Directions for enhancing the efficiency of financial resources through the introduction of distance learning
Автор: Sobirova M.E.
Журнал: Теория и практика современной науки @modern-j
Рубрика: Основной раздел
Статья в выпуске: 5 (59), 2020 года.
Бесплатный доступ
This article analyzes the implementation of distance education, enhances the effectiveness of financial resources through their introduction, and the scientific and theoretical basis for their implementation. Through this study, we also provide scientific suggestions and recommendations on how to use the methodology used in developed countries to improve the efficiency of financial resources.
Distance learning, higher education, financing
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/140289576
IDR: 140289576 | УДК: 336.142
Текст научной статьи Directions for enhancing the efficiency of financial resources through the introduction of distance learning
The development of the education sector often depends on the size of the funding and the level of effective use of the received financial resources. In different countries, the scope of financing education reforms varies greatly.
While some countries choose low-cost reforms, other countries implement major reforms that require significant financial resources.
Relevance of the topic is, there are still a number of problems in the educational system that are pending, especially in secondary and higher education. First, there is a huge unmet demand for educational services in Uzbekistan. This is due to the limited capital and teaching resources of educational institutions with a growing number of people. Secondly, in Uzbekistan, the main institutions of higher education are concentrated in the city of Tashkent and therefore citizens of remote regions often do not have the opportunity to study in them. Thirdly, there are modern courses and programs in foreign universities, which will be expensive for our citizens. Such problems exist not only in Uzbekistan. According to UNESCO, (2015) “... worldwide, the number of people willing to get an education significantly exceeds the number of places in educational institutions and according to forecasts, by 2025 the number of students in the world from 165 million people will increase by 98 million.”
In world practice, the possibilities of information and communication technologies in education, in the form of e-learning and distance education have been widely used and used to solve such problems. If earlier, individual universities offered separate elements of e-learning and distance education courses, then for the last 6-7 years they have been provided massively with the help of MOOC technologies. Mass open online course Massive Open Online Course(MOOC) is a training course with massive interactive participation using e-learning technologies and open access via the Internet, one of the forms of distance education. As additions to traditional course materials, such as videos, reading and homework, mass open online courses provide an opportunity to use interactive user forums that help create and maintain communities of students, teachers, and assistants.
BACKGROUND
Distance education systems now involve a high degree of interactivity between teacher and student, even in rural and isolated communities separated by perhaps thousands of miles.
Schlosser and Anderson (1994) refer to Desmond Keegan's theory of distance education, in which the distance learning system must artificially recreate the teaching-learning interaction and re-integrate it back into the instructional process. This is the basis of their Iowa Model: to offer to the 2
distance learner an experience as much like traditional, face-toface instruction, via intact classrooms and live, two-way audio-visual interaction.
In contrast, the Norwegian Model has a long tradition of combining mediated distance teaching with local face-to-face teaching (Rekkedal, 1994).
We all know that the development of the distance education system requires a great source of financial resources. A series of complex studies of the effectiveness of financial resources was conducted.
In particular, Dobrin and Sukhoi (2010) emphasized that the preparation of a distance learning budget is based on the introduction of a single principle of organization and use of budgets depending on the state’s economic and financial policies.
According to Selin (2009), distance education is an investment in human capital. Society as a whole is interested in this kind of investment, it raises the level of economic growth, increases labor productivity and eliminates social problems.
That is why the share of financial resources aimed at distance learning is a priority.
Anoshkina and Mirkubonov (2009) listed the following resources as sources that will be attracted to finance distance education in Uzbekistan: the state budget and extra-budgetary funds. The development of market relations requires the search for new sources of non- traditional extra-budgetary funding for distance learning.
Blanchard (2010) considers that innovations in distance learning are the main factor determining the growth of GDP, and, in turn, the level of financing costs is crucial for ensuring the effectiveness of innovative development.
In institutions of the educational system of Uzbekistan, a two-stage certification is provided: Bachelor. It is a basic higher education. Having completed training for four years, each student masters the basic skills and sufficient knowledge in their specialty. After mastering the program, the state commission awards graduates with the qualification “bachelor” of the corresponding profile. Qualification is confirmed by the established diploma.
In the chart below, compiled according to the data of the Ministry of Higher Education, the yellow line shows the quota of admission to all state universities from 1997 to 2018, the red line shows the number of applicants who have passed documents in this period.
students addmision to universities in Uzbekistan in thousand people
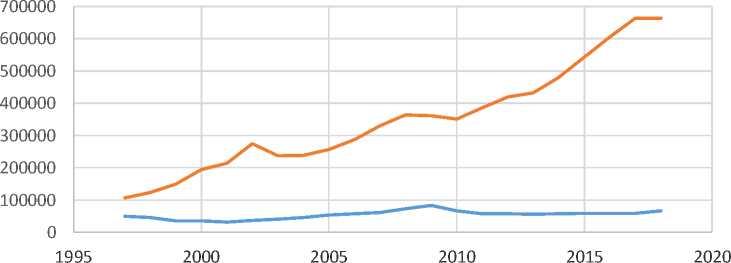
^^^^^^^^м quota ^^^^^^^^ш number of applicants
Chart 1. The growth dynamics of quota places and the number of applicants.
Source: Ministry of Higher Education .
Based on the scientific views of economists above and the background information about Uzbekistan educational system, we can say that there are a number of things that need to be done to ensure the effective use of funds through the introduction of distance learning.
2.Challenges and analysis of solutions.
According to the National Testing Center, in 2019, more than 1 million applicants were registered. This figure is 200 thousand more than last year, and the number of people wishing to get higher education in Uzbekistan is growing annually. At the same time, the potential of universities to accept a large number of students is significantly limited.
According to the World Bank, higher education enrollment in Uzbekistan has declined in recent years and amounted to only 9% in 2017 (of the corresponding age category of the population) compared to the global average of 38%.
How are things in other countries? For a comparative analysis of the countries of the world, we will refer to the UNESCO indicator - Gross Entry Ratio to First Tertiary Programs, 2015. The indicator calculates the proportion of students who entered universities in 2015 to the total population of an age corresponding to the level of education. This indicator is also used as an indicator of the accessibility of higher .education to the country's population.
|
Country |
% of entrance |
|
Serbia |
97.4 |
|
New Zealand |
95.6 |
|
Turkey |
92.3 |
|
Chile |
87.9 |
|
Switzerland |
86.9 |
|
Denmark ** |
85.4 |
|
Belarus |
84.4 |
|
Russia |
84.2 |
|
Japan |
81.1 |
|
Kazakhstan |
69.2 |
|
USA |
50.9 |
|
Afghanistan |
15 |
|
Angola |
10.1 |
|
Burundi |
10 |
|
Uzbekistan |
9.6 |
|
Burkina Faso |
9.1 |
|
Madagascar |
7.7 |
|
Mozambique |
6.6 |
|
Mauritania |
6 |
|
Eritrea |
3.6 |
Table 2. The percentage of students enrolled in the population of the age category corresponding to the time of study at the university, in 2015 (* - 2016, ** - 2014).
Source: UNESCO.
Table 2 shows that in Uzbekistan, only 9.6% of the number of people belonging to the age category of potential applicants entered universities in 2015.
The world practice of spreading the practice of online education and the latest trends in the field of personnel training indicate the potential role of this trend in solving a large number of acute socio-economic problems of developing countries, including Uzbekistan.
It should be noted that state support for the development of a national DL network is one of the most important factors for the successful development of distance education and can take various forms, such as:
-
- direct financing;
-
- financing through various social and educational funds;
-
- developing national educational standards and systems certification;
-
- Support for the issuance of diplomas and state certificates
A very acute problem related to the need to optimize the cost of educational services offered through the Internet. The balance between the initial costs, the number of students and the quality of the methodological support used can solve the problem of the cost-effectiveness of distance learning, moreover, a contradiction is noted that, on the one hand, the main types of software for web browsers and servers are supplied almost free of charge or for a minimal fee, the main expenses therefore fall on the acquisition of hardware and on the provision of a communication channel.
Consider, for example, the conduct of a standard 72-hour DO training course over a two-month period. Usually a group consists of 20 people, and the approximate cost of training is $ 300, then the revenue will be 20x300 = $ 6000. Considering the costs of conducting training courses (Table 5), in general, the initial costs are $ 4170, if we assume that taxes are paid in the amount of 24%, then the payback period will be 8 months (4 turns, 2 months).
|
Cost item |
Rate |
Qty |
Amount $ |
|
Copyright fee |
5% fee from revenue |
- |
300 |
|
Teacher payment |
$ 0.5 per 1 hour |
72*20 |
720 |
|
Payment to the system administrator |
40$ per week |
8 |
320 |
|
Advertising |
7% |
- |
490 |
|
CD preparation |
20$ per set |
20 |
400 |
|
Curator payment |
50$per week |
8 |
400 |
|
internet |
60$ per month |
2 |
120 |
|
Administrative cost |
400$ per month |
2 |
800 |
|
Certificate |
1$ |
20 |
20 |
|
Equipment rental |
$ 200 - server 100$-comp teacher |
2 |
600 |
|
Total |
4170 |
||
Table3: Cost of conducting and maintaining the online course
Source:made by author
Although, the costs of organizing and conducting distance education can be initially quite high, they pay off the services that this form of education offers for their students; first of all, for students in rural and remote from scientific centers of the regions, with the quality of education that is not inferior to fulltime education, and without interruption from work for adults, without leaving the family, and the associated additional costs, for everyone, including schoolchildren. Independent experts believe that distance learning is 20-25% cheaper than the traditional one. Microsoft believes that the cost of network education can be reduced by at least twice against the traditional one, since the teacher is able to give lessons anywhere in the world, just as students can study in any educational institution in the world that offers such services without leaving native home. Savings can thus be achieved at the expense of other factors. In this respect, it is also important that all students, no matter how many of them, use the same teaching materials, which do not require additional costs for their replication, are also the most recent, as they are constantly updated on the Internet.
RECOMMENDATION
What can be useful in the introduction of distance education in Uzbekistan and what are the directions for improving the efficiency of financial resources include the following:
First, manufacturability. The use of technology is developed by the technology itself, namely it expands the possibilities and effectiveness of distance education. This will require the teacher and student to develop the skills to use technology and media technologies effectively.
The second is saving. The introduction of distance education in the traditional does not require the cost of additional audiences, libraries, dormitories, as well as additional human resources. Teachers can be given the 8
opportunity to develop distance courses, which, in turn, will affect the quality of education.
And finally, the social aspect. Equal opportunities will open for students and teachers, regardless of their location, health status and social status. Opportunity as a choice of school for training, and for retraining and advanced training.
CONCLUSION
The consistent introduction of distance education in the process of universities in Uzbekistan undoubtedly contributes greatly to the development of the education system. Today's rapid informational development of society has shown that the correspondence form of education is ineffective and should be actively replaced by the DL. At present, many higher educational institutions of the republic actively “run in” and timidly begin to introduce courses of DL into the educational process. Distance learning in the future should fully replace the process of correspondence learning, and also allow people of any age, social status and people with disabilities to study.
In the long term development of distance learning, the use of information technologies in the country, it is necessary to develop criteria for monitoring the quality of new teaching methods, prepare a regulatory framework for effective functioning, constantly introduce new information technologies, develop and modernize infrastructure, primarily in the field of telecommunications . The solution of these problems is possible with an integrated approach that will form the basis for the rapid development of information technologies and their introduction into the educational process. Thus, the use of information technologies and distance learning has ceased to be a novelty for us and, undoubtedly, will make its worthy contribution to the formation of the information society in our country, and will be the main factor in improving the quality and efficiency of education and financial resources of the state budget.
Список литературы Directions for enhancing the efficiency of financial resources through the introduction of distance learning
- Аношкина В., Миркурбонов Н.М. Ўзбекистонда олий таълим. Таҳлилий тавсиянома №1 (12), UNDP ICT Policy Project, 2009. -2-p-p.
- Бобохужаев Ш. И. Особенности использования дистанционной формы обучения в учебном процессе: Международная научно-практическая конференция: Cборник тезисов докладов, Т.: Изд-во ТФИ, 2006.
- Barron, A., & Orwig, G. (1993). New technologies for education. Englewood, CO: Libraries Unlimited.
- Horton, W. (1994, June). How we communicate. Paper presented at the meeting of the Rocky Mountain Chapter of the Society for Technical Communication. Denver, CO.
- Holloway, R.E., & Ohler, J. (1991). Distance education in the next decade. In G.J. Anglin, (ed.), Instructional technology, past, present, and future (pp. 259-66). Englewood, CO: Libraries Unlimited.


