E-banking analysis during COVID-19 pandemics
Автор: Kovinić Nikola, Savić Marko, Pavlović Nikola
Журнал: Ekonomski signali @esignali
Статья в выпуске: 2 vol.17, 2022 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Electronic banking presents a general term used to denote a process allowing legal and physical entities to perform personal and commercial banking transactions by using electronic and telecommunication networks. It covers various jobs such as assets transfers, current account statements, bill payments, the closest ATM locating, attaining the information about financial products and services, loan applications, and some other activities performed with the use of a computer, smartphone, or some other technical devices. The subject of this research study is the analysis of the e-banking usage during COVID-19 pandemics in the Republic of Serbia and Bosnia and Herzegovina. COVID-19 pandemics influenced a great number of transactions to be done online, i.e. by using digital payment options. Furthermore, it affected banks to develop extra benefits for their users, as well as, to promote current e-architecture referring to the possibilities of e-banking use.
E-banking, COVID-19, payment and credit cards, payments, distribution networks
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/170204029
IDR: 170204029 | DOI: 10.5937/ekonsig2202169K
Текст научной статьи E-banking analysis during COVID-19 pandemics
Since the end of the last century and the beginning of this century, banking has been going through significant changes, adapting to new circumstances and challenges in the environment [Sanader, 2014, 86]. This led to creation of a new concept, i.e. electronic banking. Electronic banking was gradually introduced into the banking system [Zelenović, 2015, 48] Electronic banking, also known as E-Banking, is the provision of banking services electronically without any time or geographical restrictions. Therefore, it can be concluded that electronic banking enables easy and modern access to banking services for clients. Banking services are available to people living in remote areas without physical presence of banks. [Stankić, 2008, 49]
The task of this study is to analyze the use of e-banking during the pandemic of the CO1ID-19 virus in the Republic of Serbia and Bosnia and Herzegovina. The ob?ective of this introductory study is to prove, on the basis of the collected material, the existence of the increasing use of e-banking (electronic banking) in the time of the CO1ID-19 virus pandemic and to point out the importance of the increasing use of digital payments by users of banking services.
Based on everything presented in the study, the basic hypothesis and special hypotheses can be distinguished.
Basic (general) hypothesis: Electronic banking (e-banking) records an obvious growth during the pandemic of the CO1ID-19 virus in the period 2020/2021. in the monitored countries (Republic of Serbia and Bosnia and Herzegovina).
Special hypotheses :
-
- H1: "Distribution networks of electronic banking record growth during the pandemic of the CO1ID-19 virus in the observed countries."
-
- H2: "The pandemic of the CO1ID-19 virus as an instigator of the increased use of electronic banking in the future."
Republic of Serbia
In the period from March 2020 to January 2021, the number of electronic banking users in the Republic of Serbia increased by 14.83%. ,t the end of the fourth quarter of 2020, we had 3,156,041 electronic banking users in the Republic of Serbia. In the same observed period, the number of mobile banking users increased to 2,162,362 users, or 26.99%. ,s the use of electronic banking increases, so does the number of transactions and the value of transactions. The number of transactions in 2020 carried out using electronic banking increased by 50.77% compared to 2019. The number of transactions made by entrepreneurs, natural persons and legal entities using electronic banking increased in the same observed period from 25,076,935 transactions to 37,809,125 transactions, which represents an increase from 326,008
million dinars to 519,917 million dinars.
,ccording to the National Bank of Serbia data, the use of the most modern forms of payment in our country continued to increase in the second quarter of 2021. [NBS, 2021] The number of concluded electronic banking contracts for natural persons and legal entities at the end of the second quarter of 2020 was 2,933,227 and at the end of the second quarter of 2021 it was 3,308,616, which represents a growth of 12.80%. ,s for the number of concluded mobile banking contracts for natural personsand legal entities, it was even higher and at the end of the second quarter of 2020 it amounted to 1,921,347, while at the end of the second quarter of 2021 it amounted to 2,556,111, which represents an increase of 33.04 %. Furthermore, the increase is noticeable compared to the first quarter of 2021, the number of electronic banking users (individuals and legal entities) increased by 3.51%, whereas the number of mobile banking users (natural personsand legal entities) in the same observed period increased by 12.32%. The stated growth is higher than the growth recorded between the previous two quarters - the fourth quarter of 2020 and the first quarter of this year, since the growth in the num- ber of users of electronic and mobile banking in that period amounted to 1% and 5% respectively. [NBS, 2021]
,ccording to the available data, it can be clearly seen that the number of natural persons using mobile and electronic banking increased significantly at the end of the second quarter of 2021 compared to the end of the second quarter of 2020. When it comes to the use of mobile banking by natural persons, that number increased by 33.12%, from 1,880,854 at the end of the second quarter of 2020 to 2,503,819 at the end of the second quarter of 2021. When it comes to the use of electronic banking by natural persons, that number increased by 13.26%, from 2,651,509 at the end of the second quarter of 2020 to 3,003,002 at the end of the second quarter of 2021.
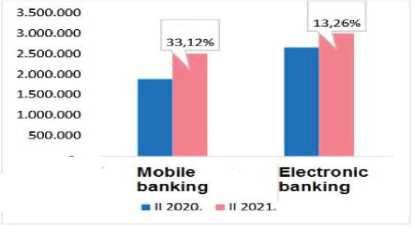
Figure 1 . Percentage ofnaturalpersons using mobile and electronic banking (NBS, 2021, 1)
,lso, it can be clearly seen that the number of legal entities and entrepreneurs using mobile and electronic banking increased significantly at the end of the second quarter of 2021 compared to the end of the second quarter of 2020. When it comes to the use of mobile banking by legal entities and entre- preneurs, that number increased by 29.14%, from 40,493 at the end of the second quarter of 2020 to 52,292 at the end of the second quarter of 2021. In this same period, the number of legal entities and entrepreneurs using electronic banking increased by 8.48% (from 281,718 to 305,614).
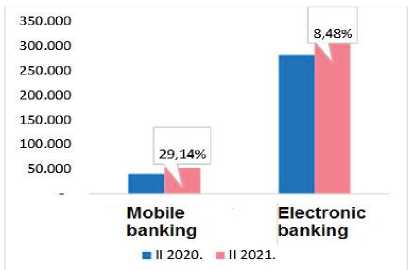
Figure 2. Percentage oflegal entities and entrepreneurs who use mobile and electronic banking [NBS, 2021b, 1]
,t the end of the second quarter of 2021, the number of transactions performed by individuals, legal entities and entrepreneurs using mobile banking increased by 39.13% and number of transactions using electronic banking by 22.83% compared to the end of the second quarter of 2020. The number of transactions of natural persons using mobile banking increased by 32.37% at the end of the second quarter of 2021 compared to the end of the second quarter of 2020, from 8,200,356 transactions to 10,855,100 transactions. However, the number of transactions performed by natural persons using electronic banking decreased by 1.57% at the end of the second quarter of 2021 compared to the end of the second quarter of 2020, from 6,189,897 transactions to 6,092,555 transactions.
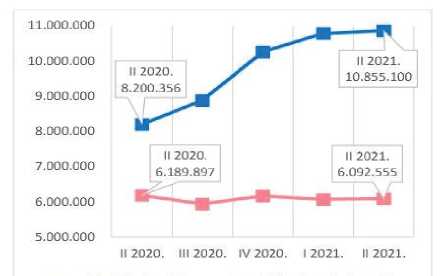
■ Mobile banking • Electronic banking
Figure 3 . Number oftransactions performed by naturalpersons [NBS, 2021, 2]
The number of transactions performed by legal entities and entrepreneurs using mobile banking increased by 103.57%, from 859,665 transactions at the end of the second quarter of 2020 to 1,749,989 transactions at the end of the second quarter of 2021. In the same period, the number of transactions by legal entities and entrepreneurs using electronic banking increased by 28.33%, from 27,467,021 transactions to 35,248,105 transactions.
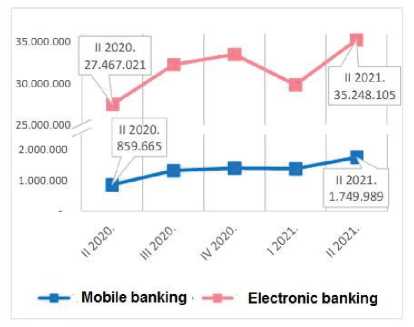
Figure 4 . Number oftransactions performedby legal entities and entrepreneurs [NBS, 2021, 2]
The use of payment and credit cards for the purchase of goods and services on the Internet is experiencing significant growth. During 2020, a total of 21,206,889 transactions in all currencies were performed using cards and paying for goods and services on the Internet. This represents a growth of 61.86% compared to 2019. When we look only at transactions that were performed in the dinar equivalent, we can see that in 2020, compared to 2019, there was an increase of
103.76%, that is, 14,316,356 transactions were performed.
The popularity of buying goods and services on the Internet is not decreasing either, so the number of dinar payments (that is, on the websites of Serbian stores) amounted to more than 5.4 million, i.e. by 70.99% more than in the second quarter of 2020. Moreover, the value of the mentioned transactions was over 13.1 billion dinars, which is 80.32% more than the value of payments made in the second quarter of 2020. [NBS, 2021] When it comes to transactions in Euros and US dollars, the growth in the number of payments is slightly more modest - 30.83% and 21.06%, respectively, while the value of payments recorded a significant increase, thus for the Euro it is 107.48%, and for the dollar 124, 86%. [NBS, 2021]
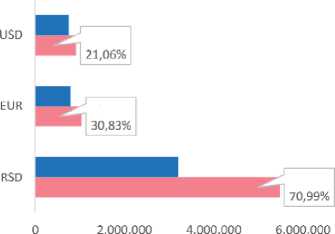
■ 112020. ell 2021.
Figure 5 . Internetpurchase ofgoods and services using cards [NBS, 2021]
Table 1 . Number and value ofcard transactions used to purchase goods and services
|
Number and value |
II 2020. |
II 2021. |
Change % |
|
RSD: |
|||
|
number |
3.205.385 |
5.480.973 |
70,99% |
|
value |
7.300.490.184 |
13.164.322.020 |
80,32% |
|
EUR: |
|||
|
number |
791.847 |
1.035.947 |
30,83% |
|
value |
24.607.256 |
51.055.831 |
107,48% |
|
USD |
|||
|
number |
756.664 |
916.002 |
21,06% |
|
value |
12.620.783 |
28.379.201 |
124,86% |
Source: [NBS, 2021, 3]
,t the end of the second quarter of 2021, the number of ,TMs was 3,122 which is 168 more than at the end of the second quarter of 2020. Furthermore, in the same observed period, the number of POS terminals increased by 14,617, so that at the end of the second quarter of 2021, we have a total of 109,787 installed POS terminals in the Republic of Serbia. The very fact that the number of POS terminals increased by 10,486 at the end of the first quarter of 2021
clearly indicates that the interest of the citizens of the Republic of Serbia in card payments has increased significantly, which is the result of the measures taken by the National Bank of Serbia in the previous period.
Table 2 . Number ofdevices and virtualpoints ofsale
|
Card payments |
II 2020. |
II 2021. |
Change % |
|
POS terminals |
95.170 |
109.787 |
15,36% |
|
,cceptance 1irtual points network of sale |
1.405 |
2.492 |
77,37% |
|
,TM |
2.954 |
3.122 |
5,69% |
|
Transactions performed at POS terminals at stores in the RS using cards issued by a payment service provider from the Republic of Serbia |
69.887.676 |
89.710.736 |
28,36% |
|
Transactions performed at POS terminals at stores in the RS using cards not issued by a payment service provider from the Republic of Serbia |
2.355.639 |
4.998.789 |
112,37% |
|
Payment cards issued |
9.118.000 |
9.920.270 |
8,80% |
Source: [NBS, 2021, 4]
,t the end of the second quarter of 2021, the total number of payment cards was 9,920,270, which is 2.84% more than at the end of the first quarter of the same year, and 8.80% more than at the end of the second quarter of 2020. In total 89,710,736 payments were made by the cards issued in the Republic of Serbia at the end of the second quarter of 2021, which represents an increase of 28.36% compared to the second quarter of 2020. On the other hand, 4,998,789 payments were made by foreign cards in stores in the Republic of Serbia at the end of the second quarter of 2021, which represents an increase of 112.21% compared to the second quarter of 2020. This data clearly shows us that the number of tourists increased significantly in
2021 compared to 2020, even though the CO1ID-19 virus pandemic was in full swing.
Based on the performed analysis, the first special (H1) hypothesis may be confirmed, which reads: " Distribution networks of electronic banking record growth during the CO1ID-19 virus pandemic in the Republic ofSerbia ."
Bosna and Herzegovina
In Bosnia and Herzegovina (BiH), digital technologies in the field of ebanking were used for ,TM withdrawals and card payments. [Jazić, 2021, 3] During 2020, 2,170,556 cards were active in BiH, while in 2021, that number increased by 48,373 cards, in total of 2,218,929 cards.
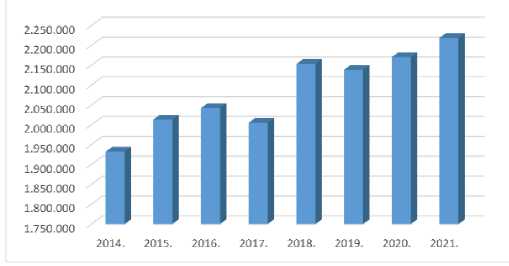
Figure 6 . Number ofissued cards by year in BiH (CBBH, 2022a, 3)
During 2020, transactions were carried out via payment and credit cards in the amount of 11,535,123,080 convertible marks or 5.9 billion Euros, of which 71% were performed on ,TM machines, 28% of transactions were performed via POS devices, and only 1% via the Internet. [CBBH, 2021] In
2021, transactions in the amount of 11,957,151,297 KM were performed by cards, in the country and abroad, which means that there was an increase in the value of transactions in the amount of 422,028,217 KM compared to 2020. [CBBH, 2022, 5]
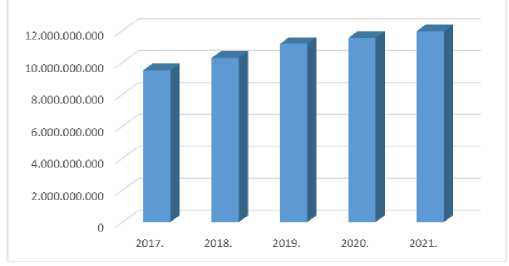
Figure 7 . 1alue ofcard transactions by year in BiH (CBBH, 2022b, 5).
The structure of consumption (,TM, POS and internet) in the amount of 11,957,151,297 KM is as follows:
-
- cash in the amount of 8,750,565,618 KM (in 2020, this amount was smaller and amounted to 8,165,945,556 KM) was withdrawn through ,TM machines, both in the country and abroad;
-
- 2,941,546,480 KM was withdrawn on POS machines (in 2020, that
amount was higher
and amounted to 3,188,540,041 KM);
-
- 265,039,199 KM was consumed via the Internet. (In 2020, that amount was smaller and amounted to 180,637,483 KM). [CBBH, 2022, 6].
In percentages, 73% of the value was withdrawn on ,TM machines, 25% through POS devices, while 2% of the value of card transactions was performed vi a the Internet. [CBBH, 2022, 6]
Overview of card transactions in 2021
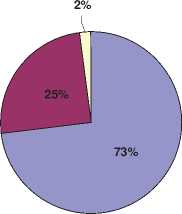
-
□ ATM
-
□ POS
□ Internet
Figure 8 . Overview ofcard transactions in 2021 [CBBH, 2022, 7]
Despite the pandemic caused by the CO1ID-19 virus, the predominant use of cards is exclusively for cash withdrawals. [CBBH, 2021] In 2021, the average turnover per card was 5,389 KM, which is 75 KM more than in 2020, when the average annual turnover per card was 5,314 KM.
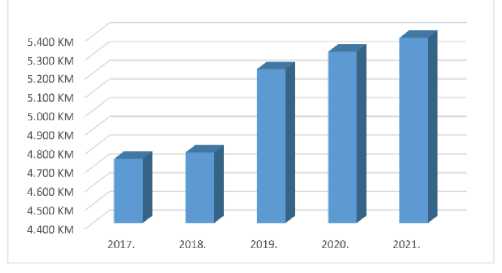
Figure 9 . ,verage turnover per card. [CBBH, 2022d, 10]
During 2020, there was an increase in the number of transactions compared to 2019, and the total number of transactions was 113,574,237. In 2021, the total number of transactions increased compared to 2020 and amounted to 115,381,820. The average value of one transaction was 104 KM in 2021, and it is higher than in 2020 by 2 KM.
CBBH data show that the total value of transactions in 2020 by cards issued by the banks in BiH and by foreign cards in BiH, at ,TMs and POS devices, is lower than in 2019, which is a consequence of the restrictions on the movement of the population caused by the pandemic of the CO1ID-19 virus. In 2021, 593,829,115 KM was realized by bank cards issued by the banking institutions of BiH on ,TM and POS devices of banks abroad, which is 71,784,121 KM more than in 2020, when 522,043,994 KM were realized. In 2020, 1,576,558,757 KM were realized at ,TM and POS devices in BiH by bank cards issued by foreign banking institutions, while in 2021, 2,019,296,723 KM were realized.
Banks are constantly working to introduce a greater number of ,TM and/or POS devices. In the past year, a total of 1,628 ,TM devices (previous year 2020: 1,627) and
30,657 POS devices (2020: 30,371) were installed. Out of the total number of installed POS devices, 29,977 were installed in stores and 680 at bank counters. [CBBH, 2022, 18] In spite of evident progress and great desire, in most financial institutions in BiH, ma?or problems have appeared in the legal regulation of e-banking. One of the ma?or obstacles is the impossibility of greater use of the digital signature, without which it is almost impossible to undertake further activities that should be aimed at improving e-banking. It should also be noted that current limitations in the field of e-banking in BiH are related to the aspect of personal data protection, the importance of raising awareness and trust of clients regarding the use of digital products. This is also supported by the fact that a long-term period was needed for clients to began to actively use cards to withdraw money at ,TMs. For a significant increase in the number of transactions performedthrough e-banking and the value when it comes to shopping on the Internet, using mobile or electronic banking, it is necessary for banks to significantly increase clients' trust toand awareness on e-banking.
Based on the performed analysis, the first special (H1) hypothesis can be confirmed, which reads:
"Distribution networks of electronic banking record growth during the CO1ID-19 virus pandemic in Bosnia and Herzegovina . "
Conclusion
The development of information and communication technology had a great influence on the development of the banking sector. This contributed to banks being able to provide electronic banking services to their clients. Electronic banking today is not a special service offered only by some banks, but a common service offered by all banks to their clients. Electronic banking enables users of banking services to perform their business electronically, from home, office or any other place 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. In order for electronic banking to function well, it is necessary for the bank to develop a good information system and good protection of information and transactions.
The sub?ect of this research study is the analysis of the use of ebanking during the pandemic of the CO1ID-19 virus in the Republic of Serbia and Bosnia and Herzegovina. The CO1ID-19 virus pandemic caused an increasing number of transactions to be carried out online, i.e. through digital payment options. It also conditioned banks to develop additional benefits for their users, as well as to improve the existing digital infrastructure related to the possibilities of using e-banking.
Here, a general hypothesis and additional hypotheses were set. The main (general) hypothesis of the research was: "Electronic banking (e-banking) records an obvious growth during the pandemic of the CO1ID-19 virus in the period 2020/2021. in the observed countries (Republic of Serbia and Bosnia and Herzegovina)". Based on the presented general hypothesis, the first specific (H1) hypothesis read: "Distribution networks of electronic banking record growth during the pandemic ofthe CO1ID-19 virus in the observed countries". The second specific (H2) hypothesis read: "The CO1ID-19 virus pandemic as an instigator of the increased use ofelectronic banking in the future".
Based on the performed analysis and obtained results, we can confirm the first special (H1) hypothesis in both analyzed countries. ,lso, based on the performed analysis, we can confirm another special (H2) hypothesis. Based on these two confirmed special hypotheses, we can confirm the basic (general) hypothesis of the research, which reads: " Electronic banking (e-banking) records an obvious growth during the pandemic ofthe CO1ID-19 virus in the period 2020/2021. in the observed countries ". We conclude that the research has confirmed the general hypothesis and auxiliary hypotheses.
Список литературы E-banking analysis during COVID-19 pandemics
- Akhisar, I., Tunay, B., Tunay, N. (2015) The effects of innovations on bank performance: The case of electronic banking services. Istanbul: Marmara University, Banking and Insurance School, Actuary Department
- Bank, O.S.(nbs) N. (2021) Overview of data related to the provision of payment services and the issuance of electronic money for the second quarter of 2021. Belgrade
- Central Bank of BiH (CBBH) (2022) Card use in Bosnia and Herzegovina in 2021. Sarajevo
- Central Bank of BiH (CBBH) (2022) Card use in Bosnia and Herzegovina in 2021. Sarajevo: Service for Monitoring and Development of Payment Systems
- Central Bank of BiH (CBBH) (2021) Card business in 2020-Increase in the number of active cards, value and number of transactions. Visited 03/14/2022, https://www.cbbh.ba/press/Show News/1337
- Jazic, A. (2021) Digital transformation: Inevitability accelerated by the health crisis. Sarajevo
- Kovačević, M., Đurović, M.S. (2014) Law - theory and practice. Novi Sad: University of the Academy of Economics in Novi Sad, Faculty of Economics and Engineering Management - FIMEK
- National Bank of Serbia (NBS) (2021) The use of modern forms of payment continues to grow. Visited on April 10, 2022, https://www.nbs.rs/sr/scripts/sho wcontent/index,html?id= 17304
- Sanader, D. (2014) Mobile banking: New trends in the contemporary banking sector. Bankarstvo, vol. 43, br. 5, str. 86-109
- Stankić, R. (2008) Electronic business. Belgrade: Faculty of Economics in Belgrade
- Zelenović, V. (2015) Marketing in banking. Subotica: Faculty of Economics in Subotica


