Effect of artificial light on physiological and hematological parameters of individuals of Phoxinus phoxinus (Linnaeus, 1758)
Автор: Lavnikova A.V., Pushnica V.A., Biritskaya S.A., Bukhaeva L.B., Golubets D.I., Ermolaeva Ya.K., Kulbachnaya N.A., Maslennikova M.A., Milovidova I.V., Karnaukhov D.Yu., Silow E.A.
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 4 т.19, 2023 года.
Бесплатный доступ
In the natural environment, the life activity of organisms takes place under conditions of stable daily, lunar and annual light cycles. However, human activities aimed at creating comfortable conditions for people have resulted in light becoming one of the factors of anthropogenic environmental pollution. Artificial lighting at night can cause physiological and behavioural changes and disturbances in aquatic organisms, affecting their vital functions. Fish are one of the groups of aquatic organisms that are most susceptible to the influence of light at night, largely due to the anatomical structure of their eyes. The aim of this work was to test whether keeping Phoxinus phoxinus (Linnaeus, 1758) under constant light exposure promotes the growth of inflammatory processes in them, and also to study whether lighting at night affects oxygen consumption. Experiments showed that the oxygen consumption of P. phoxinus increased statistically significantly (p = 0.04303) at night with light compared to night without light. In an experiment in which blood cell counts were performed, the results showed a statistically significant increase in leukocytes (p = 0.01506) in the third experimental group of four kept under constant artificial light for 17 days. Based on the results of our study, it has been confirmed that keeping fish under abnormal light conditions, i.e. using different sources of artificial light at night near water bodies, can lead to physiological changes that can have a negative impact on the life of organisms. In fish, the level of oxygen consumption increases, indicating an increase in the level of metabolism, which in turn affects the growth and formation of organisms, causing a decrease in the intensity of various physiological processes such as feeding and reproduction. There is also an increase in the level of leukocytes, which indicates an increase in inflammatory processes in the organisms, which can lead to a decrease in immune function and, as a result, the susceptibility of fish to various diseases.
Aquaculture, circadian rhythms, hormones, stress
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/143180983
IDR: 143180983
Текст научной статьи Effect of artificial light on physiological and hematological parameters of individuals of Phoxinus phoxinus (Linnaeus, 1758)
Light is one of the most important factors influencing the development and growth of organisms (Wang Tao et al. , 2013). Organisms are sensitive to even small amounts of light, as the deep connection between "light and biological matter" is predetermined by a long evolutionary process (Karandashov et al. , 2013). Throughout the existence of life, organisms have evolved under conditions of stable daily, lunar and annual light cycles. As a result, organisms have adapted to these cycles at both the physiological and behavioural levels.
Over the years, however, human activities have increasingly altered natural light patterns, with negative effects on the environment. Today, artificial lighting at night is considered one of the factors of anthropogenic pollution that can affect all levels of biological organisation of both terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems (Hölker et al. , 2010; Jermacz et al. , 2020; Gaston et al. , 2014; Zapata et al. , 2019). tudies investigating the effects of light pollution on aquatic organisms in coastal marine ecosystems (Navarro-Barranco, Hughes 2015; Bolton et al. , 2017; Longcore, Rich, 2004) show that current and projected future use of artificial lighting at night can lead to disruption of natural cycles with significant global consequences.
Under natural conditions, the presence of uncontrolled sources of artificial light near water, particularly in recreational areas and along coastlines frequented by tourists, can have a negative impact not only on the vital activities of individual aquatic organisms, but also on ecosystems as a whole. For example, artificial lighting has been shown to have a species-specific effect on the behaviour of aquatic organisms. Gammarids of the species Dikerogammarus villosus ( owinsky, 1894) actively avoid all types of light, so in a natural environment exposed to light pollution, individuals of D. villosus will remain permanently in shelter, which may reduce opportunities for foraging and/or mating. However, Gammarus jazdzewskii Rudolph, Coleman, Mamos & Grabowski, 2018 does not respond to light from HP (high pressure sodium lamps) and LED (broad spectrum) lighting. Thus, the lack of avoidance behaviour may lead to increased vulnerability of this species to predation (Czarnecka et al. , 2022).
It is worth noting that natural changes in lighting, or photoperiod, also affect the circadian rhythms of all living organisms. Thus, when the cycle of day and night is disrupted and light sources continue to shine at night, circadian mechanisms are also disrupted, in particular the production of a hormone such as melatonin. An experiment has been conducted in which it was found that artificial lighting (even at minimal intensity) at night leads to a significant decrease in melatonin secretion in Perca fluviatilis Linnaeus, 1758 (Brüning et al. , 2015). It is also noted that when exposed to brighter artificial light (20, 200 and 400 lux) at night, Salmo salar Linnaeus, 1758 showed reduced melatonin production compared to salmon exposed to lower light intensities (0 and 1 lux) (Porter et al. , 2001). In addition to melatonin production, photoperiod affects the production of other hormones necessary for survival and reproduction. A study on Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum, 1792) showed that in daily-fed fish, the diurnal dynamics of plasma thyroxine (T4) and cortisol depend on the light regime (light:dark, 6:18, 12:12, 18:6). Under the latter two regimes, cortisol levels were elevated in the morning and the maximum level of T4 consistently shifted from evening to morning as light conditions increased (Reddy, Leatherland, 2003). Light also affects the production of sex hormones, which are responsible for the maturation and reproduction of organisms. When kept under constant light conditions, sexual maturation of many fish species is inhibited (Davie et al. , 2007, García-López, 2006, Rodríguez et al. , 2005, Porter et al. , 1999). Migaud et al. (2006) found that gonadogenesis in P. fluviatilis ceased completely when kept under constant lighting conditions of 500 lux. As a result, animals exposed to light pollution have reduced locomotor activity and growth rate (Luarte et al. , 2016), as well as reduced reproductive capacity (Touzot et al. , 2019; 2020), due to the disruption of biological processes.
In addition to the processes described above, there are others that can potentially be affected by lighting. These include parameters such as the rate of oxygen consumption and haematological indicators (haemoglobin levels, erythrocyte and leukocyte counts, haematocrit) (Islam et al., 2022). It is believed that fish blood parameters can be used as an effective and sensitive indicator to monitor physiological and pathological changes. This is because they provide sufficient statistics on the various physiological responses of fish to environmental changes that affect their normal state (Cazenave et al., 2005; Elahee and Bhagwant, 2007;
harmin et al. , 2016; Islam et al. , 2019). In turn, assessment of oxygen consumption can contribute to a more complete understanding of the changes that occur in the body under the influence of light.
The aim of this work was to analyse the effect of artificial lighting on oxygen consumption in fish of the species Phoxinus phoxinus (Linnaeus, 1758) and also to investigate whether keeping this species under conditions of constant light contributes to the occurrence of inflammatory processes in the organism.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
Experimental animals and housing
P. phoxinus is a ubiquitous species, dwelling in both expansive and compact bodies of water, with particular susceptibility of the latter to light pollution. The research conducted employed a circular net to handpick minnows from Lake No. 15 located near Bolshie Koty village in the outhern Baikal area between 2021-2022. The fish's dimensions spanned from 8-9 cm, however, their gender was not determined before experimentation. Prior to conducting the tests, the specimens underwent a month of acclimation under laboratory conditions. To conduct the experiments, three individuals of P. phoxinus were kept per aquarium in constant conditions. The temperature was maintained at 12°Ϲ, and Baikal bottled water was used for aeration and water parameters. Technical term abbreviations such as P. phoxinus were explained upon their first use. Only the lighting was altered during the experiments, while a 12:12 period of light and darkness was used for the control groups.
Experimental procedures
All studies comply with international ethical standards and in agreement with the commission for experimental research of the Research Institute of Biology of I U. In 2021, an experiment was carried out in which the oxygen consumption of minnows was measured when kept under certain light conditions. Oxygen consumption was defined as the difference in dissolved oxygen measurements in the aquarium before and after exposure to light. Before each measurement (30 minutes), the oximeter «PME miniDO2T Logger» (U A) was placed in a container with water, the temperature of which was the same as in aquariums. In addition, aeration was turned off in the aquariums themselves to avoid large errors in the measurement of dissolved oxygen. After this, the fishes spent an hour under illumination of 70-80 Lx. Then the oxygen consumed by the fishes was measured again. A total of 16 measurements were taken in the daytime (14:00), 16 measurements in the dark (19:00, the experiment was carried out in December 2021) and 16 measurements in the dark (19:00) under illumination.
In 2022, the leukocyte formula of the peripheral blood of the usual minnow was determined using the differential counting method during the experiment. For the experiment, 4 groups were formed: in each group there were 3 control and 3 experimental individuals. Experimental individuals from the first group were exposed to round-the-clock LED lighting (70-80 Lx) for 10 days, from the second for 14 days, from the third - 17, fishes from the fourth group were exposed to constant artificial lighting for 21 days. Blood was collected from the tail vein by cutting off the tail (caudotomy) immediately after catching the fishes from the aquariums (before this, the fishes were exposed to clove oil). After this, smears were made. mears were stained according to Pappenheim. A total of 30 smears were made, and it should be noted that 6 smears were made immediately after acclimation of the fishes. Next, 50 photographs were taken from each smear using a Leica DMLB light microscope with a connected camera. Using these photographs, blood cells were counted and identified in the ImageJ program (using the Cell Counter plugin). 4 main groups of cells were identified: erythrocytes and leukocyte cells were represented by: lymphocytes, neutrophils, monocytes (Ivanova, 1982).
Statistical analysis
All statistical analyses were conducted using the Kruskal-Wallis and Dunn's post hoc tests in R tudio. The data collected from light-exposed fish were compared to that of control fish, and any significant differences between pairwise comparisons were considered at a p-value of less than 0.05.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The results of an experiment that examined oxygen consumption showed that fishes are sensitive to the effects of artificial light. It was found that the level of oxygen consumption in fishes of the species P. phoxinus increases statistically significantly (at p<0.05) at night when using LED artificial lighting sources in comparison with the night without light, as shown in Table 1. The results of this experiment are also confirmed by literature data. For example, a study on the effect of photoperiod on the energy parameters of cyprinids found that oxygen consumption in fishes decreased in the dark, but increased with 24-hour lighting, which in turn affected the total food consumption (Ruchin, 2012). It is also worth noting that an increase in oxygen consumption will indicate an increase in metabolic rate. However, this process cannot continue continuously, and ultimately, maximizing oxygen uptake can lead to an internal imbalance that will affect the growth and forming of fishes, causing a decrease in various physiological processes such as feeding and reproduction (Nelson, 2016).
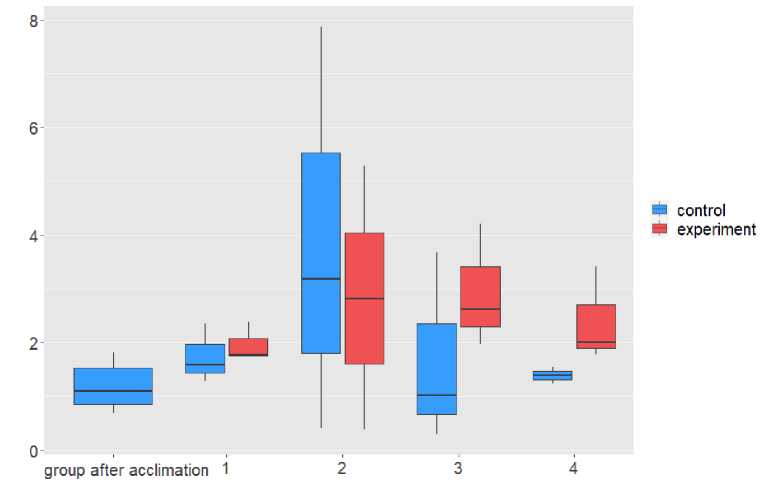
The growth of inflammatory processes in fishes was determined by the ratio of the total number of leukocytes to the total number of blood cells. An increase in the indicator indicated a growing inflammatory process in the fish’s organism. The results of our study showed a statistically significant (at p<0.05) increase in the level of leukocytes in the third experimental group (as can be seen in Table 2), which was kept under constant light for 17 days. The result obtained can be assessed as a demonstration of the reaction to exposure to LED light sources. To a certain extent, the results of our experiment are consistent with published literature data, which also confirm that when fish are kept in light conditions that are unusual for them, clearly defined lymphopenia, mono-, neutro- and basophilia are manifested, and with excessive exposure to the light factor, excess cortisol can cause the destruction of lymphocytes and an increase in neutrophils (Ruchin, 2009). It should be noted that an increase in the level of white blood cells in the blood indicates a stress response. This happens because during times of stress, a large number of antibodies are produced, which can lead to an increase in the number of white blood cells (Raphael and Kuttan, 2003; Begg and Pankhurst, 2004; Beyea et al., 2005). At the same time, constant exposure to an irritating factor leads to chronic stress, which results in an increase in level of cortisol, which affects the metabolic processes in fishes. In addition, there is a chronic increase in level of circulating glucose (Barton et al., 1987), changes in food conversion efficiency (Barton et al., 1987), and accumulation of lipids in liver tissue (Jerez-Cepa et al., 2019). All this along affects the functioning of the organism.
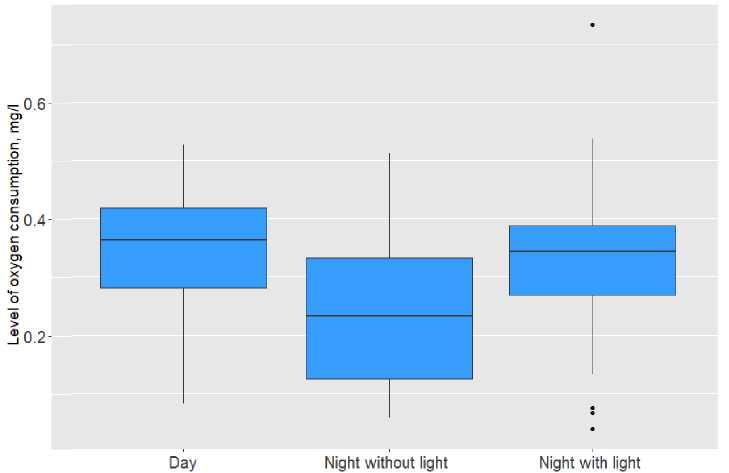
Figure 1. The level of oxygen consumption of P. phoxinus under different lighting conditions
Table 1 Levels of statistical significance (p) in pairwise comparisons of data on the level of oxygen consumption by fish
using Dunn's post hoc test
|
Day |
Night without light |
Night with light |
|
|
Day |
0,01828 |
0,5564 |
|
|
Night without light |
0,01828 |
0,04303 |
|
|
Night with light |
0,5564 |
0,04303 |
Table 2 Levels of statistical significance (p) for pairwise comparisons of the percentage of leukocytes to total blood cells in P. phoxinus using Dunn's post hoc test
|
Control |
1 group |
2 group |
3 group |
4 group |
|
|
Control |
0,2327 |
0,09306 |
0,01506 |
0,06342 |
|
|
1 group |
0,2327 |
0,6737 |
0,2838 |
0,5659 |
|
|
2 group |
0,09306 |
0,6737 |
0,5153 |
0,8783 |
|
|
3 group |
0,01506 |
0,2838 |
0,5153 |
0,6188 |
|
|
4 group |
0,06342 |
0,5659 |
0,8783 |
0,6188 |
Experimental groups
Figure 2 Comparison of the percentage of leukocyte group cells to the total number of blood cells in different experimental groups
CONCLUSION
The results of our experiment confirm that artificial lighting affects physiological indicators and can also cause disturbances in the immune system, which can subsequently affect the general condition of organisms and their adaptation to the environment. However, the experiments are conducted in controlled laboratory conditions, without the influence of environmental factors such as predators, prey, shelter, which are usually present in natural conditions, and without other factors associated with anthropogenic pollution (pollution of water bodies with household and industrial waste, sewage, noise pollution). In future work, in our opinion, it is worth taking these parameters into account.
This study shows that the natural cycle of light and dark is important for the normal functioning of fishes, for this reason it is necessary to select suitable light conditions for organisms in aquaculture. We understand that the species of fishes used in this study is of low economic importance and is unpretentious to living conditions; however, even this species can be affected by artificial lighting.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The work was carried out with the support of the Ministry of science and higher education of the Russian Federation.
CONFLICT OF INTERESTS
The authors declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest.
Список литературы Effect of artificial light on physiological and hematological parameters of individuals of Phoxinus phoxinus (Linnaeus, 1758)
- Barton B, Schreck C, Barton L (1987) Effects of chronic cortisol administration and daily acute stress on growth, physiological conditions, and stress responses in juvenile rainbow trout. Dis Aquat Org 2: 173-185
- Begg K, Pankhurst N (2004) Endocrine and metabolic responses to stress in a laboratory population of the tropical damselfish Acanthochromis polyacanthus. J Fish Biol 64: 133-145
- Beyea M, Benfey T, Kieffer J (2005) Hematology and stress physiology of juvenile diploid and triploid shortnose sturgeon (Acipenser brevirostrum). Fish Physiol Biochem 31: 303-313
- Bilton H, Robins G (1971) Effects of starvation, feeding, and light period on circulus formation on scales of young sockeye salmon (Oncorhynchus nerka). J Fish Res Board Can 28 (11): 1749 -1755
- Bjornsson B (1997). The biology of salmon growth hormone: from daylight to dominance // Fish Physiol Biochem 17 (1): 9-24
- Bolton D, Mayer-Pinto M, Clark G, Dafforn K, Brassil W, Becker A, Johnston E (2017) Coastal urban lighting has ecological consequences for multiple trophic levels under the Sea. Sci Total Environ 576: 1-9
- Bowden T (2008) Modulation of the immune system of fish by their environment. Immunol 25 (4): 373-383
- Britz P, Pienaar A (1992). Laboratory experiments on the effect of light and cover on the behaviour and growth of African catfish, Clarias gariepinus (Pisces; Clariidae). J Zool 227 (1): 43-62
- Brüning A, Hölker F, Franke S, Preuer T, Kloas W (2015) Spotlight on fish: Light pollution affects circadian rhythms of European perch but does not cause stress. Sci Total Environ 511: 516-522
- Cazenave J, Wunderlin D, Hued A, Angeles-Bistoni M (2005) Haematological parameters in a neotropical fish, Corydoras paleatus (Jenyns, 1842) (Pisces, Callichthyidae), captured from pristine and polluted water. Hydrobiologia 537: 25-33
- Clarke W, Shelbourn J, Brett J (1978) Growth and adaptation to sea water in 'underyearling' sockeye (Oncorhynchus nerka) and coho (O. kisutch) salmon subjected to regimes of constant or changing temperature and day lenght. Can J Zool 56 (11): 2413-2421
- Czarnecka M, Jermacz t, Glazinska P, Kulasek M, Kobak J (2022) Artificial light at night (ALAN) affects behaviour, but does not change oxidative status in freshwater shredders. Environ Pollut 306: 119476
- Davie A, Mazorra de Quero C, Bromage N, Treasurer J, Migaud H (2007) Inhibition of sexual maturation in tank reared haddock (Melanogrammus aeglefinus) through the use of constant light photoperiods. Aquacult 270: 379-389
- Elahee K, Bhagwant S (2007) Hematological and gill histopathological parameters of three tropical fish species from a polluted lagoon on the west coast of Mauritius. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 68: 361-371
- Garcia-Lopez A, Pascual E, Sarasquete C, Martinez-Rodriguez G (2006) Disruption of gonadal maturation in cultured Senegalese sole Solea senegalensis Kaup by continuous light and/or constant temperature regimes. Aquacult 261: 789798
- Gaston K, Duffy J, Gaston S, Bennie J, Davies T (2014) Human alteration of natural light cycles: causes and ecological consequences. Oecologia 176: 917-831
- Holker F, Wolter C, Perkin E, Tockner K (2010) Light pollution as a biodiversity threat. Trends Ecol Evol 25: 681-682
- Islam M, Uddin M, Uddin M, Shahjahan M (2019) Temperature changes influenced the growth performance and physiological functions of Thai pangas Pangasianodon hypophthalmus. Aquacult Rep 13: 100179
- Islam S, Akhter F, Jahan I, Rashid H, Shahjahan M (2022) Alterations of oxygen consumption and gills morphology of Nile tilapia acclimatized to extreme warm ambient temperature. Aquacult Rep 23: 1-6
- Ivanova N. (1982) Atlas of fish blood cells (comparative morphology and classification of blood cells in fish). -M .: Light and food industry, p.184 [in Russian]
- Jerez-Cepa I, Gorissen M, Mancera J, Ruiz-Jarabo I (2019) What can we learn from glucocorticoid administration in fish? Effects of cortisol and dexamethasone on intermediary metabolism of gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata L.). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol Integr Physiol 231: 1-10
- Jermacz L, Nowakowska A, Kletkiewic H, Kobak J (2020) Experimental evidence for the adaptive response of aquatic invertebrates to chronic predation risk. Oecologia 92: 341-350
- Karandashov V (2013) Peculiarities of optic irradiation in the blue range of spectrum and perspectives of its application in practical medicine. Laser medicine 17 (2): 49-55 [in Russian]
- Lavrovsky V, Esavkin Yu (1979) Cultivation of juvenile rainbow trout under different light conditions. Izvestiya TSHA 2: 157-163 [in Russian]
- Leonardi M, Klempau A (2003) Artificial photoperiod influence on the immune system of juvenile rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) in the Southern Hemisphere. Aquacult 221 (1-4): 581-591
- Longcore T, Rich C (2004) Ecological Light Pollution. Front Ecol Environ 2: 191-198
- Luarte T, Bonta C, Silva-Rodriguez E, Quijon ' P, Miranda C, Farias A, Duarte C (2016) Light pollution reduces activity, food consumption and growth rates in a sandy beach invertebrate. Environ Pollut 218: 11471153
- Meske C, Munster R (1984) Versuchzuroptimierten Aufzucht von Welsbrut (Silurus glanis). Inform Fishwirt 31 (4): 189-193
- Migaud H, Wang N, Gardeur J, Fontaine P (2006) Influence of photoperiod on reproductive performances in Eurasian perch Perca fluviatilis. Aquacult 252: 385-393
- Navarro-Barranco C, Hughes L (2015) Effects of Light Pollution on the Emergent Fauna of Shallow Marine Ecosystems: Amphipods as a Case Study. Marine Pollution Bulletin 94: 235-240
- Nelson J 2016 Oxygen consumption rate v. rate of energy utilization of fishes: a comparison and brief history of the two measurements. J Fish Biol 88: 10-25
- Pereira D, Adelman I (1985) Interactions of temperature, size and photoperiod on growth and smoltification of chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha). Aquacult 46 (3): 185-192
- Piaia R, Townsed C, Boldisserotto B (1999) Growth and survival of fingerlings of silver catfish exposed to different photoperiods. Aquac Int 7 (3): 201-205
- Porter M, Duncan N, Handeland S, Stafansson S, Bromage N (2001) Temperature, light intensity and plasma melatonin levels in juvenile Atlantic salmon. J Fish Biol 58: 431-438
- Porter M, Duncan N, Mitchell D, Bromagea N (1999) The use of cage lighting to reduce plasma melatonin in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) and its effects on the inhibition of grilsing. Aquacult 176: 237-244
- Raphael, T, Kuttan G, (2003) Immunomodulatory activity of naturally occurring monoterpenes carvone, limonene, and perillic acid. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol 25: 285-294
- Reddy P, Leatherland J (2003) Influences of photoperiod and alternate days of feeding on plasma growth hormone and thyroid hormone levels in juvenile rainbow trout. J Fish Biol 63: 197-212
- Rodriguez L, Begtashi I, Zanuy S, Carrillo M (2005) Long-term exposure to continuous light inhibits precocity in European male sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax, L.): hormonal aspects. Gen Comp Endocrinol 140: 116-125
- Ruchin A (2008) Influence of constant and variable illumination on growth, physiological and hematological parameters of fry of the Siberian sturgeon (Acipenser baerii). J. Zool., 87, 8, 964-972. [in Russian]
- Ruchin A (2009) Influence of light characteristics on the development, growth and physiological and biochemical parameters of fish and amphibians: author. dis. doctor of biol. Sciences: 03.00.16 / A. B. Ruchin; Mordovian state. un-t im. N.P. Ogaryov. -Saransk, - 54 p. [in Russian]
- Ruchin A (2012) Influence of the photoperiod on power indicators of cyprinidae fishes. Astrakhan Bulletin of environmental education 4 (22): 144-150 [in Russian]
- Sharmin S, Salam M, Haque F, Islam M, Shahjahan M (2016) Changes in hematological parameters and gill morphology in common carp exposed to sublethal concentrations of Malathion. Asian J Med Biol Res 2 (3): 370-378
- Touzot M, Lengagne T, Secondi J, Desouhant E, Thery M, Dumet A, Duchamp N, Mondy N (2020) Artificial light at night alters the sexual behaviour and fertilization success of the common toad. Environ Pol 259: 113883
- Touzot M, Teulier L, Lengagne T, Secondi J, Thery M, Libourel P, Guillard L, Mondy N (2019) Artificial light at night disturbs the activity and energy allocation of the common toad during the breeding period. Conserv Physiol 71: 1-9
- Vlasov V, Maslova N, Ponomarev S, Bakaneva Yu (2013) Effect of illumination on the fish growth and development. Vestnik ASTU Ser.: Fisheries, Aquatic bioresources and their rational use 2: 24-34 [in Russian]
- Wang Tao, Cheng Yongzhou, Liu Zhaopu; Yan Shaohua, Long Xiaohua (2013) Effects of light intensity on growth, immune response, plasma cortisol and fatty acid composition of juvenile Epinephelus coioides reared in artificial seawater. Aquacult 414-415: 135139
- Zapata M, Ma"zeika S, Sullivan P, Gray S (2019) Artificial lighting at night in estuaries - implications from individuals to ecosystems. Estuar Coast 42: 309-330


