Effect of iron dusts on physiological responses of gram seedlings (Cicer arietinum L.) under laboratory conditions
Автор: Das C.R., Bhaumik R., Mondal N.K.
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 3 т.8, 2012 года.
Бесплатный доступ
A laboratory experiments was conducted for the assessment of physiological and biochemical responses of iron dust under the influence of different pH levels (6.5, 5.0, 3.0) and two concentration of iron dust (0.1 mg and 0.6 mg) with two particle size (100 µm and 300 µm) sprayed on the Cicer arietinum L. seed surface for fifteen day exposure. Observation was made on germination percentage and germination rate, vigour index, % phytotoxicity of root and shoot, chlorophyll, sugar, protein and proline content in both treated and control plant. The present results revealed that the seed color changes to brown under iron stress. The lower germination percentage and germination rate gradually decrease with pH of the medium but both the parameters were not significantly affected by the iron dust. Moreover higher % phytotoxicity was observed under all treatments compared to control and also lower values of this parameter were recorded in shoot than root. The reduction trend in chlorophyll and protein content was recorded at low pH but reverse result was recorded for sugar. Moreover highest proline was recorded under highly acidic condition.
Gram seeds (cicer arietinum l.), ph level, iron dust, phytotoxicity, biochemical constituents
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14323672
IDR: 14323672
Текст научной статьи Effect of iron dusts on physiological responses of gram seedlings (Cicer arietinum L.) under laboratory conditions
The industries constitute a source of geographic and environmental disturbance due to mining and the emission of iron dust (Wong and Tam, 1977; Lopes et al., 2000; Paling et al., 2001). The iron dust, or iron ore particulate matter, represents the major pollutant released by these industries, during both the processing and storage of final products in open stock yards. These pollutants can be deposited either near the source or carried away, depending on the particle size, wind and landscape features. This type of pollutant can directly affect photosynthesis, through abrasion, stomata blockage and smothering of the leaves, once the particles settle down on the organ surface (Hirano et al., 1995; Naidoo and Chirkoot, 2004). Indirect effects may involve chemical and physical modification of the soil properties. Germination and the early growth stages are the most vulnerable periods of a plant life cycle; thus, any environmental stress, combined with the sensitivity of the species, can interfere with a species establishment success (Fan and Wang, 2000; Grantz et al., 2003). This condition is likely to affect the vegetation dynamic, causing further ecological problems (Narayan et al., 1994; Wen et al., 2006). Iron hydroxides constitute the main ore exploited by the industries. Particulate matter derived from the crushing and beneficiation of iron ore is primarily inert and usually unavailable for plants as nutrient source. However, iron particulate accumulation in the soil due to heavy deposition or poor drainage, in combination with low pH of the substrate, may increase the availability of iron (Fe) to plants (Wong et al., 1978). Even though Fe is an essential micronutrient, high levels of this element in the soil can lead to toxicity or nutritional alterations, which can negatively affect plant metabolism (Connolly and Guerinot, 2002). The metal tolerance of plants may be attributed to different enzymes, stress proteins and phytochelatins (Van-Asche and Clijsters, 1990). The accumulation of metals at high concentration causes retardation of growth, biochemical activities and also generation of – SH group containing enzymes (Weckx and Clijsters, 1996). In the present investigation, Indian gram seed (Cicer arietinum L) is used to study the effect of different concentration of iron dust and pH of the medium on germination, vigour index, phytotoxicity, and changes of biochemical constituents under laboratory conditions.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Gram seed (Cicer arietinum L.) were chosen to have their germination and initial growth tested under the influence of iron dust and different pH levels. The pH values studied were 6.5, 5.0 and 3.0, which were adjusted by adding diluted 0.1(N) nitric acid and 0.1(N) NaOH solutions. The doses of iron dust were 0.1mg and 0.6 mg based on the average amount daily deposited in the vicinity of an iron ore industry (Lopes et al., 2000) and exposure of two particle size (100µm and 300µm). The pH without iron dust treatment was used as the control.
Healthy uniform gram seed ( C. arietinum ) was chosen as test plant and pre-soaked in distilled water for overnight. Before germination the gram seeds were surface sterilized with 0.1% HgCl 2 solution for 30 seconds and washing in double distilled water thoroughly for several times to remove excess of chemical and dried on absorbent to eliminate fungal attack. Sixteen selected seed were placed on moist sterile filter paper inside a sterilized Petri plate (9 cm dia. and 1.5 cm depth) for seed germination and seedling growth. The Petri dishes were covered with a net and kept in a growth room under optimum temperature (29 ± 1 °C) and adequate light ventilated condition. Light was supplied by four 40 watt white fluorescent lamps at a distance of 1 m (1,200 lux). Fifty seeds were placed in Petridish for germination. Observations were made for up to day 5 of incubation. Radical emergence of up to 1.5 mm was taken as a visible sign of germination. The length of shoot and root were recorded by using a centimeter scale, percentage of Phytotoxicity for shoot and root of 15 day old seedlings were calculated by the following formula (Chou and Lin, 1976).
Root or shoot length of control -Root or shoot length of treatment % Phytotoxicity =---------------------------------- — ----------------------X100
Root or shoot length of control
The seedling vigour index (SVI) was calculated by the following method suggested by Abdul-Baki and Anderson (1993). SVI = germination percentage (shoot length + root length). For biochemical estimation of total chlorophyll (Arnon, 1949), protein (Lowry et al., 1951), soluble sugar (Mc Cready et al., 1950) and proline content (Bates, Waldren and Teare, 1973) were mediated from the leaves of the plants under various treatments of iron dusts using standard methods. Sample no. are S1 (pH 6.5), S2 (pH 5.0), S3 (pH 3.0), S4 (pH 6.5 and 0.1mg 100µm), S5 (pH 6.5 and 0.6mg 100µm), S6 (pH 5.0 and 0.1mg 100µm), S7 (pH 5.0 and 0.6mg 100µm), S8 (pH 3.0 and 0.1mg 100µm), S9 (pH 3.0 and 0.6mg 100µm), S10 (pH 6.5 and 0.1mg 300µm), S11 (pH 6.5 and 0.6mg 300µm), S12 (pH 5.0 and 0.1mg 300µm), S13 (pH 5.0 and 0.6mg 300µm), S14 (pH 3.0 and 0.1mg 300µm), S15 (pH 3.0 and 0.6mg 300µm).
RESULTS
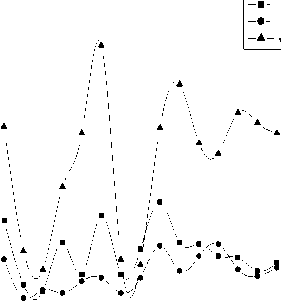
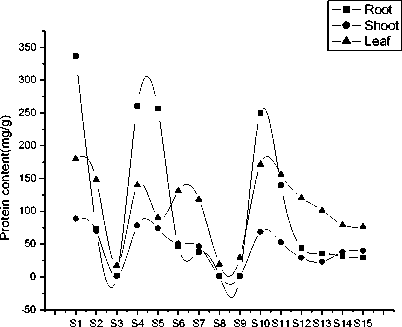
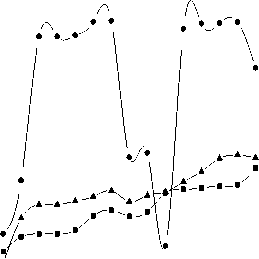
compared to control (Fig. 2a). Again during the germination period most of the gram seeds under iron dust exposure developed a dark color on the seed coats. The results of the pigment content showed that chlorophyll ‘a’, ‘b’ and total chlorophyll gradually decreased with increasing acidity of the medium. Again keeping pH constant (6.5), with increasing exposure of iron dust 0.1mg to 0.6 mg chlorophyll ‘a’, ‘b’ and total chlorophyll drastically reduced but again increased with decreasing the pH of the medium. However, more intense reduction of chlorophyll ‘a’, ‘b’ and total chlorophyll was recorded for further increasing the acidity of the medium. The iron dust which was added in treatment S4 to S9 was 100µm but when size of the iron again increased to 300µm, it was found that pattern of pigment reduction is same as before (Fig.3a). Sugar content in root for all the treatments are very low compared to shoot and leaves except S10 where sugar content in shoot much less than root and leaves. It was found that highest sugar content was recorded at pH 3.0 and lowest at pH 6.5 in shoot and leaf respectively. But application of iron dust (100 µm and 300 µm) doses not provides any significant sugar content in different parts of the plant (Fig. 3c). Protein content was recorded highest in root (S1, S4, S5 and S9) and lowest in shoot (S1, S4, S10, and S13). The variation of protein content was also noted pH dependent. With decreasing the pH of the medium from 6.5 to 3.0, the protein content reduces from 337.06 mg/g to 2.18 mg/g. Similarly shoot protein content reduces from 89.03mg/g to 0.98 mg/g with increasing the acidity of the medium (Fig. 3b). Again unchanged results in protein content was recorded when particle size of iron dust vary with pH. Interestingly it was found that there was no variation of secondary metabolites when amount of iron dust changes with constant pH. Again the results of proline content was recorded different in different pH of the medium. Similar unchanged results of proline was recorded when pH of the medium kept constant with variation of iron dust in different sizes (Fig.3d).
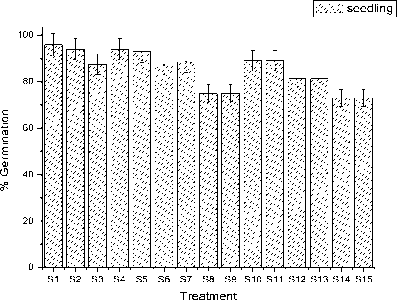
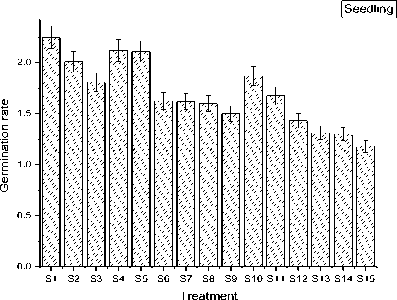
-
(a) . Percentage of seed germination under different pH (6.5, 5.0, 3.0) and iron dust (0.0, 0.1, 0.6) mg exposure of two particle size (100 and 300) mg. Significance differences between treatments are observed. Values are means ± SE (n=3) over two independent experiment.
-
(b) . Percentage of seed germination rate under different pH (6.5, 5.0, 3.0) and iron dust (0.0, 0.1, 0.6 )mg exposure of two particle size (100 and300) mg. Significance differences between treatments are observed. Values are means ± SE (n=3) over two independent experiment.
Figure 1. Percentage of seed germination and germination rate of gram seedling under different treatments after 15 day of sowing of iron dust.
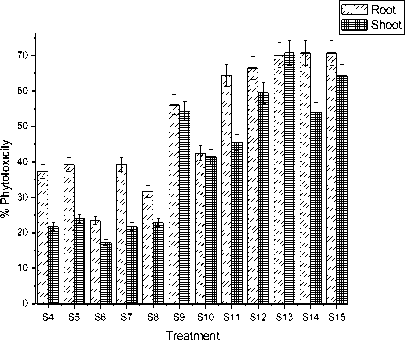
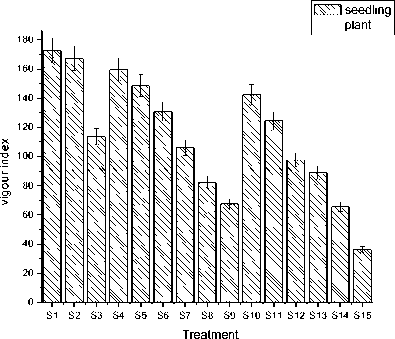
-
(a) . Percentage of phytotoxicity of seedling under different pH (6.5, 5.0, 3.0) and iron dust (0.0, 0.1, 0.6 ) mg exposure of two particle size (100 and 300) mg. Significance differences between treatments are observed. Values are means ± SE (n=3) over two independent experiment.
-
(b) . Vigour index of seedling plant under different pH (6.5, 5.0, 3.0) and iron dust (0.0, 0.1, 0.6) mg exposure of two particle size (100 and 300 mg. Significance differences between treatments are observed. Values are means ± SE (n=3) over two independent experiment.
Figure 2. Percentage of phtotoxicity and vigour index of gram seedling under different treatments after 15 day of sowing of iron dust.
0.16
0.15
0.14
0.13
0.12
g 0.11
0.10
0.09
0.08
0.07
0.06
0.05
0.04
0.03
0.02
0.01
0.00
a
b
T.
Chlo.
Chlo.
Chlo.
S1 S2 S3 S4 S5 S6 S7 S8 S9 S10S11S12S13S14S15
Treatment
Treatment
-
(a) . Chlorophyll content of seedling under different pH and iron dust concentrations after 15 day of sowing.
-
(b) . Protein con tent of seedling under different pH and iron dust concentrations after 15 day of sowing.
E. 40
S1 S2 S3 S4 S5 S6 S7 S8 S9 S10S11 S12S13S14S15
Treatment
—■— Root
-•- Shoot
-A- Leaf
—■— Root
-•- Shoot
-A- Leaf
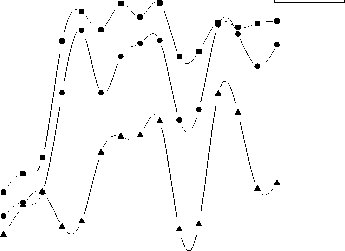
S1 S2 S3 S4 S5 S6 S7 S8 S9 S10S11S12S13S14S15
Treatment
-
(c) . Sugar content of seedling under different pH and iron dust concentrations after 15 day of sowing.
d). Proline content of seedling under different pH and iron dust concentrations after 15 day of sowing.
Figure 3. Biochemical parameters of seedling under different pH and iron dust exposure after 15 day of sowing.
DISCUSSION
Both percentage of germination and rate of germination of seeds was highly affected by pH of the medium. This is quite possible because seed physiology greatly influenced by the acidity of the medium (Fan and Wang, 2000). Moreover, highly acidic condition disrupts the whole metabolic processes including glycolysis which probably due to imbalance of pH gradient within the cells structure (Kuki et al., 2009). The vigour index reduces under acidic condition is due to changes the nature of permeability of seed coat and subsequently its affects on germination and which is indicates the overall performance of the seeds and seedlings (Abirami et al., 2010). Percentage of Phytotoxicity of root was found to be more than shoot, this is due to the fact that metal accumulation on root due to binding of metal on the cell wall of root and retarded cell division and cell elongation (Woolhouse, 1983). From the experimental findings it was revealed that, the color change in seed coat during germination is usually related to phenol oxidation (Rashid et al., 2005). Phenols are commonly present in many parts of the seeds, including the coat and embryo, and they are primarily related to the regulation of seed germination as well as to defense against herbivores and pathogen infestation (Muscolo et al., 2004; Rashid et al., 2005). In contrast, the browning of the gram seed coat in the treatments with iron dust was probably due to phenol oxidation by the metal. The presence of elemental Fe0, as in iron dust, can cause oxidation of phenol to quinines (Rush et al., 1995). Hence, it is thought that the oxidizing characteristic of the iron dust might have accelerated the oxidation of seed coat phenols and/or contributed to the accumulation of internal Fe in the seeds of Cicer arietinum which might have affected the germination process. Chlorophyll content showed reduction trend with decreasing pH of the medium is probably due to the damage of chloroplast under such acidic condition. Singh and Srivastava, (2002) endorsed the same for incorporation of cement kiln dust into leaf tissues. Similar trend of reduction was reported by Pandey et al., (1999) in maize crop, Pandey and Simba, (1990b) for water melon, and Pandey and Simba, (1989) for gram leave. Soluble sugar is an important constituent and source of energy for all living organisms. Plants manufacture this organic substance during photosynthesis and breakdown during respiration. The concentration of soluble sugar is indicative of the physiological activity of a plant and it determines the sensitivity of plants to air pollution. The sugar content was found to be reduced with the increase in the of amount iron dust applied. Reduction in soluble sugar content under stress condition can be attributed to increased respiration and decreased CO2 fixation because of chlorophyll deterioration (Tripathi and Gautam, 2007).The same observation was reported by Uma and Ramana Rao (1996) where plants polluted by dust. The reduction in protein content might be due to the results of decreased photosynthesis and/or break down of existing protein or due to reduced de novo synthesis (Singh and Jothi, 1999). In the present study revealed that the protein content was found to be decreased in all treatment sets. This reduction in protein content might be due to the enhanced rate of protein denaturation (Tripathi and Gautham, 2007; Prasad and Inamdar, 1990a). The enhanced protein denaturation and breakdown of existing protein to amino acid is the main cause of reduction in protein content (Constantinidou and Kozlowski, 1979). ). In our study, we found that prolin concentration is significantly higher when iron exposure was increased. This accumulation of prolin has also been reported as being a sign of stress in plant (Rai et al., 2003) which at higher concentration act as a solute for intercellular osmotic adjustment (Silveira et al., 2003).
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Список литературы Effect of iron dusts on physiological responses of gram seedlings (Cicer arietinum L.) under laboratory conditions
- Abdul-Baki, A. and Anderson, J. D. (1993).Vigour determination in soybean seed by multiple criteria. Crop Sc., 13, 630-33.
- Abirami, K., Rema, J., Mathew, P.A., Srimvasan, S. and Hamza, S. (2010) Effect of different propagation media on seed germination, seedling growth and vigour of nutmeg (Myristica fragrans Houtt). J. Medical Plant Res., 4(19), 2054-2058.
- Arnon, D.I. (1949) Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplast. Polyphenol oxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol., 24, 1-15.
- Bates, L.S., Waldren, R.P., and Teare, T.D. (1973) Rapid determination of proline for water stress studies. Plant Soil., 39, 205-7.
- Chou, C.H., Lin, H.J. (1976) Autointoxication mechanism ofOriza sativa L. Phytotoxic effects of decomposing rice residues in soil. J. Chem. Ecol., 2, 353-367.
- Connolly, E.L., and Guerinot, M.L. (2002). Iron stress in plants. Genome Biol., 3, 10241-10245.
- Constantinidoa, H.A. and Kozlowski, T.T. (1979) Effect of SO2 and O3 on Ulmus American seedlings. 1. Visible injury and growth, 2. Carbohydrate, protein and lipids. Can. J. Bot., 57, 170-184.
- Fan, H. B., and Wang, Y. H. (2000) Effects of simulated acid rain on germination, foliar damage, chlorophyll contents and seedling growth of five hardwood species growing in China. Forest Ecol. and Manage., 126, 321-329.
- Grantz, D. A., Garner, J. H. B. and Johnson, D. W. (2003) Ecological effects of particulate matter. Environ. Internatio., 29, 213-239.
- Hirano, T., Kiyota, M., and Aiga, I. (1995). Physical effects of dust on leaf physiology of cucumber and kidney bean plants. Environ. Pollut., 89, 255-261.
- Kuki K.N., Oliva, M.A. and Costa, A.C. (2009) The Simulated Effects of Iron Dust and Acidity During the Early Stages of Establishment of Two Coastal Plant Species. Water Air Soil Pollut., 196, 287-295.
- Lopes, S.A., Oliva, M.A., and Martinez, C.A. (2000) Impacto das imissões de dióxido de enxofre e deposição de material particulado de ferro em espécies vegetais de restinga: avaliação ecofisiológica. In E. Espíndola, C. aschoal, O. Rocha, M. Bohrer, & A. Oliveira Neto (Eds.), Ecotoxicologia (pp. 53-71). São Paulo: RiMa
- Lowry, O.H., Rose Brough, N.J., Fan, A.L., and Randal, R.J (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biolog. Chem., 19, 265-275.
- Mc.Cready, R.M., Guggolz, J., Siliviera, V. and Owens, H.S. (1950) Determination of starch and amylase in vegetables. Analytical Chem., 22, 1156.
- Muscolo, A., Panuccio, M.R., and Sidari, M. (2004) The effect of phenols on respiration enzymes in seed germination. Plant Growth Regula., 35, 31-35.
- Naidoo, G. and Chirkoot, D. (2004) The effects of coal dust on photosynthetic performance of the mangrove, Avicennia marina in Richards Bay, South Africa. Environ. Pollut., 127, 359-366.
- Narayan, D., Agrawal, M., Pandey, J., and Singh, J. (1994) Changes in vegetation characteristics downwind of an aluminum factory in India. Annals of Bot., 73, 557-565.
- Paling, E.I., Humphries, G., McCardle, I., and Thomson, G. (2001) The effects of iron ore dust on mangroves in Western Australia: lack evidence for stomatal damage. Wetland Ecol. Manage., 9, 363-370.
- Pandey, D.D. and. Simba, A.K, (1989) Effect of cement kiln dust on chlorophyll in gram leaves. Indian J. Ecol., 16, 178-179.
- Pandey, D.D. and. Simba, A.K, (1990b) Effect of cement kiln dust on chlorophyll in wheat leaf. Environ. Ecol., 8, 461-463.
- Pandey, D.D., Nirala, A.K. and. Gaulam, R.R, (1999) Impact of stone crusher dust pollution on maize crop. Indian J. Environ. Ecoplan., 2, 43-46.
- Prasad, M.S.V. and Inamdar, J.A. (1990a) Effect of cement kiln dust pollution on blackgram (Vigna mungo L.). Proc. Indian Acad. Sci., (Plant Sci.)., 100, 435-443.
- Rai, S.P., Luthra, R. and Kumar, S. (2003) Salt tolerant mutants glycophytic salinity response (GRS) genes in Catharanthus roses. Theor. Appl. Genet., 106, 221-230.
- Rashid, A., Furness, N. H., Eliis, B. E., and Upadhyaya, M. K. (2005) Inhibition of seed germination and seedling growth by hounds-tongue (Cynoglosum officinale L.). Weed Biol. and Manage., 5, 143-149.
- Rush, J.D., Cyr, J.E., Zhao, Z. and Bielski, B.H. (1995) The oxidation of phenol by ferrate (VI) and ferrate (V). A pulse radiolysis and stopped flow study. Free Radical Res., 22, 349-360.
- Silveira, J.A., Viegas Rde, A., da Rocha, I.M., Moreira, A.C., Moreira Rde, A. and Oliveira, J.T. (2003) Prolin accumulation and glutamine synthase activity are increased by salts induced proteolysis in cashew leaves. J. Plant Physiol., 160, 115-123.
- Singh, P. and Jothi, S. (1999) Reduction in protein contents in a few plants as indicator of air pollution. Poll. Res., 18, 281-283.
- Singh, R.B. and Shrivastava, A.K. (2002) Cytotoxic effects and biological damages in Clitoria ternatie by cement dust. Nat. Environ. Poll. Res., 1, 457-461.
- Tripathi, A.K. and Gautam, M. (2007) Biochemical parameters of plants as indicators of air pollution. J. Environ. Biol., 28, 127-132.
- Uma, C.H., Rao, T.V.R., (1996) Effect of cement kiln dust pollution on Hibiscus cannabinus L. Geobios., 23, 59-64.
- Van Assche, F. and Clijsters, H. (1990) Effects of metals on enzyme activity in plants. Plant Cell Environ., 13, 195-206.
- Weckx, J. and Clijsters, H. (1996) Oxidative damage and deference mechanisms in primary leaves of Phaseolus vulgaris. Physiol. Plant., 96, 506-512.
- Wen, D., Kuang, Y., Liu, S., Zhang, D., Lu, Y., and Li, J. (2006) Evidences and implications of vegetation damage from ceramic industrial emission on a rural site in the Pearl River delta of China. J. Forestry Res., 17, 7-12.
- Wong, M.H. and Tam, F.Y. (1977) Soil and vegetation contamination by iron ore tailing. Environ. Pollut.,14, 242-254.
- Wong, M.H., Chan, K.C., and Choy, C.K. (1978) The effect of the iron ore tailing on the costal environment of Tolo harbor, Hong Kong. Environ. Res., 15, 342-356.
- Woolhouse, H.W. (1983) Toxicity and tolerance in response of plants to heavy metals.In. OL Lang, PS Nobel,CB Osmod and H Zeiglerreda: Encyclopedia of Plant physiol., 12, 245-300.


