Determination of total ionization dose by ray trace analysis based on a geodesic sphere
Автор: Sherstennikova G.N., Shaura A.S.
Журнал: Сибирский аэрокосмический журнал @vestnik-sibsau
Рубрика: Авиационная и ракетно-космическая техника
Статья в выпуске: 1 т.19, 2018 года.
Бесплатный доступ
When designing the spacecraft, it is necessary to take into account the deleterious action of various factors in outer space. The main factor limiting active life of spacecraft is ionization radiation and it is the cause of most failures. Its influence is accompanied by ionization losses of the energy of charged particles in active and passive areas of semi- conductors and integrated circuits; that leads to emergence of radiation effects and it is characterized by the value of absorbed dose. At present there are several approaches to forecast the value of total ionization dose (TID): Monte- Carlo methods, methods that take into account only standard shield geometry (sphere, plane) and ray trace analysis (or sector-based analysis). The paper presents a modification of ray trace analysis that uses a geodesic sphere for sector construction and pro- vides regularly distribution of tracing rays in space unlike classical approach with using a parametrical representation of a sphere. Our approach enables to take into consideration real density of materials and allows using fewer sectors to meet the requirements of the method 154.PM-129 and keeping calculation accuracy. This is especially important for carrying out element-by-element radiation analysis taking into account heterogeneous protection through shielding of calculated point by elements of spacecraft design. This method is implemented as an extension for SolidWorks CAD. The input data for calculation are the following: 3d-model of equipment component as a part of spacecraft and radiation attenuation tables. The accuracy and the speed of the analysis depends on the number of tracing rays, and it is possible to carry out the calculation for several types of ionizing radiation at the same time. As an example of using the proposed method and a software module, we carried out radiation analysis of the block of the on-board digital computer for the spacecraft “Sfera”; its active life duration is 10 years on a high-elliptic orbit and 15 years on a geostationary orbit. As a result, we revealed that for the elements of the block minimum and maxi- mum total ionization doses differed substantially. It means that taking into account shielding properties of structural elements of device and blocks makes significant contribution to TID calculation.
Solidworks, total ionization dose, ray trace analysis, ionization radiation, geodesic sphere
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/148177807
IDR: 148177807 | УДК: 519.688
Текст научной статьи Determination of total ionization dose by ray trace analysis based on a geodesic sphere
Introduction. During the performance of their missions, spacecraft are exposed to various destabilizing factors affecting the availability of radio electronic equipment and its element base. Among the many known factors (space vacuum, micrometeorites, null gravity, infrared emission, etc.), the primary item limiting the active life of devices and the application of specific electronic components in on-board equipment is the ionizing radiation of outer space [1]. According to GSFC Space Science Mission Operations Team, 59 % of all space missions were affected by perturbations of “space weather”. Changes in space weather are mainly related to solar activity, which causes fluctuations in the radiation background of the Van Allen belts, resulting in temporary anomalies in the operation of satellites, important electronic components are destroyed, solar cells are being degraded, etc. In January 1994, two Canadian communication satellites (Telesat’s Anik E1, E2) were disabled in a geostationary orbit, similar anomalies occurred in January 1997 with Teslar 401 satellite, and in May 1998 with Equator-S, Polar and Galaxy-IV [2]. According to ESWW conference materials published in 2012–2015 [3], in the periods from 2001–2015, there were more than 10 failures of “Thaicom 5”, “Galaxy 15”, “AMC 14”, “Arabsat 4A”, “Artemis-Ariane 5”, “Inmarsat”, and according to the materials of “Central Research Institute of Mechanical Engineering” only in 2015 there were 30 failures. In this regard, the assessment of radiation resistance of products designed for space is a necessary development stage.
The main sources of ionizing radiation are cosmic rays, divided into solar, galactic (representing charged high-energy particles, born and accelerated beyond the limits of the solar system) and the natural radiation belts of the Earth [4]. Radiation is a stream of primary charged particles – electrons, protons and heavy charged particles, as well as secondary particles – products of nuclear transformations of primary charged particles.
The effect of ionizing radiation on radio electronic equipment is accompanied by ionization losses of particle energy in active and passive regions of semiconductors and integrated circuits; that leads to the manifestation of radiation effects [5]:
-
- dose effects in gradual degradation of electronic component parameters as a result of accumulation of absorbed dose;
-
- displacement effects caused by structural damage due to knockout atoms from the lattice point with subsequent degradation of the basic electrophysical characteristics of silicon;
-
- single effects, caused by the passage of a separate charged particle through the sensitive volume of a semiconductor.
Single radiation effects have a probabilistic nature; dose effects and displacement effects are cumulative, therefore, when creating modern spacecraft designed for the lifetime of 10–15 years with complex configuration, it is required to know the spatial distribution of the absorbed dose in the elements of spacecraft construction, taking into account their mutual screening.
At the present time there are several approaches to forecast the value of total ionization dose (TID): the Monte Carlo methods, which are based on modeling the trajectories of individual particles [6]; methods that take into account only standard shield geometry; and methods that use sectoring or the construction of tracing beams. The Monte Carlo methods allow to provide arbitrary protection and they directly model the material-radiation interaction, but they are the most difficult to implement and resource-intensive to use, although, as a rule, they use known libraries GEANT4 [7] and MCNPX [8]. Modeling only the simplest shield geometry (sphere, plane) implemented in the majority of known programs – CREME96 [9], COSRAD [10], SHIELDOSE [11], OMERE [12], does not allow to carry out element-by-element analysis and complex screening [13]. Therefore, in practice, it is the most reasonable to use the sectoring method (ray trace analysis), since it allows us to take into account the heterogeneity of protective properties of blocks, equipment and constructional elements of spacecraft in various directions, and it is much easier to implement then Monte Carlo methods.
Ray trace analysis. When performing element analysis to determine the value of the accumulated dose in accordance with branch standard 134–1034 [14], the ray trace analysis is used. Its algorithm is stated in 154. PM-129 [15] and consists of the following steps.
Step 1. On the element of block being considered, we select the point M where we need to determine the dose. The space around it is divided into a number of sectors with solid ωij angles (fig. 1), and in the direction of each ij sector we construct a tracing lij ray with the start at the design point M.
Step 2 . For each l ij ray we define the l ijk intersections with the elements of spacecraft construction, other blocks and components.
Step 3 . Taking into account the density ρ k of intersected bodies, we determine the effective protection Xi j in each ij direction:
K
X ij = ∑ l ijk ⋅ρ k . (1)
k = 1
Step 4 . After that, using the tables of attenuation, we determine the contribution D ( X ij ) ∙ ω ij of each sector to the final accumulated dose and carry out summation over all ij directions:
mn
D Σ = 21 π∑ i = 1 ∑ j = 1 D ( X ij ) ⋅ω ij . (2)
The key stages of the algorithm are the construction of tracing rays and the determination of their intersections with the elements of spacecraft construction.
Tracing ray construction. As a rule, to construct sectors and rays, the parametric representation of a sphere is most often used with the help of azimuth and zenith angles (UV – parametrization of the sphere, fig. 1). With this partition, the cells are different in shape and area, and the sectors are not only significantly different in magnitude, but their distribution in space is highly unequal: on the poles of the sphere there are more sectors and they are smaller than in the equatorial region (fig. 2, a ).
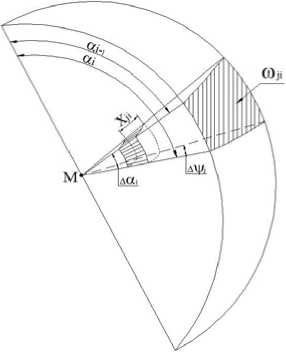
Fig. 1. The scheme of constructing sectors for UV-parameterization of a sphere [15]
Рис. 1. Схема построения секторов при UV-параметризации сферы [15]
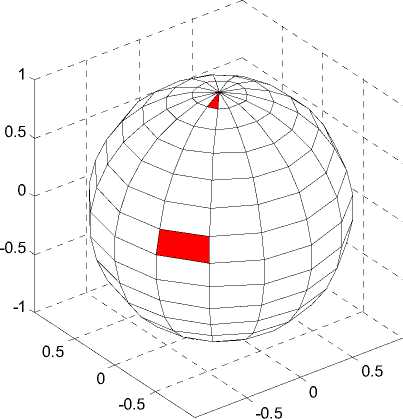
Fig. 2. Two-parametrical representation of a sphere: a – cells are different in form and area; b – unequal distribution of tracing rays
-1
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
-0.2
-0.4
-0.6
-0.8
-0.8 -0.6 -0.4 -0.2 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8
b
Рис. 2. Двухпараметрическое представление сферы: а – различные по форме и площади ячейки; б – неравномерное распределение трассирующих лучей
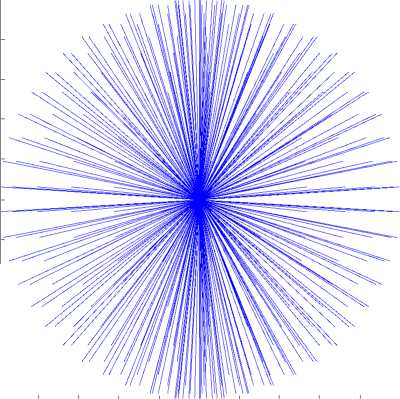
Increasing the number of sectors rises the ratio of maximum and minimum area of cells, and for 500–600 sectors the ratio is ten times. As a result, there is unequal distribution of rays, condensation on the poles and rarefied in the region of the equator (fig. 2, b ). In some cases, this inequality in the distribution of tracing rays in space leads to the dependence of the accumulated dose on the orientation of the divided sphere relative to spacecraft due to the presence of various kinds of holes, connectors, stiffeners, etc. in the models. In this regard, the requirement of the methodology 154.PM-129 [15] of ensuring equal protection within the sector is often ignored, so we refused this partition and turned to constructing sectors based on the geodesic sphere.
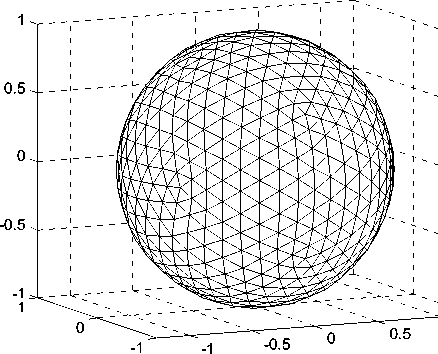
Geodesic sphere is a result of sphere triangulation using the method of recursive decomposition of icosahedrons (fig. 3). Its specific feature is that faces differ minimally from regular triangles and they are almost equal in area at the same time [16].
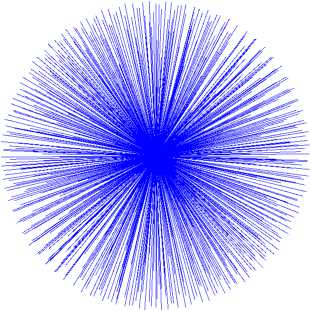
The number of faces and vertices of a geosphere depends on the triangulation order: the higher the degree of triangulation, the greater the number of faces and vertices of the geosphere. With the increase of triangulation order, the grid becomes smoother, and its faces approach the surface of the sphere (fig. 4, a). The tracing rays constructed on such a grid are uniformly distributed in space (fig. 4, b), and solid angles formed by the sectors are almost similar in size.
This approach allows us to use a smaller number of sectors to meet the requirements of the methodology 154. PM-129 [15] and maintain the accuracy of the calculation.
Definition of intersections. The next important step of the algorithm is to determine the intersections of rays with constructional elements. This is the most timeconsuming operation in terms of time and computing costs, so it does not make any sense to look for intersections of each ray with each body for complex 3D-models. However, using the algorithms of computational geometry it is possible to quickly determine whether the ray intersects elementary geometric bodies, such as a sphere and a rectangular parallelepiped [17].
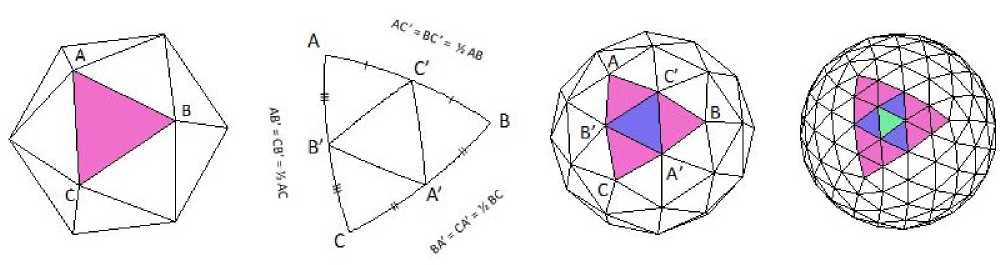
Fig. 3. The principle of geosphere construction by recurrent splitting of regular icosahedrons
Рис. 3. Принцип построения геосферы путем рекуррентного разбиения икосаэдра
0.5
-0.5
-1 1
Fig. 4. Geosphere application for approximation of spherical surface:
a – geodesic sphere (642 vertices and 1280 faces); b – the corresponding distribution of tracing rays
-0.5
-1
-0.5 -1
0 0.5
b
Рис. 4. Применение геосферы для аппроксимации сферической поверхности:
а – геодезическая сфера (642 вершины и 1280 граней); б – соответствующее распределение трассирующих лучей
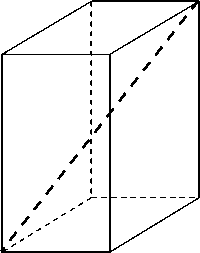
A rectangular parallelepiped with faces parallel to the coordinate planes can be circumscribed around any considered body of spacecraft models. Such a parallelepiped is uniquely determined by any two its vertices ( x – , y – , z – ) and ( x + , y + , z + ) adjacent to one of its diagonals. The ray with the start at the point ( x 0 , y 0 , z 0 ) and the directing vector ( l , m , n ) is described by a parametric system of equations:
' x = x 0 + It ,
■ y = y 0 + mt , (3)
z = z 0 + nt .
Let’s consider the relative position of the ray and each pair of planes parallel to the coordinate and containing opposite faces of the parallelepiped (fig. 5, a ).
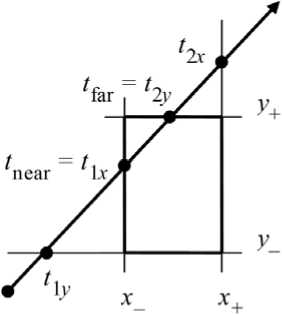
For the pair of planes x = x– and x = x+ parallel to the plane YZ , the ray given by the system (3), for l = 0, is parallel to them and does not intersect the chosen parallelepiped for x 0 < x – or x 0 > x + . Otherwise, we calculate the relations:
x_ - x x. - x0
t =----- 0 and t2, =—--- 0.
1 x 2 x
Suppose t 1 x < t 2 x , subsequently t near = t 1 x , and t far = t 2 x (fig. 5, b ). Assuming that m ≠ 0, and considering the second pair of y = y– and y = y+ planes containing the faces of the parallelepiped, we find the values t 1y and t 2y :
t i y = y^yOL and 1 2 y = y +Z y L.
mm
If t 1 y > t near , then t near = t 1 y , and if t 2 y < t far , then t far = t 2 y . For t near > t far or t far < 0, the ray does not pass through the parallelepiped. Assuming that n ≠ 0, we consider the last pair of planes z = z – and z = z + and find t 1 z and t 2 z :
t 1
z
^^^^^^B
1 z
n
and t 2 z =
z + - z 0
n
If as a result of similar comparisons we get 0 < t near < t far or 0 < t far , in this case the ray intersects the selected parallelepiped, and further it makes sense to look for possible intersections of the ray with curvilinear surfaces of the body inscribed in this parallelepiped to determine the entry and exit points of the ray, segments of its path inside the body.
To determine intersections with curved surfaces, we can use the built-in functions IModelDoc2 :: RayIntersections and IModelDoc2 :: GetRayIntersectionsPoints from Solid-Works.Interop.sldworks in API SolidWorks [18].
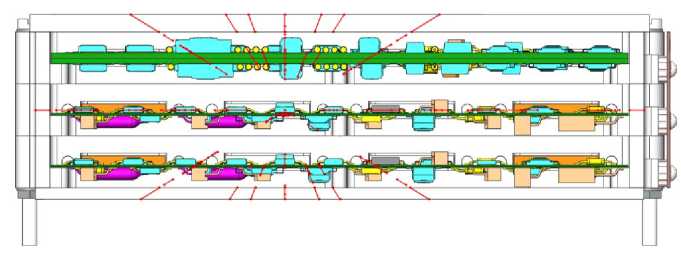
Having found all the intersections, we need to calculate the effective protection in each direction. Fig. 6 shows an example of tracing rays passing through the elements and the parts of a real block construction. On the selected fragment the beam passes through 4 bodies: a microcircuit, two layers of a board and a block cover.
Knowing the li j k segments traversed by the ray in the intersected bodies of the model, and the apparent densities ρ k of these bodies (fig. 6, b ), we determine the effective protection X ij in the ij direction by the formula (1). Next, we determine the total accumulated dose of ionizing radiation (2).
Software implementation. From the point of view of a design engineer, it is most convenient to calculate accumulated doses of ionizing radiation directly in CAD used for the design, an engineer makes changes in the design and arrangement of individual blocks, calculates and introduces protective screens. We used SolidWorks, therefore we created a calculation module for it that allowed us to use the available CAD capabilities and at the same time solve new tasks effectively. As input data for for the calculation we used 3D-model of the spacecraft block and the tables of attenuation given in the technical enquiry.
(+)
b
Fig. 5. General concept of definition of the intersection points of a ray and a rectangular parallelepiped [17]: a – defining a rectangular parallelepiped by means of two vertices adjacent to one diagonal; b – relative position of a ray and each pair of the parallel planes containing opposite faces of parallelepiped
a
Рис. 5. Общий принцип определения точек пересечений луча и прямоугольного параллелепипеда [17]: а – задание параллелепипеда с помощью двух вершин, прилежащих к одной диагонали; б – взаимное расположение луча и каждой пары параллельных плоскостей, несущих противоположные грани параллелепипеда
a
Fig. 6. Example of tracing rays passing through constructional elements of the block: a – cut-away view of the block and rays; b – line segments lijk passed by the ray in constructional elements and apparent densities of materials ρ k corresponding to them
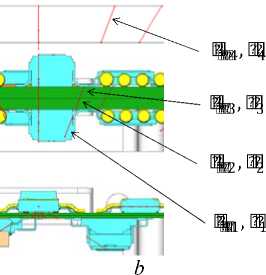
Рис. 6. Пример прохождения трассирующих лучей через элементы конструкции блока: a – общий вид блока и лучей в разрезе; б – отрезки li j k , проходимые лучом в элементах конструкций, и соответствующие им объемные плотности материалов ρ k
a
b
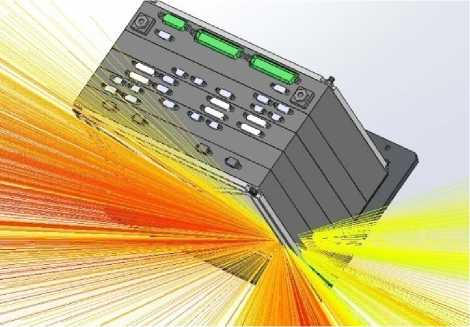
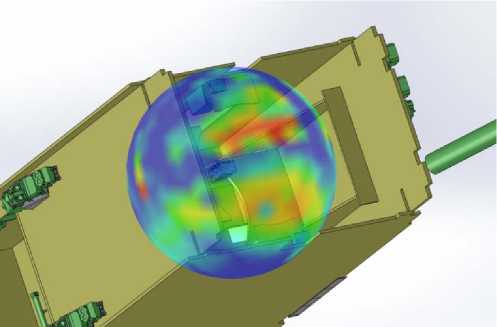
Fig. 7. Visual representation of calculation results: a – directions making the greatest contribution to a total ionization dose; b – general representation of space distribution of effective protection
Рис. 7. Визуальное представление результатов расчета: a – направления, вносящие наибольший вклад в накопленную дозу; б – общее представление о пространственном распределении эффективной защиты
The calculation can be performed simultaneously for several types of ionizing radiation (protons, electrons, total impact), while the number of tracing rays can be chosen in advance, thus determining the accuracy and the speed of the analysis.
The results can be presented visually in order to simplify the task of identifying the weakest points in the design of protection. Fig. 7, a shows the course of the rays, colored in accordance with their contribution to the total dose, by applying the filter to select the most dangerous directions. The projection of effective protection of each sector on the spherical shell circumscribed around the analyzed block is presented in fig. 7, b .
Analysis of results. As an example of the use of the proposed method and software module, we carried out a radiation analysis of the on-board digital computer sys- temblock for “Sfera” spacecraft with active life duration 10 years in a highly elliptical orbit and 15 years in geostationary orbit. We analyzed more than 400 sensing elements, while the 3D-model of the block of the spacecraft included more than 2500 bodies.
Increasing the fineness of splitting and the number of rays straining after greater accuracy significantly influences the time of the analysis, so in this case it is always necessary to look for the compromised solution between the desired accuracy and admissible duration of calculation. The graphs (fig. 8) show that the computation time increases exponentially with increase of the number of rays. At the same time, the accuracy of the calculation increases as well, but, for example, at 10 000 rays the decrease of the maximum deviation of accumulated doses from 7 to 3 % requires 4 times more time.
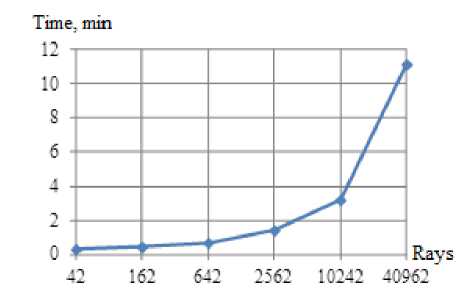
Fig. 8. Duration and accuracy of calculation depending on the number of rays: a – calculation time for a one point;
b – average (AVG) and maximum (MAX) value of accumulated dose deviations
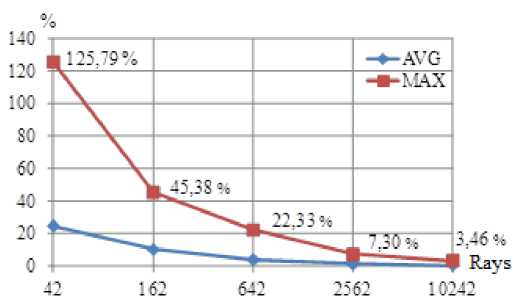
b
Рис. 8. Продолжительность и точность расчета в зависимости от количества лучей: а – время расчета одной точки; б – средняя (AVG) и максимальная (MAX) величина отклонений накопленных доз
For the elements of the block, the minimum accumulated dose was 5.3 krad, and the maximum one was 50.2 krad; that means that within one product the values of the minimum accumulated dose for specific electronic components may differ significantly, and that taking into account protective properties of the constructional elements of the apparatus and blocks can make a significant contribution to the calculation. This means that element-by-element radiation analysis has significant advantages over the evaluation of the stability of blocks as single and indivisible components of spacecraft.
Conclusion. The approach presented in the work and its software implementation allow performing element-by-element radiation analysis in the development of on-board equipment spacecraft taking into account real geometry of constructions and material density.
Determining the value of accumulated dose at various points of the developed block at the designing stage makes it possible to place less resistant elements into more protected areas, it is especially important for import substitution.
Further project development includes designing the host of functions offering locations and the level of required protection, as well as the addition of the possibility to take into account the emission of point sources (e. g. spacecraft engines).
Список литературы Determination of total ionization dose by ray trace analysis based on a geodesic sphere
- Першенков В. С., Скоробогатов П. К., Улимов В. Н. Дозовые эффекты в изделиях современной микро-электроники: учеб. пособие. М.: НИЯУ МИФИ, 2011. 172 с.
- Кузнецов В. Д. Космическая погода и риски космической деятельности//Космическая техника и технологии. 2014. № 3 (6). С. 3-13.
- European space weather week . URL: http://www.stce.be/ESWW (дата обращения: 26.10.2017).
- Действие проникающей радиации на изделия электронной техники/В. М. Кулаков . М.: Сов. Радио, 1980. 224 с.
- Таперо К. И., Улимов В. Н., Членов А. М. Радиационные эффекты в кремниевых интегральных схемах космического применения. М.: Бином. Лаборатория знаний, 2014. 304 с.
- Alex F. Bielajew. Fundamentals of the Monte Carlo method for neutral and charged particle transport/The University of Michigan Department of Nuclear Engineering and Radiological Sciences. 2001. P. 338.
- GEANT: Detector Description and Simulation Tool/R. Brun //Publication Geneva: CERN, 1993. P. 430.
- X-5 Monte Carlo Team, MCNP-A General Monte Carlo N-Particle Transport Code/Los Alamos National Laboratory. 2003.
- CREME96: A Revision of the Cosmic Ray Effects on Micro-Electronics Code/Tylka A. J. //IEEE Trans, on Nuclear Science. 1997. Vol. 44, No.6. Pp. 2150-2160, Dec.
- Интегрированный пакет программ СOSRAD . URL: http://www.cosrad.sinp. msu.ru (дата обращения: 26.10.2017).
- Seltzer S. M. SHIELDOSE: A Computer Code for Space-Shielding Radiation Dose Calculations, National Bureau of Standards. NBS Technical Note 1116. U. S. Government Printing Office, Washington, D. C., 1980.
- Varotsou A. OMERE Advanced Manual. TRAD, 2010. P. 48.
- Анализ современного программного обеспечения для оценки локальных условий функционирования СБИС на борту космических аппаратов в части ионизирующих излучений космического пространства/В. С. Анашин //МЭС-2014. М.: ИППМ РАН. 2014.
- ОСТ 134-1034-2012. Аппаратура, приборы, устройства и оборудование космических аппаратов. Методы испытаний и оценки стойкости бортовой радиоэлектронной аппаратуры космических аппаратов к воздействию электронного и протонного излучений космического пространства по дозовым эффектам. М.: Российское космическое агентство, 2012.
- Методика расчета поглощенных доз ионизирующих излучений космического пространства для орбит изделий разработки ОАО «ИСС». 154.ПМ -129. ОАО «ИСС», 2005.
- Wang N., Lee J.-L. Geometric properties of the icosahedral-hexagonal grid on the two-sphere//SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 2011, № 33. Р. 2536-2559.
- Никулин Е. А. Компьютерная геометрия и алгоритмы машинной графики. СПб.: БХВ -Петербург, 2003. 560 с.
- 2012 SOLIDWORKS API Help -Ray Intersections Method (IModelDoc2) . URL: http://help.solidworks.com/2012/English/api/sldworksapi/solidworks.interop.sldworks~solidworks. interop.sldworks.imodeldoc2~rayintersections.html (дата обращения: 26.10.2017).


