Effect of different soil salinity levels on certain biochemical parameters of kidney bean plants
Автор: Verma B.K., Varshney K.A.
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 1 т.18, 2022 года.
Бесплатный доступ
A pot experiment was designed to find out the effect of various salinity levels (0 - 12 mScm-1) on total chlorophyll contents, nitrate reductase activity, betaine contents and Na+ and K+ contents of Kidney bean plants ( Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Results revealed that increasing soil salinity brought about marked reduction in total chlorophyll contents, nitrate reductase activity and K+ ion contents. However, Na+ ion contents and betaine contents got increased. Both the genotypes perform well up to 4 mScm-1. At 8 and 12 mScm-1 electrical conductivity levels the behaviour of them was observed significantly antagonistic demonstrating their susceptibility towards saline conditions.
Salinity, chlorophyll, nitrate reductase, betaine, phaseolus vulgaris
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/143178339
IDR: 143178339
Текст научной статьи Effect of different soil salinity levels on certain biochemical parameters of kidney bean plants
Soil salinity affects almost every aspect of the physiology and biochemistry of plants and significantly reduces yield. Great efforts have been devoted to understand physiological facets of tolerance to salinity in plants. Although there are comparatively salt tolerant cultivars of kidney bean, it has proved difficult to enrich elite lines with genes from wild species that confer tolerance. The paucity of success achieved by past attempts to generate salt tolerant cultivars both through conventional breeding programmes and through some biotechnological approaches has fuelled hopes that the problems might be solved through cultural techniques allowing plants to with stand the deleterious effects of salts better.
The present research work was undertaken to estimate the biochemical attributes like total chlorophyll, nitrate reductase activity, Na+ and K+ contents and betaine contents of two kidney bean varieties under different salinity levels.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A pot culture experiment was carried out in Department of Botany, Bareilly College, Bareilly of which each pot (9" earthenware) contained 7.0 kg of normal garden soil having EC 1.2 mScm–1. The artificial salinization was induced by using NaCl and CaCl 2 in 1: 1 ratio at 4, 8 and 12 mScm–1 at 25°C. A polythene lining was provided inside the pots. The salinity treatments were given at fortnightly intervals. EC of soil was checked regularly by Conductivity Bridge (Systronics make) following the method of Varshney and Baijal, 1977). After collecting the fresh leaves and other green tissues, 1 gm sample was weighed and chlorophyll contents were determined by using Arnon’s formulae in acetone extracts. Nitrate reductase activity was determined from the leaf samples following the method of Steward and Orebamjo (1979).
Calculation:
NRA = CF (Correction factor) x DF (Dilution factor) x OD (Optical density) x Time
The Na+ and K+ contents in dry leaf samples were determined by Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer (Model- Perkin-Elmer, 2380) directly and expressed in meqg–1 dry weight. Betaine contents were determined by the method of Hitz et al. (1982).
The data were statistically analyzed by analysis of variance method
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Total chlorophyll contents
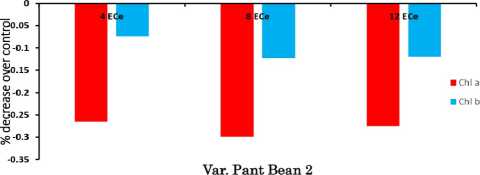
The effect of salinity on chlorophyll formation was significant (Table 1).The chlorophyll contents decreased gradually with increasing levels of soil salinity (4-12 mScm–1) as compared to control (1.2 mScm–1). Chl. a suffered relatively more than chl, b in both the varieties of kidney bean. Our results are in agreement with those of Panda and Khan (2003); Mandel and Singh (2001). Total chlorophyll contents maintained comparatively more in leaves than in other green tissues even upto 12 mScm–1. The exhibition of retention of the contents was found more or less same in both the varieties. However, var. PDR-14 of kidney bean performed relatively well.
Nitrate reductase activity
The effect of soil salinity regimes on NRA was found significant (Fig. 1). Increasing soil salinity was found to decrease NRA as compared to control. Our findings are more or less similar to those of Pandey and Srivastava (1989); Gill and Singh (1992). So far as the decreasing trend is concerned, it was recorded better in var. Pant bean-2 than var. PDR-14. Maximum NRA was noted in former variety of kidney bean. Highest reduction in NRA was found in var. Pant bean-2 showing its susceptible nature.
Betaine and total QACs
The data portrayed in Fig. 2 and 3 was found significant and reveal that soil salinity brought about a marked accumulation of betaine and total quaternary ammonium compounds in both the varieties of kidney bean in leaves as well as seedlings.
In leaves and seedlings both, the mode of accumulation was recorded more or less same. However, var. Pant bean-2 performed better for betaine and QACs both. Similar results have also been reported by Hitz et al . (1982); Steward and Lee (1974); Wyn Jones and Storey (1977).
It may be suggested that beetaine like QACs are localized in the cytoplasm where they act as benigs osmotica to balance decreased vacuolar water potential or as products of ammonia detoxification. Irrespective of the physiological role of these compounds, their accumulation in considerable amount can be crucial to the nitrogen economy of plants (Pan et al., 1981).
Na+ and K+ contents
The effect of soil salinity on Na+ and K+ contents was significant (Table 2). Present findings revealed that Na+ contents increased and K+ contents decreased with increasing episodes of salinity. These observations successfully corroborate the findings of Sultana et al. (2002). The excessively accumulated Na+ contents restricted the uptake of K+ ions by Kidney bean plants. Our results are supported by Islam et al. (1995) and Dionision and Tobita (2000).
Table 1. Chlorophyll contents (µgg-1 fresh wt.) in plants of kidney bean ( Phaseolus vulgaris L.) var. Pant bean 2 and var. PDR-14 under saline conditions
|
Treatment |
ECe (mScm-1) |
In leaves |
In other green tissues |
||||||
|
Chl-a |
Chl-b |
a:b ratio |
Total Chl |
Chl-a |
Chl-b |
a:b ratio |
Total Chl |
||
|
var. Pant bean |
|||||||||
|
NaCl+CaCl 2 |
Control |
0.301 |
0.581 |
0.818 |
0.882 |
0.123 |
0.283 |
0.434 |
0.406 |
|
4 |
0.221 |
0.538 |
0.410 |
0.459 |
0.093 |
0.238 |
0.390 |
0.331 |
|
|
8 |
0.211 |
0.509 |
0.351 |
0.811 |
0.092 |
0.221 |
0.416 |
0.313 |
|
|
12 |
0.218 |
0.511 |
0.356 |
0.826 |
0.091 |
0.168 |
0.341 |
0.259 |
|
|
var. PDR-14 |
|||||||||
|
NaCl+CaCl 2 |
Control |
0.388 |
0.589 |
0.658 |
0.977 |
0.222 |
0.349 |
0.686 |
0.571 |
|
4 |
0.254 |
0.419 |
0.606 |
0.673 |
0.212 |
0.305 |
0.675 |
0.517 |
|
|
8 |
0.238 |
0.370 |
0.608 |
0.608 |
0.124 |
0.212 |
0.584 |
0.336 |
|
|
12 |
0.228 |
0.398 |
0.572 |
0.626 |
0.079 |
0.168 |
0.470 |
0.247 |
|
Values are mean of three replicates
Table . Na+ and K+ contents in plants of kidney bean ( Phaseolus vulgaris L.) var. Pant bean 2 and var. PDR-14 under saline conditions
|
Varieties |
Na+ Contents (meq/g-1) |
K+ Contents (meq/g-1) |
||||||
|
Control |
4 1 |
8 1 |
1 |
Control |
4 1 |
8 1 |
1 |
|
|
var. Pant bean |
||||||||
|
a. In seedlings |
0.011 |
0.09 |
0.41 |
0.45 |
0.023 |
0.011 |
0.003 |
0.003 |
|
b. In leaves |
0.16 |
0.22 |
0.32 |
0.41 |
0.083 |
0.061 |
0.050 |
0.01 |
|
var. PDR-14 |
||||||||
|
a. In seedlings |
0.32 |
0.34 |
0.41 |
0.40 |
0.17 |
0.16 |
0.11 |
0.09 |
|
b. In leaves |
0.91 |
0.98 |
1.03 |
1.00 |
0.64 |
0.52 |
0.48 |
0.14 |
NaCl+CaCl,
In leaves
NaCl+CaCl,

Figure 1. Chlorophyll contents (µgg-1 fresh wt.) in plants of kidney bean ( Phaseolus vulgaris L.) var. Pant bean 2 and var. PDR-14 under saline conditions.
NaCl+CaCl2
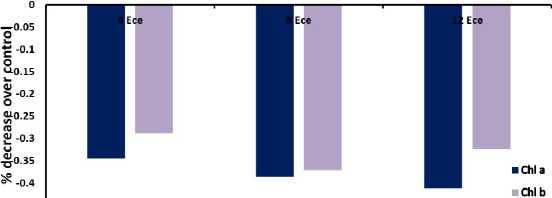
Var. PDR -14 In leaves
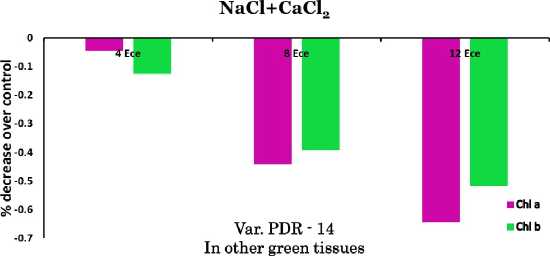
Figure . Na+ and K+ contents in plants of kidney bean ( Phaseolus vulgaris L.) var. Pant bean 2 and var. PDR-14 under saline conditions
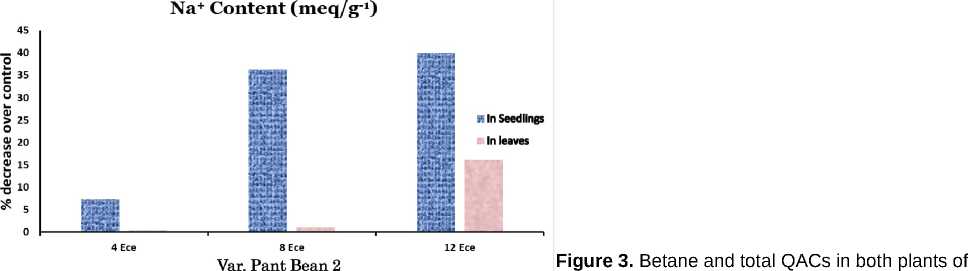
kidney bean ( Phaseolus vulgaris L.) var. Pant bean 2 and var, PDR-14 under saline conditions.

CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest.
Список литературы Effect of different soil salinity levels on certain biochemical parameters of kidney bean plants
- Dionisio, S.M.L. and Tobita, S. (2000). Effect of salinity on sodium content and photosynthetiic response of rice seedling different in salt tolerance. J. Plant Physiol. 157(1): 54-58.
- Gill, K.S. and Singh, O.S. (1992). Effect of salinity and forms of nitrogen on growth, nitrogen metabolism and chemical composition of rice varieties at seedling stage. J. Potassium Res., 8(3): 255-263.
- Hitz, W.D., Ladyman, J.A.R. and Hanson, A.D. (1982). Betaine synthesis and accumulation in barley during field water stress. Crop Sci., 22(2): 47-54.
- Islam, M.T., Islam, M.A. Badruddin, M. and Dutta, R.K. (1995). Effect of salinity stress on the ionic balance and tolarance of rice genotypes. Bangladesh J. Nuclear Agric., 11: 59-66.
- Mandal, M.P. and Singh, R.A. (2001). Impact of salt stress on chlorophyll content in rice genotypes. J. Res. Birsa Agric. Uni., 13(1): 61-63.
- Pan, S.M., Moreau, R.A., Yu, C. and Huang, A.H.C. (1981). Betaine accumulation and betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase in spinach leaves. Plant Physiol., 67: 1105-1108.
- Panda, S.K. and Khan, M.H. (2003). Salt stress influences lipid peroxidation and antioxidants in the leaf of an Indica rice (Oriza sativa L.). Physiology and Molecular Biology of Plants, 9(2): 273-278.
- Pandey, U.K. and Srivastava, R.D.L. (1989). Salinity index in relation to nitrate reductase (NR) activity and proline accumulation in paddy genotypes. Indian J. Plant Physiol., 32(2): 175-177.
- Steward, G.R. and Orebanjo, T.O. (1979). Some unusual characteristics of nitrate reduction in Erythrana senegalensis. DC. New Phytol., 83: 311319.
- Stewart, C.R. and Lee, J.A. (1974): The role of proline accumulation in halophytes. Planta, 120: 270-89.
- Sultana, N., Ikeda, T. and Kashem, M.A. (2002). Effect of seawater on photosynthesis and dry matter accumulation in developing rice grains. Photosynthetica, 40(1): 115-119.
- Varshney, K.A. and Baijal, B.D. (1977. Effect of salt stress on seed germination of some pasture grasses. Comp. Physiol. Ecol., 3: 104-106.
- Wyn Jones, R.G., Storey, R., Leigh, R.A., Ahmad, N. and Pollard, A. (1977). A hypothesis on cytoplasmic osmoregulation. In: Regulation of cell membrane activity in plants. 127: 137. (Marre, E., Ciferri, O. edts.) Elsevier/North Holland Biomedical Press, Amsterdam. Pp. 121-136


