Effect of chelating agents and metal ions on nickel bioavailability and chlorophyll fluorescence response in wheat- an approach for attenuation of Ni stress
Автор: Patnaik Nilima, Mohanty Monalisa, Satpathy Bijaylaxmi, Kumar Patra Hemanta
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 3 т.8, 2012 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The objectives of the study are to analyze the physiological changes, biochemical alterations and attenuation of nickel toxicity effects in wheat seedlings under combined applications of Ni ions, metal chelators (EDTA/Citric Acid) and metal ions (Zn2+ /Mg2+). Wheat (Triticum aestivum L cv UP262) seedlings were grown hydroponically using different concentrations of Ni up to 7 days along with chelators and metal ions for study. The seedling growth was maximum with NiCl2-Zn2+ (100µM) and minimum with NiCl2-EDTA (100µM) treatments. Total chlorophyll content was maximum in the seedlings treated with NiCl2-Zn2+ (100µM) and minimum in NiCl2-EDTA (100µM) treatments. NiCl2-EDTA (100µM) showed less Fo and Fm values and therefore, a trend in the decrease in OJIP transient indicates the maximum alteration of photochemical activity of PS-II in presence of NiCl2-EDTA (100µM) treatment. Similar observation was found by NiCl2 -EDTA (200µM) treatment where Fo and Fm values were noted to decline. High nickel content in roots of the seedlings was noted as compared to shoots.
Chelating agents, metal ions, nickel, chlorophyll-a fluorescence, biochemical alterations
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14323678
IDR: 14323678
Текст научной статьи Effect of chelating agents and metal ions on nickel bioavailability and chlorophyll fluorescence response in wheat- an approach for attenuation of Ni stress
agents; Metal ions;
Nickel; Chlorophyll-a fluorescence; Biochemical
alterations
Soil contamination is a major environmental concern due to dispersal of industrial and urban wastes generated by human activities (Ghosh and Singh 2005). Disposal of wastes, accidental and process spillage, mining and smelting of ores, sewage sludge application to agricultural soils are responsible factors for contamination of our ecosystem. However, elevated concentrations of both essential and nonessential heavy metals in the soil can lead to toxicity symptoms and growth inhibition in most plants and Ni is one of them (Hall 2002). The average worldwide concentration of Ni in soil is 8 ppm. Nickel concentrations in plants are usually 1µg/g dry wt. and the concentration above 50µg/g was found toxic . Ni is an essential trace element (0.01-5µg/g dry wt.) for some plants (Seregin and Kozhevnikova 2006). The increase in solubility and exchangeability of nickel in soils also results in an increase of this element in plant tissue (Alloway 1990). Ni is considered as an essential micronutrient for plants but is strongly phytotoxic at high concentrations and has a destructive effect on growth, mineral nutrition, photosynthesis and membrane function (Woolhouse 1983; Pandolfini et al., 1992; Rao and Sresty 2000; Peralta et al., 2000; Reichman 2002). Ni phytotoxicity has also been attributed to its adverse effects on photosynthesis, mineral nutrition, sugar transport and water relations (Seregin and Kozhevnikova 2006). Nickel toxicity is mainly dealt with organic acids in plants in terms of transportation and detoxification (Jocsak et al., 2005) and results in the induction of reactive oxygen species (ROS) such as O2-and H2O2 (Gajewska and Sklodowsaka 2007).
The effects of Nickel on plant growth and metabolism have been studied and reviewed from time to time. However, its interacting effects in presence of chelating agents and metal ions are less studied. The objectives of the study were to analyze the interacting effects of Ni in presence of chelating agents and metal ions on physiological and biochemical alterations in wheat seedlings. The reduction of nickel toxicity effects in the seedlings under combined applications of Ni ions, metal chelators (EDTA/Citric Acid) and metal ions (Zn2+/Mg2+) was also assessed by phytoremediation
101 protocols under in vitro hydroponic experiments using seedlings of wheat cultivar (Triticum aestivum L. cv UP262) as a model.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Plant Material
Graded dry seeds of wheat (Triticum aestivum L. cv. UP 262) were obtained from Orissa University of Agriculture and Technology, Bhubaneswar (India). Seeds of uniform size were selected and surface sterilized with 0.1% mercuric chloride (HgCl2) for about five minutes and then was washed several times with tap water followed by distilled water. The surface sterilized seeds were placed in sterilized petriplates over saturated cotton pads for germination. Twenty five milliliters of either distilled water (control) or solutions of nickel chloride (NiCl2.7H2O) containing specific concentrations of nickel were poured into each petriplates. The seeds were germinated under controlled condition at 25º C in darkness for two days. Emergence of 2 mm primary root was used as the operational definition of germination.
Germination Percentage
Uniform sized surface sterilized seeds were kept over cotton pads saturated with distilled water (control) or solutions of nickel chloride in the darkness in different petriplates for two days. Different concentrations of Ni (10–1000µM) were chosen for this study. Chelating agents (EDTA, CA) and metal ions (Zn2+, Mg2+) were also used for treating the seeds for the study of germination percentage with reference to control. Vigor Index (VI) and Tolerance indices (TI) were determined by following the formula as given by Iqbal and Rahmati (1992).
VI = Seedling Length (cm) × Germination percentage
TI = (Mean root length of Ni treated seedlings/Mean root length of seedlings grown in control) × 100
Seedling Growth
Two-days-old uniform surface sterilized germinated seeds were transferred to well aerated Hoagland’s nutrient solution (half strength) and Hoagland’s solution supplemented with varying concentrations of nickel chloride placed in hydroponic culture vessels for seedling growth. The seedlings were grown in the growth chamber and the white light was provided (12h photo period) by white fluorescent tubes (36 W Philips TLD) with a photon flux density of 52 µE/m2s (PAR).
Growth Parameters
Seven days old wheat seedlings supplemented with different nickel concentrations were used for study of various growth parameters like root length, shoot length, fresh matter and dry matter. Seedlings supplemented with NiCl 2 -chelating agents (100µM) and NiCl 2 -metal ions (100µM) were also analysed for their different growth parameters. Both nickel treated and control seedlings were kept in an oven at 80º C for a period of 3 days or more (till constant weight was attained) for dry weight determination.
Analysis of Chlorophyll Content
The extraction and analysis of leaf chlorophyll content was conducted by using 10 ml of 80% acetone following the method of Porra (2002). The leaf samples from different culture pots were kept in dark in refrigerator for 28 hours or more (48 hours) at 40C. The absorbance of extracted liquid was observed at 663.6 nm and 646.6 nm for Chlorophyll-a and Chlorophyll-b respectively.
Analysis of Chlorophyll-a fluorescence
The Chlorophyll-a fluorescence was measured from the upper surface of the four fully open leaves from the growing apex using a handy PEA (Hansatech Instruments, Norfolk, UK). Prior to measurement, a leaf clip (4mm diameter measuring area) with closed lid was inserted into the leaf and dark adaption was made for 10 minutes, after which fluorescence was induced on application of red light saturation pulse (3000µmole photon/m2s; Strasser et al., 1995). The OJIP fluorescence levels were recorded after 50µs (Fo), 2ms (Fj), 30ms (Fi) and 400ms (Fm) respectively.
Analysis of Nickel content
Seven days old wheat seedlings collected from culture pots supplemented with different Ni concentrations were oven dried and grinded separately to fine powders. The Nitric acid (HNO 3 ) and Perchloric acid (HClO 4 ) in the ratio of 10:1 were added to the weighed and grinded plant powder samples (shoots and roots separately) and kept for 24 hours overnight (Bonet et al. , 1991). Then the plant samples were digested in acid using MDS-8 (Microwave Digestion Unit) until a clear soluble solution was obtained. The acid digested solutions were filtered and the final volume was made up to 50 ml. Ni2+content of treatments were estimated by Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer (Perkin Elmer, AAnalyst 200,USA).
RESULTS
Germination Study
The inhibition of seed germination was noted with application of Ni2+ at a concentration of 100µM, leading to 50% inhibition at 800µM (Fig.1). The seed germination was less hampered in presence of chelating agents and metal ions like Citric Acid, Zn2+ and Mg2+ except EDTA treatment.
Changes in growth parameters
Treatment of different concentrations of Ni2+ showed considerable changes in different growth parameters of seven days grown wheat seedlings (Table 1.). Shoot length decreased markedly with increase in Ni2+ concentrations (100µM to 1000µM). The shoot length of the seedlings treated with Ni2+ (10µM) was noted highest as compared to all other treatments of Ni2+. The seedlings treated with 1000µM-Ni2+ had minimum length as shown in Table 1. The seedlings treated with NiCl 2 and chelating agents/metal ions showed relative decrease in plant growth (measured in terms of shoot length) in the following order
Control > NiCl 2 – Zn2+ (100 µM) > NiCl 2 – Mg2+ (100µM) > NiCl 2 - CA (100 µM) > NiCl 2 - EDTA (100 µM)
The root length also markedly decreased with increasing concentrations of NiCl 2 in the growth medium. The seedlings treated with NiCl 2 and chelating agents/metal ions showed relative decrease in the root growth (measured in terms of root length) in the similar order as observed in shoot growth study.
The shoot fresh weight gradually decreased with increase in the concentrations of NiCl 2 . However, the seedlings treated with NiCl 2 -Mg2+/Zn2+(100µM) showed a increase in the biomass unlike addition of chelating agents viz. EDTA/CA. Analysis of the root fresh matter indicated that the seedlings treated with NiCl 2 -Zn2+(100µM) showed an enhanced biomass unlike addition of Mg2+, EDTA and CA. Similar growth trend values were found for dry biomass production as compared to fresh weight values.
The seedlings of Triticum aestivum was examined for tolerance in different concentrations
103 of Ni. It was observed that tolerance of T. aestivum gradually decreased by increasing concentrations of Ni treatments. Ni treatment at 10 µM showed high percentage (85.32%) of Tolerance Index in seedlings of T. aestivum while Ni treatments of 100 µM and Ni-Zn-100 µM exhibited 81.30% and 84.51% of tolerance respectively. Nickel treatment at 1000 µM showed lowest percentage of tolerance (14.93%) in T. aestivum as compared to control (Fig.2).
Nickel stress adversely affected Seedling Vigour Index (SVI) which was decreased with increasing level of NiCl 2 . The SVI was found higher in seedlings treated in control followed by 10 µM and 100 µM where as the seedlings treated with 1000 µM had the least seedling vigour index. However, the seedlings treated with metal chelators and ions varied from 1364 to 2438.10. The order of decrease in SVI was recorded as Control>10 µM>Ni-Zn-100 µM >100 µM> Ni-Mg-100 µM>200 µM> Ni-EDTA-100 µM>Ni-CA-100 µM>400 µM >800 µM> 1000 µM (Fig. 3).
Analysis of Chlorophyll Content
The decrease in chlorophyll-a content was found with the increase in concentration of NiCl 2 except 10 µM (Table 2). The chlorophyll-a content was found maximum with 10µM-NiCl 2 treatment and minimum in 1000µM-NiCl 2 . Among the seedlings treated with metal ions (Zn2+/Mg2+), the chlorophyll-a content was maximum in the seedlings treated with 100µM-Zn2+-NiCl 2 and minimum in 100µM-NiCl 2 as shown in Table.2.
There was a similar trend of increase/decrease in chlorophyll-b content of the seedlings treated with different concentrations of NiCl 2 as shown Chlorophyll-a (Table 2). The chlorophyll-b content decreased with increasing concentration of NiCl 2 .
The seedlings treated with metal ions (Zn2+/Mg2+) had maximum chlorophyll-b content with 100µM-NiCl 2 -Mg2+ . The seedlings treated with chelating agents (EDTA/CA) had maximum chlorophyll-b content with 100µM-NiCl 2 -CA application.
The total chlorophyll content was the highest in the seedlings treated with NiCl 2 (10µM) and lowest in seedlings treated with NiCl 2 (1000µM) as shown in Fig.4. Among the seedlings treated with chelating agents (EDTA/CA) and metal ions (Zn2+/Mg2+), the total chlorophyll content was found maximum in the seedlings treated with Zn2+-NiCl 2 ( 100µM) and minimum in NiCl 2 -EDTA(100µM) as shown in Fig.4. The chlorophyll a/b ratio was highest in the seedlings treated with 1000µM-NiCl 2 and lowest in 800µM-NiCl 2 as shown in Table.2.The seedlings treated in 100µM-Zn2+-NiCl 2 had the maximum chlorophyll a/b ratio and minimum in seedlings treated with Mg2+-NiCl 2 (100µM).
Analysis of Chlorophyll-a Fluorescence
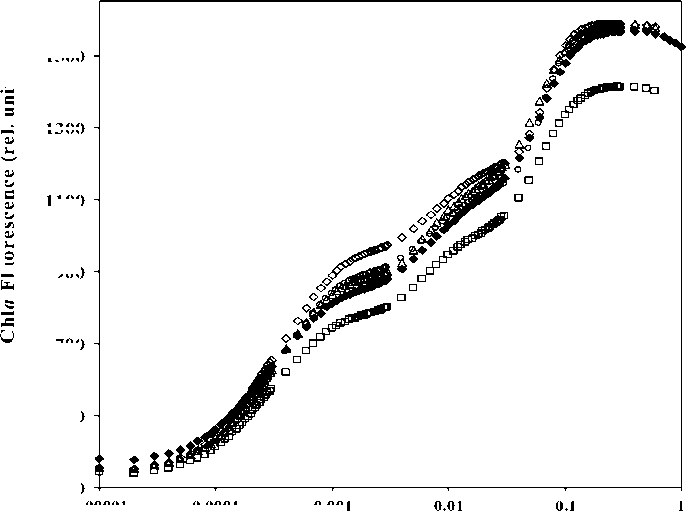
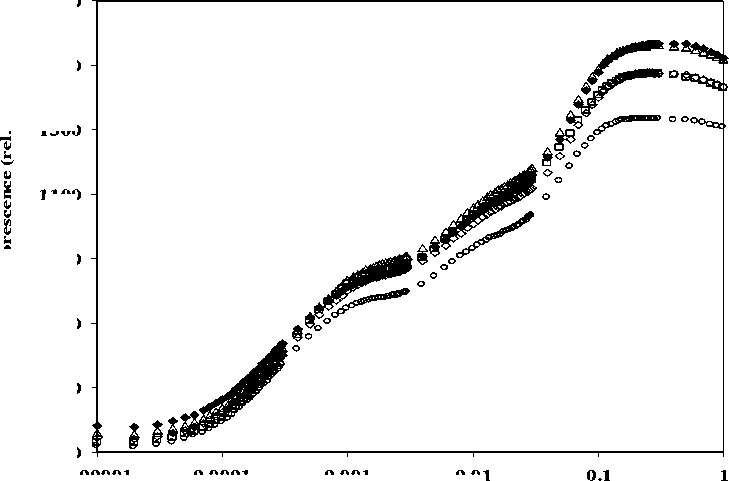
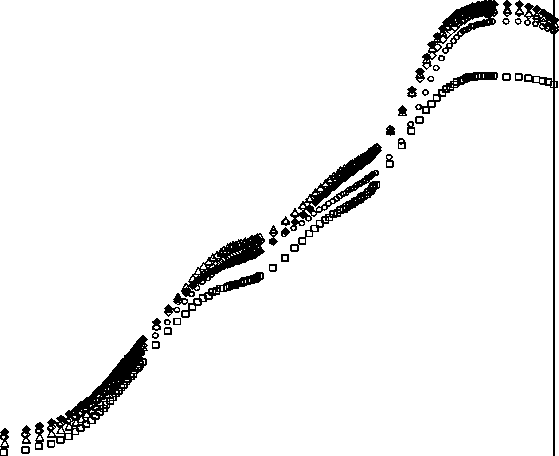
OJIP analysis with applications of different concentration of nickel ions indicated that there was no significant change in Fo value (Fig.5) but Fm value along with the transient changed when treated with NiCl2 (10µM). But in other treatments the OJIP transient did not show much variation. The EDTA-NiCl2 (100µM) treatment showed a decreased in Fo and Fm values (Fig.6). A decrease in Fm indicates that there was maximum alteration of photochemical activity of PS-II in 100µM-EDTA-NiCl2 containing nutrient medium. Similar observation was noted where the decrease in Fo and Fm values were observed with 200µM-EDTA-NiCl2 treatment (Fig.7).
Nickel Bioavailability
Total Nickel content in wheat seedlings was analyzed in shoots and roots (Fig.8). Nickel content in roots of the seedlings indicated high amount of Ni than in shoots. There was highest nickel content in 100µM-NiCl 2 treatment and the least amount was found in 10µM-NiCl 2 in roots. Similar trend was observed in shoots of the wheat seedlings.
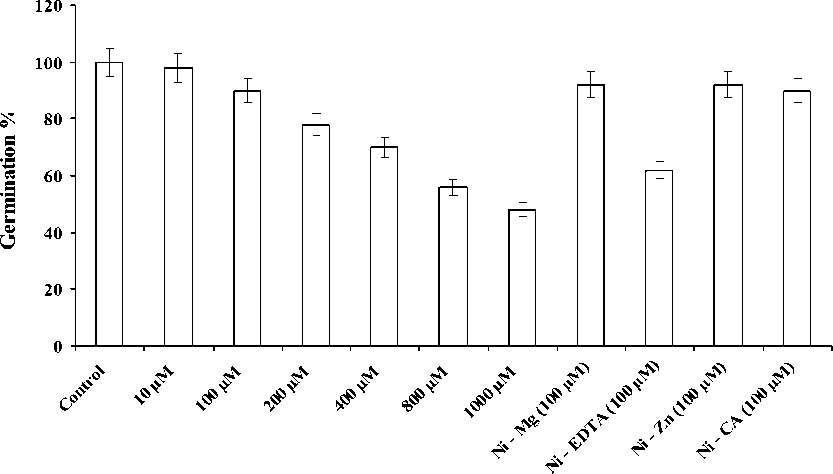
Figure 1 Effect of different concentrations of Nickel ions, chelating agents and metal ions on germination of wheat seedlings.
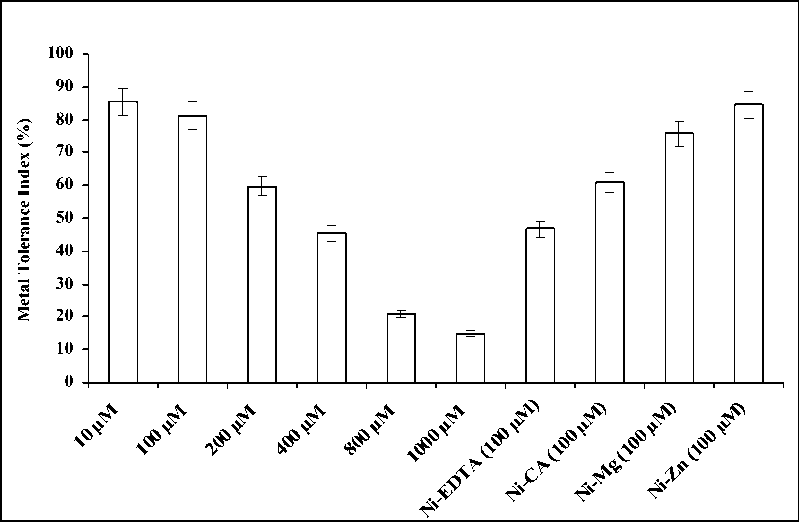
Figure 2 Effect of different concentrations of Nickel ions, chelating agents and metal ions on metal
tolerance of wheat seedlings.
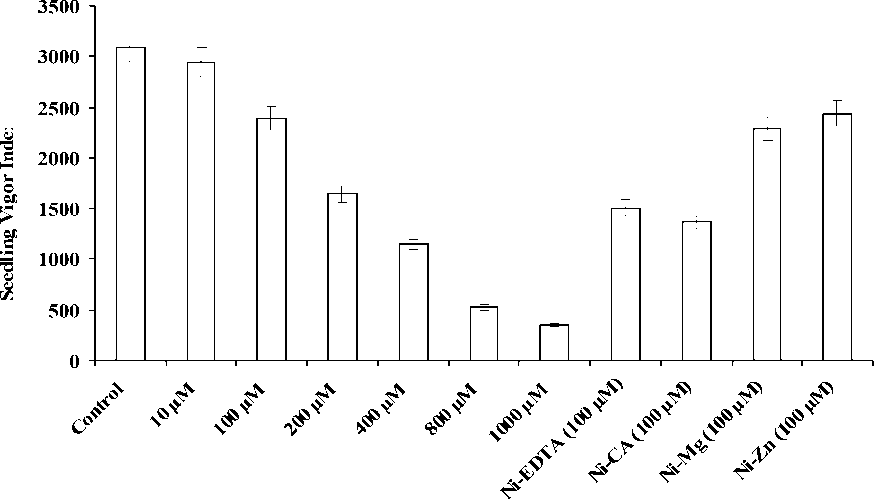
Figure 3 Effect of different concentrations of Nickel ions, chelating agents and metal ions on seedling
vigour of wheat.
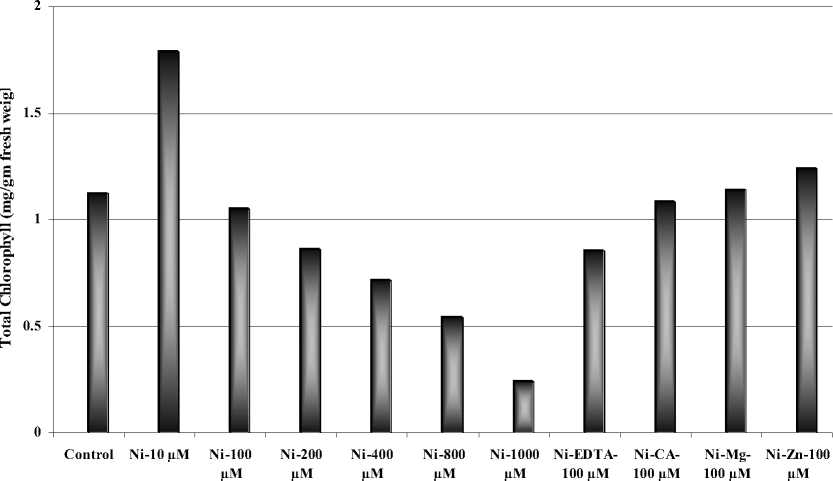
Figure 4 Effect of different concentrations of Nickel ions, chelating agents and metal ions on total chlorophyll content of wheat seedlings.
♦ Control □ Ni 10µM A Ni 100µM ° Ni 200µM о Ni 400µM
0.0001
0.001
Time (seconds)
300 0.00001
Figure 5 Effects of different concentrations of NiCl 2 on chlorophyll-a fluorescence in wheat seedlings.
о Ni-Mg (100µM) □ Ni-Zn (100µM) △ Ni-Ca (100µM) О Ni-EDTA (100µM) ♦ Control
0.00001
0.0001
0.001
0.01
Time (seconds)
Figure 6 Effects of NiCl 2 , metal ions and EDTA (100µM) on chlorophyll-a fluorescence in wheat seedlings.
о 9
h
♦ Control □ Ni-EDTA (200µM) △ Ni-CA (200µM) ° Ni-Zn (200µM) о Ni-Mg (200µM)

0.00001 0.0001 0.001 0.01 0.1 1
Time (seconds)
Figure 7 Effects of NiCl 2 , metal ions and EDTA (200µM) on chlorophyll-a fluorescence in wheat seedlings.
□ Root (R) □ Shoot (S)
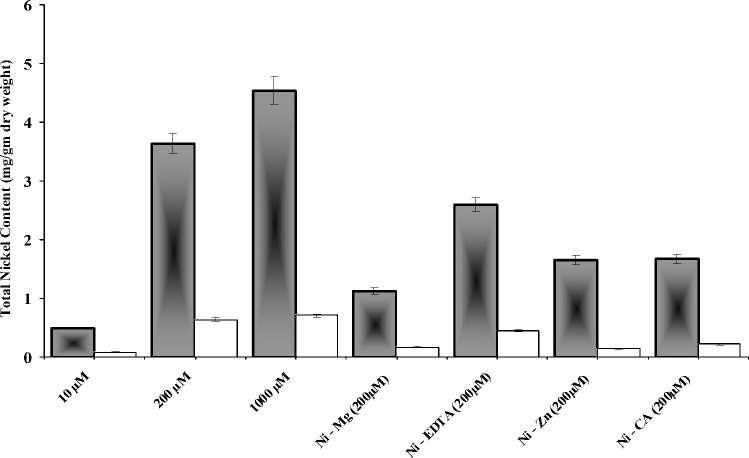
Figure 8 Effect of NiCl 2, chelating agents and metal ions on Nickel bioavailability in wheat seedlings.
Table 1. Effect of Nickel ions, chelating agents and metal ions on growth parameters of 7 days old wheat seedlings. (values are mean of three replicates±SEM)
|
Chlorophyll-a Treatments mg/gm fr. wt. |
Chlorophyll-b Chlorophyll a//b mg/gm fr.wt. |
|
0.941 Control ± 0.004 10 µM - NiCl 2 ± 1 0 .5 .0 9 0 6 4 100 µM - NiCl 2 ± 0 0 .8 .0 8 0 3 4 200 µM - NiCl 2 ± 0 0 .7 .0 2 0 0 4 400 µM - NiCl 2 ± 0 0 .6 .0 0 0 0 6 800 µM - NiCl 2 ± 0 0 .4 .0 4 0 0 5 1000 µM - NiCl 2 ± 0 0 .2 .0 3 0 4 5 100 µM - EDTA - NiCl 2 ± 0 0 .7 .0 2 0 4 5 100 µM - CA - NiCl 2 ± 0 .9 .0 3 03 100 µM - Mg2+ - NiCl 2 ± 0 0 .9 .0 6 0 4 4 100 µM - Zn2+ - NiCl 2 ± 1 0 .0 .0 7 0 4 6 |
0.180 ± 0.006 5.238 0.192 ± 0.1.09022 8.313 0.170 ± 0.006 5.19 0.143 ± 0.1.0033 5.035 0.114 ± 0.004 5.263 0.101 ± 0.004 4.356 0.005 ± 0.002 8 ±00.1.03025 5.485 ±00.1.05025 6.145 ±00.1.07062 5.477 ±00.1.06083 6.393 |
DISCUSSION
Heavy metals are detrimental because of their non-biodegradable nature, long biological half-life and their potential to accumulate in different body parts (Behbahaninia et al. , 2009). The heavy metals that affect the plant growth and metabolism include Fe, Cu, Zn, Mn, Co, Ni, Pb, Cd, Cr etc. Nickel, on the other hand, has been considered as an essential micronutrient but at high concentrations it causes adverse effects in plants (Welch 1995).
The study shows harmful effects of nickel chloride on growing wheat seedlings at higher concentrations. The study also depicts the roles of different chelating agents (Citric Acid, EDTA) and metal ions (Zinc, Magnesium) in attenuating the toxic effects of nickel. Chelates are substances that render insoluble cations soluble for their availability to the plants (Lindsay 1974). Low toxicity multidentate chelating agents such as EDTA are used to enhance the bioavailability of heavy metals for plant uptake (Leyval et al, 1995; Turnau 1998). The enhancement performance of Ni by wheat seedlings in presence of different chelating agents has been undertaken.
The germination rate was significantly reduced with increasing concentrations of NiCl2 in the nutrient solution which may be due to inhibition of biosynthetic activity (Peralta et al., 2001). Growth parameters viz. shoot and root length, fresh and dry weight of developing wheat seedlings were recorded in response to different concentrations of NiCl2 and supplementation of chelating agents and metal ions. The root length and shoot length were significantly reduced at 1mM NiCl2 in wheat seedlings. However, at 10 µM NiCl2 the growth was slightly stimulated. Supplementation of Zn2+ with NiCl2 in nutrient solution stimulated the plant growth in comparison to other chelating agents and metal ions. The possible competitive role of Zn with Ni uptake caused growth stimulation in wheat seedlings suppressing the entry of Ni to plants, otherwise Ni would have exerted growth inhibitory effects as noticed with 100µM-NiCl2 application. The chlorophyll biosynthesis was also reflected in the similar manner using Zn2+- NiCl2 and CA-NiCl2 combinations for plant growth.
Tolerance to heavy metals in plants may be defined as the ability to survive in soil that is manifested by an interaction between a genotype and its environment (Macnair et al. , 2000). Tolerance to Ni treatments in T. aestivum was lower as compared to control. This information can be considered a contributing step in exploring and finding of tolerance limit of T. aestivum at different levels of treatment.
Seedling Vigor Index (SVI) is the potential of seed germination and seedling size against the toxicity and tolerance of metal. The toxic effect on SVI in this present study could also be viewed in wheat seedlings grown in different treatments. Reduced SVI was possessed by T. aestivum with increasing concentration of Ni from 100 µM to 1000 µM probably due to less resistance.
In OJIP analysis, the seedlings treated with 100µM-EDTA-NiCl 2 showed less Fo and Fm values. Therefore, there was a trend in the decrease in OJIP transient which indicates the maximum alteration of photochemical activity of PS-II in presence of 100µM-EDTA-NiCl 2 treatment. There was similar observation in 200µM-EDTA-NiCl 2 treatment in which there was decrease in Fo and Fm value.
The bioavailability of nickel in wheat seedlings was also analyzed in shoots and roots. Nickel content in roots of the seedlings indicated high amount of Ni than in shoots. The in situ remediation of excessive soil metals is receiving great attention because the alternative method of soil removal and replacement is very expensive (Kukier and Chaney 2000). Thus, bioremediation plays an important role for in situ bioremediation of soil contaminated with heavy metals.
Chelate-enhanced phytoextraction has received a lot of attention in the past decade. This technique can cleanse metal polluted soils by solubilizing contaminating metals, allowing them to be taken up by plants that would subsequently be removed from the site. The role of heavy metal chelators and metal ions in enhancing chlorophyll biosynthesis and stimulating plant growth may be considered as effective agents for attenuating the problem of nickel toxicity. The present study is a preliminary assessment of Nickel phytotoxicity in wheat seedlings. The study further includes the effect of chelating agents in response to the growth and chlorophyll biosynthesis. Nickel is a naturally occurring element which can be found in all environmental media: air, soil, sediment, and water. The concentration of nickel in plants generally reflects the concentration in soil although the relationship is more related to soluble and exchanged forms of nickel. Factors that increase solubility and exchangeability of nickel in soils also result in an increase of the element in plant tissue (Alloway 1990) which is necessary for healthy growth and is essential for metabolic processes (Alloway 1990; NRC 2005). Chelation of heavy metals is a ubiquitous detoxification strategy described in wide variety of plants. Natural element hyperaccumulator plant species can be effective in phytomining or phytoextraction of particular elements from contaminated or mineralized soils (Lasat 2002; McGrath et al., 2002; Chaney et al., 2005; Banuelos 2006). The present study with the applications of metal ions and chelators provides an insight for phytodetoxification and phytoremediation strategies to be taken up in future experiments.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors are grateful to the Head of the Department, P. G. Dept. of Botany for providing necessary facilities. The authors acknowledge UGC, New Delhi for providing financial assistance from DRS-SAP-II and DRS-Research Fellowship in Science for Meritorious Students in Botany.
Список литературы Effect of chelating agents and metal ions on nickel bioavailability and chlorophyll fluorescence response in wheat- an approach for attenuation of Ni stress
- Alloway, B.J. (1990) Heavy Metals in Soils. Blackie Academic and Professional. New Delhi, India 339.
- Banuelos, G.S. (2006) Phyto-products may be essential for sustainability and implementation of phytoremediation. Environ. Pollut., 144, 19-23.
- Behbahaninia, A., Mirbagheri, S.A., Khorasani, N., Nouri, J., Javid, A.H. (2009) Heavy metal contamination of municipal effluent in soil and plants. J Food Agric. Environ., 7 (3-4), 851-856.
- Chaney, R.L, Angle, J.S., McIntosh, M.S., Reeves, R.D., Li, Y.M., Brewer, E.P., Chen, K.Y., Roseberg, R.J., Perner, H., Synkowski, E.C., Broadhurst, C.L., Wang, S., Baker, A.J.M. (2005) Using hyperaccumulator plants to phytoextract soil Ni and Cd. Z. Naturforsch., 60C, 190-198.
- Gajewska, K., Sklodowska, M. (2007) Effect of nickel on ROS content and antioxidative enzyme activities in wheat leaves. Biometals., 20, 27-36.
- Ghosh, M., Singh, S.P. (2005) A review on phytoremediation of heavy metals and utilization of its by-products. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res., 3(1), 1-18.
- Jocsak, I., Vegvari, G.Y., Droppa, M. (2005) Heavy metal detoxification by organic acids in barley seedlings. Acta. Biol. Szeged., 49, 99-101
- Hall, J.L. (2002) Cellular mechanisms for heavy metal detoxification and tolerance. J. Exp. Bot., 53, 1-11.
- Iqbal, M.Z., Rahmati, K. (1992) Tolerance of Albizia lebbeck to Cu and Fe application. Ekologia., 11, 427-430.
- Kukier, U., Chaney, R.L. (2000) Influence of the zinc hyperaccumulator. Can. J. Soil. Sci., 80, 581-593.
- Lasat, M.M. (2002) Phytoextraction of toxic metals -A review of biological mechanisms. J. Environ. Qual., 31, 109-120.
- Lindsay, W.L. (1974) Role of chelation in micronutrient availability in Plant Roots and its Environment. ed. FW Carson Univ press of Virginia Charlottesville VA USA 507-24.
- Leyval, C., Singh, B.R., Joner, E.J. (1995) Occurrence and infectivity of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in some Norwegian soils influenced by heavy metals and soil properties. Water Air Soil Poll., 83, 203-216.
- McGrath, S.P., Zhao, F.J., Lombi, E. (2002) Phytoremediation of metals, metalloids, and radionuclides. Adv. Agron., 75, 1-56.
- Macnair, M.R., Tilstone, G.H., Smith, S.E. (2000) The genetics of metal tolerance and accumulation in higher plants. In: Phytotremediation of contaminated soil and water (Eds.: N. Terry, G. Banuelos), CRC Press, LLC 235-250.
- National Research Council (NRC) (2005) Mineral Tolerance of Animals. Second Edition The National Academies Press Washington DC 496.
- Nieboer, E., Richardson, D.H.S. (1980) The replacement of the nondescript term 'heavy metal' by a biologically and chemically significant classification of metal ions. Environ. Pollut. (Series B), 1, 2-26.
- Pandolfini, T., Gabbrielli, R., Comparini, C. (1992) Nickel toxicity and peroxidase activity in seedlings of Triticum aestivum L. Plant Cell Environ., 15, 719-725.
- Peralta, J.R., Gardea-Torresdey, J.L., Tiemann, K.J., Gomez, E., Arteaga, S., Rascon, E., Parsons, J.G. (2000) Study of the effects of heavy metals on seed germination and plant growth on alfalfa plant (Medicago sativa) grown in solid media. Proceedings of the 2000 conference on Hazardous Waste Research, Denver, Colorado, May 23-24. P. 135-140.
- Rao, K.V.M., Sresty, T.V.S. (2000) Antioxidative parameters in the seedlings of pigeon pea (Cajanus cajan (L.) Mullspaugh) in response to Zn and Ni stresses. Plant Sci., 157, 113-128.
- Reichman, S.M. (2002) The responses of plants to metal toxicity: a review focusing on copper, manganese and zinc. The Australian Minerals and Energy Environment Foundation 54.
- Seregin, I.V., Kozhevnikova, A.D. (2006) Physiological role of nickel and its toxic effects on higher plants. Russ. J. Plant Physiol., 53, 257-277.
- Turnau, K. (1998) Heavy metal content and localization in mycorrhizal Euphoria cyparission from zinc wastes in Southern Poland. Acta Soci. Bot. Poloniae., 67, 105-113
- Welch, R.M. (1995) Micronutrient nutrition of plants. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci., 14, 49-82.
- Woolhouse, H.W. (1983) Toxicity and tolerance in the responses of plants to metals. Encyclopaedia of Plant Physiology Springer-Verlag Berlin 12C, 245-300.
- http://www.lenntech.com/periodic/water/nickel/nickel-and-water.htm>, dt. 28.4.2012


