Effect of salt stress on grain reserve composition in ten durum wheat cultivars
Автор: Kahrizi Sonia, Sedghi Mohammad
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 3 т.9, 2013 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Saline soils are defined as those that contain sufficient soluble salts in the root zone to impair plant growth. Wheat is one of the three major cereals dominating world agriculture to date. Durum wheat is the hardest wheat and the concept of durum wheat quality is complex and confusing. Quality factors such as protein content, gluten strength and color have different priorities in various durum wheat markets. Changes in the grain quality of ten durum wheat cultivars under salt stress studied at the greenhouse condition. A factorial experiment was carried out based on completely randomized design with three replications. Treatments were salinity including 0, 60 and 120 mM and ten durum wheat cultivars (Boomer, PGS, 71135, 61130,605, C1351, KND, KDM, Haurani and G1252). Biochemical grain reserves such total protein and carbohydrate content, gluten, phosphorous and beta carotene were measured. Results showed that interaction of salt and cultivars was significant for all studied traits except of beta-carotene. At this experiment, gluten content changed very little with salinity levels. Cultivar 71135 at all salinity levels had the highest gluten content. With increasing of salt severity, the content of protein and carbohydrate decreased and content of phosphorous increased compared with control. In 60 mM salinity, cultivars 61130 and 71135, in 120 mM, 71135 and KDM and in control, 61130 and PGS respectively, had the highest and lowest content of protein. Cultivars 71135 and 61130 had the highest and PGS had the lowest phosphorous content in control. At 60 mM, cultivars 71135 and PGS respectively, had the highest and lowest phosphorous content. At 120mM, 71135 and Haurani respectively, had the highest and lowest phosphorous content. In three salt levels, cultivar 71135 was determined as the most tolerant cultivar according to content of grain reserve composition results.
Durum wheat, gluten, grain composition, grain quality, salinity
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14323757
IDR: 14323757
Текст научной статьи Effect of salt stress on grain reserve composition in ten durum wheat cultivars
Salinity is common in arid regions due to an inability to flush accumulated salts from the soil (Bahizire, 2007). Saline soils are defined as those that contain sufficient soluble salts in the root zone to impair plant growth (Omami, 2005).Wheat is one of the three major cereals dominating world agriculture to date. Durum wheat is the hardest wheat and durum milling produces a coarse particle called semolina, ideal for pasta (Sisson, 2004). Little researches have carried out about the salinity effects on grain or seed quality and there is little information about relation between salinity and grain quality (Zheng et al., 2009). The concept of durum wheat quality is complex and confusing (Marchylo and Dexter, 1996).Grain quality is very important in durum wheat. Zhang et al., (2007) indicated that genotype, environment, and their interaction affect the most of quality traits and amount of protein fractions. After anthesis, kernel growth is directly impacted by soil and air temperature, water and N, as well as source–sink relations with leaves and stems (Graybosch et al., 1996). Quality factors such as protein content, gluten strength and color have different priorities in various durum wheat markets (Marchylo and Dexter, 1996). Protein content is controlled by genetic, environment and soil fertility. Positive correlations between environmental factors and wheat protein content have been reported during grain filling (Rao et al., 1993; Graybosch et al., 1996; Huebner et al., 1997). There is relation between cooking quality of semolina products and quality and quantity of protein in the grain endosperm. Khan et al., (2008) showed that salinity increased protein content of wheat grains and the gluten content of salt tolerant cultivars was higher than that of salt sensitive ones. In contrast, Katerji et al., (2005) reported salinity did not affect the grain quality of the sensitive cultivar, but affected the grain quality of the tolerant one, mostly in a positive way by a decrease of the ash-content. Some researchers have introduced the protein content as a factor in determination of pasta cooking quality (Deckard et al., 1996). According to
Galterio et al ., (1993) protein alone does not indicate desirable quality of pasta bake and composition of grain protein especially gluten has great effect on cooking quality. Results of cooking quality of pasta are affected by content and quality of protein, gluten quality and percentage of pigments (Dexter and Matsuo, 1977; Fabriani and Lintas, 1988). The protein quality in the grain is also affected by the entanglement of the glutenin subunits into protein macromolecules which are influenced by the environment in which the wheat plant is cultivated (Jia et al ., 1996). Frequently there is a negative relationship between grain yield and protein content (Fowler, 2003).
When pasta is cooked in boiling water, the protein network becomes loose and permits exudates to escape during starch gelatinization (Resmini and Pagani, 1983). Higher protein in pasta can cause more stability in the cooking process, enough to swell and a small amount of pasta material is released in water (Dexter et al ., 1987). In general, high rate of gluten and protein is associated with good quality of pasta and high volume of bread and bulgur (Katerji et al ., 2005). The importance of wheat is attributed to the gluten storage proteins present in the endosperm, conferring unique viscoelastic properties to dough (Shewry et al ., 1997). Gluten storage proteins divided into two major classes: gliadins that confer extensibility and glutenins that cause elasticity. Regarding to salt stress effect on proteins in wheat grains, Shen et al., (2007) found that protein content increased and protein accumulation amount decreased with increasing soil salt content. Salt stress has a different effect on carbohydrate contents. Some authors have reported carbohydrates accumulation in various plants under salinity condition (Parida et al ., 2003; Azooz et al .
2004). On the other hand, Mostafa (2004) observed that at low and moderate salinity levels, sugars and consequently the total carbohydrates are decreased. Accumulation of sugars in different parts of plants is enhanced in response to the variety of environmental stresses (Prado et al ., 2000). Color of semolina is due to carotenoids, especially lutein (a xanthophyll) and regarded as an important trait by customers. High percentage of carotenoids is associated with good quality of semolina (Katerji et al ., 2005). Effect of genetic and environmental conditions on grain weight and carotenoid synthesis and decomposition can directly or indirectly affect the amount of yellow pigments (Clarke et al ., 2006). Hessler et al ., (2002) found that starch increase in large size grains that could be estimated by grain weight has weakening effect on percentage of yellow pigment. Clarke et al ., (2006) found that under cold and humid conditions, percentage of yellow pigments increased. The objectives of this study were to determine the effects of salinity on the grain quality and reservoirs composition in ten durum wheat cultivars at greenhouse conditions.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
In order to evaluate the salinity impact on the grain quality of durum wheat a factorial experiment was conducted based on completely randomized design with three replications at the University of Mohaghegh Ardabili, Ardabil, Iran in a greenhouse at 25.15°C day/night temperature and 14/10 hours day/night photoperiod. Treatments were salinity including 0, 60 and 120 mM that were applied in two stages, one before shooting and the other before booting and ten durum wheat cultivars including Boomer, PGS, 71135, 61130, 605, C1351, KND, KDM, Haurani and G1252. These cultivars were obtained from the Research Institute of
Maragheh. Seeds of each cultivar were sterilized with 0.5% sodium hypochlorite for 4 minutes, rinsed with distilled water and planted in pots. The pots were filled with soil, fertilizer and fine sand about one-third each of them. After planting, irrigation was performed according to need of plants once every four days. Seeds were harvested after physiological maturity and were tested.
Grain quality Assay:
Beta carotene content was measured according to standard method (AACC, 14-50) that was modified by Fares et al ., (1991). One g grain flour with 5 ml N-butyl alcohol-saturated water was extracted on shaker for three hours. After centrifugation, supernatant was used and absorbance measured by a spectrophotometer. Content of protein was measured according to standard method (AACC, 12-46, Anonymous, 1983) using Kjeldahl apparatus. After determining the amount of nitrogen in the sample, it was multiplied by 7.25 and protein content in the flour was presented in percent. Content of arid gluten was measured by washing with hands with 25 g flour according to standard method (AACC, 10-38, Anonymous, 1983).Phosphorous content was measured according to Warraich et al ., (2002).One g of grain was digested in 20 ml concentrated nitric acid and then, 10 ml 72% acid hyper chloric was added to the solution for warming and losing of color to the last degree. The digested material was cooled and transferred to a 100 ml flask. Then, 5 ml sulfuric acid, 5 ml ammonium vanadate and 5 ml ammonium molybdate were added to solution and was maintained for 3 min. Reading was done using a standard curve with photometer (Beckman 1211) and blue filter paper correctly and P content were calculated. Percentage of carbohydrates in the grains was measured according to Dubois et al .
(1951). First, spectrophotometer was calibrated with 500 ml of 4% phenol and 5.2 ml of 96% sulfuric acid. Some grains were milled into flour and then it was transferred to 10 ml tubes. At this stage, all glycosidic bonds were broken and a color solution is created and amount of heat is produced in presence of sulfuric acid. At this stage, 500 ml phenol 4% and 5.2 ml of 96% sulfuric acid was added to all test tubes. Solutions were transferred to cuvettes and the absorbance was read at a wavelength of 490 nm for standards and sample. The carbohydrate concentration in the samples was determined by a standard graph and was calculated as the percentage of carbohydrates. The data were analyzed with SAS 9.1 after normality test and means compared with the LSD method.
RESULTS
Interaction of salt and cultivars was significant for all studied traits except of beta-carotene (Table 1). The highest and lowest protein content was observed in cultivars 61130 and KNDat60mM 71135 and KDM at 120 mM and 61130andPGS at control, respectively (Table 2). At this experiment, protein content decreased with increasing of salt severity for some cultivars, but in KND protein content increased. The rest cultivars had the constant protein content at all salinity levels. At this experiment, gluten content changed very little with salinity levels. Cultivar 71135 at all salinity levels had the highest gluten content (Table 2). At 60 mM, carbohydrate content decreased with increasing of salt severity (120 mM) (Table2). At control, 60 and 120 mM salinity levels, cultivars 71135 and PGS, respectively had the highest and lowest carbohydrate content. Cultivars 71135 and 61130 had the highest and PGS had the lowest phosphorous content in control. At 60 mM cultivars 71135 and PGS respectively, had the highest and lowest phosphorous content. At 120mM, 71135 and Haurani respectively, had the highest and lowest phosphorous content (Table 2). With increasing in salt severity, content of phosphorous increased in comparison with control. In table 1, interaction of salt and cultivars was not significant for content of beta-carotene. It means salt had not significant effect on content of betacarotene in grain of different cultivars. There were significant differences (P<1%) between levels and between cultivars (Fig. 1). Cultivar 71135 had the highest beta-carotene content but KND and PGS had the lowest beta-carotene content.
Table 1 Analysis of variance for the effect of salinity on qualitative characters of grain in ten durum wheat cultivars
Mean squares
|
Source of variation |
d.f |
Protein |
Carbohydrate |
Beta carotene |
Gluten |
Phosphorous |
|
Replication |
2 |
0.032ns |
0.019ns |
0.027ns |
0.014ns |
0.00002ns |
|
Salinity |
2 |
4.448** |
42.291** |
2.029** |
0.136** |
0.087** |
|
Cultivar |
9 |
9.913** |
126.388** |
0.836** |
2.639** |
0.025** |
|
Salinity * cultivar |
18 |
0.065** |
0.181* |
0.025ns |
0.024** |
0.0005* |
|
Error |
58 |
0.016 |
0.078 |
0.018 |
0.006 |
0.0002 |
|
c.v% |
0.90 |
0.51 |
3 |
0.69 |
4.43 |
*, ** Significant in 5% and 1%, respectively ns: Non significant
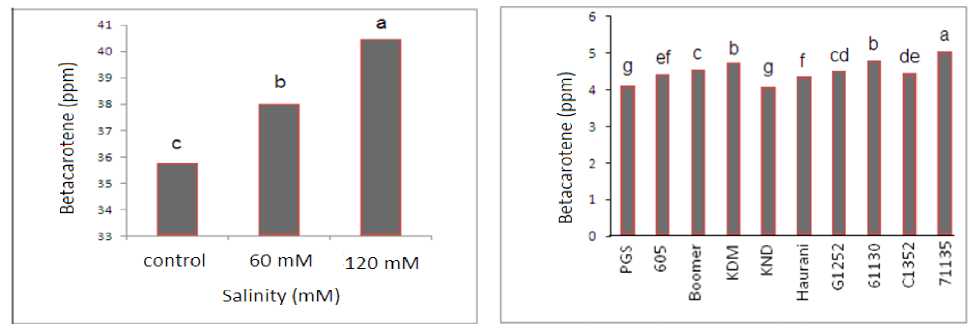
Figure 1 Comparison of means for the main effect of salt levels (P<1%) and durum wheat cultivars (P<1%) on beta carotene content
Table 2 Comparison of means for salt and cultivar interaction on some of qualitative characters of durum wheat grain
|
Qualitative |
characters |
||||
|
Salinity levels |
Cultivars |
Protein (%) |
Carbohydrate (%) |
Gluten (%) |
Phosphorous (%) |
|
Boomer |
15.067 b |
57.133 d |
10.730 cd |
0.290 b |
|
|
Haurani |
14.133 c |
51.633 e |
10.613 de |
0.233 c |
|
|
C1351 |
14.133 c |
57.200 d |
10.570 e |
0.253 c |
|
|
PGS |
12.467 f |
50.600 f |
10.190 f |
0.180 d |
|
|
Control |
G1252 |
14.400 c |
58.333 bc |
10.970 b |
0.250 c |
|
KND |
12.767 e |
51.300 e |
10.277 f |
0.203 d |
|
|
KDM |
15.133 b |
57.733 cd |
10.860 bc |
0.313 b |
|
|
605 |
13.867 d |
51.833 c |
10.607 de |
0.240 c |
|
|
71135 |
15.700 a |
61.100 a |
11.960 a |
0.327 a |
|
|
61130 |
15.767 a |
58.667 b |
11.747 a |
0.327 a |
|
|
Boomer |
14.033 b |
55.267 d |
10.737 c |
0.387 cd |
|
|
Haurani |
13.200 d |
49.400 f |
10.460 d |
0.347 ef |
|
|
C1351 |
13.167d |
55.067 d |
10.700 c |
0.360 e |
|
|
PGS |
12.100 e |
48.333 g |
10.113 e |
0.283 gh |
|
|
60 mM |
G1252 |
13.667 c |
55.567 cd |
10.823 c |
0.363 de |
|
KND |
12.067 e |
49.033 f |
10.087 e |
0.307 gh |
|
|
KDM |
14.267 b |
56.133 bc |
10.823 c |
0.397 bc |
|
|
605 |
13.300 d |
50.033 e |
10.353 d |
0.333 fg |
|
|
71135 |
15 a |
58.400 a |
11.697 a |
0.477 a |
|
|
61130 |
15 a |
56.400 b |
11.330 b |
0.420 a |
|
|
Boomer |
14.300 c |
55.533 c |
10.850 c |
0.330 d |
|
|
Haurani |
13.867 de |
49.567 e |
10.600 de |
0.317 d |
|
|
C1351 |
13.700 ef |
55.467 c |
10.727 cd |
0.343 d |
|
|
PGS |
12.700 g |
48.400 f |
10.140 f |
0.240 f |
|
|
G1252 |
14.100 cd |
56.300 b |
10.820 c |
0.337 d |
|
|
120 mM |
KND |
14.900 b |
49.233 e |
10.107 f |
0.267 e |
|
KDM |
12.533 g |
56.267 b |
10.867 c |
0.360 c |
|
|
605 |
13.533 f |
56.300 d |
10.433 e |
0.327 d |
|
|
71135 |
15.567 a |
58.600 a |
11.833 a |
0.423 a |
|
|
61130 |
15.300 a |
56.533 b |
11.420 b |
0.390 b |
|
In each column, means with at least one same letter have not significant difference by LSD %1.
DISCUSSION
Poustini and Zehtab-Salmasi, (1997) reported the increase in protein content under salt stress. Shuhua et al., (2002) indicated that the protein content of wheat cultivars was increased markedly with the content of whole soil salt being improved, but the 1000-grain weight and the yield were decreased. Also, because of acceleration in crop maturity and reduction in photosynthate transfer period under saline conditions, they likely reduce the amount of starch and consequently, increase the percentage of nitrogen and protein in grains. Dorgham, (1991) reported that salinity causes to using of inorganic nitrogen fixation into protein synthesis. Mostafa, (2004) observed that at low and moderate salinity levels, sugars and consequently the total carbohydrates are decreased. Sarwat and El-Sherif, (2007), reported that in barley, increasing of salt severity causes decrease in carbohydrate content in grain. When the current photosynthesis artificially or by environmental stresses decreases, more carbohydrates transport from shoot into grains (Austin et al., 1980). Gill and Singh, (1985) has reported that germination, growth, respiration and other related processes can be affected in seeds that are subjected to environmental stresses. Changes in anyone of these processes can affect other metabolic activities, particularly the carbohydrate metabolism that plays an important role in germination and seed development. Salinity causes increasing in respiration rate which lead to decrease in assimilate transport to grains and consequently, decrease the amount of stored carbohydrate and increase the protein content (Poustini, 2002). Torres and Bingham, (1973) reported decrease in phosphorous content under salt stress and noted that it is due to decrease in phosphorous absorption. In three salt levels, cultivar 71135 was determined as the most tolerant cultivar according to content of grain reserve composition results. Beside the 71135, 61130 was semi- tolerant cultivar. PGS was determined as the sensitive cultivar according to content of grain reserve composition results.
Список литературы Effect of salt stress on grain reserve composition in ten durum wheat cultivars
- Anonymous. (1983) American Association of Cereal Chemists AACC. Approved Methods of the AACC. Method No. 38-10 & 46-12, AACC. St. Paul, MN, USA.
- Austin, R.B., Organ, C.L., Ford, M.A. and Blakwell, R.D. (1980) Contribution to grain yield from pre-anthesis assimilation in tall and dwarf barely phenotypes in two contrasting seasons. Ann. Bot., 45, 309-319.
- Azooz, M.M., Shaddadand, M.A., and Abdel-Latef, A.A. (2004) The accumulation and compartmentation of proline in relation to salt tolerance of three sorghum cultivars. Indian J. Plant Physiol, 9, 1-8.
- Bahizire, F.B. (2007) Effect of salinity on germination and seedling growth of canola (Brassica napus L.), M.S. thesis, Stellenbosch Univ., South Africa.
- Clarke, F.R., Clarke, J.M., McCaig, T.N., Knox, R.E. and DePauw R.M. (2006) Inheritance of yellow pigment concentration in seven durum wheat crosses. Can J. Plant Sci, 86, 133-141.
- Deckard, E.L., Joppa, L.R., Hammondand, J.J., and Harelard, G.A. 1996. Grain protein determinants of the Langdon durum-dicoccoides chromosome substitution lines. Crop Sci, 36, 1513-1516.
- Dexter, J.E and Matsuo, R.R. (1977) Effect of Semolina Extraction Ratio on Semolina Characteristics and Spaghetti Quality. Canadian Grain Commission, Winnipeg, Manitoba. Cereal Chem, 55, 352-841.
- Dexter, J.E., Matsuo R.R. and Martin, D.G. (1987) The relationship of durum wheat test weight to milling performance and spaghetti quality. Cereal Food World, 32, 772-777.
- Dorgham, E.A. (1991) Effect of water stress, irradiation and nitrogen fertilization on grain filling, yield and quality of certain wheat cultivars, Ph.D. thesis, Ain Shams Univ., Cairo, Egypt.
- Dubois, M.K., Gilles, J.I., Hamilton, P.A., Roberts, K.F. and Smith, F. (1951) Qualitative analysis of sugar by paper chromatography. Nature London pp. 167-168.
- Fabriani, G. and Lintas, C. (1988) Durum: Chemistry and technology. American Association of Cereal Chemistry. Minessota. USA: 332.
- Fares, C., Platani, C., Tamma, G. and Lecesse, F. (1991) Microtest for the evaluation of the color in genotypes of durum wheat. Molini D'Italy, 12, 19-21. (In Italian)
- Fowler, D.B. (2003) Crop nitrogen demand and grain protein concentration of spring and winter wheat. Agron J, 95, 260-265.
- Galterio, G., Grita, L. and Brunori, A. (1993) Pasta-making quality in Triticum durum. New indices from the ratio among protein components separated by SDS-page. Plant Breeding, 110, 290-296.
- Gill, K.S., and Singh, O.S. (1985) Effect of salinity on carbohydrate metabolism during paddy (Oryza sativa) seed germination under salt stress condition. J. Exp. Biol, 23, 384-386.
- Graybosch, R.A., Peterson, C.J., Shelton, D.R. and Baenziger, P.S. (1996) Genotypic and environmental modification of wheat flour protein composition in relation to end use quality. Crop Sci, 36, 296-300.
- Hessler, T.G., Thomson, M.J., Benscher, D., Nachit, M.M. and Sorrells, M.E. (2002) Association of a Lipoxygenase Locus, Lpx-B1, with Variation in Lipoxygenase Activity in Durum Wheat Seeds. Crop Sci, 42,1695-1700.
- Huebner, F.R, Nelsen, T.C., Chung, O.K. and Bietz, J.A.(1997) Protein distributions among hard red winter wheat varieties as related to environment and baking quality. Cereal Chem, 74, 123-128.
- Jia, Y.Q., Fabreand, J.L., Aussenac, T.(1996) Effects of growing location on response of protein polymerization to increased nitrogen fertilization for the common wheat cultivar Soissons: Relationship with some aspects of the bread-making quality. Cereal Chem, 73, 526-532.
- Katerji, N., vanHoorn, J.W., Fares, C., Hamdy, A., Mastrorilli, M. and Oweis, T. (2005) Salinity effect on grain quality of two durum wheat varieties differing in salt tolerance. Agric. Water Manag, 75, 85-91.
- Khan, N.A., Shamim, M. and Shambhoo, P. (2008) Biochemical changes in wheat plants in response to salinity. Int. J. Plant Sci, 3, 11-15.
- Marchylo, B.A. and Dexter, J.E. (1996) Durum and pasta quality now and into the 21stCentury. In Proceedings of the 46th Australian Cereal Chemistry Conference in Association with 6thInternational Gluten Workshop, Sydney, Australia, September, 1996, Wrigley, C.W. (ed). Royal Australian Chemical Institute, Melbourne, Australia, 345-352.
- Mostafa, D.M. (2004) Metabolic imbalance and salinity tolerance of two maize cultivars, M.S. thesis, El-Minia Univ., Elminia, Egypt.
- Omami, E.N. (2005) Response of amaranth to salinity stress, Ph.D. thesis, Pretoria Univ., South Africa.
- Parida, A.K., Das, A.B. and Mittra, B. (2003) Effect of NaCl stress on the structure, pigment complex composition and photosynthetic activity of mangrove (Bruguiera Parviflora) Chloroplasts. Photosynthetica, 41, 191-200.
- Poustini, K. (2002) Evaluation of the response of 30wheat cultivars to salinity. Iranian J. Agric. Sci, 3, 57-64.
- Poustini, K. and Zehtab-Salmasi, S. (1997) Effect of salinity on dry matter production and remobilization in two wheat cultivars. Iranian J. Agric. Sci, 29, 11-16.
- Prado, F. E., Boero, C., Gallarodo, M. and Gonzalez, J. A.(2000) Effect of NaCl on germination, growth and soluble sugar content in Chenopodium quinoa wild seeds. Bot. Bull. Academia Sinica, 41, 27-34.
- Rao, A.C.S., Smith, J.L., Jandhyala, V.K., Papendick, R.I. and Parr, J.F. (1993) Cultivar and climatic effects on the protein content of soft whit winter wheat. Agron J, 85, 1023-1028.
- Resmini,P. and Pagani, M.A. (1983) Ultra structure studies of pasta: A review. Food Microstructure journal, 2, 1-12.
- Sarwat, M.I. and El-Sherif, M.H. (2007) Increasing salt tolerance in some Barley genotypes (Hordeum vulgare) by using kinetin and benzyladenin. World J. Agric. Sci, 3, 617-629.
- Shen, Y., Guo, W., Zhou, Y., Zhu, X., Feng C. and Peng, Y. (2007) Effects of salinity stress on the dynamic changes in the accumulation of grain protein and its components in wheat. J. Triticeae Crops, 26, 100-103.
- Shewry, P.R., Tatham, S.S. and Lazzeri, P.(1997) Biothechnology of wheat quality. J Sci Food Agr, 73, 397-406.
- Shuhua, L., Xing, X., Hongxia, L., Min, Q., Jun, H. and Haili, M. (2002) Effect of salinity on seed protein and yield characters of wheat. Agric. Res. Arid Areas, 20, 38-41.
- Sisson, M.J. (2004) Pasta. In Wrigley, C., Corke, H&Walker, C. (ed.) Encyclopadia of Grain Science, Elsevier, Australia, pp. 409-418.
- Torres, B.C., and Bingham, F.T. (1973) Salt tolerance of Mexican wheats. I. Effect of NO3 and NaCl on mineral nutrition, growth and grain production of four wheats. Soil Sci. Soc. America Proc, 37, 711-715.
- Warraich, E.A., Basra, S.M.A., Ahmad, A., Ahmed, R. and Aftab, M. (2002) Effect of Nitrogen on Grain Quality and Vigor in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Int. J. Agric. Biol, 4,517-520.
- Zhang, P.P., He, Z., Zhang, Y., Xia, X.C., Liu, J.J., Yan, J. and Zhang, Y. (2007) Pan bread and Chinese white salted noodle qualities of Chinese winter wheat cultivars and their relationship with gluten protein fractions. Cereal Chem, 84, 370-378.
- Zheng, Y., Xu, X., Li, Z., Yang, X., Zhang, C., Li, F. and Jiang, G. (2009) Differential responses of grain yield and quality to salinity between contrasting winter wheat cultivars. Seed Sci. Biotech, 3, 40-43.


