Effects of some environmental variables on urease in germinating chickpea ( Cicer arietinum L.) seed
Автор: Shaela Pervin M., Sarowar Jahan M.G., Masud Rana A.y.K.Md., Sana N.K., Habibur Rahman M., Shaha R.K.
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 3 т.9, 2013 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Enzyme activity is influenced by a large number of factors. Environmental conditions such as pH, temperature, salt concentration, substrate concentration, activators, and inhibitors may change the three dimensional shape of an enzyme, altering its rate of activity and/or its ability to bind substrate. The effects of such environmental factors were evaluated. The optimum pH and temperature of the purified urease were 7.2 and 48 0C, respectively, using urea as substrate. The optimum substrate (urea) concentration for urease was 25 mM. The enzyme showed the highest activity when incubated for 30 min at 48 0C. EDTA, a metal chelator, decreased the enzyme activity significantly. This may be due to the removal of metal ions located on or near the active site. Divalent cations like Ba 2+ and Mg 2+ slightly stimulated the enzyme at a concentration of 1-3 mM whereas Na + and K + produced little or no effect on the activity. Ca 2+ enhanced urease activity by 120.47%, while Pb 2+, Cu 2+, Zn 2+ and Hg 2+ almost completely inhibited the urease activity.
Chickpea, cicer arietinum, environmental variable, enzyme activity, urease
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14323779
IDR: 14323779
Текст научной статьи Effects of some environmental variables on urease in germinating chickpea ( Cicer arietinum L.) seed
Urease is a nickel-containing enzyme that catalyses the hydrolysis of urea into ammonia and carbon dioxide (Varner, 1976). This enzyme has been isolated and characterized from various bacteria, fungi, and plants (Mobley et al. 1995; Hausinger, 1993; Hausinger and Karplus, 2001; Follmer, 2008). Its primary function is allowing the organism to use urea as a nitrogen source. In plants, urease is involved in systemic nitrogen transport pathways, and is thought to act as a toxic defense protein (Polacco and Holland, 1993). In addition, the enzyme plays a role in seed germination by degrading urea formed from arginase activity (Zonia et al., 1995). In humans, bacterial ureases are important virulence factors in a number of diseases of the urinary tract and gastroduodenal region, including cancer (Burne and Chen, 2000).
The increasing need for specifically removing urea from far different environments has prompted a growing biotechnological interest in this enzyme (Qin and Cabral, 2002). Actual or potential applications range from the treatment of industrial wastes (George et al., 1997) or alcoholic beverages (Matsumoto, 1993) to the design of life-support systems for manned space missions (Schussel and Atwater, 1995) Systems based on immobilized or microencapsulated urease are also being studied for use in haemodialysis (Keunbok et al., 1995; Roberts, 1998).
The three-dimensional structure of a protein is often the key to its enzyme function. This configuration is governed by its primary structure and its environment. The environmental factor which alters the shape of the enzyme, or which blocks access of the substrate to the active site, will affect enzyme activity. Such environmental factors include salt concentration, PH, temperature, substrate concentration, activators, and inhibitors etc.
Identifying the environmental factors influencing the urease activity may provide insights for various aspects of the property of the enzyme. Thus, the purpose of this study was to evaluate the effects of some environmental factors on the partially purified urease.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Materials
Chickpea ( Cicer arietinum L.) Seeds were collected from Bangladesh Agriculture Research Institute (BARI), substation of Ishwardi, Pabna,
Bangladesh. The seeds were soaked in distilled water for 6 h, germinated in the dark at 220C for 48, 72, 96, 120, 144, 168, 192 and 216 h including soaking time. The germinated seeds at different intervals were stored separately in the deep freeze (-100C) for further experimental purpose.
BSA, SDS/PAGE-chemicals and Sephadex G-75 were purchased from Sigma Chemicals Ltd., USA. Standard proteins, DEAE-cellulose were purchased from Pharmacia Fine Chemicals Ltd., Sweden. All other chemicals used for this research were of analytical grade.
Enzyme extraction
Unless mentioned otherwise all the operations were done at 40C. Ten grams of germinated seeds were pasted in a mortar and pestle and then suspended in 40 ml of 20% chilled (-200C) acetone. After occasional gentle stirring for 3 h the suspension was filtered through double layer of cheese cloth. The filtrate was then collected and centrifuged for 15 min. The supernatant was used as “crude extract”.
Purification of urease
All steps of purification were carried out at 4 0C. The enzyme was purified to homogeneity by the following successive steps.
Acetone precipitation
The “crude extract” was adjusted to 50% saturation by the addition of acetone (chilled to -200C) under constant and gentle stirring. The resulting precipitate was collected by centrifugation, dissolved in minimum volume of pre-cold 50 mM phosphate buffer pH 7.0 and dialyzed against the same buffer for 24 h. The dialyzed solution was then centrifuged for 10 min and the clear supernatant thus obtained was designated as “crude enzyme solution”.
Gel filtration chromatography
Gel filtration was carried out on Sephadex G-200 column (150X3.0 cm). The “crude enzyme solution” after dialysis against 50 mM phosphate buffer, pH 7.0, was loaded onto the Sephadex G-200 column pre-equilibrated with the same buffer and the protein was eluted with the buffer. The enzymatically active fractions were pooled and dialyzed against 50 mM phosphate buffer, pH 7.8 for 24 h.
DEAE-cellulose chromatography
The dialyzed enzyme solution was loaded on the DEAE-cellulose column (20X3.0 cm), preequilibrated with 50 mM phosphate buffer, pH 7.8. The bound proteins were eluted with a linear gradient of NaCl (100 – 500 mM) in the same buffer at a flow rate of 0.5 mlmin-1. Absorbance at 280 nm, protein concentration and urease activity was determined. The active fractions were collected.
Enzyme assay
Urease activity was assayed following the method as described (Janyaraman, 1985). Urea solution (3% in 0.2 M phosphate buffer, pH 7.0) was used as substrate. One unit of urease activity was defined as the amount required for liberating 1 μmol of ammonia per minute at 55ºC. Protein concentration was determined by the method of Lowry et al., (1951), using BSA as the standard.
SDS-PAGE pattern of subunit
SDS-PAGE was performed according to the method of Laemmli (1970) on a Bio-rad mini electrophoresis system. The standard proteins used were β-lactoglobulin (18.4 kDa), carbonic anhydrase (29 kDa), ovalbumin (43 kDa), bovine serum albumin (68 kDa), phosphorylase-b (97.4 kDa) and β-galactosidase (116 kDa). PAGE was performed with 7% gels and the electrophoresis was run at 2000 V and 50 A.
Optimum pHof the enzyme
To study the effect of pH on enzyme activity, the enzyme solutions (0.6%) were dialyzed against 50 mM buffer of different pH (AcONa - HCl, pH 2.0-3.0; AcONa - CH 3 COOH, pH 4.0-5.0; NaH 2 PO 4 - Na 2 HPO 4 , pH 5.5-8.0; Na 2 B 4 O 7 - HCl, pH 8.5-9.0; Na 2 B 4 O 7 -Na 2 CO 3 , pH 9.5.) for 24 h with frequent changes of buffers. After necessary adjustment of pH by adding 0.1 N HCl or 0.1 N NaOH, the enzyme activity was assayed using urea as substrate.
Optimum temperature and thermal inactivation
In order to determine the optimum temperature, the enzyme solutions (0.5%) in 50 mM phosphate buffer, pH 7.2, were incubated at various temperatures ranging from 10 - 900C for 15 min in a temperature controlled water bath and the activity was assayed. Approximately 25–30 different enzyme solutions were incubated in assay buffer (50 mM phosphate buffer pH 7.2) at the desired temperature (700C). At definite time intervals, two solutions were withdrawn, cooled and transferred immediately to the assay solution (50 mM phosphate buffer pH 7.2 and 1 ml of 0.2% urea). Residual activity was determined by the usual enzyme activity assay method at 480C.
Effect of various chemicals and metal ions on the activity of urease
Effect of various compounds and metal ions on the activity of urease was examined by incubating the enzyme solution at room temperature in the presence of different ion or compound for 5 min and aliquots were withdrawn and assayed under standard reaction conditions (480C, pH 7.2).
Effect of urea concentration
The effect of urea concentration on the activity of enzyme was examined. For the study urea solution of different concentrations were taken in different test tubes and the enzyme activity was measured.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Urease plays an important role in germination and in seedlings’ nitrogen metabolism. After 120 h of germination the activity increased gradually and showed maximum activity at 192 h after germination and then declined rapidly (Data not shown). Therefore, we used 192 h germination for further experimental purpose.
The purification results of germinated chickpea seed urease is summarized in Table 1. Specific activity of the extracted enzyme increased throughout the purification steps and the final purification fold achieved was nearly 45. The specific activity of the final preparation was 489.57 mUmg-1.
Purification of enzyme
The dialyzed enzyme solution obtained from 50% acetone fractionation was applied to Sephadex G-200 column pre-equilibrated with 50 mM phosphate buffer, pH 7.0 and was eluted with the same buffer at a flow rate of 25 ml/h. The components of the crude enzyme solution separated as two major peaks, F-1 and F-2 and a minor peak F-3 (Figure 1). The active fraction (F-1) indicated by solid bar was pooled and concentrated by freeze dryer. The concentrated enzyme was dialyzed against 50 mM phosphate buffer, (pH 7.5) for 24 h and applied to a DEAE-cellulose column, pre-equilibrated with the same buffer and eluted by gradient of sodium chloride (0.1 - 0.5 M) in the same buffer. As shown in Figure 2, the components of F-1 fraction were separated into three minor peaks (F-1a, F-1b and F-1c) without activity and a major peak (F-1d) having urease activity. F-1d fraction as indicated by solid bar was pooled and used for further experimental purposes.
The molecular weight of the purified urease (F-1d fraction) as determined by gel filtration on Sephadex G-200 was 510,000. The molecular weight of the chickpea seeds urease reported in this investigation is in relative agreement with molecular weights estimated for urease from other sources. Fishbein et al., (1970) have purified urease from seeds of jack bean has a molecular mass of 480,000; while Das et al ., (2002) have isolated urease from dehusked pigeonpea ( Cajanus cajan L . ) seeds with molecular weight of 540,000. The plant and fungal ureases are homo-oligomeric proteins consisting of identical subunits, while the bacterial ureases are multimers formed from a complex of two or three subunits of different size (Miyagawa et al ., 1999). The purified chickpea seeds urease also had six subunits. Molecular mass of each subunit was 85,000 (Data not shown). Sung et al., (1989) found that purified urease from seeds of jack bean contain six subunits, each of 80,000. Das et al., (2002) investigated that urease from dehusked pigeonpea seeds was a hexamer of identical subunits (90,000). Our result on subunit molecular mass relatively coincided with those results.
Effect of pH on the activity of chickpea seed urease pH plays an important role in the activity of enzyme. The urease isolated from chickpea seed was found to yield maximum activity at pH 7.2 (Figure 3). From the result it might be concluded that the urease isolated from chickpea seeds belongs to the category of basic urease. This result is similar to those reported for urease from jack bean (Sung et al., 1989) and pigeonpea (Das et al.,
2002) but different from that isolated from mulberry leaves (Hirayama et al., 2000) and the pathogenic fungus Coccidiodes immitis (Mirbod et al., 2002)
Effect of temperature on the activity of chickpea seed urease
The effect of temperature on urease activity was shown in Figure 4. An initial increase in temperature up to 55°C increased the rate of enzyme’s catalyzed reaction which resulted in increase of urease activity. However, beyond the temperature 55°C the enzyme denatured rapidly and thus loosed its activity. This result is closely related to those reported by Das et al ., (2002) and Srivastava et al., (2001) but differs from that stated by El-Shora (2001).
Effect of urea concentration on the activity of chickpea seed urease
The optimum substrate concentration of urease was 25 mM. Urease activity increased with substrate concentration, reached an optimum value and then decreased with rising urea concentration (Figure 5). The results could be explained by substrate inhibition at higher urea concentrations. The enzyme showed the highest activity when incubated for 30 min under standard conditions (480C, pH 7.2). The rate of hydrolysis of urea increases with an increase in urea concentrations until a maximum is reached, beyond which hydrolysis decreases (Singh and Nye, 1984; Lal et al ., 1993).
Effect of various metal ions and chemicals on the activity of chickpea seed urease
Identification of proper ions and their suitable concentrations for rendering halotolerant and thermostability to the enzymes are very important for their applications at commercial levels. Effect of various metal ions and chemicals on the activity of chickpea urease was studied (Table 2). Calcium ions exhibited distinct role in the urease action. The urease activity increased in presence of calcium ion at low concentrations (3 mM or less) but decreased at higher calcium concentrations, which is consistent with the results reported elsewhere (Lee and Calhoun 1997). EDTA, a metal chelator, decreased the enzyme activity significantly. This may be due to the removal of metal ions located on or near the active site. Divalent cations like Ba2+ and Mg2+ slightly stimulated the enzyme at a concentration of 1-3 mM whereas Na+ and K+ produced little or no effect on the activity. Inhibition studies primarily give insight about the nature of the enzymes, its cofactor requirements and the active center of the enzyme (Sigman and Mooser, 1975). Besides, inhibition of urease by heavy metal ions is important not only in view of heavy metal ion pollution, appropriate levels of urease activity in agricultural soils may be endangered, but also this inhibition may be exploited in constructing urease inhibition-based sensing systems (Preininger and Wolfbeis, 1996; Krawczyk et al., 2000; Kuswandi, 2003) for in situ and real time determination of trace levels of the ions, e.g. in environmental monitoring, food control and biomedical analysis. Heavy metal ions inhibit both plant (Preininger and Wolfbeis, 1996; Shaw, 1954; Shaw and Raval, 1961; Krajewska, 1991; Krajewska et al., 2004; Zaborska et al., 2004) and bacterial ureases (Nakano et al., 1984; Kenny, 1983). The inhibition has been habitually ascribed to the reaction of the metal ions with the thiol groups of the enzyme (Kuswandi, 2003, Toren and Burger, 1968; Hellerman et al., 1943). Inhibitory effects of some heavy metals was studied and found that Cu2+, Zn2+, Pb2+ and Hg2+ almost completely inhibited enzyme activity, indicating the presence of thiol (-SH) group in the enzyme active site. These results are in good agreement with those from pigeon pea urease (Srivastava et al.
2002) and jack bean ureases (Krajewska et al., 2004; Zaborska et al., 2004).
Table 1. Urease activities in the course of purification of chickpea seed urease
|
Step of Purification |
Total Protein (mg) |
Total Activity (mU) |
Specific Activity (mU/mg) |
Yield (%) |
Purification Fold |
|
Crude Extract |
1676 |
18236 |
10.88 |
100 |
1 |
|
Acetone Precipitation and Dialysis |
430.42 |
12513 |
29.07 |
68.61 |
2.67 |
|
Gel Filtration |
87.39 |
9532 |
109.07 |
52.27 |
10.02 |
|
DEAE-cellulose |
18.03 |
8827 |
489.57 |
48.40 |
44.99 |
Table 2. Effect of various metallic salts and chemicals on the activity of urease purified from chickpea seed
|
Reagent |
Relative Activity (%) |
||
|
1 mM |
3 mM |
5 mM |
|
|
None |
100 |
100 |
100 |
|
BaCl 2 |
105 |
113 |
103 |
|
MgCl 2 |
103 |
110 |
104 |
|
NaCl |
98 |
97 |
95 |
|
KCl |
99 |
98 |
96 |
|
CuCl 2 |
32 |
30 |
31 |
|
ZnCl 2 |
50 |
49 |
45 |
|
HgCl 2 |
12 |
12 |
14 |
|
PbSO 4 |
24 |
23 |
22 |
|
CaCl 2 |
105 |
115 |
92 |
|
•EDTA |
61 |
50 |
42 |
• Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
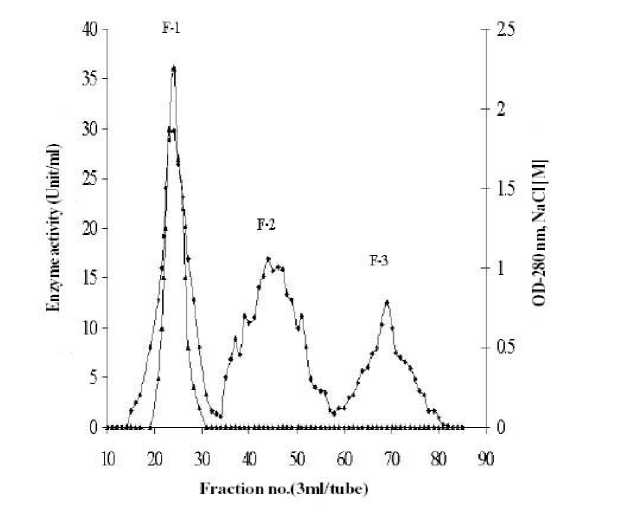
Figure 1. Gel filtration of 50% acetone fractionated crude extract on Sephadex G-200. The crude enzyme solution was applied to the column (2.0 x 50.0 cm) pre-equilibrated with 50 mM phosphate buffer, pH 7.0, at 40C and developed with the same buffer with a flow rate of 25ml/h. ( ) OD at 280 nm and ( ▲ ) enzyme activity.
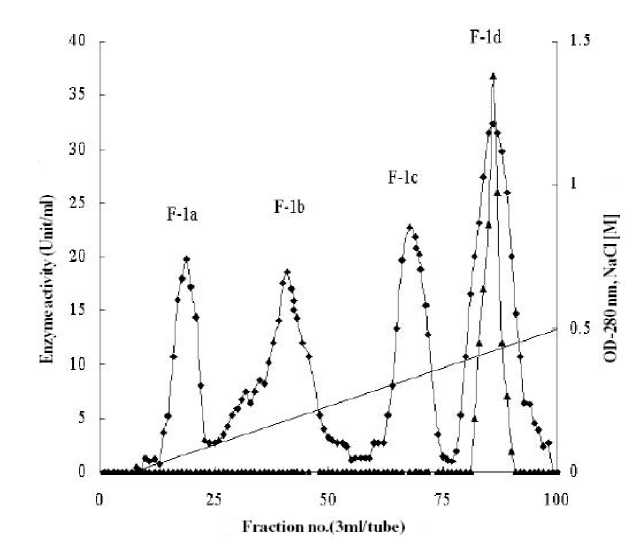
Figure 2. Ion exchange chromatography of F-1 fraction on DEAE cellulose column. The fraction obtained by gel filtration was applied to the column (1.5 x 3.0 cm) pre washed with 50 mM phosphate buffer, pH 7.5 and eluted with a gradient of NaCl (0.1– 0.5 M) in the same buffer with a flow rate of 25 ml/h. ( ♦ ) OD at 280 nm and ( ▲ ) enzyme activity.
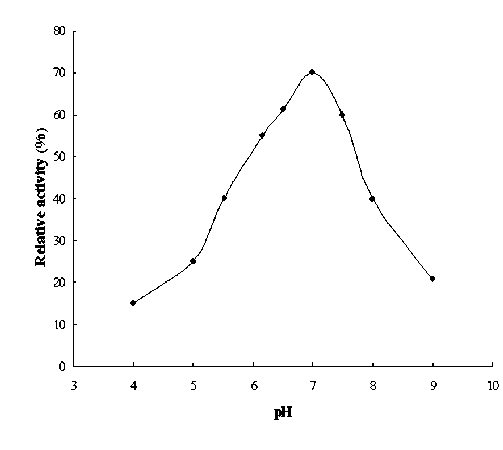
Figure 3. Effect of pH on the activity of chickpea seed urease.
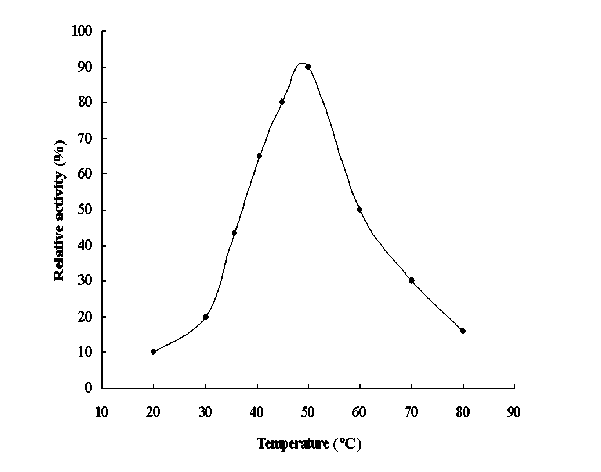
Figure 4. Effect of temperature on the activity of chickpea seed urease. The activity was expressed as 100%.
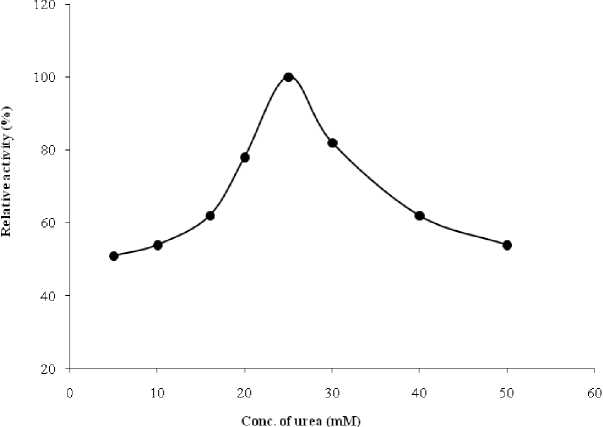
Figure 5. Effect of urea concentration on the activity of chickpea seed urease.
CONCLUSION
After partial purification of the urease from germinating chickpea seed, several environmental factors viz., pH, temperature, salt concentration, substrate concentration, activators, and inhibitors were chosen to investigate the effects on the enzymatic activity. However, further study is required to elucidate the precise mechanism of these effects and their significance in the metabolism of urease in the intact plant.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors gratefully acknowledge the research facilities provided by the Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, University of Rajshahi, Rajshahi-6205, Bangladesh.
Список литературы Effects of some environmental variables on urease in germinating chickpea ( Cicer arietinum L.) seed
- Burne, R.A., Chen, Y.Y. (2000) Bacterial ureases in infectious diseases. Microbes. Infect., 2, 533-542.
- Das, N., Kayastha, A.M., Srivastava, P.K. (2002) Purification and characterization of urease from dehusked pigeonpea (Cajanus cajan L.) seeds. Phytochem., 61(5), 513-521.
- El-Shora, H.M. (2001) Properties and immobilization of urease from leaves of Chenopodium album (C3). Botan. Bull. Acad. Sinica, 42, 251-258.
- Fishbein, W., Nagarajan, K., Scurzi, W. (1970) Urease Catalysis and Structure: VI. Correlation of sedimentation coefficients and electrophoretic mobilities for the polymeric urease isozymes. J. Biol. Chem., 245, 5985-5992.
- Follmer, C. (2008) Insights into the role and structure of plant ureases. Phytochem., 69, 18-28.
- George, S., Chellapandian, M., Sivasankar, B., Jayaraman, K. (1997) A new process for the treatment of fertilizer effluents using immobilized urease. Bioprocess Eng., 16, 83-85.
- Hausinger, R.P. (1993) Biochemistry of Nickel. Plenum Publishing Corp., New York.
- Hausinger, R.P., Karplus, P.A. (2001) Urease. In Wieghardt, K., Huber, R., Poulos, T.L., Messerschmidt, A. (ed.), Handbook of Metalloproteins. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., West Sussex, UK, pp. 867-879.
- Hellerman, L., Chinard, F.P., Deitz, V.R. (1943) Ascorbic Acid and Urease. J. Biol.Chem., 147, 443-462.
- Hirayama, C., Sugimura, M., Saito, H., Nakamura, M. (2000) Purification and properties of urease from the leaf of mulberry, Morus alba. Phytochem., 53 (3), 325-330.
- Jayaraman, J. (1981) Laboratory Manual in Biochemistry, 1st ed. Wiley Eastern Ltd. New Delhi, India.
- Kenny, G.E. (1983) Inhibition of the Growth of Ureaplasma urealyticum by a new ureases inhibitor, flurofamide. Yale. J. Biol. Med., 56 (5-6), 717-722.
- Keunbok L., Boadi D. K., Neufeld R. J., (1995) Steady state analysis of a fixed bed reactor for Urea hydrolysis with microencapsulated Urease. Chem. Eng. Sci., 50, 2263-2273.
- Krajewska, B. (1991) Urease immobilized on chitosan membrane-inactivation by Heavy_metal Ions. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol., 52 (2), 157-162.
- Krajewska, B., Zaborska, W., Chudy, M. (2004) Multi-step analysis of Hg2+ ion inhibition of jack bean urease. J. Inorg. Biochem., 98 (6), 1160-1168.
- Krawczyk, T.K.V., Moszczynska, M., Trojanowicz, M. (2000) Inhibitive determination of mercury and other metal ions by potentiometric urea biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron., 15 (11-12), 681-691.
- Kuswandi, B. (2003) Simple optical fibre biosensor based on immobilised enzyme for monitoring of trace heavy metal ions. Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 376 (7), 1104-1110.
- Laemmli, U.K. (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of head of bacteriophage T4. Nature, 227, 680-685.
- Lal, R.B., Kissel, D.E., Cabrera, M.J., Schwah, A.P. (1993) Kinetics of urea hydrolysis in wheat residue. Soil Boil. Biochem., 25, 1033-1036.
- Lee, S.G., Calhoun, D.H. (1997) Urease from a potentially pathogenic coccoid isolate: purification, characterization, and comparison to other microbial ureases. Infect. Immun., 65(10), 3991-3996.
- Lowry, O.H., Roserbrough, N.J., Farr A.L., Randall, R.J. (1951) Protein measurement with the follin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem., 193, 265-275.
- Matsumoto K. (1993) Removal of urea from alcoholic beverages by immobilized acid urease. Bioprocess Technol., 16, 255.
- Mirbod, F., Schaller, R.A., Cole, G.T. (2002) Purification and characterization of urease isolated from the pathogenic fungus Coccidioides immitis. Medical Mycology, 40(1), 35-44.
- Miyagawa, K., Sumida, M., Nakao, M., Harada, M., Yamamoto, H., Kusumi, T., Yoshizawa, K., Amachi, T., Nakayama, T. (1999) Purification, characterization, and application of an acid urease from Arthrobacter mobilis. J. Biotechnol., 68(2-3), 227-236.
- Mobley H.L.T., Island M.D., Hausinger R.P. (1995) Molecular biology of microbial ureases. Microbiol. Rev., 59, 451-480.
- Nakano, H., Takenishi, S., Watanabe, Y. (1984) Purification and Properties of Urease from Brevibacterium ammoniagenes. Agric. Biol. Chem., 48, 1495-1502.
- Polacco, J.C., Holland, M.A. (1993) Roles of urease in plant cells. In Jeon, K.W., Jarvik, J. (ed.), International Review of Cytology. Academic Press, Inc., San Diego. vol. 145, pp. 65-103.
- Preininger, C., Wolfbeis, O.S. (1996) Disposable cuvette test with integrated sensor layer for enzymatic determination of heavy metals. Biosens. Bioelectron., 11(10), 981-990.
- Qin, Y., Cabral, J. M.S. (2002) Properties and new applications of urease. Biocatal. Biotrans., 20, 1-14.
- Roberts, M. (1998) The regenerative dialysis (REDY) sorbent system. Nephrology, 4, 275-278.
- Schussel, L.J., Atwater, J.E., (1995) A Urease Bioreactor for Water Reclamation Aboard manned Spacecraft. Chemosphere, 30 (5), 985-994.
- Shaw, W.H.R. (1954) The Inhibition of Urease by Various Metal Ions. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 76, 2160-2163.
- Shaw, W.H.R., Raval, D.N. (1961) The Inhibition of Urease by Metal Ions at pH 8.9. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 83, 3184-3187.
- Sigman, D.S., Mooser, G. (1975) Chemical studies of enzyme active sites. Annu. Rev. Biochem., 44, 899-931.
- Singh, R., Nye, P.H. (1984a) The effect of soil pH and high urea concentration on urease activity in soil. J. Soil Sci., 35, 519-27.
- Srivastava, P.K., Kayastha, A.M., Jagannadham, M.V. (2002) Kinetics of inhibition and molecular asymmetry in pigeonpea (Cajanus cajan) urease. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Biophys., 6(1), 1-6.
- Srivastava, P.K., Kayastha, A.M., Srinivasan, S. (2001) Characterization of gelatin-immobilized pigeonpea urease and preparation of a new urea biosensor. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem., 34, 55-62.
- Sung, H.Y., Lee, W.M., Chiou, M.J., Chang, C.T. (1989) A procedure for purifying jack bean urease for clinical use. Proc. Nat. Sci. Counc., Republic of China, Part B, 13(4), 250-257.
- Toren, E.C., Burger, F. (1968) Trace determination of metal ion inhibitors of the glucose-glucose oxidase system. J. Mikrochim. Acta., 56, 1049-1058.
- Varner J.E. (1976) Urease. In Boyer, P. B., Lardy, H., Myrback, K. (ed.), The Enzymes, Academic Press, New York, pp. 247-256.
- Xu H.D., Chen R.R., Yao G.R., Liu X.X., Li G.M., Huang Y.P., Water Treat. 2 (1987) 136.
- Zaborska, W., Krajewska, B., Olech, Z. (2004) Heavy metal ions inhibition of jack bean urease: Potential for rapid contaminant probing. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem., 19(1), 65-69.
- Zonia, L.E., Stebbins, N.E., Polacco, J.C. (1995) Essential role of urease in germination of nitrogen-limited Arabidopsis thaliana seeds. Plant Physiol., 107, 1097-1103.


