Efficient somatic embryogenesis and plantlet regeneration induced from mature embryo culture under heavy metals stress conditions in a millet crop sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench]
Автор: Roselin Roobavathi M., Vikrant
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 1 т.21, 2025 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The present study aims to establish the somatic embryogenesis and plantlet regeneration in Sorghum bicolor ( cv. PAC501) under heavy metals (lead and cadmium) stress conditions. Mature embryos were inoculated in MS-medium containing (10mg/L, 25mg/L, 50mg/L, 75mg/L, and 100mg/L) of PbSO4 and CdCl2 (10mg/L, 25mg/L, 50mg/L, 75mg/L, 100mg/L, 150mg/L, and 200mg/L) each with IAA (1.0mg/L), BAP (0.5mg/L), zeatin (0.1mg/L), and proline (0.7mg/L). Significantly, high frequency (87.2±0.21%) of somatic embryogenesis was initially obtained with IAA (1.0mg/L), BAP (0.5mg/L), zeatin (0.1mg/L), and proline (0.7mg/L) while in comparison, 2,4-D (2.5mg/L) along with same concentrations of BAP, zeatin, and proline was proved as relatively less efficient (67.4±0.64%) for somatic embryogenesis. Furthermore, results reveal that sub-culture of embryogenic callus on cytokinins; BAP, Kn, and Zn (0.1mg/L, 0.5mg/L, and 1.0mg/L) of each added regeneration medium, kinetin (0.5mg/L) was recorded as the most effective cytokinin (77.8±0.93%) for plantlets regeneration. Moreover, during heavy metals treatments, the least frequency (2.9±3.32%) of lead tolerant somatic embryos was obtained with PbSO4 (75mg/L) in presence of the same concentrations of IAA, BAP, zeatin, and proline. Significantly, the very low frequency (3.7±0.67%) of lead tolerant plantlets regeneration was recorded with PbSO4 (75mg/L) and Kn (0.5mg/L). In contrast, during CdCl2 stress treatment, the cadmium tolerant somatic embryos (3.1±3.24%) were obtained with CdCl2 (150mg/L) and IAA, BAP, zeatin, and proline. Further, cadmium tolerant plantlets (4.23±2.33%) were also achieved on medium containing kinetin (0.5mg/L) with CdCl2 (100mg/L) indicating that lead proves to be more toxic for somatic embryogenesis and plantlets regeneration than cadmium. Later, the regenerated tolerant plantlets were transferred to pots and gradually acclimatized in greenhouse.
Heavy metal, millets, mature embryo, regeneration, somatic embryogenesis, sorghum
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/143183772
IDR: 143183772
Текст научной статьи Efficient somatic embryogenesis and plantlet regeneration induced from mature embryo culture under heavy metals stress conditions in a millet crop sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench]
Sorghum or Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench is the fifth most cultivated crop all over the world. It is commonly used as food, fodder, fiber sources, and biofuel (Gnansounou et al., 2005; Rooney et al., 2007). Interestingly, sorghum has natural adaptability towards harsh environments and exhibits its tolerance against drought, salinity and water logging (Hadebe et al., 2017; Huang, 2018; Varoquaux et al., 2019).
Heavy metal stress is one of the major abiotic stresses which affect badly the plant’s growth and development. The main source of heavy metal contamination is identified as industrial effluent, battery usages, usage of organic and inorganic fertilizers, mining etc. Moreover, heavy metals gradually accumulate in plant and animals through food chain that cause the adverse impacts on the physiology and biochemical process in organisms (Muratova et al., 2015).
Interestingly, sorghum is widely used as crop against phytoremediation of heavy metal contamination in soil (Marchiol et al., 2007; Soudek et al., 2014; Zhuang et al., 2009). Furthermore, lead and cadmium have been found as the most toxic heavy metals that contaminate the soil in India (reported by Ministry of Jal Shakti, India-2019). Also, as per WHO opinion, cadmium is one of the most toxic heavy metals which are highly dangerous to human health. The minimal concentration of these metalloids can cause severe toxicity in metabolism of living organism (Drouhot et al., 2014; Camizuli et al., 2018).
The mechanism of plant tolerance to heavy metals can be divided into avoidance strategies, leading to limitations of cadmium uptake, and tolerance strategies, including accumulation and storage of cadmium by binding it to amino acids, proteins and peptides (Tran and Popova, 2013). The main symptoms of cadmium phytotoxicity are visually manifested through inhibition of plant growth, leaf chlorosis, and necrosis of above head and underground organs (Hernadez and Cooke, 1997).
In vitro regeneration technique is one of the most efficient methods to achieve crop improvement for high yield, tolerance to abiotic stresses through genetic biotechnology (Tiecoura et al., 2003) and somaclonal variation (Matheka et al., 2008; Radchuk et al., 2012). In order to overcome the existing challenges, in vitro plant tissue culture is known as an alternative approach to enhance the tolerance of the plant against abiotic factors like salinity, drought, heavy metal stresses etc., that are treated as the major factors of reducing the productivity of the crops (Vikrant, 2015).
Moreover, it is obligate necessary to build the well-structured establishment of somatic embryogenesis and plantlet regeneration under abiotic stress or mutagenic conditions for the recovery of tolerant millet crops (Ceasar and Ignacimuthu, 2009; Vikrant, 2015). Hence, it is imperative now to develop sorghum plant as stress tolerance that can sustain and show productivity even during adverse climatic conditions.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Collection and Sterilization of Plant Material
Sorghum bicolor (cv.PAC501) seeds were collected from IIMR, Hyderabad (India). The seeds were initially surface sterilized using ‘tween-20’ followed by 70% of ethanol (v/v) for 30 seconds. Further, explants were then treated with HgCl 2 (0.1%) for 5 minutes followed by the washing with sterilized distilled water (4-5 times) in laminar air flow chamber. Sterilized sorghum seeds were further subjected to 3-4 hours of soaking and later mature embryos were excised easily from the seeds and used as explants. The sterilized mature embryo explants were subjected to nutrient medium further.
Nutrient Medium for Callus induction and Somatic Embryogenesis
Excised mature embryos were inoculated in MS-basal medium containing auxins (2,4-D and IAA) along with cytokinins (BAP and zeatin), amino acid (proline), sucrose (3%w/v) and agar (0.8% w/v) (Table 1). The cultures were incubated at 25±2°C in the dark for callus induction and subsequently sub-cultured in respective fresh nutrient medium at every two weeks.
Nutrient Formulation for Plantlet Regeneration
After six weeks, the embryogenic callus was subcultured to MS-regeneration medium supplemented with various concentrations of cytokinins (BAP, kinetin and zeatin) and proline (Table 2). These cultures were incubated at 25±2°C with 16/8h (light/dark) photoperiod for 14 days. The germination of somatic embryos and regeneration of plantlets were observed after 10 days of sub-culture.
Heavy Metal Stress Treatments
In order to evaluate the effects of lead (Pb) metalloid stress on callus induction, somatic embryogenesis and plantlet regeneration, concentrations (10mg/L, 25mg/L, 50mg/L, 75mg/L, and 100 mg/L) of PbSO 4 (w/v) were used along with the combination of IAA (1.0mg/L), BAP (0.5mg/L), zeatin (0.1mg/L), and proline (0.7mg/L) (Table 3) .
Similarly, to determine the effects of cadmium metalloid stress on sorghum regeneration, the mature embryo explants were inoculated in MS-medium containing various concentrations (10mg/L, 25mg/L, 50mg/L, 75mg/L, 100mg/L, 150mg/L, and 200mg/L) of CdCl 2 (w/v) in combination with IAA (1.0mg/L), BAP (0.5mg/L), zeatin (0.1mg/L), and proline (0.7mg/L) (Table 5) .
Plantlets Regeneration under Heavy Metal/s Stress
In vitro regenerated plantlets were further transferred to the plastic pot containing the vermicompost, sand, and soil in 1:1:1 proportion. These potted plantlets were maintained under the greenhouse conditions for the hardening.
Statistical Analysis
Each experiment was performed three times and the data for mean percentage of somatic embryogenesis was calculated using the formula (No. of callus forming somatic embryos/Total no. of callus x 100). Furthermore, the Duncan’s Multiple Range Test (DMRT) was undertaken to calculate its significance value.
RESULTS
In present study, the mature embryos were used as explants to induce the embryogenic callus formation followed by differentiation of somatic embryos in sorghum crop using MS-medium fortified with various concentrations and combinations of auxins and cytokinins along with or without proline (Table 1).
Callus induction and Somatic Embryogenesis
In basal medium, mature embryos were found to show germination symptoms and developed into young plants after 3-5 days (Fig. 1A) of culture initiation while the explants inoculated in nutrient medium supplemented with 2,4-D (1.0mg/L, 2.0mg/L, 2.5mg/L, and 3.0mg/L) alone was proved to be less efficient for the induction of callus followed by somatic embryogenesis. Moreover, the maximum embryogenic frequency (15.3±3.51%) was observed with 2,4-D (2.0mg/L) while the minimum (9.7±3.58%) was recorded with higher concentration of (3.0mg/L) 2,4-D (Table 1) .
Also, the explants that were treated with various concentrations (1.0mg/L, 2.0mg/L, 2.5mg/L, and 3.0mg/L) of 2,4-D along with Zn (0.1mg/L), were found to be little effective for callus induction and differentiation of somatic embryos while higher concentrations (2.0mg/L and 2.5mg/L) of 2,4-D could be reasonably good for compact and nodular callus induction ( Fig. 1B) which could show later somatic embryogenesis (49.6±2.14% and 50.9±1.63%) respectively (Table 1).
Moreover, maximum number of somatic embryos per callus (15.1±0.89) was recorded in explants that were treated with 2,4-D (2.5mg/L) in combination with Zn (0.1mg/L) after 14-days of culture initiation. Significantly, further high concentration (3.0mg/L) of 2,4-D with Zn (0.1mg/L) was turned out to be considerably inhibitory for callus induction and somatic embryogenesis (22.3±0.33%) while even the low concentration (1.0mg/L) of 2,4-D was proved to be inefficient for callus induction and somatic embryogenesis (11.1±1.42%).
Furthermore, MS-medium fortified with 2,4-D and Zn was proved to be more efficient for induction of callus followed by differentiation of somatic embryos when BAP (0.5mg/L) and proline (0.7mg/L) were added. Significantly, after 14-days of culture initiation, mature embryo was found to show compact and nodular callus formation from the slightly germinated mature embryos particularly growing with (2.0mg/L or 2.5mg/L), zeatin (0.1mg/L), BAP (0.5mg/L), and proline (0.7mg/L) and later these nodules were observed to be converted into somatic embryos (Fig. 1B & C) respectively.
However, the other combinations and concentrations of PGRs exhibit relatively less embryogenic callus formation. The combination of 2,4-D (2.0mg/L or 2.5mg/L), zeatin (0.1mg/L), BAP (0.5mg/L), and proline (0.7mg/L) exhibits efficient and high embryogenesis (63.2±1.67% and 67.4±0.64%) respectively. Moreover, maximum number of somatic embryos differentiated per callus (39.2±0.15) was obtained with the explants that were growing with 2,4-D (2.5mg/L) along with Zn (0.1mg/l), BAP (0.5mg/L) and proline (0.7mg/L). Results indicate that BAP (0.5mg/L) and proline (0.7mg/L) were proved to be effective to enhance the frequency of callusing and somatic embryogenesis when these were used in presence of 2,4-D and Zn.
Meanwhile, the other auxin IAA (1.0mg/L, 2.0mg/L, 2.5mg/L, and 3.0mg/L) was used for callus induction which is significantly inefficient to induce the callus and somatic embryo formation. The embryogenic frequency (21.3±1.53%) was recorded with high concentration of 2,4-D (2.5mg/L). The higher (3.0mg/L) concentration and lower concentration (1.0mg/L) does not promote the embryogenic callus induction (18.7±1.53% and 19.0±1.0%) respectively.
Significantly, IAA was proved to be more effective for callus induction and somatic embryogenesis in combination with Zn, BAP and proline than same combination of Zn, BAP and proline with 2,4-D. Initially, mature embryo were treated with various concentrations (1.0mg/L, 2.0mg/L, 2.5mg/L and 3.0mg/L) of IAA along with Zn (0.1mg/L) and IAA (2.5mg/L) in combination with Zn (0.1mg/L) was proved to be the most effective combination in terms of compact and embryogenic callus formation (Fig. 1D) and moreover, this medium resulted the maximum embryogenic frequency (32.4±1.38%) while the same combination 2,4-D (2.5mg/L) with Zn (0.1mg/L) was observed to be more efficient and resulted (50.9±1.63%) indicating that 2,4-D auxin is more effective than IAA with zeatin (0.1mg/L) to trigger embryogenic potentials of the mature embryo explant tissues.
Furthermore, this combination of IAA and other additives could show the maximum frequency (87.2±0.21%) of embryogenic callus formation and this medium was also recorded as the best combination in terms of maximum number (55.3±0.33) of somatic embryos per embryogenic callus ( Table 1 ). Interestingly, same concentration (1.0mg/L) of 2,4-D in combination with the same concentrations of Zn (0.1mg/L), BAP (0.5mg/L) and proline (0.7mg/L) was emerged as the less potent (61.8±1.15%) for callus induction and somatic embryogenesis during embryo culture. Germination of Somatic Embryo and Plantlets Regeneration
The embryogenic calli were sub-cultured into the regeneration medium supplemented with various equivalent concentrations (0.1mg/L, 0.5mg/L, and 1.0mg/L) of BAP, Kn and Zn . In case of embryogenic callus that was transferred to MS-basal medium without addition of PGRs, somatic embryos were observed to show quick germination and develop into plantlets (Fig. 1G) and the frequency of plantlet regeneration exhibited with basal medium was found to be (63.2±0.27%) and number of regenerated plantlets per embryogenic callus (12.8±0.79%) was recorded ( Table 2 ).
Moreover, in order to evaluate the effects of various cytokinins on somatic embryo germination and plantlets regeneration in sorghum millet, various cytokinins (BAP, kinetin and zeatin) at equivalent concentrations (0.1mg/L, 0.5mg/L, and 1.0mg/L) were tested. Results indicate that Kn (0.5mg/L) was proved to be the most potent cytokinin for promoting somatic embryo germination followed by plantlets regeneration (Fig. 1H) and moreover, the maximum frequency (77.8±0.93%) of embryogenic calli showing plantlets regeneration and also the maximum number of regenerated plantlets per embryogenic callus (55.3±0.80) were recorded.
However, in case of BAP cytokinin, the maximum frequency (37.8±0.54%) of plantlet regeneration was observed with embryogenic calli growing on (0.1mg/L) of BAP supplemented medium while zeatin (0.5mg/L) could show maximum plantlets regeneration frequency (32.6±0.43%).
Significantly, during this study, results indicate that among the tested cytokinins (BAP, Kn, and Zn) at equivalent concentrations (0.1mg/L, 0.5mg/L, and 1.0mg/L), Kn was proved to be the most effective cytokinin in terms of promoting germination of somatic embryos and plantlets regeneration while BAP and Zn were proved to be little ineffective ( Table 2 ). The regenerated plantlets were later transferred to the pot containing soil with vermicompost for acclimatization under greenhouse conditions (FIG. 1I) .
Effects of Lead Stress on Somatic Embryogenesis
After establishment of the best nutrient medium containing IAA (1.0mg/L), zeatin (0.1mg/L), BAP (0.5mg/L), and proline (0.7mg/L) for callus induction and somatic embryogenesis during mature embryo culture in sorghum millet, heavy metals stress treatments were undertaken for induction of heavy metals tolerant somatic embryos and plantlets regeneration. Hence, mature embryo was cultured into the nutrient medium supplemented with IAA (1.0mg/L), zeatin (0.1mg/L), BAP (0.5mg/L), and proline (0.7mg/L) along with various concentrations (10mg/L, 25mg/L, 50mg/L, 75mg/L, and 100mg/L) of PbSO 4 .
Moreover, further higher concentration (25mg/L) of PbSO 4 was observed to cause significantly inhibitory for the induction of somatic embryos (Fig. 2F) , Later it begins to turn gradually browning and begins to show gradual toxicity. During the further higher concentration (50mg/L) of PbSO 4 treatment, induced calli could show compact callusing but was proved to be inhibitory to differentiate somatic embryos significantly rather produce rhizogenic callus which started to produce the root and eventually dried up (Fig. 2G). Moreover, the high concentration of PbSO 4 (75mg/L) was observed to be considerably toxic in which the calluses were necrosed after few days (Fig. 2H) while during very high concentration of PbSO 4 (100mg/L) treatment, mature embryos were found to be completely non-responsive for callus induction indicating that 100mg/L of PbSO 4 proves to be highly toxic for in vitro morphogenesis in sorghum mature embryo culture.
In sorghum, the lower concentration (10mg/L) of PbSO 4 shows inhibitory effects towards the embryogenesis. The somatic embryogenesis up in high frequencies (71.9±1.56% and 64.4±0.61%) were observed in explants that were treated with the lower concentrations (10mg/L and 25mg/L) of PbSO 4 , which are significantly lower than the frequency (87.2±0.21%) of somatic embryogenesis that was obtained during control experiment without PbSO 4 treatment. Moreover, further increase in PbSO 4 concentration (50mg/L) was proved to be significantly inhibitory (26.9±2.24%) for the induction of callus and differentiation of somatic embryo (Table 3) .
However, the least mean frequency (2.9±3.32%) for somatic embryogenesis was observed in explants that were treated with high concentration (75mg/L) of PbSO 4 solutions (Table 3) . However, very high concentration (100mM) of PbSO 4 shows callus formation poorly and such calli were failed to induce somatic embryogenesis indicating the toxicity level of PbSO 4 for morphogenesis. Plantlets Regeneration under Lead - Heavy Metals Stress
During the regeneration of plantlets, MS-regeneration medium supplemented with kinetin (0.5mg/L) without addition of PbSO 4 , was considered as control experiment that leads to achieve the high frequency of plantlet regeneration (Fig. 2I) . Moreover, the lower concentrations (10mg/L and 25mg/L) of PbSO 4 were failed to show the inhibitions in plantlet germination from somatic embryos (Fig. 2J & K) respectively. However, the higher concentration (50mg/L) of PbSO 4 was turned out to be strongly inhibitory for the plantlet regeneration. Later, 12-week-old lead tolerant regenerated plantlet grown with 25mg/L of PbSO 4 was gradually acclimatized in plastic cup containing vermicompost, sand, and soil in 1:1:1 proportion under greenhouse conditions ( Fig. 2L ).
The lower concentrations (10mg/L and 25mg/L) of PbSO 4 were found to show efficient plantlet regeneration (51.9±1.23% and 45.9±0.37%) respectively, however, frequency of plantlet regeneration was obtained lesser than the regeneration frequency recorded in control treatments. The lowest plantlets regeneration frequency (23.8±0.29%) was recorded with concentration (50mg/L) of PbSO 4 . The toxicity of Pb highly affects the frequency of plantlet regeneration from somatic embryos (3.7±0.67%) that was observed with 75mg/L of PbSO 4 (Table 4) .
Effects of Cadmium - Stress on Somatic Embryogenesis
Mature embryo explants that were treated with IAA (1.0mg/L), Zn (0.1mg/L), BAP (0.5mg/L), and proline (0.7mg/L) without CdCl 2 could produce the compact and nodular callus while during cadmium stress treatments similar to PbSO 4 -treatment, the lower concentrations of CdCl 2 (10mg/L and 25mg/L) were failed to show inhibitory response in terms of callus induction (Fig. 3A & B) respectively. However, the higher concentration (75mg/L) of CdCl 2 could show significant inhibitions caused by the toxicity of CdCl 2 but even though compact and nodular callus formation (Fig. 3C) was observed .
In comparison to control experiment (87.2±0.21%), during CdCl 2 treatments, the maximum frequency (69.2±0.7%) of somatic embryogenesis was obtained with the lower concentration (10mg/L) of CdCl 2. indicating the inhibitory response of CdCl 2 . Moreover, with the further increase in CdCl 2 concentrations, gradual reductions in frequency of somatic embryogenesis were recorded and therefore, the minimum frequency (03.1±3.24%) was obtained with very high concentration (150mg/L) of CdCl 2 -treatments. However, there was no significant difference in terms of embryogenesis frequency obtained with 10mg/L of CdCl 2 (69.2±0.7%) and (66.9±1.63%) that was recorded with 25mg/L of CdCl 2 concentration in nutrient medium. Significantly, even the high concentration (100mg/L) of CdCl 2 proves to be inefficient to cause heavy metal stress inhibition response on embryogenesis (39.2±2.26%). Moreover, very high concentration (200mg/L) was turned out to be lethal (Table 5) .
Plantlets Regeneration under Cadmium - Heavy Metals Stress
The embryogenic callus was transferred into the nutrient medium consisted of kinetin (0.5mg/L) along with respective CdCl2 concentrations (Table 6). The plantlet germination from somatic embryos was recorded as the maximum frequency (77.8±0.93%) with control and eventually reduced (61.9±0.43% and 57.5±0.38%) in case of embryogenic calli that were transferred to the nutrient media consisted of 10mg/L and 25mg/L of CdCl2 respectively along with Kn (0.5mg/L). The higher concentration (50mg/L) of CdCl2 is efficient enough to support the tolerant plantlet regeneration (Fig. 3I).
While the least frequency of plantlet regeneration (13.3±3.21%) was obtained in embryogenic calli treated with 75mg/L of CdCl2 solutions (Table 6) whereas, the high concentration (100mg/L) is exhibiting high toxicity and affects the germination frequency negatively (4.23±2.33%). Moreover, very high concentration (150mg/L) is proved to be lethal. Finally, in vitro regenerated plantlet (Fig. 3J) grown under CdCl2 (50mg/L) stress conditions was further transferred to plastic cup for gradual acclimatization (Fig. 3K) in greenhouse.
Table 1 : Sorghum ( Sorghum bicolor L.), effects of auxins (2,4-D and IAA) in combination with cytokinins (Zn and BAP) and proline on percentage of explants showing embryogenic callus induction and number of somatic embryos per embryogenic callus during mature embryo culture in MS- nutrient medium.
|
Concentration of Auxins (mg/L) |
Concentration of Cytokinins (mg/L) |
Concentration of Proline (mg/L) |
Percentage of Embryogenic Callus (Mean ± SD) |
No.of Somatic Embryos/ Embryogenic Callus (Mean ± SD) |
||
|
2, 4- D |
1.0 |
- |
0 |
12.3±2.09 |
10.1±0.64 |
|
|
2.0 |
15.3±3.51 |
12.5±2.21 |
||||
|
2.5 |
13.3±0.57 |
11.4±3.41 |
||||
|
3.0 |
9.7±3.58 |
02.7±4.72 |
||||
|
1.0 |
Zn |
0.1 |
0 |
11.1±1.42 |
03.1±3.41 |
|
|
2.0 |
49.6±2.14 |
14.7±2.38 |
||||
|
2.5 |
50.9±1.63 |
15.1±0.89 |
||||
|
3.0 |
22..3±0.33 |
11.1±0.63 |
||||
|
1.0 |
Zn + BAP |
0.1 + 0.5 |
0.7 |
61.8±1.15 |
34.5±1.27 |
|
|
2.0 |
63.2±1.67 |
33.5±0.86 |
||||
|
2.5 |
67.4±0.64 |
39.2±0.15 |
||||
|
3.0 |
54.5±1.71 |
16.2±0.27 |
||||
|
IAA |
1.0 |
- |
0 |
19.0±1.0 |
8.2±2.22 |
|
|
2.0 |
19.3±0.57 |
8.5±3.41 |
||||
|
2.5 |
21.3±1.53 |
9.1±3.57 |
||||
|
3.0 |
18.7±1.53 |
7.8±2.51 |
||||
|
1.0 |
Zn |
0.1 |
0 |
23.2±0.25 |
11.3±0.71 |
|
|
2.0 |
27.7±1.53 |
12.1±0.37 |
||||
|
2.5 |
32.4±1.38 |
13.2±0.32 |
||||
|
3.0 |
12.4±2.12 |
6.91±0.33 |
||||
|
1.0 |
Zn + BAP |
0.1 + 0.5 |
0.7 |
87.2±0.21 |
55.3±0.33 |
|
|
1.5 |
81.1±0.52 |
49.4±0.82 |
||||
|
2.0 |
74.2±1.44 |
34.8±1.16 |
||||
|
2.5 |
61.7±1.93 |
29.2±2.14 |
||||
|
3.0 |
48.3±0.33 |
14.2±1.71 |
||||
Table 2: Sorghum ( Sorghum bicolor L.), effects of various concentrations of cytokinins on percentage of embryogenic callus showing plantlets regeneration and number of regenerated plantlets per embryogenic callus during mature embryo culture in MS-nutrient medium supplemented with BAP, Kn, and Zn.
|
Concentration of Cytokinins (mg/L) |
Percentage of Embryogenic Callus showing Plantlets Regeneration (Mean±SD) |
No. of Regenerated Plantlets/ Embryogenic Callus (Mean±SD) |
|
|
BAP |
0 |
63.2±0.27 |
12.8±0.79 |
|
0.1 |
37.8±0.54 |
17.5±1.53 |
|
|
0.5 |
27.3±0.63 |
11.3±0.20 |
|
|
1.0 |
21.4±0.27 |
10.8±0.71 |
|
|
Kn |
0.1 |
45.8±0.67 |
28.3±1.63 |
|
0.5 |
77.8±0.93 |
55.3±0.80 |
|
|
1.0 |
33.3±0.77 |
12.9±0.81 |
|
|
Zn |
0.1 |
26.2±0.37 |
11.5±1.41 |
|
0.5 |
32.6±0.43 |
13.9±0.93 |
|
|
1.0 |
28.4±0.25 |
11.9±0.71 |
|
Table 3: Sorghum ( Sorghum bicolor L.), effects of lead (Pb) heavy metal stress on percentage of somatic embryogenesis and number of somatic embryos per embryogenic callus during mature embryo culture in MS-medium supplemented with (IAA, zeatin,BAP, and proline) and various concentrations of PbSO 4 .
|
Concentration (mg/L) |
Concentration of PbSO4 (mg/L) |
Percentage of Somatic Embryogenesis (Mean±SD) |
No. of Somatic Embryos/ Embryogenic Callus (Mean±SD) |
|
IAA (1.0) + Zeatin (0.1) + BAP (0.5) + Proline (0.7) |
0 |
87.2±0.21a |
55.3±0.33 |
|
10 |
71.9±1.56b |
44.1±1.14 |
|
|
25 |
64.4±0.61c |
39.2±0.95 |
|
|
50 |
26.9±2.24d |
12.9±0.56 |
|
|
75 |
02.9±3.32e |
0.4±3.81 |
|
|
100 |
0 |
0 |
Table 4: Sorghum ( Sorghum bicolor L.), effects of lead (Pb) heavy metal stress on percentage of plantlet regeneration and number of regenerated plantlets per embryogenic callus during mature embryo culture in MS-medium supplemented with Kn and various concentrations of PbSO 4 .
|
Concentration of Kn (mg/L) |
Concentration of PbSO4 (mg/L) |
Percentage of Plantlet Regeneration (Mean±SD) |
No. of Regenerated Plantlets / Embryogenic callus (Mean±SD) |
|
0.5 |
0 |
77.8±0.93a |
55.3±0.80 |
|
10 |
51.9±1.23b |
39.2±1.32 |
|
|
25 |
45.9±0.37c |
33.5±2.19 |
|
|
50 |
23.8±0.29d |
17.8±1.78 |
|
|
75 |
03.7±0.67e |
1.4±3.91 |
|
|
100 |
0 |
0 |
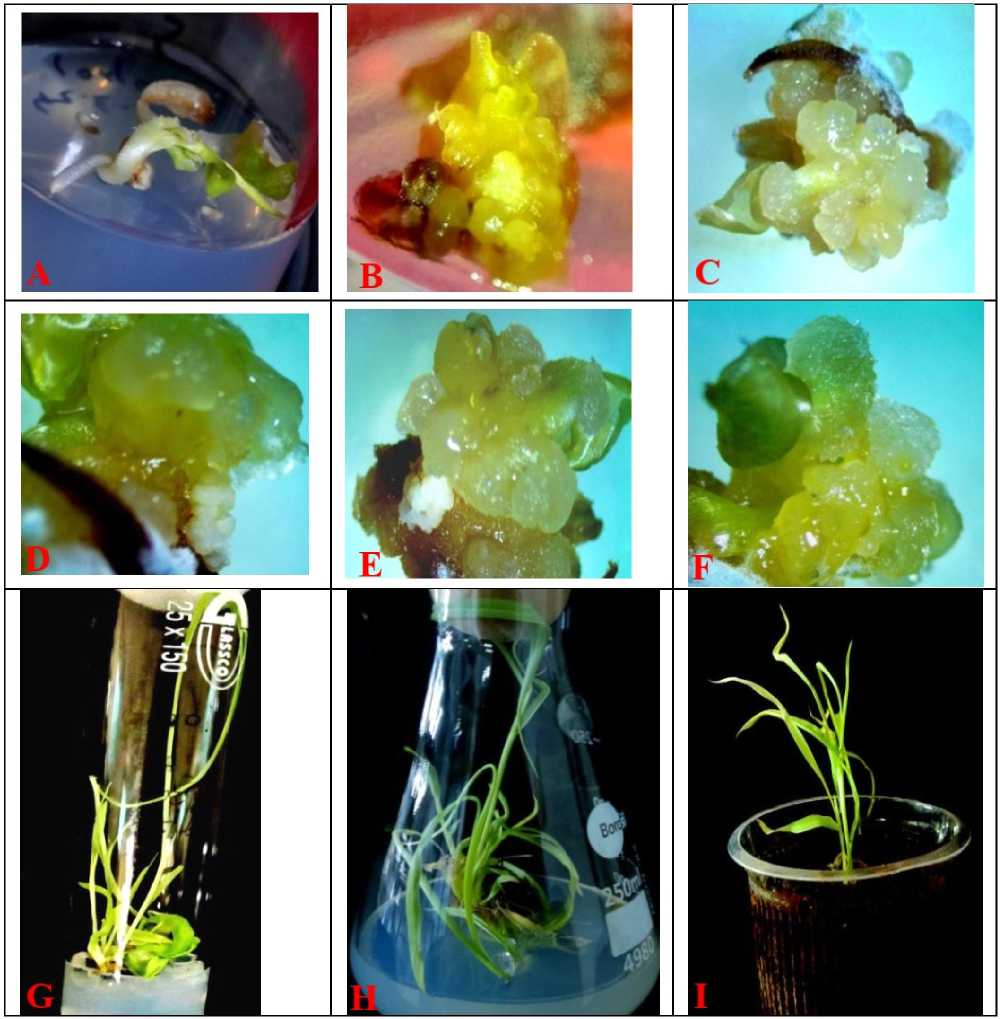

Figure 1: Sorghum bicolor L. Mature embryo culture on MS- medium supplemented with various concentrations of auxins (2.4-D and IAA) and cytokinins (Zn and BAP) either alone or in combinations, also in presence or absence of proline;
-
(A) In control or MS-basal medium, mature embryo germinates and develops into young plant– after 3-5 days of culture initiation; (B) Mature embryo shows inhibited germination and induces callus induction followed by differentiation of somatic embryos on medium supplemented with 2,4-D (2.5mg/L) and Zn (0.1mg/L) (C) Mature embryo with slight germination induces compact and nodular callus formation followed by somatic embryogenesis on medium supplemented with 2,4-D (2.5mg/L), Zn (0.1mg/L), BAP (0.5mg/L), and proline (0.7mg/L) (D) Explant induces callus formation with some nodular structures leading to somatic embryogenesis on medium added with IAA (2.5mg/L) and Zn (0.1mg/L) after 2-3 weeks of culture; (E) Compact callus differentiates somatic embryos on medium supplemented with IAA (1.0mg/L), Zn (0.1mg/L), BAP (0.5mg/L), and proline (0.7mg/L) (F) Somatic embryogenesis on medium supplemented with IAA (1.5mg/L), Zn (0.1mg/L), BAP (0.5mg/L), and proline (0.7mg/L) – after 2 weeks of culture initiation; (G) Somatic embryo germination and plantlet regeneration from embryogenic callus on transfer to MS-basal medium ( H) Plantlet regeneration on MS-medium supplemented with Kn (0.5mg/L) – after 10-12 weeks of culture initiation; (I) Potted plantlet – After 7 days of Transplantation.
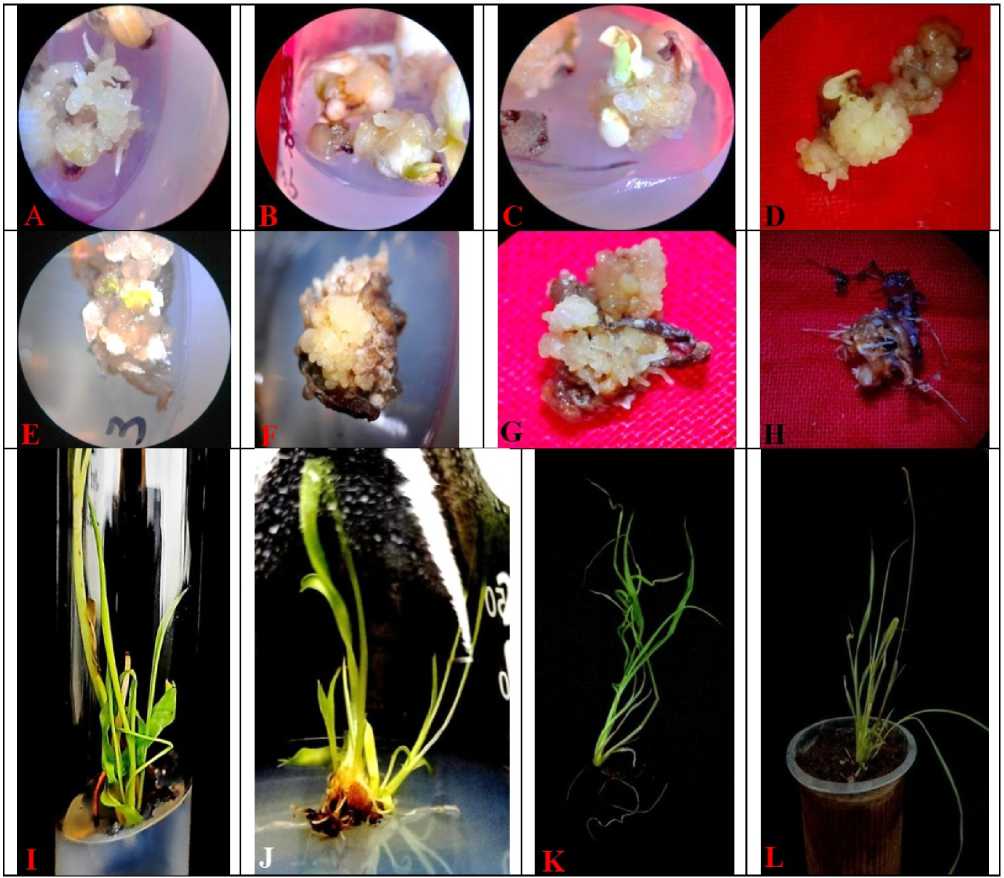
Figure 2. Sorghum bicolor L. Mature embryo culture on MS-medium supplemented with IAA (1.0mg/L), Zn (0.1mg/L),
BAP (0.5mg/L), and proline (0.7mg/L) as control and also supplemented with various concentrations of PbSO 4 showing induction of callus and somatic embryogenesis;
-
(A) Induction of callus from mature embryo in control MS-medium without PbSO 4 (B) Compact callus formation from mature embryo treated with 10mg/L of PbSO 4 (C) Callus formation under 25mg/L of PbSO 4 (D) Somatic embryogenesis in control MS-medium without PbSO 4 (E) Differentiation of somatic embryos on induced compact callus growing with 10mg/L of PbSO 4 (F) Formation of embryogenic compact callus growing under MS-medium supplemented with 25mg/L of PbSO 4 (G) Somatic embryogenesis in mature embryo derived callus growing with 50mg/L of PbSO 4 (H) Mature embryo derived callus treated with 75mg/L of PbSO 4 gradually shows necrosis without differentiation of somatic embryos– after 21-days of culture initiation (I) Regeneration of plantlets form embryogenic callus on transfer to MS-medium supplemented with 0.5mg/L of Kn without PbSO 4 ( J) Plantlet regeneration on transfer of embryogenic callus to MS-medium added with 0.5mg/L of Kn and 25mg/L of PbSO 4 – after 12- weeks of culture initiation; (K) Regenerated plantlet grown on 0.5mg/L of Kn along with 25mg/L of PbSO 4 under ex vitro condition (L) PbSO 4 (25mg/L) - treated tolerant plantlet under acclimatization conditions after 11-days of transfer.
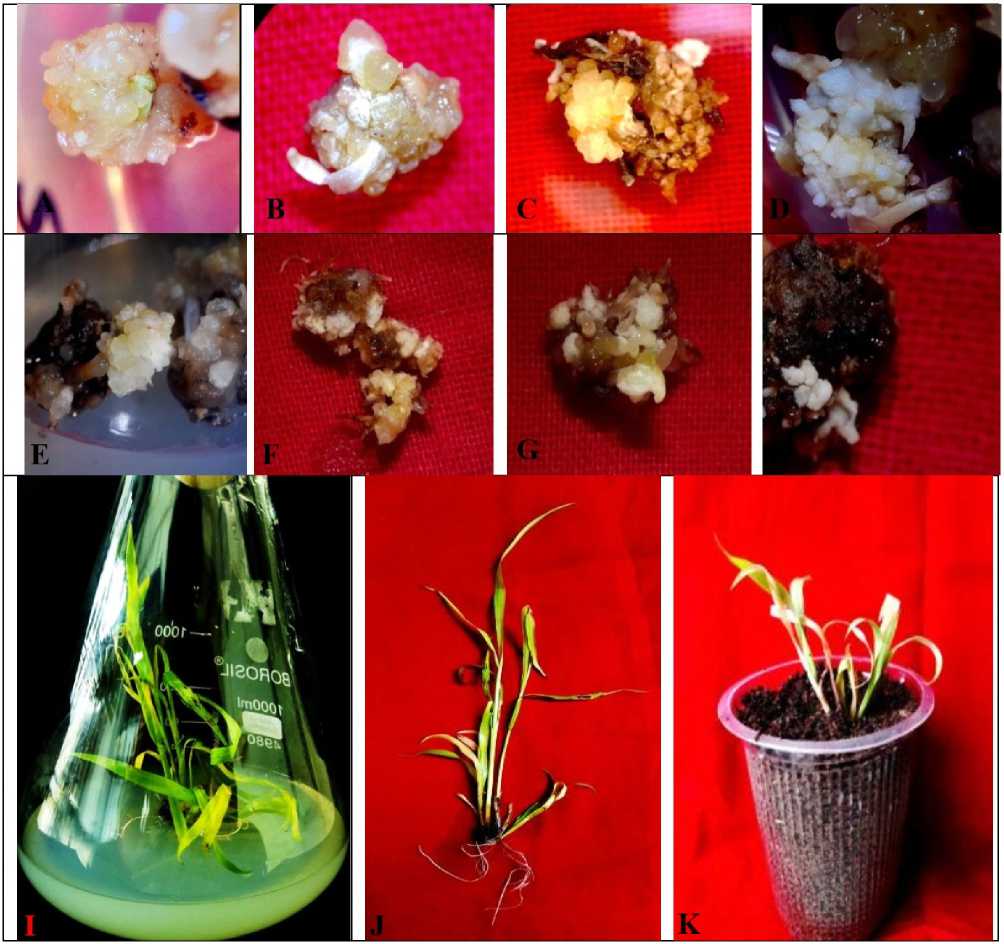

Figure 3: Sorghum bicolor L. Mature embryo culture on MS-medium supplemented with IAA (1.0mg/L), Zn (0.1mg/L), BAP (0.5mg/L), and proline (0.7mg/L) as control and also supplemented with various concentrations of CdCl 2 showing induction of callus and somatic embryogenesis;
-
(A) Induction of callus from mature embryo treated with 10mg/L of CdCl 2 (B) Callus formation from mature embryo treated with 25mg/L of CdCl 2 treatment (C) Callus formation under 75mg/L of CdCl 2 (D) Somatic embryogenesis in callus treated with 10mg/L of CdCl 2 (E) Differentiation of somatic embryos induced on callus growing with 25mg/L of CdCl 2 (F) Development of embryogenic callus growing under MS-medium supplemented with 75mg/L of CdCl 2 (G) Somatic embryogenesis in callus treated with 100mg/L of CdCl 2 (H) Growth of embryogenic callus derived from mature embryo treated with 150mg/L of CdCl 2 – after 3-4 weeks of culture initiation; (I) Plantlet regeneration in embryogenic callus on transfer to MS- medium supplemented with 0.5mg/L of Kn and 50mg/L of CdCl 2 - after 13-weeks of culture initiation ( J) Cadmium chloride (50mg/L) tolerant regenerated plantlet under ex vitro condition (K) Potted plantlet growing under CdCl 2 (50mg/L) stress condition after 8-days of transplantation.
Table 5: Sorghum ( Sorghum bicolor L.), effects of cadmium (Cd) heavy metal stress on percentage of somatic embryogenesis and number of somatic embryos per embryogenic callus during mature embryo culture in MS-medium supplemented with various concentrations of CdCl 2 along with IAA, BAP, zeatin, and proline.
|
Concentration (mg/L) |
Concentration of CdCl2 (mg/L) |
Percentage of Somatic Embryogenesis (Mean±SD) |
No. of Somatic Embryos/ Embryogenic Callus (Mean±SD) |
|
IAA (1.0) + BAP (0.5) + Zeatin (0.1) + Proline (0.7) |
0 |
87.2±0.21a |
55.3±0.33 |
|
10 |
69.2±0.77b |
44.0±0.54 |
|
|
25 |
66.9±1.63b |
43.7±2.16 |
|
|
50 |
58.3±0.86c |
39.2±1.77 |
|
|
75 |
51.9±1.62d |
37.4±0.82 |
|
|
100 |
39.2±2.26e |
11.2±3.15 |
|
|
150 |
03.1±3.24f |
1.3±4.38 |
|
|
200 |
0 |
0 |
Table 6: Sorghum ( Sorghum bicolor L.), effects of cadmium (Cd) heavy metal stress on percentage of plantlet regeneration and number of plantlets per embryogenic callus during mature embryo culture in MS-medium supplemented with kinetin and various concentrations of CdCl 2 .
|
Concentration of Kn (mg/L) |
Concentration of CdCl2 (mg/L) |
Percentage of Plantlet Regeneration (Mean±SD) |
No. of Regenerated Plantlets/ Embryogenic Callus (Mean±SD) |
|
0.5 |
0 |
77.8±0.93a |
55.3±0.80 |
|
10 |
61.9±0.43b |
46.8±1.74 |
|
|
25 |
57.5±0.38b |
40.2±1.39 |
|
|
50 |
39.2±0.49c |
27.6±1.71 |
|
|
75 |
13.3±3.21d |
08.4±0.93 |
|
|
100 |
4.23±2.33e |
02.8±4.73 |
DISCUSSION
Generally, the biotic and abiotic stresses show negative impacts over plants and retard the growth and development by inhibiting the uptake of water and nutrients and compromise membrane permeability (Arif et al. , 2020). The contaminations of ground water, exploitation of land used for agriculture, crop plants, etc., are highly affected by the heavy metal/s in high concentration (Gismera et al ., 2005; Fawzy, 2008).
The alteration of biochemical, physiological and metabolic pathway of crop plants significantly affect grain yield by heavy metal/s contamination (Hossain et al., 2010; Rascio and Navari-Izzo, 2011). In vitro regeneration via somatic embryogenesis is playing major significant role in crop improvement and also has proved a meaningful tool for gene transformation techniques in food crops (Tiecoura et al., 2003; Vikrant, 2015).
Induction of Callus and Somatic Embryogenesis
The suitable and competent explants have been suggested as primary requirements for the achievement of successful embryogenesis, plantlet regeneration and genetic transformation (Grootboom et al ., 2008). Literature reveals that callus induction and plantlet regeneration have been established in sorghum crop by employing the various explants such as, immature inflorescence (Gupta et al ., 2006; Jogeswar et al ., 2007), shoot segment (Brar et al. , 1997), shoot tips (Bhaskaran and Smith, 2006) and mature embryo (McKinnon et al., 1986).
As per the available reports, among various explant tissues identified, mature embryos are considered as potential explants for in vitro study deals with somatic embryogenesis and plantlet regeneration because of being easily available abundantly throughout the year (Sudhakar et al., 2004; Jha et al., 2008; Vikrant, 2015). The present study aims with the impacts of heavy metals stresses on induction of embryogenic callus followed by tolerant plantlets regeneration during mature embryo culture.
Significantly, during previous studies on sorghum mature embryo culture, auxins have been found to be the main source to induce the somatic embryogenesis (Elkonin et al ., 1995; Nguyen et al., 2007; Gurel et al., 2012; Chen et al., 2015; Do et al., 2016; Omer et al ., 2019) along with or without the cytokinins like BAP and Kn (Belide et al., 2017; Espinoza-Sánchez et al., 2018). Additionally, the amino acids like proline are known to enhance the induction of embryogenic callus and plantlet regeneration in maize and sorghum (Rao et al., 1995; Omer et al., 2019).
The report states that the combinations of auxins and cytokinins induce the differentiation of embryogenic callus (Thomas and Maseena, 2006). However, the present study reveals that the combinations of auxin (1.0mg/L of IAA) and cytokinins (0.5mg/L of BAP and 0.1mg/L of zeatin) along with the amino acid (0.7mg/L of L-Proline) induce the highest frequency (87.2±0.21%) of embryogenic callus and somatic embryogenesis . Significantly, in contrast, other studies indicate the combination of other auxin 2,4-D along with BA, kinetin and zeatin increases the percentage of embryogenic callus induction in Eleusine coracana (Ceasar and Ignacimuthu, 2008), Sorghum bicolor (Belide et al., 2017; Espinoza-Sánchez et al., 2018).
However, during present study, 2,4-D alone was proved to be less efficient for callus induction and somatic embryogenesis while 2,4-D along with Zn resulted better combination and therefore, 2,4-D (2.0mg/L and 2.5mg/L) along with Zn (0.1mg/L) could show the almost equal frequency of embryogenic callus formation (49.6±2.14% and 50.9±1.63%) respectively. Moreover, in general 2,4-D auxin proves to be less potent than IAA in terms of callus induction and somatic embryogenesis. The other combination of auxins; 2,4-D and IAA, either alone or with cytokinins (BAP and zeatin) does not exhibit embryogenesis significantly (Table 1) .
Germination of Somatic Embryo and Plantlet Regeneration
Список литературы Efficient somatic embryogenesis and plantlet regeneration induced from mature embryo culture under heavy metals stress conditions in a millet crop sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench]
- Arif Y.K., Singh P., Siddiqui H., Bajguz A. and Hayat S. (2020). Salinity induced physiological and biochemical changes in plants: An omic approach towards salt stress tolerance. Plant Physiol. Biochem., 156, 64-77.
- Baskaran P., Rajeswari B.R. and Jayabalan N. (2006). Development of an In Vitro Regeneration System in Sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench] using Root Transverse Thin Cell Layers. Turkish J. Botany. 30, 1-9.
- Belide S., Vanhercke T., Petrie J.R. and Singh S.P. (2017). Robust genetic transformation of sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L.) using differentiating embryogenic callus induced from immature embryos. Plant Methods,13,109.
- Bhaskaran S. and Smith R.H. (2006). Control of morphogenesis in sorghum by 2,4-D and cytokinins. Ann Bot., 64.
- Brar, D. S., Rambold, S., Gamborg, O., & Constabel, F. (1979). Tissue culture of corn and sorghum. Zeitschrift für Pflanzenphysiologie, 95(5), 377-388.
- Ceasar S.A. and Ignacimuthu S. (2008). Efficient somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from shoot apex explants of different Indian genotypes of finger millet (Eleusine coracana (L.) Gaertn.). In Vitro Cell Dev Biol-Plant, 44, 427-435.
- Chen X., Li O., Shi L., Wu X., Xia B. and Pei Z. (2015). To establish the regeneration system of sweet sorghum immature embryos. Adv. Appl. Biotechnol., 333,83-91.
- Chraibi K.M., Latche A., Roustan J.P. and Fallot J. (1991). Stimulation of shoot regeneration from cotyledons shoot regeneration from cotyledons of Helianthus annus by ethylene inhibitors; silver and cobalt. Plant Cell Rep., 10, 204-207.
- Do P.T., Lee H., Mookkan M., Folk W.R. and Zhang Z.J. (2016). Rapid and efficient Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) employing standard binary vectors and bar gene as a selectable marker. Plant Cell Rep., 35, 20652076.
- Doganlar Z.B.P. and Yurekli F. (2009). Interactions between cadmium and phytochelatin accumulation in two different sunflower cultivars. Fresenius Environ Bull., 18, 304-310.
- Drouhot S., Raoul F., Crini N., et al., (2014). Responses of wild small mammals to arsenic pollution at a partially remediated mining site in Southern France. Sci. Total Environ., 470-471, 1012-1022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.10.053
- Elkonin L.A., Lopushanskaya R.F. and Pakhomova N.V. (1996). Embryogenic callus of Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench) by amino acids. Maydica. 40, 153-157.
- Epelde L., Mijangos I., Becerril J.M. and Garbisu C. (2009). Soil microbial community as bioindicator of the recovery of soil functioning derived from metal phytoextraction with sorghum. Soil Biol. Biochem., 41, 1788-1794.
- Espinoza-Sánchez E. A., Sánchez-Peña Y.A., Torres-Castillo J.A., García-Zambrano E.A., Ramírez J.T., Zavala-García F. and Sinagawa-García S.R. (2018). Somatic embryogenesis induction from immature embryos of Sorghum bicolor L. (Moench). Phyton-Int. J. Exp. Bot, 87, 105-112.
- Fawzy E.M. (2008). Soil remediation using in situ immobilization techniques. Chemistry and Ecology, 24(2), 147-156.
- George L. and Eapen S. (1989). Callus growth and plant regeneration in some Indian cultivates of Sorghum. Current Science, 58, 308-310.
- Gismera M.J., Lacal J., daSilver P., Garcia R., Sevilla M.T. and Procopio J.R. (2004). Study of metal fractionation in river sediments. A comparison between kinetic and sequential extraction procedures. Environ. Pollut., 127, 175-182.
- Gnansounou E., Dauriat A. and Wyman C.E. (2005). Refining sweet sorghum to ethanol and sugar: Economic trade-offs in the context of North China. Bioresour. Technology, 96, 985-1002.
- Grootboom A.W., Mkhonza N.L., O'Kennedy M.M., Chakauya E., Kunert K. and Chikwamba R.K. (2008). In vitro culture and plant regeneration of sorghum genotypes using immature zygotic embryos as plant source. Int. J. Bot., 4, 450-455.
- Gupta S., Khanna V.K., Rameshwar S. and Garg G.K. (2006). Strategies for overcoming genotypic limitations of in vitro regeneration and determination of genetic components of variability of plant regeneration traits in sorghum. PCTOC. 86:376-388.
- Gurel S, Gurel E, Miller TI, Lemaux PG (2012) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Sorghum bicolor using immature embryos. Methods Mol. Biol., 847, 109-122.
- Hadebe S.T., Modi A.T. and Mabhaudhi T. (2017). Drought tolerance and water use of cereal crops: a focus on sorghum as a food security crop in sub-saharan Africa. Journal of Agronomy and Crop Science, 203, 177-191.
- Harshavardhan D., Rani T.S., Ulaganathan S. and Seetharama N. (2002). An improved protocol for regeneration of Sorghum bicolor from Isolated Shoot Apices. Plant Biotechnol., 19(3),163-171.
- Hernandez L.E. and Cooke D.T. (1997). Modifications of root plasma membrane lipid composition of cadmium treated Pisum sativum. J. Exp. Bot., 48, 1375-1381.
- Hossain M.A., Hasanuzzaman M. and Fujita M. (2010). Upregulation of antioxidant and glyoxalase systems by exogenous glycine betaine and proline in mung bean confer tolerance to cadmium stress. PMBP, 16(3), 259-272.
- Huang R. (2018). Research progress on plant tolerance to soil salinity and alkalinity in sorghum. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 17, 739-746.
- Jha P., Yadav C.B., Anjaiah V. and Bhat V. (2009). In vitro plant regeneration through somatic embryogenesis and direct shoot organogenesis in Pennisetum glaucum (L.) R, Br. In vitro Cell Dev. Biol. Plant, 45, 145-154.
- Jogeswar G., Ranadheer D., Anjaiah V. and Kishor P.B.K. (2007). High frequency somatic embryogenesis and regeneration in different genotypes of Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench from immature inflorescence explants. In Vitro Cell Development Biology Plant, 43,159-166.
- Kingsley A.P. and Ignacimuthu S. (2014). Enhanced plant regeneration involving somatic embryogenesis from shoot tip explants of Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench. Asian J. Plant Sci. Res., 4, 26-34.
- Kishore S.N., Visarada K.B.R.S., Lakshmi A.Y., Pashupatinath E., Rao S.V. and Seetharama N. (2006). In vitro culture methods in Sorghum with shoot tips the explant Material. Plant Cell Reports, 25, 174-182.
- Kuriakose S.V. and Prasad M.N.V. (2008). Cadmium stress affects seed germination and seedling growth in Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench by changing the activities of hydrolyzing enzymes. Plant Growth Regul, 54, 143-156.
- Kuruvinashetti M.S., Patil V.M., Sumangala B. and Maheshwar H. (1998). High frequency plant regeneration from embryogenic callus cultures in genus Sorghum. IJAS, 68(1), 27-28.
- Liu D., Cao X., Zhang H., Liu Z., Yang J. and Wang K. (2014). Effects of Pb. Cd, stress on the growth and Pb, Cd uptake of forage sorghum. Acta AgrestiaSinica, 22(4), 776-782.
- Marchiol L., Fellet G., Perosa D. and Zerbi G. (2007). Removal of trace metals by Sorghum bicolor and Helianthus annuus in a site polluted by industrial wastes: a field experience. Plant Physiol.Biochem., 45, 379-387.
- McKinnon C., Gunderson G. and Nabors M.W. (1986). Plant regeneration by somatic embryogenesis from callus cultures of sweet sorghum. Plant Cell Rep., 5, 349-51.
- Michel-López C.Y., Espadasy G.F., Fuentes O.G., Santamaría J.M., González-Mendoza D., Ceceña-Duran C. and Grimaldo J.O. (2016). Bioaccumulation and effect of cadmium in the photosynthetic apparatus of Prosopis juliflora. Chem. Speciat. Bioavailab., 28, 1-6.
- Mishra A. and Khurana P. (2003). Genotype dependent somatic embryogenesis and regeneration from leaf base cultures of Sorghum bicolor. JPBB, 12, 53-56.
- Murashige T. and Skoog F. (1962). A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant, 15, 473-497.
- Muratova A., Lyubun Y., German K. and Turkovskaya O. (2015). Effect of cadmium stress and inoculation with a heavy-metal-resistant bacterium on the growth and enzyme activity of Sorghum bicolor. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res., Mythili P., Madhavi A., Reddy V.D. and Seetharam N. (2001). Efficient regeneration of pearl millet Pennisetum glaucum (L.) from shoot tip cultures. Indian J. Exp. Biol, 39, 1274-1279.
- Nayak P. and Sen S.K. (1989). Plant regeneration through somatic embryogenesis from suspension cultures of a minor millet, Paspalum scrobiculatum L. Plant Cell Rep, 8, 296-299.
- Nguyen T., Thu T.T., Claeys M. and Angenon G. (2007). Agrobacterium- mediated transformation of sorghum (Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench) using an improved in vitro regeneration system. PCTOC, 91,155-164.
- Nirwan R.S. and Kothari S.L. (2004). High frequency shoot organogenesis in Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench. JPBB, 13, 149-152.
- Okem A., Moyo M., Stirk W., Finnie J. and Van S.J. (2016). Investigating the effect of Cd and aluminium on growth and stress-induced responses in the micropropagated medicinal plant Hypoxishemero callidea. Plant Biol., 18, 805-815.
- Omer R.A., Suliman S. and Beshi M.M. (2021). Regeneration of Sorghum through Tissue Culture Techniques. Int. J. Genetic Engineering, 9(1), 16-20.
- Patnaik D., Mahalakshmi A. and Khurana P. (2005). Effect of water stress and heavy metals on induction of somatic embryogenesis in wheat leaf base cultures. Ind. J. Exp. Bio., 43, 740-745.
- Pola S.R. and Mani S.N. (2006). Somatic embryogenesis and plantlet regeneration in Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench, from leaf segments. JCMB, 5(2), 99-107.
- Prunhauser L. and Gyulai G. (1993). Effect of copper on shoot and root regeneration in wheat, triticale, rape and tobacco tissue cultures. PCTOC, 35, 131-139.
- Radchuk V., Radchuk R., Pirko Y., Vankova R. and Gaudinova A. (2012). A somaclonal line SE7 of finger millet (Eleusine coracana) exhibits modified cytokinin homeostasis and increased grain yield. JXB, 63, 5497-5506.
- Rao A.M., Sree K.P. and Kishor P.B.K. (1995). Enhanced plant regeneration in grain and sweet sorghum by asparagine, proline and cefotaxime. PCR. 15:72-75.
- Rascio N. and Navari-Izzo F. (2011). Heavy metal hyper accumulating plants: how and why do they do it? And what makes them so interesting? Plant Science, 180(2), 169-181.
- Rooney W.L., Blumenthal J., Bean B. and Mullet J.E. (2007). Designing sorghum as a dedicated bioenergy feedstock. Biofuels, Bioproducts and Biorefining, 1, 147-157.
- Roustan J.P., Latche A. and Fallot J. (1989). Stimulation of Daucus carrota somatic embryogenesis by inhibitors of ethylene synthesis: Cobalt and Nickel. Plant Cell Rep., 8,182.
- Rout G,R,, Samantaray S. and Das P. (1998). The role of nickel on somatic embryogenesis in Setaria italica L., in vitro. Euphytica, 101, 319-324.
- Seetharama N., Sairam R.V. and Rani T.S. (2000). Regeneration of Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench from shoot tip cultures and field performance of the progeny. PCTOC, 61,169-173.
- Soudek P., Petrova S., Vankova R., Song J. and Vanek T. (2014). Accumulation of heavy metals using Sorghum sp. Chemosphere, 104, 15-24.
- Srivastav S. and Kothari S.L. (2002). Embryonic callus induction and high frequency plant regeneration in pearl millet. Cer. Res. Commun., 30, 69-74.
- Thomas T.D. and Maseena E.A. (2006). Callus induction and plant regeneration in Cardiospermum halicacabum (L.) an important medicinal plant. Scientia Horticulturae, 108,332-336.
- Tiecoura K., Ledoux L. and Dinant M. (2003). Tissue culture of pearl millet. Agronomie Africaine, 15 (3), 105-121.
- Tran T.A. and Popova L.P. (2013). Functions and toxicity of cadmium in plants: recent advances and future prospects. Turk. J. Bot., 37,1-13.
- Varoquaux N., Cole B., Gao C., et al., (2019). Transcriptomic analysis of field droughted sorghum from seedling to maturity reveals biotic and metabolic responses. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA 116, 27124-27132.
- Vijayarengan P. (2005). Nitrogen and potassium status of green gram (Vigna radiata) cultivars under nickel stress. Nature Environmental Pollution and Technology, 4(1), 65-69.
- Vijendra PD, Huchappa KM, Lingappa R, Basappa G,
- Jayanna SG, Kumar V (2016) Physiological and Biochemical Changes in Moth Bean (Vigna aconitifolia L.) under Cadmium Stress. J. Bot., http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6403938
- Vikrant (2015). Induction of Somatic Embryos from Mature Embryo Culture under Abiotic Stress and Estimation of Proline Status in a Millet Crop, Paspalum scrobiculatum L. IJABR, 6 (1), 96-109.
- Visarada K.B.R.S., SaiKishore N., Balakrishna D. and Rao S.V. (2003). Transient gus expression studies in Sorghum to develop a simple protocol for Agrobacterium mediated genetic transformation. Journal of Genetics and Breeding, 57, 147-154.
- Wuana R.A. and Okieimen F.E. (2011). Heavy metals in contaminated soils: A review of sources, chemistry, risks and best available strategies for remediation. ISRN Ecology, 2011,1-20.
- Xu Z., Wang D., Yang L. and Wei Z. (1984). Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in callus cultured immature inflorescence of Setaria italica. Plant Cell Rep., 3, 144-150.
- Zhuang P., Wensheng S., Zhian L., Bin L., Jintian L. and Jingsong S. (2009). Removal of metals by sorghum plants from contaminated land. J. Environ. Sci., 21,1432-1437.

![Efficient somatic embryogenesis and plantlet regeneration induced from mature embryo culture under heavy metals stress conditions in a millet crop sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench] Efficient somatic embryogenesis and plantlet regeneration induced from mature embryo culture under heavy metals stress conditions in a millet crop sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench]](/file/cover/143183772/efficient-somatic-embryogenesis-and-plantlet-regeneration-induced-from-mature.png)
