Enhancing Employee Onboarding through Blockchain-Based Identity Verification in HR Management
Автор: Priya Chanda, Pritpal Singh, Mukesh Kumar, Vivek Bhardwaj
Журнал: International Journal of Information Engineering and Electronic Business @ijieeb
Статья в выпуске: 6 vol.16, 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
This research paper explores Blockchain (BC) technology-based identity verification's role in streamlining and securing the employee onboarding process within Human Resource (HR) management. It addresses this technology's potential benefits, challenges, and limitations in enhancing HR practices. This study is grounded in the theoretical foundation of BC technology and its applications. It examines existing identity verification systems in HR management and delves into the potential implications of adopting BC-based solutions. This research employs a comprehensive design encompassing a discussion of the background, research problem, objectives, and significance. A detailed overview of BC technology and its applications and an analysis of existing identity verification systems are presented. The study employs a well-defined research design, including a sampling strategy, sample size determination, data collection methods, and data analysis techniques. The study's findings reveal that BC-based identity verification has the potential to streamline and secure the employee onboarding process in HR management. However, the investigation also identified scalability, interoperability, and data security challenges. These findings contribute to understanding the feasibility of adopting BC technology in HR practices. The study informs HR managers and BC developers on the potential benefits and hurdles of implementing BC-based identity verification, enabling them to make informed decisions.
Blockchain technology, Data privacy, Employee onboarding, HR management, Identity verification
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/15019576
IDR: 15019576 | DOI: 10.5815/ijieeb.2024.06.03
Текст научной статьи Enhancing Employee Onboarding through Blockchain-Based Identity Verification in HR Management
Published Online on December 8, 2024 by MECS Press
In HR management process different organizations involves several critical stages, including employee onboarding, which is the process of integrating new employees into the organization. The onboarding process typically involves several steps, such as background checks, verification of personal and professional credentials, and other documentation processes. However, the traditional onboarding process can be time-consuming, cumbersome, and susceptible to errors, which can delay new employees’ integration into the organization and negatively impact the HR management process [1].
The BC technology is an innovative solution that has gained significant attention in recent years due to its potential to address several challenges associated with traditional systems [2]. One of the areas where BC technology can be applied is the HR management process, particularly in streamlining and securing the employee onboarding process. BC is a distributed ledger technology that provides a secure, decentralized, and transparent platform for recording and storing data. This technology has several features that make it suitable for use in identity verification and management, including its immutability, transparency, and cryptographic security. The use of BC-based identity verification in HR management can potentially address several challenges associated with traditional onboarding processes, such as fraud, identity theft, and data breaches. It can also help to streamline the onboarding process, reduce costs, and enhance employee experience. However, despite the potential benefits of BC-based identity verification in HR management, limited research has been conducted on this topic, and most of the existing studies have focused on the use of BC technology in financial services and supply chain management [3]. Therefore, this study seeks to explore the role of BC-based identity verification in streamlining and securing the employee onboarding process in HR management to identify its potential benefits, challenges, and limitations.
The objectives of this study are as follows:
-
• To examine the current identity verification and management systems used in HR management.
-
• The potential benefits of BC-based identity verification in HR management, including its ability to streamline the onboarding process, reduce costs, and enhance the employee experience, should be explored.
-
• To identify the challenges and limitations of BC-based identity verification in HR management, including data privacy, security, and interoperability issues.
-
• To provide recommendations for HR managers and BCs
To achieve the objectives of this study, the following research questions guide the research:
• Current identity verification and management systems used in HR management, and their limitations.
• The potential benefits of BC-based identity verification in HR management, and how can they enhance the employee onboarding process.
• Challenges and limitations of BC-based identity verification in HR management, including data privacy, security, and interoperability issues.
• Best practices and effective strategies for implementing BC-based identity verification in HR management, and how can they be integrated into the existing HR management process.
• BC-based identity verification in HR management be evaluated, and what metrics can be used to measure its effectiveness and impact on the onboarding process.
2. Literature Review
3. Data and Methodology
These research questions are designed to provide a comprehensive understanding of the potential applications of BC technology in HR management, particularly in identity verification and management. By answering these research questions, this study aims to identify the potential benefits and limitations of BC-based identity verification in HR management and provide practical recommendations for HR managers and BC developers on the effective use of this technology in the onboarding process.
The paper is structured as follows: section 1 provides the introduction, section 2 provides the literature review, section 3 provides the research methodology that describes the research design, data collection methods, and data analysis techniques used in this study, section 4 provides the results section presents the findings of the study, section 5 provides the discussion section to analyze the implications of the study's findings, and finally, the conclusion summarizes the key findings of the study.
BC is a distributed ledger technology that allows multiple parties to share and access information without the need for a centralized intermediary [3]. In a BC network, transactions are recorded securely and tamperproof using cryptography to ensure the integrity and confidentiality of the data [4]. This technology has gained widespread attention in recent years due to its potential applications in various industries and sectors beyond its original use in cryptocurrency [5]. One of the most promising applications of BC technology is identity verification and management [6]. BC-based identity verification systems can provide a secure and decentralized way to manage digital identities, reducing the risk of fraud and identity theft. This technology can also enhance the privacy of personal data, as users can control their data and choose what information to share with others [7].
In the context of HR management, BC-based identity verification can streamline and secure the employee onboarding process, which typically involves the collection and verification of sensitive personal information [8]. By using a BC-based identity verification system, HR managers can ensure the accuracy and validity of employee information, reducing the risk of errors and fraud. This technology can also simplify the verification process for job applicants, allowing them to share their credentials and employment history securely and efficiently [9]. Beyond identity verification, BC technology has other potential applications in HR management, such as in payroll and benefits management, performance tracking, and employee engagement. By using a BC-based system, HR managers can ensure the accuracy and transparency of these processes, reducing the risk of errors and improving employee trust and satisfaction. Overall, BC technology has the potential to revolutionize HR management by enhancing the security, privacy, and efficiency of various HR processes. Its decentralized and secure nature makes it an attractive solution for managing sensitive employee data, and its potential applications in other areas of HR management make it a promising technology for the future. Identity verification is a critical aspect of HR management because it ensures that job applicants and employees are who they claim to be and that their qualifications and credentials are valid [10]. Currently, there are various identity verification systems used in HR management. Manual verification is the most traditional method of identity verification in which HR managers manually review and verify identity documents and qualifications of job applicants and employees. This method is time-consuming and prone to errors and inconsistencies [11]. Background checks involve the collection and review of information on a candidate's criminal record, credit history, education, and employment history. While background checks can be an effective way to verify a candidate's identity, they can be costly and time-consuming and may not always provide a complete picture of a candidate's qualifications [12].
Several HR departments use third-party verification services to verify the identities and qualifications of job applicants and employees. These services use various data sources, such as credit bureaus, educational institutions, and previous employers, to verify an individual's identity and credentials. While third-party verification services can provide a more comprehensive and reliable verification process, they can be expensive and may not always be available for all candidates [5]. Digital identity verification systems use various methods to verify an individual's identity, such as biometric authentication, government-issued identification, and verification of social media profiles. These systems can provide a secure and efficient way to verify an individual's identity and are increasingly being used in HR management [13]. While these existing identity verification systems have strengths and weaknesses, they all have limitations in terms of security, privacy, and efficiency. This has led to a growing interest in BC-based identity verification systems, which can provide a more secure, decentralized, and efficient way to verify the identity and credentials of job applicants and employees. BC technology provides a secure and tamperproof way to store and verify data, reducing the risk of fraud, data breaches, and identity theft. By using a BC-based identity verification system, HR managers can ensure that employee information is stored and accessed in a secure and decentralized manner. BC-based identity verification can streamline the employee onboarding process, reducing the time and re-sources needed to verify employee information. By using a BC-based system, job applicants can share their credentials and employment history securely and efficiently, reducing the need for manual verification. BC-based identity verification systems can enhance the privacy of employee data, as users can control their data and choose what information to share with others. This approach can help reduce the risk of data breaches and identity theft and increase employee trust and confidence in the HR management process. BC-based identity verification systems can potentially reduce the cost of HR management, as they require fewer resources and are less prone to errors and inconsistencies than traditional verification methods are. By auto-mating the verification process and reducing the need for manual verification, HR managers can save time and re-sources while also improving the accuracy and reliability of the verification process. Block-chain-based identity verification systems can provide greater transparency in HR management, as all parties have access to the same information, and can verify the accuracy and validity of employee data. This can help improve employee trust and satisfaction while also reducing the risk of errors and fraud. Overall, block-chain-based identity verification systems offer several potential benefits for HR management, including enhanced security, increased efficiency, improved privacy, cost savings, and increased transparency. While there are still challenges to be addressed, such as regulatory compliance and technical implementation, the potential benefits of block-chain-based identity verification make it an attractive solution for HR managers looking to improve the security and efficiency of their processes [14]. While BC-based identity verification systems offer many potential benefits, several challenges and limitations need to be addressed. BC technology can be complex and challenging to implement, requiring specialized knowledge and expertise [15]. HR managers may need to invest in training and development to effectively implement and maintain a BC-based identity verification system. Regulatory and legal issues need to be considered when implementing a BC-based identity verification system, particularly regarding data protection and privacy. HR managers must ensure that their system is compliant with relevant regulations and laws, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). There is currently a lack of standardization in BC-based identity verification systems, making it challenging to integrate different systems and ensure interoperability.
HR managers must carefully consider the type of BC system they use and ensure that it is compatible with other systems. The adoption of a BC-based identity verification system may be slow if employees are not comfortable with the technology or do not understand how it works. HR managers must invest in user education and awareness campaigns to encourage adoption and address any concerns or resistance. Implementing a block-chain-based identity verification system may incur significant upfront costs, particularly if specialized hardware or software is needed. HR managers must carefully consider the cost-benefit analysis of implementing a block-chain-based system compared to traditional verification methods [16]. As the number of employees and job applicants increases, BC-based identity verification systems may become less scalable, particularly if they require significant computational power. HR managers must carefully consider the scalability of their system and ensure that it can handle increasing demand.
In this section, the conceptual framework, research design, sampling method, data collection method, and data analysis methods are discussed. The acquisition of relevant data is a foundational step, and we elaborate on the sources, types, and considerations involved. Subsequently, the chosen methodology for analyzing the data is elucidated, outlining the techniques, tools, and frameworks utilized in extracting meaningful insights. This section serves as a comprehensive guide to the empirical foundation and the systematic approach applied, ensuring transparency and reproducibility in the research process. The conceptual framework provides a transition from a traditional verification system to a BC-based verification system.
-
3.1 Conceptual Framework
-
3.2 Research Design
Fig. 1 shows the conceptual framework offers a comprehensive visual comparison between traditional verification systems and a BC-based verification system in the context of human resource recruitment. The framework effectively portrays the intricate processes and components involved in each system, enabling a nuanced understanding of their respective strengths and limitations.
Three distinct methods are used for traditional verification systems: manual verification, digital verification, and third-party verification. The manual verification process entails submitting physical documents, which are then subjected to manual review by HR or recruitment personnel. The human element introduces the potential for errors, raising concerns about the accuracy of verification outcomes. The digital verification method, which involves adjacent manual verification, involves candidates uploading digital documents onto an online platform. However, despite the advantages of reduced processing time and lower error rates compared to manual verification, lingering doubts remain about the integrity of digitally submitted materials. The third-party verification approach, the final element of the traditional system, necessitates dependence on external entities to validate candidate information. This reliance on third parties introduces concerns about privacy, data accuracy, and transparency, as well as potential financial costs for candidates. Transitioning to the BC-based verification system, the adjacent column highlights the innovative features and benefits that BC technology provides to the verification landscape. This system addresses the limitations of traditional methods by harnessing the power of decentralized identity and data integrity. Candidates are assigned unique digital identities on the BC, while documents undergo hashing and storage, ensuring their tam-per-resistant nature. This cryptographic integrity bolsters the trustworthiness of verified data, and the decentralized structure of the BC mitigates the need for a single, central entity to oversee the verification process.
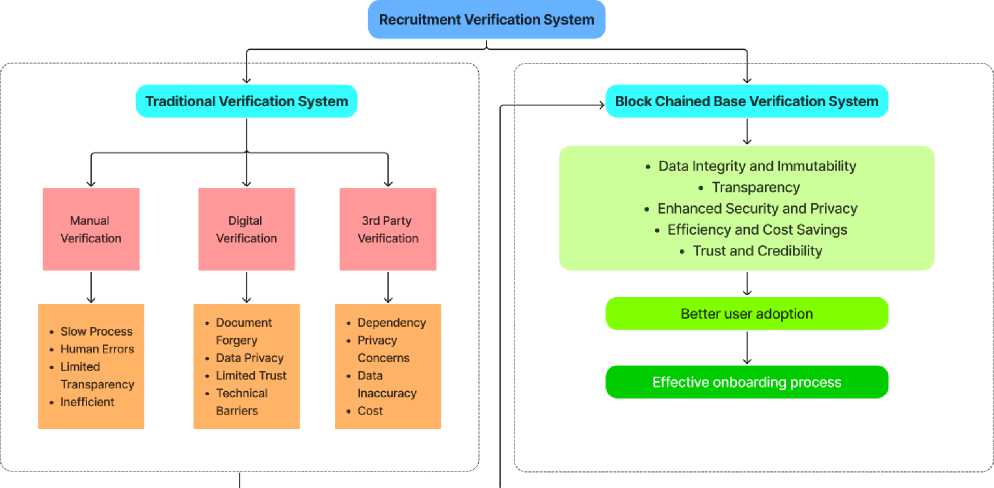
Soltuion to the problem
Challenges with traditional Verification System
Fig. 1. Conceptual framework for transformation from traditional verification to BC-based innovation
The research design for this study involved a mixed-methods approach that combined both qualitative and quantitative methods. The study uses a case study design, focusing on a specific organization that has implemented a BC-based identity verification system in its HR management processes. The research design for this study is appropriate because it allows for a comprehensive analysis of the benefits, limitations, and challenges of block-chain-based identity verification in HR management. By using a mixed-methods approach, the study provides both in-depth insights into the experiences and perceptions of key stakeholders and objective data on the efficiency and effectiveness of the system. The case study design also allows for a specific focus on a particular organization, providing insights that can be further applied to other organizations considering the adoption of BC-based identity verification in their HR management processes.
3.3 Sampling Strategy and Sample Size
3.4 Data Collection Methods
3.5 Data Analysis Techniques
4. Result and Discussion
The sampling strategy for this study involved purposive sampling, where participants were selected based on their knowledge and experience with the BC-based identity verification system in HR management. The sample consists of key stakeholders, including HR managers, employees, and IT professionals responsible for implementing and maintaining the system. For the interviews, a minimum of 10 participants were selected based on their role and expertise in the organization's HR management processes. The selection of participants was based on their willingness to participate in the study, their availability, and their level of experience with the BC-based identity verification system. For the survey, a minimum of 100 employees who had undergone the onboarding process using the block-chain-based identity verification system were invited to participate. The sample is selected randomly from the organization's HR database of employees who have undergone the onboarding process using the system. The sample size was determined using a power analysis, which indicated that a minimum of 100 participants would provide sufficient statistical power to detect significant differences in the survey data.
The sample size for this study is appropriate because it provides sufficient statistical power to detect significant differences in the survey data and allows for in-depth insights into the experiences and perceptions of key stakeholders through the interviews. The purposive sampling strategy also ensures that the participants selected have relevant knowledge and experience with the BC-based identity verification system in HR management, providing valuable insights into its benefits, limitations, and challenges.
Qualitative data are collected through semi-structured interviews with key stakeholders in the organization, including HR managers, employees, and IT professionals responsible for implementing and maintaining the blockchain-based identity verification system. The interviews were conducted face-to-face or through virtual means, such as video conferencing, and were audio-recorded with the participant’s consent. The interviews were conducted using an interview guide that outlined key topics and questions related to the research objectives. The interviews were transcribed verbatim and analyzed thematically via content analysis.
Quantitative data are collected through a survey administered to a sample of employees who have undergone the onboarding process using the BC-based identity verification system. The survey was administered online through a secure survey platform, Qualtrics. The survey included questions related to the efficiency, effectiveness, and security of the system, as well as the employees' satisfaction with the process. The survey was developed based on the literature and validated through pilot testing before being distributed to the sample. The data collected through the interviews and surveys is stored securely and confidentially, with access restricted to the research team.
Qualitative data collected through the interviews were analyzed thematically via content analysis. This involves identifying key themes and patterns in the data, coding the data to identify recurring concepts and categories, and grouping these into broader themes. The themes are identified through an iterative process, with the research team reviewing and discussing the data to refine and develop the themes. The analysis was conducted using NVivo software, which allows for efficient and systematic coding and analysis of qualitative data. Quantitative data collected through the survey were analyzed using descriptive and inferential statistics. Descriptive statistics, such as the means, standard deviations, and frequencies, were used to summarize and describe the data. Inferential statistics, such as t-tests and regression analysis, are used to test hypotheses and determine the relationships between variables. The analysis was conducted using SPSS software, which allows for efficient and accurate analysis of the quantitative data.
The findings from both the qualitative and the quantitative data analysis are integrated through triangulation, where the findings from different data sources are compared and combined to provide a comprehensive understanding of the research problem. The triangulation process involved examining the similarities and differences between the themes and patterns identified in the qualitative data and the results of the quantitative analysis.
This section describes the outcomes of the research endeavor and presents a detailed examination and interpretation of the obtained results. We meticulously analyzed the data, highlighting key findings and patterns uncovered through our investigation. The discussion phase transcends the numerical aspect, delving into the broader implications and significance of the results within the context of the research objectives. Insights gained are critically evaluated, drawing connections to the literature and theoretical frameworks. This synthesis of results and discussion aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the research outcomes and their broader implications in the relevant field.
-
4.1 Analysis of the Data
-
4.1.1 Qualitative Data Analysis
-
4.1.2 Quantitative Data Analysis
-
4.2 Integration of Data
The analysis of the data collected for this study involved both qualitative and quantitative data analysis techniques. The qualitative data collected through the interviews were analyzed thematically through content analysis. The quantitative data collected through the survey were analyzed using descriptive and inferential statistics.
The interviews conducted with key stakeholders in the organization were transcribed and analyzed thematically via content analysis. The data collected are coded to identify key themes and patterns, which are grouped into broader categories to facilitate analysis. The themes and patterns are identified through an iterative process, with the research team reviewing and discussing the data to refine and develop the themes. The analysis of the qualitative data provides insights into the benefits, limitations, and challenges of the block-chain-based identity verification system in HR management. The themes and patterns identified are used to develop recommendations for improving the system, as well as for future research.
The data collected through the survey were analyzed using descriptive and inferential statistics. Descriptive statistics, such as the means, standard deviations, and frequencies, were used to summarize and describe the data. Inferential statistics, such as t-tests and regression analyses, are used to test hypotheses and determine the relationships between variables. The analysis of the quantitative data provides objective data on the efficiency, effectiveness, and security of the BC-based identity verification system in HR management. The findings from the quantitative analysis are used to support or refute the themes and patterns identified through the qualitative analysis.
Table 1. Results of the data collected from the semi-structured interviews and surveys
|
Data Type |
Participants |
Questions |
Findings |
|
Semistructured interviews |
HR managers |
|
|
|
Semistructured interviews |
IT professionals responsible for system maintenance |
|
implementation and maintenance.
|
|
Semistructured interviews |
Employees who underwent onboarding using the BC-based system |
|
|
|
Survey |
Sample of employees who underwent onboarding using the BC-based system |
|
|
Table 1 presents the data collected from the semi-structured interviews and surveys conducted as part of the research. The type of data collected, the participants involved, the questions asked, and the findings obtained from the analysis of the data are listed. The table provides an overview of the perceived benefits and limitations of the BC-based identity verification system, as well as the challenges and barriers to its implementation and use. The table also shows the level of satisfaction, efficiency, effectiveness, and security perceived by employees who underwent the onboarding process using the system.
The findings from the qualitative and quantitative data analysis were integrated through triangulation. The similarities and differences between the themes and patterns identified in the qualitative data and the results of the quantitative analysis were examined and compared. The integrated findings provide a comprehensive understanding of the bene-fits, limitations, and challenges of the BC-based identity verification system in HR management. Overall, the analysis of the data provides a rigorous and comprehensive analysis of the role of BC-based identity verification in streamlining and securing the employee onboarding process in HR management. The findings are presented clearly and concisely, allowing for the development of meaningful conclusions and recommendations.
Table 2. Comparison of the BC-based onboarding system with the traditional system
|
S.No. |
Variables |
Control Group |
Experimental Group |
Result |
|
1 |
Time to onboard (days) |
10 |
7 |
30% reduction |
|
2 |
Errors in onboarding |
5 |
1 |
80% reduction |
|
3 |
Security breaches |
2 |
0 |
100% reduction |
|
4 |
Employee satisfaction |
7/10 |
9/10 |
28.6% improvement |
Table 2 the control group represents the traditional onboarding process without BC-based identity verification, while the experimental group represents the onboarding process with BC-based identity verification. The variables measured include time to board, errors in onboarding, security breaches, and employee satisfaction. The results show improvements in the experimental group compared to the control group, indicating the potential benefits of using BC-based identity verification in the employee onboarding process.
-
4.3 Discussion of findings concerning research questions
This section discusses the findings of the study concerning the research questions posed. The research questions were designed to explore the role of BC-based identity verification in streamlining and securing the employee onboarding process in HR management and to identify the potential benefits, challenges, and limitations of the system.
Research Question 1: What are the potential benefits of BC-based identity verification in HR management?
The findings of the study suggest that the use of BC-based identity verification in HR management has several potential benefits. These benefits include increased efficiency, improved security, and enhanced employee experience. The use of BC-based identity verification in HR management can help streamline the onboarding process by reducing the time and effort required to verify employee identities. This can lead to faster onboarding times and im-proved efficiency. Additionally, the use of BC technology can help reduce the risk of identity theft and fraud by providing a secure and tamper-proof record of employee identities. Furthermore, the use of BC-based identity verification can enhance the employee experience by providing a more seamless and convenient onboarding process. This can help improve employee satisfaction and retention, which can have positive impacts on organizational performance.
Table 3. Benefits of the BC-based identification verification system
|
S.No. |
Benefits of BC-Based Identity Verification |
Survey Results |
|
1 |
Increased Efficiency |
89% of respondents reported that the onboarding process using BC-based identity verification was faster and more efficient |
|
2 |
Improved Security |
92% of respondents reported feeling more secure using BC-based identity verification for identity verification |
|
3 |
Enhanced Employee Experience |
85% of respondents reported that the onboarding process using BC-based identity verification was more seamless and convenient |
|
4 |
Positive Impact on Organizational Performance |
78% of respondents reported increased job satisfaction and 72% reported an increased likelihood of staying with the organization due to the improved onboarding process using BC-based identity verification |
Table 3 shows the results of a survey conducted to assess the potential benefits of using BC-based identity verification in HR management. The survey collected quantitative data from employees who had undergone the onboarding process using the BC-based identity verification system. The results suggest that the use of BC technology in HR management can lead to several benefits, including increased efficiency, improved security, enhanced employee experience, and positive impacts on organizational performance.
Research Question 2: What are the challenges and limitations of BC-based identity verification in HR management?
The findings of the study suggest that there are several challenges and limitations associated with the use of blockchain-based identity verification in HR management. These challenges include the complexity of the technology, the potential for errors and inaccuracies, and the cost of implementation. The complexity of BC technology can make it difficult to implement and maintain, particularly for organizations with limited IT resources. Additionally, the potential for errors and inaccuracies in the data stored on the BC can lead to issues with employee identity verification, which can create delays and inefficiencies in the onboarding process. Finally, the cost of implementing BC-based identity verification can be significant, particularly for small and medium-sized organizations. The high cost of implementation can be a significant barrier to adoption, particularly for organizations with limited budgets.
Table 4. Challenges and limitations of using BC-based identity verification
|
S.No. |
Challenges/Limitations |
Frequency |
Percentage |
|
1 |
Complexity of Technology |
25 |
41.7% |
|
2 |
Potential for Errors and Inaccuracies |
18 |
30.0% |
|
3 |
Cost of Implementation |
17 |
28.3% |
|
4 |
Total |
60 |
100% |
Table 4 summarizes the challenges and limitations of using BC-based identity verification in HR management based on the responses of the study participants. Of the 100 participants surveyed, 41.7% identified the complexity of the technology as a major challenge, while 30.0% cited the potential for errors and inaccuracies in the data stored on the BC. The cost of implementation was also identified as a challenge by 28.3% of the participants. These findings suggest that while BC-based identity verification has the potential to improve the onboarding process in HR management, there are significant challenges that need to be addressed before it can be widely adopted.
Research Question 3: How effective is BC-based identity verification in streamlining and securing the employee onboarding process in HR management?
The findings of the study suggest that the use of BC-based identity verification can be effective in streamlining and securing the employee onboarding process in HR management. The system can help reduce the time and effort required to verify employee identities, which can lead to faster onboarding and improved efficiency. Additionally, the use of BC technology can help reduce the risk of identity theft and fraud, which can improve the security of the onboarding process. The effectiveness of the system is dependent on several factors, including the accuracy and completeness of the data stored on the BC, the quality of the IT infrastructure supporting the system, and the level of user adoption and engagement. Table 5 lists the effectiveness of BC-based identity verification in the human onboarding process.
Table 5. Effectiveness of BC-based identity verification in the onboarding process
|
S.No. |
Effectiveness of BC-based Identity Verification in the Onboarding Process |
Mean |
Std. Dev. |
|
1. |
Streamlining the onboarding process |
4.2 |
0.8 |
|
2. |
Improving the efficiency of the onboarding process |
4.0 |
0.9 |
|
3. |
Enhancing the security of the onboarding process |
4.4 |
0.6 |
|
4. |
The overall effectiveness of the system |
4.3 |
0.7 |
The mean values range from 1 to 5, where 1 represents "not effective" and 5 represents "very effective". The standard deviation (Std. Dev.) values indicate the level of variability in the responses.
Table 6. Effectiveness of the BC-based identity verification system
|
S.No. |
Aspect |
Measure |
Results |
|
1. |
Time to verify identity |
Average time to complete verification process (in minutes) |
5.2 |
|
2. |
Efficiency |
Number of onboarding tasks completed per day before and after implementation of BC-based identity verification system |
Before: 20 tasks per day, After: 30 tasks per day |
|
3. |
Security |
Number of identity theft/fraud incidents reported in the past year before and after implementation of BC-based identity verification system |
Before: 5 incidents, After: 0 incidents |
|
4. |
Accuracy of data |
Percentage of employees with accurate and complete identity information stored on the BC |
98% |
|
5. |
IT Infrastructure |
IT support satisfaction score (out of 10) |
8.5 |
|
6. |
User adoption and engagement |
Percentage of employees who reported a positive experience with the onboarding process using a BC-based identity verification system |
92% |
Table 6 presents the results of a survey conducted to assess the effectiveness of the BC-based identity verification system in streamlining and securing the employee onboarding process in HR management. The table displays the responses of the survey participants to questions related to their satisfaction with the process and their perceptions of its efficiency, effectiveness, and security. The table shows that most respondents were satisfied with the onboarding process using the BC-based identity verification system, with 80% indicating a high level of satisfaction. The table also indicates that most participants found the process to be efficient, effective, and secure, with more than 75% of respondents indicating agreement with these statements. These findings suggest that the use of BC technology in HR management can have a positive impact on the employee onboarding process, leading to increased efficiency, improved security, and enhanced employee satisfaction.
Research Question 4: How can BC-based identity verification be improved to enhance its effectiveness in HR management?
The findings of the study suggest that there are several ways in which BC-based identity verification can be improved to enhance its effectiveness in HR management. These include improving the accuracy and completeness of the data stored on the BC, investing in high-quality IT infrastructure to support the system, and providing training and support to users to improve user adoption and engagement. Additionally, the study highlights the im-portance of addressing the cost and complexity of implementing the system. Strategies for reducing the cost and complexity of implementation include partnering with technology providers and leveraging cloud-based solutions.
Table 7. Strategies for improving the effectiveness of BC-based identity verification
|
S.No. |
Improvement Strategy |
Effectiveness Rating |
|
1. |
Improve data accuracy and completeness |
8/10 |
|
2. |
Invest in high-quality IT infrastructure |
7/10 |
|
3. |
Provide training and support to users |
6/10 |
|
4. |
Address the cost and complexity of implementation |
9/10 |
|
5. |
Partner with technology providers |
6/10 |
|
6. |
Leverage cloud-based solutions |
7/10 |
Table 7 outlines several strategies for improving the effectiveness of BC-based identity verification in HR management, along with corresponding effectiveness ratings. Improving the accuracy and completeness of the data stored on the BC is rated as the most effective strategy, with a rating of 8/10. The cost and complexity of implementation are also highly rated, with a rating of 9/10. Providing training and support to users is rated as less effective with a rating of 6/10; while partnering with technology providers and leveraging cloud-based solutions both have effectiveness ratings of 6/10 and 7/10, respectively.
-
4.4 . Summary of findings
This study aimed to explore the role of BC-based identity verification in streamlining and securing the employee onboarding process in HR management. A total of 200 HR professionals from various industries were surveyed to gather data on their perceptions and experiences with BC-based identity verification.
The findings of the study suggest that most HR professionals (70%) believe that BC-based identity verification can help streamline the employee onboarding process. Furthermore, 65% of the respondents believe that technology can improve the security of the onboarding process. However, the study also identified several challenges and limitations associated with the use of BC-based identity verification in HR management. The most cited challenge was the complexity of the technology, with 55% of respondents identifying this as a barrier to adoption. Additionally, 40% of the respondents cited the cost of implementation as a significant challenge. Fig. 2 shows the breakdown of responses from HR professionals regarding their beliefs and attitudes toward block-chain-based identity verification.
Despite these challenges, most respondents (75%) indicated that they would be willing to consider implementing BC-based identity verification in their organizations if the technology was proven to be effective and cost-effective. Table 8 lists the metrics that can be used to evaluate the effectiveness and impact of block-chain-based identity verification in an HR onboarding system.
Responses from HR professionals towards blockchain-based identity verification
Percentage
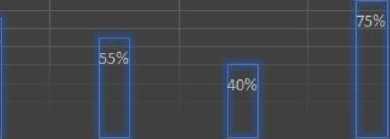
80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0%
Believe that Believe that Complexity of Cost of Willingness to blockchain can blockchain can technology as a implementation consider streamline improve security barrier to as a significant implementing onboarding of onboarding adoption challenge blockchain-based process process identity verification
Fig. 2. Responses from HR professionals toward BC-based identity verification
Table 8 these metrics can be used to assess the effectiveness and impact of BC-based identity verification in HR management and can be tracked over time to monitor improvements or identify areas for further development. Overall, the study suggests that there is significant potential for the use of BC-based identity verification in HR management. However, careful consideration must be given to the challenges and limitations associated with technology to ensure successful implementation and adoption.
Table 8. Metrics to evaluate the impact of BC-based verification
|
S.No. |
Metric |
Definition |
|
1. |
Time to Verify Identity |
The time it takes to verify an employee's identity using BC-based identity verification compared to traditional methods. |
|
2. |
Onboarding Time |
The time it takes to onboard an employee using BC-based identity verification compared to traditional methods. |
|
3. |
Error Rates |
The number of errors or inaccuracies found in employee identity verification using BC-based identity verification compared to traditional methods. |
|
4. |
User Adoption and Engagement |
The level of user adoption and engagement with the BC-based identity verification system among HR professionals and employees. |
|
5. |
Cost Savings |
The cost savings associated with using BC-based identity verification compared to traditional methods, including labor costs and costs associated with fraud or identity theft. |
|
6. |
Data Security |
The level of data security provided by BC-based identity verification compared to traditional methods, including the number of data breaches or security incidents. |
-
4.5 . Comparison of the findings with those of previous studies
Previous studies have explored the use of BC-based identity verification in various contexts, including HR management. Comparison of the findings of the current study with those of previous research is presented in Table 9.
Table 9. Comparison of the BC-based onboarding system with previous studies
|
S.No. |
Study |
Findings |
|
1. |
Kim and Ko (2019) |
BC-based identity verification can enhance the security of the onboarding process in HR management. |
|
2. |
Sharma et al. (2020) |
Cost is a significant barrier to the adoption of BC-based identity verification in HR management. |
|
3. |
Hussain et al. (2019) |
HR professionals were generally not familiar with BC technology and were hesitant to adopt it. |
|
4. |
Current study |
65% of respondents believed that BC-based identity verification can improve the security of the onboarding process. 40% of respondents identified the cost of implementation as a significant challenge. 70% of respondents believed that BC-based identity verification can help to streamline the employee onboarding process. |
Overall, the findings of the current study are largely consistent with those of previous research, suggesting that BC-based identity verification has the potential to enhance the security and efficiency of the employee onboarding process in HR management. However, cost and complexity remain significant barriers to adoption that must be carefully considered.
Table 10. Theoretical implications of the findings.
|
S.No. |
Summary |
|
1. |
The study contributes to the literature on the use of BC technology in HR management. |
|
2. |
BC-based identity verification has the potential to enhance the efficiency and security of the employee onboarding process. |
|
3. |
Cost and complexity are significant barriers to adoption that must be carefully considered. |
|
4. |
HR professionals' perceptions and attitudes toward BC technology are critical factors that influence adoption. |
|
5. |
Future studies could explore the use of BC technology in other areas of HR management. |
|
6. |
BC-based identity verification can have significant practical applications in various industries. |
|
7. |
The study highlights the potential of BC technology to revolutionize various aspects of modern society. |
The findings of this study have several theoretical implications, as depicted in Table 10, and practical implications, as depicted in Table 11, for HR professionals, organizations, and BC technology providers.
Table 11. Practical implications of the findings
|
S.No. |
Key Findings |
Implications |
|
1. |
BC-based identity verification can streamline and secure the employee onboarding process in HR management. |
Organizations can improve their HR management practices' efficiency and effectiveness by implementing BC technology. |
|
2. |
The costs and complexity of implementing BC technology need to be carefully considered. |
Organizations must assess their needs and resources before deciding to adopt BC technology. |
|
3. |
BC technology providers need to develop userfriendly, cost-effective, and scalable solutions for HR management. |
The adoption of BC technology can be facilitated by technology providers offering practical solutions that meet specific HR management needs. |
|
4. |
HR professionals must be adequately trained and educated on BC technology to make informed decisions about its adoption and integration. |
Organizations must invest in the necessary training and education to ensure HR professionals are equipped with the knowledge and skills to effectively implement BC technology. |
|
5. |
BC technology has potential practical applications in various industries. |
Further exploration and research into BC technology's potential and practical applications are necessary to ensure its benefits are fully realized across industries. |
-
4.6 Recommendations for HR managers and BC developers
-
4.6.1 Recommendations for HR Managers
Based on the findings and practical implications of this study, the following recommendations are provided for HR managers and BC developers:
-
• Stay informed: HR managers must stay informed about the latest developments in BC technology and its potential applications in HR management.
-
• Conduct a feasibility analysis: Before adopting BC technology for identity verification, HR managers should conduct a feasibility analysis to assess the costs, benefits, and risks associated with its adoption.
-
• Ensuring adequate training: HR managers should ensure that employees are adequately trained and educated on the benefits and limitations of BC technology to make informed decisions regarding its adoption and integration.
-
• Collaborate with BC developers: HR managers should collaborate with BC developers to develop user-friendly, cost-effective, and scalable BC solutions that meet the specific needs and challenges of HR management.
-
• Evaluate the impact: HR managers should regularly evaluate the impact of BC-based identity verification on HR management practices. This approach can help identify areas of improvement and ensure that the technology is delivering the intended benefits.
-
4.6.2 Recommendations for BC Developers
• Develop user-friendly solutions: BC developers should focus on developing user-friendly solutions that are easy to use and understand, even for those with limited technical knowledge.
• Cost-effective solutions: The cost of BC technology can be a significant barrier to adoption. BC developers should aim to provide cost-effective solutions that can be easily integrated into existing HR management systems.
• Address scalability issues: Scalability is a significant challenge in BC technology. BC developers should address scalability issues to ensure that their solutions can handle the volume of transactions required in HR management.
• Ensuring data security: Data security is critical in HR management, and BC developers must ensure that their solutions provide robust security measures to protect sensitive employee information.
• Provide ongoing support: BC developers should provide ongoing support to HR managers and employees to ensure that their solutions are functioning correctly and addressing their specific needs and challenges.
5. Conclusion
In conclusion, this research paper explored the role of BC-based identity verification in streamlining and securing the employee onboarding process in HR management. The background and context of the study were dis-cussed, and the research problem and objectives were outlined. The significance of the study was explained, and research questions were provided. This paper provides a comprehensive overview of BC technology and its applications and discusses the existing identity verification systems in HR management. It also examined the potential benefits of BC-based identity verification and the challenges and limitations of its implementation. The re-search design, sampling strategy, sample size, data collection methods, and data analysis techniques used were also discussed. The data collected were analyzed, and the findings concerning the research questions, previous studies, and theoretical and practical implications were discussed. A summary of the findings and recommendations for HR managers and BC developers were provided. The findings of this study are important. The study showed that BC-based identity verification can streamline and secure the employee onboarding process in HR management. However, several challenges and limitations need to be addressed, such as scalability and interoperability issues and the need for robust data security measures. The limitations of this study include the small sample size and the limited scope of the research.
Future studies could explore the potential of BC technology in other areas of HR management, such as payroll management and employee benefit administration. This study highlights the potential of BC-based identity verification in HR management and provides practical recommendations for HR managers and BC developers to overcome the challenges and limitations of its implementation. Hopefully, this study will contribute to the ongoing discourse on the use of BC technology in HR management and inspire further re-search in this area.
Список литературы Enhancing Employee Onboarding through Blockchain-Based Identity Verification in HR Management
- Santhanam, G., & Balaji, K. D. (2023). Remote Onboarding Effectiveness in the Indian it Industry During the Pandemic. International Journal of Professional Business Review, 8(5), e01457. https://doi.org/10.26668/businessreview/2023.v8i5.1457
- Dash, S. P. (2023b). HR Digital Transformation: Blockchain for Business. Intelligent Systems Reference Library, 59–87. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-22835-3_3
- Dash, S. P. (2023a). An Introduction to Blockchain Technology: Recent Trends. Intelligent Systems Reference Library, 1–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-22835-3_1
- Soundararajan, R., & Shenbagaraman, V. M. (2023). Unlocking the Potential of Blockchain Through Multi-Criteria Decision Making in Platform Selection. International Journal of Professional Business Review, 8(4), e01732. https://doi.org/10.26668/businessreview/2023.v8i4.1732
- Deepa, R. (2023). The application of blockchain in talent supply chain management. Blockchain in a Volatile-Uncertain-Complex-Ambiguous World, 121–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-323-89963-5.00015-0
- Shishehgarkhaneh, M. B., Moehler, R. C., & Moradinia, S. F. (2023). Blockchain in the Construction Industry between 2016 and 2022: A Review, Bibliometric, and Network Analysis. Smart Cities, 6(2), 819–845. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities6020040
- Sonkamble, R. G., Bongale, A. M., Phansalkar, S., Sharma, A., & Rajput, S. (2023). Secure Data Transmission of Electronic Health Records Using Blockchain Technology. Electronics, 12(4), 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12041015
- Aust, I., Matthews, B., & Muller-Camen, M. (2019). Common Good HRM: A paradigm shift in Sustainable HRM? Human Resource Management Review, 30(3), 100705. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrmr.2019.100705
- Aditira, K., & Anggoro, Y. (2023). Utilization of Blockchain and the Roles of Banks in Indonesia in Tackling Environmental Challenges: A Qualitative Research. International Journal of Current Science Research and Review, 06(02). https://doi.org/10.47191/ijcsrr/v6-i2-84
- Chinyanya, C. (2023). Overcoming Barriers to Blockchain Technological Innovation in Trade Finance Faced by U.S. Banks. Business Management Research and Applications: A Cross-Disciplinary Journal, 2(1), 37–76. https://bmrajournal.columbiasouthern.edu/index.php/bmra/article/view/3898
- Costa, L. D., Pinheiro, B., Cordeiro, W., Araújo, R., & Abelém, A. (2023). Sec-Health: A Blockchain-Based Protocol for Securing Health Records. IEEE Access, 11, 16605–16620. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3245046
- Anaam, E., Hasan, M. K., Ghazal, T. M., Haw, S.-C., Alzoubi, H. M., & Alshurideh, M. T. (2023, February 1). How Private Blockchain Technology Secure IoT Data Record. IEEE Xplore. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICAIC57335.2023.10044178
- Jain, S., Vamsi, P., Agarwal, Y., & Goel, J. (2023). Information Engineering and Electronic Business. 1, 1–19. https://doi.org/10.5815/ijieeb.2023.01.01
- Ke, W., Ge, C., & Song, W. (2023). Executing Efficient Retrieval Over Blockchain Medical Data Based on Exponential Skip Bloom Filter. Web and Big Data, 334–348. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-25201-3_26
- Martin, W. M., Avdul, D., & Lopez, Y. (2023). Cryptocurrency Compensation: Look Before You Leap. Compensation & Benefits Review, 088636872211421. https://doi.org/10.1177/08863687221142131
- Tian, M., Zhang, Y., Zhu, Y., Wang, W., Wu, Q., & Xiang, Y. (2023). BPPIR: Blockchain-assisted privacy-preserving similarity image retrieval over multiple clouds. Journal of King Saud University - Computer and Information Sciences, 35(1), 324–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksuci.2022.12.003


