Drug repurposing approach: in-silico studies on natural antiviral analogues as therapeutic agents for COVID-19
Автор: Velayutham G., Nallathambi M., Govindasamy H., Gopalsamy R.G.
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 2 т.21, 2025 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The severe acute respiratory coronavirus 2 syndrome, commonly acknowledged as COVID-19, has become a public health issue. Originally, it emerged in Wuhan, China in December 2019. Due to its strong contagion, it spread to almost 187 countries. Precautionary steps remain the only binding technique to avoid transmissions from the entity before an appropriate form of care or vaccination is established. In the middle of the contagion, new molecule discovery and production are labour-intensive and tiring. The principle of the discovery of therapeutically powerful molecules from the library of known molecules is medication repurposing.The goal of this article is to estimate and classify natural antiviral analogues as inhibitor medicines such as 7-O-Methyl-glabranine, Odorinol, Taspine, Lycorine, Fulvoplumierin Calmolide A, Coriandrin, Inophyllum B, Inophyllum P and Apigenin for COVID-19 main protease inhibitors and compared with commercial antiviral medication Nelfinavir. The 3D association of SARS coronavirus proteins main protease were reserved from Protein Data Bank and docking assessments done with AutoDock Vina software among target proteins and ligands. The research indicated further sensitivity to the negative dock energy against large protease in all inhibitor products. Studies in molecular docking have shown that Inophyllum P is a natural coumarin derivative of exceptional inhibition with a binding energy value of -8.4, -9.7 kcal / mol of 5N5O and 6LU7 enzyme, relative to the other compounds and Nelfinavir antiviral medication (Binding energy -7.8 and -8.1 Kcal/mol). The medication repurpose method gave great insight into treatments that may be effective in the management of corona virus disease.Therefore, the new in-silico test offers structural understanding of COVID-19 protease and too its molecular connection to some protease inhibitors recognised.
Antiviral, adme, covid-19, diosgenin, hesperidin, molecular docking
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/143184705
IDR: 143184705
Текст научной статьи Drug repurposing approach: in-silico studies on natural antiviral analogues as therapeutic agents for COVID-19
Environmental and economic characteristics can greatly promote the efflux of secondary metabolites such as tropical plant bioactive compounds. Additionally, secondary plant-concealed metabolites are deemed prodigiously in tropical regions and are progressed in remedies (Guerriero et al., 2018; Yang et al., 2018) Innumerable medicinal plant natural products were already evaluated for antiviral action (Zakaryan et al., 2017). The flavonoid analogue 7-O-Methyl-glabranine having significant antiviral activity against dengue virus and extracted from the medicinal plant Tephrosia madrensis (Jo et al., 2020; Sanchez et al., 2000) Odorinol displayed notable antiviral effect on anikhet disease virus and excerted from Aglaia roxburghiana Miq. Var. Beddomei (Meliaceae) therapeutic plant (Phillipson & Zenk, 1980). The natural therapeutic plant derivative Taspine isolated from Croton lechleri M (Euphorbiaceae) and having significant antiviral effect against several virus species, Simian sarcoma virus, auscher virus, and avian myeloblastosis virus through inhibiting NA-directed DNA polymerase (Manske & Brossi, 1990). The natural antiviral analogue Lycorine was isolated from the therapeutic plant Clivia miniata egel (Amaryllidaceae) and displayed remarkable inhibition ability against Poliomyelitis virus at 1µg/mL (Ieven et al., 1982). The compound Fulvoplumierin was the inhibitor of HIV-1 (human immunodeficiency virus type 1) reverse transcriptase and extracted from the medicinal plant Plumeria rubra L. (Apocynaceae) (Tan et al., 1991). The natural coumarin analogue Calmolide A isolated from the leaves of medicinal plant Calophyllum lanigerum (Guttiferae) and showed significant antiviral effect against HIV (Murray et al., 1982). The natural isocoumarin derivative Coriandrin isolated from the Coriandrum sativus medicinal plant and revealed significant antiviral effect against HIV (Towers, 1989). The natural coumarin derivatives Inophyllum and Podophyllum B were inhibitors of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase and found in the medicinal plant Calophyllum inophyllum Linn. (Guttiferae) (Patil et al., 1993). The natural flavonoid derivative Apigenin displayed significant antiviral effect against Herpes virus and extensively dispersed in the plant demesne (Thayil & Thyagarajan, 2016; Beladi et al., 1977). The natural antiviral analogues were represented in Figure. 1. We also looked at 7-O-Methyl-glabranine, Odorinol, Taspine, Lycorine, Fulvoplumierin Calmolide A, Coriandrin, Inophyllum B, Inophyllum P and Apigenin as possible SA S inhibitor candidates (PDB ID: 5N5O and 6LU7), as well as Nelfinavir, antiviral medication. The findings of this report will give more researchers the prospect of discovering the correct COVID-19 medicines.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Molecular docking
Molecular docking tests were being used for binding mode examination, association of compounds 7- O -Methyl-glabranine , Odorinol , Taspine , Lycorine , Fulvoplumierin Calmolide A , Coriandrin, Inophyllum B, Inophyllum P , Apigenin and antiviral Nelfinavir with SA S corona virus proteins (PDB ID: 5N5O and 6LU7) by AutoDock Vina 1.1.2 (Trott & Olson, 2010) . Protein
Data Bank (http:/ has been utilized to obtain the crystal structures of the main protease SA S coronavirus (PDB ID: 5N5O) and (PDB ID: 6LU7) ChemDraw Ultra 12.0 and Chem3D Pro 12.0 programs were utilized to sketch structures of the inhibitors and too energy minimization. The AutoDock Software 1.5.6 application bundle was used to build AutoDock Vina input data. Discovery studio 2019 program package was utilized for binding pocket prediction of main protease (PDB ID: 5N5O and 6LU7) via co-crystallized ligands The amino acid residues Thr26, His41, Met49, Phe140, Leu141, Asn142, Gly143, Ser144, Cys145, His163, His164, Glu166, His172, Asp187, Gln189 and Thr190 were situated in the binding pocket of SA S corona virus protein (PDB ID: 5N5O). The amino acid residues Thr24, Thr26, Phe140, Asn142, Gly143, Cys145, His163, His164, Glu166 and His172 were situated in the binding pocket of SA S corona virus protein (PDB ID: 6LU7). The 5N5O Protein Quest Grid has been recognised as centre x,y,z: -23.002, -3.023, 4.681 with measurements x,y,z: 24 with 1.0 Å interval. The 6LU7 protein quest grid was defined as centre x,y,z:-10.656, 17.223, 67.024 in dimension x,y,z: 20 in 1.0 Å spacing. The meaning of completeness was set to 8. The other restrictions have been fixed and not specified by default for AutoDock Vina. The compound which devorates the smallest inhibitory value is the main inhibitor and the consequences were visually examined by Discovery studio 2019.
ADME and Molecular Property Prediction
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Docking studies
Docking simulations were carried out in order to advance understanding of the possible process of biological activity. The compounds 7-O-Methyl-glabranine, Odorinol, Taspine, Lycorine, Fulvoplumierin, Calmolide A, Coriandrin, Inophyllum B, Inophyllum P and Apigenin as well as Antiviral Nelfinavir compounds were evaluated for their inhibition capability with respect to SA S corona virus proteins 5N5O and 6LU7 through the software Autodock Vina. All these checked inhibitors demonstrate negative binding energy. The natural derivative Inophyllum P demonstrates astonishing inhibition capability with the binding energy value of -9.4 kcal/mol over other compounds 7-O-Methyl-glabranine (-7.5kcal/mol), Odorinol (-6.7 kcal/mol), Taspine (-7.1 kcal/mol), Lycorine (-8.1 kcal/mol), Fulvoplumierin (-6.4 kcal/mol), Calmolide A (-6.8 kcal/mol), Coriandrin (-6.3 kcal/mol), InophyllumB (-7.9 kcal/mol), Apigenin (-7.2 kcal/mol) and antiviral drug Nelfinavir (-7.8 kcal/mol) in 5N5O protein individually. Hydrogen bonding is an essential aspect of bonding equilibrium between ligand and protein, and the supporting bonding gap between atoms H-acceptor and H-donor is less than 3.5 Å (Taha et al., 2015). The related hydrogen bonding distances for the specific inhibitors in the target protein were less than 3.5 Å demonstrating the strong hydrogen link amongst ligands and receptor. Compound Inophyllum P demonstrates four associations between hydrogen bonding and 5N5O receptor. The residue of the amino acids Phe140, Leu141, Serb144, and Glu166 is associated with bond lengths of 1.89, 2.85, 2.91 and 2.59 Å in contact with hydrogen. The residues of Glu166 amino acids came in contact with hydrophobics. Figure 2 indicates the hydrophobic and hydrogen bonding interaction of amino acid residues with compound Inophyllum P in 5N5O protein. The antiviral Nelfinavir treatment demonstrates four associations with hydrogen bonding with the 5N5O receptor. The residues of Leu141, Cys142, Glu166 and Gln189 amino acids is entangled through associations between hydrogen and the bond lengths 2.46, 2.42, 2.52 and 2.82 Å. The amino acid residues Cys145 and Gln189 were mixed with in hydrophobic encounters. Figure 3 indicates the hydrogen binding and hydrophobic interaction of amino acid residues in 5N5O protein with Nelfinavir antiviral medication. Table 1 displays the molecular interactions of natural analogues on target protein 5N5O Inophyllum P natural coumarin analogue demonstrates impressive inhibition capacity with a binding energy value of -9.7 kcal/mol relative to other compounds 7-O-Methyl-glabranine (-7.7 kcal/mol), Odorinol (-6.7 kcal/mol), Taspine (-7.2 kcal/mol), Lycorine (-7.9 kcal/mol), Fulvoplumierin (-6.9 kcal/mol), Calmolide A (-8.2 kcal/mol), Coriandrin (-6.2 kcal/mol), InophyllumB (-9.3 kcal/mol), Apigenin (-7.4 kcal/mol) and antiviral drug Nelfinavir (-8.1 kcal/mol) in 6LU7 protein individually. Compound Inophyllum P displays two hydrogen bonding interactions with receptor 6LU7 The amino acid residues Gly143 and Glu166 were entangled into correlations between hydrogen and the bond lengths of 2.22 and 2.33 Å. The amino acid residues His41, Met49 and Cys145 have been enmeshed in hydrophobic encounters. Figure 4 demonstrated the bonding of hydrogen and hydrophobic constructions of amino acid residues with Inophyllum P compound in the 6LU7 protein. The antiviral medication Nelfinavir demonstrates three associations between hydrogen and receptor 6LU7. The residues of Thr26, Asn142 and Gly143 amino acids were entangled in hydrogen bonding to the 2.42, 2.47 and 1.94 Å bonding ranges. The residues of the Cys145 Leu27, His41, Met49, Cys145, Met165 and Gln189 amino acids were in touch with hydrophobia. The hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic connexions with Nelfinavir are seen in Figure 5 of amino acid residues in the 6LU7 protein. The findings revealed that the compound Inophyllum P had exceptional inhibition capacity in their respective target proteins relative to other compounds. The findings of natural antiviral analogues against SA S coronavirus (PDB ID: 6LU7) have been shortened in Table 2.
ADME and Molecular Property Prediction
The development of bioactive compounds as healers is driven by high oral bioavailability (Newby et al ., 2015) . The key forecasters of this analysis were demonstrates for example the low polar surface region, hydrogen bounding ability, intestinal absorption and decreased molecular versatility (Azam et al ., 2012) . The natural antiviral analogues 7- O -Methyl-glabranine , Odorinol , Taspine , Lycorine , Fulvoplumierin Calmolide A , Coriandrin, Inophyllum B, Inophyllum P , Apigenin passes Lipinski's " ule of 5" with 0 infringement and compound Nelfinavir passes " ule of 5" with 1 infringement MW > 500 (Table 3). The molecular conformational changes were defined by the number of revolving ties and the potential for the receptor binding. The compounds 7- O -Methyl-glabranine , Odorinol , Taspine , Lycorine , Fulvoplumierin, Calmolide A , Coriandrin, Inophyllum B, Inophyllum P , Apigenin were under 10 rotatable bonds except Nelfinavir (12 rotate bonds), which are formed without the chirality core, and have poor oral bioavailability conditions. The property topological Polar Surface Area (tPSA) revealedthe blood-brain barrier penetration and the passive molecular transport across membranes (Ertl et al ., 2000) . Checked substances with tPSA values < 140Å2 fulfil the requirements for subsequent oral administration for gastrointestinal absorption. In comparison, all of the compounds studied except for Lycorine (tPSA= 99.46Å2), Apigenin (tPSA =
90.90 Å2) and Nelfinavir (tPSA = 127.20 Å2) have a lower blood brain barrier (tPSA> 90 Å2), which reveals the detrimental effects of the Central Nervous System (CNS). The tested compounds demonstrated absorption percentage (percentage Abs = > 50), suggesting strong bioavailability. Bioavailability by oral route was appropriate (> 50 percent). The compounds Odorinol , Taspine , Lycorine , Fulvoplumierin, Coriandrin and Apigenin were very water soluble(-logS> -4) excluding compounds 7- O -Methyl-glabranine (-logS -5.32), Calmolide A (-logS -4.70), InophyllumB (-logS -5.28), InophyllumP (-logS-5.28) and Nelfinavir (-logS -6.36) have moderate water solubility. The side effects of liver impairment were not suspected in the case of compounds 7- O -Methyl-glabranine , Odorinol , Lycorine , Fulvoplumierin Coriandrin, Inophyllum B, Inophyllum P and Nelfinavir since they were predicted to be CYP2D6 non-inhibitors. A part of the P-glycoprotein (P-gp) family transporter ATP-binding cassette (ABC) includes the intestinal absorption, pharmaceutical metabolism and brain penetration; its caginessmay significantly alter the bioavailability and defence of the drug (Fromm, 2000) . Phospholipidosis convinced medication is a condition known for the further growth of phospholipids in tissues and for medication-related toxicity (Nonoyama & Fukuda, 2008) .
Table 1. Molecular docking interaction of compounds ( 1a-1k ) against protease ofSA Scoronavirus (PDB ID: 5N5O)
|
Compounds |
Main protease of SA S coronavirus (PDB ID: 5N5O) |
||
|
Binding affinity (kcal/mol) |
No. of H-bonds |
H-bonding residues |
|
|
7- O -Methyl-glabranine(1a) |
-7.5 |
2 |
Gly143, Glu166 |
|
Odorinol(1b) |
-6.7 |
3 |
Ser144, Cys145 |
|
Taspine(1c) |
-7.1 |
0 |
- |
|
Lycorine(1d) |
-8.1 |
5 |
Leu141, Ser144, Cys145, His163 |
|
Fulvoplumierin(1e) |
-6.4 |
2 |
Glu166, Gln189 |
|
Calmolide A(1f) |
-6.8 |
2 |
Cys145, His164 |
|
Coriandrin(1g) |
-6.3 |
4 |
Gly143, Ser144, Cys145 |
|
Inophyllum B(1h) |
-7.9 |
0 |
- |
|
Inophyllum P(1i) |
-8.4 |
1 |
His141 |
|
Apigenin(1j) |
-7.2 |
5 |
Leu141, Asn142, Ser144, Glu166, |
|
Arg188 |
|||
|
Nelfinavir (1k) |
-7.8 |
4 |
Leu141, Cys145, Glu166, Gln189 |
Table 2. Molecular docking interaction of compounds (1a-1k) against protease ofSA Scoronavirus (PDB ID: 6LU7)
|
Compounds |
Main protease ofSA Scoronavirus (PDB ID: 6LU7) |
||
|
Binding affinity (kcal/mol) |
No. of H-bonds |
H-bonding residues |
|
|
7- O -Methyl-glabranine (1a) |
-7.7 |
0 |
- |
|
Odorinol (1b) |
-6.7 |
2 |
Ser144, Cys145 |
|
Taspine (1c) |
-7.2 |
1 |
Glu166 |
|
Lycorine (1d) |
-7.9 |
2 |
Phe140, Leu141 |
|
Fulvoplumierin(1e) |
-6.9 |
4 |
Leu141, Gly143, Cys145, Glu166 |
|
Calmolide A (1f) |
-8.2 |
2 |
Cys145, His164 |
|
Coriandrin (1g) |
-6.2 |
1 |
Gly143 |
|
Inophyllum B (1h) |
-9.3 |
0 |
- |
|
Inophyllum P (1i) |
-9.7 |
1 |
His164 |
|
Apigenin (1j) |
-7.4 |
2 |
Glu166, Asp187 |
|
Nelfinavir (1k) |
-8.1 |
3 |
Thr26, Asn142, Gly143 |
Table 3. Virtual ADME (absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion) and molecular property prediction of the potent compounds ( 1a-1k ).
|
Comp. |
tPSAa |
%Abs b |
MWc |
oBd |
HBD e |
HBA f |
M g |
IlogPh (MlogP ) |
LogSi |
CYP2D6 Inhibitor |
|
Rule |
≤140 ´Å2 |
>50 |
≤500 |
≤10 |
≤5 |
≤10 |
40–130 |
<5 |
>-4 |
- |
|
7- O -Methyl- |
3.86 |
|||||||||
|
glabranine (1a) |
48.67 |
92.20 |
350.41 |
5 |
0 |
4 |
104.62 |
(2.64) |
-5.32 |
No |
|
Odorinol (1b) |
69.64 |
84.97 |
318.41 |
8 |
2 |
3 |
93.38 |
2.47 (1.45) |
-3.11 |
No |
|
Taspine (1c) |
82.12 |
80.66 |
355.34 |
4 |
0 |
7 |
97.68 |
2.78 (1.88) |
-3.68 |
Yes |
|
Lycorine (1d) |
99.46 |
74.68 |
317.29 |
0 |
3 |
6 |
80.85 |
1.95 (0.32) |
-1.87 |
No |
|
Fulvoplumie rin(1e) |
67.51 |
85.70 |
230.22 |
2 |
1 |
4 |
63.95 |
1.88 (1.76) |
-2.25 |
No |
|
Calmolide A (1f) |
68.90 |
85.22 |
370.44 |
2 |
1 |
5 |
106.11 |
3.83 (2.85) |
-4.70 |
Yes |
|
Coriandrin (1g) |
48.67 |
92.20 |
232.23 |
1 |
0 |
4 |
61.64 |
2.33 (1.64) |
-3.26 |
No |
|
Inophyllum B (1h) |
68.90 |
85.22 |
404.46 |
1 |
1 |
5 |
116.97 |
3.73 (3.25) |
-5.28 |
No |
|
Inophyllum P (1i) |
68.90 |
85.22 |
404.46 |
1 |
1 |
5 |
116.97 |
3.73 (3.25) |
-5.28 |
No |
|
Apigenin (1j) |
90.90 |
77.63 |
270.24 |
1 |
3 |
5 |
73.99 |
1.89 (0.89) |
-3.94 |
Yes |
|
Nelfinavir (1k) |
127.20 |
65.11 |
567.78 |
12 |
4 |
5 |
166.17 |
3.87 (3.20) |
-6.36 |
No |
Abbreviations: a Topological polar surface area; b Absorption; c Molecular weight; d Number of rotatable bonds; e Number of hydrogen bond donors; f Number of hydrogen bonds acceptors; g Molar refractivity; h Logarithm of compound partition coefficient between n-octanol and water; iLogarithm of water solubility.
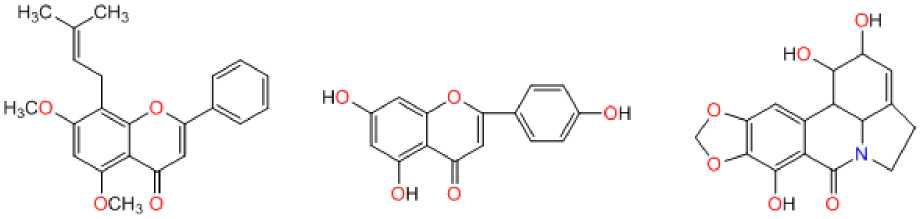
Lycorine
Poliomyelitis virus
оснэ о
Apigenin
Herpes virus
7-O-Met hylglabra nine
Dengue Virus
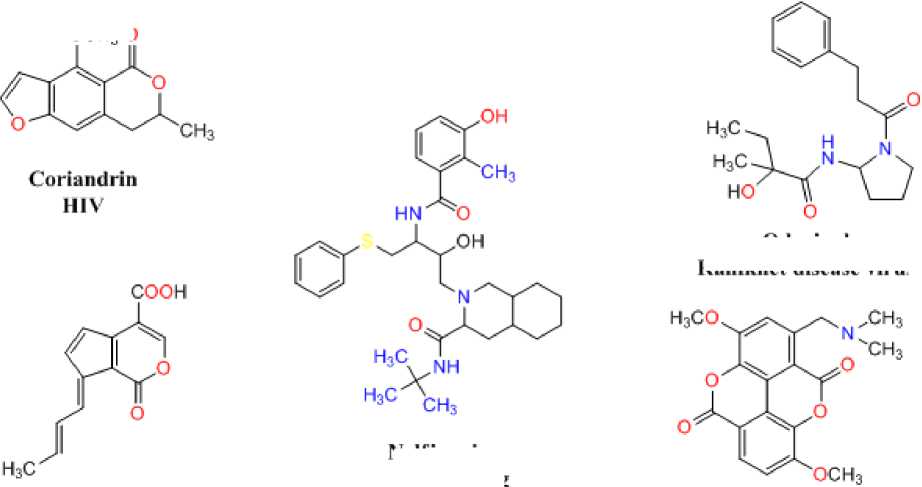
Nelfinavir
Antiviral Drug
Odorinol
Ranikhet disease virus
Fulvoplumicrin
(HIV-1) reverse transcriptase
Taspine avian myeloblastosis virus, Rauscher virus. Simian sarcoma virus
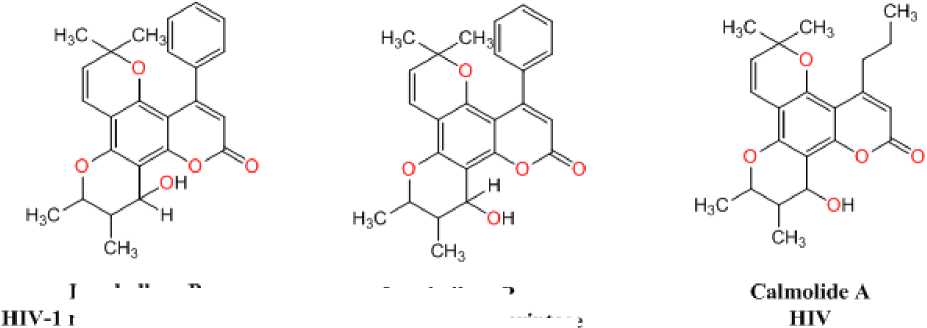
Inophyllum В reverse transcriptase
Figure 1: Natural antiviral analogues
Inophyllum P
HIV-1 reverse transcriptase
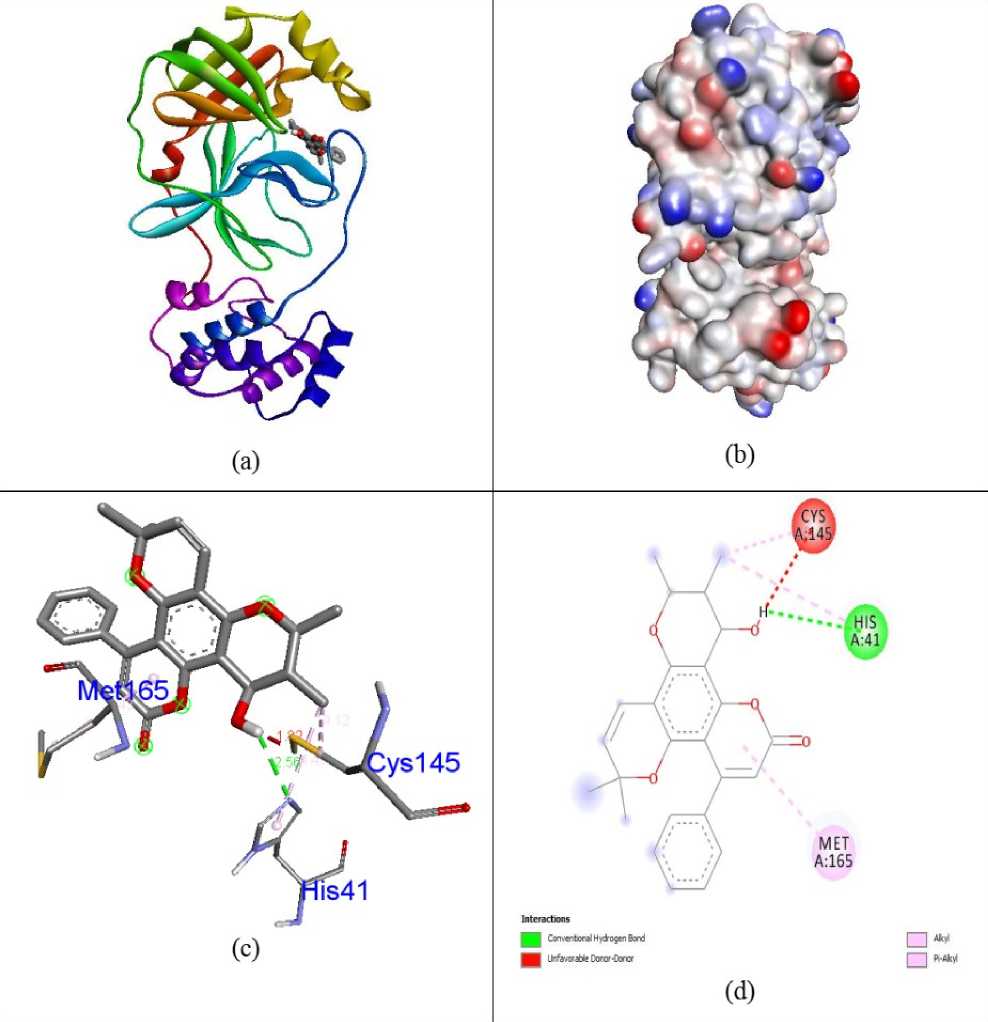
ys145
is41
МИ
MET A:165
И Concenter* н vicce" Bond
В Unf»>txatte Conor-Donor
Figure 2: Docked complex (a), molecular surface (b), 3D (c), and 2D (d) interaction modes of Inophyllum P within the binding site of 5N5O protein.
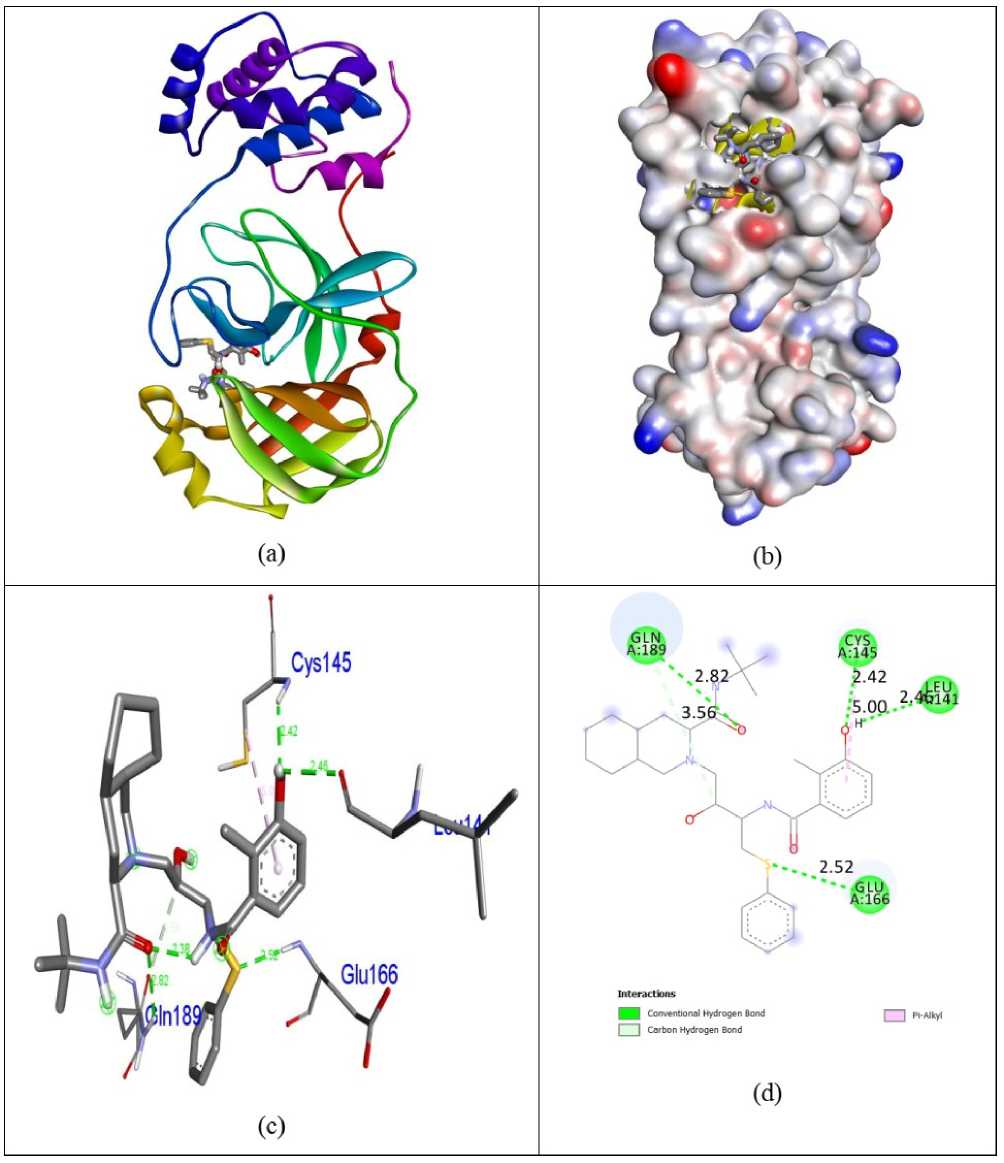
Figure 3: Docked complex (a), molecular surface (b), 3D (c), and 2D (d) interaction modes of antiviral drug Nelfinavir within the binding site of 5N5O protein.
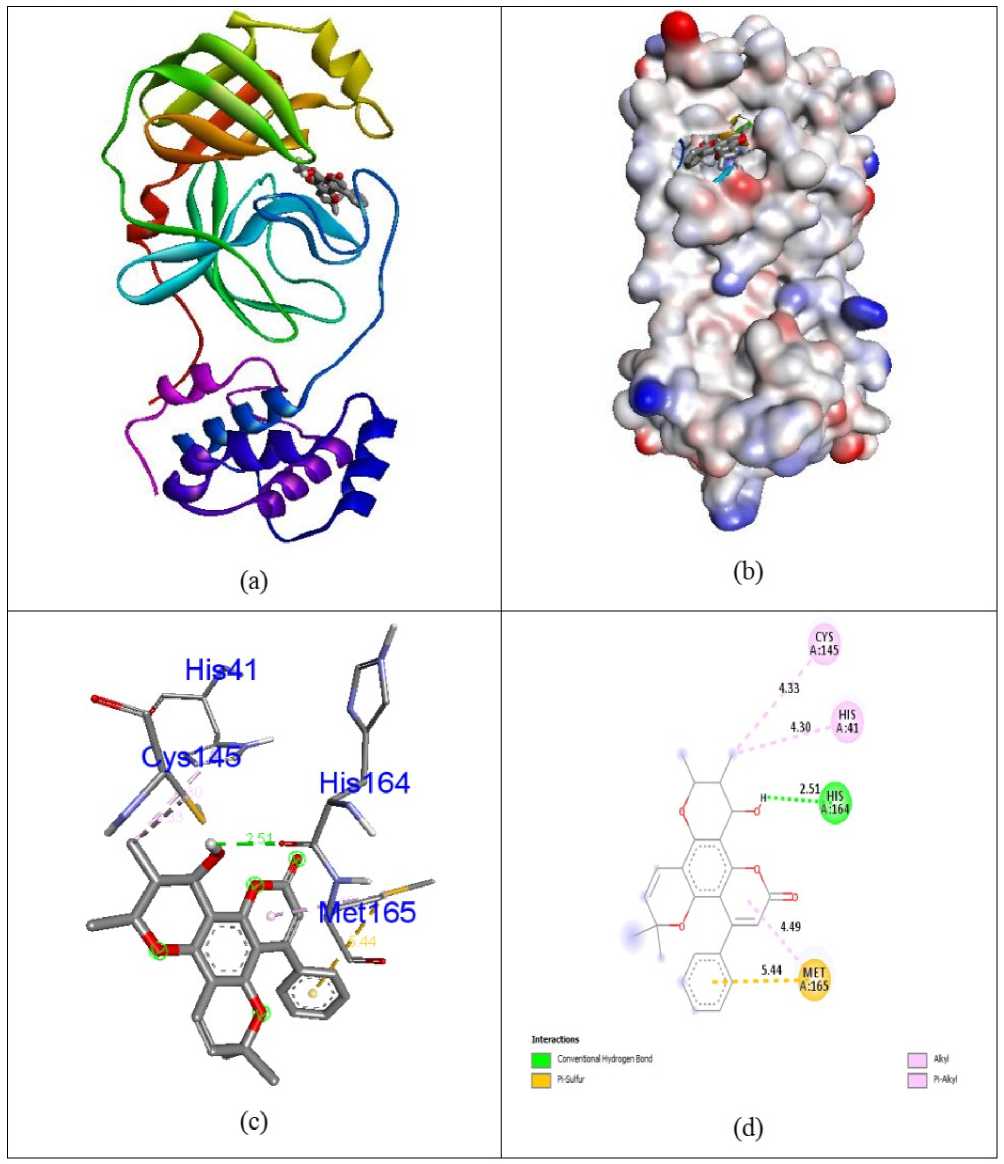
Figure 4: Docked complex (a), molecular surface (b), 3D (c), and 2D (d) interaction modes of Inophyllum P within the binding site of 6LU7 protein.
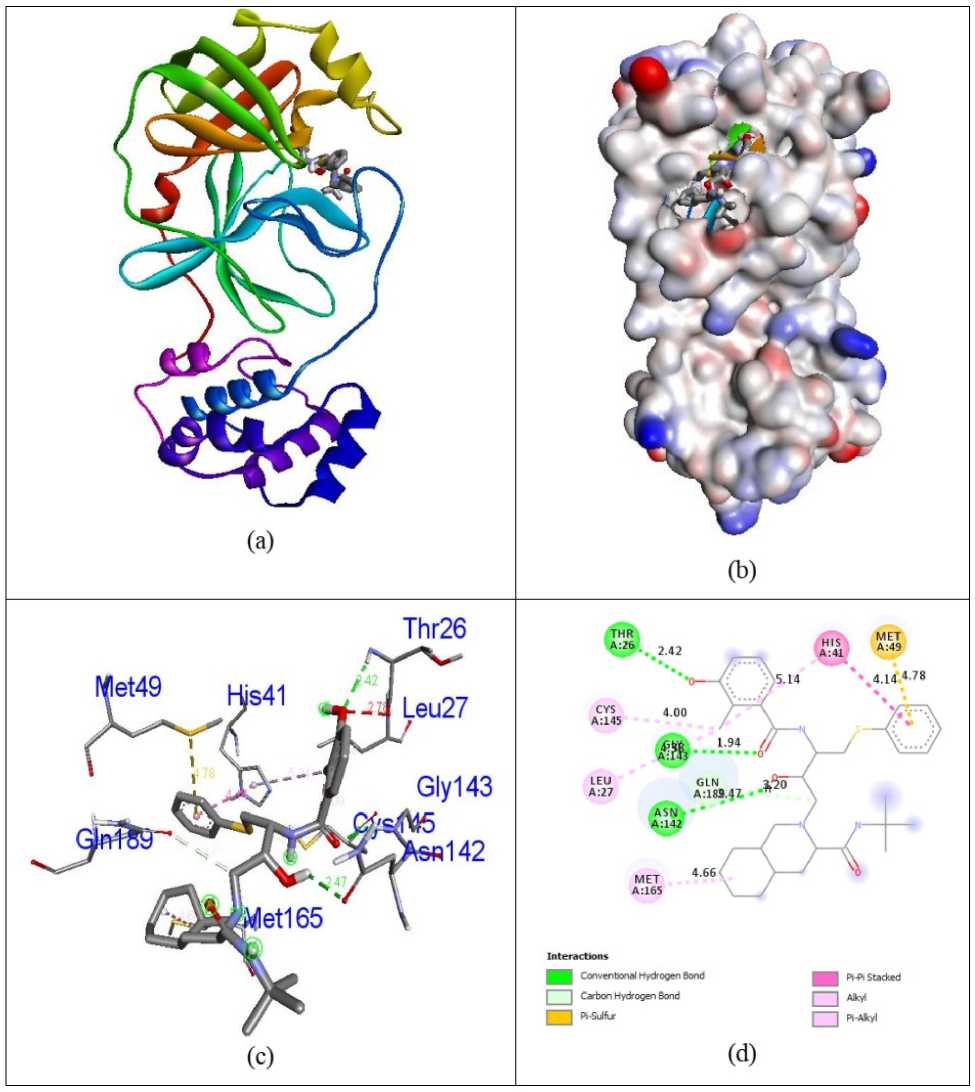
Figure 5: Docked complex (a), molecular surface (b), 3D (c) within the binding site of 6LU7 protein.
The findings indicate that the studied compounds 7-
O -Methyl-glabranine , Odorinol , Taspine ,
Fulvoplumierin Coriandrin, Apigenin was not a part of P-gp substrate and phospholipidosis was not promoted. The checks for P-gp-phospholipidosis was anticipated in Lycorine, Calmolide A, Inophyllum B, Inophyllum P, and Nelfinavir. The overall findings of ADME and toxicity indicate respectable pharmacological profile and and 2D (d) interaction modes of antiviral drug Nelfinavir rapid gastrointestinal ingestion through blood-brain blood barrier penetration in the isolated compounds 7 O-Methyl-glabranine, Odorinol, Taspine, Lycorine, Fulvoplumierin, Calmolide A, Coriandrin, Inophyllum B, Inophyllum P and Apigenin. All compounds evaluated were known as drug-like and passed " ule of 5" of Lipinski. The restrictions predicted are all within the context of accepted principles.
CONCLUSION
Actually, COVID-19 has arisen in the human community, in China, and is a possible danger to health internationally. Nevertheless, there is no scientifically agreed medication to treat the condition. The already available COVID-19 drugs coping with key protease The goal of the current study was to inspect some natural analogues extracted from medicinal plants that could be tossed off to fight COVID-19. The most frequently proposed compounds in therapeutic plants that may function as major inhibitors of COVID-19 key protease (PDB ID: 5N5O, 6LU7) were 7- O -Methyl-glabranine , Odorinol , Taspine , Lycorine ,
Fulvoplumierin Calmolide A , Coriandrin, Inophyllum B, Inophyllum P and Apigenin with negative binding energies. Studies in molecular docking have shown that Inophyllum P is a natural coumarin derivative of exceptional inhibition with a binding energy value of -8.4, -9.7 kcal/mol of 5N5O and 6LU7 enzyme, relative to the other compounds and Nelfinavir antiviral medication (Binding energy -7.8 and -8.1 Kcal/mol). However, advance study is necessary in order to inspect the possible application of these compounds in medicinal plants.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest.


