Effect of salt stress on expression of carotenoid pathway genes in tomato
Автор: Babu Merlene Ann, Singh Devesh, Gothandam K.M.
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 3 т.7, 2011 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Carotenoids, the naturally occurring isoprenoids form essential components of photosynthetic antenna and reaction centre complexes. Thus they play a significant role in absorption, dissipation and transfer of light energy for the process of photosynthesis. The effects of salt stress on carotenoid gene expression in tomato leaves were studied. For that tomato plants were subjected to different concentration of salt water. Morphological characters such as plant height, no. of fruits per plant, chlorophyll content and expression of four major carotenoid pathway genes such as phytoene synthase, phytoene desaturase, zeta carotene desaturase and lycopene beta cyclase were analysed. The quantitative expression analysis using real time PCR has shown a decrease in the expression of all the studied genes as the salt concentration increased. Among the different concentrations of NaCl used for the experiment, it was seen that 200 mM was most detrimental for the carotenoid gene expression. Lycopene beta cyclase, the enzyme that converts lycopene to beta carotene was seen to be highly affected compared to other genes studied showing a 1.87 fold inhibition in its expression at 200 mM NaCl.
Carotenoid pathway genes, chlorophyll content, real time pcr, salt stress
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14323541
IDR: 14323541
Текст научной статьи Effect of salt stress on expression of carotenoid pathway genes in tomato
Abbreviations: PSY - Phytoene synthase; PDS - Phytoene desaturase; ZDS - zeta carotene desaturase; LCY-β - Lycopene beta cyclase; BCT - Beta actin; RT PCR - Real time PCR
Tomato is one of the most abundantly consumed vegetable worldwide which contains many health beneficial factors like carotenoids. It can be consumed both in raw and cooked form. Abiotic stress is one of the most harmful factor concerning the growth and productivity of plant (Grover et al .,
2001). Abiotic stress like salinity, drought, high temperature, cold, and freezing can be detrimental to the plant in such a way that they are reduced in their yield in comparison to their potential yield in normal plants (Graiphenberg et al., 2000; Yokoi et al., 2002). Salt stress can lead to osmotic stress and ionic stress thereby impairing the vital cellular functions (Munns 2002; Kao et al., 2003; Sayed, 2003). Osmotic stress results in reduced availability of water causing dehydration, stomata closure, reduced CO2 supply, slower rate of biochemical reactions are some of the factors that prevails during periods of dehydration. Salinity affects some of physiological processes of plants such as increased respiration rate, changes in the plant growth, and changes in mineral distribution, membrane instability and failure in the maintenance of turgor pressure (Joset et al. 1996; Murphy and Durako 2003, Muranaka et al. 2002; Hasegawa et al. 2000). During salt stress the accumulation of external sodium ions will hamper the intracellular potassium ion influx, thereby changing the sodium: potassium ratio. Besides it prevents the uptake of many fundamental nutrients due to competitive interactions and ion selection of membranes. This affects the photosynthetic electron transport system to a wide extent, thereby affecting photosynthesis (Sudhir et al., 2005).
Many of the pathways will be affected in response to abiotic stresses like salt stress. Carotenoid biosynthetic pathway is one such pathway of paramount importance as it produces carotenoids, which plays a major role in photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is one of the mostly affected factors due to salt stress (Sudhir and Murthy, 2004; Stoeva and Kaymakanova, 2008; Lu et al., 2010). They form essential components of photosynthetic antenna and reaction centre complexes. Thus they play a crucial role in harvesting light energy during photosynthesis as reported by Mimuro and Katoh (1991). Apart from carotenoids, the intermediates of this pathway such as Geranyl geranyl pyrophosphate act as precursors for the synthesis of many other metabolites as chlorophyll, phytols, steroids, plastoquinone, tocopherols etc which has got great impact throughout the life cycle of plants as reported by Fraser and Bramley (2004). The pathway also produces various plant hormones such as zeatin, abscisic acid, gibberellins etc. Zeatin holds a vital role as regulators of plant cell proliferation and differentiation. Gibberellins stimulate stem elongation by inducing cell division and elongation. Abscisic acid is a major player in the adaptation of the plant to stress (Kempa et al., 2008). Thus understanding the expression of some of the carotenoid biosynthetic genes such as PSY, PDS, ZDS, LCY-β will be of paramount importance as molecular understanding of these pathways will provide great insights towards the genetic engineering of tolerance to these stresses.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Tomato plant growth conditions
PKM 1 variety tomato seeds were purchased from local dealers and grown in green house at VIT University, Vellore at controlled conditions.
Salt treatment
Six sets of plants (three replicates) were treated with six different concentration of NaCl such as 25 mM, 50mM, 100 mM, 150 mM, and 200 mM respectively. For control the plants were treated with normal water.
Morphological characters
Morphological characters such as plant height and number of fruits per plant of the salt treated tomato plants were noted after 90 days of treatment with respective concentrations of NaCl as mentioned above.
Chlorophyll estimation
Salt treated and control plant leaves were also collected for the estimation of chlorophyll content. The chlorophyll content was estimated according to the protocol mentioned by Arnon (1949).
RNA isolation and cDNA synthesis
Leaves from Lycopersicon esculentum plants were collected after 90 days of treatment and thoroughly cleaned. They were subsequently frozen and ground using mortar and pestle under liquid nitrogen. Total RNA was isolated using conventional Trizol reagent according to manufacturer’s protocol. First strand cDNA synthesis was performed using High capacity cDNA reverse transcription kit from AB systems.
Selection of genes and design of primers
Four carotenoid biosynthetic genes such as PSY, PDS, ZDS, LCY-β along with beta actin as endogenous control were subjected to the study. The nucleotide sequences of the respective genes were obtained from National Centre of Biotechnology Information. Primers sequences of 17- 27 nucleotides were designed using Applied Biosystems Primer Express Software version 3.0 to give PCR products of 150-200 base pairs size in RT PCR studies. Primers used were as follows. For PSY forward 5’ –TTG TTT CTC CTT GTG ACG TCT CA-3’, reverse 5’ – GTT TCC CTC CCG GAC TGA TT – 3’ ; for PDS forward 5’- AGT CAA AAG GTG GCC AAG TCA -3’, reverse 5’- TTC CAT CCT CAT TCA GCT CAA TC -3’; for LBC forward 5’- GGC CCT GCA GGA CTT GCT -3’, reverse 5’- ATT GAA CAA ACA GAG AGA GTC CTG CTT -3’; for ZCD forward 5’- CAA CGC TCC AAA AGG GCT ATT -3’, reverse 5’- GCT TTG GCC CCC ATA AT -3’.
Real Time PCR (RT PCR)
The cDNA obtained from the samples were subjected to relative standard curve quantitation experiment in Applied Biosystems StepOne™ RT PCR system Thermal Cycling Block. The experiment was carried out in a 20 µl reaction set up consisting of 2 X SYBR Green master mix, 900 nM each of forward and reverse primer and the cDNA sample of the particular gene under study. The standard dilution series was prepared to obtain the relative standard curve from which the relative transcript levels can be obtained. The following program was applied for 40 cycles. Holding stage at 95˚C for ten minutes. Cycling stage in which 95˚C was maintained for 15 seconds and 60˚C for one minute. The specificity of the PCR products were confirmed using melt curve analysis using temperature ranging from 60˚C to 90˚C. Relative expression levels were normalized using BCT as an endogenous control.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Salt stress is an abiotic stress factor that causes various deleterious effects on the overall plant growth and development (Ghanem et al., 2008). In this study two of the morphological traits denoting the plant growth such as ‘plant height’ and ‘no of fruits per plant’ were noted. It was seen that both the shoot length and no of fruits declined as the salt concentration increased which is evident from results shown in Table 1. There exist several internal and external factors that influence the overall growth and development of plants. Plant growth hormones, which are the signaling molecules helps in transmitting signals between the cells and within the cells, thus aids in development of plants in each and every stage of their life is one such internal factor. External factors include water relations, proper nutrient supplies etc. All these above factors such as water relations, carbon supply, hormonal balance involved in the control of growth of plants exposed to high salt concentrations (Albacete et al., 2008). Exposure of plants to NaCl reduced the availability of water for the plants, thus causes osmotic stress. The dominance of Na+ and Cl- ions inhibits the uptake of other minerals vital for plant’s growth (Ghanem et al., 2008; Albacete et al., 2008; Hamdia and Shaddad, 2010). Previous researches have speculated that concentration of hormones such as auxin, cytokinin, zeatin changes in response to salinity (Hamayun et al., 2010; Ghanem et al., 2008, Albacete et al., 2008). This hormonal imbalance, osmotic stress etc is believed to play a significant role in the salinity induced changes in the shoot vigour and yield of plants (Albacete et al., 2008).
Photosynthesis which is source of energy for all aerobic life on earth is one of the processes badly affected by high salt conditions. In plants photosynthesis occurs in organelles named chloroplast. Several pigment such as chlorophyll and carotenoids present in the chloroplasts are some of the internal factors that hold a major role in photosynthesis (Doganlar et al ., 2010). Even though chloroplasts exist in all the cells in the green parts of the plant, most of the energy is captured in leaves. Thus leaves of tomato were used in the above stated work. The expression pattern of four different genes in the carotenoid biosynthetic pathway was analysed in tomato leaves after subjecting different tomato plants to 25 mM, 50 mM, 100 mM, 150 mM and 200 mM concentrations of sodium chloride respectively. The genes under study were PSY,PDS, ZDS, LCY-β . The quantitative expression analysis using RT PCR showed a varied expression pattern of these genes in plants exposed to sodium chloride in comparison to control plants. The expression of these genes decreased as concentration of NaCl increased.
In the case of PSY , the enzyme that catalyse the first committed step in the pathway, the expression decreased 1.06, 1.22, 1.57, 1.59 and 1.90 folds in 25 mM, 50 mM, 100 mM, 150 mM and 200 mM NaCl treated tomato plants respectively in comparison to control plants. The expression of PDS , which converts phytoene to phytofluene and phytofluene to zeta carotene through a desaturation step, was also noted in the above salt treated plants. When compared to untreated (control) plants a decrease of
1.08, 1.17, 1.27, 1.46 and 1.86 folds were observed in 25 mM, 50 mM, 100 mM, 150 mM and 200 mM salt treated plants respectively. ZDS ,which is responsible for the synthesis of the antioxidant lycopene from zeta carotene exhibited a decrease in its expression of 1.23, 1.35, 1.40, 1.43 and 1.73 folds in tomato plants exposed 25 mM, 50 mM, 100 mM, 150 mM and 200 mM NaCl respectively. A decline in the expression levels of LCY-β which produce beta carotene, the most potent provitamin A carotenoid, was perceived in salt treated plants. It decreased to 1.31, 1.47, 1.62, 1.69 and 1.87 folds in 25 mM, 50 mM, 100 mM, 150 mM and 200 mM NaCl treated tomato plants respectively in comparison to control plants.
Earlier most of the studies have been focused on the expression pattern of carotenoid biosynthetic genes in tomato fruits, as it is the edible part of the plant. The expression of the carotenoid genes in fruits was boosted up upon exposure to salt stress. The increased expression produced increased levels of antioxidant enzymes which aid in the scavenging of reactive oxygen species, thus protecting the tomato plants from salt stress (Smidova and Izzo, 2009). An extensive research on the expression profile of carotenoids in leaves of plants exposed to salt stress were not done, were as quantitation of chlorophyll pigment in the same was an area of much interest. In this work a decrease in the total chlorophyll content was observed as salt concentration increased as shown in Table 1. Previous reports suggested that the decrease in the total chlorophyll content was observed which can be either due to its degradation or inhibition in its synthesis level (Doganlar et al ., 2010).
To develop salt tolerant plants, a proper understanding regarding the molecular mechanisms and genetic expression of the factors contributing towards the growth and development of plant is vital. As carotenoids helps in harvesting light energy and thus form essential components of photosynthetic antenna and reaction centre complex, our major interest was to analyze the expression pattern in leaves of tomato plants and thus explore its part played in hampering photosynthesis. This work clearly states that Lycopersicon esculentum plants under salt stress shows a decreased expression of carotenoid biosynthetic genes in leaves, thus plays a significant role in hampering photosynthesis rate, thereby reduces the yield and the productivity of plants.
Table 1. Chlorophyll content and morphological characters of the salt treated tomato plants
|
Sample |
Total chlorophyll mg/gm |
Plant Height (cm) |
No. of fruits per plant |
|
Control |
1.4191 ± 0.097 |
162.56 |
15 |
|
25mM |
1.3677 ± 0.069 |
147.32 |
12 |
|
50mM |
1.3218 ± 0.066 |
127 |
10 |
|
100mM |
1.2348 ± 0.096 |
116.84 |
7 |
|
150mM |
1.0855 ± 0.052 |
101.6 |
6 |
|
200mM |
0.9742 ± 0.043 |
81.28 |
4 |
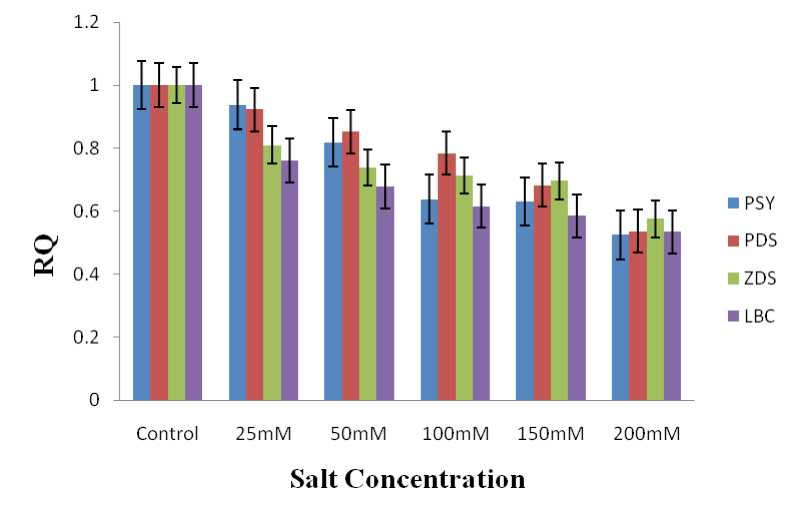
Figure 1. Expression level of carotenoid pathway genes under different salt stress condition in tomato leaves. PSY - Phytoene synthase, PDS - Phytoene desaturase, ZDS - Zetacarotene desaturase, LBC - Lycopene beta cyclase.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Список литературы Effect of salt stress on expression of carotenoid pathway genes in tomato
- Albacete et al. (2008) Hormonal changes in relation to biomass partitioning and shoot growth impairment in salinized tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) plants. J. Exp. Bot. 59:4119-4131.
- Arnon, D.I. (1949) Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplast polyphenol oxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol. 24:1-15.
- Doganlar, Z.B., Demir, K., Basak, H. and Gul, I. (2010) Effects of salt stress on pigment and total soluble protein contents of three different tomato cultivars. Afr. J. Agr. Res. 5:2056-2065.
- Fraser, P.D. and Bramley, P.M. (2004) The biosynthesis and nutritional uses of Carotenoids. Lipid Res. 43:228-265.
- Ghanem et al. (2008) Hormonal changes during salinity induced leaf senescence in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). J. Exp. Bot. 59:3039-3050.
- Graifenberg, A., Giustiniani, L., Barsanti, L. and Botrini, L. (2000) Effects of salt stress on tomato fruit quality. Colture Protette 29:71-80.
- Grover et al. (2001) Understanding molecular alphabets of the plant abiotic stress responses. Curr. Sci. 80:206-211.
- Hamayun et al. (2010) Effect of salt stress on growth attributes and endogenous growth hormones of soybean cultivar Hwangkeumkong. Pak. J. Bot. 42:3103-3112.
- Hamdia, M.A. and Shaddad, M.A.K. (2010) Salt tolerance of crop plants. J. Stress Physiol. Biochem. 6:64-90.
- Hasegawa, P.M., Bressan, R.A., Zhu, J.K. and Bohnert, H.J. (2000) Plant cellular and molecular response to high salinity. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 51:463-499.
- Joset, F, Jeanjean, R and Hagemann M. (1996) Dynamics of the response of cyanobacteria to salt stress: deciphering the molecular events. Physiol. Plant 96:738-744.
- Kao, W.Y., Tsai, T.T. and Shih, C.N. (2003) Photosynthetic gas exchange and chlorophyll a fluorescence of three wild soybean species in response to NaCl treatments. Photosynthetica 41:415-419.
- Kempa, S., Krasensky, J., Dal Santo, S., Kopka, J. and Jonak, C. (2008) A Central Role of Abscisic Acid in Stress-Regulated Carbohydrate Metabolism. PLoS ONE 3(12):e3935 DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003935
- Lu, S., Li, T. and Jiang, J. (2010) Effect of salinity on sucrose metabolism during tomato fruit development. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 9:842-849.
- Mimuro, M. and Katoh, T. (1991) Carotenoids in photosynthesis: absorption, transfer and dissipation of light energy. Pure Appl. Chem. 63:123-130.
- Munns, R. (2001) Comparative physiology of salt and water stress. Plant Cell Environ. 25:239-250.
- Muranaka, S., Shimizu, K. and Kato, M. (2002) Ionic and osmotic effects of salinity on single-leaf photosynthesis in two wheat cultivars with different drought tolerance. Photosynthetica 40:201-207
- Murphy, K.S.T. and Durako, M.J. (2003) Physiological effects of short term salinity changes on Ruppia maritima. Aqua. Bot. 75:293-309.
- Sayed, O.H. (2003) Chlorophyll fluorescence as a tool in cereal crop research. Photosynthetica 41:321-330.
- Smidova, Z. and Izzo, R. (2009) Improvement of nutritional value of tomatoes under salt stress conditions. Czech J. Food Sci. 27:138-139.
- Stoeva, N. and Kaymakanova, M. (2008) Effect of salt stress on growth and photosynthesis rate of bean plants. J. Cent. Eur. Agr. 9:385-392.
- Sudhir, P. and Murthy, S.D.S. (2004) Effects of salt stress on basic processes of photosynthesis. Photosynthetica 42:481-486.
- Sudhir, P., Pogoryelov, D., Kovacs, L., Garab, G. and Murthy, S.D.S. (2005) The effect of salt stress on photosynthetic electron transport and thylakoid membrane proteins in the cyanobacterium Spirulina platensis. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 38:481-485.
- Yokoi, S., Bressan, R.A. and Hasegawa, P.M. (2002) Salt stress tolerance of plants. JIRCAS Working reports 25-33.


