Effect of agrobacterium induced necrosis, antibiotic induced phytotoxicity and other factors in successful plant transformation
Автор: Magdum Sandip S.
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 3 т.9, 2013 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Agrobacterium tumefaciens infection and antibiotic wash are the critical steps of Agrobacterium mediated plant transformation procedure, most time responsible for lower transformation efficiency due to necrosis and phytotoxicity caused by biotic stress of Agrobacterium and abiotic stress by antibiotics respectively. Ammi majus Egyptian origin medicinal plant and Pearl millet cereal grain crop were studied for their stress responses to Agrobacterium mediated transformation (AMT). Agrobacterium strains LBA4404 (O.D.=0.6-0.8) and EHA105 (O.D.=0.2-0.4) were used for transformation experiments to infect calli of Ammi majus and embryogenic calli of Pearl millet respectively. Incase of antibiotic wash, Cefotaxime 500 mg L -1 was used for LBA4404 infected Ammi majus calli and Timentin 300 mg L -1 was used for EHA105 infected embryogenic calli of Pearl millet. Effects of Agrobacterium infection, antibiotic and NaOCl washes on Agrobacterium removal and both explants physiological changes during transformation experimental procedures were studied. At the end of the experiments explants survival efficiency of Ammi majus and pearl millet were 8% and 5% respectively. Biotic and abiotic stress factors responsible for lower efficiency were investigated with various other factors and strategies were discussed which are need to be considered for higher transformation events and target tissue survival.
Abiotic, agrobacterium tumefaciens, ammi majus, biotic, pearl millet, phytotoxicity
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14323791
IDR: 14323791
Текст научной статьи Effect of agrobacterium induced necrosis, antibiotic induced phytotoxicity and other factors in successful plant transformation
Agrobacterium mediated genetic transformation is a natural and simple way to do genomic changes in plant characters. Fundamentally this transformation process is highly tailored gene shifting and integration method which has the potential to change the functionality of plant cell through stable genetic changes. In the present study two important plants were considered namely, Ammi majus and Pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum L.) for study the biotic and abiotic stress factor on plant tissue during transformation process. A successful
Agrobacterium -mediated plant transformation requires efficient procedures for suppressing bacteria following co-cultivation and a comprehensive approach to reduce suppressing effects of antibiotics on plant propagation. Highly efficient Agrobacterium mediated plant transformation has not yet been well-established; however, applications of in vitro culturing, antibiotic and chemical washing biochemically damage plant tissue and these stress factors were responsible for unsuccessful transformation experiments.
Ammi majus (L.), also known as bishop’s weed from Apiaceae family is one of the wild pharmacopoeial plant species. The seed contains furanocoumarins (Hamerski and Matern, 1998), which stimulate pigment production in the skin that is exposed to bright sunlight (Bown, 1995; Chevallier, 1996). In recent study, leaf, stem and calli of Ammi majus were used for efficient genomic DNA isolation (Magdum, 2013). Modification of plant metabolic pathway for higher production of medically important secondary metabolite or byproduct requires basic changes in the genomic DNA of Ammi majus , which could be achieved by Agrobacterium mediated transformation (AMT).
Pearl millet is widely grown as a multi-purpose cereal grain crop principally for food, feed, fodder, fuel, and much on more than 26 million hectares, primarily in arid and semi-arid regions of India and Africa. It is a high yielding, drought tolerant summer crop and can be grown in low rainfall areas where other crops such as maize and sorghum are not profitable (FAO, 2004). Due to lack of Agrobacterium attachment site in monocots, like pearl millet, the absence of wound response and the associated activation of virulence genes would be the reasons of absence of crown gall tumor formation and recalcitrance. But there actively dividing, embryogenic cells, which are co-cultivated with Agrobacterium in the presence of acetosyringone, which is a potent inducer of virulence genes (Vasil, 2005) and the possibility of gene transfer exists in monocots. A number of researchers reported recently about AMT in monocots (Assem et al., 2009; Ceasar and Ignacimuthu, 2011; Jha et al., 2011; Karthikeyan et al., 2011; Duan et al., 2012) but it was observed that no recovery of regenerates has been possible. Although the communication between plant cell and Agrobacterium via chemical signaling and transport is not yet fully understood, many studies of Agrobacterium-mediated transformation have reported necrosis and a poor survival rate of target plant tissues (Hansen, 2000; Olhoft et al., 2001; Chakrabarty et al., 2002; Das et al., 2002; Toldi et al., 2002; Dan et al., 2004; Zheng et al., 2005; Assem et al., 2009; Ceasar and Ignacimuthu, 2011; Jha et al., 2011; Karthikeyan et al., 2011).
Hansen and Durham, (2000) have also reported that co-cultivation of wheat and maize tissues with Agrobacterium resulted in necrosis (Fig.1) due to programmed cell death, Some factors may be the result of, or linked to, hypersensitive defense reaction in plants to Agrobacterium infection, which may involve the recognition of specific signal from the Agrobacterium that triggers the burst of reactive oxygen species at the infection site.
Antibiotics in the regeneration medium also affects on regeneration efficiency (Nauerby et al., 1997; Ling et al., 1998; Ieamkhang and Chatchawankanphanich, 2005). Some researchers have used timentin to inhibit systemic bacteria in tissue culture and to suppress Agrobacterium in genetic transformation (Cheng et al., 1998; Ieamkhang and Chatchawankanphanich, 2005).
Beta-lactum group antibiotics known as minimal toxicity to plant tissue, like Cefotaxime and carbenicillin, have been widely accepted and commonly been used as effective treatment for suppression of Agrobacterium cells (Okkels and Pedersen, 1988; Tang et al., 2000; Alsheikh et al., 2002).
The effects of various antibiotics on Agrobacterium suppression and plant regeneration were studied in Arabidopsis (Lin et al., 1995), papaya (Yu et al., 2001), pine (Tang et al., 2004; Tereso et al., 2006), tobacco (Nauerby et al., 1997; Cheng et al., 1998), tomato (Ieamkhang and Chatchawankanphanich, 2005) and wheat (Han et al., 2007). Alsheikh et al., (2002) also reported that no single antibiotic was effective in controlling all of the strains. Simple AMT procedure contains steps like Agrobacterium co-cultivation with plant tissue and antibiotic washing to disinfect Agrobacterium for normal growth of plants, but experiments ends with lower number of live transformants due necrosis and phytotoxicity by biotic stress of Agrobacterium and abiotic stress of antibiotic use respectively (Fig.1).
In this study, we observed the effect of Agrobacterium infection, antibiotic and chemical agent washing on plant tissue physiology, like browning/necrosis and response towards the growth of transforming tissues. Factors need to be considered for increasing efficiency of successful transformation was addressed.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Explant preparation
Standardization of plant tissue culture protocols for both plants, Ammi majus and Pearl millet, were done in a separate study. Ammi majus leaf explants were used for successful callus induction on Ammi majus callus induction medium (AMCIM) contains MS salts (Murashige and Skoog, 1962) with 3% sucrose and 0.8% agar, pH 5.8, with 2 mg L-1 IAA, 2 mg L-1 Kn and 1000 mg L-1 CH. Ammi majus shoot induction medium (AMSIM) contains only contains Glutamine 50mg L-1 in addition to AMCIM.
Immature embryos of pearl millet were used as explants for its callus induction on MS salts with 3% sucrose and 0.8% agar, pH 5.8, were used in Pearl millet Callus Induction Medium (PMCIM), which was supplemented with 3 mg L-1 2, 4-D and Pearl millet Shoot Induction Media (PMSIM) were supplemented with 3 mg L-1 BAP. The previously cultured and healthy calli were taken for both plant studies for Agrobacterium infection and transformation. Calli was cut into same size 3 mm to 4 mm pieces of tissues by using a sterile scalpel and blade and used as explants in further study.
Agrobacterium Culture Preparation
Glycerol stocks of the strains (LBA4404 and EHA105) of Agrobacterium tumefaciens with respective plasmids were inoculated to 10 ml LB broth (Bacto-tryptone 10 gm L-1,Yeast Extract 5 gm L-1, NaCl 5 gm L-1, pH 7.2) with the suitable antibiotics (Kanamycin and Rifampicin) concentration and grown overnight in incubator shaker at 220 RPM and 28 < C. This mother culture was re-grown in 50 ml LB broth with respective antibiotic concentration, till the optical density reached 0.6 to 0.8 for LBA4404 and 0.2 to 0.4 for EHA105 at 600nm.
LBA infection to Ammi majus
In vitro cultured calli of Ammi majus , which was having good, healthy growth, was taken for transformation experiment. Transfer calli explants, immediately after cutting, to the bacterial suspension in the petri dish, and co cultivate with
LBA4404 for about 3 min. Blot the explants dry over a sterile blotting paper and placed on co-cultivation media (CCM) with composition of MS salts + 3% sucrose + 0.8% agar + Acetosyringone 200 µM, (pH 5.8).
EHA 105 infection to embryogenic calli of Pearl millet
In vitro grown embryogenic calli and active EHA105 Agrobacterium culture were incubated in a conical flask for 10 min with gentle shaking. The explants were then blotted dry on an autoclaved blotting paper and placed on CCM. All plates wrapped with aluminum foil and Placed in BOD chamber for two days of co-cultivation at 24oC in dark condition.
Washing of co-cultivated Ammi majus explants with Cefotaxime
After tow days, Agrobacterium infected tissues were transferred to sterile conical flask and washed them with distilled water for the 3 times. Add 25 ml ½ MS liquid media with 500 mg L-1 Cefotaxime. Put conical flask in the shaker incubator for 1 Hr at 120 RPM at 24oC. Wash the tissues again with distilled water in the sterile conical flask. Blot them on sterile blotting paper and put them on the culturing plates by using new sterile forceps. Repetition of the antibiotic washing procedure followed, when re-growth of Agrobacterium on tissues were observed. Every 3 weeks, explants are sub cultured on fresh culturing medium containing the Cefotaxime (500 mg L-1).
Washing of co-cultivated Pearl millet explants with Timentin
After two days bacterial growth was observed on infected embryogenic calli of prael millet. So explants were washed with water and then incubated with ½ MS liquid media added Timentin
300 mg L-1 for 1 Hr with continues shaking at 120 RPM at 24oC. The explants were blot dried on an autoclaved tissue paper. Then the explants placed on fresh culturing medium with added Timentin 300 mg L-1.
Chemical washing of targeted explants
Abiotic effect of NaOCl washing techniques on the tissue for complete removal of infected Agrobacterium after co-cultivation has been attempted. After antibiotic wash, give three washes to agroinfected tissue with distilled water. Then tissues washed with 1% NaOCl for 2 min. Then wash the tissues for 3 times with distilled water. Dry them on blotting paper and culture them on respective growth culture media. We observed the effect of NaOCl washing on Agrobacterium growth and tissue of Ammi majus and Pearl Millet.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Callus and shoot induction of Ammi majus and Pearl millet:
For callus and shoot induction different hormone composition were used to optimize the growth. For Ammi majus AMCIM, AMSIM and for pearl millet PMCIM and PMSIM were the optimized composition for callus and shoot induction respectively. In case of Ammi majus, leafs found best as explants for callus induction and immature embryos were found best as explants for in vitro growth of pearl millet. The embryos start callusing within 2-3 days in respective medium. Callus cultivation of both plants were different, as Ammi majus produces green calli in light at 250C (Fig.2A) and pearl millet produces white embryogenic calli (EC) in dark at 250C in BOD incubator (Fig.2B). For shoot induction both plants were incubated in light with their respective media composition. In pearl millet extensive rooting were observed from calli without activated charcoal. Addition of activated charcoal (0.2 %) shows effective root inhibition.
Two days incubation in dark after transfection, good growth of Agrobacterium on the tissues was observed. Color of the Ammi majus dark green callus tissue was changed to light green (Fig.3A,B) and pearl millet white calli observed as light brown (Fig.3C,D). Pearl millet explants were showed browning due to ROS and phenolics secretion, due to this regeneration efficiency was affected. Evidences of biotic stress due to Agrobacterium -induced necrosis in target plant tissues and its link to reactive oxygen species were presented (Fig.3).
Effect of Antibiotic washing on calli of Ammi majus
In Ammi majus transformation experiments, 500 mg L-1 Cefotaxime were effectively suppressed LBA4404 than 250 mg L-1. After co-cultivation period of 48 hrs 1st antibiotic wash was given to calli and they were cultured on AMCIM containing 500 mg L-1 Cefotaxime, no depigmentation observed and tissues were brownish green (Fig.4A). Regrowth of Agrobacterium was observed on surrounding of each callus after 2 days of 1st antibiotic wash due to the transient bacteriostatic activity of Cefotaxime. After 2nd antibiotic wash, calli were cultured on AMCIM containing 500 mg L-1 Cefotaxime and at this time depigmentation were observed on calli and tissues were brownish yellow (Fig.4B). It’s showing abiotic stress and phytotoxicity of Cefotaxime on calli of Ammi majus. Again re-growth of Agrobacterium was observed after 2 days of 2nd antibiotic wash. Repeated the antibiotic wash for 3rd time and tissues were brownish white and depigmentation observed (Fig.4C). Regeneration rate of Ammi majus calli were affected by phytotoxicity of antibiotic wash and it slower than unwashed tissues.
Effect of antibiotic washing on EC of Pearl millet
Timentin were used in pearl millet experiment which effectively suppress EHA101 at 300 mg L-1 than 100 mg L-1. After co-cultivation period of 48 hrs 1st antibiotic wash was given to pearl millet EC and they were cultured on PMCIM containing 300 mg L-1 Timentin. After 1st wash itself white embryogenic calli become yellowish white, slight browning were observed (Fig.5A). Re-growth of Agrobacterium was observed after 3 days due to transient bacteriostatic activity of Timentin, so 2nd antibiotic wash was carried out. EC’s were blot dried and cultured on PMCIM containing 300 mg L-1 Timentin, tissues were brownish yellow (Fig.5B). Again re-growth of Agrobacterium was observed and 3rd antibiotic wash was given to agroinfected calli, tissues browning were observed (Fig.5C) with minimum growth rate.
Effect of chemical (NaOCl) washing
NaOCl effectively kill the Agrobacterium , but not complete removal of Agrobacterium from plant tissue at lower concentration <1% for 2 min. As we increased the washing time and concentration of NaOCl, Ammi majus calli were shown immediate depigmentation (Fig.6A), which was responsible for tissue death. Incase of pearl millet, NaOCl wash to agroinfected tissue were shown effect like extensive browning after culturing (Fig.6B) and this abiotic stress affected on tissue regeneration rate by killing plant cells.
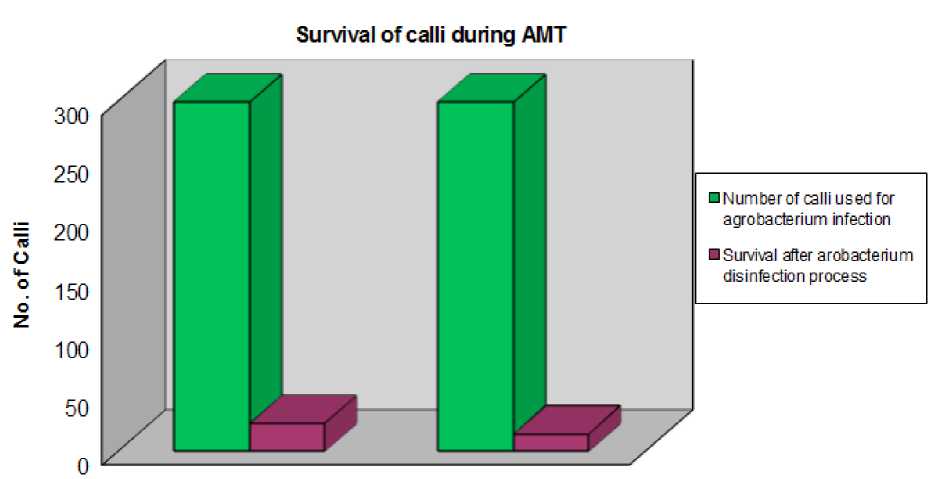
Graph plotted bellow showing 92% calli of Ammi majus and 95% calli of pearl millet were dead because of virulence of Agrobacterium , antibiotic containing media and antibiotic/ chemical washing (Fig.7).
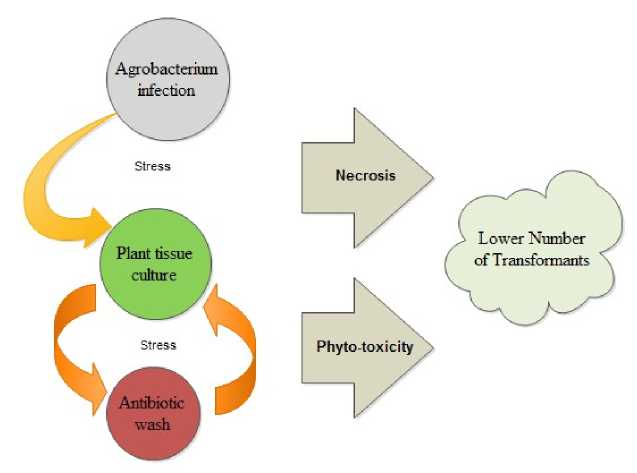
Figure 1 Effect of biotic stress of Agroinfection and abiotic transformation process.
stress of antibiotic wash on plant
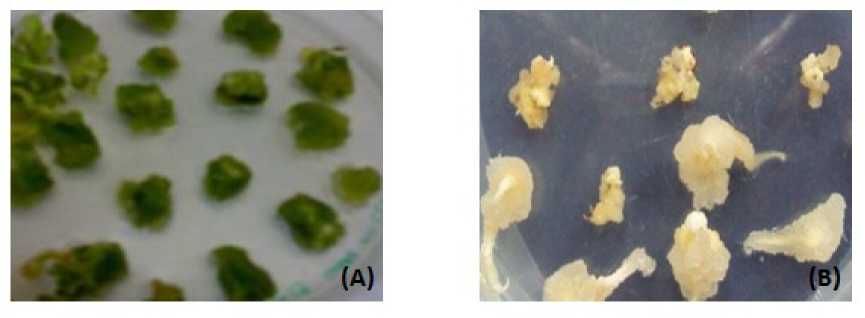
Figure 2 Callus induction of Ammi majus (A) and Pearl millet (B) on respective CIM
Table 1. Group of antioxidants used in plant transformation
|
Group |
Antioxidants |
Action |
|
I |
Ascorbic acid, Citric acid, DTT, Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVPP) and Vitamin C |
Reduce tissue browning, promote organogenesis, somatic embryogenesis and shoot growth from buds during micropropagation. |
|
II |
Cysteine, Phenoxane, 3-ter-butyl-4-hydroxyanisole and Vitamin E |
Antioxidants can enhance shoot, root, and plant growth. |
|
III |
Ascorbate, Glutathione and α-tocopherol |
Promote callus and shoot organogenesis but also inhibit somatic embryogenesis. |
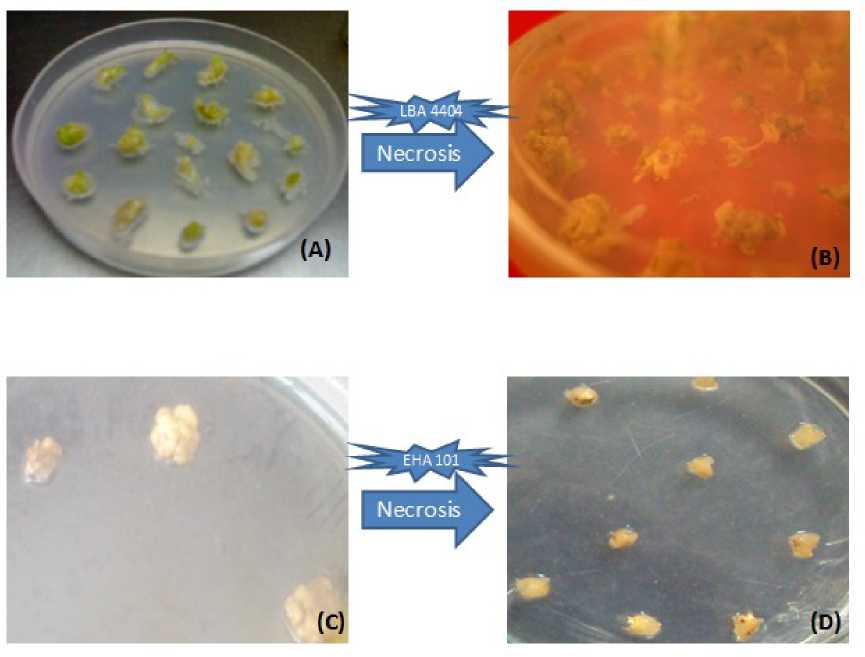
Figure 3 (A) LBA4404 infected Ammi majus calli (B) Agrobacterium induced biotic necrosis effect on Ammi majus calli (C) EHA105 infected Pearl millet calli (D) Agrobacterium induced biotic necrosis effect on Pearl millet calli
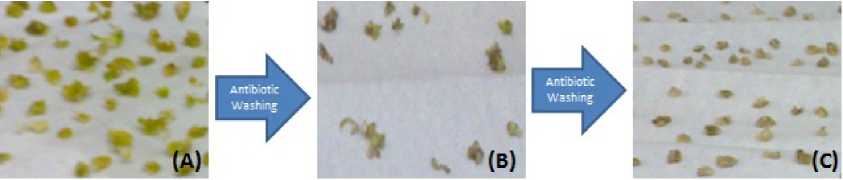
Figure 4 Effect of Cefotaxime washing on calli of Ammi majus (A) Calli were slight brownish green after 1st antibiotic wash (B) Browning of calli observed after 2nd antibiotic wash (C) After 3rd antibiotic wash calli were unhealthy dark brown.
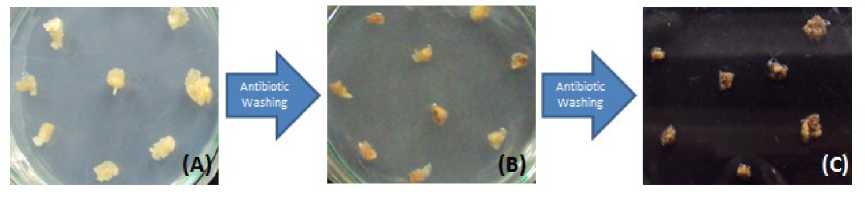
Figure 5 Effect of Timentin washing on EC of pearl millet (A) EC were slight brownish white after 1st antibiotic wash (B) Light browning of EC observed after 2nd antibiotic wash (C) After 3rd antibiotic wash EC were unhealthy dark brown.
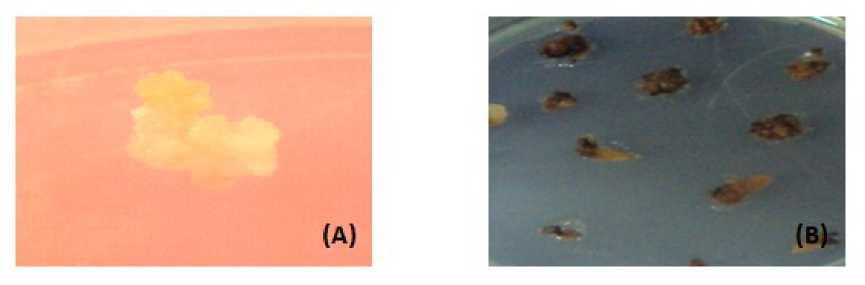
Figure 6 Effect of NaOCl washes to extensive Agrobacterium grown (A) calli of Ammi majus and (B) EC of pearl millet
Am mi majus
Pearl millet
Figure 7 Graph shows 8% Ammi majus calli and 5% pearl millet EC were survived after Agrobacterium infection, antibiotic and chemical washes.
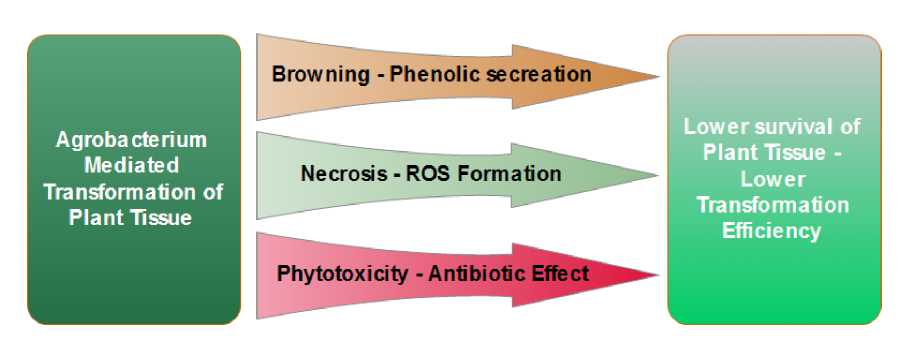
Figure 8 Reason of lower AMT efficiency
Список литературы Effect of agrobacterium induced necrosis, antibiotic induced phytotoxicity and other factors in successful plant transformation
- Alsheikh, M.K., Suso, H.P., Robson, M., Battey, N.H. and Wetten, A. (2002) Appropriate choice of antibiotic and Agrobacterium strain improves transformation of antibiotic-sensitive Fragaria vesca and F. v. semperflorens. Plant Cell Rep., 20: 1173-1180.
- Assem, S.K., Eissa, H.F. and Saleh, O.M., (2009) Optimization of Agrobacterium-mediated transformation conditions for Egyptian bread wheat CV.G164. Egypt J. Genet. Cytol., 38: 221-234.
- Barrett, C. and Cassells, A.C. (1994) An evaluation of antibiotics for the elimination of Xanthomonas campestris pv. pelargonii (Brown) from Pelargonium x domesticum cv. 'Grand Slam'. Plant Cell, Tiss. Organ Cult., 36: 169-175.
- Belide, S., Hac, L., Singh, S.P., Green, A.G. and Wood, C.C. (2011) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of safflower and the efficient recovery of transgenic plants via grafting. Plant Methods., 7: 1-12.
- Bown, D. (1995) Encyclopaedia of Herps and their Uses. Dorling Kindersley, London.
- Ceasar, S.A. and Ignacimuthu, S. (2011) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of finger millet (Eleusine coracana (L.) Gaertn.) using shoot apex explants. Plant Cell Rep., 30: 1759-1770.
- Chakrabarty, R., Viswakarma, N., Bhat, S.R., Kirti, P.B., Singh, B.D. and Chopra V.L. (2002) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of cauliflower: optimization of protocol and development of Bt-transgenic cauliflower. J. Biosci., 27: 495-502.
- Cheng, Z.M., Schnurr, J.A. and Kapaun, J.A. (1998) Timentin as an alternative antibiotic for suppression of Agrobacterium tumefaciens in genetic transformation. Plant Cell Rep., 17: 646-649.
- Chevallier, A. (1996) The encyclopaedia of medicinal plants. Dorling kindersly, London.
- Costa, M.G.C., Nogueira, F.T.S., Figueira, M.L., Otoni, W.C., Brommonschenkel, S.H. and Cecon, P.R. (2000) Influence of the antibiotic timentin on plant regeneration of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.) cultivars. Plant Cell Rep. 19: 327-332.
- Dan, Y. (2008) Biological functions of antioxidants in plant transformation, In Vitro Cell Dev. Biol. Plant., 44: 149-161.
- Dan, Y., Munyikawa, T.R.I., Kimberly, A.R. and Rommens, C.M.T. (2004) Use of lipoic acid in plant culture media. US Patent Pub. No.: US 2004/0133938 A1.
- Das, D., Reddy, M., Upadhyaya, K. and Sopory, S. (2002) An efficient leaf-disc culture method for the regeneration via somatic embryogenesis and transformation of grape (Vitis vinifera L.). Plant Cell Rep. 20: 999-1005.
- Duan, Y., Zhai, C., Li, H., Li, J., Mei, W., Gui, H., Ni, D., Song, F., Li, L., Zhang, W. and Yang, J. (2012) An efficient and high-throughput protocol for Agrobacterium mediated transformation based on phosphomannose isomerase positive selection in Japonica rice (Oryza sativa L). Plant Cell Rep., 31: 1611-1624.
- FAO. (2004) Food and agriculture organization of the United Nations. Pennesitum americanum (L.) Leeke: species description. http://www.fao.org/ag/AGP/AGPC/doc/Gbase/DATA/Pf000297.htm
- Gonzalez Padilla, I.M., Webb, K. and Scorza, R. (2003) Early antibiotic selection and efficient rooting and acclimatization improve the production of transgenic plum plants (Prunus domestica L.). Plant Cell Rep., 22: 38-45.
- Greenberg, J.T., Guo, A., Klessig, D.F. and Ausubel, F.M. (1994) Programmed cell death in plants: a pathogen-triggered response activated coordinately with multiple defense functions. Cell., 77: 551-563.
- Hamerski, D. and Matern, V. (1988) Elicitor-induced biosynthesis of psoralens in Ammi majus L suspension cultures microsomal conversion of demethylsuberosin into (+) marmesin and psoralen. Eur. J. Biochem., 171: 369-375.
- Han, S.N., Oh, P.R., Kim, H.S., Heo, H.Y., Moon, J.C., Lee, S.K., Kim, K.H., Seo, Y.W. and Lee, M.O. (2007) Effects of Antibiotics on Suppression of Agrobacterium tumefaciens and Plant Regeneration from Wheat Embryo. J. Crop Sci. Biotech., 10: 92-98.
- Hansen, G. (2000) Evidence for Agrobacterium-induced apoptosis in maize cells. Mol. Plant Microb. Interact., 13: 649-657.
- Ieamkhang, S. and Chatchawankanphanich, O. (2005) Augmentin as an alternative antibiotic for growth suppression of Agrobacterium for tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) transformation. Plant Cell, Tiss. Organ Cult., 82: 213-220.
- Jha, P., Shashi, Rustagi, A., Agnihotri, P.K., Kulkarni, V.M. and Bhat, V. (2011) Efficient Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Pennisetum glaucum (L.) R. Br. using shoot apices as explant source. Plant Cell, Tiss. Organ Cult., 107: 501-512.
- Karthikeyan, A., Pandian, S.K. and Ramesh, P.M. (2011) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of leaf base derived callus tissues of popular indica rice (Oryza sativa L. sub sp. indica cv. ADT 43). Plant Sci., 181: 258-268.
- Kneifel, W. and Leonhardt, W. (1992) Testing of different antibiotics against gram positive and gram negative bacteria isolated from plant tissue cultures. Plant Cell, Tiss. Organ Cult., 29: 139-144.
- Le, V.Q., Belles-Isles, J., Dusabenyagasani, M. and Tremblay, F.M. (2001) An improved procedure for production of white spruce (Picea glauca) transgenic plants using Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Exp. Bot., 52: 2089-2095.
- Leifert, C., Camotta, H. and Waites, W.M. (1992) Effect of combinations of antibiotics on micropropagated Clematis, Delphinium, Hosta, Iris, and Photinia. Plant Cell, Tiss. Organ Cult., 29: 153-160.
- Leifert, C., Camotta, H., Wright, S.M., Waites, B., Cheyne, V.A. and Waites, W.M. (1991) Elimination of Lactobacillus plantarum, Corynebacterium spp., Staphylococcus saprophyticus and Pseudomonas paucimobilis from micropropagated Hemerocallis, Choisya and Delphinium cultures using antibiotics. J. Appl. Bact., 71: 307-330.
- Liau, C.H., You, S.J., Prasad, V., Hsiao, H.H., Lu, J.C., Yang, N.S. and Chan, M.T. (2003) Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of an Oncidium orchid. Plant Cell Rep., 21: 993-998.
- Lin, J.J., Assad-Garcia, N. and Kuo, J. (1995) Plant hormone effect of antibiotics on the transformation efficiency of plant tissue by Agrobacterium tumefaciens cells. Plant Sci., 109: 171-177.
- Ling, H.Q., Kriseleit, D. and Ganal, M.W. (1998) Effect of ticarcillin/potassium clavulanate on callus growth and shoot regeneration in Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.). Plant Cell Rep., 17: 843-847.
- Magdum, S.S. (2013) A Reliable and High Yielding Method for Isolation of Genomic DNA from Ammi majus. I. Res. J. Biological Sci., 2: 57-60.
- Mamidalaa, P. and Nanna, R.S. (2009) Influence of antibiotics on regeneration efficiency in tomato, Plant Omics Journal, 2: 135-140.
- Monnier, M. (1990) Induction of Embryogenesis in Suspension Culture. In Pollard, J.W. and Walker, J.M. (ed.), Plant Cell and Tissue Culture. Humana Press, New Jersey, pp. 149-157.
- Murashige, T. and Skoog, E. (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant, 15: 473-497.
- Nauerby, B., Billing, K. and Wyndaele R. (1997) Influence of the antibiotic timentin on plant regeneration compared to car benicillin and cefotaxime in concentrations suitable for elimination of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Plant Sci., 123: 169-177.
- Okkels, E.T. and Pedersen, M.G. (1988) The toxicity to plant tissue and to Agrobacterium tumefaciens of some antibiotics. Acta Hort., 225: 199-207.
- Olhoft, P.M., Lin, K., Galbraith, J., Nielsen, N.C. and Somers, D.A. (2001) The role of thiol compounds increasing Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of soybean cotyledonary-node cells. Plant Cell Rep., 20: 731-737.
- Park, S.U. and Facchini, P.J. (2000) Agrobacterium rhizogenes-mediated transformation of opium poppy, Papaver somniferum l., and California poppy, Eschscholzia californica cham., root cultures. J. Exp. Bot., 51: 1005-1016.
- Tang, W., Luo, H. and Newton, R.J. (2004) Effects of antibiotics on the elimination of Agrobacterium tumefaciens from loblolly pine (Pinus taeda) zygotic embryo explants and on transgenic plant regeneration. Plant Cell, Tiss. Organ Cult., 70: 71-81.
- Tereso, S., Miguel, C., Maroco, J. and Oliveira, M.M. (2006) Susceptibility of embryogenic and organogenic tissues of maritime pine (Pinus pinaster) to antibiotics used in Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation. Plant Cell, Tiss. Organ Cult., 87: 33-40.
- Thomzik, J.E. (1995) Agrobacterium-Mediated Transformation of Stem Disks from Oilseed Rape (Brassica napus L.). In Gartland K.M.A. and Davey, M.R. (ed.), Agrobacterium Protocols. Humana Press Inc., New Jersey, pp. 79-85.
- Toldi, O., Tóth, S., Pónyi, T. and Scott, P. (2001) An effective and reproducible transformation protocol for the model resurrection plant Craterostigma plantagineum Hochst. Plant Cell Rep., 21: 63-69.
- Vasil, I.K. (2005) The story of transgenic cereals: The challenge, the debate, and the solution -a historical perspective. In Vitro Cell Dev. Biol., 41: 577-583.
- Yu, T.A., Yeh, S.D. and Yang, J.S. (2001) Effects of carbenicillin and cefotaxime on callus growth and somatic embryogenesis from adventitious roots of papaya. Bot. Bull. Acad. Sin., 42: 281-286.
- Zaragozá, C., Muñoz-Bertomeu, J. and Arrillaga, I. (2004) Regeneration of herbicide-tolerant black locust transgenic plants by SAAT. Plant Cell Rep., 22: 832-838.
- Zheng, Q.S., Ju, B., Liang, L.K. and Xiao, X.H. (2005) Effects of antioxidants on the plant regeneration and GUS expressive frequency of peanut (Arachis hypogaea) explants by Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Plant Cell, Tiss. Organ Cult., 81: 83-89.


