Development of wide bandgap one-dimensional MOF/TiO2 photonic crystal and its gas-sensing properties
Автор: Tian Yu., Lysyakov A., Wang H., Xie H.
Журнал: Бюллетень науки и практики @bulletennauki
Рубрика: Технические науки
Статья в выпуске: 6 т.10, 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Metal-organic framework (MOFs) materials are a type of coordination polymer that have seen significant breakthroughs in material science over the past decade. Because of their high specific surface area and porosity, they are widely used for gas adsorption, storage, and separation. Additionally, their structural tunability allows for a wide variety of MOFs, with more remarkable properties yet to be discovered as research continues. When MOFs are applied in photonic crystals, adjustments to their structure enable them to act as specific gas-sensitive materials, causing shifts in the photonic crystal's forbidden band after gas adsorption. This generates distinguishable signals for effective sensing. In conventional single-metal MOFs, doping with another metal to prepare photonic crystals increases defect size while reducing symmetry and simplicity, leading to more pronounced forbidden bands and improved sensing. Therefore, in this thesis, we aim to partially replace the chromium in MIL-101 with magnesium and then self-assemble it with titanium dioxide to prepare photonic crystals. This approach aims to leverage the exceptional properties of MOFs, resulting in photonic crystals with improved gas-specific recognition and sensitivity, further enhancing their gas-sensing capabilities.
One-dimensional photonic crystals, preparation of photonic crystals, gas sensing properties, laser reflectance spectroscopy
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14130175
IDR: 14130175 | УДК: 628.91: | DOI: 10.33619/2414-2948/103/34
Разработка одномерного фотонного кристалла MOF/TiO2 с широкой полосой пропускания и его газочувствительные свойства
Металлоорганическая каркасная структура материалов является типом координационных полимеров, которые за последнее десятилетие совершили значительный прорыв в материаловедении. Благодаря высокой удельной поверхности и пористости, они широко применяются для адсорбции, хранения и разделения газов. Кроме того, их структурная настраиваемость позволяет создавать широкий спектр металлоорганических каркасных структур, и по мере продолжения исследований, вероятно, будут обнаружены новые замечательные свойства. Когда металлоорганические каркасные структуры применяются в фотонных кристаллах, их изменение позволяет им действовать как специфические газочувствительные материалы, вызывая смещение запрещенной зоны фотонного кристалла после адсорбции газа. Это создает различимые сигналы для эффективного зондирования. В обычных монокристаллах с одним металлом легирование другим металлом при создании фотонных кристаллов увеличивает размер дефектов, снижая симметрию и упрощая структуру, что приводит к более выраженным запрещенным полосам и улучшенной чувствительности. Поэтому мы планируем частично заменить хром в MIL-101 на магний, а затем самостоятельно собрать его с диоксидом титана для получения фотонных кристаллов. Этот подход позволяет использовать исключительные свойства металлоорганических каркасных структур, что приводит к фотонным кристаллам с улучшенным распознаванием и чувствительностью к специфическим газам, что дополнительно повышает их газочувствительные возможности.
Текст научной статьи Development of wide bandgap one-dimensional MOF/TiO2 photonic crystal and its gas-sensing properties
Бюллетень науки и практики / Bulletin of Science and Practice
UDC 628.91^ 543.424.4
A photonic crystal is a class of crystals with a unique structure resulting in specific electromagnetic wave propagation characteristics, notably a photonic band gap—a frequency range where waves cannot propagate through its periodic structure. Light within this range is reflected back to the original medium, creating a “forbidden band”. This property enables photonic crystals to selectively allow certain wavelengths to pass through while blocking others, making them valuable in sensing applications.
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) are a new class of porous crystalline materials with a three-dimensional structure, primarily consisting of two components: junctions and connecting bridges. Metal ions form the connecting points, while organic ligands create the bridges, resulting in a spatially extended 3D structure. MOFs represent a novel type of porous material alongside traditional zeolites and carbon nanotubes. Unlike traditional zeolites and carbon nanotubes, MOFs are composed of metal ions from transition elements in the periodic table and organic ligands, using self-assembly and doping methods. This combination forms a porous material with a regular periodic mesh structure. MOFs feature high porosity, low density, a large specific surface area, and regular pore channels with adjustable diameters. These characteristics provide a robust topological structure, versatility, and many other advantages [1].
In the previous research, J. Goel found a method to synthesize crystalline and hydrophilic CTF-HUST-A1 using a benzylamine-functionalized monomer. The choice of base reagent plays a significant role in enhancing crystallinity and hydrophilicity [2].
Z. Cheng found efficient visible-light-driven photocatalytic hydrogen evolution in phosphorus-doped covalent triazine-based frameworks [3].
In Y. Lin’s research, DUT-67(Zr) was synthesized through a solvothermal route and used for photocatalytic selective synthesis of thioanisole under light illumination [4].
-
Y. Horiuchi has realized the catalytic oxidation of benzyl alcohol reaction with substituents of benzyl alcohol and malononitrile under the condition of temperature of 363 K, and UV irradiation by utilizing UiO-66 (Zr) , the reaction rate has been greatly improved [7].
The high porosity and structural variability of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) make them promising for drug slow-release applications [8].
Common methods of loading drugs into MOFs include: (1) incorporating drugs into the structure of MOFs; (2) adsorbing drugs into the pores of MOFs; and (3) using the drug molecule itself as a micro-unit structure within the target material. Horcagada, Gref, and colleagues successfully obtained various MOFs crystal structures by pairing and assembling iron (Fe) with multiple carboxylic acid ligands. By dispersing these MOFs into specific concentrations of drug solutions, the method of drug adsorption into the pore sizes of MOFs was achieved, leading to a class of highly effective anticancer drugs [9].
Meanwhile, MOFs, known for their high porosity and unique structural properties, have seen significant development in recent years. After conducting adsorption experiments on a wide range of MOFs obtained through different assembly methods, researchers have identified MOFs as promising candidates for hydrogen storage. Yaghi's research group discovered that the metalorganic framework MOF-5Zn4O (BDC) 3 demonstrated excellent performance in hydrogen storage [10].
Based on these, the thesis chooses to partially replace the chromium in MIL-101 with magnesium and then self-assemble with titanium dioxide to create photonic crystals. This approach leverages the excellent performance of metal-organic frameworks, improving the specific recognition and sensitivity of these photonic crystals to gases, with significant applications in gas sensing.
The most fundamental characteristic of photonic crystals is the photonic forbidden band, which prevents electromagnetic waves within a specific wavelength and frequency range from passing through the crystal, regardless of the propagation direction. This creates a selective pathway for electromagnetic waves. The photonic forbidden band is determined by the specific composition of the photonic crystal, including its spatial structure and dielectric constant. A higher dielectric constant ratio increases the likelihood of a band gap. Additionally, asymmetric photonic crystal structures tend to reduce symmetry and increase the probability of forming a photonic forbidden band.
When the structure of a photonic crystal is disrupted, or when specific defects are introduced, the photons with frequencies close to the defect are confined, creating a localized field. Once the photons exit the defect, their light significantly attenuates. Defects can be of various types, including point defects, line defects, and plane defects.
Since Albert Einstein proposed the spontaneous radiation effect in 1905, it has had a profound impact on all fields of physics. Initially, spontaneous radiation was considered a random natural process without any governing laws or methods for control. The emergence of photonic crystals, however, has challenged this notion by introducing new ways to manipulate spontaneous radiation. From the formula,
W = П V I2 РФ )
We can know that the probability of spontaneous radiation follows a pattern, with the likelihood increasing as the density of states rises. This characteristic underlines the unique nature of photonic crystals, which can reduce the probability of spontaneous radiation.
When an atom is added to a photonic crystal, and the frequency of its spontaneous radiation aligns with the forbidden band of the photonic crystal, the radiation is suppressed and cannot be transmitted outward. In contrast, adding atoms to the photonic crystal can disrupt its original structure, creating defects that significantly increase its density of states, thereby enhancing the effect of spontaneous radiation. This demonstrates that spontaneous radiation is not uncontrollable, and that we can modulate its intensity through photonic crystals, leading to what is known as the Purcell effect.
Photonic Crystal Optical Waveguide. Thanks to the unique properties of photonic crystals-specifically, photonic forbidden bands and photonic localization-optical information transmission in any direction can occur with minimal loss, enhancing energy efficiency. This property makes it possible for optical waveguides to be integrated into chips.
Photonic Crystal Fiber. Conventional optical fiber is perforated along its horizontal axis, ensuring a periodic aperture. This structure helps reduce bending loss in conventional optical fiber. Thanks to the unique properties of photonic forbidden bands, photonic crystal fibers maintain single-mode transmission even at points of bending or folding, reducing energy loss caused by these movements.
Photonic Crystal Sensor. The high tunability of photonic crystals allows them to respond to changes in the surrounding environment. When environmental conditions change, it can alter the shape of the photonic crystal microcavity, affecting the distribution of the refractive index, which in turn changes the resonant frequency of the photonic crystal, enabling sensing functionality. Depending on the specific external conditions, photonic crystal sensors can be classified into various types, such as temperature sensors and gas sensors.
Thanks to the unique properties of photonic crystals-photonic forbidden bands and localized fields-optical information can be transmitted in any direction with minimal loss. This enhances the energy efficiency of information transmission, enabling optical waveguides to be integrated into chips. Conventional optical fiber is perforated along the horizontal axis, ensuring a periodic aperture. This structure helps reduce bending loss. Photonic forbidden bands in photonic crystals allow single-mode transmission even at points of bending or folding, reducing energy loss due to such deformations in the optical fiber. The high tunability of photonic crystals allows them to respond to environmental changes by altering the shape of the photonic crystal microcavity, which affects the distribution of the refractive index and changes the photonic crystal's resonant frequency, enabling sensing functionality. Depending on various external conditions, photonic crystal sensors can be classified into different types, such as temperature sensors and gas sensors.
Experimental reagents : Cr ( NO 3 ) 3 ·9H 2 O, Mg(NO 3 ) 3 ·6H 2 O, H 2 BDC, HF, C 2 H 5 OH, H 2 O, TiO 2 .
Mg partially replaces Cr in MIL-101. The raw materials were measured with an electronic balance: 2.4 g of chromium nitrate nonahydrate (Cr(NO 3 ) 3 ·9H2O), 1.0 g of terephthalic acid (H2BDC), and 0.154 g of magnesium nitrate hexahydrate (Mg(NO3)2·6H2O). Next, 0.3 ml of hydrogen fluoride (HF) was mixed with 30 ml of distilled water. After mixing, magnetic heating and stirring were applied to the solution, which was then placed in an electrically heated, constanttemperature blast drying oven and heated at 180 degrees Celsius for 12 hours to obtain MIL-101 (Cr, Mg). The resulting solution was placed in a centrifuge for centrifugal drying and purification, producing a higher-purity powdered sample. Anhydrous ethanol was then added to create a sample of MIL-101 with chromium partially replaced by magnesium, as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1. From left to right, the mixed solution, the centrifugally dried powder and the final sample.
Table
LABORATORY INSTRUMENTS
|
EXPERIMENTAI NSTRUMENT |
MODEL MANUFACTURER |
|
Electric thermostatic air-drying oven |
DGG-9030A Beijing Jinsheng Micro Nano Technology Co., LTD |
|
Xiangyi centrifuge |
TG16-WS Shanghai Jinghong Experimental Equipment Co., LTD |
|
Electronic balance |
J223BF Changchun Leprotactinium Technology Co., LTD |
|
Magnetic heating agitator |
78-1 Jintan City Baita new treasure instrument factory |
|
Sizing table |
202-00A Beijing Jinsheng Micro Nano Technology Co., LTD |
|
Electric thermostatic drying oven |
DGG-9030A Shanghai Kuntian Experimental Instrument Co., LTD |
Sample self-assembly of one-dimensional photonic crystals with TiO 2ю To fabricate onedimensional photonic crystals using 1.5 cm × 1.5 cm silicon wafers as the base structure, the wafers must undergo specific pre-treatments, including rinsing with deionized water, soaking in special solutions, and drying at a constant temperature of 80°C. Following the pre-treatment, TiO 2 and MIL-101 (Mg, Cr) are spin-coated in layers on a homogenizing table at 3000 rpm. Each layer is then heated and shaped in a constant-temperature blower drying oven to ensure the stability of the crystal structure. As shown in Figure 2, one-dimensional photonic crystals with a stable structure were successfully fabricated.

Figure 2. Samples during preparation

Following the above preparation process, MIL-101 with bimetallic Mg, Cr substitution was successfully synthesized and characterized using X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), and scanning electron microscopy (SEM).
FTIR characterization. An infrared Fourier spectrometer (FTIR, Nicolet 6700) was used to characterize the distribution of their chemical bonds in the prepared samples, as shown in Figure 3.
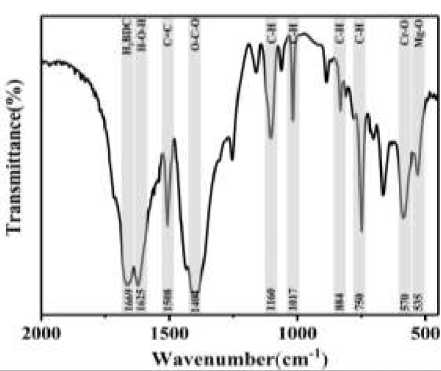
Figure 3. FT-IR patterns of photonic crystals synthesized from MIL-101 (Mg, Cr) and TiO2
The higher Bragg peaks in the experimental results suggest a smaller particle size, while the wave peak at 1625 cm-1 indicates the presence of H-O-H bonds, suggesting that the sample contains incompletely dried water. The wave peak at 1508 cm-1 indicates the presence of C=C double bonds, and the band at 1404 cm-1 corresponds to O-C-O bonds in the framework structure, specifically to tensile vibrations. Wave peaks at 1160, 1017, 884, and 750 cm-1 confirm the presence of C-H bonds, indicating the organic ligand terephthalic acid in the samples. Most notably, the significant change in the wave peaks around 1669 cm-1 indicates successful doping with dihydroxy terephthalic acid. The presence of Cr-O and Mg-O bonds at wave numbers 570 and 535 cm-1, respectively, confirms that partial substitution of magnesium for chromium in the original MIL-101 has been achieved, leading to new crystal structure.
XRD characterization. An X-ray diffractometer was used to characterize the phase structure of the fabricated samples, utilizing CuKα radiation (λ = 1.541 A), with a tube voltage of 40 kV and a tube current of 200 mA. The results of this characterization are shown in Figure 4.
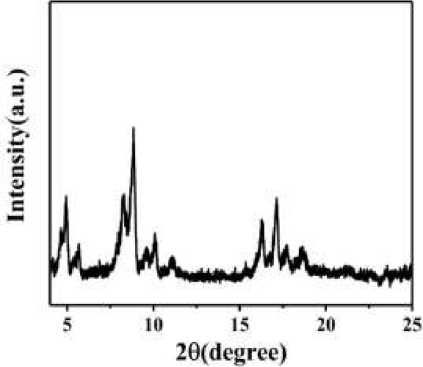
Figure 4. XRD patterns of photonic crystals synthesized from MIL-101 (Mg, Cr) and TiO2
The characterization results and comparison with reference data show that the XRD diffraction spectra of the samples prepared in this experiment and those of MIL-101 (Cr) align closely at 8-8.5 degrees and 15-18 degrees. This indicates that the samples are successfully doped with Mg while maintaining the structure of MIL-101, allowing them to be layered with spin-coated TiO2 to create a new class of one-dimensional photonic crystals. This development provides a strong foundation for the subsequent alcohol gas sensing experiments.
SEM Figure. Figure 5 displays the scanning electron microscopy (SEM) image of the MIL-01 (Mg, Cr) layered structure. The boundary between the layers is distinct, and the structure is c ear. We measured the corresponding thickness of each layer through the cross-section: the MIL-101 (Mg, Cr) layer has a thickness ranging from 70 nm to 250 nm, while the TiO 2 layer is about 100 nm thick.
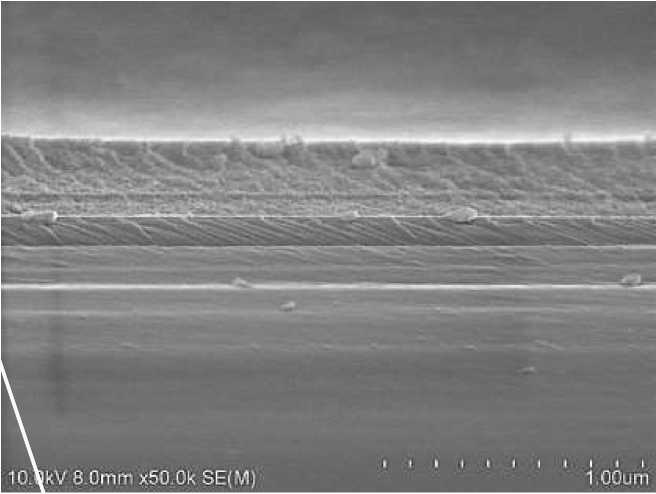
Figure 5. SEM structures of photonic crystals prepared from MIL-101 (Mg, Cr) and TiO2
Reflectance spectrum. A homemade sealed measurement chamber was used to assess the samples. A halogen light source with a stable bandwidth produced incident light perpendicular to the sample at room temperature, and the reflected light was received by a fiber-optic spectrometer. Figure 6 shows the shift in the reflectance spectrum versus wavelength.
Changes in the refractive index of the MOF layer depend on the refractive index and volume of adsorbed vapors. Since the refractive indices of the vapors used are relatively low, the primary factor affecting refractive index changes is the adsorption capacity of the MOFs. The structure of MIL-101, after doping with Mg2+, is altered, enhancing its response to various gases.
The reflectance spectra of the one-dimensional photonic crystal sensor for alcohol gases, ranging from 0 ppm to 1100 ppm, are shown in Figure 6. The segment between 550 nm and 650 nm is a clear reference point for these measurements. As the concentration increases, the wavelength at the reference point exhibits a notable red shift.
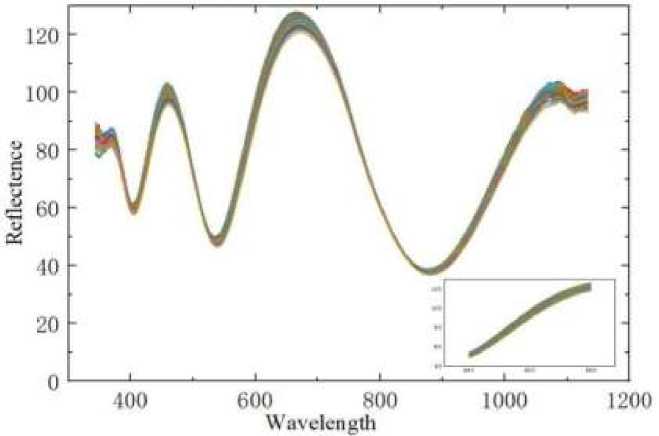
Figure 6. Reflectance spectrum
Analysis of sensing experiments. Comparing the red shift in wavelength with the corresponding concentration of ethanol gas reveals a linear relationship. The change in wavelength increases as the gas concentration rises, and after linear fitting, the relationship is described by y=0.00184x+5.19, with a coefficient of determination of R2=0.94525, as shown in Figure 7.

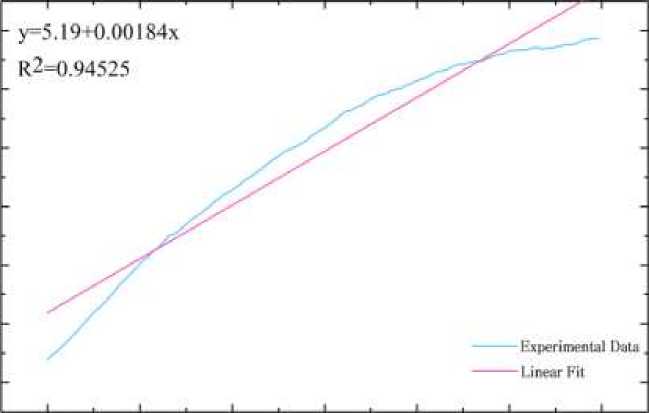
О 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 3000
Concentration(ppni)
Figure 7. Linear fit of Bragg peak position to ethanol gas concentration
By analyzing and summarizing the data from repeat experiments, it can be observed that the one-dimensional photonic crystal sensor with MIL-101 as the substrate demonstrates a high degree of regularity, repeatability, and stability over eight cycles. The variation in the number of cycles versus wavelength is shown in Figure 8.
The concentration of alcohol gas shows a linear relationship with the number of nanometers in the wavelength shift. The optical response of the photonic crystal sensor is confirmed to be stable and reliable through multiple repetitions of the experiment with varying response times.
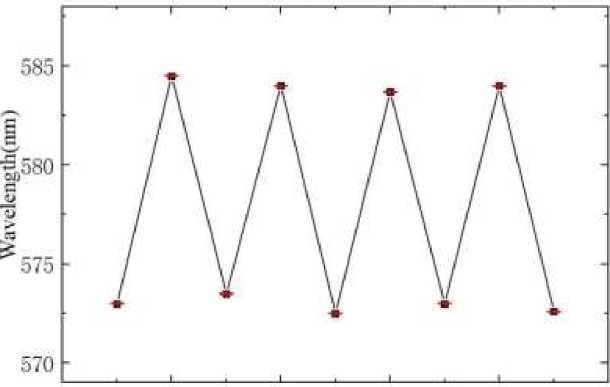
О 2 4 6 8 10
Cycles
Figure 8. Repeatability test of sensing results (8 cycles)
Conclusions
In this paper, MIL-101 materials obtained by partial substitution of Cr with Mg were prepared using the following steps:
The doping of Mg increases the structural porosity of the original gas-sensitive material and alters its polarity, thereby greatly enhancing its sensitivity for gas-specific recognition. This unique property is used to prepare one-dimensional photonic crystals, on which various tests were conducted.
Self-assembly with TiO 2 was achieved through the spin-coating method, where MIL-101 (Mg, Cr) was layered with TiO 2 to create the target one-dimensional photonic crystals.
The one-dimensional photonic crystals underwent sensing experiments with alcoholic gases to study the linear relationship between gas concentration and the number of nanometers of peak drift, as well as reproducibility, response time, and stability. Reflectance spectra were also tested to obtain complete optical characterization.
The one-dimensional photonic crystal obtained by self-assembly of MIL-101 (Mg, Cr) with TiO2 shows a good linear relationship between the reflectance spectra and the concentration of embedded gas. It also exhibits excellent reversibility and reproducibility over a test cycle exceeding two months, enabling the sensor to successfully investigate the effect of repeated cycles on sensor performance. The proposed sensors fabricated from MIL-101 have significant potential for indoor air quality control, electronic processing, and various medical diagnostics.
Список литературы Development of wide bandgap one-dimensional MOF/TiO2 photonic crystal and its gas-sensing properties
- Goel J., Kadirvelu K., Rajagopal C., Garg V. K. Removal of lead (II) by adsorption using treated granular activated carbon: batch and column studies // Journal of hazardous materials. 2005. V. 125. №1-3. P. 211-220. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.05.032 EDN: KJTPYH
- Zhang S., Cheng G., Guo L., Wang N., Tan B., Jin S. Strong-base-assisted synthesis of a crystalline covalent triazine framework with high hydrophilicity via benzylamine monomer for photocatalytic water splitting //Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 2020. V. 59. №15. P. 6007-6014. DOI: 10.1002/anie.201914424
- Cheng Z., Fang W., Zhao T., Fang S., Bi J., Liang S., Wu L. Efficient visible-light-driven photocatalytic hydrogen evolution on phosphorus-doped covalent triazine-based frameworks // ACS applied materials & interfaces. 2018. V. 10. №48. P. 41415-41421. DOI: 10.1021/acsami.8b16013
- Liu Y., Zou J., Guo B., Ren Y., Wang Z., Song Y., Wu L. Selective photocatalytic oxidation of thioanisole on DUT-67 (Zr) mediated by surface coordination // Langmuir. 2020. V. 36. №9. P. 2199-2208. DOI: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.9b02582 EDN: WGICXF
- Drache F., Cirujano F. G., Nguyen K. D., Bon V., Senkovska I., Llabres i Xamena F. X., Kaskel S.Anion exchange and catalytic functionalization of the zirconium-based metal-organic framework DUT-67 // Crystal Growth & Design. 2018. V. 18. №9. P. 5492-5500. DOI: 10.1021/acs.cgd.8b00832 EDN: YHBYAH
- Ohkubo K., Fujimoto A., Fukuzumi S. Visible-light-induced oxygenation of benzene by the triplet excited state of 2, 3-dichloro-5, 6-dicyano-p-benzoquinone // Journal of the American Chemical Society. 2013. V. 135. №14. С. 5368-5371. DOI: 10.1021/ja402303k EDN: RQGYDN
- Toyao T., Saito M., Horiuchi Y., Matsuoka M. Development of a novel one-pot reaction system utilizing a bifunctional Zr-based metal-organic framework // Catalysis Science & Technology. 2014. V. 4. №3. P. 625-628. DOI: 10.1039/C3CY00917C
- Kehe K., Szinicz L. Medical aspects of sulphur mustard poisoning // Toxicology. 2005. V. 214. №3. P. 198-209. DOI: 10.1016/j.tox.2005.06.014
- Horcajada P., Chalati T., Serre C., Gillet B., Sebrie C., Baati T., Gref R. Porous metal-organic-framework nanoscale carriers as a potential platform for drug delivery and imaging // Nature materials. 2010. V. 9. №2. P. 172-178. DOI: 10.1038/nmat2608 EDN: MYVNNB
- Rosi N. L., Eckert J., Eddaoudi M., Vodak D. T., Kim J., O'Keeffe M., Yaghi O. M. Hydrogen storage in microporous metal-organic frameworks // Science. 2003. V. 300. №5622. P. 1127-1129. DOI: 10.1126/science.1083440 EDN: GPEAPJ


