; graph 8 – the content of petroleum products in water, % mass.
THE STUDY OF PROPERTIES OF NANOMATERIALS
The process of dispensing the demulsifying composition was carried out through the nozzle devices of the reagent dispenser using an aerosol, which makes it possible to uniformly distribute nanodispersed fullerene particles by surfactant molecules in the suspension-emulsion medium of the oil sludge under study.
The specific consumption of the created demulsifier (0.5% fullerene was added to the KMKA) for the destruction of oil sludge was 180 g/t of oil. During the storage period of oil sludge in open storage ponds, its fractional composition changes. Therefore, together with the demulsifying composition, a middle distillate fraction was used (n.c. – 350оC in a volume of 20% wt. For oil), which reduced the viscosity of the dispersed oil medium and intensified the destruction of the emulsion-suspension mixture.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The process of destruction of the oil sludge emulsion is shown in Figure 1. similar results were obtained when the destruction of the oil sludge mixture sampled in the storage ponds of TAIF-NK JSC.
As a result of the research, it was found that, despite the presence of a low content of water, salts, and mechanical impurities in oil (0.50 wt%; 396 mg/l; 0.050 wt%, respectively), the depth of destruction of the considered emulsion reaches 85% (Fig. a, b). This fact indicates the presence of an intermediate layer, which contains oil, mineralized water and particles of mechanical impurities (Fig. c). Therefore, during the preparation and processing of oil sludge in production conditions, it is necessary to organize a recycle in order to re-process the main stream and the intermediate (newly formed) layer. Also, drainage water must undergo additional processing from small dispersed globules of oil and mechanical impurities by settling and filtration, if necessary (Fig. d).
When analyzing the results of the process of destruction and separation of emulsion suspension oil sludge of control samples, the destructive ability of a composite demulsifying mixture in the composition with nanodispersed fullerene particles was theoretically substantiated.
When dosing the reagent into the oil sludge composition, fullerene nanoparticles, distributed uniformly in the volume of the demulsifier, entrain hydrophobic molecules of surfactants, facilitate transportation and diffusion processes in the continuous medium of the latter to the phase separation boundary, and increase adsorption on the smallest particles of mechanical impurities. These particles, in turn, act as emulsion stabilizers. At the same time, the detergent and wetting effect of surfactants is improved. The structure of the dispersed medium changes from diphilic to hydrophilic. In this case, the contacts with the hydrocarbon part of the emulsion are broken for particles with a monophilic surface. Then, from the phase separation boundary, the particles pass into the water volume, this process stimulates the destruction of the layers on the surface of the emulsified water. The process of dehydration of oil products begins to occur faster.
CONCLUSION
This paper examines the processes of destruction of stable emulsion suspension oil sludge systems, which are achieved by adding fullerene nanoparticles to demulsifying medium. When conducting experiments with control samples, the destructive ability of the proposed demulsifier in the composition with nanodispersed fullerenes in relation to stable emulsions has been demonstrated. It is possible to intensify and increase the efficiency of the oil dehydration process.
Список литературы Destruction of stable emulsions using nanodispersed fullerenes
- Chulkova A.O., Prochukhan K.Yu., Shafikova E.A., Apkarimova G.I., Prochukhan Yu.A. The effectiveness of demulsifiers in the destruction process of oil acid emulsions. Neftepromysl. Delo. 2016; 7: 26 – 29 (in Russian).
- Sladovskaya O.Yu., Otazhonov S.I., Galina L.A., Sladovsky A.G. Modern demulsifiers for the destruction of oil-water emulsions. Vestn. Tekhnolog. Un-ta. 2018; 21(2): 49 – 53 (in Russian).
- Kang W., Yin X., Yang H., Zhao Y., Huang Z., Hou X., Sarsenbekuly B., Zhu Z., Wang P., Zhang X., Geng J., Aidarova S. Demulsification performance, behavior and mechanism of different demulsifiers on the light crude oil emulsions. Colloid. Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects. 2018; 545:197 – 204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2018.02.055.
- Akberova A.F. Intensification of the process of destruction of stable oil-water emulsions using new effective composite demulsifiers. Neftegaz. Delo. 2019; 17(2): 68 – 73 (in Russian). https://doi.org/10.17122/ngdelo-2019-2-68-73.
- Akhmadova Kh.Kh., Takaeva M.A., Musaeva M.A., Syrkin A.M. The history of the development and use of demulsifiers in the extraction and preparation of oil for refining. Istoriya Pedagog. Estestvoznan. 2015; 1: 27 – 34 (in Russian).
- Cao J., Xu Z., Gong Q., Jin Z., Zhang L. Study on the emulsion stability of shengli oilfield chunliang crude oil. Shiyou Xuebao, Shiyou Jiagong. 2016; 32(5): 997 – 1004. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1001-8719.2016.05.018.
- Sladovskaya O.Y., Tsyganov D.G., Bashkirtseva N.Y., Mukhametzyanova A.A. Peculiarities of the process of destruction of stable water-oil emulsions in intermediate layers. J. Chem. Technol. Metallurg. 2018; 53( 2): 191 – 201.
- Grenoble Z., Trabelsi S. Mechanisms, performance optimization and new developments in demulsification processes for oil and gas applications. Adv. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2018; 260: 32 – 45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2018.08.003.
- Tyugaeva E.S., Dolomatov M.Yu. Reasons for the formation of stable oil emulsions and methods for their destruction. Universum: Tekhnich. Nauki. 2017; 4 (37): 64 – 69 (in Russian).
- Huseynova L.V., Huseynova M.A. The environmentally friendly technologies for oil sludge utilizing. Modern Sci. 2018; 3: 143 – 147.
- Nafikova R.A., Dikhtyar T.D. Improving the technology for the preliminary preparation of oil sludge for centrifugation using ultrahigh frequency currents. Neftepromysl. Delo. 2014; 4: 52 – 55 (in Russian).
- Gron V.A., Korostovenko V.V., Shakhrai S.G. The problem of the formation, processing and disposal of oil sludge. Usp. Sovremen. Estestvoznan. 2013; 9: 159 – 162 (in Russian).
- Shirinkin S.V. Fullerenes. History of discovery and use. Energiya: Ekonomika, Tekhnika, Ekologiya. 2013; 10: 63 – 66 (in Russian).
- Mikhailov A.G., Novikova E.E. Fullerenes as a modification of carbon: production methods and use. Rossiya Molodaya: Peredovye Tekhnologii – Promyshlennost’! 2013; 2: 289 – 292 (in Russian).
- Sodikov F., Tabarov S., Tuychiev Sh., Tuychiev L., Aknazarova Sh. Fullerenes C60 and C70 are surface-active substances. Vestn. Tadzhik. Nats. Un-ta. Ser. Estestvenn. Nauk. 2016: 1-3 (200): 88 – 90 (in Russian).
- Kel A.V. Fullerenes and carbon nanotubes. Innovatsion. Nauka. 2016: 11-3: 23 – 25 (in Russian).
- Altunina L.K., Svarovskaya L.I. Detergent compositions for oil sludge reclamation. Petrol. Chem. 2012; 52(2): 130 – 132. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0965544112010033.
- Saikia N.J., Sengupta P., Gogoi P.K., Borthakur P.C. Physicochemical and cementitious properties of sludge from oil field effluent treatment plant. Cement Concr. Res. 2001; 31( 8): 1221 – 1225.
- Deza M., Sikirić M.D., Shtogrin M.I. Fullerenes and disk-full-erenes. Russ. Mathemat. Surv. 2013; 68(4): 665 – 720. https://doi.org/10.1070/RM2013v068n04ABEH004850.
- Kroto H. C60, fullerenes, giant fullerenes and soot. Pure and Appl. Chem. 1990: 62(3): 407 – 415. https://doi.org/10.1351/pac199062030407.


