Elucidating the effect of salinity stress in enhancing the phenolic acid content in Rauwolfia Serpentina in vitro
Автор: Puneet S. Singh, Babita Patni
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 3 т.16, 2020 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Rauwolfia serpentina (Apocynaceae) is a woody perennial shrub and important medicinal plant. Due to increased interest by both the scientific community regarding the medicinal uses of this plant species, a protocol for in vitro callus induction of Rauwolfia has been developed due to low germination rate (15%-20%). The leaf and stem explants were transferred to MS medium containing different combinations of plant growth hormones; 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) + 2-benzyl amino purine (BAP).The concentration of 2,4-D (2.0mg/l) + BAP (1.0 mg/l) produced better results for callus induction in both leaf and stem explants. The least results were recorded in callus induced from leaf explants under the influence of 2, 4-D (2.0 mg/l) and BAP (1.5 mg/l). The present investigation aims to increase the phenolic content in vitro responsible for the antioxidant activity of Rauwolfia. Thus salinity stress has been applied in vitro to increase the phenolic acid content and various enzymes such as SOD (superoxide dismutase) and PAL (Phenyl alanine ammonia lyase) has been studied. The phenolics content was more in leaf callus at moderate salinity level of 15 ppm compared to control and other treatments at 10ppm and 20 ppm. There was increase in total phenolic acid content and antioxidant activity of Rauwolfia under moderate salinity. Result of the experiment showed that the SOD activity was highest at 20ppm followed by 15 ppm and 10 ppm salt treatment. Activities of PAL in the callus increased progressively with the increasing salt concentrations. Increased PAL activity in the leaf callus was linearly and positively correlated with increasing NaCl concentrations and the peak activity in the leaf callus was observed at NaCl concentration of 20 ppm.
Rauwolfia serpentina, in vitro, callus induction, salinity stress, phenolics, SOD, PAL
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/143173850
IDR: 143173850
Текст научной статьи Elucidating the effect of salinity stress in enhancing the phenolic acid content in Rauwolfia Serpentina in vitro
Rauwolfia serpentina or 'sarpagandha' is an evergreen, flowering plant in the family Apocynaceae. This plant is used medicinally both in the Modern Western Medical system and also in Ayurveda, unani and folk medicine (Dey et al., 2010). Rauwolfia serpentina contains several bioactive chemicals and rich source of phenolics. The major alkaloid present in root, stem and leaves of the plant is Reserpine varies from 1.7 to 3.0 %.
In vitro propagation offers not only a means for mass multiplication of existing germplasm stocks, but also for the conservation of important elite and RET (rare, endangered & threatened) species which are facing the danger of extinction.
Plant responses to salinity stress have shown that there are protein pattern changes along with biological changes in the adaptation process which makes the plant more fit to the altered environment (Mohammad et al., 2010). Salinity stress in Rauwolfia can lead to increase in its phenolic compounds. Increase in polyphenol content in different tissues under increasing salinity has also been reported. The total phenolic content increased in Rauwolfia with moderately saline level. (Larsen et al ., 1993). Phenolic compounds play important role in plant driven antioxidant activity which is due to their redox properties, permit them to act as reducing agents, hydrogen donors, singlet oxygen quenchers or metal chelators. (Kujala et al., 1999).
In the present study an attempt is made to increase the phenolic acid content of the plant, Rauwolfia serpentina by the in vitro application of salinity stress. Rauwolfia releases many phenolic compound and alkaloids which are responsible for its antioxidant activity.Thus our aim is to increase the antioxidant activity of the plant with application of salinity stress. Besides this Rauwolfia is an endangered species and it has low seed germination rate. Seed germination (1520%) was observed in Rauwolfia, but only 10-13% plant development from the germinated seeds. Generic nature of plant plays a major role in defining the quantity of active principles. This plant is of medicinal importance due to secondary metabolites. Cultivation and production of secondary metabolites is constant under standard conditions. Hence production of plant by tissue culture method will be helpful in producing the plants of specific type of significant importance.
Antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), peroxidase (POD) and catalase (CAT) have been considered as a defensive team, whose combined purpose is to protect cells from oxidative damage (Mittler et al., 2002).
Keeping the above facts in mind, the present investigation was undertaken with the following objectives: Optimization of callus induction from leaf and shoot explants of Rauwolfia serpentina, in vitro application of salinity stress in callus of Rauwolfia serpentina, elucidating the effect of antioxidant properties.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Callus induction from leaf and shoot explants
Young leaf and internodal region of stem Rauwolfia serpentina are used as explant..The samples are rinsed with water for 30 minutes followed by washing with 1.0% solution of Tween-20 for 25 minutes. Explants were rinsed properly until the detergent was completely washed out. Explants were treated with 0.1 % bavistin to prevent fungal contamination. Finally, the explants were treated with the 70% ethanol for one minute followed by 0.1% sodium hypochlorite for 3-5 minute. After each treatment, explants were rinsed three times with sterilized double distilled water. Murashige and Skoog medium was used as basal medium fortified with 3% (w/ v) sucrose, 100 mg/l myoinositol, 0.5 mg/l nicotinic acid, 0.5 mg/l pyridoxine-HCl, 2.0 mg/l glycine, 0.1 mg/l thiamine along with auxins and solidified with 0.8% agar. Plant growth regulators were added to the medium. Stock solutions are prepared for BAP (6-Benzylaminopurine) (1 mg/l) and 2, 4 –D (2mg /l). The pH of the medium was adjusted to 5.8 and solidified with 0.8% (w/v) agar–agar was added prior to autoclaving at 121°C for 15 min.
The culture was then inoculated using leaf and stem explants under sterile conditions in laminar air flow. The cultures were incubated under controlled conditions at 25 ± 2°C, 60 ± 10% relative humidity and 61/8-h photoperiod provided by white fluorescent lamps.
In vitro application of salinity stress in callus of Rauwolfia serpentina
NaCl was supplemented at different concentrations (10 ppm, 15 ppm, 20ppm) in MS medium to analyze the effect of salinity on callus induction. Calli grown in the medium fortified with 2,4-D, BAP were maintained as controls and NaCl was added in the same medium at 10 ppm, 15 ppm and 20 ppm. For each treatment, callus were subcultured into 3 jam bottles.
Estimation of Superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity
The superoxide dismutase activity (SOD activity) was estimated in the callus in vitro . (Gianopolitis and Reis , 1997). 1 unit of SOD activity is defined as the amount of enzyme required to cause 50% inhibition of NBT photoreduction rate and is expressed as U mg-1 of fresh weight. For the extraction of superoxide dismutase 0.01 g callus sample was taken in an ice cooled mortar and pestle to which 4 ml ice cold extraction buffer was added. Then the mixture was homogenized and the homogenate was filtered through muslin cloth. The filtrate was then centrifuged at 16,000 g for 15 min at 4 °C. Then the supernatant obtained was used as crude enzyme extract for quantification of enzyme activity.
50 μl of enzyme extract was added to 1.5 ml reaction mixture (50 mM Phosphate buffer (pH 7.8) 0.1 μM EDTA, 13 mM Methionine, 75 μM NBT, 2 μM Riboflavin) and the tubes were shaken and were illuminated with two 20W fluorescent tubes. The reaction was allowed to proceed for 15 minutes. Then the light was switched off and the tubes were covered with a black cloth and the absorbance was recorded at 560 nm.
Estimation of Phenyl alanine ammonia lyase (PAL) activity
The phenyl alanine ammonia lyase activity (PAL activity) was estimated in vitro in the callus (Edwards and Kessmann, 1997).For the extraction of enzyme 0.01 g of callus sample was crushed in liquid nitrogen and extracted with 2 ml ice cold extraction buffer. Then the resultant slurry was centrifuged at 10,000 g for 15 min at 4°C. The supernatant was used as crude extract for enzymatic analysis. For estimation of enzyme activity 200 μl of enzyme extract was mixed with 800 μl of 0.05 M Tris-Cl (pH 8.8) containing 0.2 mM phenyl alanine as substrate, and the reaction mixture was incubated at 37 °C for 60 min. Then the reaction was stopped by adding 200 μl of 0.5 M HCl. Then cinnamic acid formed was extracted with 2 ml of toluene and the OD was recorded at 290 nm with toluene as blank.
Estimation of total phenolics content
Phenols were estimated in the callus (Sadasivam and Manickam , 1997). 0.01 g callus sample was grinded in 5 ml 80% methanol. The extract was agitated at 70ºC for 15 minutes. Now this methanolic extract was used for estimation of total phenols. To the 1 ml sample 5 ml distilled water was added to make the final volume 6 ml. To this 250 μl Folin’s reagent was added and the mixture was incubated for 3 min at room temperature. After incubation, 1 ml 20% sodium carbonate and 1 ml distilled water were added and the solution was incubated for 1 hr at room temperature. Absorbance was recorded at 725 nm. The amount of total phenols was estimated from the standard curve and expressed as mg GA g-1 FW.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Optimization of different growth regulators in MS media for callus induction in leaf and stem tissue of Rauwolfia serpentina.
Callus is an unorganized mass of plant cells and its formation is controlled by growth regulating substances present in the medium (auxins and cytokinins). MS medium containing agar (0.8%), 3.0% sucrose (w/v) and different concentration and combination of plant growth regulators like 2,4-D and BAP were tested for callus initiation ( Table 1 ).No callus induction was observed when only BAP was applied either to stem or leaf tissues. In the media supplemented with BAP and 2, 4-D, the leaf segments remain green for long period.
The callus was induced with the combination of 2,4-D and BAP in all the four applied concentrations 1.0 +1.0, 1.5 + 1.5, 2.0 +1.0, 2.0 +1.5 (mg/l) respectively, on leaf tissues. The best results of callus induction were observed with 2,4–D (2.0 mg/l) and BAP (1.0 mg/l). The callus formed was green and relatively dry. However other two combinations: (2,4-D) 1.5 + 1.5 (BAP) (mg /l) and (2,4-D) 1.0 + 1.0 (BAP) (mg /l) also produced better results. Small fragile creamish green callus is observed.
The callus was induced in nodal explants in MS medium supplemented with (1.0 or 1.5 mg/l) BAP + (1.0 or 1.5 mg/l) of 2,4-D. Two weeks old callus, was sub cultured in the same medium for its proliferation. Excellent loose textured friable callus was obtained after 3-4 weeks of subculture. The callus was achieved under the influence of 2, 4-D and BAP hormones at the rate of 2.0 + 1.0 (mg/l), 2.0 + 1.5 (mg/l) respectively (Figure 14).
Antioxidant assay
Elucidating the effect of salinity stress on Phenolic acid content.
Rauwolfia is a good source of phenolic antioxidant compounds. The antioxidant activity of phenolic compounds can play an important role in neutralizing ROS (Zheng and Wang , 2001). The main function of phenolic is to maintain the stable concentration of free radical by producing and scavenging them and cinnamic acid can be diverted into numerous other their physiological function may be shown by regulation phenolic or flavonoid compounds (Evans et al., 1997).
There is enhancement in phenolic compounds after treatment of leaf callus with moderate salinity (15 ppm).Total phenolic concentration increased from 2.3 (mg GA g-1 FW) to 3.97 (mg GA g-1 FW) in 10 ppm and 15 ppm salt treatment respectively. In contrast, at higher salinity (20 ppm), the accumulation of these compounds declined (2.5 mg GA g-1 FW). After 10 days, by increasing of salt concentration from 10 ppm to 15 ppm, phenolic contents were significantly increased by 17.2 % (3.7 mg GA g-1 FW to 4.34 mg GA g-1 FW). However, at higher salinity polyphenol concentration was diminished (Table 2).Similar results were obtained after 15 days, maximum phenolic activity (5.20 mg GA g-1 FW) was recorded at 15 ppm. The concentration of phenolics were less in control. As a result the amount of polyphenols in leaf were maximal at 15 ppm.
We observed a correlation between the phenolic content and antioxidant activity. The close correlation between antioxidant activity and phenolic content has been demonstrated by the other workers (Naciye et al., 2008). A significant linear correlation was found between the values for the concentration of phenolic compounds and the antioxidant activity of extracts from M. Peregrinum (Stankovic 2011) An increase in total phenolic content and antioxidant activity of Rauwolfia under salinity can reduce salinity stress.
Elucidating the effect of salinity on Superoxide Dimutase (SOD) activity
SOD is considered as a key enzyme in the antioxidant defence system as it regulates the concentration of O2- and H 2 O 2 . Different levels of SOD activity might occur depending on stress intensity, species or genotype, growth conditions, stress period, plant age (Sgherri et al., 2000). In this study, the activities of antioxidant enzyme, SOD showed a progressive increase in callus with increasing salinity (Table 3). The activities of SOD were markedly higher at 20 ppm NaCl. For example, leaf callus showed a significantly increased activity of SOD by 23.3 % at 20 ppm (NaCl) after 5 days of treatment treatment compared to control. Similar results were recorded after 10 days and 15 days. The SOD activity was highest at 20ppm (16.66 units/mg protein) followed by 15 ppm (14 units/mg protein) and 10 ppm (11.66 units/mg protein) salt treatment after 10 days. Even after 15 days, highest SOD activity was recorded at 20 ppm in callus (20 units/ mg protein) compared to control and other salt treatments.
Considering the changes in SOD activity , these results suggest a possibility that increased SOD activities might enable plants to protect themselves against salt stress. This also correlates with work of (Franck et al . 1995) on Prunus . Similar results were reported in cotyledons and hypocotyls of Jatropha curcas seedlings when subjected to salinity (Chen et al., 1999). SOD production is one of the stress confrontation systems under oxidative stress that is activated in drought and salinity conditions (Zaefyzadeh et al., 2009). Many studies found a positive correlation between salt stress and the abundance of SOD in plants cells (Cavalcanti et al., 2007). Results in published reports also indicate that SOD overexpression may be involved in the increase of stress protection observed in some transgenic plants (Yiu and Tseng , 2005).
Elucidating the effect of salinity on Phenylalanineammonialyase (PAL) activity
PAL, a key enzyme in the phenylpropanoid pathway, is involved in the defence response of plant cells. The determination of PAL enzyme activities should be explained during the stress to obtain a better understanding of how resistant and sensitive varieties differ in their response (Hura et al., 2008). Thus, PAL has been generally recognized as a marker of environmental stress in different plant species (MacDonald and D’Cunha, 2007).
Effects of salinity on PAL activity in the callus were shown in (Table 4.) . The PAL activity was highest at 20ppm (1.2 units/mg protein) followed by 15 ppm (1.35 units/mg protein ) and 10 ppm (1.9 units/mg protein) after 5 days. Activities of PAL in the callus increased progressively with the increasing salt concentrations after 10 days. They increased by 53.3%, 132.5% and 233.3 % at salt concentrations of 10 ppm, 15 ppm and
20 ppm compared to the control, respectively. Final levels of PAL activity were higher than the initial levels when data was recorded after 15 days. The highest activity in PAL increased by 184.2 % at NaCl concentration of 20 ppm in comparison to control.
There is increase in PAL activity in response to salinity. Thus, a positive correlation has been found between values of PAL activity and salinity . Similar results were reported in Paulownia elongate , PAL activity was enhanced by three times with increasing salinity levels (Miladinova et al., 2008) . The present findings suggested that the enhancement of PAL activity in callus of Rauwolfia serpentina could be related to the implication of this enzyme in the plant response to salt stress.
Table 1. Effect of different phytohormonal combinations (2,4-D + BAP) on callus induction in leaf and stem tissues of R. serpentina .
|
S.No |
Type of explant |
Growth Regulators (mg/l) |
Callus Induction Status |
Nature of Callus |
|
|
2, 4-D |
BAP |
||||
|
1 |
Leaf |
1.0 |
1.0 |
++ |
Light green callus, fragile |
|
2 |
Leaf |
1.5 |
1.5 |
++ |
Creamish green, Fragile |
|
3 |
Leaf |
2.0 |
1.0 |
+++ |
Dark green callus |
|
4 |
Leaf |
2.0 |
1.5 |
+ |
Initiation of callus |
|
5 |
Stem |
1.0 |
1.0 |
+ |
Initiation of callus |
|
6 |
Stem |
1.5 |
1.5 |
+ |
Initiation of callus |
|
7 |
Stem |
2.0 |
1.0 |
++ |
Creamish green, fragile callus |
|
8 |
Stem |
2.0 |
1.5 |
++ |
Brownish, fragile callus |
Table 2. Effect of salinity stress on phenolic content in callus of Rauwolfia serpentina at different intervals of days.
|
S.No |
Days after treatment |
salinity |
Phenolic acid content (mg GA g-1 FW) at different NaCl concenterations |
|||
|
Control |
10 ppm |
15 ppm |
20 ppm |
|||
|
1 |
5 |
1.2 |
2.3 |
3.97 |
2.5 |
|
|
2 |
10 |
3.21 |
3.7 |
4.34 |
3.80 |
|
|
3 |
15 |
3.5 |
4.09 |
5.20 |
4.5 |
|
Table 3. Effect of salinity stress on Superoxide dimutase in callus of Rauwolfia serpentina at different intervals of days.
|
S.No |
Days after salinity treatment |
Superoxide Dimutase activity units/mg protein) at different NaCl concenterations |
|||
|
Control |
10 ppm |
15 ppm |
20 ppm |
||
|
1 |
5 |
6 |
7.2 |
8 |
8.4 |
|
2 |
10 |
8.33 |
11.66 |
14 |
16.66 |
|
3 |
15 |
10.27 |
12.33 |
16.9 |
20 |


Figure 4: Callus from stem explants in MS media supplemented with 2,4-D (2.0 mg/l) and BAP (1.5 mg/l) after 5 weeks of culture.
Figure 3: Callus from stem explants in MS media supplemented with 2,4-D (2.0 mg/l) and BAP (1.0 mg/l) after 5 weeks of culture.
Table 4. Effect of salinity stress on Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase activitiy (PAL) in callus of Rauwolfia serpentina at different intervals of days.
|
S. No |
Days after salinity treatment |
Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase activity (unit /mg protein) at different NaCl concentrations |
|||
|
Control |
10 ppm |
15 ppm |
20 ppm |
||
|
1 |
5 |
1.2 |
1.5 |
1.64 |
2.4 |
|
2 |
10 |
1.35 |
2.07 |
3.14 |
4.5 |
|
3 |
15 |
1.9 |
2.28 |
3.99 |
5.4 |
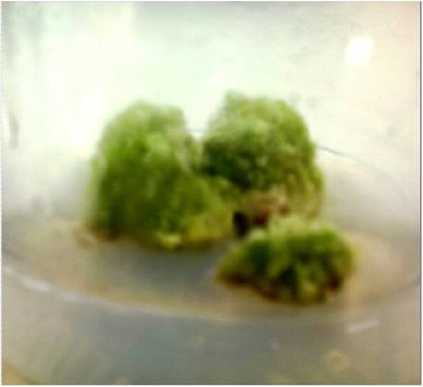
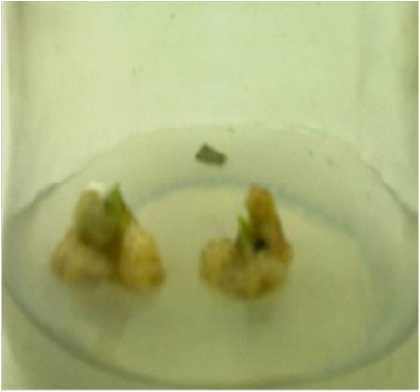
Figure 2: Callus from leaf explants in MS media supplemented with 2,4-D (1.5 mg/l) and BAP (1.5 mg/l) after 5 weeks of culture.
Figure 1 : Callus from leaf explants in MS media supplemented with 2,4-D(2.0 mg/l) and BAP(1.0 mg/l) after 10 weeks of culture
CONCLUSION
Rauwolfia serpentina is a medicinally famous herb used for various medicinal purposes. As Rauwolfia is an endangered species and it has low seed germination rate (15% - 20%) therefore an efficient protocol for callus induction of an important medicinal plant, R. serpentina, is developed in this study by optimization of various growth regulators and media. The best condition is obtained from leaf and stem explants cultured on MS medium supplemented with 2, 4 – D (2.0 mg/l) and BAP (1.0 mg/l). These results may facilitate large-scale multiplication and conservation of R. serpentina, leading to increased plant materials to produce active compounds from this species.
The high contents of phenolic compounds was recorded at moderate salinity level. There were significant increase in superoxide dismutase (SOD) antioxidant enzymes in Rauwolfia callus when exposed to salinity stress. A positive correlation between salt stress and the abundance of SOD in the callus of Rauwolfia has been found. The PAL activity was highest at 20ppm (higher salinity). Thus increase in PAL enzyme activity leads to increase in phenolic content. Such tests would be useful for elucidating the salt tolerance mechanisms of Rauwolfia serpentina plant, and may provide useful bioassays that help to devise strategies for reducing the risks associated with salinity toxicity.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
All authors have declared that they do not have any conflict of interest for publishing this research.
Список литературы Elucidating the effect of salinity stress in enhancing the phenolic acid content in Rauwolfia Serpentina in vitro
- Cavalcanti, F. R., Lima J. P., Ferreira, S. L., Viégas, R. A. and Silveira J. A. (2007). Roots and leaves display contrasting oxidative response during salt stress and recovery in cowpea. J. Plant Physiol. 164: 591–600.
- Chen, C. N. and Pan, S. M. (1999). Assay of superoxide dismutase activity by combining electrophoresis and densitometry. Bot. Bull. Acad. Sin. 37: 107–111.
- Dey, A. and De, J. N. (2010). Ethnobotanical aspects of Rauwolfia serpentina Benth. ex Kurz. in India, Nepal and Bangladesh. J. Med. Plant Res. 5: 144-150.
- Edwards, R. and Kessmann, H. (1997). The effect of plant age and nodulation on the isoflavonoid content of red clover. Journal of Plant Physiology. 150 : 603–610.
- Franck, T., Kevers, C. and Gasper, T. (1995). Protective enzymatic systems against activated oxygen species compared in normal and hyperhydric shoots of Prunus avium raised in vitro. Plant Growth Regul. 16: 253-256.
- Giannopolitis, C. N. and Ries, S.K. (1997). Superoxide dismutases occurrence in higher plants. Plant Physiol. 54: 309-314.
- Hura, T., Hura, K. and Grzesia, S. (2008). Contents of total phenolics and ferulic acid and PAL activity during water potential changes in leaves of maize single cross hybrids of different drought tolerance. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 194: 104-112.
- Kujala, T. S., Kahkonen, M. P., Hopia, A. I., Vuorela, H. J., Rauha, J. P. and Pihlaja, K. (1999). Antioxidant activity of plant extracts containing phenolic compounds. Journal of Food Chemistry. 47: 3954-3962.
- Larsen, J. C., Strube, M. and Dragstedt L. O. (1993). Naturally Occurring Antitumourigens, Plant Phenols. The Nordic Council of Ministers, Copenhagen. 12: 39-40.
- MacDonald M. J. And Cunha, G. B. (2007). A modern view of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase. Biochem. Cell Biol. 85: 273–282.
- MacDonald M.J., D’Cunha G.B. (2007), A modern view of phenylalanine ammonia lyase Biochemistry and Cell Biology, 85: 273-282
- Miladinova, K., Ivanova, K., Georgieva, T., Geneva, M. and Markovska, Y. (2008). Influence of salt stress on ex vitro growth and antioxidative response of two Paulownia clones. Acad. Georgi Bonchev str. 21: 113.
- Mittler, R. (2002). Oxidative stress, antioxidants and stress tolerance. Trends Plant Sci. 7: 405–410.
- Mohammad, A. A. and Mohammad, A. A. (2010). Effect of salt stress on some defensive mechanism of transgenic and wild varieties grown in vitro. Nature and Science. 8(12) : 181-193.
- Naciye, E., Guler, A. and Erol, A. (2008). Antioxidant activity of rosemary extract, blackseed essential oil , carnosic acid, rosamarinic acid and sesamol., Food chem.,. 110(1): 76-82.
- Rice–Evans, C. A., Miller, N. J. and Paganga, G. (1997). Antioxidant properties of phenolic compounds. Trends Plant Sci. 2: 152-159
- Sadasivam S, Manickam A (1996) Methods in Biochemistry, 2nd edn., editors: Sadasivam S., Manickam A., New Age International Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi pp. 185-189.
- Sgherri, C. M., Maffei, M. and Navari-Izzo, P. (2000). Antioxidative enzymes in wheat subjected to increasing water deficit and rewatering. J. Plant Physiol. 17: 273-279.
- Stanković, M. (2011).Total phenolic content, flavonoid concentration and antioxidant activity of Marrubium peregrinum. Kragujevac J. Sci. 33: 63-72.
- Yiu, J. C. And Tseng, M. J. (2005).Manipulation of superoxide dismutase and catalase exhibit enhanced sulfur dioxide tolerance in transgenic Chinese cabbage. Acta Hortic. 692: 91–99.
- Zaefyzadeh, J. A., Quliyev, R. A. and Babayeva, S. M. (2009). The effect of the interaction between genotypes and drought stress on the superoxide dismutase and chlorophyll content in Durum wheat landraces. Turk J. Biol. 33: 1-7.
- Zheng, W. and Wang, S. Y. (2001). Antioxidant activity and phenolic compounds in selected herbs. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 49: 5165–5170.


